042aae99f914a088e00eeadfa4ed9640.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 UNDERSTANDING HOTEL ORGANIZATIONS
UNDERSTANDING HOTEL ORGANIZATIONS
 Organizational Chart Line and Staff Functions Business Forms Revenue Sources Profit and Costs Contents
Organizational Chart Line and Staff Functions Business Forms Revenue Sources Profit and Costs Contents
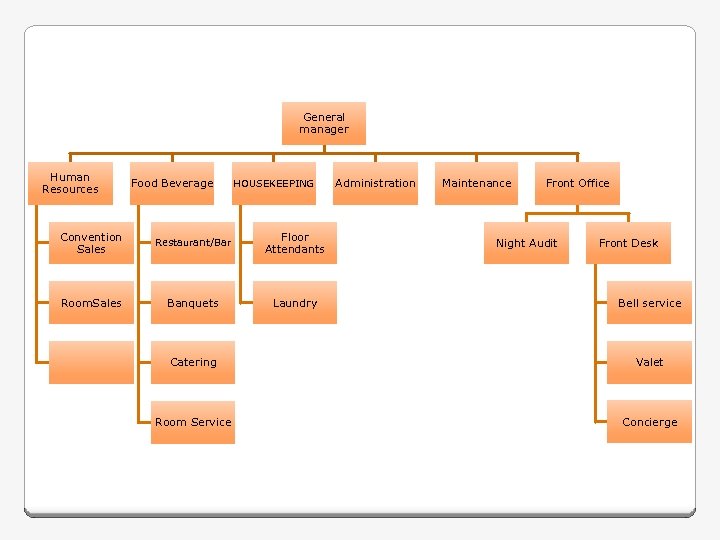 General manager Human Resources Food Beverage HOUSEKEEPING Convention Sales Restaurant/Bar Floor Attendants Room. Sales Banquets Laundry Administration Maintenance Front Office Night Audit Front Desk Bell service Catering Valet Room Service Concierge
General manager Human Resources Food Beverage HOUSEKEEPING Convention Sales Restaurant/Bar Floor Attendants Room. Sales Banquets Laundry Administration Maintenance Front Office Night Audit Front Desk Bell service Catering Valet Room Service Concierge
 Like most service related organizations, hotels are divided between LINE functions and STAFF functions
Like most service related organizations, hotels are divided between LINE functions and STAFF functions
 Line Functions Line functions are the tasks assigned to employees that bring them in regular contact with guests. Line operations in a hotel are the Rooms Division & Food and Beverage Division. Line employees are hands-on participants in the assembly and delivery of the hotel’s services. Line = Revenue
Line Functions Line functions are the tasks assigned to employees that bring them in regular contact with guests. Line operations in a hotel are the Rooms Division & Food and Beverage Division. Line employees are hands-on participants in the assembly and delivery of the hotel’s services. Line = Revenue
 ROOMS DEPARTMENT Performs the lodging function of a hotel. Includes Front Office, Reservations Uniformed Services and Housekeeping Tasks performed: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Receive reservation Receive guests Assign rooms to guests Maintain status of room (available or vacant? ) Receive mail / phone messages for guests Maintain security & cleanliness in rooms and public areas Answer guests’ questions Close coordination needed by all subunits
ROOMS DEPARTMENT Performs the lodging function of a hotel. Includes Front Office, Reservations Uniformed Services and Housekeeping Tasks performed: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Receive reservation Receive guests Assign rooms to guests Maintain status of room (available or vacant? ) Receive mail / phone messages for guests Maintain security & cleanliness in rooms and public areas Answer guests’ questions Close coordination needed by all subunits
 FOOD AND BEVERAGE DEPARTMENT Provide food and beverage for guests May include coffee shop, restaurant, poolside snack bar, room service, banquet, function rooms, lobby bar, nightclub / disco, room service Provides banquet and catering services for events in the hotel
FOOD AND BEVERAGE DEPARTMENT Provide food and beverage for guests May include coffee shop, restaurant, poolside snack bar, room service, banquet, function rooms, lobby bar, nightclub / disco, room service Provides banquet and catering services for events in the hotel
 Food and Beverage Department cont. Consists of kitchen (food preparation) and F&B service Contains individual F&B outlets – restaurants and coffee shop etc (each managed by a manager) Full service hotels have convention and catering subunit Stewarding subunit does the purchasing, cleaning and washing, expediting and arranging facilities for food and beverage
Food and Beverage Department cont. Consists of kitchen (food preparation) and F&B service Contains individual F&B outlets – restaurants and coffee shop etc (each managed by a manager) Full service hotels have convention and catering subunit Stewarding subunit does the purchasing, cleaning and washing, expediting and arranging facilities for food and beverage
 OTHER LINE FUNCTIONS Telecommunications Concessions, rentals, and commissions Fitness and recreation facilities
OTHER LINE FUNCTIONS Telecommunications Concessions, rentals, and commissions Fitness and recreation facilities
 Staff Functions Staff functions are those behind the scenes activities that support the line functions and have little contact with guests. Example: Engineering, security, human resources, marketing, accounting Staff = Cost
Staff Functions Staff functions are those behind the scenes activities that support the line functions and have little contact with guests. Example: Engineering, security, human resources, marketing, accounting Staff = Cost
 Sales and Marketing Department Individual sales manager in charge of corporate accounts, conventions, tour and travel markets. Low intradepartmental interdependence. Human Resources Department Consists of employee recruitment, benefits administration, training subunits Accounting Department Prepares payroll, manages accounts receivables, accounts payables, handles purchases and cost controls, store room operations, night audits Engineering and Security Repairs, maintenance, guest and property security
Sales and Marketing Department Individual sales manager in charge of corporate accounts, conventions, tour and travel markets. Low intradepartmental interdependence. Human Resources Department Consists of employee recruitment, benefits administration, training subunits Accounting Department Prepares payroll, manages accounts receivables, accounts payables, handles purchases and cost controls, store room operations, night audits Engineering and Security Repairs, maintenance, guest and property security
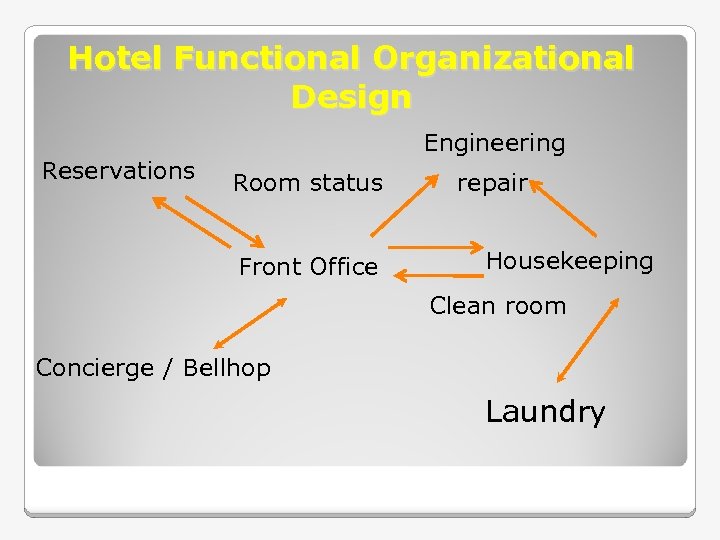 Hotel Functional Organizational Design Reservations Engineering Room status Front Office repair Housekeeping Clean room Concierge / Bellhop Laundry
Hotel Functional Organizational Design Reservations Engineering Room status Front Office repair Housekeeping Clean room Concierge / Bellhop Laundry
 LODGING BUSINESS FORMS
LODGING BUSINESS FORMS
 The five basic lodging business forms: Owner operated Owner managed Independent Franchised Management Contract Lodging Business Forms
The five basic lodging business forms: Owner operated Owner managed Independent Franchised Management Contract Lodging Business Forms
 Understood to have been the first type of lodging management association Hotel is run by an owner and the owner’s family Currently popular Bed and Breakfast hotel is considered owner operated Owner Operated
Understood to have been the first type of lodging management association Hotel is run by an owner and the owner’s family Currently popular Bed and Breakfast hotel is considered owner operated Owner Operated
 The owner has hired additional (nonfamily) personnel to help with the running of the property The overall management is in the hands of the owner, but day to day operations can be in the hands of others Owner Managed
The owner has hired additional (nonfamily) personnel to help with the running of the property The overall management is in the hands of the owner, but day to day operations can be in the hands of others Owner Managed
 The owner has no role or management in day to day operations An independent group of managers are responsible to the owner for the hotel’s performance The hotel is not chain affiliated Independent
The owner has no role or management in day to day operations An independent group of managers are responsible to the owner for the hotel’s performance The hotel is not chain affiliated Independent
 Independently owned hotels that affiliate themselves with a chain The chain provides standard operating procedures and guidelines to maintain a consistent level of quality and service The chain has limited control Franchised
Independently owned hotels that affiliate themselves with a chain The chain provides standard operating procedures and guidelines to maintain a consistent level of quality and service The chain has limited control Franchised
 You can expect to pay in the range of $90, 000 to $150, 000 in initial fees for a first-class hotel franchise like Hilton‘s Homewood Suites. Additional costs typically include royalty fees, reservation fees, marketing fees, frequent traveler fees, and miscellaneous charges for items like training or commissions. These numbers are calculated assuming a 300 -room hotel with 60% occupancy for the first year, so actual costs can vary. Total costs over ten years can run as high as $10 million or more. Franchise Costs/Benefits
You can expect to pay in the range of $90, 000 to $150, 000 in initial fees for a first-class hotel franchise like Hilton‘s Homewood Suites. Additional costs typically include royalty fees, reservation fees, marketing fees, frequent traveler fees, and miscellaneous charges for items like training or commissions. These numbers are calculated assuming a 300 -room hotel with 60% occupancy for the first year, so actual costs can vary. Total costs over ten years can run as high as $10 million or more. Franchise Costs/Benefits
 Those with the best relationships with their franchisors reported gross operating profits per room (GOPAR) of $12, 400, which translates to over $3. 2 million per year in a 300 room hotel. Top Franchises: Marriott (Ritz Carlton), Hilton, Four Seasons, Park Plaza, Holiday Inn Franchise Costs/Benefits
Those with the best relationships with their franchisors reported gross operating profits per room (GOPAR) of $12, 400, which translates to over $3. 2 million per year in a 300 room hotel. Top Franchises: Marriott (Ritz Carlton), Hilton, Four Seasons, Park Plaza, Holiday Inn Franchise Costs/Benefits
 Independently owned hotels that affiliate themselves with a chain The chain maintains a high level of control as the chain operates the hotel on the owner’s behalf Many hotel companies offer both franchises and management contracts. Management fees are paid as a % of revenues Management Contract
Independently owned hotels that affiliate themselves with a chain The chain maintains a high level of control as the chain operates the hotel on the owner’s behalf Many hotel companies offer both franchises and management contracts. Management fees are paid as a % of revenues Management Contract
 Revenues, Profits and Costs
Revenues, Profits and Costs
 A revenue source is the result of a product or service a hotel makes available to guests for a price. Sleeping Rooms Meeting / Function Space Outlets / Ancillary Revenue Sources
A revenue source is the result of a product or service a hotel makes available to guests for a price. Sleeping Rooms Meeting / Function Space Outlets / Ancillary Revenue Sources
 The sleeping room is the most profitable of all of the hotel’s products A sleeping room is an accommodation unit The price of each of these units is called the room rate Occupancy is the measurement of how many rooms are sold each night verses how many rooms the hotel has to sell. e. g. 75 rooms sold of 100 rooms available = 75% occupancy rate Sleeping Rooms
The sleeping room is the most profitable of all of the hotel’s products A sleeping room is an accommodation unit The price of each of these units is called the room rate Occupancy is the measurement of how many rooms are sold each night verses how many rooms the hotel has to sell. e. g. 75 rooms sold of 100 rooms available = 75% occupancy rate Sleeping Rooms
 Many hotels incorporate the revenue source of non-sleeping rooms sales Meeting rooms, or function rooms are used for any type of group meeting The revenue sources from meeting/function space comes from: 1. Selling space for a specified period 2. Providing food and beverage service in these rooms Meeting/Function Space
Many hotels incorporate the revenue source of non-sleeping rooms sales Meeting rooms, or function rooms are used for any type of group meeting The revenue sources from meeting/function space comes from: 1. Selling space for a specified period 2. Providing food and beverage service in these rooms Meeting/Function Space
 An outlet is a food and beverage point of sale Ancillary revenue sources are revenue sources outside of sleeping rooms or food and beverage such as gift shops or spa services. Outlets/Ancillary Revenue Sources
An outlet is a food and beverage point of sale Ancillary revenue sources are revenue sources outside of sleeping rooms or food and beverage such as gift shops or spa services. Outlets/Ancillary Revenue Sources
 The hotel sleeping room is the most profitable portion of all hotel products because of profit margin. Profit margin is determined by comparing sales revenue verses the costs incurred in providing a product or service. Profit Margin
The hotel sleeping room is the most profitable portion of all hotel products because of profit margin. Profit margin is determined by comparing sales revenue verses the costs incurred in providing a product or service. Profit Margin
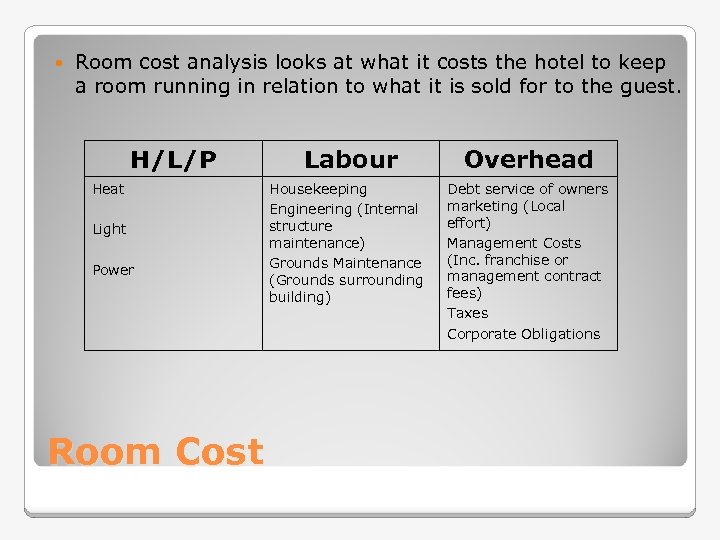 Room cost analysis looks at what it costs the hotel to keep a room running in relation to what it is sold for to the guest. H/L/P Heat Light Power Room Cost Labour Housekeeping Engineering (Internal structure maintenance) Grounds Maintenance (Grounds surrounding building) Overhead Debt service of owners marketing (Local effort) Management Costs (Inc. franchise or management contract fees) Taxes Corporate Obligations
Room cost analysis looks at what it costs the hotel to keep a room running in relation to what it is sold for to the guest. H/L/P Heat Light Power Room Cost Labour Housekeeping Engineering (Internal structure maintenance) Grounds Maintenance (Grounds surrounding building) Overhead Debt service of owners marketing (Local effort) Management Costs (Inc. franchise or management contract fees) Taxes Corporate Obligations
 ABC Hotel sells a room for an average of $150 per night. The cost incurred in preparing each room for sale are: Heat Light Power $2. 00 Housekeeping Engineering/Grounds Debt service of owners Marketing Management costs Corporate obligations Taxes, etc Total: $31. 00 $3. 00 $2. 00 Compare this to the actual cost to the price sold (room rate) and the room cost can be determined: Room cost = Actual Cost Room Rate = $9. 00 $5. 00 $0. 50 $2. 25 $2. 75 $2. 00 $2. 50 $ 31. 00 $150. 00 = 21. 0% Room Rate – Room Cost = Profit Room Cost Example
ABC Hotel sells a room for an average of $150 per night. The cost incurred in preparing each room for sale are: Heat Light Power $2. 00 Housekeeping Engineering/Grounds Debt service of owners Marketing Management costs Corporate obligations Taxes, etc Total: $31. 00 $3. 00 $2. 00 Compare this to the actual cost to the price sold (room rate) and the room cost can be determined: Room cost = Actual Cost Room Rate = $9. 00 $5. 00 $0. 50 $2. 25 $2. 75 $2. 00 $2. 50 $ 31. 00 $150. 00 = 21. 0% Room Rate – Room Cost = Profit Room Cost Example
 A common misconception in the hospitality industry is to consider food sales as profitable as room sales. This is not the case Food cost is the cost of a particular food item in relation to the price for which it is sold Put simply, the food cost percentage is the percentage of the profit taken up but the actual cost of the item Food Cost
A common misconception in the hospitality industry is to consider food sales as profitable as room sales. This is not the case Food cost is the cost of a particular food item in relation to the price for which it is sold Put simply, the food cost percentage is the percentage of the profit taken up but the actual cost of the item Food Cost
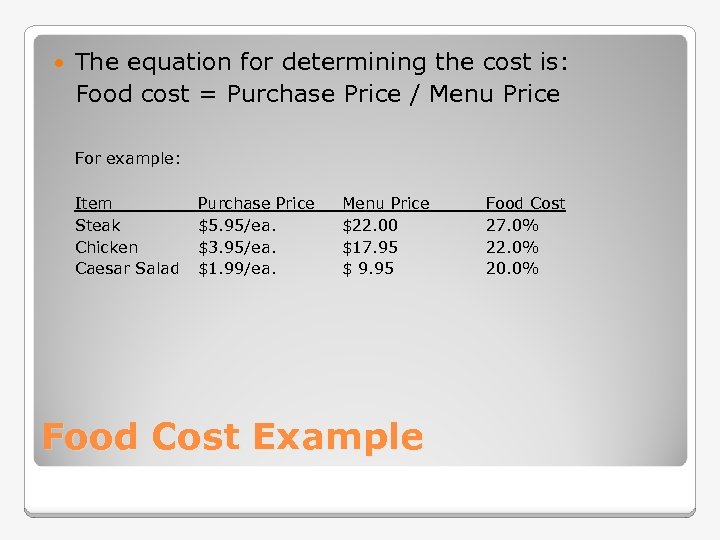 The equation for determining the cost is: Food cost = Purchase Price / Menu Price For example: Item Steak Chicken Caesar Salad Purchase Price $5. 95/ea. $3. 95/ea. $1. 99/ea. Menu Price $22. 00 $17. 95 $ 9. 95 Food Cost Example Food Cost 27. 0% 22. 0% 20. 0%
The equation for determining the cost is: Food cost = Purchase Price / Menu Price For example: Item Steak Chicken Caesar Salad Purchase Price $5. 95/ea. $3. 95/ea. $1. 99/ea. Menu Price $22. 00 $17. 95 $ 9. 95 Food Cost Example Food Cost 27. 0% 22. 0% 20. 0%
 Each night when a room goes unsold the hotel loses that opportunity to ever sell it again This is called opportunity cost The “Empty Room Theory” states that once a room goes unoccupied, it is gone forever Opportunity Cost
Each night when a room goes unsold the hotel loses that opportunity to ever sell it again This is called opportunity cost The “Empty Room Theory” states that once a room goes unoccupied, it is gone forever Opportunity Cost
 ABC Hotel has 400 sleeping rooms Consider the following example: Room Cost Room Rate Profit Margin Sleeping Room $30. 00 $150. 00 $120. 00 _______________________________ The daily maximum room profit potential is: Weekly: Monthly: Yearly: $48, 000 ($120 x 400) $336, 000 $1, 400, 000 $17, 520, 000 is the maximum potential room profit that ABC Hotel could make in a year. Each unoccupied room subtracts from that number. It is easy to understand why hotel operators focus so much attention on occupancy. Opportunity Cost Example
ABC Hotel has 400 sleeping rooms Consider the following example: Room Cost Room Rate Profit Margin Sleeping Room $30. 00 $150. 00 $120. 00 _______________________________ The daily maximum room profit potential is: Weekly: Monthly: Yearly: $48, 000 ($120 x 400) $336, 000 $1, 400, 000 $17, 520, 000 is the maximum potential room profit that ABC Hotel could make in a year. Each unoccupied room subtracts from that number. It is easy to understand why hotel operators focus so much attention on occupancy. Opportunity Cost Example
 A captive audience are guests who are staying at the hotel who will utilise the outlet in the hotel. Captive audience quotients apply to both outlet/ancillary sales and catering sales Group catering contribution is the catering business acquired by a hotel that has all, or a large percentage of, the attendees staying at the hotel itself Captive Audience Quotient
A captive audience are guests who are staying at the hotel who will utilise the outlet in the hotel. Captive audience quotients apply to both outlet/ancillary sales and catering sales Group catering contribution is the catering business acquired by a hotel that has all, or a large percentage of, the attendees staying at the hotel itself Captive Audience Quotient
 Managing Quality Control Set standards Select employees Train employees Involve employees Evaluate Reward achievement 35
Managing Quality Control Set standards Select employees Train employees Involve employees Evaluate Reward achievement 35


