185ca7217550bc1765610593ae928608.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Understanding Banking and Securities © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 1

Characteristics of Money • Medium of exchange • Measure of value • Store of value © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 2

Forms of Money • Currency • Demand deposits • Time deposits © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 3

Substitutes for Currency and Checks • Credit cards • Debit cards • Smart cards © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 4
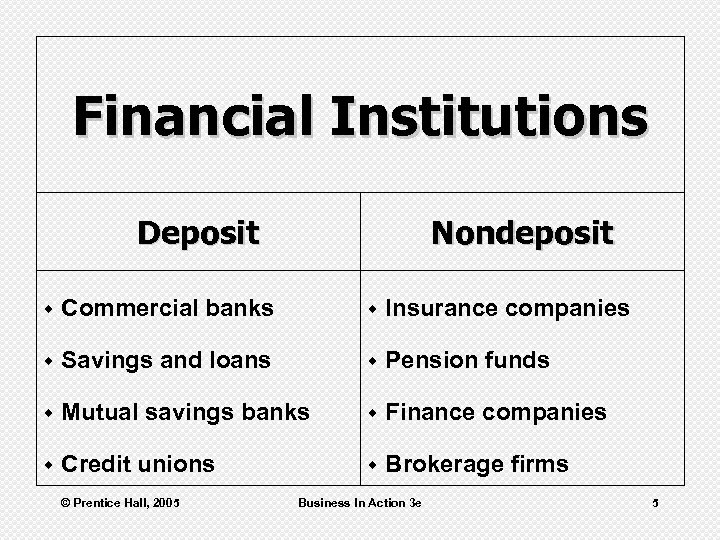
Financial Institutions Deposit Nondeposit w Commercial banks w Insurance companies w Savings and loans w Pension funds w Mutual savings banks w Finance companies w Credit unions w Brokerage firms © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 5
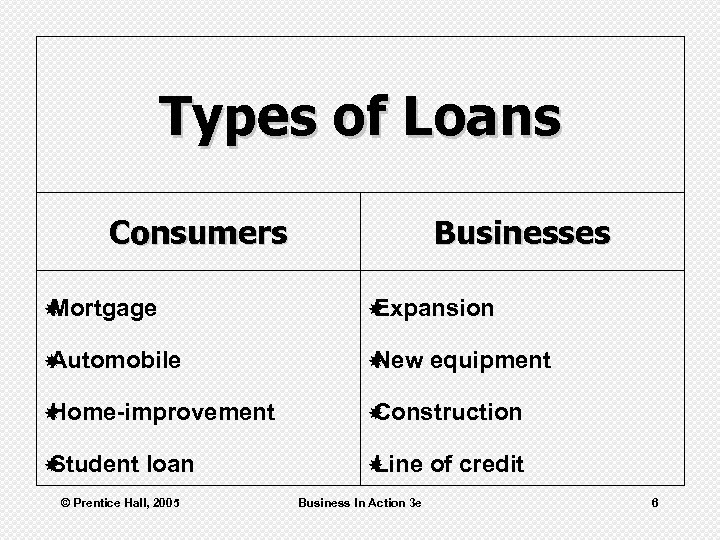
Types of Loans Consumers Businesses Mortgage Expansion Automobile New Home-improvement Construction Student Line loan © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e equipment of credit 6

Electronic Banking • Automated teller • Electronic funds transfer • Online banking © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 7

Bank Safety and Regulation • Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation • National Credit Union Association • State Banking Commission • Office of the Comptroller of the Currency • Office of Thrift Supervision • Federal Reserve System © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 8
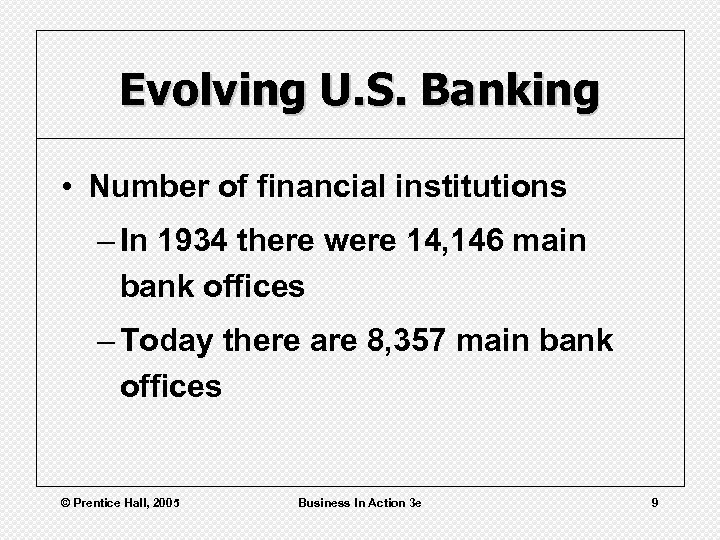
Evolving U. S. Banking • Number of financial institutions – In 1934 there were 14, 146 main bank offices – Today there are 8, 357 main bank offices © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 9

Banking Legislation • Financial Services Modernization Act (1999) • Riegle-Neal Banking Efficiency Act (1994) © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 10

Securities Investments • Stocks • Mutual funds • Bonds © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 11

Stocks: Important Terms • • • Authorized stock Issued stock Unissued stock Stock split Par value © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 12

Common Stock • • Voting rights Dividends Limited liability Liquidity © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 13

Preferred Stock • Convertible preferred stock • Cumulative preferred stock © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 14

Corporate Bonds • Secured bonds • Debentures • Convertible bonds © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 15
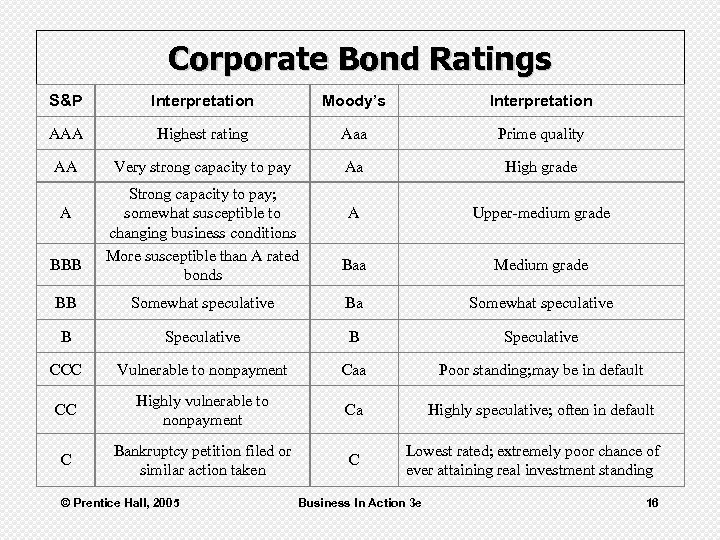
Corporate Bond Ratings S&P Interpretation Moody’s Interpretation AAA Highest rating Aaa Prime quality AA Very strong capacity to pay Aa High grade A Upper-medium grade Baa Medium grade A BBB Strong capacity to pay; somewhat susceptible to changing business conditions More susceptible than A rated bonds BB Somewhat speculative Ba Somewhat speculative B Speculative CCC Vulnerable to nonpayment Caa Poor standing; may be in default CC Highly vulnerable to nonpayment Ca Highly speculative; often in default C Bankruptcy petition filed or similar action taken C © Prentice Hall, 2005 Lowest rated; extremely poor chance of ever attaining real investment standing Business In Action 3 e 16

U. S. Government Securities and Municipal Bonds • Treasury notes • Treasury bills • Treasury bonds • U. S. savings bonds © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 17

U. S. Government Securities and Municipal Bonds • Municipal bonds • General obligation bonds • Revenue bonds • Capital gains © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 18
Mutual Funds: Important Terms • Load fund • No load fund • Open end fund • Closed end fund © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 19

Types of Mutual Funds • • Money market Growth Balanced Income Global International Index © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 20
Mutual Fund Abuses • Market timing • Late trading © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 21

Securities Market • Primary – Initial public offerings • Secondary – Securities exchanges © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 22

Securities Exchanges • Trading floor – New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) • Over-the-counter market – National Association of Securities Dealers (NASDAQ) © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 23
Buying and Selling Securities • Auction exchange (NYSE) – Exchange floor – Stock specialist • Dealer exchange (NASDAQ) – Computer – Market maker • Electronic communication networks – Computer – Broker © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 24

Orders to Buy and Sell Securities • Market order • Stop order • Limit order • Open order • Day order • Short selling • Margin trading • Discretionary order © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 25
Analyzing Financial News • Bull market – Rising market • Bear market – Falling market © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 26
Watching Market Indexes and Averages • Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) • Standard and Poor’s 500 (S&P 500) • Wilshire 5000 • NASSAQ Composite Index • Nikkei 225 Index • FT-SE 100 Index © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 27

Interpreting Financial News • Stock exchange reports • Bond quotation tables • Mutual fund quotations © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 28

Industry Challenges • Electronic trading • Round-the-clock trading • Online trading © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 29

Regulation of the Securities Market • SEC filing requirements • Fair disclosure regulations • Securities fraud © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 30

Ask Questions Before You Invest 1. Is the investment registered with the SEC? 2. Have you read the audited financial statements? 3. Is a registered broker offering the investment? 4. What’s in it for the person touting the investment? 5. Should you trust email/bulletin board advice? © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 31

Ask Questions Before You Invest 6. Are you being pressured to act? 7. Does the investment promise you’ll get rich quick? 8. Does the investment match your objectives? 9. How easy would it be to sell your investment later? 10. Does the investment originate overseas? © Prentice Hall, 2005 Business In Action 3 e 32
185ca7217550bc1765610593ae928608.ppt