81083199aa169f02a2b923138fd1b9aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 93

Unbalanced (or will it be balanced? ) forces exercise This exercise involves the class being split in two even teams of equal strength outside.

Mass and Weight Mass – measured in kilograms (kg) this is the amount of matter in an object Weight – (measured in newtons). Weight is the force due to gravity acting on a mass.
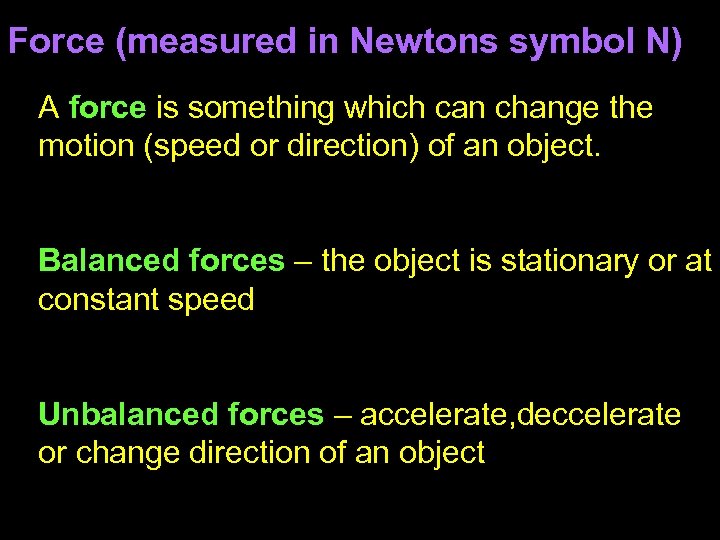
Force (measured in Newtons symbol N) A force is something which can change the motion (speed or direction) of an object. Balanced forces – the object is stationary or at constant speed Unbalanced forces – accelerate, deccelerate or change direction of an object

Finding the weight of an object. The force due to gravity is 10 Nkg-1 (a constant with symbol g) Force W(N) = mass(kg) x force due to gravity (g) often written as the formula F = mg Work out the weight of a 10 Kg bag of potatoes. weight of potatoes = 10 kg x 10 N/kg = 100 N

What is the weight of 500 g of butter? 5 Newtons 2. 3 kg of cheese? 23 Newtons 500 mg panadol tablet ? 0. 0005 kg x 10 = 0. 005 N Task: Working out your weight Use the scales to find your mass in kgs Calculate your weight in newtons using the formula F =mg

Finding the weight of an object on the moon. The force due to gravity on the moon is 6 Nkg-1 Work out the weight of a 10 kg bag of potatoes on the moon. weight of potatoes = 10 kg x 6 Nkg-1 = 60 N
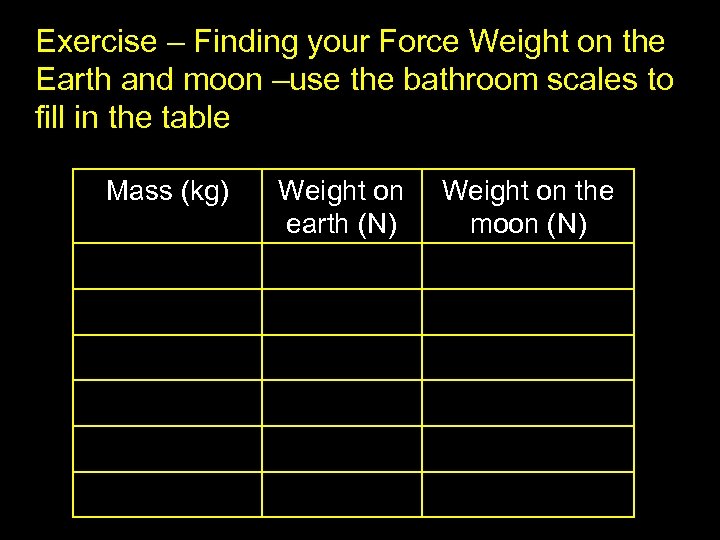
Exercise – Finding your Force Weight on the Earth and moon –use the bathroom scales to fill in the table Mass (kg) Weight on earth (N) Weight on the moon (N)

Starter read page 114 Science to 16 • Write the title force and mass • Write answers to questions on page 115 using full sentences

Force Diagrams On diagrams forces are drawn with arrows indicating the direction of the force The length of the arrows indicate the strength of the force
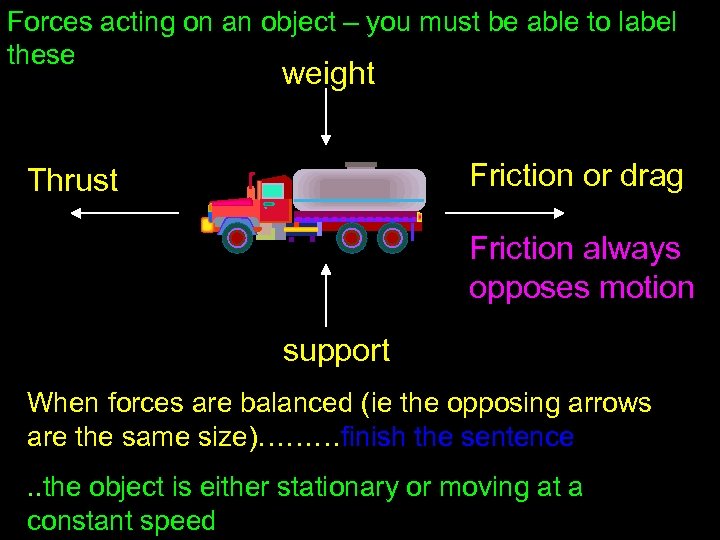
Forces acting on an object – you must be able to label these weight Friction or drag Thrust Friction always opposes motion support When forces are balanced (ie the opposing arrows are the same size)………finish the sentence. . the object is either stationary or moving at a constant speed

Forces acting on an object include Thrust – makes the object move Friction – opposes motion Weight - pull of gravity Support – upwards push

Force Facts In the absence of friction a moving object keeps on moving When a force is applied to a stationary object and makes it move, the object gains kinetic energy

Complete cyclist question 6 on sheet – analysing force diagrams

What causes motion? • Complete yr 11 yellow workbook page 194
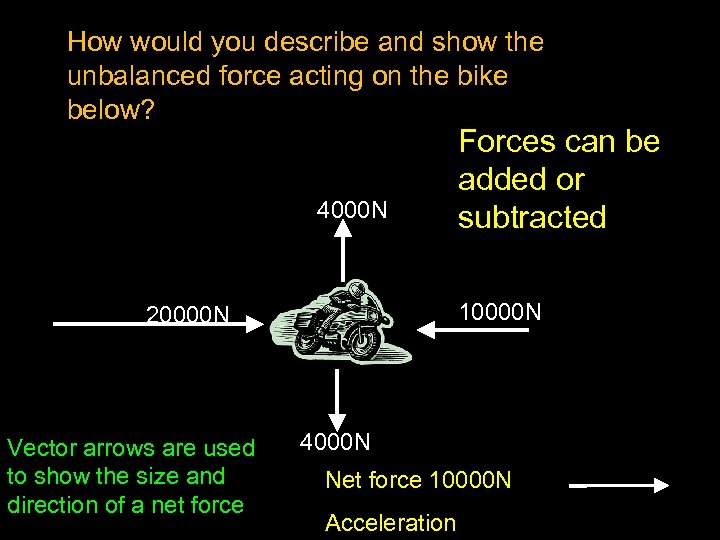
How would you describe and show the unbalanced force acting on the bike below? 4000 N 10000 N 20000 N Vector arrows are used to show the size and direction of a net force Forces can be added or subtracted 4000 N Net force 10000 N Acceleration
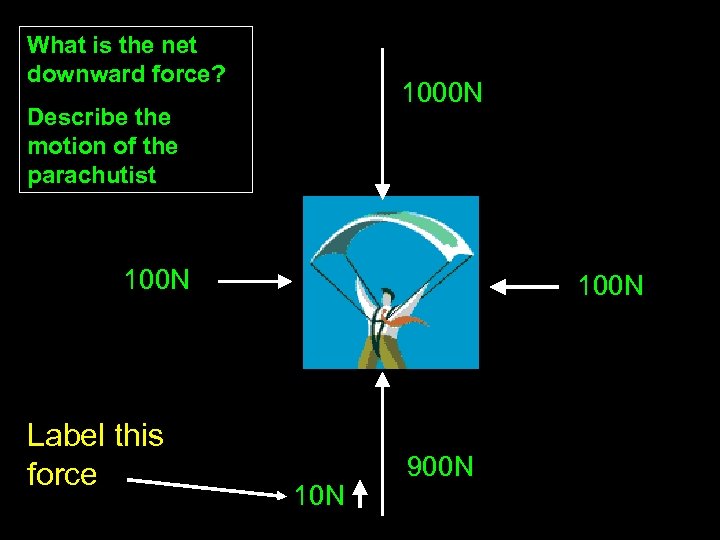
What is the net downward force? 1000 N Describe the motion of the parachutist 100 N Label this force 100 N 10 N 900 N

Friction can be helpful or a nusiance List areas where friction is helpful List areas where friction is problem
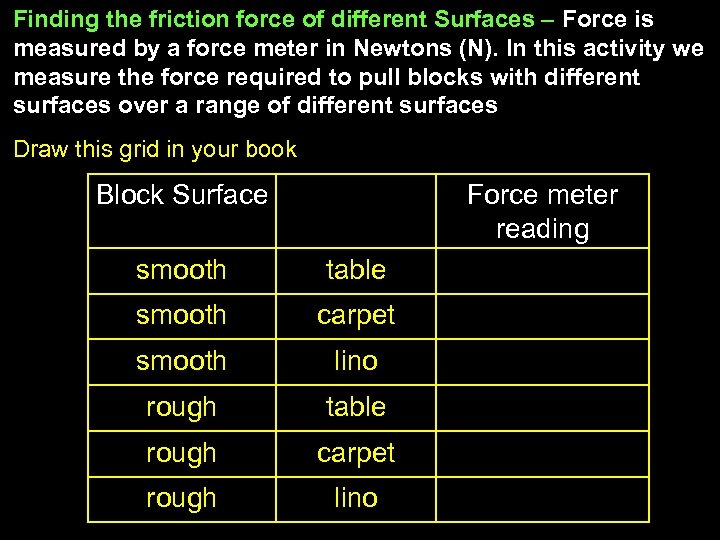
Finding the friction force of different Surfaces – Force is measured by a force meter in Newtons (N). In this activity we measure the force required to pull blocks with different surfaces over a range of different surfaces Draw this grid in your book Block Surface Force meter reading smooth table smooth carpet smooth lino rough table rough carpet rough lino

Distance /Time /Speed/ Acceleration Speed is used to describe how fast something is moving Speed is the distance travelled by an object per unit of time

Distance/Time /Speed notes d = distance (m) t = time (s) v = speed/velocity (ms-1) These are combined in the following equation to give the formula for the average velocity or speed.
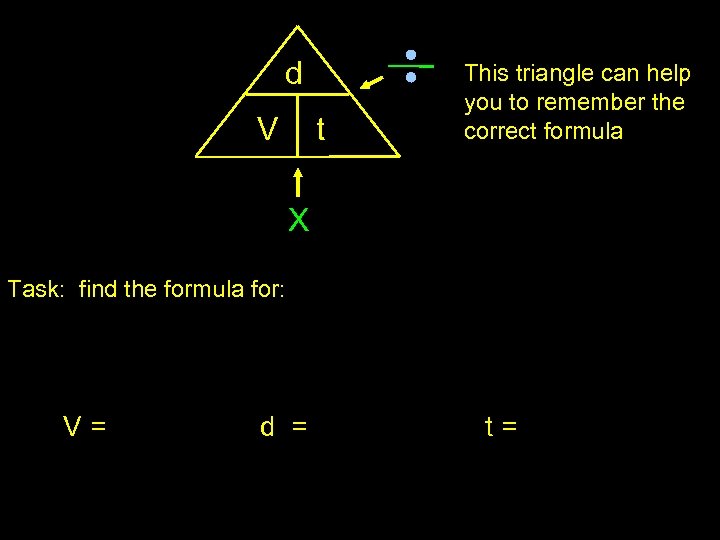
d V t This triangle can help you to remember the correct formula X Task: find the formula for: V= d = t=

The Unit of speed (aka velocity) depends on the units used to measure distance and time eg The speed limit outside of a school is 50 km/hr A snails speed is 4 millimetres per second A world class sprinter runs with a speed of 10 metres per second

The Bugati Vernon has a top speed of 400 km/hr What is its speed in metres per second? To find speed (or V) we need distance in metres and time in seconds Hint convert km to metres and 1 hour to seconds! 1 hour = 60 minutes and each minute has 60 seconds

The Bugati Vernon has a top speed of 400 km/hr What is its speed in metres per second? 1 hour = 60 minutes and each minute has 60 seconds So 1 hour = 60 min x 60 sec this = 3600 s

The Bugati Vernon has a top speed of 400 km/hr What is its speed in metres per second?

find the following 1. What is the speed of a man who walks 300 metres in 120 seconds?

1. What is the speed of a man who walks 300 metres in 120 seconds?

Toy Speeds Using one car from the front desk measure the speed of it over one metre. Draw the following table in your books. Car Name distance time (s) Speed d/t 1 1 m 1. 29 s 0. 78 m/s 2 1 m 1. 4 s 0. 71 m/s 3 1 m 1. 3 0. 76 m/s 28 1 m 1. 09 s 0. 92 m/s 4 1 m 1. 12 s 0. 89 m/s Fill in the distance, time and speed columns making sure you include the correct units.

write this in your book 1. What is the speed of a cyclist who rides 1000 metres in 150 seconds?

write this in your book 1. What is the distance in metres covered by a motorcyclist who rides at 100 kmhr-1 for 180 minutes? d=Vxt = 100 kmhr-1 x 3 hr = 300 km = 300000 m
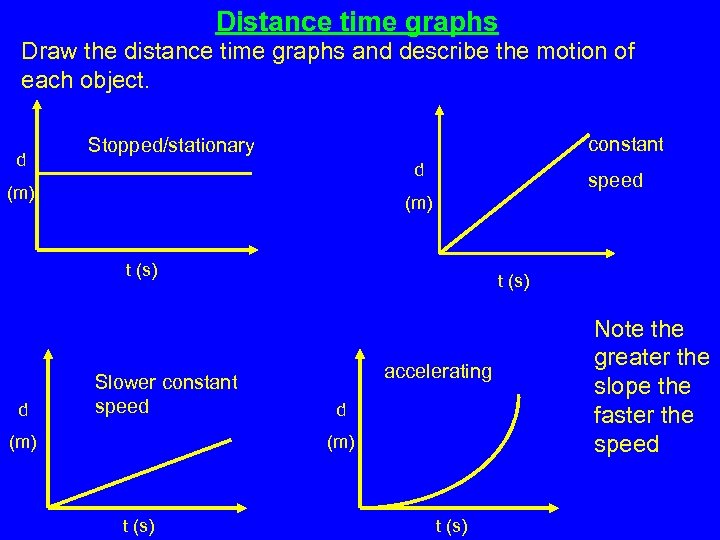
Distance time graphs Draw the distance time graphs and describe the motion of each object. d constant Stopped/stationary d (m) speed (m) t (s) d Slower constant speed (m) t (s) accelerating d (m) t (s) Note the greater the slope the faster the speed
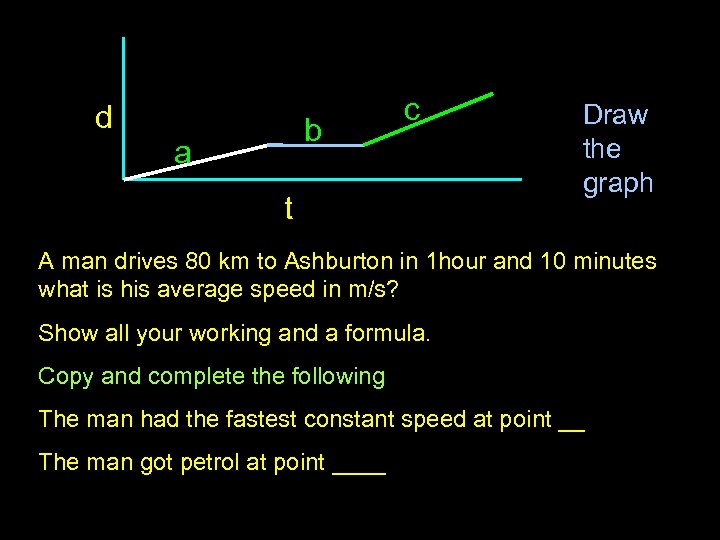
d b a c t Draw the graph A man drives 80 km to Ashburton in 1 hour and 10 minutes what is his average speed in m/s? Show all your working and a formula. Copy and complete the following The man had the fastest constant speed at point __ The man got petrol at point ____

Love him or hate him Lance Armstrong is arguably one of the best cyclists in the world, having won a record 6 Tour de France races. He achieved the record for this race by winning the event 7 times in 2005!! The first stage of the 92 nd Tour de France is the 19 km individual time trial the top two results are: 1. Dave Zabriskie (USA ) in 20 min 51 sec 2. Lance Armstrong (USA ) in 20 min 53 sec

Questions What was the average speed (ms-1) of Dave Zabriskie ? Dave Zabriskie (USA ) competed the 19 km in 20 min 51 sec Convert kilometers to metres and minutes to seconds 19 km = 19000 m 19 min 51 sec = 1251 sec Use formula to find speed

What was Lance Armstrong’s average speed in metres per second? Lance Armstrong (USA ) completed the 19 km in 20 min 53 sec

If Lance Armstrong could maintain this speed for one Hour what distance would he have traveled? (Give your answer in kilometers and metres)

Finish the questions on work sheet one
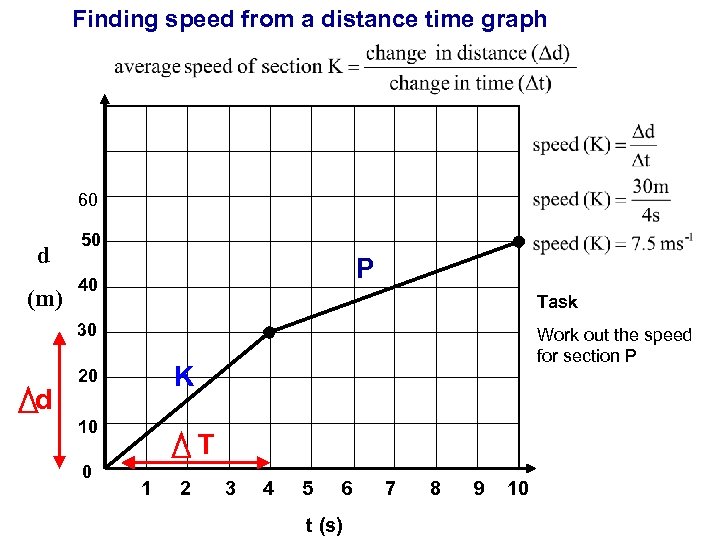
Finding speed from a distance time graph 60 d (m) 50 P 40 Task 30 K 20 10 0 d Work out the speed for section P T 1 2 3 4 5 6 t (s) 7 8 9 10
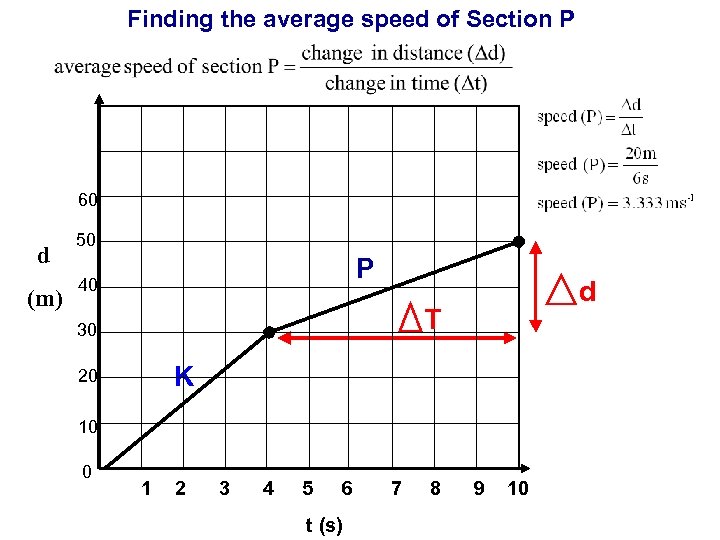
Finding the average speed of Section P 60 (m) P 40 d T 30 K 20 10 0 d 50 1 2 3 4 5 6 t (s) 7 8 9 10

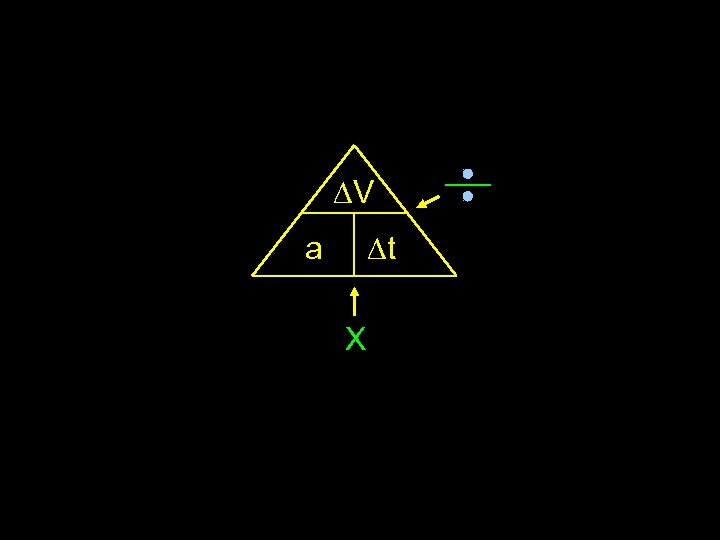
Speed / Time / Acceleration • V = speed / velocity (ms-1) • t = time (s) • a = acceleration (ms-2) also written as:
∆V a ∆t X

Calculate the acceleration of a car if changes speed from 20 m/s to 50 m/s in 3 seconds

A car travels for 320 kms at 80 km/hr how long did it take him to travel the distance? t = 4 hours
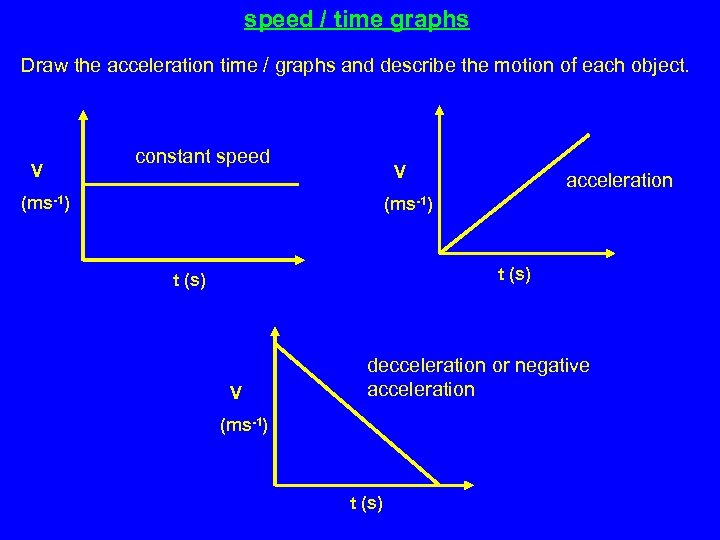
speed / time graphs Draw the acceleration time / graphs and describe the motion of each object. V constant speed V (ms-1) acceleration (ms-1) t (s) V decceleration or negative acceleration (ms-1) t (s)
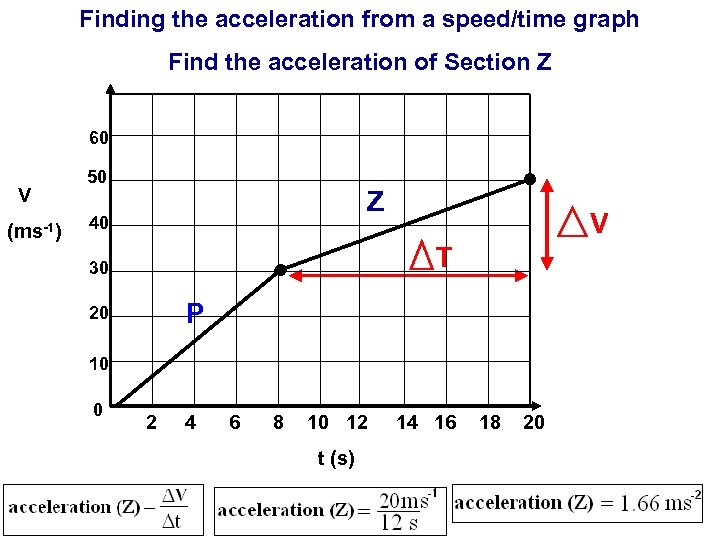
Finding the acceleration from a speed/time graph Find the acceleration of Section Z 60 (ms-1) Z 40 V T 30 P 20 10 0 V 50 2 4 6 8 10 12 t (s) 14 16 18 20
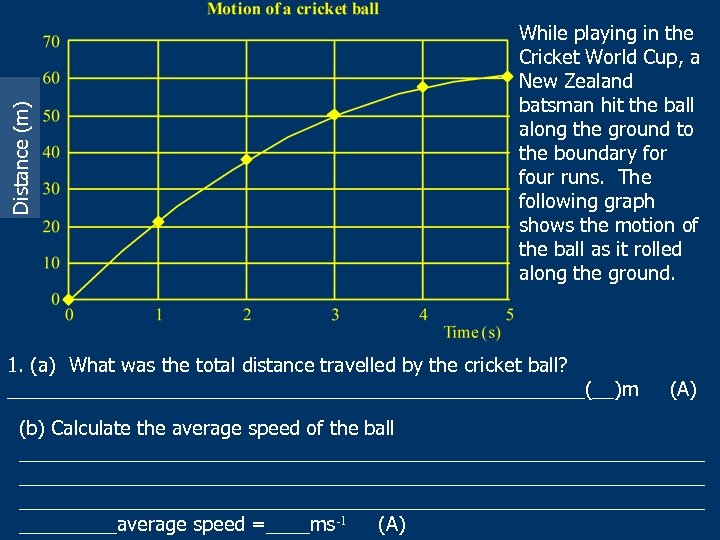
Distance (m) While playing in the Cricket World Cup, a New Zealand batsman hit the ball along the ground to the boundary for four runs. The following graph shows the motion of the ball as it rolled along the ground. 1. (a) What was the total distance travelled by the cricket ball? ___________________________(__)m (A) (b) Calculate the average speed of the ball _______________________________________________________________ _____average speed =____ms-1 (A)
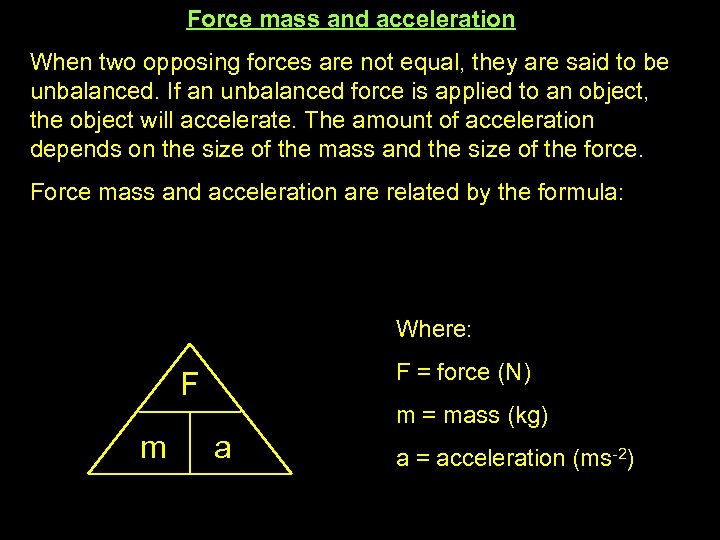
Force mass and acceleration When two opposing forces are not equal, they are said to be unbalanced. If an unbalanced force is applied to an object, the object will accelerate. The amount of acceleration depends on the size of the mass and the size of the force. Force mass and acceleration are related by the formula: Where: F = force (N) F m m = mass (kg) a a = acceleration (ms-2)

Example 1 A force of 500 N is used to accelerate a 2 kg object. What is the acceleration of the object? a = 250 ms -2

Example 2 An object accelerates at 7. 5 ms-2 when a force of 15000 N is used to accelerate it. What is the mass of the object? m = 2000 kg
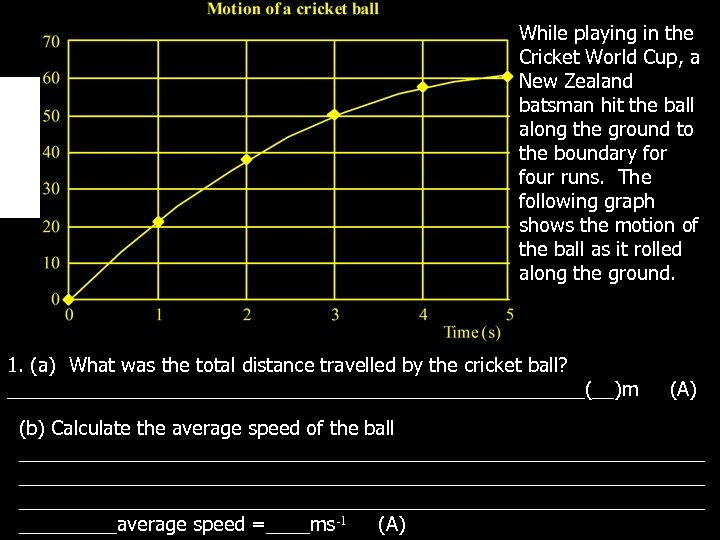
Distance (m) While playing in the Cricket World Cup, a New Zealand batsman hit the ball along the ground to the boundary for four runs. The following graph shows the motion of the ball as it rolled along the ground. 1. (a) What was the total distance travelled by the cricket ball? ___________________________(__)m (A) (b) Calculate the average speed of the ball _______________________________________________________________ _____average speed =____ms-1 (A)
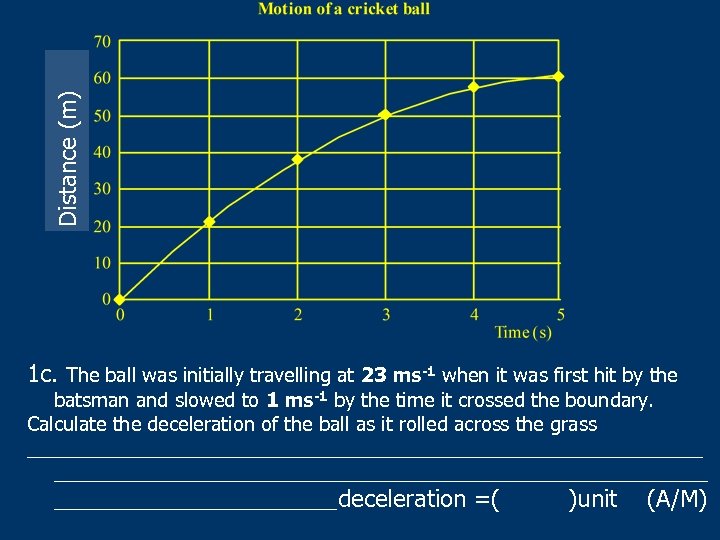
Distance (m) 1 c. The ball was initially travelling at 23 ms-1 when it was first hit by the batsman and slowed to 1 ms-1 by the time it crossed the boundary. Calculate the deceleration of the ball as it rolled across the grass _______________________________ _____________deceleration =( )unit (A/M)

2 (a) Name the force that slows the balls speed as it rolls across the grass. __________________________(A) The cricket ball used in One Day International cricket has a mass of 0. 163 kg. (b) Use your answer from 1 (c) on the previous page to calculate the net force slowing the ball down. ________________________________________________________________ ____________________Net Force =( )unit(A/M) (c) Draw and label arrows on the following diagram to represent the forces acting on the ball as it slows down. (The ball is rolling from left to right)
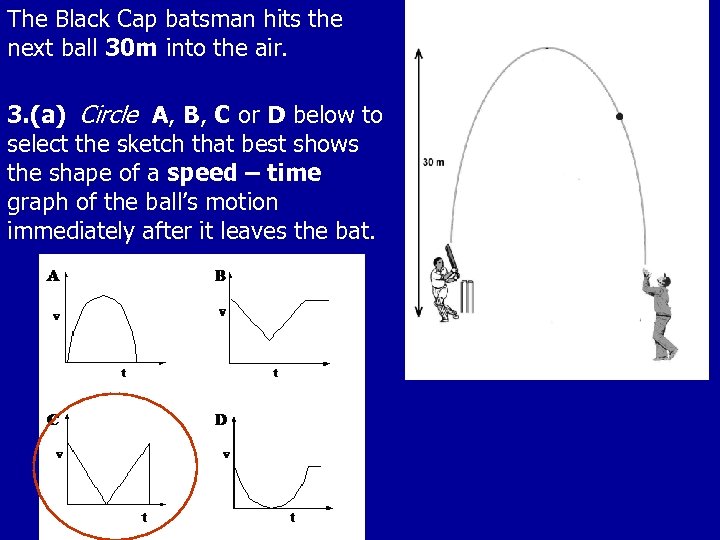
The Black Cap batsman hits the next ball 30 m into the air. 3. (a) Circle A, B, C or D below to select the sketch that best shows the shape of a speed – time graph of the ball’s motion immediately after it leaves the bat.

Complete worksheet 2 for homework

Work • Work (symbol W) is done when a force moves an object • If work is done on an object then the object gains energy • The gain in energy is equal to the work done – so both work and energy are measured in joules (J)

Work • The amount of work done depends on the size of the force and the distance the object moves • Therefore work is expressed by: W=F d • Where: F = the force in newtons which moves the object d = the distance the object moves in metres W = work in joules

Example A car is pushed 300 metres by a force of 2000 N what was the work done? W=Fxd = 2000 N x 300 m = 600000 J or 600 k. J The work done equals the energy gained by the car ie the car will gain 600 k. J of kinetic energy – providing none is lost to friction

Work is done to lift an object. The size of the force needed to lift the object is equal to the weight of the object.

Example 2 An object of mass 5 kg is lifted 2 m off the floor. Calculate the work required to do this. the weight of the object = m x g = 5 x 10 = 50 N So the force needed to lift the object is 50 N The work done to lift the object is = Fd = 50 x 2 = 100 J The work done equals the gain in energy of the mass. The mass has gained 100 J of gravitational potential energy
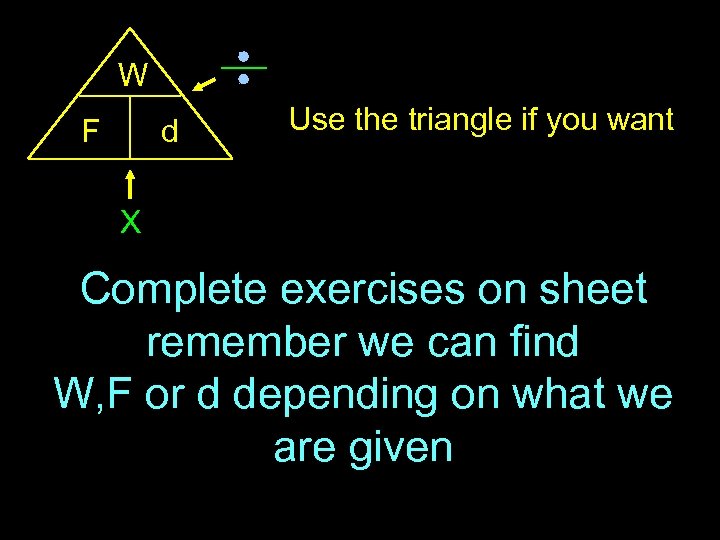
W F d Use the triangle if you want X Complete exercises on sheet remember we can find W, F or d depending on what we are given
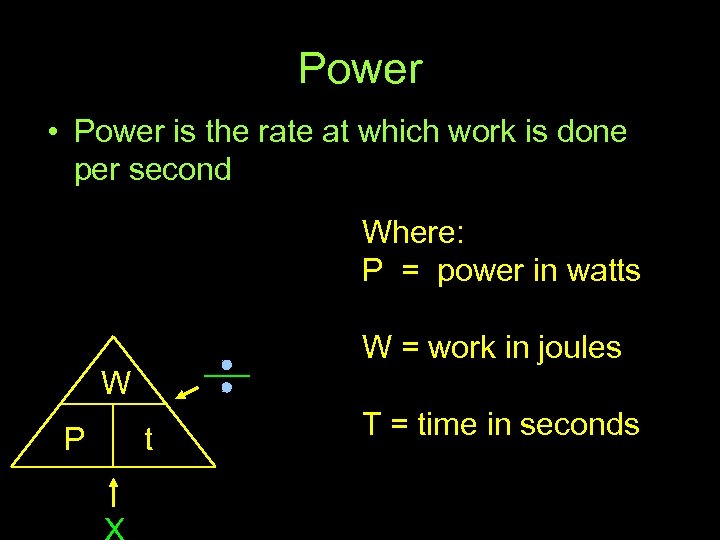
Power • Power is the rate at which work is done per second Where: P = power in watts W = work in joules W P t T = time in seconds

Question • If a 90 kg man climbs some steps with a vertical height of 15 m. How much work did he do? 1. F(weight) = mg = 90 kg x 10 = 900 N 2. W = F x d = 900 N x 15 m = 13500 J

Power question • If the man climbed the stairs in 6 seconds how much power did he use? 1. F(weight) = mg = 90 kg x 10 = 900 N 2. W = F x d = 900 N x 15 m = 13500 J P = 2250 W

Starter: Power question • A 200 kg girder was raised by a crane 30 metres on to the top of a building in 50 seconds. How much power did the crane use? 1. F(weight) = mg = 200 kg x 10 = 2000 N 2. W = F x d = 2000 N x 30 m = 60000 J P = 1200 W
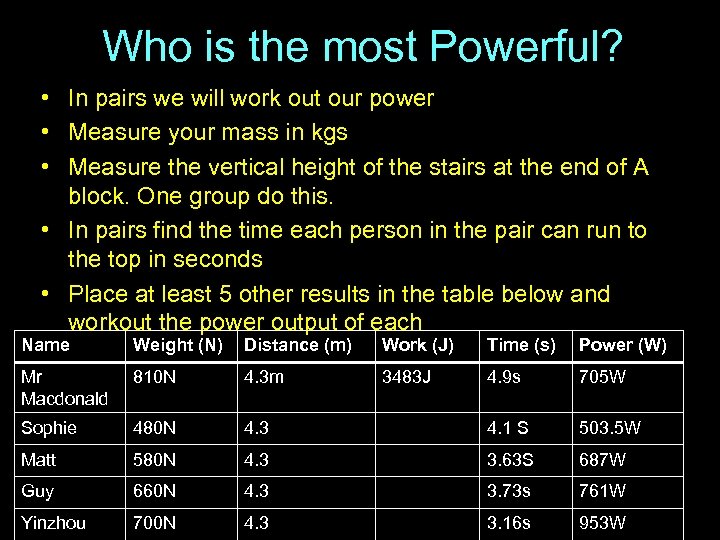
Who is the most Powerful? • In pairs we will work out our power • Measure your mass in kgs • Measure the vertical height of the stairs at the end of A block. One group do this. • In pairs find the time each person in the pair can run to the top in seconds • Place at least 5 other results in the table below and workout the power output of each Name Weight (N) Distance (m) Work (J) Time (s) Power (W) Mr Macdonald 810 N 4. 3 m 3483 J 4. 9 s 705 W Sophie 480 N 4. 3 4. 1 S 503. 5 W Matt 580 N 4. 3 3. 63 S 687 W Guy 660 N 4. 3 3. 73 s 761 W Yinzhou 700 N 4. 3 3. 16 s 953 W

Kinetic energy • Every moving object has kinetic energy (Ek ) • The faster an object moves the more kinetic energy it has. • Increasing mass or speed will increase Ek Formula Ek = ½ mv 2 Where: E k = energy in joules m = mass in kg v = velocity in ms-1

Kinetic Energy Question • A 90 kg rider and her 1200 kg horse were riding at a speed of 9 ms-1 how much kinetic energy did they have? Formula Ek = ½ mv 2 = ½ 1290 kg x (92) = 645 x 81 = 52245 J

Gravitational Potential Energy (Ep) • When an object is lifted above the earth it gains gravitational potential energy (Ep) • The greater the mass or the higher it is lifted the greater the Ep. Formula Ep = mgh Where: Ep = gravitational potential energy in joules m = mass in kg h = distance above the earth in metres (m)
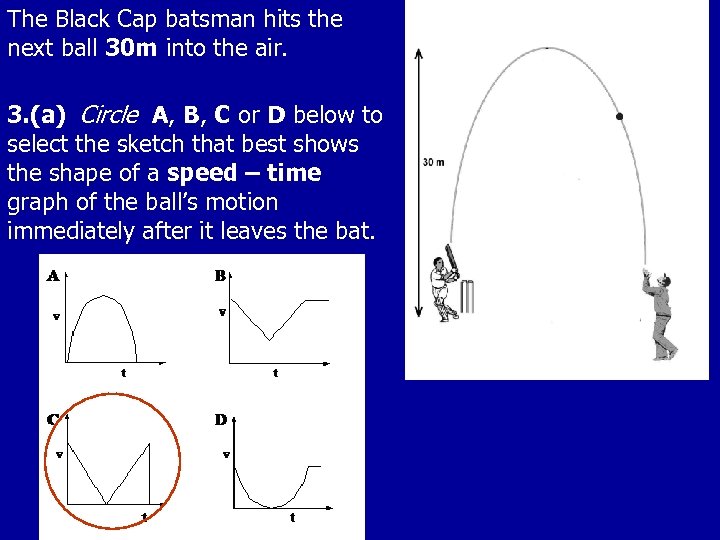
The Black Cap batsman hits the next ball 30 m into the air. 3. (a) Circle A, B, C or D below to select the sketch that best shows the shape of a speed – time graph of the ball’s motion immediately after it leaves the bat.

(b) Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the 0. 163 kg ball when it reaches its highest point using the formula EP = m. g. h • E = mgh P = 0. 163 kg x 10 x 30 m = 48. 9 J (c) Explain how the gravitational potential energy would change if the ball were hit half as high. • Hitting the ball half as high means that the ball would only gain half the amount of gravitational potential energy ie E P = mgh = 0. 163 kg x 10 x 15 m = 24. 45 J (A/M) (A)
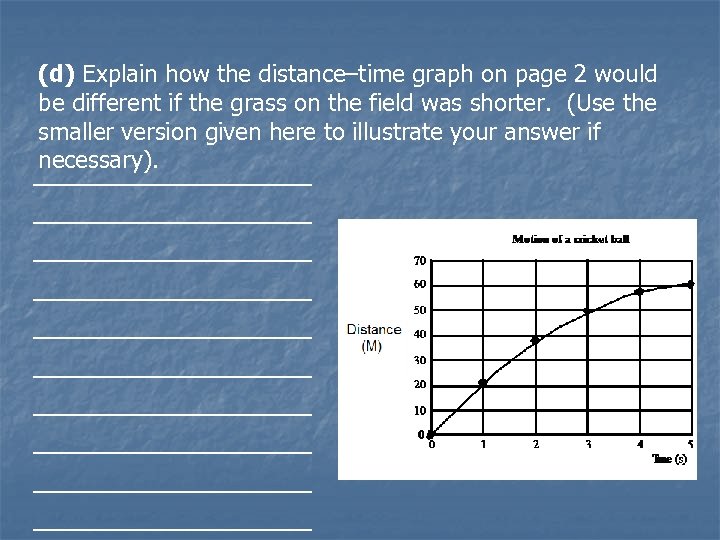
(d) Explain how the distance–time graph on page 2 would be different if the grass on the field was shorter. (Use the smaller version given here to illustrate your answer if necessary). ________________ ________________ ________________
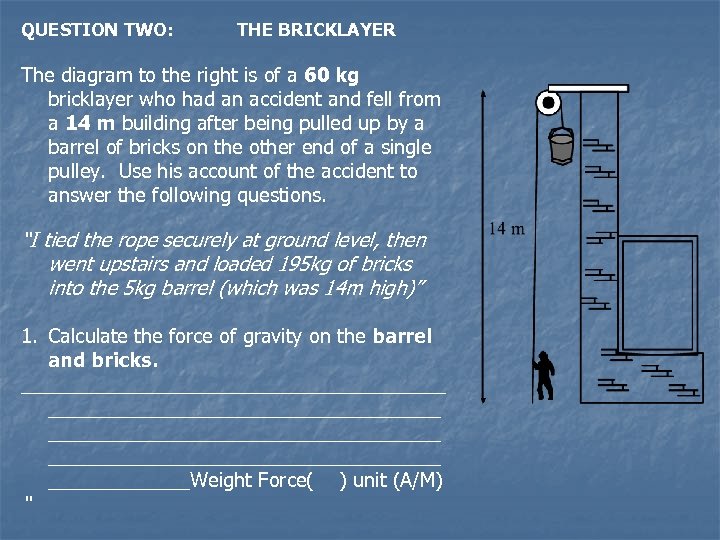
QUESTION TWO: THE BRICKLAYER The diagram to the right is of a 60 kg bricklayer who had an accident and fell from a 14 m building after being pulled up by a barrel of bricks on the other end of a single pulley. Use his account of the accident to answer the following questions. “I tied the rope securely at ground level, then went upstairs and loaded 195 kg of bricks into the 5 kg barrel (which was 14 m high)” 1. Calculate the force of gravity on the barrel and bricks. ______________________________________ _______Weight Force( ) unit (A/M) “

Then I went back down, untied the rope and held tightly to ensure a slow descent of the bricks. Imagine my surprise at being jerked off the ground so suddenly! I didn’t think to let go of the rope until my fingers were two knuckles deep into the pulley at the top. At the same time, the barrel hit the ground and the bottom fell out of it” Calculate the net force that pulled the 60 kg bricklayer into the air. _____________________________________ _____________________________________ Force = ( )unit
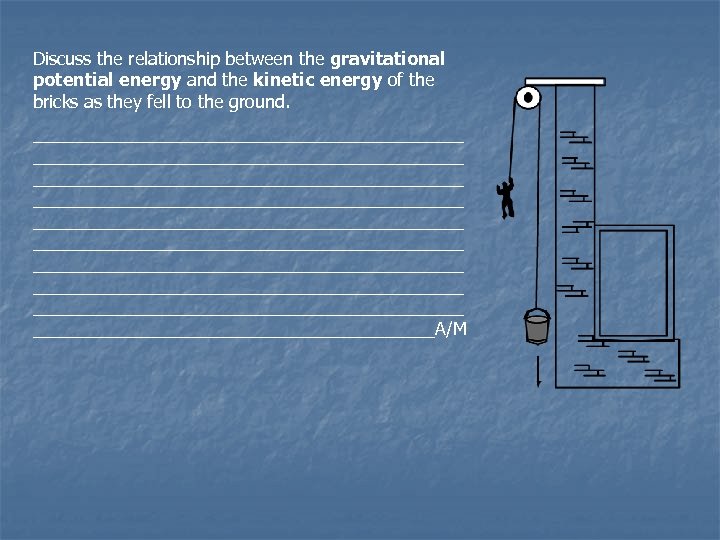
Discuss the relationship between the gravitational potential energy and the kinetic energy of the bricks as they fell to the ground. ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ______________________A/M
Fiona has just bought her first car using money she has saved from her after school supermarket job. To get to know the car she decides to take a short trip to the beach with her friend Chris. The beach is 3. 0 km (3000 m) from her house and it takes her 5 minutes to reach the beach. (i) How many seconds does it take her to reach the beach? Evidence 5 min 60 s = 300 s Achievement 300 s (ii) Calculate the average speed at which she drives from home to the beach. Give the correct units with your answer. Evidence V = d/t = 3000/300 = 10 Achievement correct formula chosen unit m s-1 or m/s unit Merit correct answer (unit not needed)
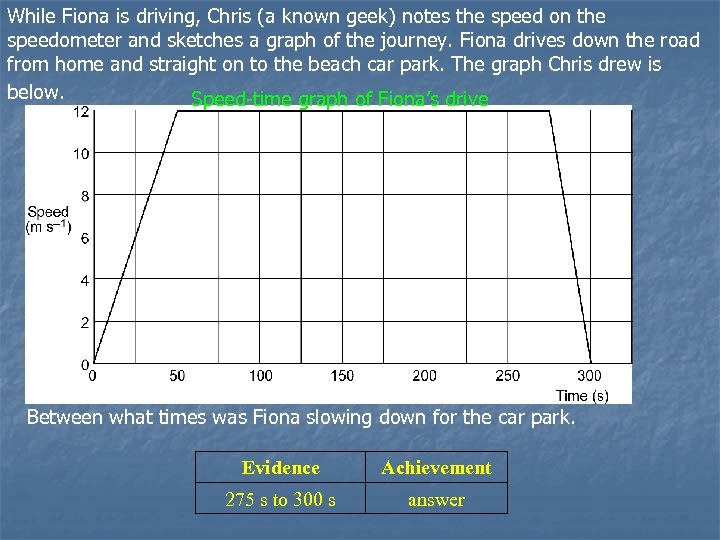
While Fiona is driving, Chris (a known geek) notes the speed on the speedometer and sketches a graph of the journey. Fiona drives down the road from home and straight on to the beach car park. The graph Chris drew is below. Speed-time graph of Fiona’s drive Between what times was Fiona slowing down for the car park. Evidence Achievement 275 s to 300 s answer
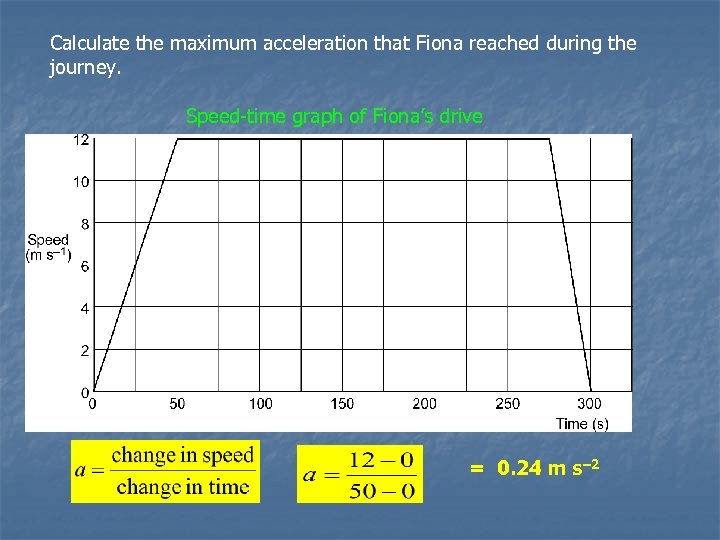
Calculate the maximum acceleration that Fiona reached during the journey. Speed-time graph of Fiona’s drive = 0. 24 m s– 2

The mass of her car is 500 kg. Calculate the unbalanced force acting on the car while she is speeding up at the start of the journey. = 12/50 = 0. 24 m s F – 2 = ma = 500 0. 24 = 120 N Evidence =12/50 = 0. 24 m s– 2 F = ma = 500 0. 24 = 120 N Achievement one formula chosen correctly Merit Linked answer from part ii) to force equation in part iii) Excellence Both parts completely correct.
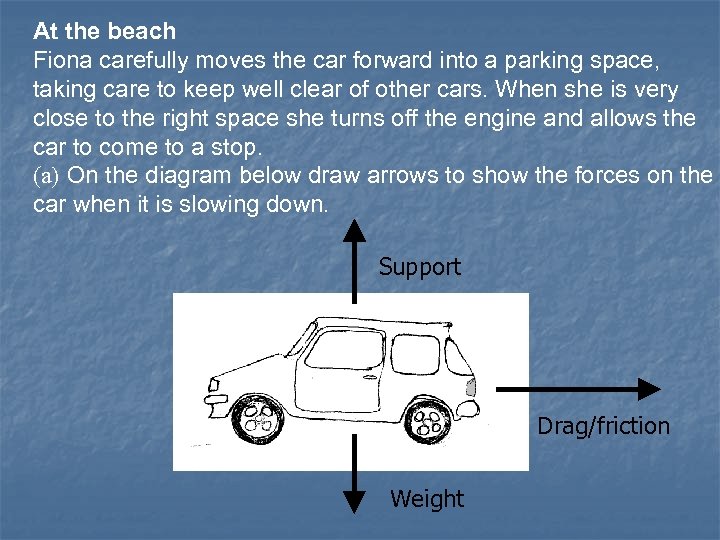
At the beach Fiona carefully moves the car forward into a parking space, taking care to keep well clear of other cars. When she is very close to the right space she turns off the engine and allows the car to come to a stop. (a) On the diagram below draw arrows to show the forces on the car when it is slowing down. Support Drag/friction Weight

Just before Fiona puts the brakes on the car is moving at 2. 0 ms-1. It takes her 0. 5 s to stop completely. The car has a mass of 500 kg. (b) Use the formula to calculate the energy of the car before she brakes from 2. 0 m s– 1. Give the correct unit with your answer Question Evidence Achievement answer correct two (b) = 0. 5 500 (2. 0)2 = 1000 unit J / joule unit

Calculate the net force on the car while it is braking. Evidence A= v/t = 2. 0/0. 5 = 4. 0 F= ma = 500 4. 0 = 2000 N Achievement one equation correctly selected Merit Excellence answer to either Both parts part correctly completely followed correct. through In a second attempt to park, the car must lose 2000 J of energy. The car takes 0. 4 m to stop. Calculate the force exerted by the brakes of the car during the braking. Evidence W=Fd F = W/d = 2000/0. 4 = 5000 N Achievement selection of formula or recognizing work = energy lost Merit Excellence Substitution of answer correct + energy in unit correct formula

Explain what happened to the energy the car had, during the braking time. Evidence Achievement Merit Energy has been Energy lost as Energy lost by converted into heat by the heat or lost by heat as a result of work done as the brakes friction exert friction on the wheels

In the sun Fiona’s parking space is in full sunshine. When she returns to the car to collect her swimming togs, she finds that it is quite hot inside. To cool it down she winds the windows down a little. (a)She decides that heat has entered through the glass of the closed windows. State the type of heat transfer that happens through clear glass. Evidence radiation Achievement correct Merit
Discuss how the colour of a car and slightly open windows could affect the temperature inside the car. Evidence Achievement A light colour would reflect radiation while a darker colour would absorb radiation. The heat could then be conducted to the interior by the metal roof. Open windows would allow rising hot air (convection) to leave the interior to be replaced by cooler air from below. Closed windows would prevent circulation. one correct statement reflection by light absorption by dark convection when open no circulation when closed. Merit two statements compared Excellence statements contrasting situations and covering both scenarios.

You will graph your results on the graph paper provided. Work out the slope of your graph and from this work out your average speed in ms -1 How does your average speed compare with others in the class?
A motorcyclist is traveling at 22 m/s for 2 minutes how far did he travel?

You will need the following formula for these starters V=IR and P=VI

Ohms law starter Question If 4 amps of current are flowing through a light connected to a 12 V supply what is the resistance of the lamp? V = I x R to get R = V/I R = 12 V/4 A = 3

If a resistor has a resistance of 6 and a voltmeter reads 24 volts in the circuit how much current is flowing in the circuit? V =IR I = V/R I = 24 V/6 = 4 A

A Hitachi power drill plugged into a socket uses 800 watts of energy. What current does it draw? P = VI P = 800 W = 3. 333 A I= V 240 V What is a watt ? The watt is the unit for power. One watt is a joule of energy used or supplied per second Why is fuse placed in a circuit? A fuse is designed to break if the current gets too large
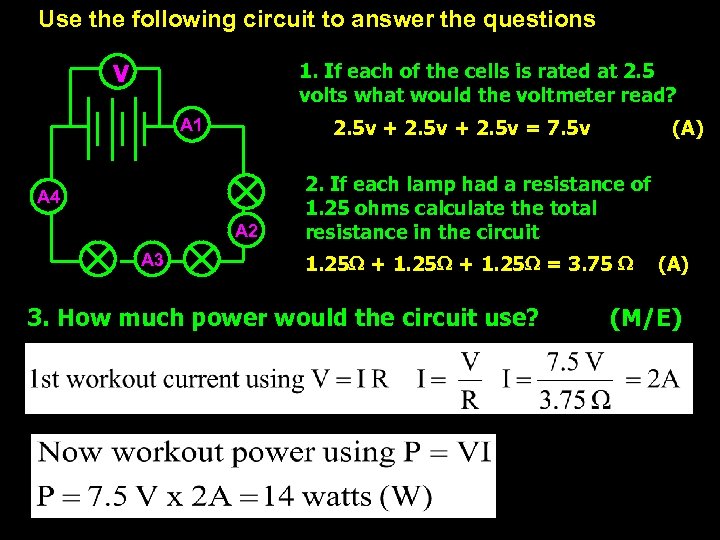
Use the following circuit to answer the questions V 1. If each of the cells is rated at 2. 5 volts what would the voltmeter read? A 1 2. 5 v + 2. 5 v = 7. 5 v A 4 A 2 A 3 (A) 2. If each lamp had a resistance of 1. 25 ohms calculate the total resistance in the circuit 1. 25 + 1. 25 = 3. 75 3. How much power would the circuit use? (A) (M/E)

A motorbike travelling from Dunedin to Christchurch adjusts his speed taking 5 seconds to go from 55 ms-1 to 10 ms-1. What is his acceleration?

Remember negative acceleration is decceleration
81083199aa169f02a2b923138fd1b9aa.ppt