ANGIOGEN.PPT
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Understanding Cancer and Related Topics Understanding Angiogenesis Developed by: Lewis J. Kleinsmith, Ph. D. Donna Kerrigan, M. S. Jeanne Kelly Brian Hollen An illustrated description of angiogenesis and its importance in cancer research. These Power. Point slides are not locked files. You can mix and match slides from different tutorials as you prepare your own lectures. In the Notes section, you will find explanations of the graphics. The art in this tutorial is copyrighted and may not be reused for commercial gain. Please do not remove the NCI logo or the copyright mark from any slide. These tutorials may be copied only if they are distributed free of charge for educational purposes.
Understanding Cancer and Related Topics Understanding Angiogenesis Developed by: Lewis J. Kleinsmith, Ph. D. Donna Kerrigan, M. S. Jeanne Kelly Brian Hollen An illustrated description of angiogenesis and its importance in cancer research. These Power. Point slides are not locked files. You can mix and match slides from different tutorials as you prepare your own lectures. In the Notes section, you will find explanations of the graphics. The art in this tutorial is copyrighted and may not be reused for commercial gain. Please do not remove the NCI logo or the copyright mark from any slide. These tutorials may be copied only if they are distributed free of charge for educational purposes.
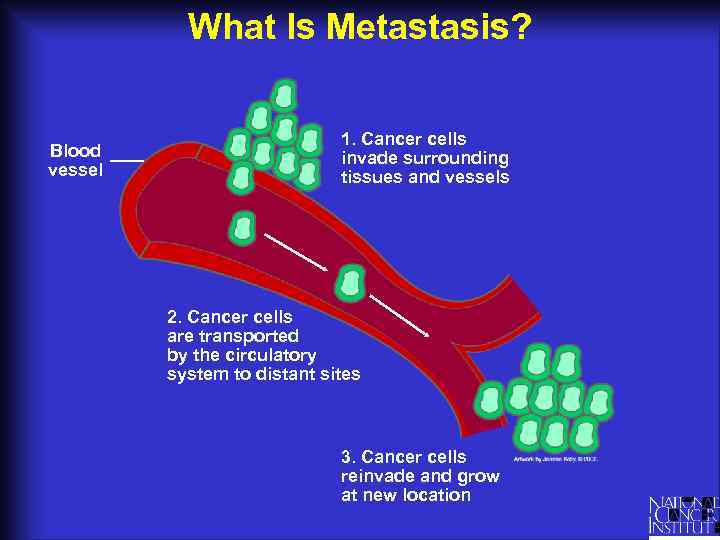 What Is Metastasis? Blood vessel 1. Cancer cells invade surrounding tissues and vessels 2. Cancer cells are transported by the circulatory system to distant sites 3. Cancer cells reinvade and grow at new location
What Is Metastasis? Blood vessel 1. Cancer cells invade surrounding tissues and vessels 2. Cancer cells are transported by the circulatory system to distant sites 3. Cancer cells reinvade and grow at new location
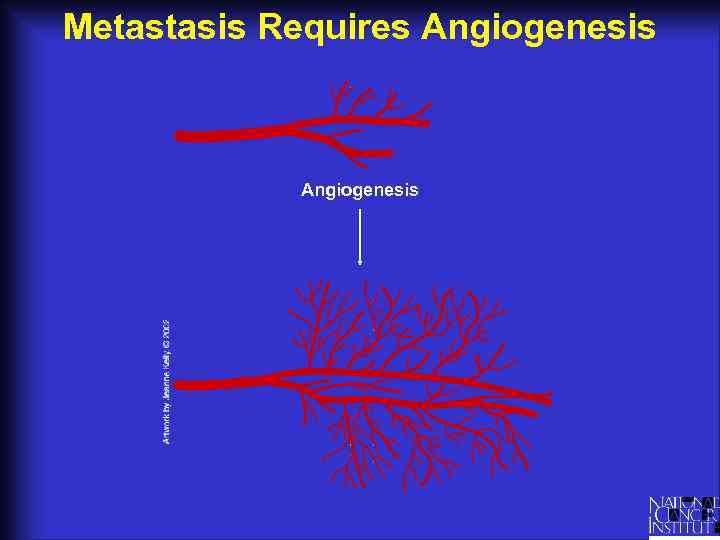 Metastasis Requires Angiogenesis
Metastasis Requires Angiogenesis
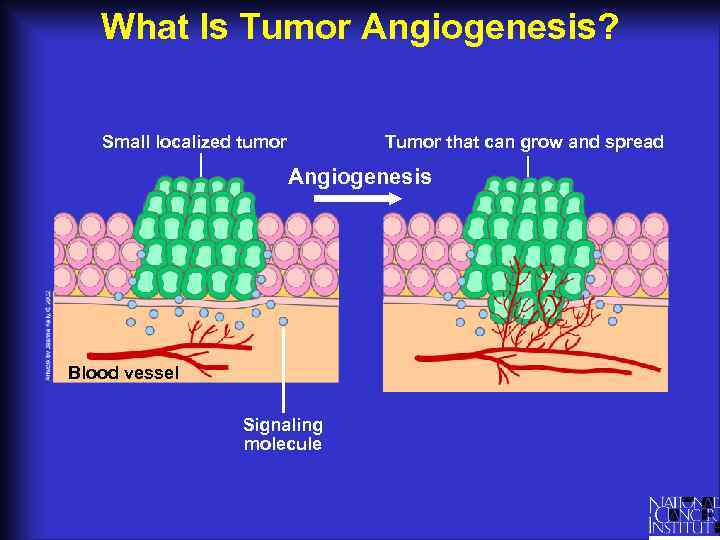 What Is Tumor Angiogenesis? Small localized tumor Tumor that can grow and spread Angiogenesis Blood vessel Signaling molecule
What Is Tumor Angiogenesis? Small localized tumor Tumor that can grow and spread Angiogenesis Blood vessel Signaling molecule
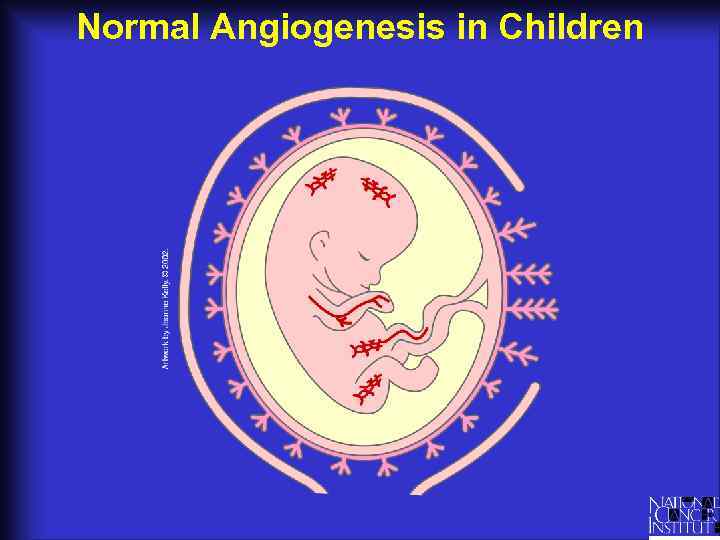 Normal Angiogenesis in Children
Normal Angiogenesis in Children
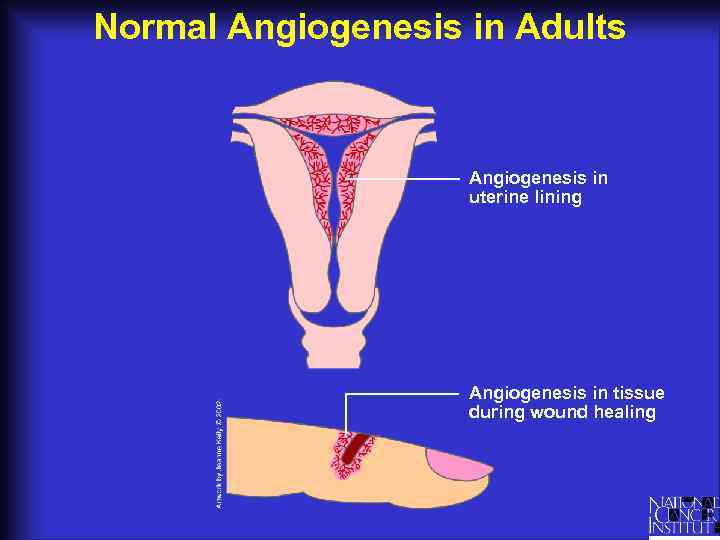 Normal Angiogenesis in Adults Angiogenesis in uterine lining Angiogenesis in tissue during wound healing
Normal Angiogenesis in Adults Angiogenesis in uterine lining Angiogenesis in tissue during wound healing
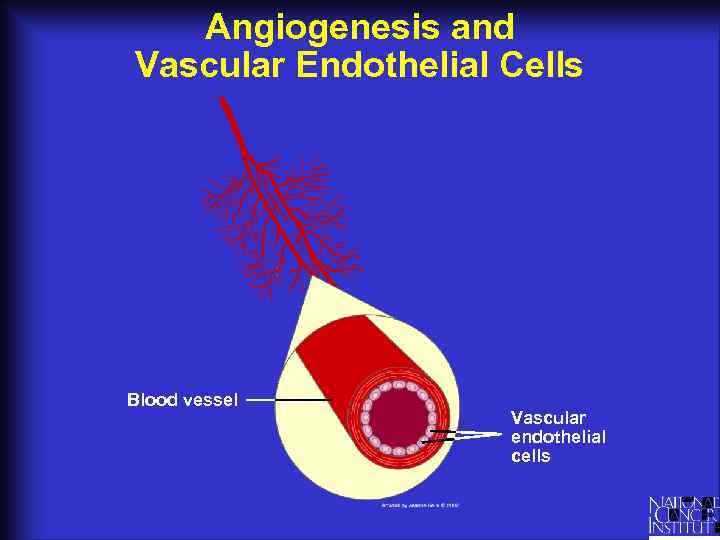 Angiogenesis and Vascular Endothelial Cells Blood vessel Vascular endothelial cells
Angiogenesis and Vascular Endothelial Cells Blood vessel Vascular endothelial cells
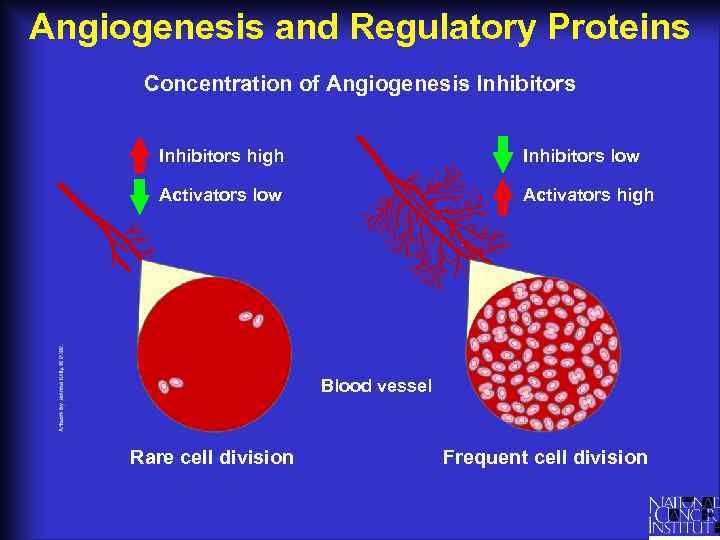 Angiogenesis and Regulatory Proteins Concentration of Angiogenesis Inhibitors high Inhibitors low Activators high Blood vessel Rare cell division Frequent cell division
Angiogenesis and Regulatory Proteins Concentration of Angiogenesis Inhibitors high Inhibitors low Activators high Blood vessel Rare cell division Frequent cell division
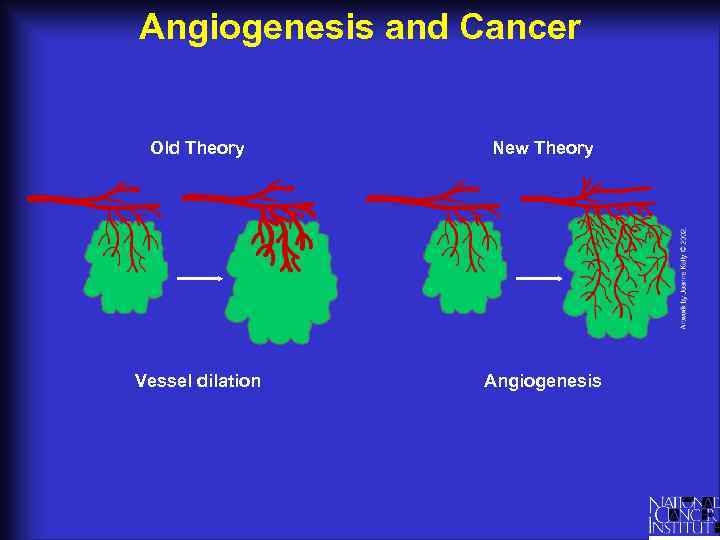 Angiogenesis and Cancer Old Theory New Theory Vessel dilation Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis and Cancer Old Theory New Theory Vessel dilation Angiogenesis
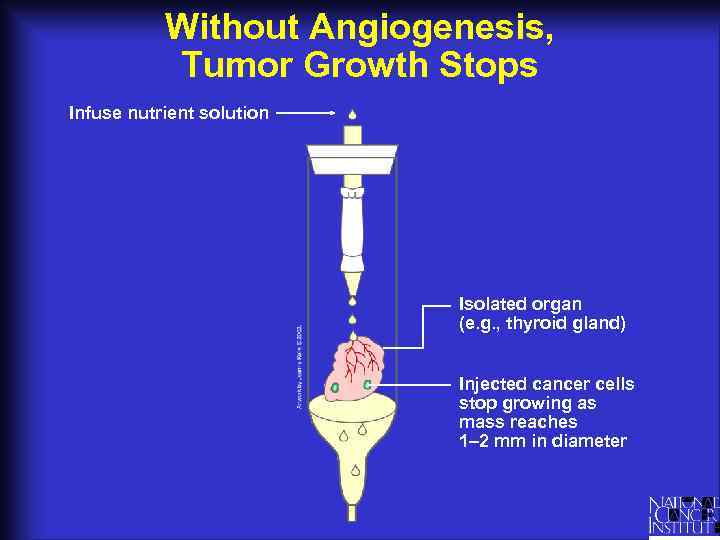 Without Angiogenesis, Tumor Growth Stops Infuse nutrient solution Isolated organ (e. g. , thyroid gland) Injected cancer cells stop growing as mass reaches 1– 2 mm in diameter
Without Angiogenesis, Tumor Growth Stops Infuse nutrient solution Isolated organ (e. g. , thyroid gland) Injected cancer cells stop growing as mass reaches 1– 2 mm in diameter
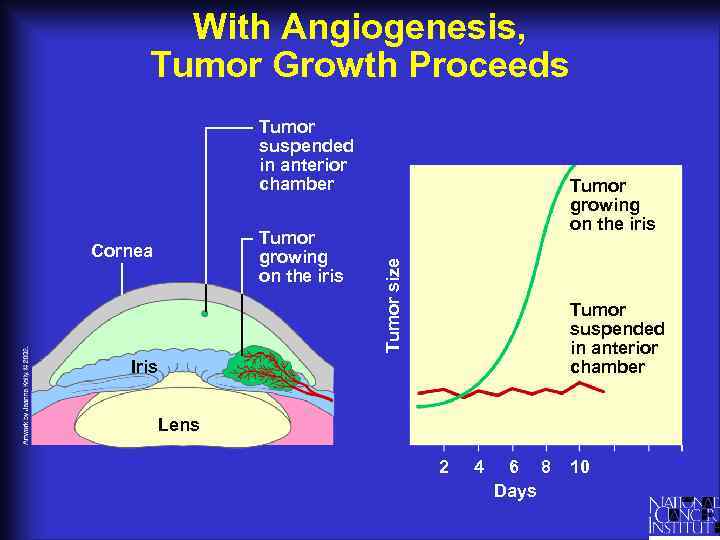 With Angiogenesis, Tumor Growth Proceeds Tumor suspended in anterior chamber Cornea Tumor size Tumor growing on the iris Tumor suspended in anterior chamber Iris Lens 2 4 6 8 Days 10
With Angiogenesis, Tumor Growth Proceeds Tumor suspended in anterior chamber Cornea Tumor size Tumor growing on the iris Tumor suspended in anterior chamber Iris Lens 2 4 6 8 Days 10
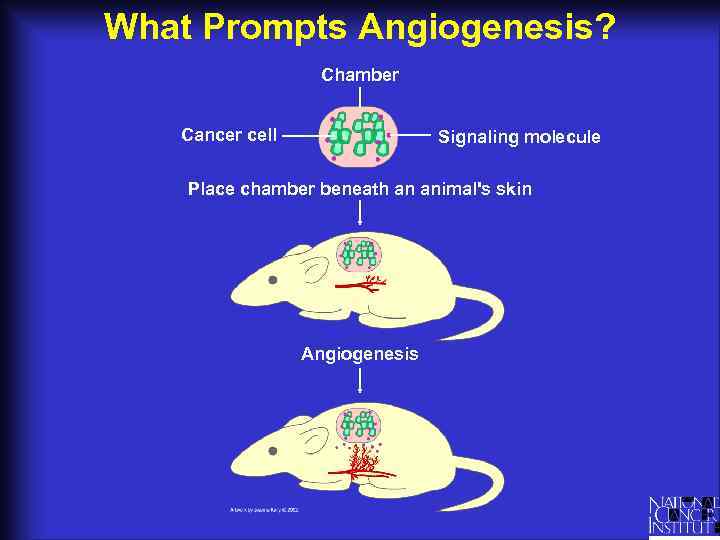 What Prompts Angiogenesis? Chamber Cancer cell Signaling molecule Place chamber beneath an animal's skin Angiogenesis
What Prompts Angiogenesis? Chamber Cancer cell Signaling molecule Place chamber beneath an animal's skin Angiogenesis
 Activators of Angiogenesis
Activators of Angiogenesis
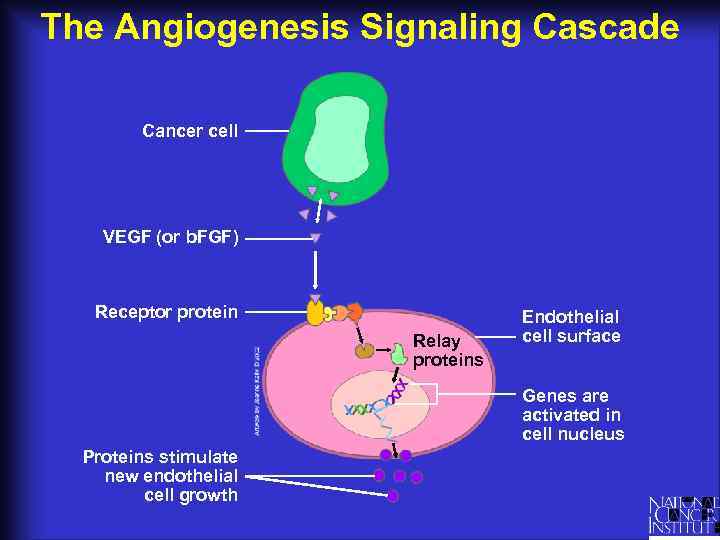 The Angiogenesis Signaling Cascade Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Relay proteins Endothelial cell surface Genes are activated in cell nucleus Proteins stimulate new endothelial cell growth
The Angiogenesis Signaling Cascade Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Relay proteins Endothelial cell surface Genes are activated in cell nucleus Proteins stimulate new endothelial cell growth
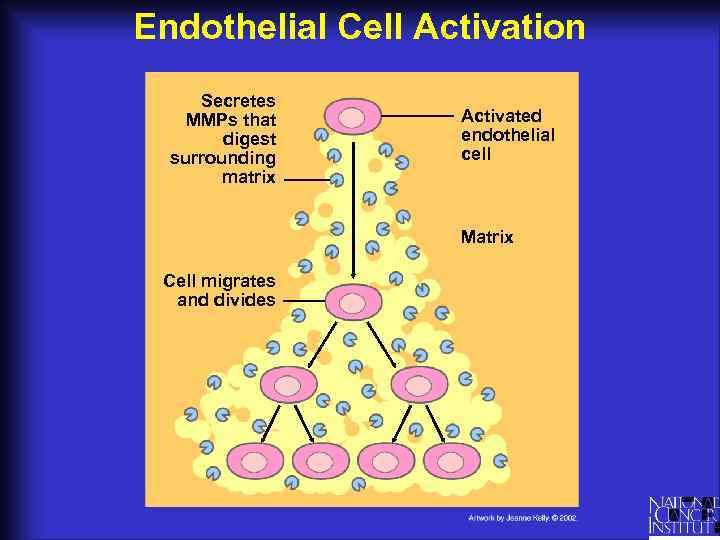 Endothelial Cell Activation Secretes MMPs that digest surrounding matrix Activated endothelial cell Matrix Cell migrates and divides
Endothelial Cell Activation Secretes MMPs that digest surrounding matrix Activated endothelial cell Matrix Cell migrates and divides
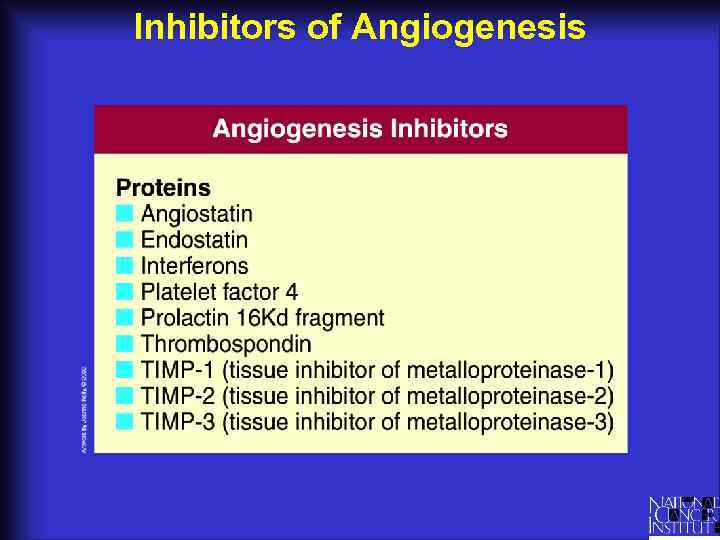 Inhibitors of Angiogenesis
Inhibitors of Angiogenesis
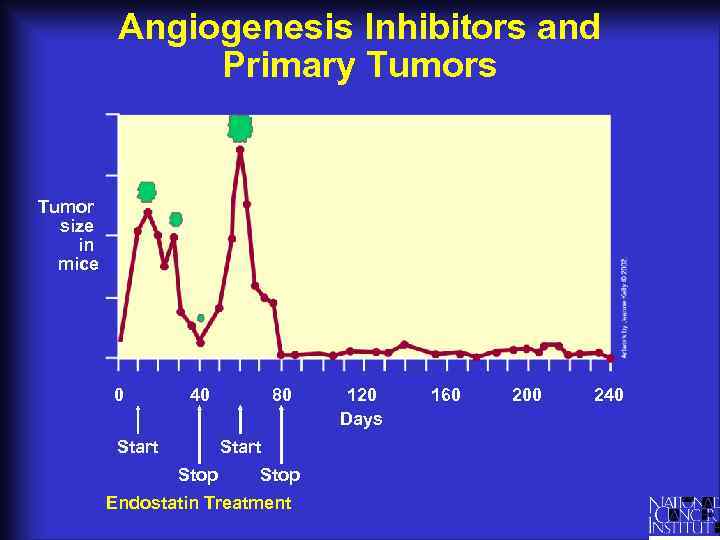 Angiogenesis Inhibitors and Primary Tumors Tumor size in mice 0 40 Start 80 Start Stop Endostatin Treatment 120 Days 160 200 240
Angiogenesis Inhibitors and Primary Tumors Tumor size in mice 0 40 Start 80 Start Stop Endostatin Treatment 120 Days 160 200 240
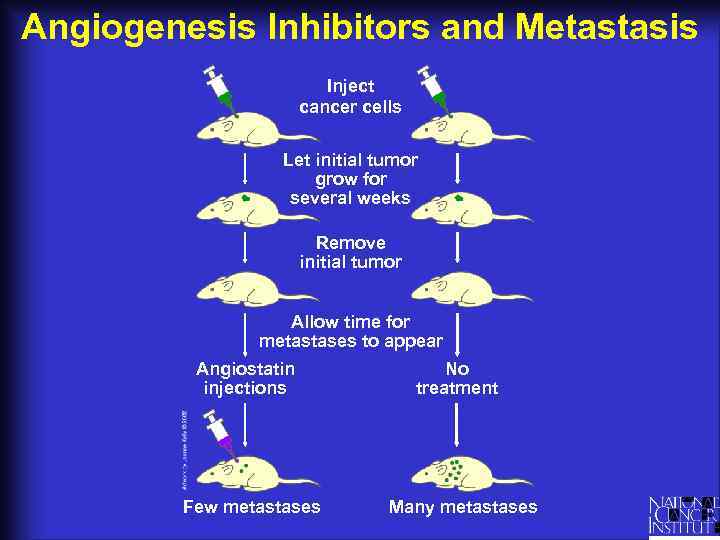 Angiogenesis Inhibitors and Metastasis Inject cancer cells Let initial tumor grow for several weeks Remove initial tumor Allow time for metastases to appear Angiostatin injections Few metastases No treatment Many metastases
Angiogenesis Inhibitors and Metastasis Inject cancer cells Let initial tumor grow for several weeks Remove initial tumor Allow time for metastases to appear Angiostatin injections Few metastases No treatment Many metastases
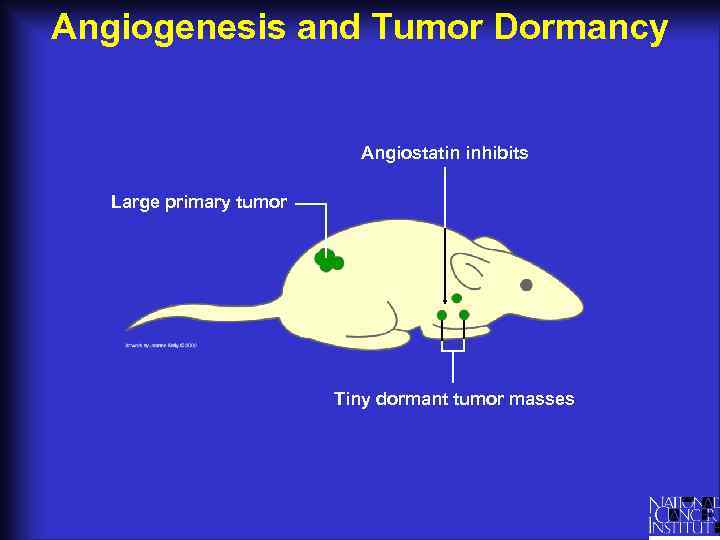 Angiogenesis and Tumor Dormancy Angiostatin inhibits Large primary tumor Tiny dormant tumor masses
Angiogenesis and Tumor Dormancy Angiostatin inhibits Large primary tumor Tiny dormant tumor masses
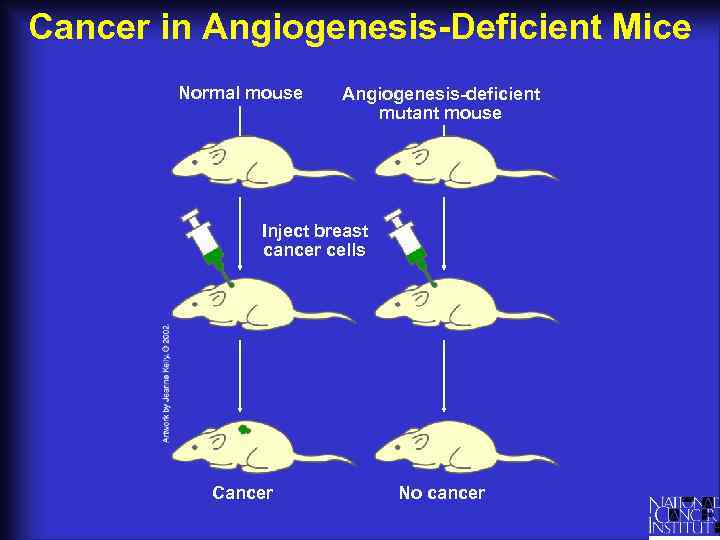 Cancer in Angiogenesis-Deficient Mice Normal mouse Angiogenesis-deficient mutant mouse Inject breast cancer cells Cancer No cancer
Cancer in Angiogenesis-Deficient Mice Normal mouse Angiogenesis-deficient mutant mouse Inject breast cancer cells Cancer No cancer
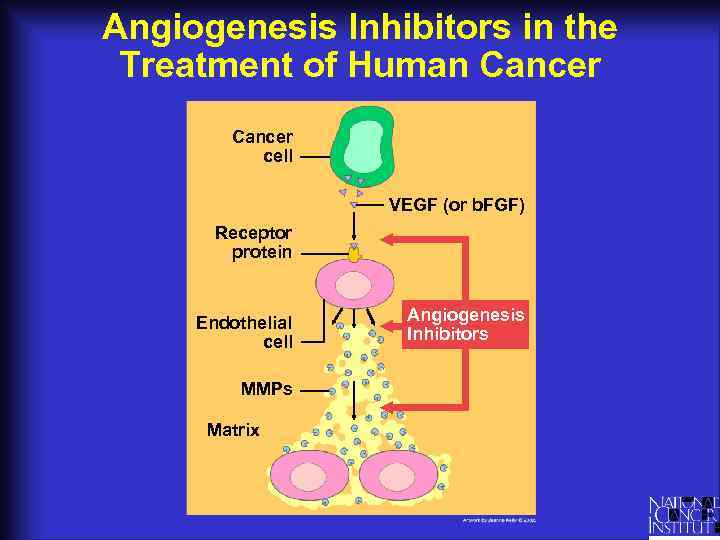 Angiogenesis Inhibitors in the Treatment of Human Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Angiogenesis Inhibitors
Angiogenesis Inhibitors in the Treatment of Human Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Angiogenesis Inhibitors
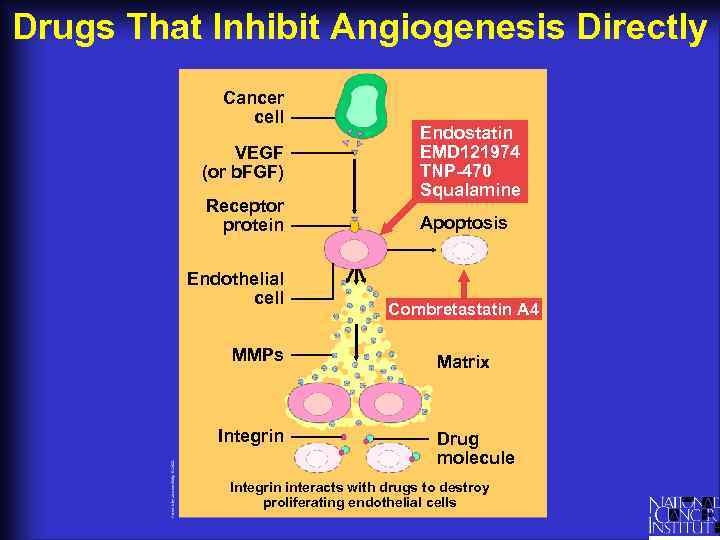 Drugs That Inhibit Angiogenesis Directly Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Integrin Endostatin EMD 121974 TNP-470 Squalamine Apoptosis Combretastatin A 4 Matrix Drug molecule Integrin interacts with drugs to destroy proliferating endothelial cells
Drugs That Inhibit Angiogenesis Directly Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Integrin Endostatin EMD 121974 TNP-470 Squalamine Apoptosis Combretastatin A 4 Matrix Drug molecule Integrin interacts with drugs to destroy proliferating endothelial cells
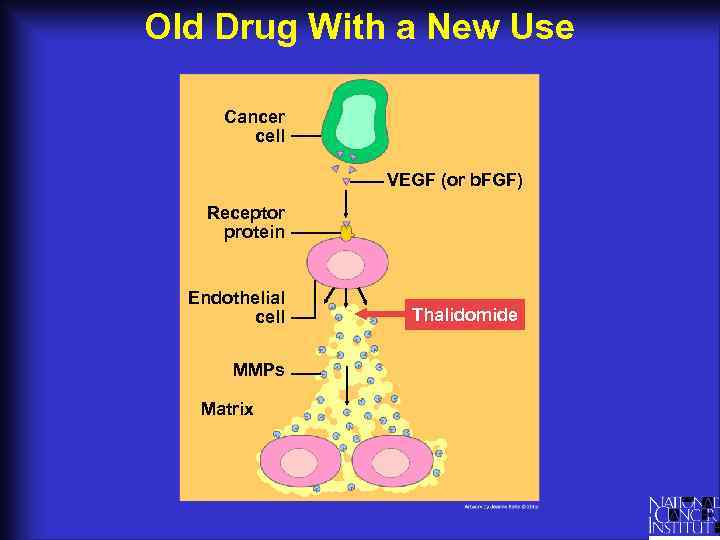 Old Drug With a New Use Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Thalidomide
Old Drug With a New Use Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Thalidomide
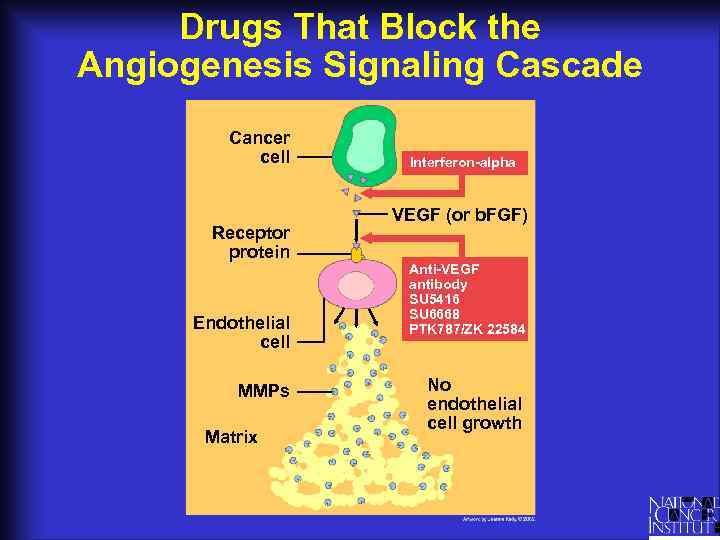 Drugs That Block the Angiogenesis Signaling Cascade Cancer cell Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Interferon-alpha VEGF (or b. FGF) Anti-VEGF antibody SU 5416 SU 6668 PTK 787/ZK 22584 No endothelial cell growth
Drugs That Block the Angiogenesis Signaling Cascade Cancer cell Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Interferon-alpha VEGF (or b. FGF) Anti-VEGF antibody SU 5416 SU 6668 PTK 787/ZK 22584 No endothelial cell growth
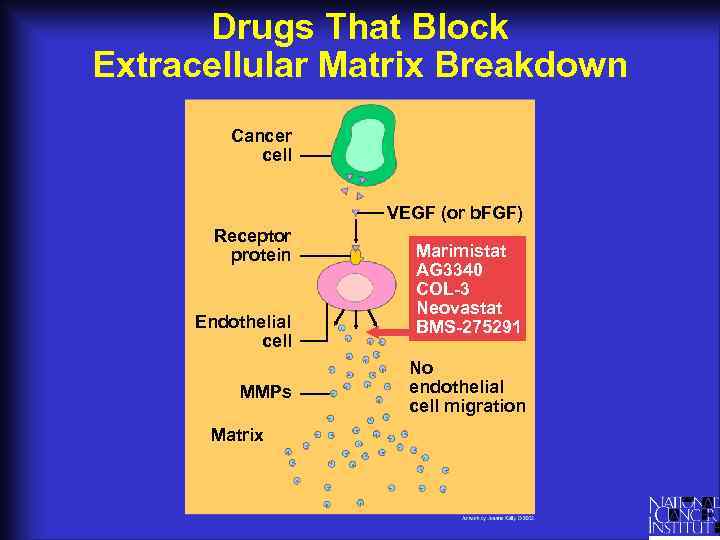 Drugs That Block Extracellular Matrix Breakdown Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Marimistat AG 3340 COL-3 Neovastat BMS-275291 No endothelial cell migration
Drugs That Block Extracellular Matrix Breakdown Cancer cell VEGF (or b. FGF) Receptor protein Endothelial cell MMPs Matrix Marimistat AG 3340 COL-3 Neovastat BMS-275291 No endothelial cell migration
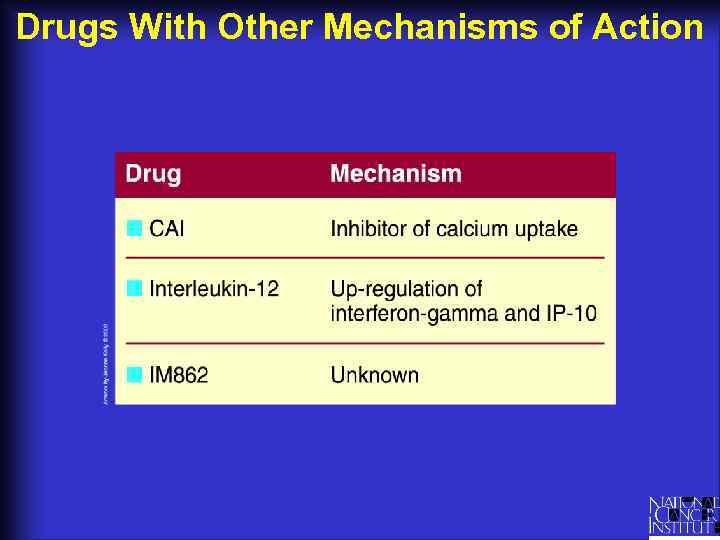 Drugs With Other Mechanisms of Action
Drugs With Other Mechanisms of Action
 On to Clinical Trials
On to Clinical Trials
 We would like to hear from you. . . If you have questions about this tutorial’s content, suggestions for new topics, or other feedback on the Web site, please send an e-mail to kerrigad@mail. nih. gov. If you have questions about this tutorial’s artwork or want permission to use it, please send an e-mail to beankelly@verizon. net.
We would like to hear from you. . . If you have questions about this tutorial’s content, suggestions for new topics, or other feedback on the Web site, please send an e-mail to kerrigad@mail. nih. gov. If you have questions about this tutorial’s artwork or want permission to use it, please send an e-mail to beankelly@verizon. net.


