9aa5c0e87b520f794bac742dd482bfbc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Understanding Smart Cities SUPREME & CO. PVT. LTD. KOLKATA, INDIA 1
Understanding Smart Cities SUPREME & CO. PVT. LTD. KOLKATA, INDIA 1
 Smart City : Introduction Definition of Smart City by Boyd Cohen : Smart cities use information and communication technologies (ICT) to be more intelligent and efficient in the use of resources, resulting in cost and energy savings, improved service delivery and quality of life, and reduced environmental footprint--all supporting innovation and the low-carbon economy. Origin of Smart city The concept of smart cities originated at the time when the entire world was facing one of the worst economic crises. In 2008, IBM began work on a 'smarter cities' concept as part of its Smarter Planet initiative. By the beginning of 2009, the concept had captivated the imagination of various nations across the globe. Initiative of European cities for being Smart European cities tend to be denser and have better public transit. Larger commitment to cycling and walking. A stronger focus on sustainability and low-carbon solutions. LEED : Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design AP : Accredited Professional Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 2 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014
Smart City : Introduction Definition of Smart City by Boyd Cohen : Smart cities use information and communication technologies (ICT) to be more intelligent and efficient in the use of resources, resulting in cost and energy savings, improved service delivery and quality of life, and reduced environmental footprint--all supporting innovation and the low-carbon economy. Origin of Smart city The concept of smart cities originated at the time when the entire world was facing one of the worst economic crises. In 2008, IBM began work on a 'smarter cities' concept as part of its Smarter Planet initiative. By the beginning of 2009, the concept had captivated the imagination of various nations across the globe. Initiative of European cities for being Smart European cities tend to be denser and have better public transit. Larger commitment to cycling and walking. A stronger focus on sustainability and low-carbon solutions. LEED : Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design AP : Accredited Professional Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 2 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014
 Why Smart Cities are needed now? The need to handle global environment and urbanization problems --Global warming and climate change --Population increase and resource depletion --Adverse effects of increasing urbanization The need to accommodate changing lifestyles --Valuing usage above ownership e. g. , increase in the sharing or renting of motor vehicles. --Focusing on non-monetary values e. g. , The givers do not exchange their expertise or other skill for money, but rather to satisfy personal values such as their wish to help people: e. g. , In India Teach India - Times Group initiative. --Having wider opportunities for work and study e. g. , the Internet is making it possible for everyone, from children to the elderly, to study when and where they want. --Overcoming restrictions of time and place e. g. , video streaming services and advances in recording functions allow viewers to watch video or TV content whenever they want, and do not require viewers to be present at specific times. --Being both a consumer and a producer e. g. , in the energy field, people who install their own solar power generator can act as both a user and a supplier. The need for a long-term approach to developing sustainable cities --Managing the lifecycles of cities --Improving economic performance over the entire Lifecycle e. g. , pollution, that are very expensive to clean up later. --Enhancing city competitiveness Source: Hitachi Group …. to be continued 3
Why Smart Cities are needed now? The need to handle global environment and urbanization problems --Global warming and climate change --Population increase and resource depletion --Adverse effects of increasing urbanization The need to accommodate changing lifestyles --Valuing usage above ownership e. g. , increase in the sharing or renting of motor vehicles. --Focusing on non-monetary values e. g. , The givers do not exchange their expertise or other skill for money, but rather to satisfy personal values such as their wish to help people: e. g. , In India Teach India - Times Group initiative. --Having wider opportunities for work and study e. g. , the Internet is making it possible for everyone, from children to the elderly, to study when and where they want. --Overcoming restrictions of time and place e. g. , video streaming services and advances in recording functions allow viewers to watch video or TV content whenever they want, and do not require viewers to be present at specific times. --Being both a consumer and a producer e. g. , in the energy field, people who install their own solar power generator can act as both a user and a supplier. The need for a long-term approach to developing sustainable cities --Managing the lifecycles of cities --Improving economic performance over the entire Lifecycle e. g. , pollution, that are very expensive to clean up later. --Enhancing city competitiveness Source: Hitachi Group …. to be continued 3
 Why Smart Cities are needed now? The need for a long-term approach to developing sustainable cities --Managing the lifecycles of cities Early phase: Provide the infrastructure needed for the operation of the city. Growth Phase: Expand intensify the infrastructure to ensure that supply can keep the pace with increasing demands of the growing demand. Mature phase: Enhance infrastructure to ensure the delivery of high-quality services based on criteria such as easeof-use and comfort. Transformation phase: Integrate infrastructure systems to satisfy social values such as aiding, or at least avoiding damage to, the natural environment. --Improving economic performance over the entire Lifecycle e. g. , pollution, that are very expensive to clean up later. --Enhancing city competitiveness: In terms of services(education , healthcare ), waste management, water management , transportation, safety etc. Source: Hitachi Group 4
Why Smart Cities are needed now? The need for a long-term approach to developing sustainable cities --Managing the lifecycles of cities Early phase: Provide the infrastructure needed for the operation of the city. Growth Phase: Expand intensify the infrastructure to ensure that supply can keep the pace with increasing demands of the growing demand. Mature phase: Enhance infrastructure to ensure the delivery of high-quality services based on criteria such as easeof-use and comfort. Transformation phase: Integrate infrastructure systems to satisfy social values such as aiding, or at least avoiding damage to, the natural environment. --Improving economic performance over the entire Lifecycle e. g. , pollution, that are very expensive to clean up later. --Enhancing city competitiveness: In terms of services(education , healthcare ), waste management, water management , transportation, safety etc. Source: Hitachi Group 4
 Smart City for growing population There is a worldwide trend toward Smart Cities as shown by the following: • • • Half of the world population is living in cities in 2013 Half of the population of Asia will be living in cities by 2020 Half of the population of Africa will be living in cities by 2035 Population in cities is expected to grow from 3. 6 Billion to 6. 3 Billion by 2050. Over 50% of urbanization involves cities of less that 500 K people India's Population in 2011 was 1. 21 billion Current Population of India in 2014 is 1. 27 billion Nine satellite cities could be covered under this scheme. About 44 cities with 10 lakh to 40 lakh population, 17 state capitals, 10 tourist and religious cities and another 20 with 5 lakh to 10 lakh population could also make it to the list. Source: The Times of India Sep 12, 2014 5
Smart City for growing population There is a worldwide trend toward Smart Cities as shown by the following: • • • Half of the world population is living in cities in 2013 Half of the population of Asia will be living in cities by 2020 Half of the population of Africa will be living in cities by 2035 Population in cities is expected to grow from 3. 6 Billion to 6. 3 Billion by 2050. Over 50% of urbanization involves cities of less that 500 K people India's Population in 2011 was 1. 21 billion Current Population of India in 2014 is 1. 27 billion Nine satellite cities could be covered under this scheme. About 44 cities with 10 lakh to 40 lakh population, 17 state capitals, 10 tourist and religious cities and another 20 with 5 lakh to 10 lakh population could also make it to the list. Source: The Times of India Sep 12, 2014 5
 "Smart Cities" includes • • • Smart Living Smart Building & Home Smart Transportation Smart Energy (Renewable generation & storage, AMI, PQM, PLM, OMS) Smart Water Management Smart Waste Management(Recycling of waste, residual management, Recovery of waste organics & Energy) Smart Education(e-Education) Smart Governance(e-governance) Smart Medical Facility(e-Medical) Smart Communications Smart Networks Environmental Awareness (i. e. changing weather conditions; human defined changes) Source: The Times of India Sep 12, 2014 6
"Smart Cities" includes • • • Smart Living Smart Building & Home Smart Transportation Smart Energy (Renewable generation & storage, AMI, PQM, PLM, OMS) Smart Water Management Smart Waste Management(Recycling of waste, residual management, Recovery of waste organics & Energy) Smart Education(e-Education) Smart Governance(e-governance) Smart Medical Facility(e-Medical) Smart Communications Smart Networks Environmental Awareness (i. e. changing weather conditions; human defined changes) Source: The Times of India Sep 12, 2014 6
 Different looks of SMART CITY …. to be continued 7
Different looks of SMART CITY …. to be continued 7
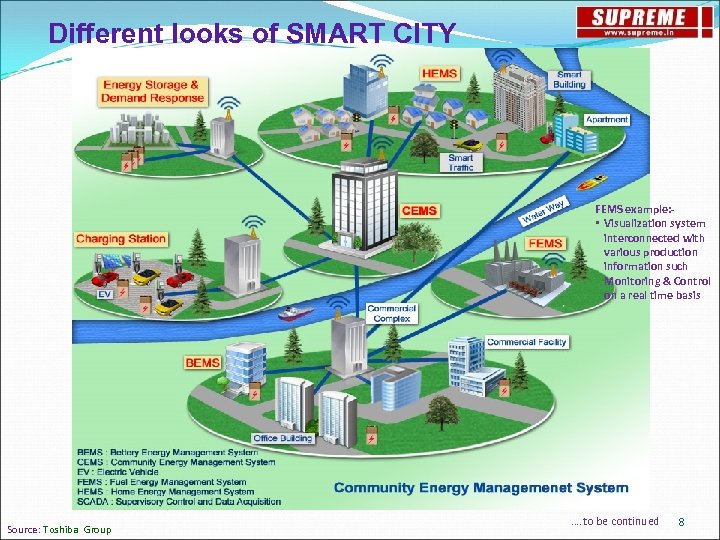 Different looks of SMART CITY FEMS example: • Visualization system interconnected with various production information such Monitoring & Control on a real time basis Source: Toshiba Group …. to be continued 8
Different looks of SMART CITY FEMS example: • Visualization system interconnected with various production information such Monitoring & Control on a real time basis Source: Toshiba Group …. to be continued 8
 Different looks of SMART CITY Remote communication services for Education & Healthcare Source: Hitachi Group …. to be continued 9
Different looks of SMART CITY Remote communication services for Education & Healthcare Source: Hitachi Group …. to be continued 9
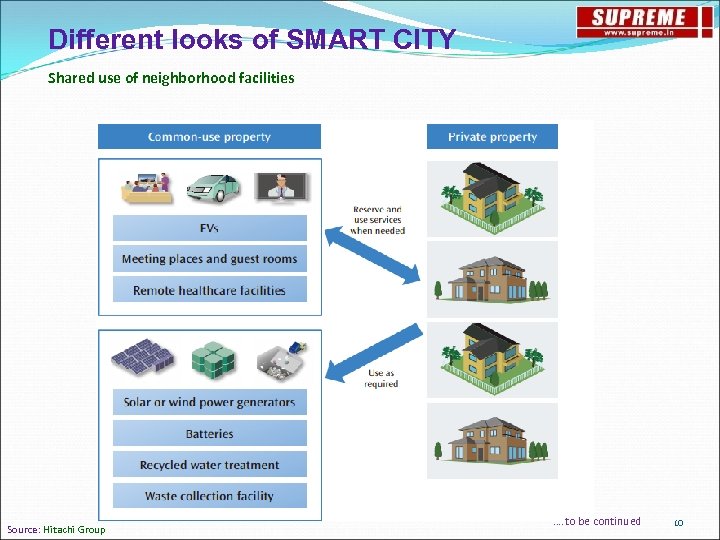 Different looks of SMART CITY Shared use of neighborhood facilities Source: Hitachi Group …. to be continued 10
Different looks of SMART CITY Shared use of neighborhood facilities Source: Hitachi Group …. to be continued 10
 Growing needs of Indian Citizens • For better health facilities 600, 000 doctors and 1 million nurses. • For effective education 1. 2 million teachers in government schools. • Smart parking solution to reduce ≈ 30% of urban traffic and annual fuel wastage by ≈ $10 billion respectively. • Smart building to reduce ≈ 40% of energy consumption. • Internet services infrastructure to meet six fold internet traffic in future. • Mobile communication services for ≈ 843. 3 million users. --1. 1 billion Mobile connected devices. --1. 8 billion Networked devices. • Remotely accessible services for healthcare, retail or banking services, citizen services etc. • Connected learning for cities, educational institutions and companies to improve student outcomes, increase efficiency, enhance safety and security, and expand research capabilities. • Smart Work Spaces in order to enable employees to collaborate together anywhere, anytime instantly. • Cisco is engaged in 90 global Greenfield and Brownfield projects, which include the Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor in India, where Cisco is developing the ICT master plan for four pilot cities in the $90 billion flagship public sector infrastructure project. Source : Cisco Systems, Inc. Corporation 11
Growing needs of Indian Citizens • For better health facilities 600, 000 doctors and 1 million nurses. • For effective education 1. 2 million teachers in government schools. • Smart parking solution to reduce ≈ 30% of urban traffic and annual fuel wastage by ≈ $10 billion respectively. • Smart building to reduce ≈ 40% of energy consumption. • Internet services infrastructure to meet six fold internet traffic in future. • Mobile communication services for ≈ 843. 3 million users. --1. 1 billion Mobile connected devices. --1. 8 billion Networked devices. • Remotely accessible services for healthcare, retail or banking services, citizen services etc. • Connected learning for cities, educational institutions and companies to improve student outcomes, increase efficiency, enhance safety and security, and expand research capabilities. • Smart Work Spaces in order to enable employees to collaborate together anywhere, anytime instantly. • Cisco is engaged in 90 global Greenfield and Brownfield projects, which include the Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor in India, where Cisco is developing the ICT master plan for four pilot cities in the $90 billion flagship public sector infrastructure project. Source : Cisco Systems, Inc. Corporation 11
 The Coming Crisis in India HEALTHCARE The number of diabetics in India is to rise from 50 million in 2010 to 100 million in 2030. Cancer incidence in India will rise 78% by 2030 By 2030, 25% of deaths in India will be from heart disease. Loss due to heart disease in India will rise from $9 billion in 2005 to $237 billion on 2015. CLEAN WATER FOR ALL Climate change is going to change water availability patters significantly over the next few decades. Indian has per capita water availability of only 1100 cubic metres per year; it had over 3000 cubic metres in the 1950 s. 60% of groundwater blocks in India will be in critical condition by 2025. By 2030, availability of water can fall short of demand by 50%. GIVING QUALITY EDUCATION 58% of Indian Children do not complete primary school. 90% of then do not finish high school. India has a higher education enrollment ratio of just 19. 4% , while develop countries have an average ratio of 58%. India will have a shortfall of 347 million workers in the non-agricultural work force by 2022. Source: The Economic Times Mar 13, 2014 PROVIDING FOOD FOR EVERYBODY Indian population now 1. 2 billion and expected population in 2040 1. 5 billion. Current food production 260 million tones and it are required to be increase up to 500 million tones by 2040. Decrease in yields predicted due to climate change up to 12%. Indian agricultural land will decline by 2% in coming two decades. About 60% of crops are still rain-fed. One-third of produce is wasted due to poor technology. GENERATING ENERGY AT LOW COSTS India is world’s 4 th largest Carbon Emitter. India’s energy production will increase by 112% by 2035, the highest growth for any country in the world. India’s annual emissions are rising at about 7 -8% by 2035; India’s energy demand is expected to rise 132%. MAKE OUR CITIES LIVEABLE Air pollution in Indian cities is among the highest in the world, with Delhi being the most-polluted city. Urban waste could increase six folds over 35 years. Two-thirds of Indian cities are already facing water crisis. Violent crime is on the rise in most Indian cities. 10% of the world’s road accidents happen in India. 12
The Coming Crisis in India HEALTHCARE The number of diabetics in India is to rise from 50 million in 2010 to 100 million in 2030. Cancer incidence in India will rise 78% by 2030 By 2030, 25% of deaths in India will be from heart disease. Loss due to heart disease in India will rise from $9 billion in 2005 to $237 billion on 2015. CLEAN WATER FOR ALL Climate change is going to change water availability patters significantly over the next few decades. Indian has per capita water availability of only 1100 cubic metres per year; it had over 3000 cubic metres in the 1950 s. 60% of groundwater blocks in India will be in critical condition by 2025. By 2030, availability of water can fall short of demand by 50%. GIVING QUALITY EDUCATION 58% of Indian Children do not complete primary school. 90% of then do not finish high school. India has a higher education enrollment ratio of just 19. 4% , while develop countries have an average ratio of 58%. India will have a shortfall of 347 million workers in the non-agricultural work force by 2022. Source: The Economic Times Mar 13, 2014 PROVIDING FOOD FOR EVERYBODY Indian population now 1. 2 billion and expected population in 2040 1. 5 billion. Current food production 260 million tones and it are required to be increase up to 500 million tones by 2040. Decrease in yields predicted due to climate change up to 12%. Indian agricultural land will decline by 2% in coming two decades. About 60% of crops are still rain-fed. One-third of produce is wasted due to poor technology. GENERATING ENERGY AT LOW COSTS India is world’s 4 th largest Carbon Emitter. India’s energy production will increase by 112% by 2035, the highest growth for any country in the world. India’s annual emissions are rising at about 7 -8% by 2035; India’s energy demand is expected to rise 132%. MAKE OUR CITIES LIVEABLE Air pollution in Indian cities is among the highest in the world, with Delhi being the most-polluted city. Urban waste could increase six folds over 35 years. Two-thirds of Indian cities are already facing water crisis. Violent crime is on the rise in most Indian cities. 10% of the world’s road accidents happen in India. 12
 Draft benchmark for Smart Cities Ø Transportation time: Maximum travel time 30 minutes in small & medium size cities and 45 minutes in metropolitan areas and High frequency mass transport within 800 meters (10 -15 minute walking distance) Ø Footpath: Continuous unobstructed footpath of minimum 2 meter wide on either side of all street Ø Bicycle tracks: Dedicated and physically segregation of bicycle tracks on all streets with carriageway more than 10 meters Ø Additional infrastructure: 95% of residences should have retail outlets, parks, primary schools & recreational areas within 400 meters walking distance Ø Water Management 24 x 7 water 100% households should be connected to waste water network 100% households are covered by daily door-step solid waste collection system No water logging incidents in a year Ø Electricity Supply 24 x 7 supply of electricity 100% metering of electricity supply 100% recovery of cost 100% of the city has wi-fi connectivity & 100 Mbps internet speed Ø Medical Facility: 30 minutes emergency response time for patients Ø Geospatial Information System (GIS) Services Integration of Disaster Rescue Information Layer Management and Editing Map Navigation Import and Export Source: The Times of India (MGI report ), NIIT-Tech 13
Draft benchmark for Smart Cities Ø Transportation time: Maximum travel time 30 minutes in small & medium size cities and 45 minutes in metropolitan areas and High frequency mass transport within 800 meters (10 -15 minute walking distance) Ø Footpath: Continuous unobstructed footpath of minimum 2 meter wide on either side of all street Ø Bicycle tracks: Dedicated and physically segregation of bicycle tracks on all streets with carriageway more than 10 meters Ø Additional infrastructure: 95% of residences should have retail outlets, parks, primary schools & recreational areas within 400 meters walking distance Ø Water Management 24 x 7 water 100% households should be connected to waste water network 100% households are covered by daily door-step solid waste collection system No water logging incidents in a year Ø Electricity Supply 24 x 7 supply of electricity 100% metering of electricity supply 100% recovery of cost 100% of the city has wi-fi connectivity & 100 Mbps internet speed Ø Medical Facility: 30 minutes emergency response time for patients Ø Geospatial Information System (GIS) Services Integration of Disaster Rescue Information Layer Management and Editing Map Navigation Import and Export Source: The Times of India (MGI report ), NIIT-Tech 13
 Energy scenario in INDIA Installed Renewable Capacity (May 2014) SOURCE Wind Power Solar Power (SPV) Small Hydro Power Biomass Power Biogas Cogeneration Waste to Power Total CAPACITY (MW) 21, 262. 23 2, 647. 00 3, 803. 65 1, 365. 20 2, 512. 88 106. 58 31, 833. 01 Growing Population’s Demand PARAMETERS DATA Energy/person 22. 2 GJ/person/year Electricity/person 543 k. Wh/capita/year CO 2 emissions 1325 Million tonnes Per person 1. 18 tonnes /capita/year Per GDP 0. 33 kg /US$ ppp Source: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India and IEA, Key World Energy Statistics …. to be continued 14
Energy scenario in INDIA Installed Renewable Capacity (May 2014) SOURCE Wind Power Solar Power (SPV) Small Hydro Power Biomass Power Biogas Cogeneration Waste to Power Total CAPACITY (MW) 21, 262. 23 2, 647. 00 3, 803. 65 1, 365. 20 2, 512. 88 106. 58 31, 833. 01 Growing Population’s Demand PARAMETERS DATA Energy/person 22. 2 GJ/person/year Electricity/person 543 k. Wh/capita/year CO 2 emissions 1325 Million tonnes Per person 1. 18 tonnes /capita/year Per GDP 0. 33 kg /US$ ppp Source: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India and IEA, Key World Energy Statistics …. to be continued 14
 Renewable energy scenario in INDIA Sl. No. Physical Progress in 2014 -15 Sector 1 GRID-INTERACTIVE POWER (MW) 2 OFF-GRID/ CAPTIVE POWER (MW) 3 Wind Power Small Hydro Power Biomass Power & Gasification Biogases Cogeneration Waste to Power Solar Power Total Waste to Energy Biomass(non-biogases) Cogeneration Biomass Gasifiers -Rural -Industrial Aero-Generators/Hybrid systems SPV Systems Water mills/micro hydel Bio-gas based energy system Total OTHER RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS Family Biogas Plants (numbers in lakh) Solar Water Heating – Coll. Areas (million m 2) Source: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India Target for Financial Year: 2014 -15 2000. 00 250. 00 100. 00 300. 00 20. 00 1100. 00 3770. 00 10. 00 80. 00 0. 80 8. 00 0. 5 60. 00 4. 00 0. 00 163. 30 1. 10 0. 50 15
Renewable energy scenario in INDIA Sl. No. Physical Progress in 2014 -15 Sector 1 GRID-INTERACTIVE POWER (MW) 2 OFF-GRID/ CAPTIVE POWER (MW) 3 Wind Power Small Hydro Power Biomass Power & Gasification Biogases Cogeneration Waste to Power Solar Power Total Waste to Energy Biomass(non-biogases) Cogeneration Biomass Gasifiers -Rural -Industrial Aero-Generators/Hybrid systems SPV Systems Water mills/micro hydel Bio-gas based energy system Total OTHER RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS Family Biogas Plants (numbers in lakh) Solar Water Heating – Coll. Areas (million m 2) Source: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India Target for Financial Year: 2014 -15 2000. 00 250. 00 100. 00 300. 00 20. 00 1100. 00 3770. 00 10. 00 80. 00 0. 80 8. 00 0. 5 60. 00 4. 00 0. 00 163. 30 1. 10 0. 50 15
 The SMART CITY standard : ISO 37120 …. to be continued 16
The SMART CITY standard : ISO 37120 …. to be continued 16
 The SMART CITY standard: Dissecting ISO 37120 Sl No. Title Core Indicators 1 The long road to zero waste cities 2 Economic indicators in the new City’s unemployment rate and population living in smart city standard poverty. 3 Why education may be the most important smart city indicator of all? Female school-aged population enrolled in school, students completing primary education & secondary education, student/teacher ratio. 4 Does your city's air quality measure up to the new smart city standard? Particulate matter (PM 2. 5 - PM 10) concentration and Greenhouse gas emissions measured in tonnes per capita. 5 How debt, spending and tax Debt service ratio. collections add up in new smart city standard? 6 Fire and emergency response indicators -- how safe is your city? Source: Smart Cities Council 03 Oct, 2014 Solid waste collection & its recycling. Number of firefighters, fire related deaths and natural disaster related deaths. …. to be continued 17
The SMART CITY standard: Dissecting ISO 37120 Sl No. Title Core Indicators 1 The long road to zero waste cities 2 Economic indicators in the new City’s unemployment rate and population living in smart city standard poverty. 3 Why education may be the most important smart city indicator of all? Female school-aged population enrolled in school, students completing primary education & secondary education, student/teacher ratio. 4 Does your city's air quality measure up to the new smart city standard? Particulate matter (PM 2. 5 - PM 10) concentration and Greenhouse gas emissions measured in tonnes per capita. 5 How debt, spending and tax Debt service ratio. collections add up in new smart city standard? 6 Fire and emergency response indicators -- how safe is your city? Source: Smart Cities Council 03 Oct, 2014 Solid waste collection & its recycling. Number of firefighters, fire related deaths and natural disaster related deaths. …. to be continued 17
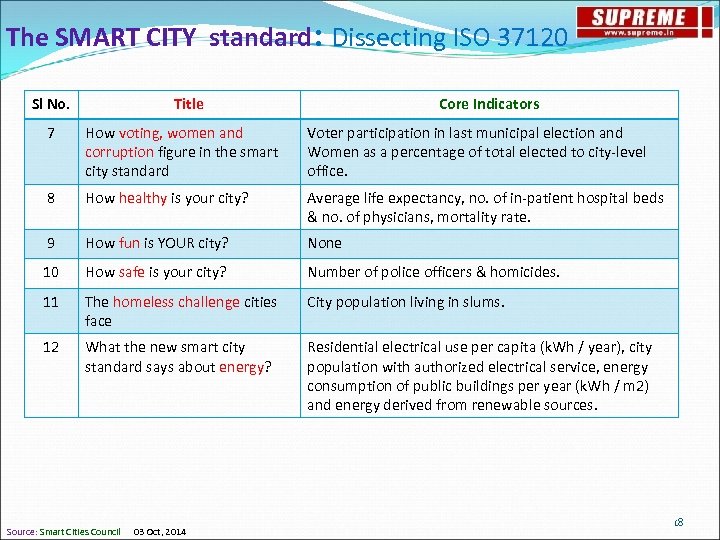 The SMART CITY standard: Dissecting ISO 37120 Sl No. Title Core Indicators 7 How voting, women and corruption figure in the smart city standard Voter participation in last municipal election and Women as a percentage of total elected to city-level office. 8 How healthy is your city? Average life expectancy, no. of in-patient hospital beds & no. of physicians, mortality rate. 9 How fun is YOUR city? None 10 How safe is your city? Number of police officers & homicides. 11 The homeless challenge cities face City population living in slums. 12 What the new smart city standard says about energy? Residential electrical use per capita (k. Wh / year), city population with authorized electrical service, energy consumption of public buildings per year (k. Wh / m 2) and energy derived from renewable sources. Source: Smart Cities Council 03 Oct, 2014 18
The SMART CITY standard: Dissecting ISO 37120 Sl No. Title Core Indicators 7 How voting, women and corruption figure in the smart city standard Voter participation in last municipal election and Women as a percentage of total elected to city-level office. 8 How healthy is your city? Average life expectancy, no. of in-patient hospital beds & no. of physicians, mortality rate. 9 How fun is YOUR city? None 10 How safe is your city? Number of police officers & homicides. 11 The homeless challenge cities face City population living in slums. 12 What the new smart city standard says about energy? Residential electrical use per capita (k. Wh / year), city population with authorized electrical service, energy consumption of public buildings per year (k. Wh / m 2) and energy derived from renewable sources. Source: Smart Cities Council 03 Oct, 2014 18
 SMART CITY initiative in INDIA ………… news highlights …. to be continued 19
SMART CITY initiative in INDIA ………… news highlights …. to be continued 19
 SMART CITY initiative in INDIA………… news highlights India's smart city craze: big, green and doomed from the start? (Source: The Guardian April 17, 2014) Urban population is expected to rise from 28% in 2001 to almost 36% in 2026, bringing the total number of people living in its cities and urban regions to 590 million. India will need 20 to 30 new cities in the next decade alone. Dholera the proposed smart city loses 1 cm of its coastline to the sea every day due to sea vast landscape getting converted into a terrain. In Dholera for several months of the year, they will find a vast, low-lying area, mostly submerged under seawater. The rest of the year, they will see the classic cracked-earth look of salt flats. MNCs line up for a slice of India’s smart-city pie(Source: The Hindu October 1, 2014) MNC are expecting a $35 -billion Io. T (Internet of Things) opportunity in India for upcoming smart cities. Philips’ connected LED Lighting solution, that allows streetlights to be instantly connected to and controlled by a remote lighting management system, has been installed at Naya Raipur, one of India’s first few smart cities. IBM has partnered with the Lodha Group to build and manage smart city infrastructure spanning 4, 000 acres at the junction of Navi Mumbai and Dombivali. The road to smart cities(Source: The Hindu October 5, 2014) Graphics processing units (GPU) play a major role in developing applications for smart cities. India’s e-governance projects are very amenable to the use of GPUs. PM Modi's US visit: US to help India develop three smart cities Allahabad, Ajmer and Visakhapatnam(Source: The Economic Times Oct 1, 2014 ) In a boost to India's 100 smart city programme, the US will help India in developing three such cities (Allahabad, Ajmer and Visakhapatnam). In collaboration with local civil society and authorities US help us to provide clean water and sewage facilities in 500 cities in the country. In the Union Budget, Finance Minister had promised allocation of a sum of Rs. 7, 060 crore for the development of the smart cities. …. to be continued 20
SMART CITY initiative in INDIA………… news highlights India's smart city craze: big, green and doomed from the start? (Source: The Guardian April 17, 2014) Urban population is expected to rise from 28% in 2001 to almost 36% in 2026, bringing the total number of people living in its cities and urban regions to 590 million. India will need 20 to 30 new cities in the next decade alone. Dholera the proposed smart city loses 1 cm of its coastline to the sea every day due to sea vast landscape getting converted into a terrain. In Dholera for several months of the year, they will find a vast, low-lying area, mostly submerged under seawater. The rest of the year, they will see the classic cracked-earth look of salt flats. MNCs line up for a slice of India’s smart-city pie(Source: The Hindu October 1, 2014) MNC are expecting a $35 -billion Io. T (Internet of Things) opportunity in India for upcoming smart cities. Philips’ connected LED Lighting solution, that allows streetlights to be instantly connected to and controlled by a remote lighting management system, has been installed at Naya Raipur, one of India’s first few smart cities. IBM has partnered with the Lodha Group to build and manage smart city infrastructure spanning 4, 000 acres at the junction of Navi Mumbai and Dombivali. The road to smart cities(Source: The Hindu October 5, 2014) Graphics processing units (GPU) play a major role in developing applications for smart cities. India’s e-governance projects are very amenable to the use of GPUs. PM Modi's US visit: US to help India develop three smart cities Allahabad, Ajmer and Visakhapatnam(Source: The Economic Times Oct 1, 2014 ) In a boost to India's 100 smart city programme, the US will help India in developing three such cities (Allahabad, Ajmer and Visakhapatnam). In collaboration with local civil society and authorities US help us to provide clean water and sewage facilities in 500 cities in the country. In the Union Budget, Finance Minister had promised allocation of a sum of Rs. 7, 060 crore for the development of the smart cities. …. to be continued 20
 SMART CITY initiative in INDIA………… news highlights Budget estimation for proposed 100 Smart Cities in India(Source: The Financial Express) Infrastructure gap: Approx $1 trillion investment is required to overcome infrastructure gap during 12 th Plan Period, while the GDP of India was $1. 87 million in 2013, there is a serious challenge on meeting the infrastructure gap with rising cost of financing, inadequate fuel supply, policy bottlenecks and constrained business environment. Annual fund requirement: About INR 35, 000 crore ($5. 8 billion) for 100 smart cities of 1 million population each. Govt to open discussion on ‘ 100 smart cities’ via portal (Source: The Hindu September 8, 2014) The Ministry of Urban Development will invite discussions from all stakeholders, including the general public, through a web portal www. smartindia. gov. in for its ambitious ‘ 100 smart cities’ initiative. Developing model village clusters(Source: The Hindu October 5, 2014) Model village clusters should be created before the inflow of rural population begins in a massive way. Rural population will decline from about 833 million in 2011 to about 260 million in 2050, while in urban areas, the population will increase from 377 million in 2011 to about 1, 200 million in 2050. Each Member of Parliament to make one village of his or her constituency a ‘model village’ by 2016. After 2016, two more villages should be selected and after 2019, at least five model villages must be established by each MP in his/her area. In India, with 6 lakh villages, the average population of a village is only about 1, 000. India, Japan sign Mo. U to develop Varanasi into ‘smart city’ (Source: The Hindu August 30, 2014) Varanasi will be developed into a ‘smart city’ in collaboration with Japan. Vizag to be developed as smart city with U. S. aid(Source: The Hindu October 1, 2014) Vizag will be developed into a ‘smart city’ in collaboration with U. S. . ‘Include Belgaum in list of smart cities’(Source: The Hindu September 18, 2014 ) The Railway Ministry is going to introduce a high-speed train between Mumbai and Bangalore via Belgaum, besides doubling the existing broad gauge line between the two metro cities. The city is a major educational hub in north Karnataka and also had good healthcare facilities. …. to be continued 21
SMART CITY initiative in INDIA………… news highlights Budget estimation for proposed 100 Smart Cities in India(Source: The Financial Express) Infrastructure gap: Approx $1 trillion investment is required to overcome infrastructure gap during 12 th Plan Period, while the GDP of India was $1. 87 million in 2013, there is a serious challenge on meeting the infrastructure gap with rising cost of financing, inadequate fuel supply, policy bottlenecks and constrained business environment. Annual fund requirement: About INR 35, 000 crore ($5. 8 billion) for 100 smart cities of 1 million population each. Govt to open discussion on ‘ 100 smart cities’ via portal (Source: The Hindu September 8, 2014) The Ministry of Urban Development will invite discussions from all stakeholders, including the general public, through a web portal www. smartindia. gov. in for its ambitious ‘ 100 smart cities’ initiative. Developing model village clusters(Source: The Hindu October 5, 2014) Model village clusters should be created before the inflow of rural population begins in a massive way. Rural population will decline from about 833 million in 2011 to about 260 million in 2050, while in urban areas, the population will increase from 377 million in 2011 to about 1, 200 million in 2050. Each Member of Parliament to make one village of his or her constituency a ‘model village’ by 2016. After 2016, two more villages should be selected and after 2019, at least five model villages must be established by each MP in his/her area. In India, with 6 lakh villages, the average population of a village is only about 1, 000. India, Japan sign Mo. U to develop Varanasi into ‘smart city’ (Source: The Hindu August 30, 2014) Varanasi will be developed into a ‘smart city’ in collaboration with Japan. Vizag to be developed as smart city with U. S. aid(Source: The Hindu October 1, 2014) Vizag will be developed into a ‘smart city’ in collaboration with U. S. . ‘Include Belgaum in list of smart cities’(Source: The Hindu September 18, 2014 ) The Railway Ministry is going to introduce a high-speed train between Mumbai and Bangalore via Belgaum, besides doubling the existing broad gauge line between the two metro cities. The city is a major educational hub in north Karnataka and also had good healthcare facilities. …. to be continued 21
 SMART CITY initiative in INDIA………… news highlights State keen on making towns ‘smart’ rather than build new ones (Source: The Hindu September 11, 2014) Upgrade our existing cities to make it smart. AP may get only 4 smart cities(Source: The Times of India Oct 5, 2014) Andhra Pradesh may get four smart cities , which may come up only in Vijayawada, Visakhapatnam, Tirupati and Nellore. The smart cities concept will be devolved on the lines of the Gujarat international financial tech city (GIFT) and the Delhi Mumbai Industrial corridor (DMIC) undertaken by the respective governments. Metro rail project already been initiated to develop Vijayawada, Visakhapatnam and Tirupati as mega cities with world class infrastructure facilities. Indore: Smart City project to get a push at global summit(Source: Hindustan Times Oct 5, 2014, ) Officials of UAE-based Smart. City, Dubai, will take part in the Global Investors' Summit in Indore and also explore the possibility of developing a smart city in Madhya Pradesh like the one in Kochi. Smart. City, Dubai, was recently given permissions to construct the first building of Kochi Smart City with an investment of $29 million under the supervision of Abdullah Almulla , the chief business development officer of Dubai Holding. The state government plans to develop a smart city on 1, 000 acres of land at a location between Indore and Bhopal. Another smart city in Madhya Pradesh is coming up near Ujjain. The master plan for the smart city in Ujjain, which will be an integrated industrial township, has already been accepted by the state government and the land acquisition has been completed. The Union government will soon start the process for construction of the smart city, being developed under Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) project. …. to be continued 22
SMART CITY initiative in INDIA………… news highlights State keen on making towns ‘smart’ rather than build new ones (Source: The Hindu September 11, 2014) Upgrade our existing cities to make it smart. AP may get only 4 smart cities(Source: The Times of India Oct 5, 2014) Andhra Pradesh may get four smart cities , which may come up only in Vijayawada, Visakhapatnam, Tirupati and Nellore. The smart cities concept will be devolved on the lines of the Gujarat international financial tech city (GIFT) and the Delhi Mumbai Industrial corridor (DMIC) undertaken by the respective governments. Metro rail project already been initiated to develop Vijayawada, Visakhapatnam and Tirupati as mega cities with world class infrastructure facilities. Indore: Smart City project to get a push at global summit(Source: Hindustan Times Oct 5, 2014, ) Officials of UAE-based Smart. City, Dubai, will take part in the Global Investors' Summit in Indore and also explore the possibility of developing a smart city in Madhya Pradesh like the one in Kochi. Smart. City, Dubai, was recently given permissions to construct the first building of Kochi Smart City with an investment of $29 million under the supervision of Abdullah Almulla , the chief business development officer of Dubai Holding. The state government plans to develop a smart city on 1, 000 acres of land at a location between Indore and Bhopal. Another smart city in Madhya Pradesh is coming up near Ujjain. The master plan for the smart city in Ujjain, which will be an integrated industrial township, has already been accepted by the state government and the land acquisition has been completed. The Union government will soon start the process for construction of the smart city, being developed under Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) project. …. to be continued 22
 SMART CITY initiative examples in INDIA……news highlights How smart tech is solving Thiruvananthapuram's big water problem (Source: Smart Cities Council Sep 26) Aging pipes, leaking infrastructure and water losses approaching 45% have made it challenging for the water authority serving the 3. 3 million people. Kerala Water Authority (KWA) is going establish a Water Management Center using the IBM Intelligent Water Software. The idea is to bring all the distribution and consumption data from water meters to a central dashboard where usage can be effectively and predictively monitored and managed. This gives KWA operators a unified and real time view of the transmission and consumption of water across Thiruvananthapuram. UST Global unveils advanced telemedicine app(Source: Smart Cities Council Oct 01) Telemedicine for mobile devices, developed by Council Associate Partner UST Global in collaboration with Mumbai-based Dr. Balabhai Nanavati Hospital and Blackberry based mobile application that uses telecommunication to enable delivery of clinical health care to remote locations. The new app helps to eliminate distance barriers and to improve access to medical specialists that would often not be consistently available in distant rural communities. A patient visits a remote clinic where staff can use the app to enter the patient's demographics, vital signs, illness details, preliminary diagnosis information and upload existing medical reports. Then assigned doctor reviews the patient details and performs consultation with the patient remotely using a video session launched through Black. Berry Messenger (BBMTM). Work in progress: Lavasa urban development(Source: The Financial Express November 12, 2014) Lavasa is being developed as a private hill city by Hindustan Construction Company (HCC). The first city in India to have adopted LIDAR technology, which is considered a more precise system of data capturing, making detailing of project planning and execution more accurate. There are 376 apartments offering studio, one-, two- and three-bedroom apartments, and 476 villas overlooking a 2 km-long promenade and the lake. My. City Technology is a joint venture initiative between Lavasa and two IT giants, Wipro and CISCO has been created, to grow Lavasa into a smart urban destination. They used Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) technology to provide high data bandwidth. City Management Service (CMS) is equivalent to a municipal corporation of a city in a quasi government mode because it provides some of the authority of a local government, but not all of it such as no powers to tax or financially penalise citizens. 23
SMART CITY initiative examples in INDIA……news highlights How smart tech is solving Thiruvananthapuram's big water problem (Source: Smart Cities Council Sep 26) Aging pipes, leaking infrastructure and water losses approaching 45% have made it challenging for the water authority serving the 3. 3 million people. Kerala Water Authority (KWA) is going establish a Water Management Center using the IBM Intelligent Water Software. The idea is to bring all the distribution and consumption data from water meters to a central dashboard where usage can be effectively and predictively monitored and managed. This gives KWA operators a unified and real time view of the transmission and consumption of water across Thiruvananthapuram. UST Global unveils advanced telemedicine app(Source: Smart Cities Council Oct 01) Telemedicine for mobile devices, developed by Council Associate Partner UST Global in collaboration with Mumbai-based Dr. Balabhai Nanavati Hospital and Blackberry based mobile application that uses telecommunication to enable delivery of clinical health care to remote locations. The new app helps to eliminate distance barriers and to improve access to medical specialists that would often not be consistently available in distant rural communities. A patient visits a remote clinic where staff can use the app to enter the patient's demographics, vital signs, illness details, preliminary diagnosis information and upload existing medical reports. Then assigned doctor reviews the patient details and performs consultation with the patient remotely using a video session launched through Black. Berry Messenger (BBMTM). Work in progress: Lavasa urban development(Source: The Financial Express November 12, 2014) Lavasa is being developed as a private hill city by Hindustan Construction Company (HCC). The first city in India to have adopted LIDAR technology, which is considered a more precise system of data capturing, making detailing of project planning and execution more accurate. There are 376 apartments offering studio, one-, two- and three-bedroom apartments, and 476 villas overlooking a 2 km-long promenade and the lake. My. City Technology is a joint venture initiative between Lavasa and two IT giants, Wipro and CISCO has been created, to grow Lavasa into a smart urban destination. They used Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) technology to provide high data bandwidth. City Management Service (CMS) is equivalent to a municipal corporation of a city in a quasi government mode because it provides some of the authority of a local government, but not all of it such as no powers to tax or financially penalise citizens. 23
 SMART CITY initiative examples in INDIA……news highlights Columns: Powering India’s smart cities India is the 4 th largest consumer of energy in the world after USA, China and Russia with 17% of world’s population. India aims to expand its solar power capacity upto 22, 000 MW by 2022 under the Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission. The Clinton Climate Initiative (CCI) had announced setting up of a 3000 MW solar power plant in Gujarat with an estimated investment of R 50, 000 crore. Rajasthan has laid the foundation for another 3000 MW solar power plant at Bhadla of Jodhpur District in 2013. Energy resources and consumption scenario in India Resources Availability Import Oil 0. 4% 80% of its crude oil consumption Natural gas 0. 4% 35% of its natural gas consumption Coal 6% 15% of its coal consumption Source: The Financial Express November 12, 2014 …. to be continued 24
SMART CITY initiative examples in INDIA……news highlights Columns: Powering India’s smart cities India is the 4 th largest consumer of energy in the world after USA, China and Russia with 17% of world’s population. India aims to expand its solar power capacity upto 22, 000 MW by 2022 under the Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission. The Clinton Climate Initiative (CCI) had announced setting up of a 3000 MW solar power plant in Gujarat with an estimated investment of R 50, 000 crore. Rajasthan has laid the foundation for another 3000 MW solar power plant at Bhadla of Jodhpur District in 2013. Energy resources and consumption scenario in India Resources Availability Import Oil 0. 4% 80% of its crude oil consumption Natural gas 0. 4% 35% of its natural gas consumption Coal 6% 15% of its coal consumption Source: The Financial Express November 12, 2014 …. to be continued 24
 The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 25 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014 …. to be continued
The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 25 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014 …. to be continued
 The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. COPENHAGEN AMSTERDAM VIENNA BARCELONA PARIS STOCKHOLM LONDON HAMBURG BERLIN HELSINKI Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 26 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014 …. to be continued
The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. COPENHAGEN AMSTERDAM VIENNA BARCELONA PARIS STOCKHOLM LONDON HAMBURG BERLIN HELSINKI Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 26 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014 …. to be continued
 The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU No. 1: COPENHAGEN Led the Siemens Green City Index for Europe One of the lowest carbon footprints/capita in the world (less than two tons/capita). Aspire to achieve carbon neutrality by 2025 All new buildings to be carbon neutral (green building ). Approximately 40% of all commutes are conducted by bike. The city also recently collaborated with MIT to develop a smart bike equipped with sensors to deliver to provide real-time info to not only the rider but also to administrators for open data aggregation on issues of air contamination and traffic congestion. No. 2: AMSTERDAM 67% of all trips are done by cycling or walking. First bike sharing project in the world was occurred in Amsterdam decades ago. At present 40 smart city projects ranging from smart parking to the development of home energy storage for integration with a smart grid. No. 3: VIENNA The “Citizen Solar Power Plant“ being developed with a goal of obtaining 50% of their energy from renewable sources by 2030. Testing out a range of electric mobility solutions from expanding their charging network from 103 to 440 stations by 2015. Residents are sharing vehicle with neighbors. No. 4: BARCELONA Bike-sharing project with more than 6, 000 bikes. Using various sensors from noise and air contamination to traffic congestion and even waste management. The life expectancy in Barcelona is among the highest of cities ( approx 83 years). No. 5: PARIS • The city has more than 20, 000 bikes for sharing. • 5% reduction in vehicle congestion in the city. • The city partnered with Bolloré to create one of the world’s first and most expansive EV car sharing programs. • Autolib’ will soon have 3, 000 EVs in its car sharing fleet. • Paris’ ecosystem was rated 11 th best in the world. …. to be continued Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 27 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014
The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU No. 1: COPENHAGEN Led the Siemens Green City Index for Europe One of the lowest carbon footprints/capita in the world (less than two tons/capita). Aspire to achieve carbon neutrality by 2025 All new buildings to be carbon neutral (green building ). Approximately 40% of all commutes are conducted by bike. The city also recently collaborated with MIT to develop a smart bike equipped with sensors to deliver to provide real-time info to not only the rider but also to administrators for open data aggregation on issues of air contamination and traffic congestion. No. 2: AMSTERDAM 67% of all trips are done by cycling or walking. First bike sharing project in the world was occurred in Amsterdam decades ago. At present 40 smart city projects ranging from smart parking to the development of home energy storage for integration with a smart grid. No. 3: VIENNA The “Citizen Solar Power Plant“ being developed with a goal of obtaining 50% of their energy from renewable sources by 2030. Testing out a range of electric mobility solutions from expanding their charging network from 103 to 440 stations by 2015. Residents are sharing vehicle with neighbors. No. 4: BARCELONA Bike-sharing project with more than 6, 000 bikes. Using various sensors from noise and air contamination to traffic congestion and even waste management. The life expectancy in Barcelona is among the highest of cities ( approx 83 years). No. 5: PARIS • The city has more than 20, 000 bikes for sharing. • 5% reduction in vehicle congestion in the city. • The city partnered with Bolloré to create one of the world’s first and most expansive EV car sharing programs. • Autolib’ will soon have 3, 000 EVs in its car sharing fleet. • Paris’ ecosystem was rated 11 th best in the world. …. to be continued Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 27 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014
 The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU No. 6: STOCKHOLM About 40% of its land mass is dedicated to green space. Rated 2 nd in Siemens Green City Index. Citizens are also amongst the highest per capita users of the Stockholm Metro system. Aspires to become carbon neutral, by 2025. Endeavour to boast about its 800 kilometers of cycling paths. Received top marks for its commitment to digital governance. Scored 1 st amongst cities for its commitment to data privacy and security for citizens. No. 7: LONDON Earned 1 st place in the smart economy category and it has long been considered the financial capital of Europe. The Startup Genome project rated London the 7 th best entrepreneurial ecosystem in world, and No. 1 in Europe. The greenest and smartest buildings of Europe is located in the city eg. , The Crystal, built by Siemens. No. 8: HAMBURG 2 nd largest city in Germany and the 1 st of two to make the top 10 ranking this year. Awarded the European Green Capital designation in 2011. High standard of living having been ranked 17 th globally by Mercer in 2012 and 8 th globally by Numbeo. Wide scale transformation is taking place at 157 hectares, Hafen City (Harbor City) , which is Europe’s largest urban regeneration project. No. 9: BERLIN Berlin is able to attract and retain the creative class and it has two zoos, three major opera houses, seven symphony orchestras, and scores of museums People prefers to walk instead of use car to travel short distance. No. 10: HELSINKI The 10 th and final spot in this year’s rankings by barely edged out Oslo. Having more than 1, 000 open datasets and have been actively promoting engagement with developers through collaborative computer programming. Launched Virium Smart City Project to provide ubiquitous data to their citizens in hopes of improving quality of life. …. to be continued Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 28 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014
The 10 SMARTEST CITIES in EU No. 6: STOCKHOLM About 40% of its land mass is dedicated to green space. Rated 2 nd in Siemens Green City Index. Citizens are also amongst the highest per capita users of the Stockholm Metro system. Aspires to become carbon neutral, by 2025. Endeavour to boast about its 800 kilometers of cycling paths. Received top marks for its commitment to digital governance. Scored 1 st amongst cities for its commitment to data privacy and security for citizens. No. 7: LONDON Earned 1 st place in the smart economy category and it has long been considered the financial capital of Europe. The Startup Genome project rated London the 7 th best entrepreneurial ecosystem in world, and No. 1 in Europe. The greenest and smartest buildings of Europe is located in the city eg. , The Crystal, built by Siemens. No. 8: HAMBURG 2 nd largest city in Germany and the 1 st of two to make the top 10 ranking this year. Awarded the European Green Capital designation in 2011. High standard of living having been ranked 17 th globally by Mercer in 2012 and 8 th globally by Numbeo. Wide scale transformation is taking place at 157 hectares, Hafen City (Harbor City) , which is Europe’s largest urban regeneration project. No. 9: BERLIN Berlin is able to attract and retain the creative class and it has two zoos, three major opera houses, seven symphony orchestras, and scores of museums People prefers to walk instead of use car to travel short distance. No. 10: HELSINKI The 10 th and final spot in this year’s rankings by barely edged out Oslo. Having more than 1, 000 open datasets and have been actively promoting engagement with developers through collaborative computer programming. Launched Virium Smart City Project to provide ubiquitous data to their citizens in hopes of improving quality of life. …. to be continued Source: A report prepared by Boyd Cohen, Ph. D. , LEED AP, is a climate strategist helping to lead communities, cities and companies on the journey towards 28 the low carbon economy. Dr. Cohen is the co-author of Climate Capitalism: Capitalism in the Age of Climate Change January 13, 2014
 SMART CITY activities in EU ………… news highlights …. to be continued 29
SMART CITY activities in EU ………… news highlights …. to be continued 29
 SMART CITY in EU European Green Capital indicators The selection of a city to be awarded the European Green Capital for 2017 will be assessed on the basis of twelve environmental indicator areas: 1. Climate change: mitigation and adaptation 2. Local transport 3. Green urban areas incorporating sustainable land use 4. Nature and biodiversity 5. Ambient air quality 6. Quality of the acoustic environment 7. Waste production and management 8. Water management 9. Waste water treatment 10. Eco innovation and sustainable employment 11. Energy performance 12. Integrated environmental management Source: European Commission …. to be continued 30
SMART CITY in EU European Green Capital indicators The selection of a city to be awarded the European Green Capital for 2017 will be assessed on the basis of twelve environmental indicator areas: 1. Climate change: mitigation and adaptation 2. Local transport 3. Green urban areas incorporating sustainable land use 4. Nature and biodiversity 5. Ambient air quality 6. Quality of the acoustic environment 7. Waste production and management 8. Water management 9. Waste water treatment 10. Eco innovation and sustainable employment 11. Energy performance 12. Integrated environmental management Source: European Commission …. to be continued 30
 SMART CITY activities examples in EU………… news highlights The new smart city – from hi-tech sensors to social innovation(Source: The Guardian 26 November 2013) At last week's Smart City World Expo in Barcelona, Jong-Sung Hwang, former CIO of the Seoul metropolitan government, informed of the city's attempt to capture real-time traffic data. For years the city invested millions of dollars in sensors embedded into the road infrastructure. Open 311 interface allows citizens to send photos or update reports on anything from pot holes to traffic signs, the imagination is the limit. Rio de Janeiro won best smart city 2013 at the World Expo, its Central Operations Centre the poster child of smart cities– a hub of 400 staff, myriad screens and an 80 square metre master screen, viewing images from the streets, a smart map of live city transport, even predictive analytics. In 2012, however, the city's 25, 000 taxis introduced a touch card payment system using GPS technology, effectively giving Seoul the real-time traffic information it had long craved at a fraction of the cost. Biometric data could help create sustainable cities of a smart nature(Source: The Guardian 23 August 2013 ) Biometric information is generated via sensors in electronic devices, such as GPS, accelerometers, light sensors and so forth. Fit these high tech gadgets with a low energy communication medium such as Bluetooth and the data created can then be read and potentially shared by smartphones and other internet-enabled devices. Wifi-enabled scales that measure your body fat percentage as well as your weight, heart rate monitors, and so on. Apps such as. Endomondo and Run. Keeper are helping cyclists and runners keep tabs on their physical exertions as well as track their routes and speed. He cites the use of GPS data to determine individuals' real-life travel patterns. Understand that en masse and you can optimise the linkages between forms of public transport or the design of new roads or cycle paths. Data is already affecting street lights in Barcelona(Source: The Guardian April 04, 2014) In certain areas of Barcelona, Cisco use video to identify the density of public squares. And suing these data the intensity of street lights can be changed. The company matches that data alongside other elements, such as whethere is a half- or full-moon and sends instructions of whether to reduce or increase the brightness of the LED street lights. …. to be continued 31
SMART CITY activities examples in EU………… news highlights The new smart city – from hi-tech sensors to social innovation(Source: The Guardian 26 November 2013) At last week's Smart City World Expo in Barcelona, Jong-Sung Hwang, former CIO of the Seoul metropolitan government, informed of the city's attempt to capture real-time traffic data. For years the city invested millions of dollars in sensors embedded into the road infrastructure. Open 311 interface allows citizens to send photos or update reports on anything from pot holes to traffic signs, the imagination is the limit. Rio de Janeiro won best smart city 2013 at the World Expo, its Central Operations Centre the poster child of smart cities– a hub of 400 staff, myriad screens and an 80 square metre master screen, viewing images from the streets, a smart map of live city transport, even predictive analytics. In 2012, however, the city's 25, 000 taxis introduced a touch card payment system using GPS technology, effectively giving Seoul the real-time traffic information it had long craved at a fraction of the cost. Biometric data could help create sustainable cities of a smart nature(Source: The Guardian 23 August 2013 ) Biometric information is generated via sensors in electronic devices, such as GPS, accelerometers, light sensors and so forth. Fit these high tech gadgets with a low energy communication medium such as Bluetooth and the data created can then be read and potentially shared by smartphones and other internet-enabled devices. Wifi-enabled scales that measure your body fat percentage as well as your weight, heart rate monitors, and so on. Apps such as. Endomondo and Run. Keeper are helping cyclists and runners keep tabs on their physical exertions as well as track their routes and speed. He cites the use of GPS data to determine individuals' real-life travel patterns. Understand that en masse and you can optimise the linkages between forms of public transport or the design of new roads or cycle paths. Data is already affecting street lights in Barcelona(Source: The Guardian April 04, 2014) In certain areas of Barcelona, Cisco use video to identify the density of public squares. And suing these data the intensity of street lights can be changed. The company matches that data alongside other elements, such as whethere is a half- or full-moon and sends instructions of whether to reduce or increase the brightness of the LED street lights. …. to be continued 31
 SMART CITY activities examples in EU………… news highlights Mississippi looks to telemedicine to improve diabetes outcomes(Source: Smart Cities Council April 23, 2014) The project will run 18 months and provide 200 diabetics from one of the state’s poorest regions with computer tablets. Software provided by Intel-GE Care Innovations and GE Healthcare will be installed on the tablets and enable medical professionals at the University of Mississippi and another regional hospital to remotely monitor patients’ test results and symptoms. At the start of the $1. 6 million project, each patient will be given a baseline exam and a treatment program that requires them to check glucose levels daily and transmit the results to the medical teams. Patients will also check their weight and blood pressure daily and transmit the information. Sweden and San Francisco point the way to zero waste future(Source: Smart Cities Council Sep 19, 2014) According to the Swedish Institute less than 1% of the country's garbage goes to landfills. Its 32 waste-to-energy (WTE) plants are incinerating almost 2 million tons of filtered garbage. Swedish households dutifully separate their newspapers, plastic, metal, glass, electric appliances, light bulbs and batteries. Newspapers are then turned into paper mass, bottles are reused or melted into new items, plastic containers become plastic raw material. In many municipalities, food waste is removed, then composted and turned into soil or biogas. Special trucks roam cities and pick up electronics and hazardous waste. Sweden, in fact, has become so good at burning trash that it looks to annually import 700, 000 tons of garbage from the UK, Italy, Norway and Ireland to feed its incinerators. Sweden largely sidesteps this problem by using an advanced, low-emission process in its WTE systems. The Swedish institute reports that heavy metal emissions from plants have been reduced by 99% since 1985. San Francisco aspires for zero waste by 2020. Smart Sensors Provide Cost-Saving Solutions in Finland (Source: Smart Cities Council April 07, 2014) In the summer overfilling at the local recycling stations was becoming more common, causing increased littering and cleaning costs. Customers were demanding increased collection intervals, while the service was getting too expensive to maintain. The wireless fill-level sensor system provided by Finland-based logistics solution company Enevo, a Council Associate Partner, measures and forecasts when waste containers will be full. Reduce the amount of collections by 51%. By combining the forecasts with traffic and vehicle information, Enevo’s system can generate millions of different route options and suggest the most cost-efficient to the user. Reduce unnecessary driving and emissions. …. to be continued 32
SMART CITY activities examples in EU………… news highlights Mississippi looks to telemedicine to improve diabetes outcomes(Source: Smart Cities Council April 23, 2014) The project will run 18 months and provide 200 diabetics from one of the state’s poorest regions with computer tablets. Software provided by Intel-GE Care Innovations and GE Healthcare will be installed on the tablets and enable medical professionals at the University of Mississippi and another regional hospital to remotely monitor patients’ test results and symptoms. At the start of the $1. 6 million project, each patient will be given a baseline exam and a treatment program that requires them to check glucose levels daily and transmit the results to the medical teams. Patients will also check their weight and blood pressure daily and transmit the information. Sweden and San Francisco point the way to zero waste future(Source: Smart Cities Council Sep 19, 2014) According to the Swedish Institute less than 1% of the country's garbage goes to landfills. Its 32 waste-to-energy (WTE) plants are incinerating almost 2 million tons of filtered garbage. Swedish households dutifully separate their newspapers, plastic, metal, glass, electric appliances, light bulbs and batteries. Newspapers are then turned into paper mass, bottles are reused or melted into new items, plastic containers become plastic raw material. In many municipalities, food waste is removed, then composted and turned into soil or biogas. Special trucks roam cities and pick up electronics and hazardous waste. Sweden, in fact, has become so good at burning trash that it looks to annually import 700, 000 tons of garbage from the UK, Italy, Norway and Ireland to feed its incinerators. Sweden largely sidesteps this problem by using an advanced, low-emission process in its WTE systems. The Swedish institute reports that heavy metal emissions from plants have been reduced by 99% since 1985. San Francisco aspires for zero waste by 2020. Smart Sensors Provide Cost-Saving Solutions in Finland (Source: Smart Cities Council April 07, 2014) In the summer overfilling at the local recycling stations was becoming more common, causing increased littering and cleaning costs. Customers were demanding increased collection intervals, while the service was getting too expensive to maintain. The wireless fill-level sensor system provided by Finland-based logistics solution company Enevo, a Council Associate Partner, measures and forecasts when waste containers will be full. Reduce the amount of collections by 51%. By combining the forecasts with traffic and vehicle information, Enevo’s system can generate millions of different route options and suggest the most cost-efficient to the user. Reduce unnecessary driving and emissions. …. to be continued 32
 SMART CITY activities examples in EU………… news highlights Five innovative city programmes from north America (Source: The Guardian 5 September 2013) 1. San Francisco: Sensors under parking spots in the city reduce congestion Sensors have been installed beneath parking spots throughout the city. The Department of Transportation computers track open spots and set prices according to availability and turnover. A mobile phone app is also used to direct drivers to open spots and allows them to refill meters remotely. By expanding payment options, the number of parking citations has markedly decreased. Environmental benefits are also evident. The program reduces circling and double parking, cutting down on the noise, pollution and frustration that accompany traffic congestion. 2. Memphis: Looking at the relationship between the police and people with mental health conditions Crisis intervention teams are responsible for interactions at each stage of the policing process. Dispatchers are taught how to recognize calls from people with mental health conditions and deploy only those officers who are trained to recognise symptoms. This programme has reduced mental health issues led to injuries from 35 to 7 out of every 100, 000 cases. 3. Chicago: Mentor programme invites low-income parents to serve as teaching assistants Chicago's parent mentor programme invites foreign-born and low-income parents to serve as teaching assistants in elementary school classrooms. Parent mentors receive workforce experience and language training, in addition to a modest regular salary. They also serve as ambassadors to their school district, organising after-school community learning centres that offer adult education, tutoring and childcare. Over 2, 000 parent mentors have graduated from the programme, with 80% going on to jobs or further education. The programme is featured in 41 Chicago schools with 20 more located throughout Illinois and the United States. For these parents, the programme's rigorous interview process, language and leadership training, work experience, and networking provide a necessary stepping stone to full-time employment and integration into their community. 4. Toronto: Employment scheme helps educated immigrants find jobs The Toronto regional immigrant employment council assembled a group of local employers, community-based organizations and government officials to help highly educated immigrants find jobs. Three- to six-month paid internships offer work experience for highly skilled immigrants, while introducing them to mentors and networking opportunities. Bridge loans help them finance necessary licensing exams and training courses. 5. California: Smart waste collection helps bridge inequality gaps The Smart Riverside facility in Riverside, California, collects reusable "waste" and converts it into hands-on education tools. The programme finances itself, using sales of non-salvageable materials to cover their extensive activities. So far, the Smart Riverside programme has served over 5, 000 households. 33
SMART CITY activities examples in EU………… news highlights Five innovative city programmes from north America (Source: The Guardian 5 September 2013) 1. San Francisco: Sensors under parking spots in the city reduce congestion Sensors have been installed beneath parking spots throughout the city. The Department of Transportation computers track open spots and set prices according to availability and turnover. A mobile phone app is also used to direct drivers to open spots and allows them to refill meters remotely. By expanding payment options, the number of parking citations has markedly decreased. Environmental benefits are also evident. The program reduces circling and double parking, cutting down on the noise, pollution and frustration that accompany traffic congestion. 2. Memphis: Looking at the relationship between the police and people with mental health conditions Crisis intervention teams are responsible for interactions at each stage of the policing process. Dispatchers are taught how to recognize calls from people with mental health conditions and deploy only those officers who are trained to recognise symptoms. This programme has reduced mental health issues led to injuries from 35 to 7 out of every 100, 000 cases. 3. Chicago: Mentor programme invites low-income parents to serve as teaching assistants Chicago's parent mentor programme invites foreign-born and low-income parents to serve as teaching assistants in elementary school classrooms. Parent mentors receive workforce experience and language training, in addition to a modest regular salary. They also serve as ambassadors to their school district, organising after-school community learning centres that offer adult education, tutoring and childcare. Over 2, 000 parent mentors have graduated from the programme, with 80% going on to jobs or further education. The programme is featured in 41 Chicago schools with 20 more located throughout Illinois and the United States. For these parents, the programme's rigorous interview process, language and leadership training, work experience, and networking provide a necessary stepping stone to full-time employment and integration into their community. 4. Toronto: Employment scheme helps educated immigrants find jobs The Toronto regional immigrant employment council assembled a group of local employers, community-based organizations and government officials to help highly educated immigrants find jobs. Three- to six-month paid internships offer work experience for highly skilled immigrants, while introducing them to mentors and networking opportunities. Bridge loans help them finance necessary licensing exams and training courses. 5. California: Smart waste collection helps bridge inequality gaps The Smart Riverside facility in Riverside, California, collects reusable "waste" and converts it into hands-on education tools. The programme finances itself, using sales of non-salvageable materials to cover their extensive activities. So far, the Smart Riverside programme has served over 5, 000 households. 33
 SMART CITY in EU………… news highlights Smart waste revolution to drive $42 billion in revenues over next decade Tightening regulations around trash disposal, coupled with the increasing cost of landfilling, are driving demand for smarter solutions in the municipal solid waste (MSW) industry. Total volume of waste generated globally is expected to grow by nearly 50% over the next 10 years, the adoption of innovative technologies for MSW is both a business opportunity and an environmental imperative. The report notes that 43% of the global MSW stream is handled today by some aspect of smart technology. Still, the smart waste market is expected to grow rapidly. Revenues over the next decade are expected to climb to more than $42 billion. Emerging smart waste technologies will create more integrated waste management offerings that move beyond the traditional use of labor, diesel trucks and open pits to discard MSW. These offerings are expected to enhance MSW collection, generate renewable energy and optimize the environmental performance of landfills. The report points out that smart energy recovery -- which includes facilities like incineration plants, landfill gas capture projects and advanced bio refineries -- is the most mature smart waste segment. Headset provides '3 D sound scape' to help blind people navigate cities A new navigational headset which have been developed by Microsoft and the Guide Dogs with the governmentfunded Future Cities Catapult let you hear your surroundings as a “ 3 D sound scape”. The headset contains a GPS tracker, compass and gyroscope, and can be programmed to talk to you through your route, like a pedestrian sat-nav. Paired with a smart phone, it uses location information from Microsoft’s Bing maps, which can be supplemented by tiny Bluetooth-enabled beacons stuck to lamp-posts around the city. Source: Smart Cities Council Oct 01, 2014 The Guardian 7 November 2014 34
SMART CITY in EU………… news highlights Smart waste revolution to drive $42 billion in revenues over next decade Tightening regulations around trash disposal, coupled with the increasing cost of landfilling, are driving demand for smarter solutions in the municipal solid waste (MSW) industry. Total volume of waste generated globally is expected to grow by nearly 50% over the next 10 years, the adoption of innovative technologies for MSW is both a business opportunity and an environmental imperative. The report notes that 43% of the global MSW stream is handled today by some aspect of smart technology. Still, the smart waste market is expected to grow rapidly. Revenues over the next decade are expected to climb to more than $42 billion. Emerging smart waste technologies will create more integrated waste management offerings that move beyond the traditional use of labor, diesel trucks and open pits to discard MSW. These offerings are expected to enhance MSW collection, generate renewable energy and optimize the environmental performance of landfills. The report points out that smart energy recovery -- which includes facilities like incineration plants, landfill gas capture projects and advanced bio refineries -- is the most mature smart waste segment. Headset provides '3 D sound scape' to help blind people navigate cities A new navigational headset which have been developed by Microsoft and the Guide Dogs with the governmentfunded Future Cities Catapult let you hear your surroundings as a “ 3 D sound scape”. The headset contains a GPS tracker, compass and gyroscope, and can be programmed to talk to you through your route, like a pedestrian sat-nav. Paired with a smart phone, it uses location information from Microsoft’s Bing maps, which can be supplemented by tiny Bluetooth-enabled beacons stuck to lamp-posts around the city. Source: Smart Cities Council Oct 01, 2014 The Guardian 7 November 2014 34
 THANK YOU 35
THANK YOU 35


