5f377233e7c710f647fa7e87c2de407c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

UNDERSTANDING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF ASTHMA USING A GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM Mohammad A. Rob Management Information Systems University of Houston-Clear Lake

Contents • • Introduction Geographic Information System (GIS) Asthma Epidemic: An Example Applications of GIS in Spatial Distribution of Asthma • Business Geography: A New Discipline • Conclusion

Introduction • Geographic Information System (GIS) is used to make strategic decisions when data have spatial (geographical) distribution • Government agencies use it for assessment and planning in areas such as housing, healthcare, land use, transportation, and environmental monitoring • Businesses use it to locate optimum retail location and delivery route

Introduction • Current corporate databases do not contain geospatial reference • However, GIS tools can be used to add geographical coordinates to existing data • Thus existing data can be presented on a map and make strategic decisions • Major database vendors (Microsoft, IBM, Oracle, Informix) are adding a “spatial” data type to their enterprise database systems

Introduction • The use of GIS tools require more knowledge of information technology than geography • GIS datasets are already available through the Web • Most organizations perform GIS analysis without getting involved with the mapping technology • There are GIS technicians, analysts, programmers, and managers

Introduction • Soon there will be GIS specialists like IT specialists in every organization • Many IT specialists will become GIS specialists • We discuss the basic principles and functionality of a GIS • We also illustrate how GIS tools can be used to analyze and interpret user data using an example of asthma epidemiology

Geographical Information System (GIS) • What is GIS? – GIS is a computerized system for input, storage, management, display, and analysis of data that can be precisely linked to a geographical location • GIS datasets come as layers: – a layer for roads – a layer for rivers – a layer for zip code boundary – all within a particular geographical boundary

Geographical Information System (GIS) • A layer may consists of a vector or raster • Raster data types are images • Vectors data types are defined by points, lines and polygons (boundary) – Points: hospitals, parks, and fire hydrants – Lines: Roads, highways, and rivers – Polygon: Zip code, county, state, and country • A layer may consist of many features • Several layers are combined to create a map
Major Roads and highways of Texas
County Boundaries of Texas
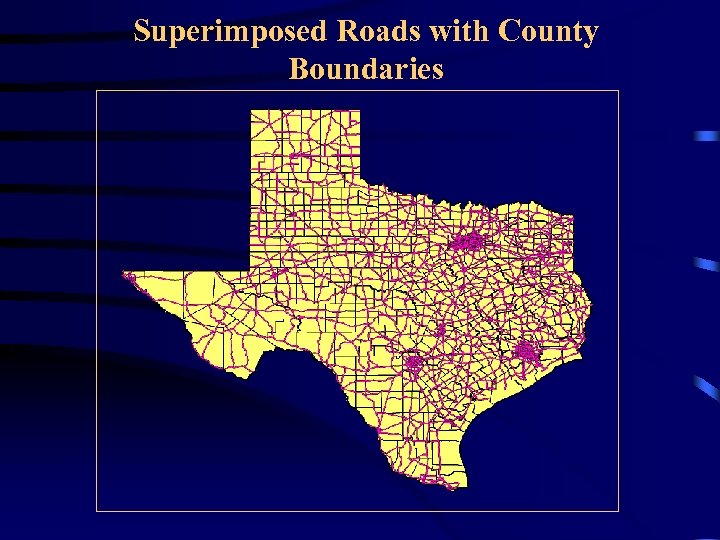
Superimposed Roads with County Boundaries
Expanded View: City of Houston

Geographical Information System (GIS) • All features in a layer are stored in a shapefile • Each shapefile has more than one file types associated with it: – one for the primary feature (points, lines, etc. ) – one for the geometrical coordinates of the primary feature: (x, y) or (x 1, y 1 -- x 2, y 2) – one for the geographical coordinate system (longitude, latitude) – all sharing the same filename
Geographical Information System (GIS)

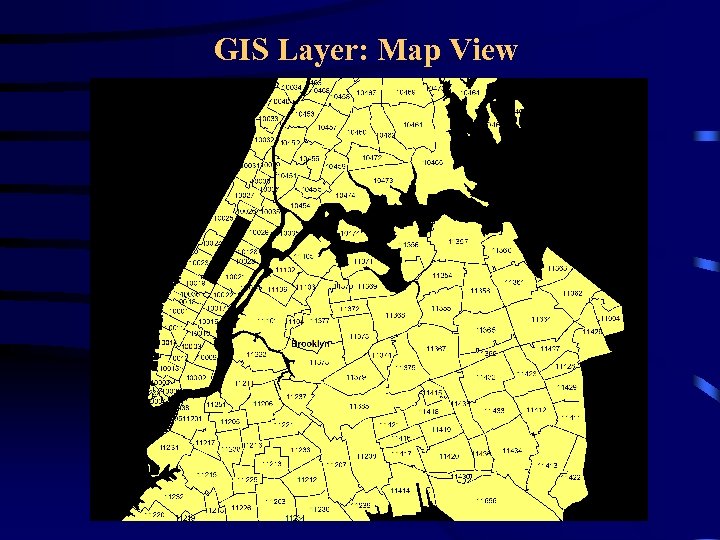
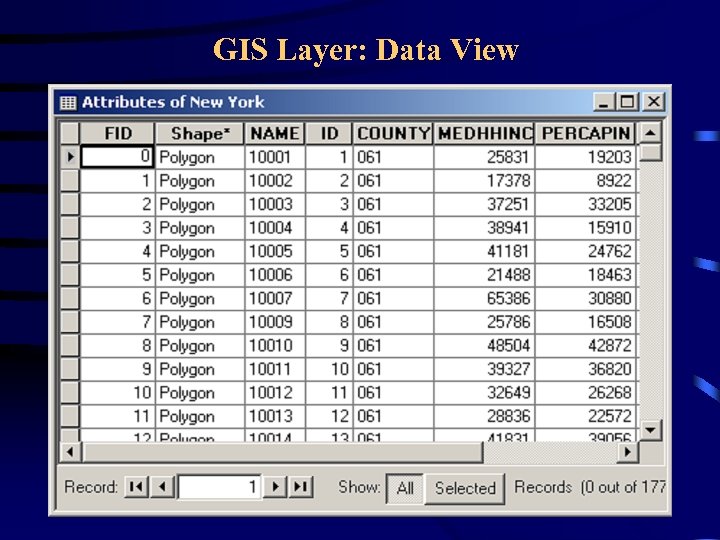
Geographical Information System (GIS) • Each GIS layer has two views: – a map view – a data view • The map acts as visual representation of data • The data view can be used to: – to create a smaller dataset or map – to combine with user data to create a new layer (as long as there is a common attribute between the GIS data and the user data)
GIS Layer: Map View
GIS Layer: Data View

Geographical Information System (GIS) • Most commonly used GIS tool is Arc. View from ESRI (Environmental Systems Research Institute) – It uses a geodatabase to store all features – Can be used as a desktop or multi-user database • Many federal, state, and local government agencies publish GIS data in the Arc. View’s shapefile format • These files can be downloaded from the Web
Geographical Information System (GIS)

Asthma Epidemic: An Example • Asthma became a public health concern, especially among children in the U. S. – About 17. 3 million Americans have asthma – More than 5000 people die from asthma per year – Asthma prevalence among children (0 -17 years) increased by ~ 5% each year during 1980 -1995 – African Americans suffer more than Caucasians – Females suffer more than males
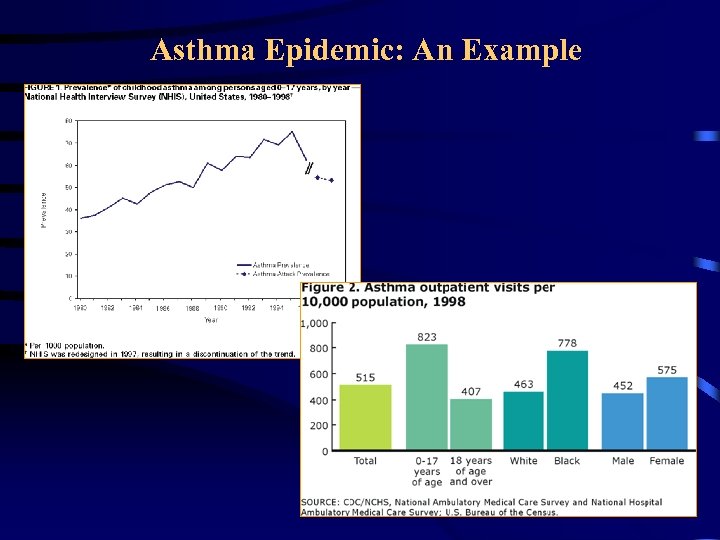
Asthma Epidemic: An Example

Applications of GIS: Spatial Distribution of Asthma • Most of the asthma data come from hospitalization records or surveying a localized population • These data do not contain any spatial or geographical coordinate, but use zip code • However, they can be joined with a spatial dataset such as a zip code layer to create a asthma layer • Zip code from the two datasets can be used as a join parameter

Asthma Study of New York City • Asthma data came from a survey of middleand high schools students in the NY City • The students were in the age group of 15 -18 years • About 4300 datasets were collected in two years from various boroughs of the city • Data were summarized by zip code, borough, gender, and race • Arc. View GIS software was used for maps
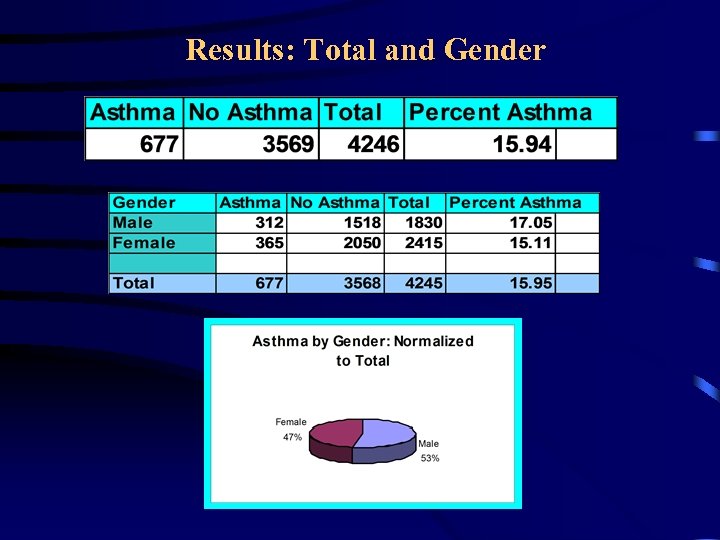
Results: Total and Gender
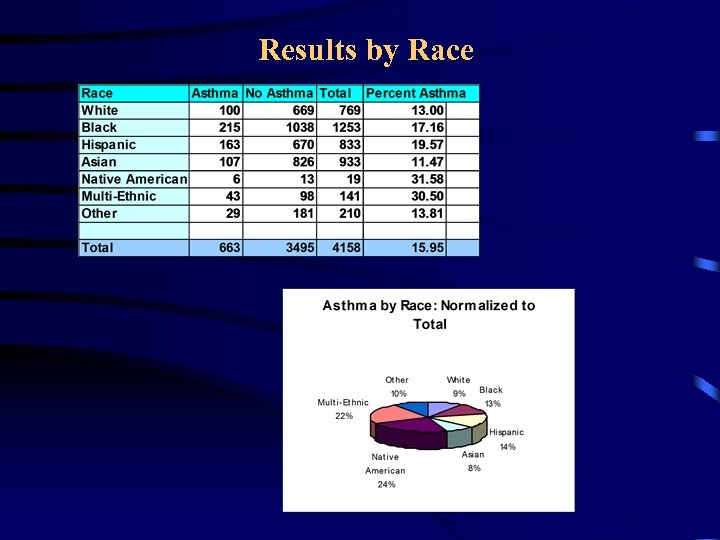
Results by Race
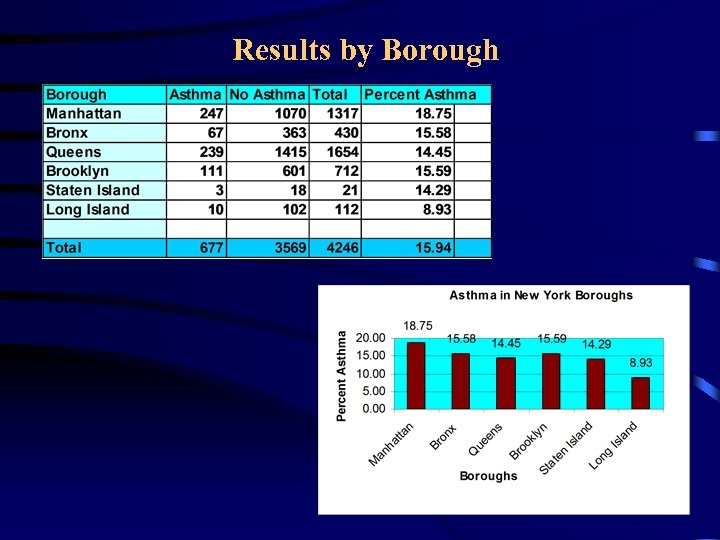
Results by Borough
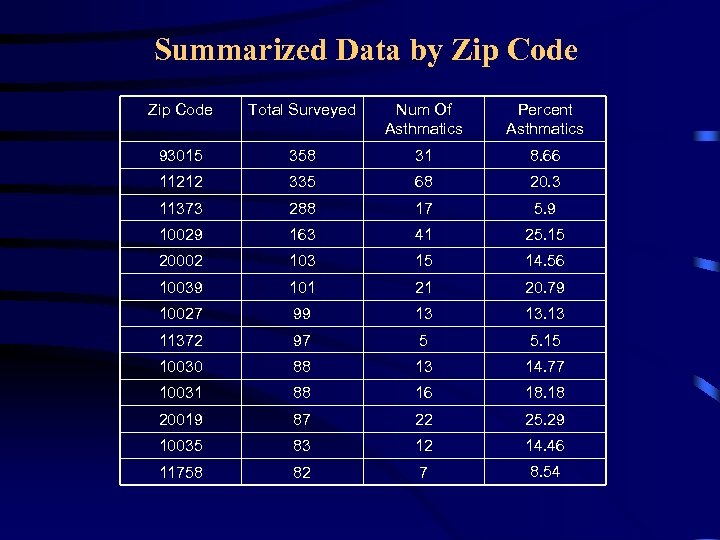
Summarized Data by Zip Code Total Surveyed Num Of Asthmatics Percent Asthmatics 93015 358 31 8. 66 11212 335 68 20. 3 11373 288 17 5. 9 10029 163 41 25. 15 20002 103 15 14. 56 10039 101 21 20. 79 10027 99 13 13. 13 11372 97 5 5. 15 10030 88 13 14. 77 10031 88 16 18. 18 20019 87 22 25. 29 10035 83 12 14. 46 11758 82 7 8. 54
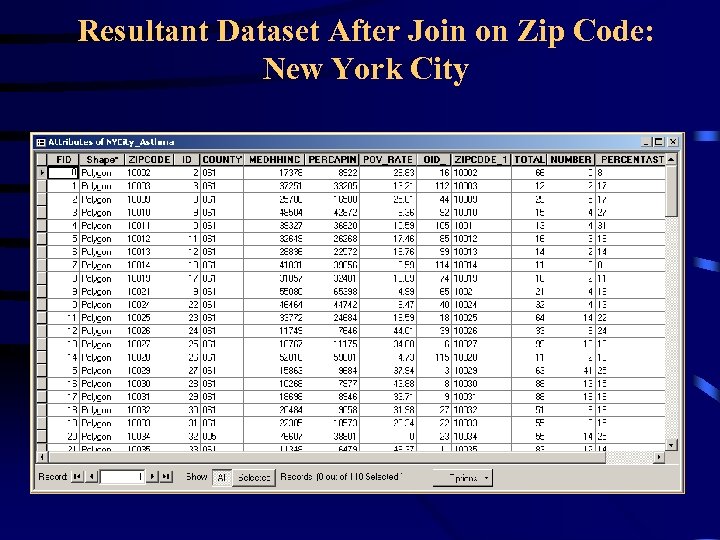
Resultant Dataset After Join on Zip Code: New York City
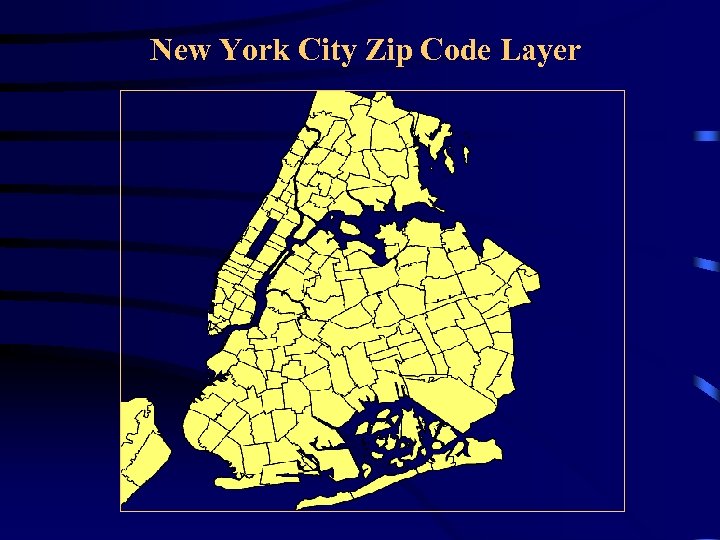
New York City Zip Code Layer
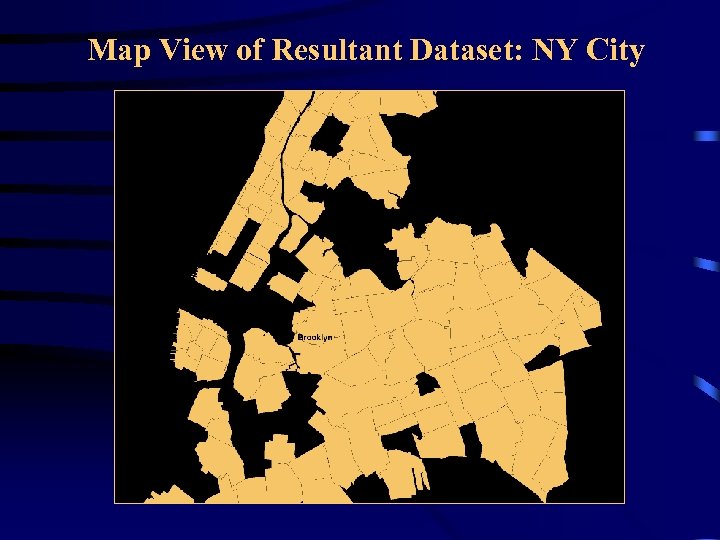
Map View of Resultant Dataset: NY City
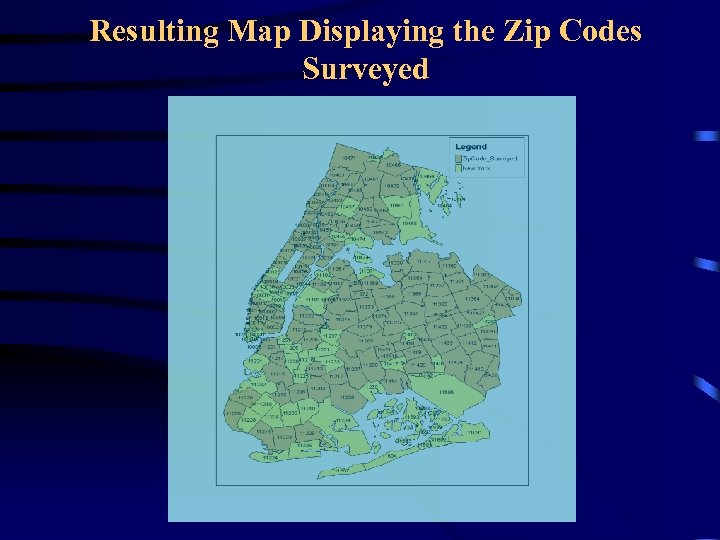
Resulting Map Displaying the Zip Codes Surveyed
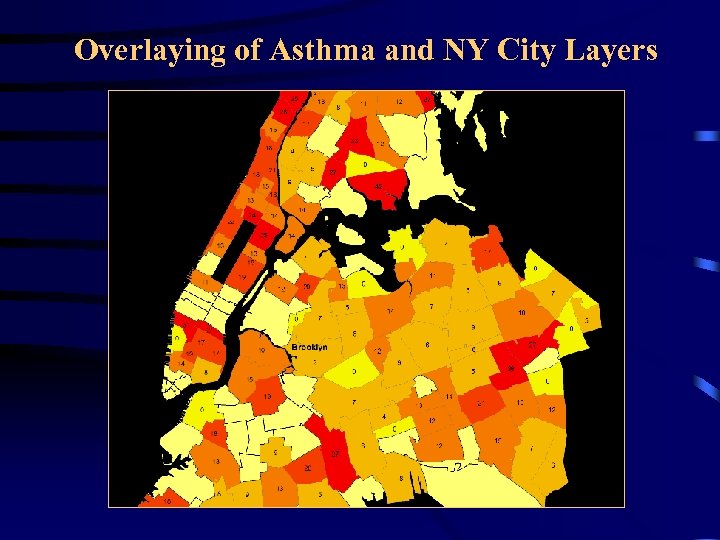
Overlaying of Asthma and NY City Layers
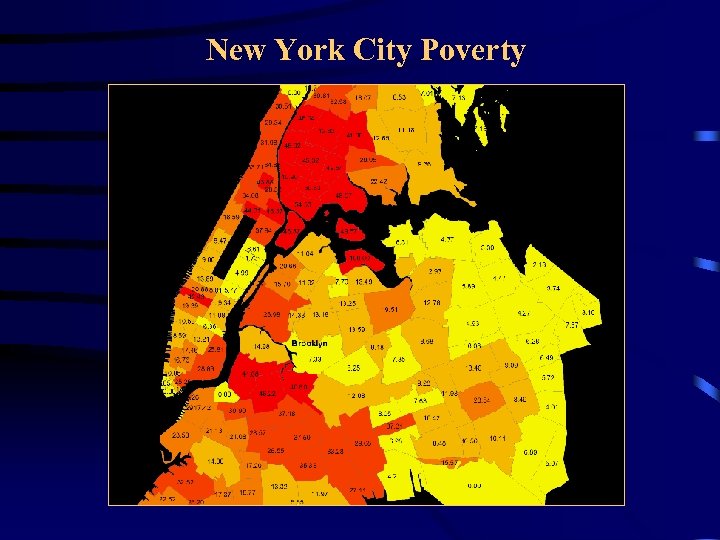
New York City Poverty
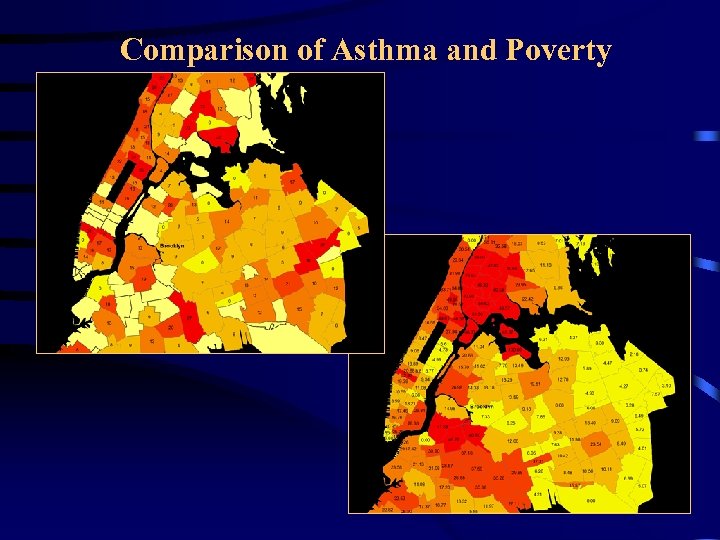

Comparison of Asthma and Poverty

GIS in Business • GIS can be used to: – Optimize sales territories and delivery route to balance workload and minimize travel – Display sales forecasts utilizing customer demographic trends – Business site selection utilizing customer demographic trends – Evaluate business acquisition opportunities by knowing business composition and consumer consumption patterns in the locality
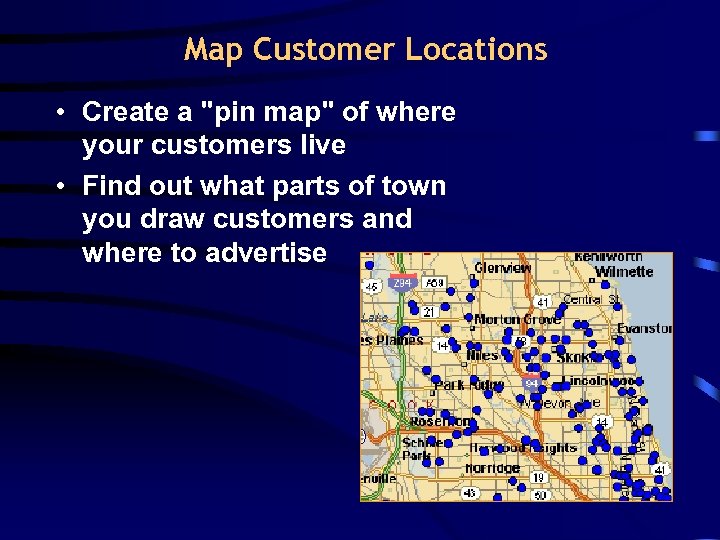
Map Customer Locations • Create a "pin map" of where your customers live • Find out what parts of town you draw customers and where to advertise
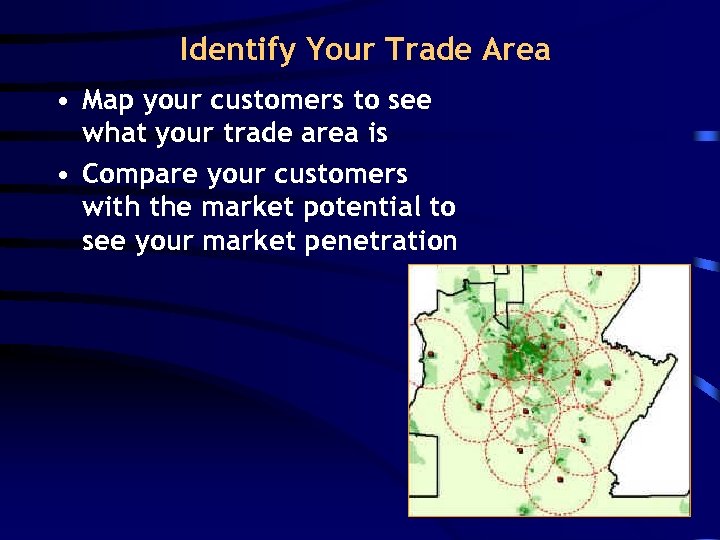
Identify Your Trade Area • Map your customers to see what your trade area is • Compare your customers with the market potential to see your market penetration

Target Your Advertising • Given your trade area, and your customer profile, you can focus advertising to the places and media that are most likely to hit your target market

Business Geography: A New Discipline • The combined use of computer-mapping, Internet, database technologies, and locationallocation modeling techniques will become a particularly important set of skills for many business students whose first jobs after graduation involve real estate, urban, demographic, retail, marketing, environmental, transportation, international trade or investment analyses. • A new discipline called “Business Geography” is evolving in many business schools across the country

Conclusion • We have provided a brief overview of a Geographical Information System • GIS uses various layers to create a map and each layer has two views: a dataset and a map • Most layers are available from local, state, and federal government agencies • Asthma epidemiology is used as an example to illustrate how user data can be combined with GIS data and make further decisions for research or healthcare planning • We have also highlighted on Business Geograhy, an evolving program in business schools
5f377233e7c710f647fa7e87c2de407c.ppt