41f6d059474f0632b4368247f70f0dc6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Understanding Consumer and Business Markets Chapter 5 Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata

The consumer market s Geographic distribution, frequently divided into rural, urban, and suburban. s Demographics, the vital statistics that describe a population. In particular: · Age. · Gender. · Family life cycle. · Education. · Income distribution. · Ethnicity. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -1

Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -2
Family life cycle s Family life cycle will determine the purchase behaviour of individuals and reason for purchase. s Single parent and two-parent family. s Young couples no children. s Family (usually two adults, two young children). s Family with teenagers. s Multi-cultural (or mixed) family. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -3

Situational influences s Situational influences are the temporary forces associated with the immediate purchase environment that affect behaviour • When consumers buy—the time influence. (day, week, season). • Where consumers buy—the place a decision is made (home, point of purchase). • How consumers buy—the way in which consumers buy (bulk etc). Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -4
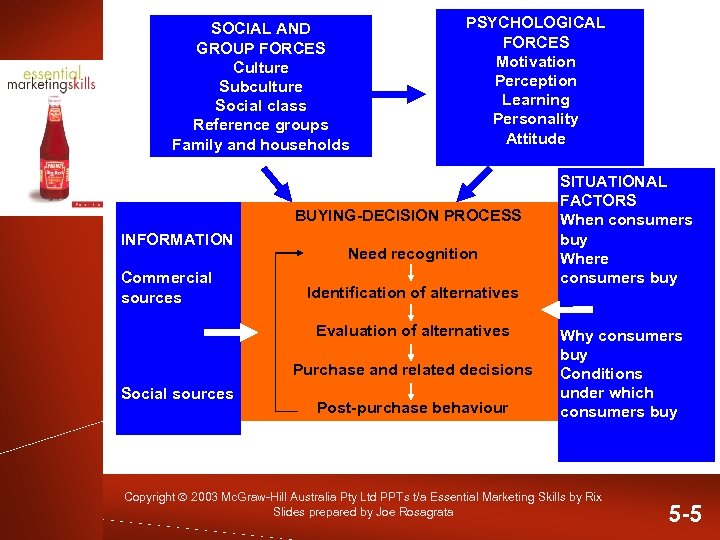
SOCIAL AND GROUP FORCES Culture Subculture Social class Reference groups Family and households PSYCHOLOGICAL FORCES Motivation Perception Learning Personality Attitude BUYING-DECISION PROCESS INFORMATION Commercial sources Need recognition Identification of alternatives Evaluation of alternatives Purchase and related decisions Social sources Post-purchase behaviour SITUATIONAL FACTORS When consumers buy Where consumers buy Why consumers buy Conditions under which consumers buy Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -5

Consumer buying behaviour influences s There are five main Buying Behaviour factors which influence consumer’s decision-making. · Motivation. · Perception. · Learning. · Personality. · Self-concept. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -6

Consumer buying behaviour influences (cont. ) Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -7

Four demand characteristics that differentiate the business market from the consumer market s Demand is derived from the demand for the ultimate consumer products in which the business product is finally used (e. g. steel). s In the short run demand is inelastic, that is, demand for a product responds very little to changes in price when: · The cost of a single part or material is a small portion of the total cost of the finished product. · If the part or material has no substitute. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata Copyright © 1997 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. 5 -8

Four demand characteristics that differentiate the business market from the consumer market (cont. ) s Demand is widely fluctuating, meaning that demand for most classes of business goods fluctuates considerably more than the demand for consumer products. s The buyers are well informed and know the relative merits of alternative sources of supply and competitive products. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -9

Influences on businessmarket demand s The number and types of potential business users. s Their buying power, s buying motives, s and buying habits. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -10

Key differences between the business market (BM) and consumer (CM) market s Small number of BMs. s BMs have larger purchasing power and buy in quantity. s BMs are concentrated. CMs are not. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -11

Key differences between the business market (BM) and consumer (CM) market (cont. ) s Sellers deal direct with business users. s BMs are usually regionally concentrated. s BMs can be vertically or horizontally concentrated. s BM’s buying motives are rational and purchase is methodical and objective. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -12

Types of buying situations 1. New task s New purchase or product category. s More people involved in new purchase. s Extensive information must be collected and evaluated on alternative products. s Seller displays creative selling ability in satisfying buyer needs. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -13

Types of buying situations (cont. ) 2. Straight re-buy s Information needs are minimal s There is no great consideration of alternatives. s Buying decision made in the purchasing department e. g. purchasing of office supplies. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -14

Types of buying situations (cont. ) 3. Modified re-buy s Situation in which the buyer wants to change (modify) the product specifications, price, terms, or suppliers. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -15

The buying centre s A Buying Centre is all the individuals who play a part in the various buying roles and who influence buying decisions, determine product specification and make the buying decision • Users—people who actually use the good or service. • Influencers—people who set the specifications of, and help determine aspects of the buying decision because of their expertise, financial position, or political power. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -16

Types of buying situations (cont. ) s Deciders—the people who make the actual buying decision regarding the product and supplier. s Gatekeepers—people who control the flow of purchasing information within the organisation, as well as between the firm and potential vendors. s Buyers—people who select the suppliers, arrange the terms of the sale and process the actual purchase orders. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -17

Buying patterns of business users s s s s Direct purchase. Frequency of purchases. Size of order. Length of negotiated period. Reciprocity arrangements. Service expectations. Dependability of supply. Leasing instead of buying. Copyright 2003 Mc. Graw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Essential Marketing Skills by Rix Slides prepared by Joe Rosagrata 5 -18
41f6d059474f0632b4368247f70f0dc6.ppt