2b6df60572ca8cde50a4918217fa8144.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
Understanding Customer Behaviour

Buying Motives Objectives • • Identify the characteristics of an effective retail sales associate Describe tasks a retail sales associate must complete Identify and discuss product information Define customer buying motives and needs Effective methods for a sales presentation Explain the steps of a sale Explain how to overcome customer objections and identify suggestion selling techniques • Methods and rules for handing objections • Rules and methods for suggestions selling • Methods to close the sale 8 -2 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Learning Objectives (Continued) • Distinguish between emotional and rational buying motives • Distinguish between patronage and product buying motives • Describe three ways to discover an individual’s buying motives • Identify and describe six buying center roles 8 -3 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Buyer Action Theory • • • Attention Interest Desire Conviction Action • Needs _ something required that is essential • Want- a desires for something not essential 8 -4 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
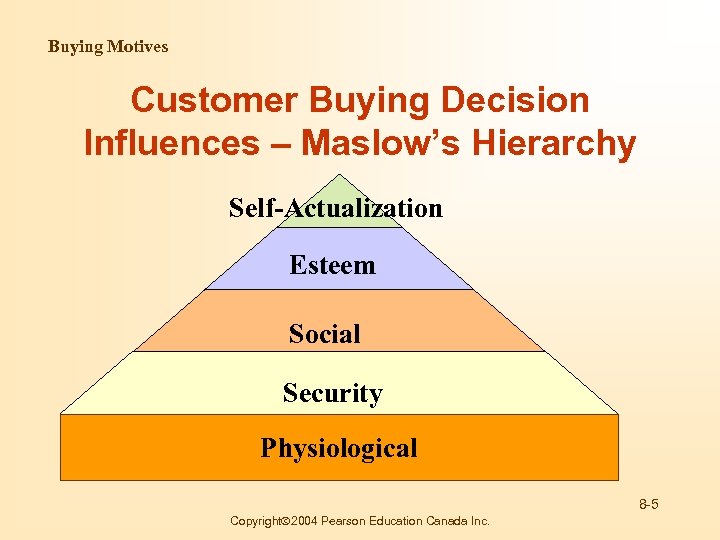
Buying Motives Customer Buying Decision Influences – Maslow’s Hierarchy Self-Actualization Esteem Social Security Physiological 8 -5 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives A buying motive is an aroused need, drive, or desire that initiates the sequence of events that may lead to a purchase. 8 -6 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Types of Buying Motives ü Emotional buying motives prompt the prospect to act as a result of an appeal to some sentiment or passion or impulse. ü Rational buying motives prompt the prospect to act because of an appeal to the prospect’s reason or better judgment. What is the lowest priced item, the longest lasting item, and most dependable item. ü Patronage buying motives cause the prospect to buy a product from one particular company rather than another. 8 -7 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
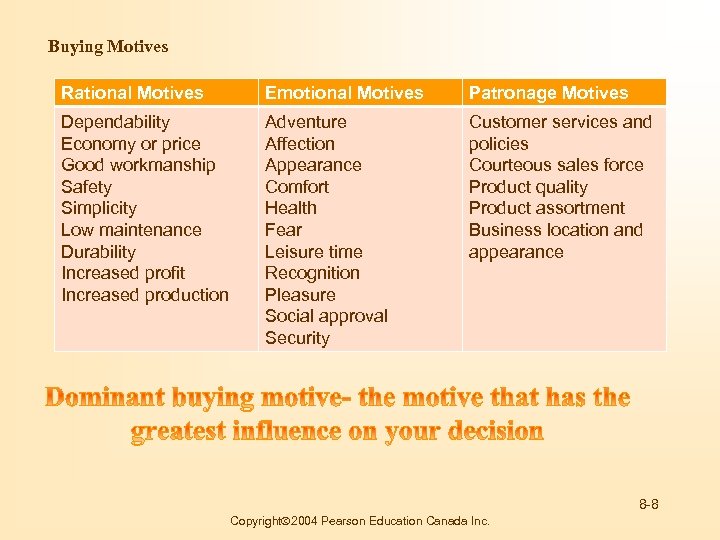
Buying Motives Rational Motives Emotional Motives Patronage Motives Dependability Economy or price Good workmanship Safety Simplicity Low maintenance Durability Increased profit Increased production Adventure Affection Appearance Comfort Health Fear Leisure time Recognition Pleasure Social approval Security Customer services and policies Courteous sales force Product quality Product assortment Business location and appearance 8 -8 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Sales Person Reaction 8 -9 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Techniques to determine Customers buying motives Buying Motives • Observing the customer – (Reactions, mannerisms, facial expressions) • Listening to the customer – remove distractions focus and listen and do not interrupt. Pick up clues to needs • Asking questions – Listen to their responses to determine their wants • Showing interest in the customer 8 -10 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

How to Ask Questions Are these good Questions Buying Motives • What are you wanting and what price range are you wanting? I see you are looking at those vacuum cleaners , do you like the look and price of it? 8 -11 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives What is personal selling • personal selling the type of selling that involves direct interaction between sales associates and customers 8 -12 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Buying Motives Advertising Personal Selling Publicity Sales Promotion 8 -13 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
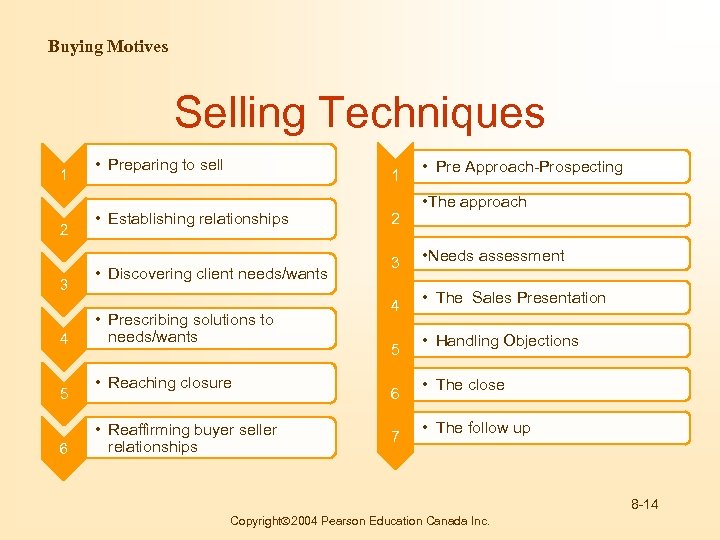
Buying Motives Selling Techniques 1 2 3 4 5 6 • Preparing to sell 1 • Establishing relationships • Discovering client needs/wants • Prescribing solutions to needs/wants • Reaching closure • Reaffirming buyer seller relationships 2 3 4 5 6 7 • Pre Approach-Prospecting • The approach • Needs assessment • The Sales Presentation • Handling Objections • The close • The follow up 8 -14 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives • Acquire knowledge about product • Identify products features and benefits • Generate sales leads- look for potential customers- prospecting • Gather knowledge to prepare for their presentation 8 -15 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Open the Sale/ The Approach The step when the customer and sales person first communication. First contact. • Be courteous and respectful • Establish good eye contact • Be enthusiastic • Show a sincere interest in the customer • Be friendly and genuine • Use the customer’s name • Time the approach appropriately 8 -16 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Greeting/Social Approach Salesperson simply welcomes the customer to the store Example: “Good afternoon, Mr. Wright” or an appropriate personal comment. Do not focus on the merchandise

Buying Motives Service Approach Salesperson asks the customer if he or she needs assistance Example: “May I help you with something? ” *Ineffective because it elicits a negative response

Buying Motives Merchandise Approach Salesperson makes a comment or asks questions about a product that the customer is looking at Example: “That shirt is made of a cotton and polyester blend, so it’s machine washable. ” *Most effective initial approach in retail sales because it focuses attention on the merchandise.

Buying Motives Presence of Customers • When should you acknowledge their presence? • Should you acknowledge their presence when waiting on a customer? • How should you wait on customers? • A customer interrupts to ask a quick question while you are helping another, what should you do? 8 -20 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives New Hire Procedures • How sales associates should greet all customers when they enter store • How to address the various types of customers • Store approach time policy (browsing time ) • How to address the presence of customers • Order to wait on customers • How to address interruptions • Annoying behaviors to avoid 8 -21 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives • Observing the customer • Listening to the customer • Asking questions • Showing interest in the customer 8 -22 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives • The sales talk and the product demonstration • The sales presentation occurs after you have established a relationship with your customer. • Convince customers of the benefits • Limit number of products shown focus on what meets their needs. 8 -23 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives 8 -24 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
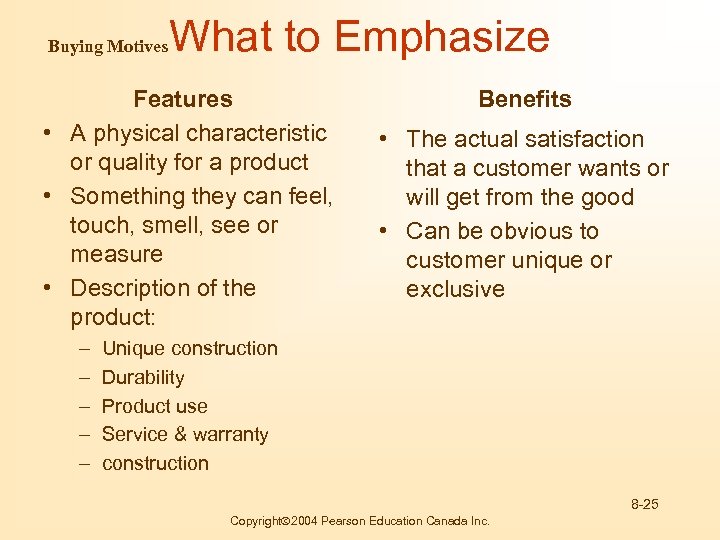
Buying Motives What to Emphasize Features • A physical characteristic or quality for a product • Something they can feel, touch, smell, see or measure • Description of the product: – – – Benefits • The actual satisfaction that a customer wants or will get from the good • Can be obvious to customer unique or exclusive Unique construction Durability Product use Service & warranty construction 8 -25 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Selling Sentences Features: Standard 5 Disc CD tray Shuffle feature Benefit: Easily hold 5 discs. Benefit: Easily Change Songs and CD’s With this player it can hold your five favorite CD’s so you can listen to all your favorite artists. You can program it to shuffle the cd’s so you can pick the order of the songs you like and want to listen to. Very a unique and easy to use feature. 8 -26 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Selling Sentence Laminate Wood Floor Buying Motives Feature Benefit • Laminate Wood • Four layer board thickness with stabilizing layer • Quick joint or interlocking system • Look of wood • Highly scratch resistant and also resists extreme impact and wear. • Easy to install, fit together no nails requires 8 -27 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
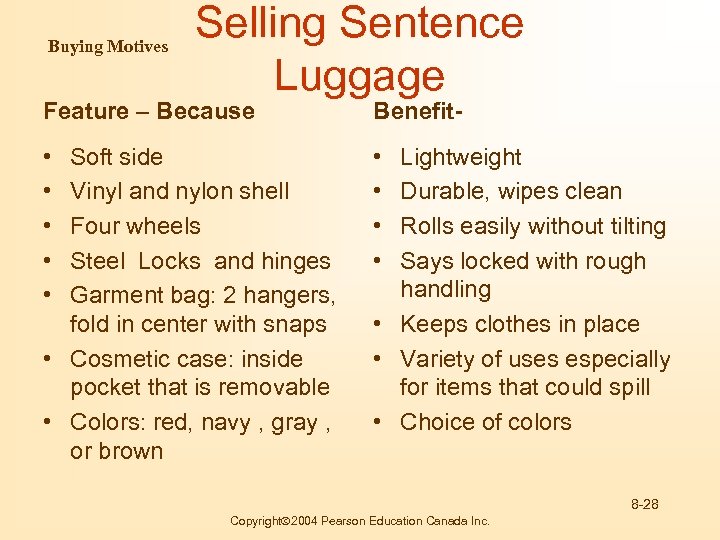
Buying Motives Selling Sentence Luggage Feature – Because Benefit- • • • Soft side Vinyl and nylon shell Four wheels Steel Locks and hinges Garment bag: 2 hangers, fold in center with snaps • Cosmetic case: inside pocket that is removable • Colors: red, navy , gray , or brown Lightweight Durable, wipes clean Rolls easily without tilting Says locked with rough handling • Keeps clothes in place • Variety of uses especially for items that could spill • Choice of colors 8 -28 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Objections • I really had something less expensive in mind. • I like it but I’m just not in love with that color. • It’s nice, but I don’t think I would use it that often. • I not sure theses overhead cranes are powerful for our construction needs 8 -29 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Objection • A point of difference between a customer and sales person that may prevent a sale. Excuse • An insincere statement used to cover up real reason not to buy. • They hide the real objection- hidden objection Types of Objections • • • The cost factor The product The company The right time Want and Need Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 8 -30

Buying Motives • • Listen carefully Pause before answering Empathize with customers Restate objections Avoid arguments Turn objections into selling points Answer honestly and continue selling 8 -31 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Yes but… • Acknowledge the objection tactfully and answer it courteously without contradicting customer. • Most used. Toss It Back • Boomeranged methods to turn the customer objection into a valid reason for buying. 8 -32 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Inquiry • Help customers answer their own objections by asking questions Show Em • Must show the customer to convince them. • Also called demonstration method. 8 -33 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Testimonial • Thrid party methods answer objection by asking or hearing others opinions Try It • All them to try the product before buying it • Very effective methods 8 -34 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Deny It • Correct wrong information or a mis understanding. • Don’t offend, establish a good rapport first. Point Counterpoint • Superior point or counter balance • You agrees on a valid point then answer point by offering an equal or superior point 8 -35 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Ethical or Not • Vanessa is attempting to sell a recliner to a young man who is getting his first apartment. He’s not sure if he’s ready to guy yet, and he might take a hand me down from a friend. She offered him attractive credit, but he still won’t buy. Vanessa tells him the price is temporary and will cost more next week. Is she behaving unethical? 8 -36 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Ethical or not • Gift giving- a customer comes in and leaves coupons/ free lunch ticket at the bank. • Sales person takes the client out to dinner and a game before the big sales presentation the next day. • Communicating or withholding information- the new household cleaner you are selling is hazardous to plants, pets & allergen kids. 8 -37 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives 8 -38 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

The Closing The Sales Buying Motives • The sales person gets the desired agreement from the customer. Closing Techniques • Direct close • Choice close • Assumption close • Minor point/stimulus close. • Summary close • Standing room only close • Closing on objection • Contingent close • Contrasting advantages & disadvantages • Suggesting ownership close • Narrative close • Related product close Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives 8 -40 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives 8 -41 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives 8 -42 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives Suggestion Selling 8 -43 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.

Buying Motives The Followup 8 -44 Copyright 2004 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
2b6df60572ca8cde50a4918217fa8144.ppt