3fe576590eddff959dca834eb7f63f75.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

UNDERSTANDING AND SOLVING ROOT CAUSE OF THE PROBLEM THROUGH VALUE MANAGEMENT / VALUE ENGINEERING By: Assoc. Prof. Sr. Dr. Mohd. Mazlan Bin Haji Che Mat President Institute of Value Management Malaysia (IVMM) December 2008 1

DEFINITIONS & CONCEPT OF VALUE MANAGEMENT 2

Definitions & Concept of VM Miles clarified Value Analysis as a philosophy implemented by the use a specific set of technique a body of knowledge and a group of learned skills © MMCM 3

Definitions & Concept of VM It is an organized creative approachhas which for its purpose the efficient identification of unnecessary cost, i. e. cost which provides neither quality, nor use nor life, nor appearance, nor customer featu ”. © MMCM 4

Definitions & Concept of VM Che Mat MM (2004) - Value Management as a rigorous, systematic and innovative methodology with multi disciplinary approach to achieve better value and cost optimization for projects, products, facilities, systems and services without sacrificing the required performance levels. © MMCM 5
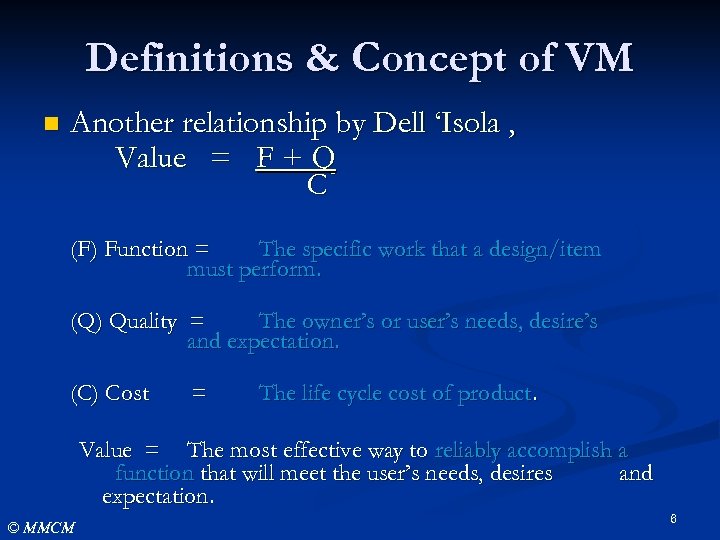
Definitions & Concept of VM n Another relationship by Dell ‘Isola , Value = F + Q C (F) Function = The specific work that a design/item must perform. (Q) Quality = The owner’s or user’s needs, desire’s and expectation. (C) Cost = The life cycle cost of product. Value = The most effective way to reliably accomplish a function that will meet the user’s needs, desires and expectation. © MMCM 6
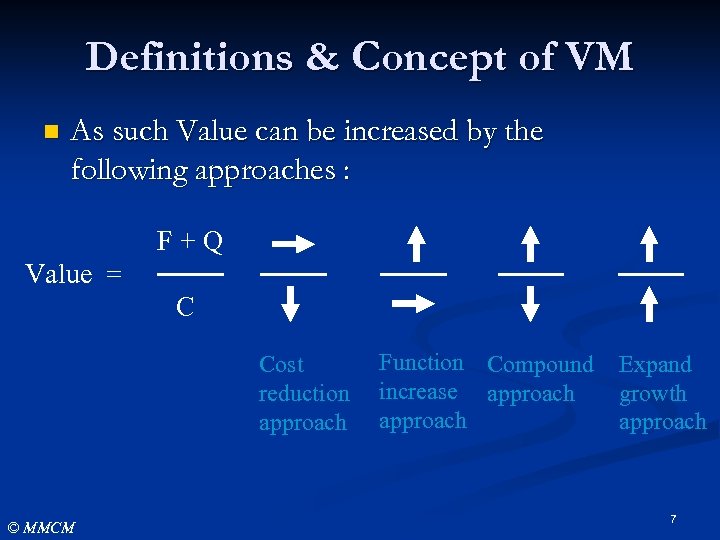
Definitions & Concept of VM n As such Value can be increased by the following approaches : F + Q Value = C Cost reduction approach © MMCM Function Compound Expand increase approach growth approach 7

Definitions & Concept of VM Management of Technology n A Technology that enables work to be performed efficiently and is applicable to all industries and job areas I. E(1911) QC(1920) VA&VE(1942) Present Devt. Mangt. Tech Rationalisation of Enterprise Development of specialised technologies I. E Increase efficiency Time QC Improves quality © MMCM VA&VE Increase value 8
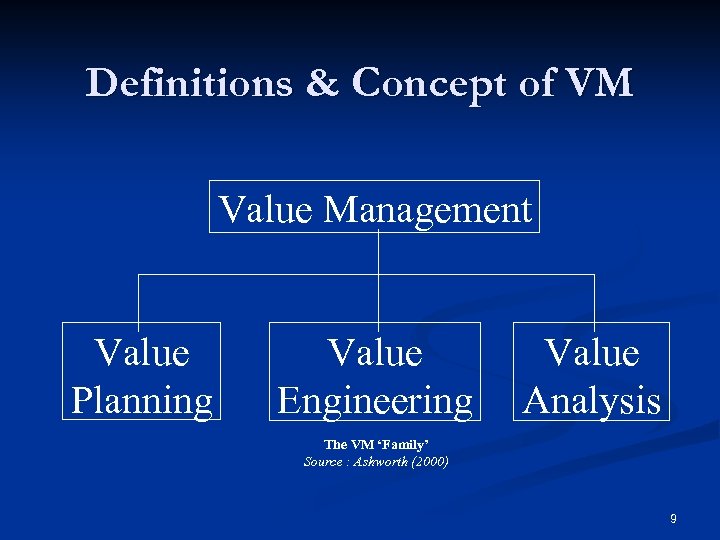
Definitions & Concept of VM Value Management Value Planning Value Engineering Value Analysis The VM ‘Family’ Source : Ashworth (2000) 9

Why use VM ? VM promotes systems thinking n VM establishes customer needs n Value management change proposal (incentive clause) n It encourages Staff development n It promotes Partnering n Is a Vehicle for Change n VM identifies unnecessary costs, which then can be removed. n © MMCM 10

Other Benefits of VM n n n n © MMCM Solves immediate and high priority problems Establishes least cost goals Identifies and defines stakeholders aims and objectives Optimize the unit/component cost Produces unique solutions Increases the marketing potentials Improves communication Improves quality Reduces time Reduces commercial risks Helps to increase the co-operation between departments Encourages fresh thinking Spreads cost-consciousness Develops hidden abilities Helps to provide better appreciation of the other man’s job 11
Misconception About VM n There is a view held by some that Value Management is simply just another cost cutting tool, however it misses an important feature of Value Management which is creativity and systems approach to validate a certain proposal. n The fundamental contribution by the Value Management exercise is to eliminate the unnecessary cost which does not contribute to the Value of the services, products, systems and that includes the construction projects. © MMCM 12

Value Studies are mandatory in: n n n All US federal projects > $ 2 M All Japan projects > $ 2 M All Saudi Government projects > $ 5 M All RC of J&Y projects > $ 5 M All Saudi Aramco projects > $ 10 M Also in UK, Germany, France, Australia, Korea, India, …etc. Source: Al-Yousefi (2008) 13

Saudi Ministry of Finance Mandate (October 2001): n n n Emphasis on Function, LCC and ROI Perform VE during early design stages Train employees on VE Include VE clauses in the Design contracts Apply VE as follows: n n n Typical repeated projects that is > SR 5 M Projects that are > SR 20 M (about $ 5 M) O & M contracts that are > SR 5 M Source: Al-Yousefi (2008) 14

VALUE MANAGEMENT JOB PLAN 15

Five Steps of the VM Job Plan PRE-STUDY INFORMATION SPECULATION JUDGEMENT DEVELOPMENT RECOMMENDATION & REPORTING POST STUDY The five steps of the Job Plan are shown diagrammatically in figure above. The significant of the arrows is that, whilst a cascade system is used, with each phase following on from and using the output of the preceding phase, there is frequently reversion to a previous phase, as a result of some discovery or unexpected development. © MMCM 16

Function Analysis Conventional concept n To find possibilities for cost reduction by analysing each factor of total cost BUILT-UP COST PROFIT OVERHEAD LABOUR & EQUIPMENTS PLANT & MACHINERIES WASTAGE MATERIAL COST © MMCM 17
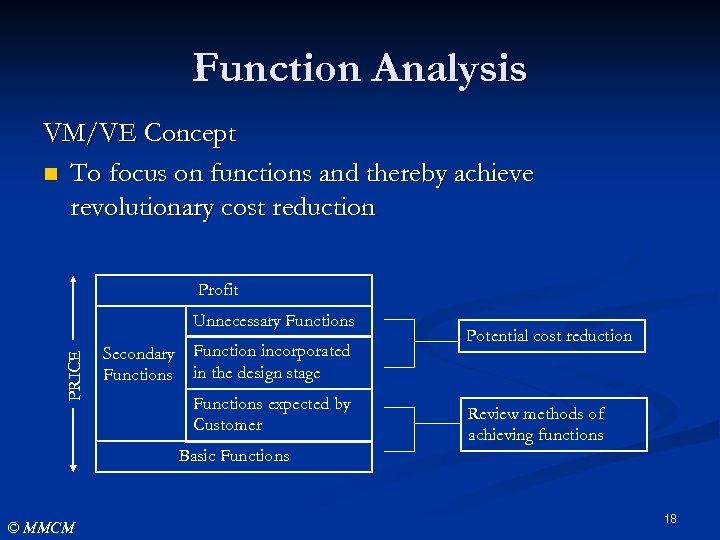
Function Analysis VM/VE Concept n To focus on functions and thereby achieve revolutionary cost reduction Profit PRICE Unnecessary Functions Secondary Functions Function incorporated in the design stage Functions expected by Customer Potential cost reduction Review methods of achieving functions Basic Functions © MMCM 18

Function Analysis TYPE OF FUNCTIONS Basic Function: The purpose or performance feature which must be attained if an item is to work or perform. It is a "must" type of objective in that it is the feature of the item which is its primary reason for existence from the users point of view. © MMCM 19
Function Analysis TYPE OF FUNCTIONS (Cont’d) Required Secondary Function: Dell ‘Isola developed other function which he called required secondary function. It is the function that must be achieved to meet codes, standards, or mandatory other requirements. © MMCM 20
Function Analysis TYPE OF FUNCTIONS (Cont’d) A Supporting Function: Any characteristic of an item which is not essential to the user for the desired application of the item and does not contribute directly to the accomplishment of a basic function. © MMCM 21
Function Analysis TYPE OF FUNCTIONS (Cont’d) An Unnecessary Function: An element or a characteristic which is not necessary for the item to work or sell. Unnecessary functions are usually the result of honest wrong beliefs and assumptions, or the perpetuation of obsolete requirements. © MMCM 22
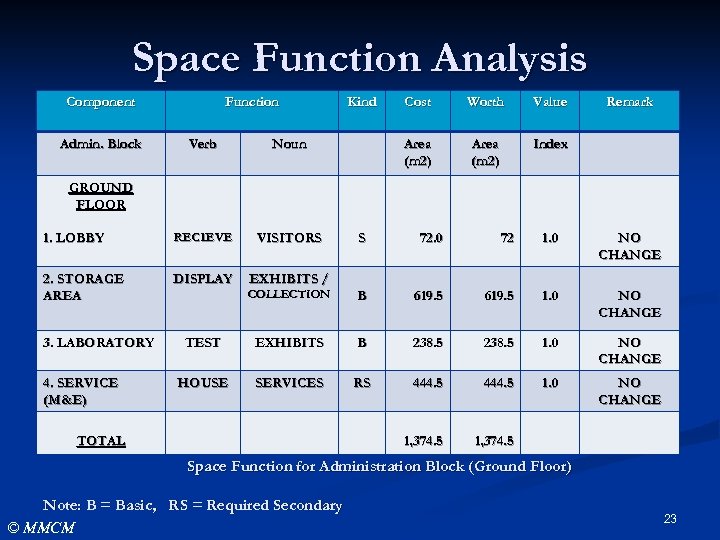
Space Function Analysis Component Admin. Block Function Verb RECIEVE VISITORS 2. STORAGE AREA DISPLAY Cost Worth Value Area (m 2) Noun 1. LOBBY Kind Area (m 2) Remark Index EXHIBITS / GROUND FLOOR 3. LABORATORY 4. SERVICE (M&E) S 72. 0 72 1. 0 NO CHANGE COLLECTION B 619. 5 1. 0 NO CHANGE TEST EXHIBITS B 238. 5 1. 0 NO CHANGE HOUSE SERVICES RS 444. 5 1. 0 NO CHANGE 1, 374. 5 TOTAL Space Function for Administration Block (Ground Floor) Note: B = Basic, RS = Required Secondary © MMCM 23
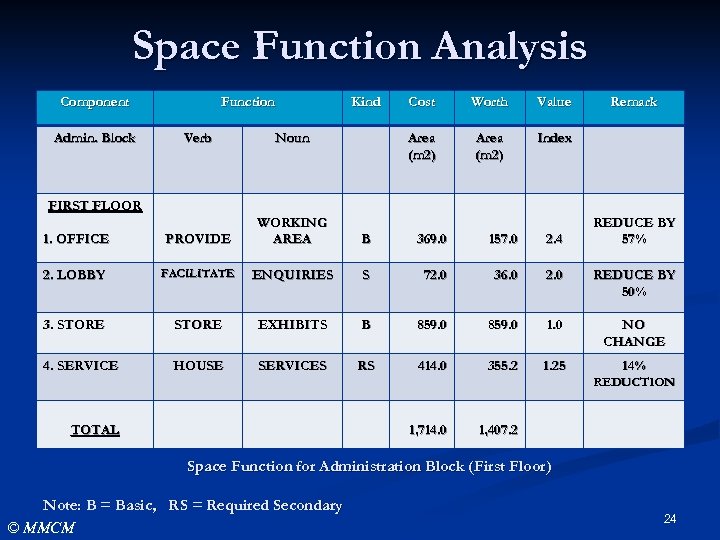
Space Function Analysis Component Admin. Block Function Kind Cost Worth Value Area (m 2) Remark Index Verb Noun 1. OFFICE PROVIDE WORKING AREA B 369. 0 157. 0 2. 4 2. LOBBY FACILITATE ENQUIRIES S 72. 0 36. 0 2. 0 REDUCE BY 50% 3. STORE EXHIBITS B 859. 0 1. 0 NO CHANGE 4. SERVICE HOUSE SERVICES RS 414. 0 355. 2 1. 25 14% FIRST FLOOR REDUCE BY 57% REDUCTION TOTAL 1, 714. 0 1, 407. 2 Space Function for Administration Block (First Floor) Note: B = Basic, RS = Required Secondary © MMCM 24

FAST DIAGRAM n FAST Diagram are prepared which: 1. 2. 3. 4. n © MMCM Shows the specific relationship of all functions with respect to each other, Tests the validity of the functions under study, Helps identify missing functions, and Broadens the knowledge of all team members with respect to the project At first glance, FAST appears to be similar to a PERT Chart. However, the basic difference between FAST diagramming and other techniques is that the FAST is function-oriented and not time-oriented. 25
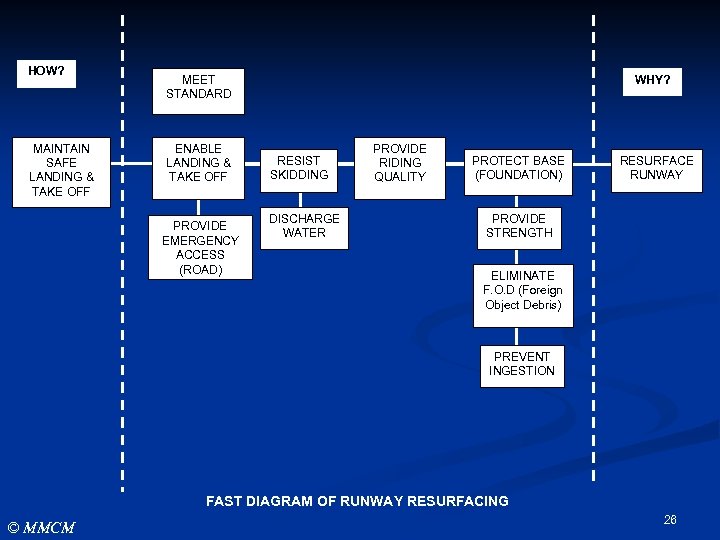
HOW? MAINTAIN SAFE LANDING & TAKE OFF MEET STANDARD ENABLE LANDING & TAKE OFF PROVIDE EMERGENCY ACCESS (ROAD) WHY? RESIST SKIDDING DISCHARGE WATER PROVIDE RIDING QUALITY PROTECT BASE (FOUNDATION) RESURFACE RUNWAY PROVIDE STRENGTH ELIMINATE F. O. D (Foreign Object Debris) PREVENT INGESTION FAST DIAGRAM OF RUNWAY RESURFACING © MMCM 26
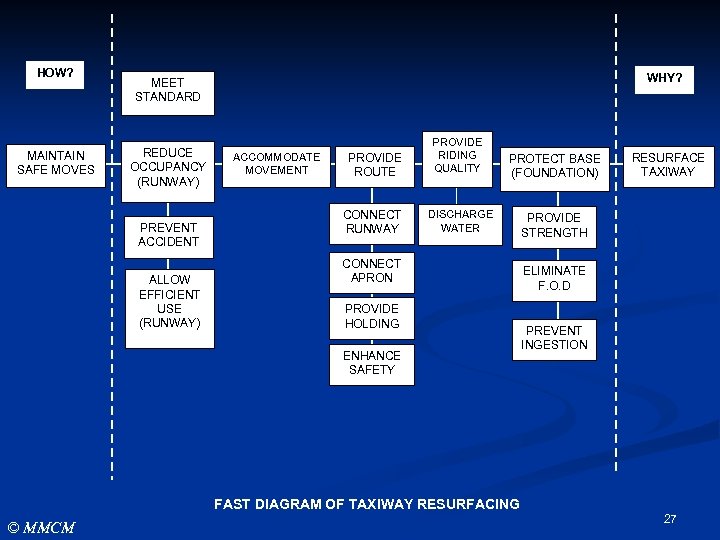
HOW? MAINTAIN SAFE MOVES WHY? MEET STANDARD REDUCE OCCUPANCY (RUNWAY) PREVENT ACCIDENT ALLOW EFFICIENT USE (RUNWAY) PROVIDE ROUTE PROTECT BASE (FOUNDATION) CONNECT RUNWAY ACCOMMODATE MOVEMENT PROVIDE RIDING QUALITY DISCHARGE WATER PROVIDE STRENGTH CONNECT APRON PROVIDE HOLDING ENHANCE SAFETY RESURFACE TAXIWAY ELIMINATE F. O. D PREVENT INGESTION FAST DIAGRAM OF TAXIWAY RESURFACING © MMCM 27
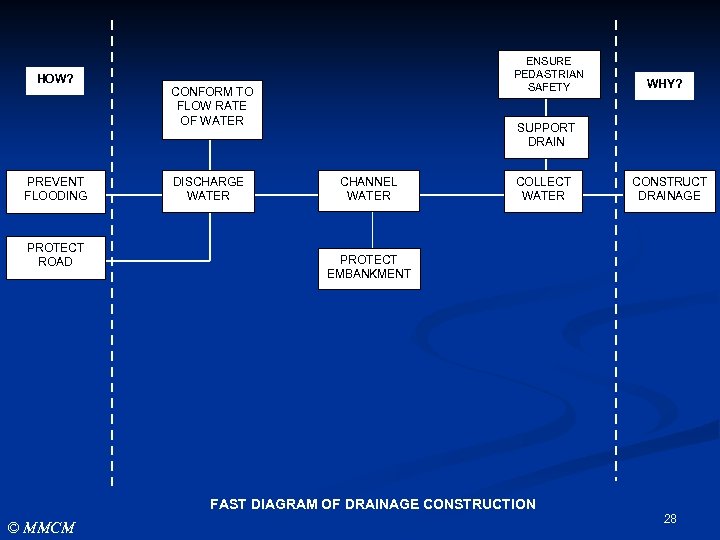
HOW? PREVENT FLOODING PROTECT ROAD ENSURE PEDASTRIAN SAFETY CONFORM TO FLOW RATE OF WATER DISCHARGE WATER WHY? SUPPORT DRAIN CHANNEL WATER COLLECT WATER CONSTRUCT DRAINAGE PROTECT EMBANKMENT FAST DIAGRAM OF DRAINAGE CONSTRUCTION © MMCM 28

RESULTS 29

Project: Education Faculty for UTM Achieved • Effective Planning of Space to Layout to customer requirements (Initial Design cost RM 35 M, after VM RM 7 M) © MMCM
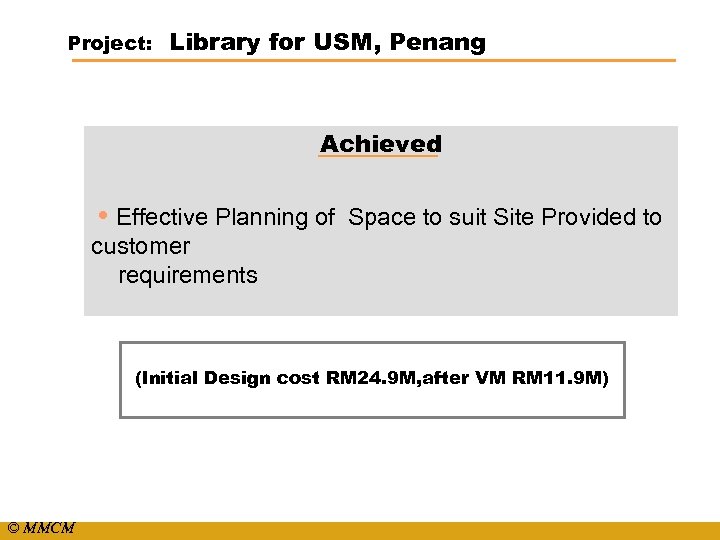
Project: Library for USM, Penang Achieved • Effective Planning of Space to suit Site Provided to customer requirements (Initial Design cost RM 24. 9 M, after VM RM 11. 9 M) © MMCM

Project: Darul Ridzuan Islamic College, Perak Achieved • Effective Planning of Layout and Design to customer requirements (Initial Design cost RM 120 M after VM RM 57 M) © MMCM

Projek Jalanraya Simpang Pulai – Lojing - Gua Project: Musang - Kuala Berang (Pakej 8) Outcome • Identified many areas in the existing solutions where value improvements can be made without loss of functions These improvements would lead to cost savings in the order of RM 18 m from the initial cost of RM 92 m. © MMCM
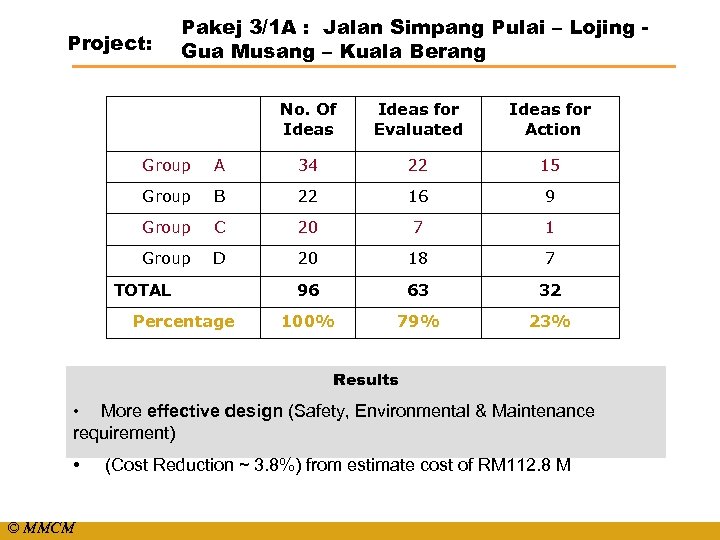
Project: Pakej 3/1 A : Jalan Simpang Pulai – Lojing Gua Musang – Kuala Berang No. Of Ideas for Evaluated Ideas for Action Group A 34 22 15 Group B 22 16 9 Group C 20 7 1 Group D 20 18 7 96 63 32 100% 79% 23% TOTAL Percentage Results More effective design (Safety, Environmental & Maintenance requirement) • • © MMCM (Cost Reduction ~ 3. 8%) from estimate cost of RM 112. 8 M
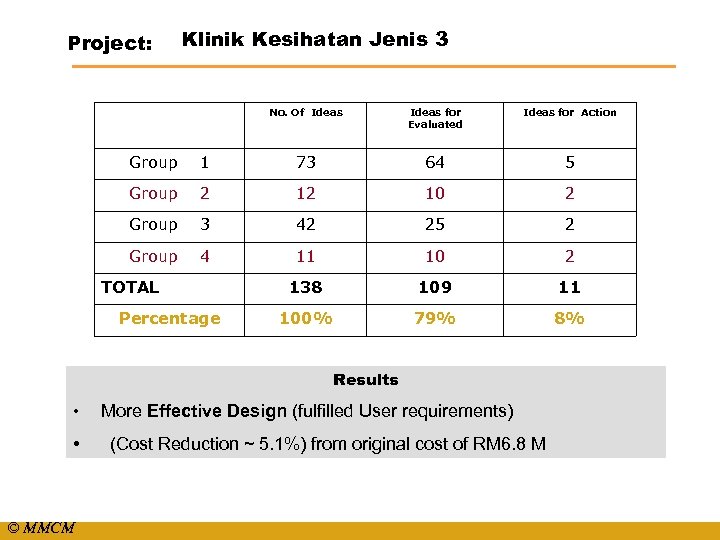
Project: Klinik Kesihatan Jenis 3 No. Of Ideas for Evaluated Ideas for Action Group 1 73 64 5 Group 2 12 10 2 Group 3 42 25 2 Group 4 11 10 2 138 109 11 100% 79% 8% TOTAL Percentage Results • • © MMCM More Effective Design (fulfilled User requirements) (Cost Reduction ~ 5. 1%) from original cost of RM 6. 8 M
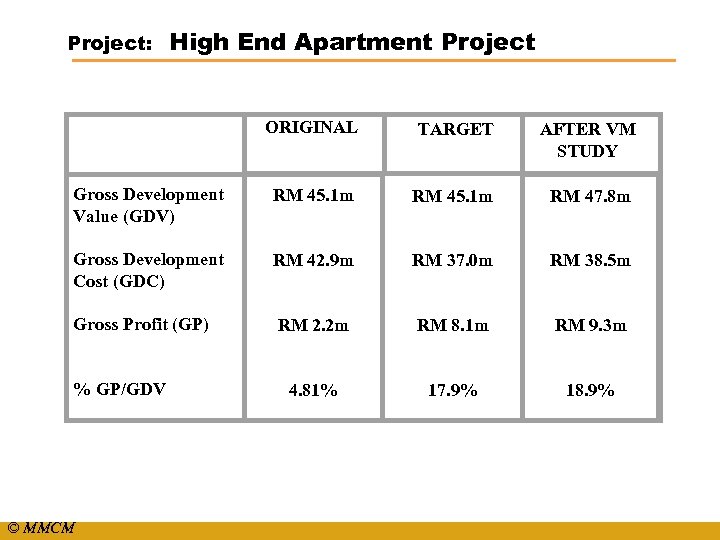
Project: High End Apartment Project ORIGINAL TARGET AFTER VM STUDY Gross Development Value (GDV) Gross Development Cost (GDC) Gross Profit (GP) % GP/GDV RM 45. 1 m RM 37. 0 m RM 8. 1 m 17. 9% RM 47. 8 m RM 38. 5 m RM 9. 3 m 18. 9% © MMCM RM 42. 9 m RM 2. 2 m 4. 81%

Conclusion Theapplication thistechnique proved beverysuccessful of has to in various human endeavors. systematic The process it offers that promote creativity innovation & towards achieving customers satisfaction in many and cases producing results arebeyond that expectations. 37 © MMCM

THANK YOU 38
3fe576590eddff959dca834eb7f63f75.ppt