aa7fc81d02b52d72c4d5377907df5e9d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

Understanding Organisational Context 2 e Slides by Claire Capon Chapter 4 Marketing mix Product lifecycle Customer growth options Boston consulting group matrix Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 1

The Marketing Mix Product Price Promotion Place Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 2
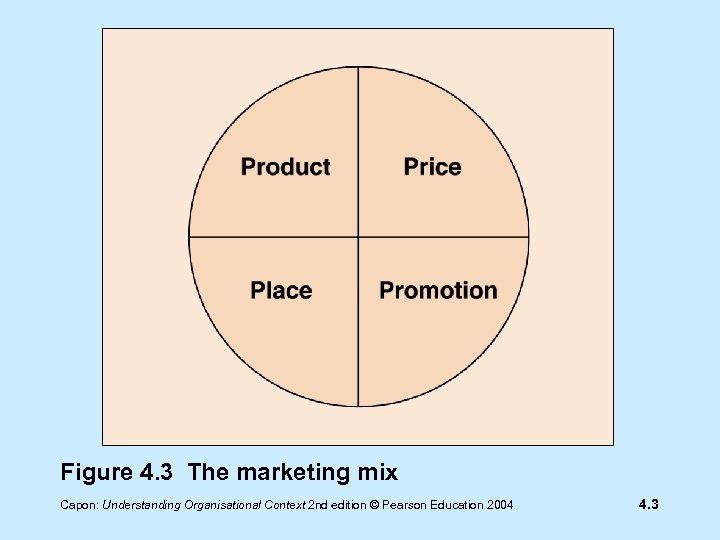
Figure 4. 3 The marketing mix Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 3

Introduction to the 4 Ps • 4 ps can be: - manipulated to increase sales and profitability - altered or improved as a product declines Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 4

Product • The manufacturer will aim to: - make as much of the product for as long as possible without further investment being required Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 5

Product - manipulate product features at little cost to give a newer, fresher face if sales go into decline - attract new customers and keep existing customers Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 6

Product • Product aspects which can be manipulated are: - style, performance and quality - branding, packaging and after-sales service Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 7

Product • Manipulation of the product: - allows the manufacturer to claim continual innovation and improvement - requires co-operation between the marketing and operations management departments Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 8

Price • Price can be: - reduced during product decline or introduction - increased when sales start to become buoyant Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 9

Price • Price manipulation: - can be done by use of special offers and finance deals - requires co-operation between the marketing and finance departments Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 10

Promotion • Advertising and promotional activity are required to: - create an awareness of and interest in the product and to ensure acceptance by the marketplace - support a successful product Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 11

Promotion • Promotion and advertising support a product by: - attracting new customers - reminding consumers making repeat purchases to buy the same brand of product as before (crucial if customer loyalty low) Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 12

Place • Manipulation of place is to ensure the right amount of the product is in the right place at the right time • Applies to all stages of the distribution process Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 13

Place Examples • Manufacturer to wholesaler • Wholesaler to retailer • Retailer to customer • Manufacturer to consumer Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 14

Place • careful positioning of goods in shops is to improve sales • e. g. sweets by the supermarket checkout • e. g. perfume next to the main doors in department stores Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 15
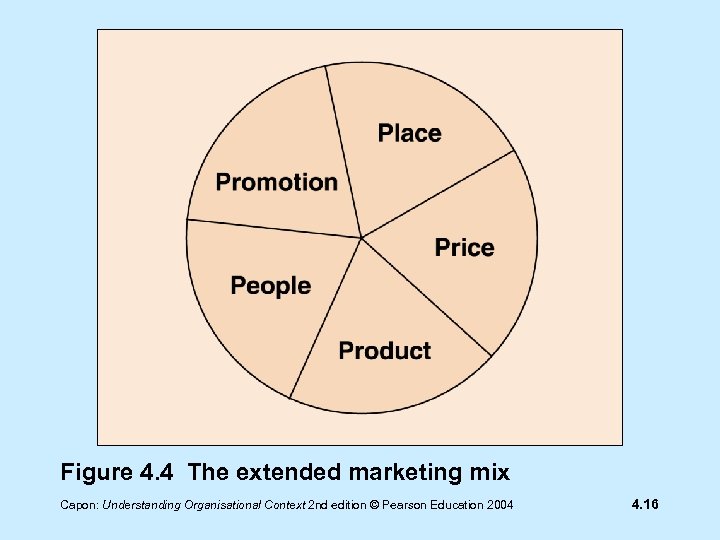
Figure 4. 4 The extended marketing mix Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 16

People • ‘People’ includes: - staff inside the organisation - customers and consumers outside the organisation Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 17

People • ‘Manipulation’ of people covers: - effective use and management of staff - sales staff building good relationships with customers Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 18

Product lifecycle Introduction Growth Maturity Saturation Decline Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 19
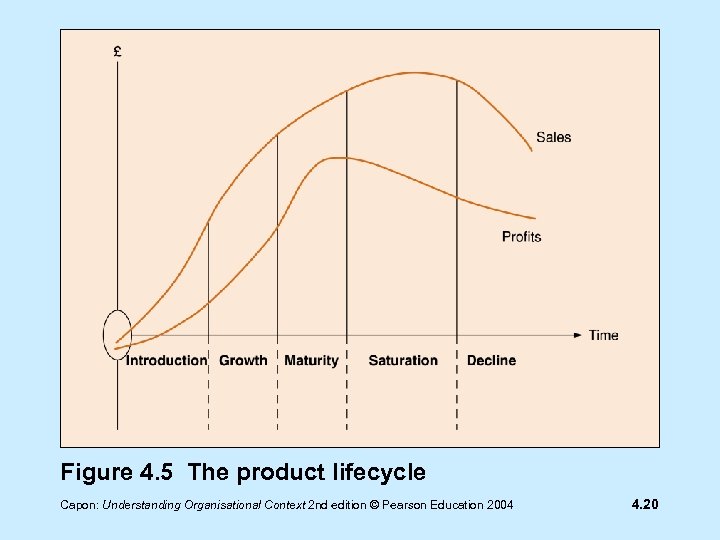
Figure 4. 5 The product lifecycle Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 20

Introduction • High costs, low sales - and no profit is made • Aim to recover development costs • Successful new product will move to growth phase Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 21

Growth • Steady costs, sales increase rapidly and high profits can be made by pioneering firms • Aim to attract first-time customers and build market share Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 22

Maturity • Steady costs, sales increase more slowly and profits peak • Aim to keep existing customers and persuade other consumers to switch from competing brands Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 23

Saturation • Steady costs, sales peak (no more growth) and reasonable profits • Profit margins start to decline, owing to increased price competition Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 24

Decline • Low costs, falling sales and falling profits - maybe loss making • Withdraw loss-making product • Keep decline product if it makes a profit in a niche market Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 25
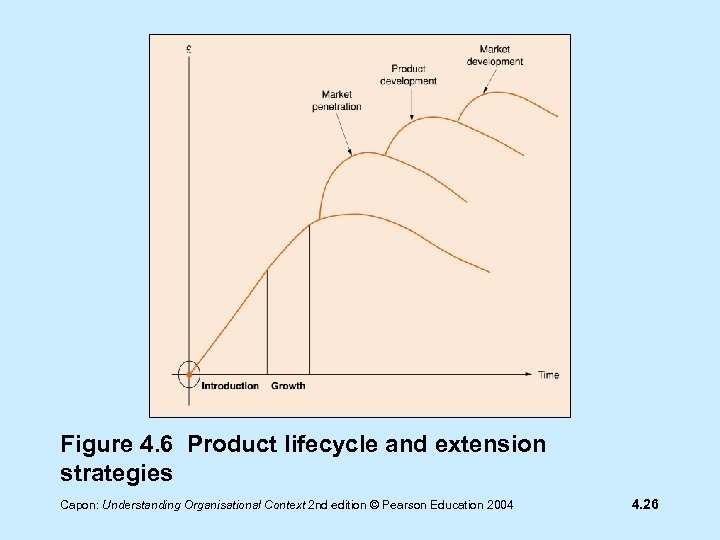
Figure 4. 6 Product lifecycle and extension strategies Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 26

Extending the product lifecycle • Extend lifecycle by: - selling more product to existing customers - market development, which is to seek new customers in home country or abroad Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 27

Extending the product lifecycle - product development which is minor product modification or improvement e. g. new model of a car Vauxhall Corsa Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 28

Extending the product lifecycle • Aim to keep the product in the saturation phase of lifecycle as: - profits are reasonable - sales peak - costs are steady Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 29

Customer growth matrix Customer loyalty Customer extension Customer acquisition Customer diversification Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 30
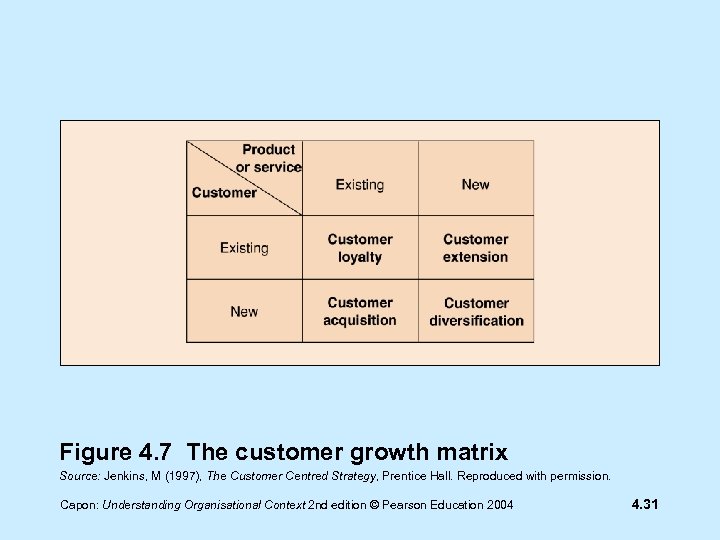
Figure 4. 7 The customer growth matrix Source: Jenkins, M (1997), The Customer Centred Strategy, Prentice Hall. Reproduced with permission. Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 31

Customer loyalty • Loyal customers will bring greater profitability by: - making frequent repeat purchases - telling friends of the benefits of the company’s products Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 32

Customer extension • Customer extension is: - extending the range of products and services available to customers - achieved via product development & diversification Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 33

Customer extension • Product development is used by companies: - structured around product divisions - with strong R & D and design functions Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 34

Customer extension - whose products have short lifecycles e. g. consumer electronic companies like SONY Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 35

Customer extension • Product diversification occurs when a company moves away from current products • Related diversification remains in same industry • Unrelated diversification changes industry Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 36

Customer acquisition • Customer acquisition is: - expanding the number of customers for existing products - easiest in growing markets - difficult in mature markets Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 37

Customer acquisition • If home markets are mature, then seek new customers in overseas markets • Engage in IB activities, e. g. Exporting or locating production or marketing activities overseas Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 38

Customer diversification • Customer diversification: - is achieved by selling a new product or service to new customers - often involves innovative use of technology Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 39

The BCG matrix Question marks Stars Cash cows Dogs Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 40
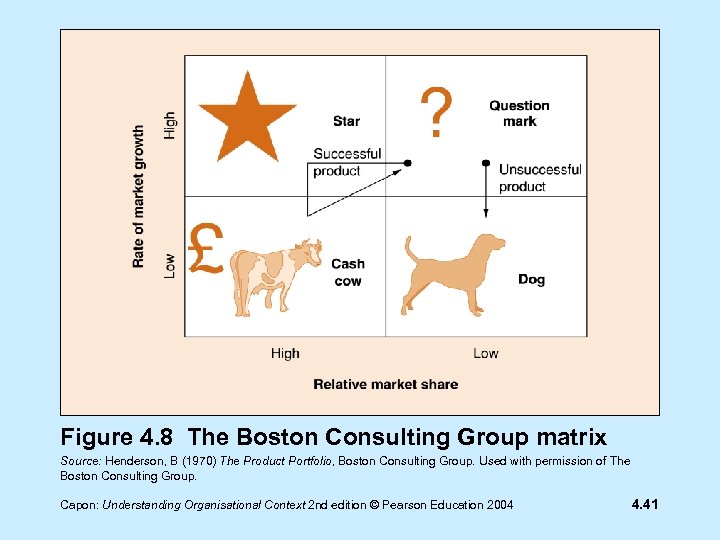
Figure 4. 8 The Boston Consulting Group matrix Source: Henderson, B (1970) The Product Portfolio, Boston Consulting Group. Used with permission of The Boston Consulting Group. Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 41

Question marks • High growth markets • Low market share • Another product is current market leader Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 42

Question marks • Unlikely to be profitable • High investment is required if a question mark is to become a market leader Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 43

Stars • Successful question marks become stars • Stars are market leaders in growth markets Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 44

Stars • Stars: - require investment to maintain market leadership in a high growth market - are marginally profitable Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 45

Cash cows • Cash cows: - are mature products - occupy slower growth markets - need less investment Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 46

Cash cows - are the most profitable products in a portfolio - are used to fund products in other quadrants Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 47

Dogs • Dogs: - Occupy no growth markets - Have low market share - May be previous cash cows - May be marginally profitable - Should be withdrawn before they become loss making Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 48

A successful product • A successful product moves around the BCG matrix • A question mark to … a star to … • … a cash cow to … a dog or back to a question mark Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 49

A less successful product • A less successful product remains in right-hand side of the BCG matrix, and is therefore a low cash generator • A question mark may move to … a dog Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 50
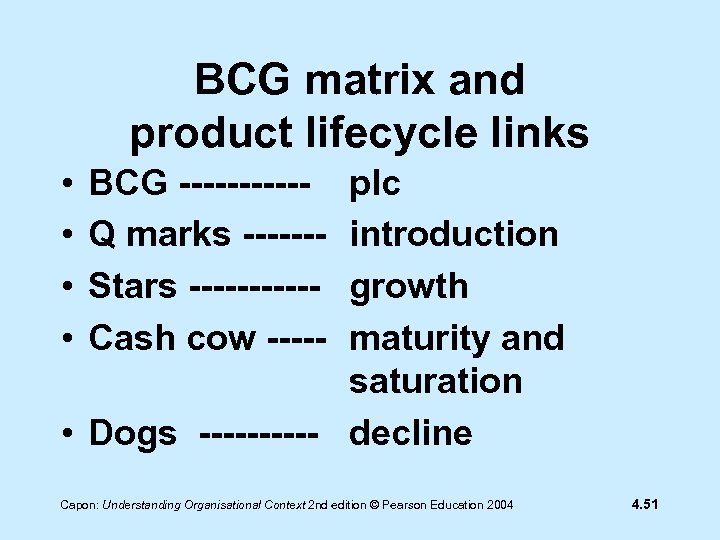
BCG matrix and product lifecycle links • • BCG -----Q marks ------Stars -----Cash cow ----- plc introduction growth maturity and saturation • Dogs ----- decline Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 51

Balanced BCG matrix • Tomorrow's products: - question marks and stars • Today's products: - cash cows • Yesterday’s products - dogs Capon: Understanding Organisational Context 2 nd edition © Pearson Education 2004 4. 52
aa7fc81d02b52d72c4d5377907df5e9d.ppt