a77ac7f4cfa795359147b7162d4f738b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

UNDERSTANDING COOPERATIVES UNIT 1 - The American Business Enterprise System Business Form Characteristics Slides for Unit 1 Rural Development – Cooperative Programs U. S. Department of Agriculture

Our Business System Principles: • Freedom of choice • Private property rights • Profit motives of owners • Owner control S 1. 1

Individually Owned (Proprietorship) • A business enterprise where the individual owns, operates, manages, and receives the earnings of the business (The oldest and most common method of doing business. ) S 1. 2

Partnership • A business enterprise owned and controlled by two or more people who have agreed to operate on a partnership basis. (Family partnerships are common in farming. ) S 1. 3

Corporation: Investor-Oriented • A (State-chartered) business that has the right to buy and sell goods and services. (Operated as a profit-making enterprise for its investors. ) S 1. 4

Corporation: Cooperative • A user-owned and user controlled (Statechartered) business in which benefits are received in proportion to use. (Commonly used in agriculture to buy, sell, and service individual farm businesses. ) S 1. 5

Hybrid: Limited Liability Company • A business structure that combines characteristics of both a partnership and a corporation. It combines the single-tax treatment of a partnership with the limited personal liability of a corporation. As in a cooperative, LLC owners are called members. (Becoming increasingly common in agricultural business today. ) S 1. 6
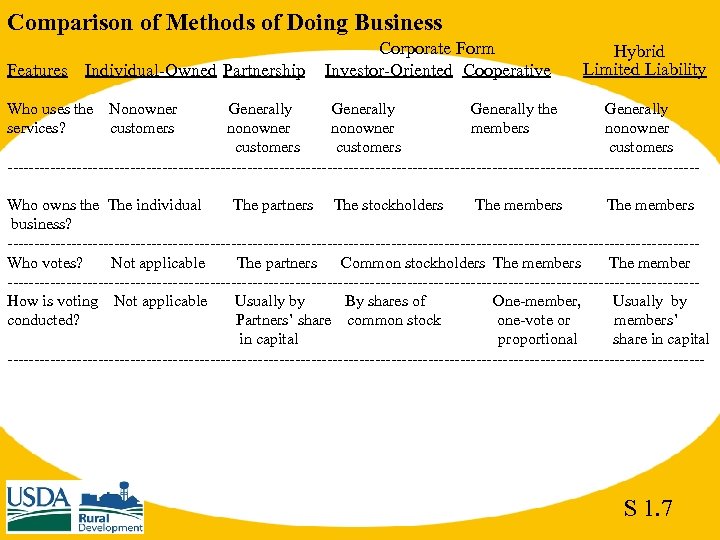
Comparison of Methods of Doing Business Features Individual-Owned Partnership Who uses the services? Corporate Form Investor-Oriented Cooperative Hybrid Limited Liability Nonowner customers Generally the Generally nonowner members nonowner customers -----------------------------------------------------------------Who owns the The individual The partners The stockholders The members business? -----------------------------------------------------------------Who votes? Not applicable The partners Common stockholders The member -----------------------------------------------------------------How is voting Not applicable Usually by By shares of One-member, Usually by conducted? Partners’ share common stock one-vote or members’ in capital proportional share in capital ------------------------------------------------------------------ S 1. 7
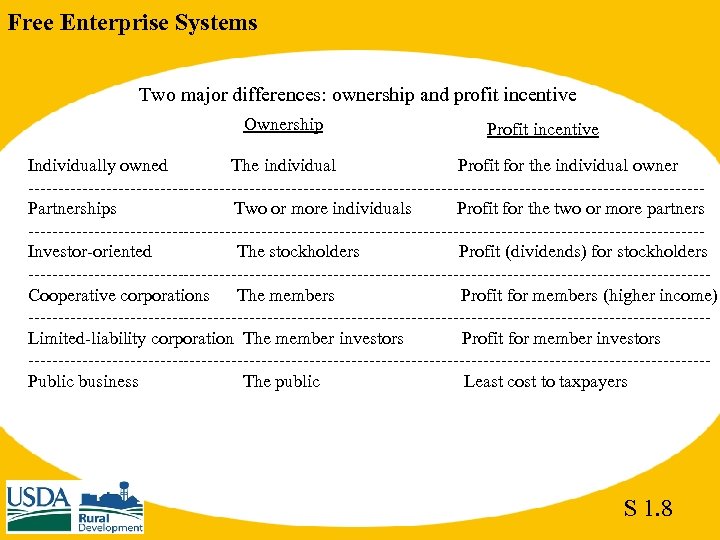
Free Enterprise Systems Two major differences: ownership and profit incentive Ownership Profit incentive Individually owned The individual Profit for the individual owner --------------------------------------------------------Partnerships Two or more individuals Profit for the two or more partners --------------------------------------------------------Investor-oriented The stockholders Profit (dividends) for stockholders ---------------------------------------------------------Cooperative corporations The members Profit for members (higher income) ---------------------------------------------------------Limited-liability corporation The member investors Profit for member investors ---------------------------------------------------------Public business The public Least cost to taxpayers S 1. 8
a77ac7f4cfa795359147b7162d4f738b.ppt