f0d7ee057faad0eb2036d32d500bac3f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Understanding Security Features in J 2 EE and Novell exte. Nd Director 5 Martin Holzner Manager, exte. Nd Technical Services Novell, Inc.
Understanding Security Features in J 2 EE and Novell exte. Nd Director 5 Martin Holzner Manager, exte. Nd Technical Services Novell, Inc.
 The one Net vision 2 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
The one Net vision 2 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 The one Net vision 3 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
The one Net vision 3 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 What will be covered ? Goals of this presentation • • Learn how the Java Portlet 1. 0 (JSR 168) leverages the J 2 EE security features • 4 Learn about declarative security features in Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J 2 EE) [server side only] Learn about the security features of exte. Nd Director™ 5 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
What will be covered ? Goals of this presentation • • Learn how the Java Portlet 1. 0 (JSR 168) leverages the J 2 EE security features • 4 Learn about declarative security features in Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J 2 EE) [server side only] Learn about the security features of exte. Nd Director™ 5 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 J 2 EE Security
J 2 EE Security
 J 2 EE Security Declarative security • J 2 EE applications allow full access by default • Access can be restricted to a subset of non-anonymous identities via rules defined in the deployment descriptor – web. xml for web archives (WAR) – ejb-jar. xml for ejb archives • • At deployment time, roles need to be mapped to physical users and/or groups that exist on the J 2 EE container (which defines the resource authorization policy) • 6 Users and groups are defined via roles in the deployment descriptor At runtime, a user must present non anonymous credentials such that its identity can be evaluated against the container © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
J 2 EE Security Declarative security • J 2 EE applications allow full access by default • Access can be restricted to a subset of non-anonymous identities via rules defined in the deployment descriptor – web. xml for web archives (WAR) – ejb-jar. xml for ejb archives • • At deployment time, roles need to be mapped to physical users and/or groups that exist on the J 2 EE container (which defines the resource authorization policy) • 6 Users and groups are defined via roles in the deployment descriptor At runtime, a user must present non anonymous credentials such that its identity can be evaluated against the container © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 J 2 EE Security Controlling Access to Web Resources
J 2 EE Security Controlling Access to Web Resources
 J 2 EE Security Controlling Access to Enterprise Beans (EJB)
J 2 EE Security Controlling Access to Enterprise Beans (EJB)
 J 2 EE Security Controlling Access to Enterprise Beans (cont. )
J 2 EE Security Controlling Access to Enterprise Beans (cont. )
 J 2 EE Security Enforcing Identity for EJB access • • As a result, EJB resources are only accessible via other server side resources (Servlet, JSP, Message Driven Beans) • To enforce Identity, restrict access to all methods of the ejb • 10 With the exception of a client container, EJB resources cannot be called directly from outside the server The identity must be propagated from the calling resource or the calling resource may choose an identity based on trust (see concept of a “protection domain” in the J 2 EE spec) © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
J 2 EE Security Enforcing Identity for EJB access • • As a result, EJB resources are only accessible via other server side resources (Servlet, JSP, Message Driven Beans) • To enforce Identity, restrict access to all methods of the ejb • 10 With the exception of a client container, EJB resources cannot be called directly from outside the server The identity must be propagated from the calling resource or the calling resource may choose an identity based on trust (see concept of a “protection domain” in the J 2 EE spec) © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 J 2 EE Security Enforcing Identity for Web Resources • If a Servlet/JSP is restricted, and the current session is anonymous, the web container will check the login configuration in the deployment descriptor • Based on the rule in the “login-config” tag, the user must present valid credentials to gain access • The supported authentication methods are – – form-based (customize the dialog; plain text!) – https mutual (X. 509 certificates over SSL) – 11 http basic (user/password as Base 64 encoded) Optional: digest (one way hash) © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
J 2 EE Security Enforcing Identity for Web Resources • If a Servlet/JSP is restricted, and the current session is anonymous, the web container will check the login configuration in the deployment descriptor • Based on the rule in the “login-config” tag, the user must present valid credentials to gain access • The supported authentication methods are – – form-based (customize the dialog; plain text!) – https mutual (X. 509 certificates over SSL) – 11 http basic (user/password as Base 64 encoded) Optional: digest (one way hash) © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use BASIC or DIGEST
J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use BASIC or DIGEST
 J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use form-based authentication
J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use form-based authentication
 J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use X. 509 Certificate
J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use X. 509 Certificate
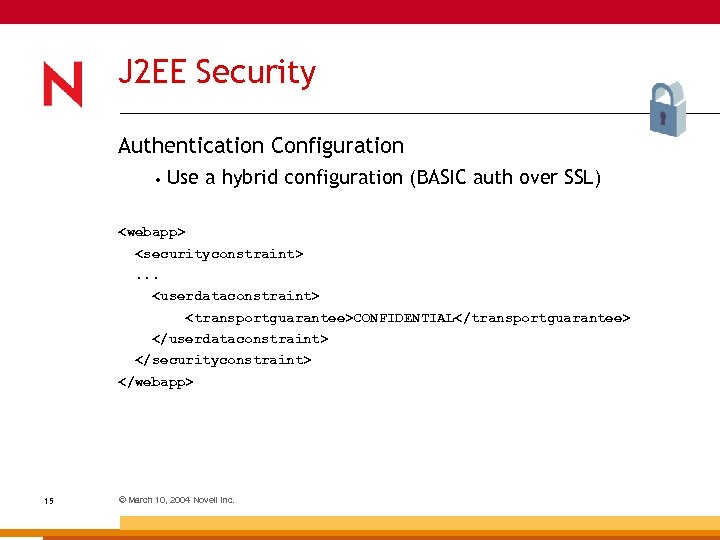 J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use a hybrid configuration (BASIC auth over SSL)
J 2 EE Security Authentication Configuration • Use a hybrid configuration (BASIC auth over SSL)
 J 2 EE Security A login page form based authentication <%@ page language="java“ session="true“ is. Thread. Safe="false" content. Type="text/html" %> …
J 2 EE Security A login page form based authentication <%@ page language="java“ session="true“ is. Thread. Safe="false" content. Type="text/html" %> …
 J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • Check a users role javax. ejb. Ejb. Context. is. Caller. In. Role() javax. servlet. Http. Servlet. Request. is. User. In. Role() • Get the current users information javax. ejb. Ejb. Context. get. Caller. Principal() javax. servlet. Http. Servlet. Request. get. Caller. Principal() 17 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • Check a users role javax. ejb. Ejb. Context. is. Caller. In. Role() javax. servlet. Http. Servlet. Request. is. User. In. Role() • Get the current users information javax. ejb. Ejb. Context. get. Caller. Principal() javax. servlet. Http. Servlet. Request. get. Caller. Principal() 17 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • More security information // Servlet 2. 1 String cyphersuite = (String)request. get. Attribute("javax. net. ssl. cipher_sui te"); // Servlet 2. 2 and later String cyphersuite = (String)request. get. Attribute("javax. servlet. request. ci pher_suite"); Object o = request. get. Attribute("javax. servlet. request. key_size") ; 18 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • More security information // Servlet 2. 1 String cyphersuite = (String)request. get. Attribute("javax. net. ssl. cipher_sui te"); // Servlet 2. 2 and later String cyphersuite = (String)request. get. Attribute("javax. servlet. request. ci pher_suite"); Object o = request. get. Attribute("javax. servlet. request. key_size") ; 18 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • More security information // Servlet 2. 1 X 509 Certificate[] certs = (X 509 Certificate[])request. get. Attribute ("javax. net. ssl. peer_certificates"); // Servlet 2. 2 and later X 509 Certificate[] certs = (X 509 Certificate[])request. get. Attribute ("javax. servlet. request. X 509 Certificate"); 19 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • More security information // Servlet 2. 1 X 509 Certificate[] certs = (X 509 Certificate[])request. get. Attribute ("javax. net. ssl. peer_certificates"); // Servlet 2. 2 and later X 509 Certificate[] certs = (X 509 Certificate[])request. get. Attribute ("javax. servlet. request. X 509 Certificate"); 19 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • More security information //request. BASIC_AUTH, DIGEST_AUTH, CLIENT_CERT_AUTH, FORM_AUTH String auth. Type = request. get. Auth. Type(); 20 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
J 2 EE Security Programmatic access to security information • More security information //request. BASIC_AUTH, DIGEST_AUTH, CLIENT_CERT_AUTH, FORM_AUTH String auth. Type = request. get. Auth. Type(); 20 © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 Demo
Demo
 Java Portlet 1. 0 Security
Java Portlet 1. 0 Security
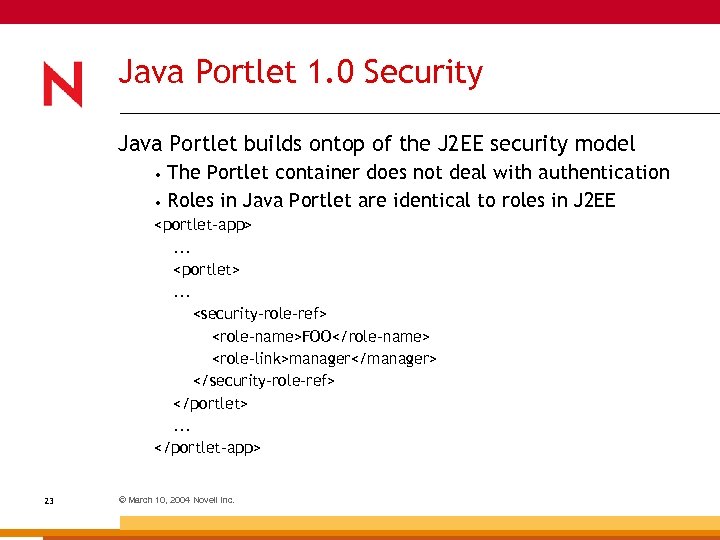 Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Java Portlet builds ontop of the J 2 EE security model The Portlet container does not deal with authentication • Roles in Java Portlet are identical to roles in J 2 EE •
Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Java Portlet builds ontop of the J 2 EE security model The Portlet container does not deal with authentication • Roles in Java Portlet are identical to roles in J 2 EE •
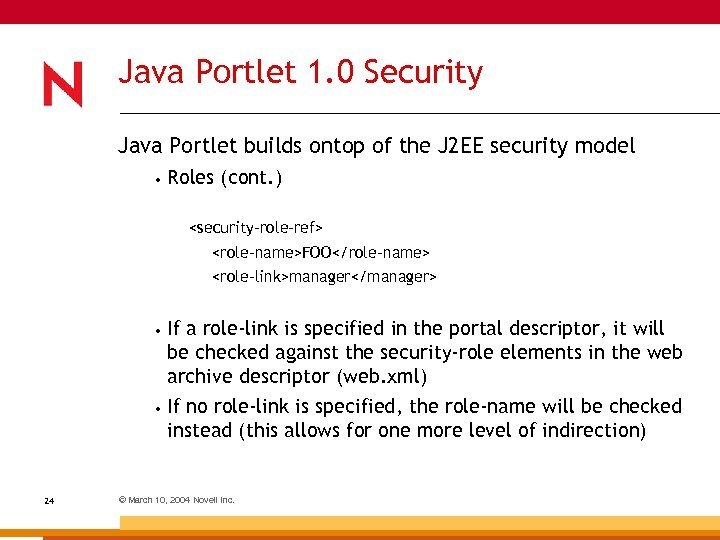 Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Java Portlet builds ontop of the J 2 EE security model • Roles (cont. )
Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Java Portlet builds ontop of the J 2 EE security model • Roles (cont. )
 Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Java Portlet Roles example • Web Archive descriptor
Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Java Portlet Roles example • Web Archive descriptor
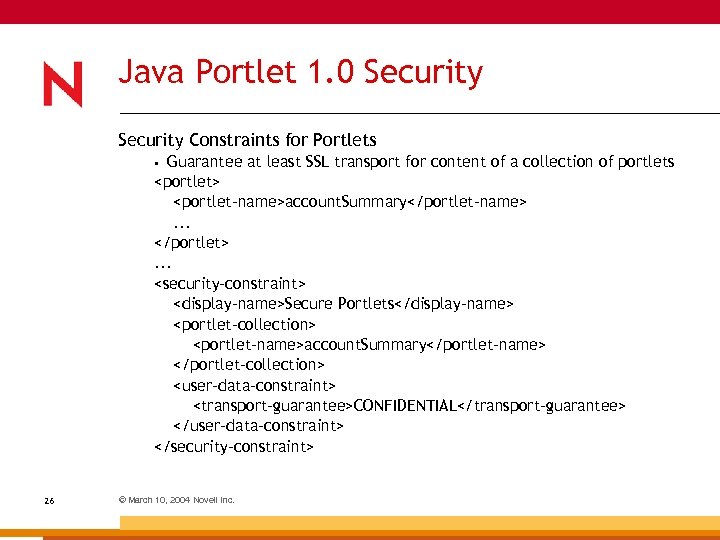 Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Constraints for Portlets Guarantee at least SSL transport for content of a collection of portlets
Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Constraints for Portlets Guarantee at least SSL transport for content of a collection of portlets
 Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Programmatic Security • javax. portlet. Request exposes these methods – – is. User. In. Role() – 27 get. Remote. User() [same as Http. Servlet. Request] get. User. Principal() [same as Http. Servlet. Request] © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
Java Portlet 1. 0 Security Programmatic Security • javax. portlet. Request exposes these methods – – is. User. In. Role() – 27 get. Remote. User() [same as Http. Servlet. Request] get. User. Principal() [same as Http. Servlet. Request] © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
 Demo
Demo
 Security in exte. Nd Director 5. 0
Security in exte. Nd Director 5. 0
 Security in exte. Nd Director 5 Director and Realms • Director uses the concept of Security realms – Realms for all supported J 2 EE containers (WL, WS, exte. Nd) – LDAP – Persistent Manager • • 30 Relation between the realm and the J 2 EE session Director will authenticate a user in all relevant security providers so that the security checks in those containers can work properly. © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.
Security in exte. Nd Director 5 Director and Realms • Director uses the concept of Security realms – Realms for all supported J 2 EE containers (WL, WS, exte. Nd) – LDAP – Persistent Manager • • 30 Relation between the realm and the J 2 EE session Director will authenticate a user in all relevant security providers so that the security checks in those containers can work properly. © March 10, 2004 Novell Inc.

 General Disclaimer This document is not to be construed as a promise by any participating company to develop, deliver, or market a product. Novell, Inc. , makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents of this document, and specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Novell, Inc. , reserves the right to revise this document and to make changes to its content, at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes. All Novell marks referenced in this presentation are trademarks or registered trademarks of Novell, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. No part of this work may be practiced, performed, copied, distributed, revised, modified, translated, abridged, condensed, expanded, collected, or adapted without the prior written consent of Novell, Inc. Any use or exploitation of this work without authorization could subject the perpetrator to criminal and civil liability.
General Disclaimer This document is not to be construed as a promise by any participating company to develop, deliver, or market a product. Novell, Inc. , makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents of this document, and specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Novell, Inc. , reserves the right to revise this document and to make changes to its content, at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes. All Novell marks referenced in this presentation are trademarks or registered trademarks of Novell, Inc. in the United States and other countries. All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. No part of this work may be practiced, performed, copied, distributed, revised, modified, translated, abridged, condensed, expanded, collected, or adapted without the prior written consent of Novell, Inc. Any use or exploitation of this work without authorization could subject the perpetrator to criminal and civil liability.


