4f697eeb5792e1e413948a521cbc54a0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

UNDP/GEF Project: “ Towards Sustainability in Yellow Sea Mariculture”, June 16 -17, 2009. Jeju, Korea Switchover of Moist Pellet to Extruded Pellet , the First Step for Sustainable Development of Flounder Culture in Jeju Island, Korea Jeong-Dae Kim 2009 -06 -09 Animal Life System College of Animal Life Sciences Kangwon National University 1 Chuncheon 200 -701, Korea
Contents 1 2 Flounder production in Jeju Island 3 Strategy and challenges forward 4 2009 -06 -09 Marine fish farming in Korea Conclusion 2
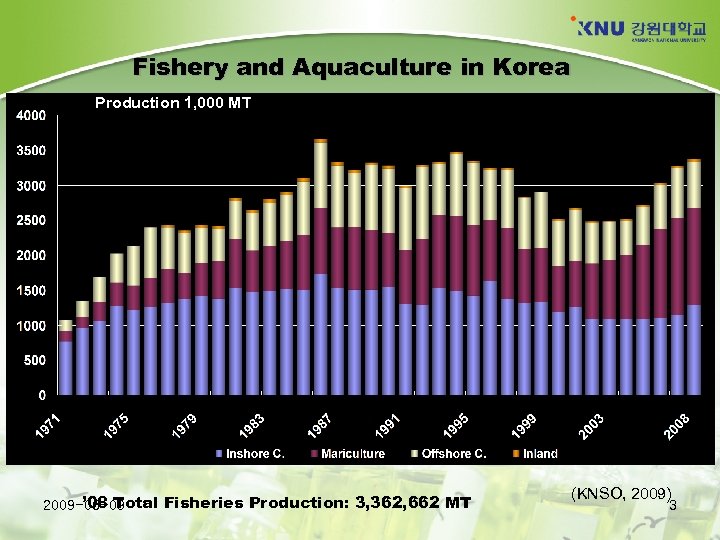
Fishery and Aquaculture in Korea Production 1, 000 MT ’ 08 Total Fisheries Production: 3, 362, 662 MT 2009 -06 -09 (KNSO, 2009) 3
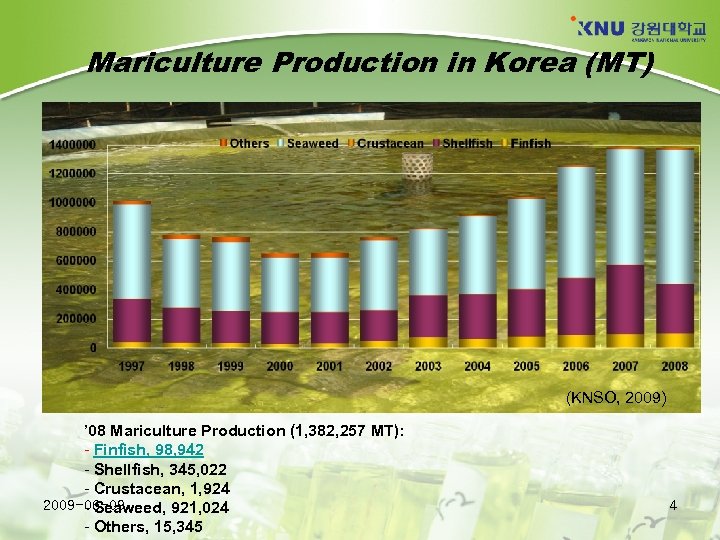
Mariculture Production in Korea (MT) (KNSO, 2009) ’ 08 Mariculture Production (1, 382, 257 MT): - Finfish, 98, 942 - Shellfish, 345, 022 - Crustacean, 1, 924 2009 -06 -09 - Seaweed, 921, 024 - Others, 15, 345 4
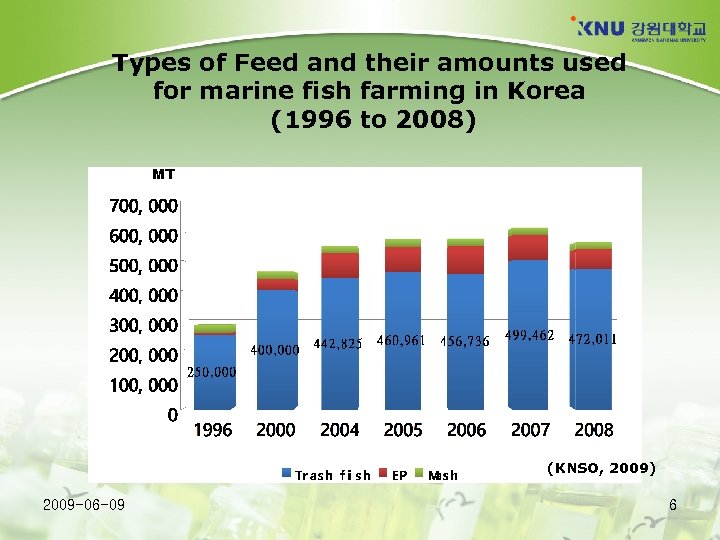
Types of Feed and their amounts used for marine fish farming in Korea (1996 to 2008) MT (KNSO, 2009) 2009 -06 -09 6

Types of Fish Feed • Live foods – Algae – Zooplankton • By-catch/trash fish – Moist pellet • Formulated – Mash – Floating – Sinking – Mixed Sinking Extruded (Floating) 2009 -06 -09 7

Seawater fish farming Flounder Production History 2007 1988 1997 Total: 1, 290 tons Yellowtail: 1, 258 tons Flounder: 16 tons 1992 Total: 4, 595 tons Flounder: 3, 199 tons Rockfish : 666 tons 2009 -06 -09 Total: 97, 644 tons Flounder: 41, 207 tons Rockfish: 35, 509 tons Total: 39, 121 tons Flounder: 26, 274 tons Rockfish : 11, 069 tons Korean Fisheries Yearbook 1989, 1991, 1998 -2008 8
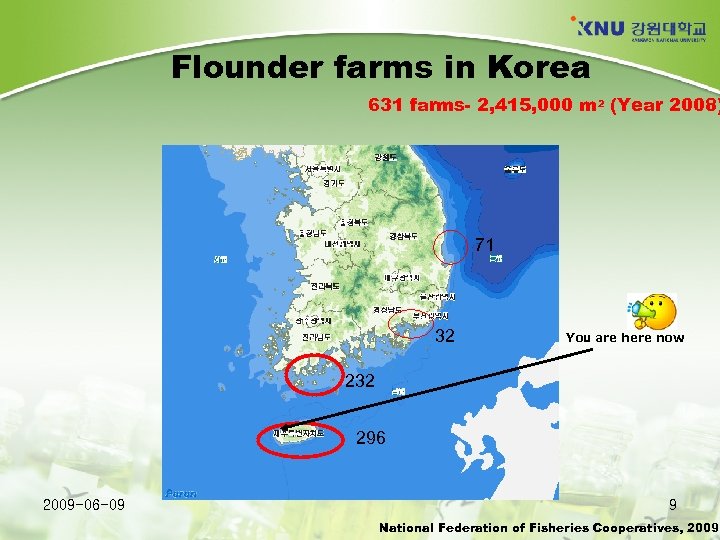
Flounder farms in Korea 631 farms- 2, 415, 000 m 2 (Year 2008) 71 32 You are here now 232 296 2009 -06 -09 9 National Federation of Fisheries Cooperatives, 2009

Jeju island • Top Region for flounder production Water temperature: - Winter above 12 ℃ - Summer below 28℃ - Subterranean water 16~18℃ 2009 -06 -09 10
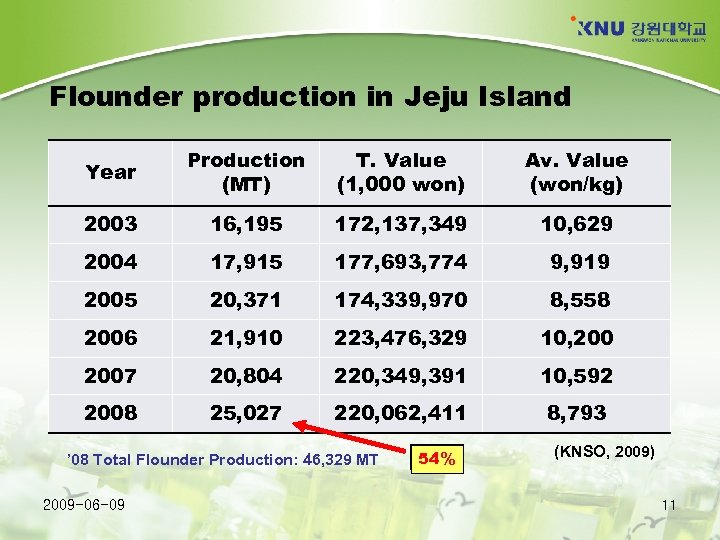
Flounder production in Jeju Island Year Production (MT) T. Value (1, 000 won) Av. Value (won/kg) 2003 16, 195 172, 137, 349 10, 629 2004 17, 915 177, 693, 774 9, 919 2005 20, 371 174, 339, 970 8, 558 2006 21, 910 223, 476, 329 10, 2007 20, 804 220, 349, 391 10, 592 2008 25, 027 220, 062, 411 8, 793 ’ 08 Total Flounder Production: 46, 329 MT 2009 -06 -09 54% (KNSO, 2009) 11

Feeds used for flounder culture in Korea (2008) in Jeju Island (2008) Total 129, 389 MT (KNSO, 2009) (Personal estimation) Total 141, 502 MT (KNSO, 2009) 2009 -06 -09 Difference (12, 113 MT of trash fish) is excluded to be used by dead fish. Flounder production in 2008: 46, 329 tons 12

EP, Mash and Trash fish • EP- Extruded Pellet • Mash- compounded powder feed or fish meal • Trash fish- raw fish MP (moist pellet) is made by mixing 90~100% raw fish with 0~10% mash EP 2009 -06 -09 13

Why is MP preferred ? - Fast growth - Good quality fillet when fish are fed the EP, - Increase in mortality due to the ascites - Poor growth - Poor quality fillet 2009 -06 -09 14

Results of on-farm experiments Location: Jeju island Feed: MP and EP Feeding period: 12 months (Dec. 19, 2007 to Nov. 3, 2008) Initial body weight: 33 g (M farm), 94 g and 120 g (S farm) No significant differences in - Growth (g) of flounder Chemical composition of whole body and muscle Flavor, texture and overall acceptability of dorsal muscle and Productivity (profit) Much higher water pollution (1. 5 to 10 folds) was found in MP groups. (Kang et al. , 2009. NFRDI) 2009 -06 -09 15
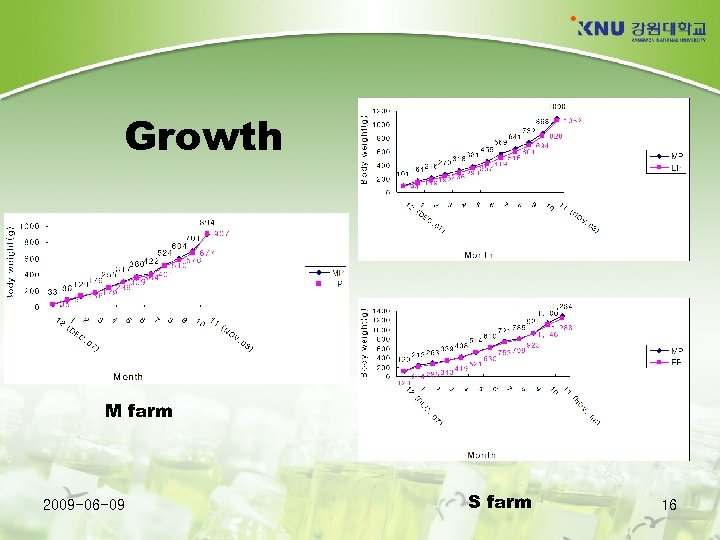
Growth M farm 2009 -06 -09 S farm 16
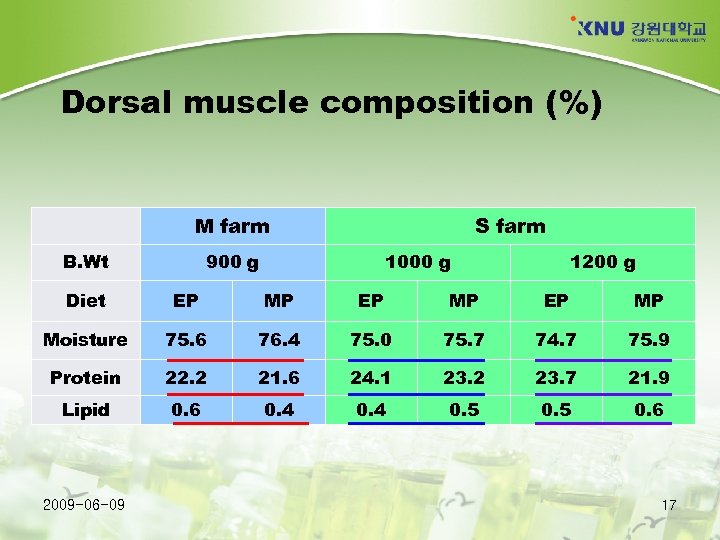
Dorsal muscle composition (%) M farm B. Wt S farm 900 g 1000 g 1200 g Diet EP MP Moisture 75. 6 76. 4 75. 0 75. 7 74. 7 75. 9 Protein 22. 2 21. 6 24. 1 23. 2 23. 7 21. 9 Lipid 0. 6 0. 4 0. 5 0. 6 2009 -06 -09 17
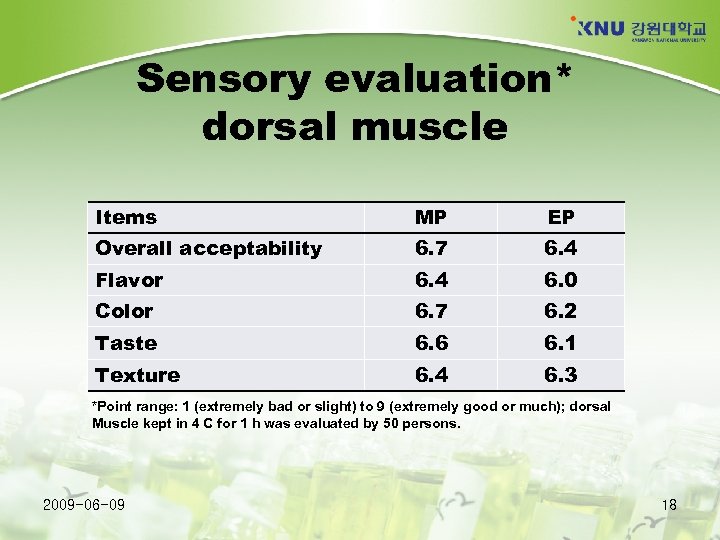
Sensory evaluation* dorsal muscle Items MP EP Overall acceptability 6. 7 6. 4 Flavor 6. 4 6. 0 Color 6. 7 6. 2 Taste 6. 6 6. 1 Texture 6. 4 6. 3 *Point range: 1 (extremely bad or slight) to 9 (extremely good or much); dorsal Muscle kept in 4 C for 1 h was evaluated by 50 persons. 2009 -06 -09 18

Why is EP not used ? • Expensive ? • Still unbelievable ? Because farmers have to buy EP for cash !!! Trash fish on credit !!! 2009 -06 -09 19
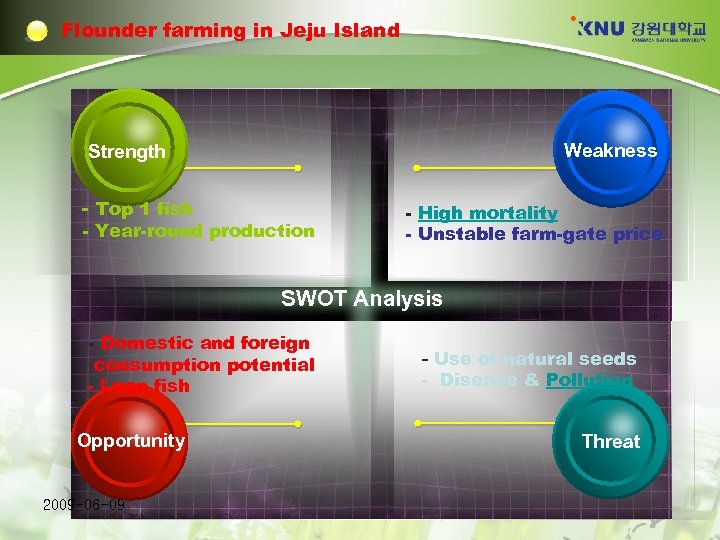
Flounder farming in Jeju Island Weakness Strength - Top 1 fish - Year-round production - High mortality - Unstable farm-gate price SWOT Analysis - Domestic and foreign consumption potential - Lean fish Opportunity 2009 -06 -09 - Use of natural seeds - Disease & Pollution Threat
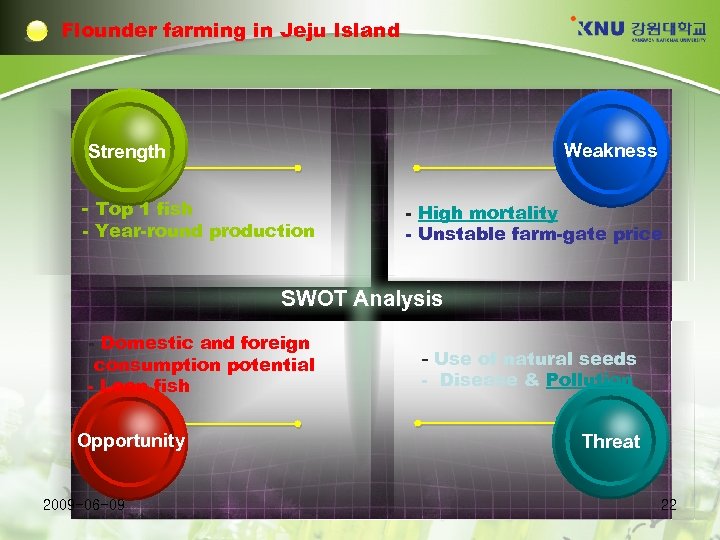
Flounder farming in Jeju Island Weakness Strength - Top 1 fish - Year-round production - High mortality - Unstable farm-gate price SWOT Analysis - Domestic and foreign consumption potential - Lean fish Opportunity 2009 -06 -09 - Use of natural seeds - Disease & Pollution Threat 22
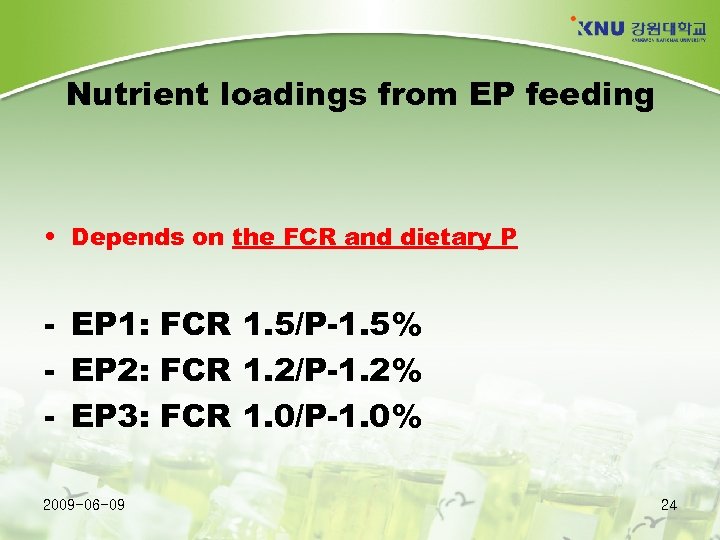
Nutrient loadings from EP feeding • Depends on the FCR and dietary P - EP 1: FCR 1. 5/P-1. 5% - EP 2: FCR 1. 2/P-1. 2% - EP 3: FCR 1. 0/P-1. 0% 2009 -06 -09 24
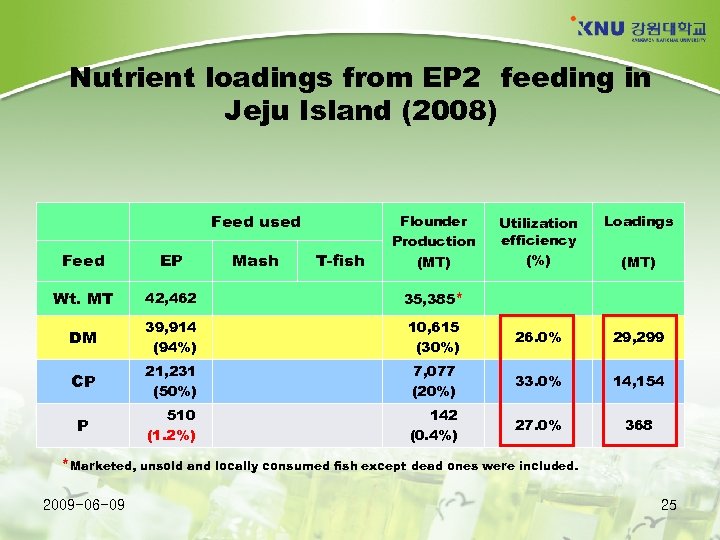
Nutrient loadings from EP 2 feeding in Jeju Island (2008) Feed used Mash T-fish Flounder Production (MT) Utilization efficiency (%) Loadings Feed EP Wt. MT 42, 462 35, 385* DM 39, 914 (94%) 10, 615 (30%) 26. 0% 29, 299 CP 21, 231 (50%) 7, 077 (20%) 33. 0% 14, 154 P 510 (1. 2%) 142 (0. 4%) 27. 0% 368 (MT) *Marketed, unsold and locally consumed fish except dead ones were included. 2009 -06 -09 25

Sustainable flounder farming does not mean a quantitative increase in production. It means the qualitative improvement Feed: MP to EP Breeding Genetics: Fast growing flounder Disease control: Vaccine Safety: HACCP and Traceability 2009 -06 -09 26

Future visions for flounder farming industry 2010 2009 -06 -09 2015 • Development of green flounder seed • Production cost of 6, 000 wons • Fillet export • HACCP & Traceability 2020 Goals • Switchover of MP to EP feed • Top 1 product of Jeju island through branded Differentiation 29
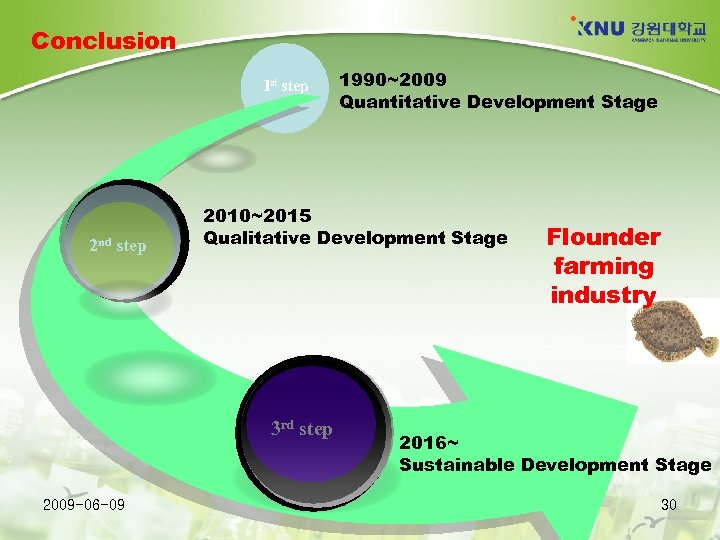
Conclusion Ist step 2 nd step 2010~2015 Qualitative Development Stage 3 rd step 2009 -06 -09 1990~2009 Quantitative Development Stage Flounder farming industry 2016~ Sustainable Development Stage 30

Let’s do it MP Switchover ofnow ! to EP Sustainability Clean sea Future food Protection of natural seed stocks 2009 -06 -09 Reduction of water pollution Jeju Island Flounder industry 31

Thank You We can’t support the growth of the aquaculture business using fish to feed fish 2009 -06 -09 32 UNDP/GEF Project: “ Towards Sustainability in Yellow Sea Mariculture”, June 16 -17, 2009. Jeju, Korea
4f697eeb5792e1e413948a521cbc54a0.ppt