ef5a907b89332fc64bc05a1f9d1e9293.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Understanding Children’s social awareness and perspective taking through the book, Freedom Summer
Understanding Children’s social awareness and perspective taking through the book, Freedom Summer
 Promoting Social Awareness through Voices SYNOPSIS Voices Reading Social Awareness Concept: “Working for equality sometimes starts with small, brave steps. ”
Promoting Social Awareness through Voices SYNOPSIS Voices Reading Social Awareness Concept: “Working for equality sometimes starts with small, brave steps. ”
 Basic Research Questions: Listening to Students’ Voices 1) What literacy/social base knowledge do 1 st-5 th grade students at two Dorchester schools bring to a read-aloud of Freedom Summer? 2) Based on pivotal scenes in Freedom Summer, how do these students write about and discuss equality? How do these students’ voices sound?
Basic Research Questions: Listening to Students’ Voices 1) What literacy/social base knowledge do 1 st-5 th grade students at two Dorchester schools bring to a read-aloud of Freedom Summer? 2) Based on pivotal scenes in Freedom Summer, how do these students write about and discuss equality? How do these students’ voices sound?
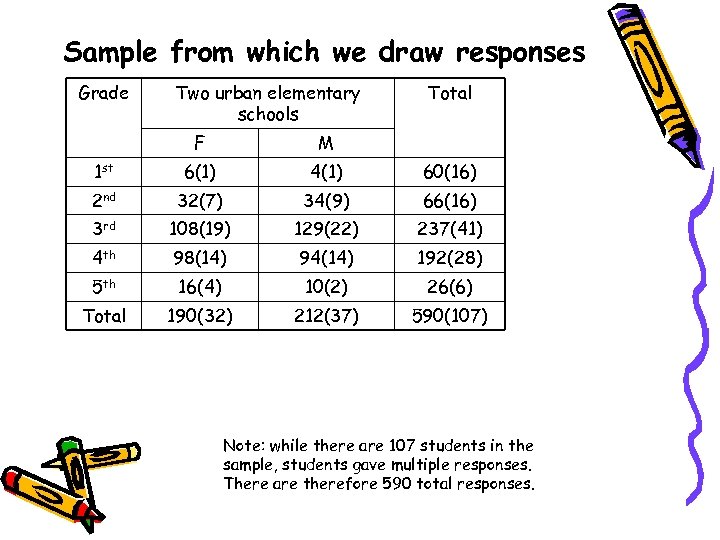 Sample from which we draw responses Grade Two urban elementary schools Total F M 1 st 6(1) 4(1) 60(16) 2 nd 32(7) 34(9) 66(16) 3 rd 108(19) 129(22) 237(41) 4 th 98(14) 94(14) 192(28) 5 th 16(4) 10(2) 26(6) Total 190(32) 212(37) 590(107) Note: while there are 107 students in the sample, students gave multiple responses. There are therefore 590 total responses.
Sample from which we draw responses Grade Two urban elementary schools Total F M 1 st 6(1) 4(1) 60(16) 2 nd 32(7) 34(9) 66(16) 3 rd 108(19) 129(22) 237(41) 4 th 98(14) 94(14) 192(28) 5 th 16(4) 10(2) 26(6) Total 190(32) 212(37) 590(107) Note: while there are 107 students in the sample, students gave multiple responses. There are therefore 590 total responses.
 Understanding the Problem (UP) Why was the pool filled with tar so that Joe and John Henry could not swim in it? Research Objectives 1. Age of social awareness 2. What constructs are used? Levels of Awareness “No Awareness” “Partial Awareness” “Full Awareness”
Understanding the Problem (UP) Why was the pool filled with tar so that Joe and John Henry could not swim in it? Research Objectives 1. Age of social awareness 2. What constructs are used? Levels of Awareness “No Awareness” “Partial Awareness” “Full Awareness”
 UP – “No Social Awareness” Student gives some explanation of pool’s filling other than social issues Examples: – “…so they could walk on it” (1 st grade girl) – “because they needed a parking lot” (4 th grade boy)
UP – “No Social Awareness” Student gives some explanation of pool’s filling other than social issues Examples: – “…so they could walk on it” (1 st grade girl) – “because they needed a parking lot” (4 th grade boy)
 UP - Partial/Vague Awareness
UP - Partial/Vague Awareness
 UP - Partial/Confused Awareness Law Confusion - “Because blacks and whites are not allowed to swim together because it was the law” (4 th grade boy) Power Confusion- “John Henry’s brother didn’t want him swimming with his friend, cause they’re different colors” (1 st grade girl)
UP - Partial/Confused Awareness Law Confusion - “Because blacks and whites are not allowed to swim together because it was the law” (4 th grade boy) Power Confusion- “John Henry’s brother didn’t want him swimming with his friend, cause they’re different colors” (1 st grade girl)
 UP – “Full Social Awareness” Student uses knowledge of race to explain the filling of the pool.
UP – “Full Social Awareness” Student uses knowledge of race to explain the filling of the pool.
 UP – Social Awareness Constructs Literal, “Black & White” Thinking – “because they were different colored and they didn’t want anyone different colored swimming in the same pool” (5 th grade boy; segregation construct)
UP – Social Awareness Constructs Literal, “Black & White” Thinking – “because they were different colored and they didn’t want anyone different colored swimming in the same pool” (5 th grade boy; segregation construct)
 UP – Power and Privilege Constructs • Intragroup Conflict Prevention & Maintain Power and Privilege: “Because some of the White people who don’t care for the Black people might say it’s not fair because the White people always swim. (2 nd grade girl) • Maintain Power and Privilege: “They just want it the way it is now so White people can do anything they want. ” (5 th grade girl)
UP – Power and Privilege Constructs • Intragroup Conflict Prevention & Maintain Power and Privilege: “Because some of the White people who don’t care for the Black people might say it’s not fair because the White people always swim. (2 nd grade girl) • Maintain Power and Privilege: “They just want it the way it is now so White people can do anything they want. ” (5 th grade girl)
 Perspective Taking (PT) Why did John Henry want to use his own nickel to buy an ice pop?
Perspective Taking (PT) Why did John Henry want to use his own nickel to buy an ice pop?
 PT – No Awareness or Vague Awareness Student identifies some factors unrelated to desegregation to explain why John Henry wanted to use his own nickel. • No Awareness Examples: – “Because he feels like he owes Joe for every time Joe lended him a nickel…” (4 th grade boy). – Joe kept buying him [John Henry] purple, and Joe kept getting green and John Henry wanted red ice pop. ” • Vague Awareness Examples: – John Henry wanted to use his own nickel because he knew that Joe bought him an ice pop almost every day and he was upset. ”
PT – No Awareness or Vague Awareness Student identifies some factors unrelated to desegregation to explain why John Henry wanted to use his own nickel. • No Awareness Examples: – “Because he feels like he owes Joe for every time Joe lended him a nickel…” (4 th grade boy). – Joe kept buying him [John Henry] purple, and Joe kept getting green and John Henry wanted red ice pop. ” • Vague Awareness Examples: – John Henry wanted to use his own nickel because he knew that Joe bought him an ice pop almost every day and he was upset. ”
 PT – Full Awareness • Bravery – “I think John Henry used his own nickel because he wanted to be brave and go in since segregation was over. He did what he had to do or he would never succeed. ” (4 th grade girl)
PT – Full Awareness • Bravery – “I think John Henry used his own nickel because he wanted to be brave and go in since segregation was over. He did what he had to do or he would never succeed. ” (4 th grade girl)
 PT – Full Awareness • Test Change – “Because he wants to try out everything that he can do by himself and see how people are rude and mean to him and see how they would treat him and see if they would treat him nice or [say] ‘Get out of my store, ’ stuff like that” (4 th grade girl)
PT – Full Awareness • Test Change – “Because he wants to try out everything that he can do by himself and see how people are rude and mean to him and see how they would treat him and see if they would treat him nice or [say] ‘Get out of my store, ’ stuff like that” (4 th grade girl)
 Research Goals • Research protocols designed to elicit students’ own knowledge without the intervention of programs like Voices. • Non-leading questions – Why was the pool filled with tar?
Research Goals • Research protocols designed to elicit students’ own knowledge without the intervention of programs like Voices. • Non-leading questions – Why was the pool filled with tar?
 Practice Emphasis in Voices Central Social Awareness Question: “What is Equality? ” Central Social Awareness Concept for Freedom Summer: “Working for equality sometimes starts with small, brave steps. ”
Practice Emphasis in Voices Central Social Awareness Question: “What is Equality? ” Central Social Awareness Concept for Freedom Summer: “Working for equality sometimes starts with small, brave steps. ”
 Practice Goals • Curriculum gives teachers tools to teach social awareness, perspective taking, and the other Voices Reading Themes • Useful Leading Questions: – How did Joe and John Henry overcome discrimination throughout the story? – How are the boys taking a step to overcome discrimination by walking into Mr. Mason’s store together?
Practice Goals • Curriculum gives teachers tools to teach social awareness, perspective taking, and the other Voices Reading Themes • Useful Leading Questions: – How did Joe and John Henry overcome discrimination throughout the story? – How are the boys taking a step to overcome discrimination by walking into Mr. Mason’s store together?
 The essential “added” ingredients every teachers needs support in gaining • Commitment of Teacher to the student as a critical social thinker. – Promoting both comprehension of text and awareness of the social world – Promoting the capacity for perspective taking and the capacity and desire to express themselves; – Promoting a safe classroom and community so students will feel supported.
The essential “added” ingredients every teachers needs support in gaining • Commitment of Teacher to the student as a critical social thinker. – Promoting both comprehension of text and awareness of the social world – Promoting the capacity for perspective taking and the capacity and desire to express themselves; – Promoting a safe classroom and community so students will feel supported.
 The essential “added” ingredients every teachers needs support in gaining • Commitment of Teacher to the student as a critical reader. – Promoting higher level reading skills by using interesting texts – Promoting a stronger sense of social justice through exposure to the stories and struggles of others – Promoting oral language skills that will be crucial for literacy from Kindergarten on up
The essential “added” ingredients every teachers needs support in gaining • Commitment of Teacher to the student as a critical reader. – Promoting higher level reading skills by using interesting texts – Promoting a stronger sense of social justice through exposure to the stories and struggles of others – Promoting oral language skills that will be crucial for literacy from Kindergarten on up
 Essential Connections of our research to Voices Reading • 1. The promotion of social awareness is a necessary condition for character development • 2. To promote character development and influence behavior the awareness needs to be made personally meaningful • 3. A supportive classroom climate is the third major ingredient in children’s social and emotional learning.
Essential Connections of our research to Voices Reading • 1. The promotion of social awareness is a necessary condition for character development • 2. To promote character development and influence behavior the awareness needs to be made personally meaningful • 3. A supportive classroom climate is the third major ingredient in children’s social and emotional learning.
 Future directions • Integrating issues from social studies into the tapestry • Evaluating the effectiveness of this approach – What counts? E. g. , progress on accountability measures in literacy (and social competence) – What matters? E. g. , what it means to be a good citizen; How an integrated approach feeds into the enhancement of school climate • Determining what professional development is needed to make it work
Future directions • Integrating issues from social studies into the tapestry • Evaluating the effectiveness of this approach – What counts? E. g. , progress on accountability measures in literacy (and social competence) – What matters? E. g. , what it means to be a good citizen; How an integrated approach feeds into the enhancement of school climate • Determining what professional development is needed to make it work
 Why there is still a lot to do! • “We can move through the water like fish, we can fly through the air like birds, yet we cannot walk arm and arm like brothers [and sisters]. ” » Martin Luther King
Why there is still a lot to do! • “We can move through the water like fish, we can fly through the air like birds, yet we cannot walk arm and arm like brothers [and sisters]. ” » Martin Luther King


