431d45bafcb5813f8d2d7182d287bca7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 UNAIDS 2011 -2015 Strategy and key tools
UNAIDS 2011 -2015 Strategy and key tools
 Purpose of the Strategy - Builds on our new vision and mission – providing a pathway towards long-term vision of getting to zero - Responds to a changing world – the HIV response is at a pivotal juncture, we need to face threats and take advantage of opportunities - Presents a transformative agenda to help break the trajectory and sustain support
Purpose of the Strategy - Builds on our new vision and mission – providing a pathway towards long-term vision of getting to zero - Responds to a changing world – the HIV response is at a pivotal juncture, we need to face threats and take advantage of opportunities - Presents a transformative agenda to help break the trajectory and sustain support
 Transformation imperative Reframing HIV response is critical at this pivotal juncture Progress scaling up treatment & stabilising/decreasing incidence But we are challenged by - Flat-lining resources - Fragmented & generic responses - 10 million people need treatment - Weak systems - Social injustice We must seize opportunities - Better tools to measure incidence - Better strategic information—drivers of vulnerability - Momentum in development of better prevention tools - Political shifts that can produce breakthrough progress
Transformation imperative Reframing HIV response is critical at this pivotal juncture Progress scaling up treatment & stabilising/decreasing incidence But we are challenged by - Flat-lining resources - Fragmented & generic responses - 10 million people need treatment - Weak systems - Social injustice We must seize opportunities - Better tools to measure incidence - Better strategic information—drivers of vulnerability - Momentum in development of better prevention tools - Political shifts that can produce breakthrough progress
 Transformation agenda Focus and efficiency to radically reduce new infections Focus – Directing resources to where they have most impact on the epidemic—to hotspots, interventions, countries Efficiency – Reducing unit cost, innovative delivery systems, involving communities, integrating services Partnership – Supporting country ownership and south-south cooperation, engaging communities and emerging economies Enhancing mutual accountability through shared ownership - People - Countries - Synergies
Transformation agenda Focus and efficiency to radically reduce new infections Focus – Directing resources to where they have most impact on the epidemic—to hotspots, interventions, countries Efficiency – Reducing unit cost, innovative delivery systems, involving communities, integrating services Partnership – Supporting country ownership and south-south cooperation, engaging communities and emerging economies Enhancing mutual accountability through shared ownership - People - Countries - Synergies
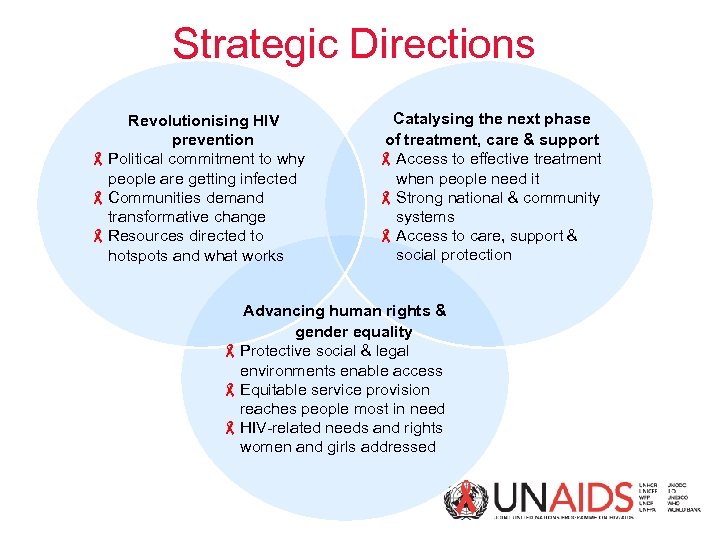 Strategic Directions Revolutionising HIV prevention - Political commitment to why people are getting infected - Communities demand transformative change - Resources directed to hotspots and what works Catalysing the next phase of treatment, care & support - Access to effective treatment when people need it - Strong national & community systems - Access to care, support & social protection Advancing human rights & gender equality - Protective social & legal environments enable access - Equitable service provision reaches people most in need - HIV-related needs and rights women and girls addressed
Strategic Directions Revolutionising HIV prevention - Political commitment to why people are getting infected - Communities demand transformative change - Resources directed to hotspots and what works Catalysing the next phase of treatment, care & support - Access to effective treatment when people need it - Strong national & community systems - Access to care, support & social protection Advancing human rights & gender equality - Protective social & legal environments enable access - Equitable service provision reaches people most in need - HIV-related needs and rights women and girls addressed
 Strategic Direction 1 Vision & Strategic Direction Objectives Impact Areas UNAIDS Partnerships Zero new HIV infections: Revolutionise HIV Prevention To generate political commitment to how and why people are getting infected Young people empowered to redress harmful social norms Vision Positive Health, Dignity and Prevention approaches scaled up To mobilise communities to demand transformative change Leaders positively incentivised to make the right decisions - Networks of PLWHIV and other key populations - Synergies with sexual and reproductive health communities Political and legal blockages mapped & addressed - To direct resources to epidemic hotspots Strategies emphasise prioritised prevention programmes Effective prevention approaches introduced & scaled up Academic and professional societies Lesson-learning partnerships Funding entities Young people -Support to countries to implement learning objectives in the International Technical Illustrative Guidance on Sexuality Education Examples of -Analytic work on HIV transmission dynamics Joint Working -Synthesis of global epidemics of HIV in sex workers
Strategic Direction 1 Vision & Strategic Direction Objectives Impact Areas UNAIDS Partnerships Zero new HIV infections: Revolutionise HIV Prevention To generate political commitment to how and why people are getting infected Young people empowered to redress harmful social norms Vision Positive Health, Dignity and Prevention approaches scaled up To mobilise communities to demand transformative change Leaders positively incentivised to make the right decisions - Networks of PLWHIV and other key populations - Synergies with sexual and reproductive health communities Political and legal blockages mapped & addressed - To direct resources to epidemic hotspots Strategies emphasise prioritised prevention programmes Effective prevention approaches introduced & scaled up Academic and professional societies Lesson-learning partnerships Funding entities Young people -Support to countries to implement learning objectives in the International Technical Illustrative Guidance on Sexuality Education Examples of -Analytic work on HIV transmission dynamics Joint Working -Synthesis of global epidemics of HIV in sex workers
 Strategic Direction 2 Vision & Strategic Direction Objectives Vision Zero AIDS-related deaths: Catalyse next phase of treatment, care & support To ensure people living with HIV can access treatment Non-drugrelated cost savings identified and gained To strengthen national & community systems to deliver services Impact Areas Better drugs and point-ofcare tools developed Community system capacity for service delivery UNAIDS Partnerships - Families, communities & faith-based organisations - Public-private partnerships - Pharmaceutical industry Capacity for registration & scale up of use of TRIPS To scale up access to care, support and social protection services Care & support services adapted to diverse needs HIV-sensitive social transfers embedded into national programmes - Companies, business associates & employers’ federations - Health providers & multi-disciplinary societies Illustrative -Reduction of HIV-related TB risk factors Examples of -Collaboration of GNP+, Int’l Community of Women with HIV/AIDS, Young Positives, Joint Working Engender. Health, IPPF, to produce The Advancing the Sexual & Reproductive Health and Human Rights of People Living with HIV guidance package
Strategic Direction 2 Vision & Strategic Direction Objectives Vision Zero AIDS-related deaths: Catalyse next phase of treatment, care & support To ensure people living with HIV can access treatment Non-drugrelated cost savings identified and gained To strengthen national & community systems to deliver services Impact Areas Better drugs and point-ofcare tools developed Community system capacity for service delivery UNAIDS Partnerships - Families, communities & faith-based organisations - Public-private partnerships - Pharmaceutical industry Capacity for registration & scale up of use of TRIPS To scale up access to care, support and social protection services Care & support services adapted to diverse needs HIV-sensitive social transfers embedded into national programmes - Companies, business associates & employers’ federations - Health providers & multi-disciplinary societies Illustrative -Reduction of HIV-related TB risk factors Examples of -Collaboration of GNP+, Int’l Community of Women with HIV/AIDS, Young Positives, Joint Working Engender. Health, IPPF, to produce The Advancing the Sexual & Reproductive Health and Human Rights of People Living with HIV guidance package
 Strategic Direction 3 Vision & Strategic Direction Objectives Impact Areas UNAIDS Partnerships Vision Zero discrimination: Advance human rights & gender equality for the HIV response To support countries to protect human rights in the context of HIV Key populations empowered to claim their rights Complete information on legal frameworks disseminated To advance country capacity for equitable service provision People living with HIV mobilised as forces of change - Regional & country networks of key populations - Civil society networks Data collection with people at higher risk strengthened & put to use To ensure needs of women & girls addressed in national HIV strategies Programmes implemented that support women & girls all their lives Programmes to counter gender-based violence implemented - Women’s rights advocates - Faith-based organisations -The Global Commission on HIV and the Law will assist in developing rights- based Illustrative recommendations for effective HIV responses. Recent dialogues rolled out through inter. Examples of agency action. Joint Working -Implement the Action Framework on Women, Girls, Gender Equality and HIV
Strategic Direction 3 Vision & Strategic Direction Objectives Impact Areas UNAIDS Partnerships Vision Zero discrimination: Advance human rights & gender equality for the HIV response To support countries to protect human rights in the context of HIV Key populations empowered to claim their rights Complete information on legal frameworks disseminated To advance country capacity for equitable service provision People living with HIV mobilised as forces of change - Regional & country networks of key populations - Civil society networks Data collection with people at higher risk strengthened & put to use To ensure needs of women & girls addressed in national HIV strategies Programmes implemented that support women & girls all their lives Programmes to counter gender-based violence implemented - Women’s rights advocates - Faith-based organisations -The Global Commission on HIV and the Law will assist in developing rights- based Illustrative recommendations for effective HIV responses. Recent dialogues rolled out through inter. Examples of agency action. Joint Working -Implement the Action Framework on Women, Girls, Gender Equality and HIV
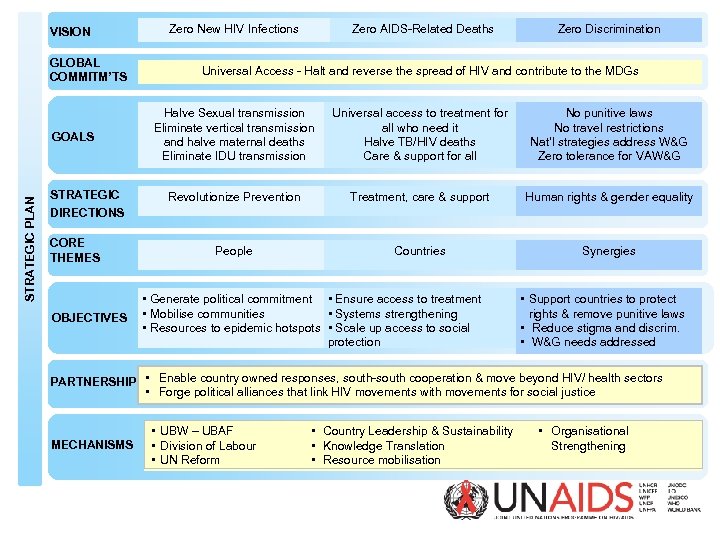 VISION GLOBAL COMMITM’TS STRATEGIC PLAN GOALS STRATEGIC Zero New HIV Infections Zero AIDS-Related Deaths Zero Discrimination Universal Access - Halt and reverse the spread of HIV and contribute to the MDGs Halve Sexual transmission Eliminate vertical transmission and halve maternal deaths Eliminate IDU transmission Universal access to treatment for all who need it Halve TB/HIV deaths Care & support for all No punitive laws No travel restrictions Nat’l strategies address W&G Zero tolerance for VAW&G Revolutionize Prevention Treatment, care & support Human rights & gender equality People Countries Synergies DIRECTIONS CORE THEMES OBJECTIVES • Generate political commitment • Ensure access to treatment • Mobilise communities • Systems strengthening • Resources to epidemic hotspots • Scale up access to social protection • Support countries to protect rights & remove punitive laws • Reduce stigma and discrim. • W&G needs addressed PARTNERSHIP • Enable country owned responses, south-south cooperation & move beyond HIV/ health sectors • Forge political alliances that link HIV movements with movements for social justice MECHANISMS • UBW – UBAF • Division of Labour • UN Reform • Country Leadership & Sustainability • Knowledge Translation • Resource mobilisation • Organisational Strengthening
VISION GLOBAL COMMITM’TS STRATEGIC PLAN GOALS STRATEGIC Zero New HIV Infections Zero AIDS-Related Deaths Zero Discrimination Universal Access - Halt and reverse the spread of HIV and contribute to the MDGs Halve Sexual transmission Eliminate vertical transmission and halve maternal deaths Eliminate IDU transmission Universal access to treatment for all who need it Halve TB/HIV deaths Care & support for all No punitive laws No travel restrictions Nat’l strategies address W&G Zero tolerance for VAW&G Revolutionize Prevention Treatment, care & support Human rights & gender equality People Countries Synergies DIRECTIONS CORE THEMES OBJECTIVES • Generate political commitment • Ensure access to treatment • Mobilise communities • Systems strengthening • Resources to epidemic hotspots • Scale up access to social protection • Support countries to protect rights & remove punitive laws • Reduce stigma and discrim. • W&G needs addressed PARTNERSHIP • Enable country owned responses, south-south cooperation & move beyond HIV/ health sectors • Forge political alliances that link HIV movements with movements for social justice MECHANISMS • UBW – UBAF • Division of Labour • UN Reform • Country Leadership & Sustainability • Knowledge Translation • Resource mobilisation • Organisational Strengthening
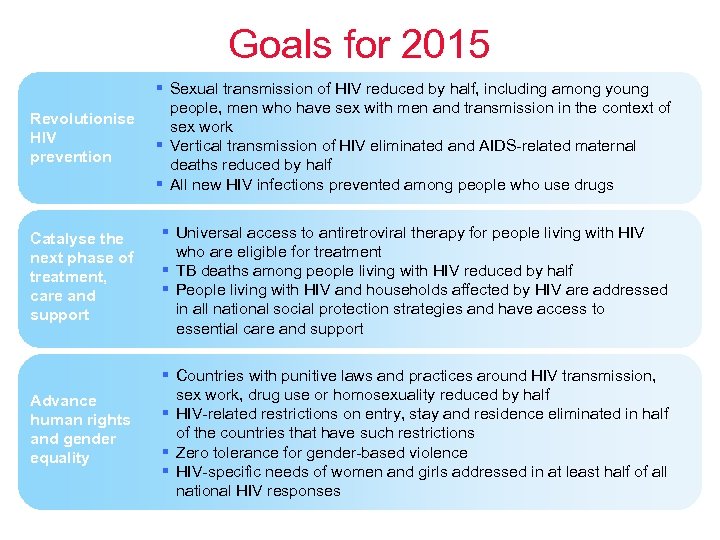 Goals for 2015 Revolutionise HIV prevention Sexual transmission of HIV reduced by half, including among young people, men who have sex with men and transmission in the context of sex work Vertical transmission of HIV eliminated and AIDS-related maternal deaths reduced by half All new HIV infections prevented among people who use drugs Catalyse the next phase of treatment, care and support Universal access to antiretroviral therapy for people living with HIV who are eligible for treatment TB deaths among people living with HIV reduced by half People living with HIV and households affected by HIV are addressed in all national social protection strategies and have access to essential care and support Advance human rights and gender equality Countries with punitive laws and practices around HIV transmission, sex work, drug use or homosexuality reduced by half HIV-related restrictions on entry, stay and residence eliminated in half of the countries that have such restrictions Zero tolerance for gender-based violence HIV-specific needs of women and girls addressed in at least half of all national HIV responses
Goals for 2015 Revolutionise HIV prevention Sexual transmission of HIV reduced by half, including among young people, men who have sex with men and transmission in the context of sex work Vertical transmission of HIV eliminated and AIDS-related maternal deaths reduced by half All new HIV infections prevented among people who use drugs Catalyse the next phase of treatment, care and support Universal access to antiretroviral therapy for people living with HIV who are eligible for treatment TB deaths among people living with HIV reduced by half People living with HIV and households affected by HIV are addressed in all national social protection strategies and have access to essential care and support Advance human rights and gender equality Countries with punitive laws and practices around HIV transmission, sex work, drug use or homosexuality reduced by half HIV-related restrictions on entry, stay and residence eliminated in half of the countries that have such restrictions Zero tolerance for gender-based violence HIV-specific needs of women and girls addressed in at least half of all national HIV responses
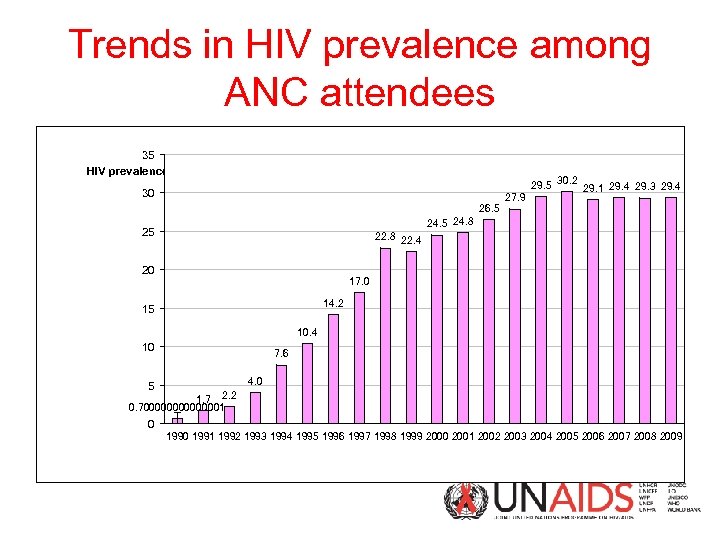 Trends in HIV prevalence among ANC attendees 35 HIV prevalence (%) 29. 5 30 26. 5 27. 9 30. 2 29. 1 29. 4 29. 3 29. 4 24. 5 24. 8 25 22. 8 22. 4 20 17. 0 14. 2 15 10. 4 10 5 7. 6 4. 0 1. 7 2. 2 0. 700000001 0 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009
Trends in HIV prevalence among ANC attendees 35 HIV prevalence (%) 29. 5 30 26. 5 27. 9 30. 2 29. 1 29. 4 29. 3 29. 4 24. 5 24. 8 25 22. 8 22. 4 20 17. 0 14. 2 15 10. 4 10 5 7. 6 4. 0 1. 7 2. 2 0. 700000001 0 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009
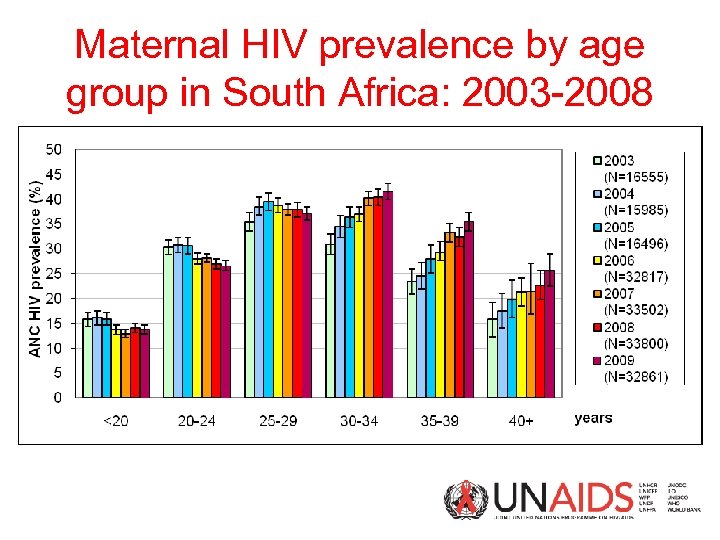 Maternal HIV prevalence by age group in South Africa: 2003 -2008
Maternal HIV prevalence by age group in South Africa: 2003 -2008
 UNAIDS Tools • Two main tools – EPP /Spectrum – NASA
UNAIDS Tools • Two main tools – EPP /Spectrum – NASA
 EPP and Spectrum • Short term projection and estimates of HIV • New generation software to be launched in March 2011
EPP and Spectrum • Short term projection and estimates of HIV • New generation software to be launched in March 2011
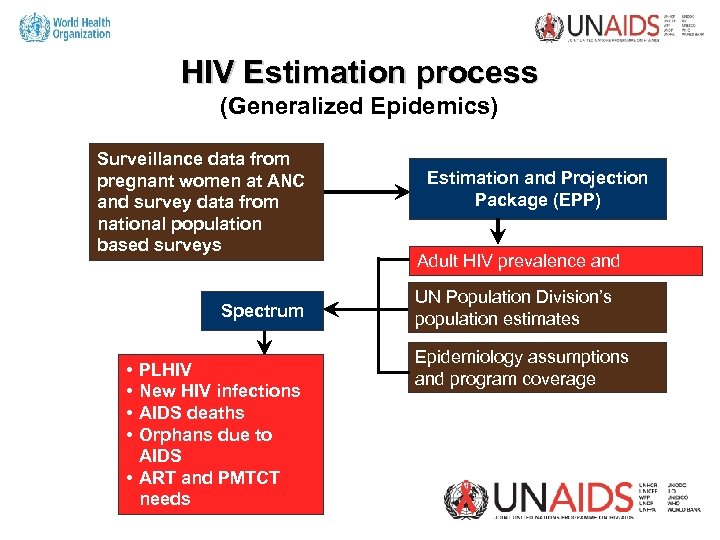 HIV Estimation process (Generalized Epidemics) Surveillance data from pregnant women at ANC and survey data from national population based surveys Spectrum • • PLHIV New HIV infections AIDS deaths Orphans due to AIDS • ART and PMTCT needs Estimation and Projection Package (EPP) Adult HIV prevalence and incidence UN Population Division’s population estimates Epidemiology assumptions and program coverage
HIV Estimation process (Generalized Epidemics) Surveillance data from pregnant women at ANC and survey data from national population based surveys Spectrum • • PLHIV New HIV infections AIDS deaths Orphans due to AIDS • ART and PMTCT needs Estimation and Projection Package (EPP) Adult HIV prevalence and incidence UN Population Division’s population estimates Epidemiology assumptions and program coverage
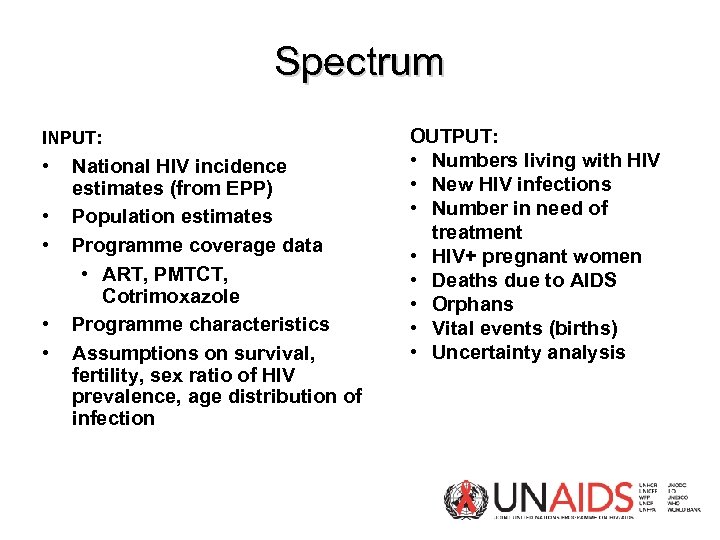 Spectrum INPUT: • • • National HIV incidence estimates (from EPP) Population estimates Programme coverage data • ART, PMTCT, Cotrimoxazole Programme characteristics Assumptions on survival, fertility, sex ratio of HIV prevalence, age distribution of infection OUTPUT: • Numbers living with HIV • New HIV infections • Number in need of treatment • HIV+ pregnant women • Deaths due to AIDS • Orphans • Vital events (births) • Uncertainty analysis
Spectrum INPUT: • • • National HIV incidence estimates (from EPP) Population estimates Programme coverage data • ART, PMTCT, Cotrimoxazole Programme characteristics Assumptions on survival, fertility, sex ratio of HIV prevalence, age distribution of infection OUTPUT: • Numbers living with HIV • New HIV infections • Number in need of treatment • HIV+ pregnant women • Deaths due to AIDS • Orphans • Vital events (births) • Uncertainty analysis
 PLHIV, annual new infections, AIDS-related deaths and total population: 15 -49 years in South Africa
PLHIV, annual new infections, AIDS-related deaths and total population: 15 -49 years in South Africa
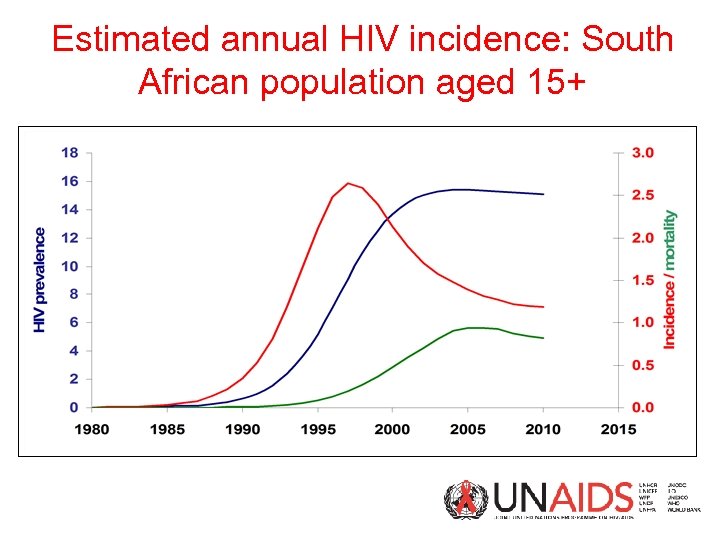 Estimated annual HIV incidence: South African population aged 15+
Estimated annual HIV incidence: South African population aged 15+
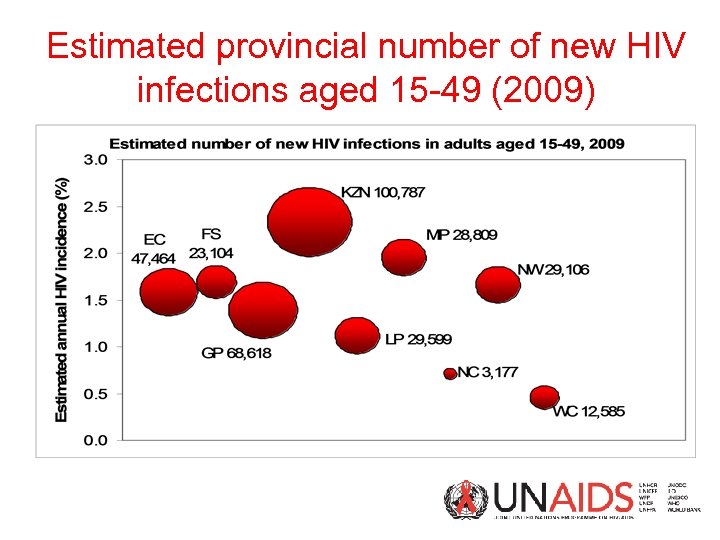 Estimated provincial number of new HIV infections aged 15 -49 (2009)
Estimated provincial number of new HIV infections aged 15 -49 (2009)
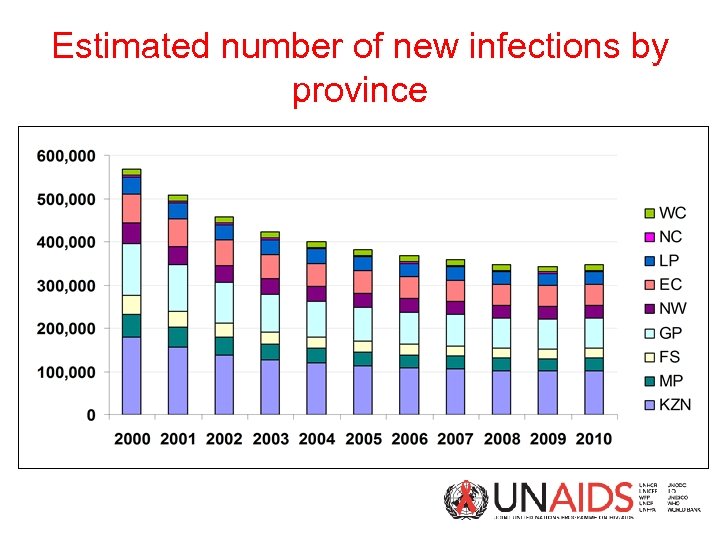 Estimated number of new infections by province
Estimated number of new infections by province
 Purpose and objectives on NASA • Identify all sources of financing for HIV/AIDS & TB; • Measure all the public, external and private financial resources allocated/ committed and spent for HIV/AIDS and TB activities; • Identify the providers of HIV/AIDS & TB services; • Identify activities on which the funds were spent, according to the NASA classifications and priorities; • Identify the beneficiaries of the spending on HIV/AIDS and TB activities
Purpose and objectives on NASA • Identify all sources of financing for HIV/AIDS & TB; • Measure all the public, external and private financial resources allocated/ committed and spent for HIV/AIDS and TB activities; • Identify the providers of HIV/AIDS & TB services; • Identify activities on which the funds were spent, according to the NASA classifications and priorities; • Identify the beneficiaries of the spending on HIV/AIDS and TB activities
 Rationale for doing NASA • Budgetary allocations indicate commitment • Little data on how previous allocations have been spent in various programmes, activities and outcomes. • Resource tracking of HIV/AIDS expenditure enables countries to monitor spending according to its National Strategic Plan (NSP) • Measures degree of harmonization and alignment of all actors’ involved in HIV/AIDS • Measure financing gap, so as to improve decision-making and resource mobilization processes
Rationale for doing NASA • Budgetary allocations indicate commitment • Little data on how previous allocations have been spent in various programmes, activities and outcomes. • Resource tracking of HIV/AIDS expenditure enables countries to monitor spending according to its National Strategic Plan (NSP) • Measures degree of harmonization and alignment of all actors’ involved in HIV/AIDS • Measure financing gap, so as to improve decision-making and resource mobilization processes
 Rationale (2) • NASA contributes to the strengthening of comprehensive tracking of actual spending from all sources that comprises the national response to HIV and AIDS in a country • Leveraging technical and financial support for: – development, – implementation, – management, – monitoring and evaluation of the national HIV/AIDS response.
Rationale (2) • NASA contributes to the strengthening of comprehensive tracking of actual spending from all sources that comprises the national response to HIV and AIDS in a country • Leveraging technical and financial support for: – development, – implementation, – management, – monitoring and evaluation of the national HIV/AIDS response.
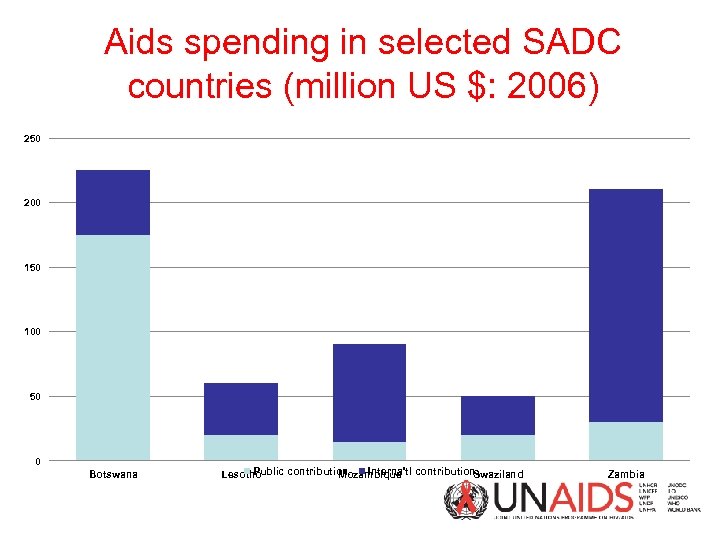 Aids spending in selected SADC countries (million US $: 2006) 250 200 150 100 50 0 Botswana Public contribution. Interna'tl Lesotho Mozambique contribution Swaziland Zambia
Aids spending in selected SADC countries (million US $: 2006) 250 200 150 100 50 0 Botswana Public contribution. Interna'tl Lesotho Mozambique contribution Swaziland Zambia
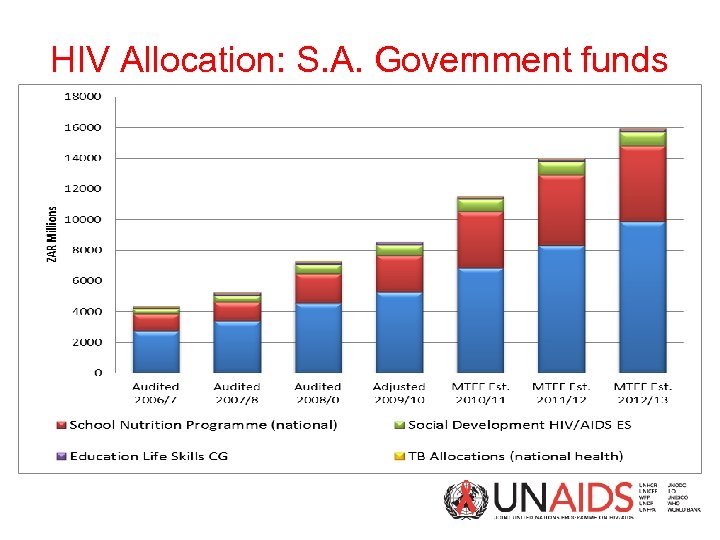 HIV Allocation: S. A. Government funds
HIV Allocation: S. A. Government funds
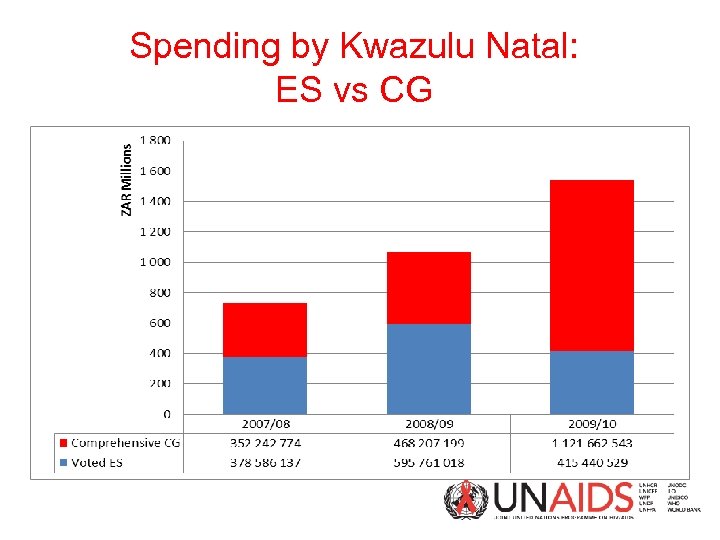 Spending by Kwazulu Natal: ES vs CG
Spending by Kwazulu Natal: ES vs CG
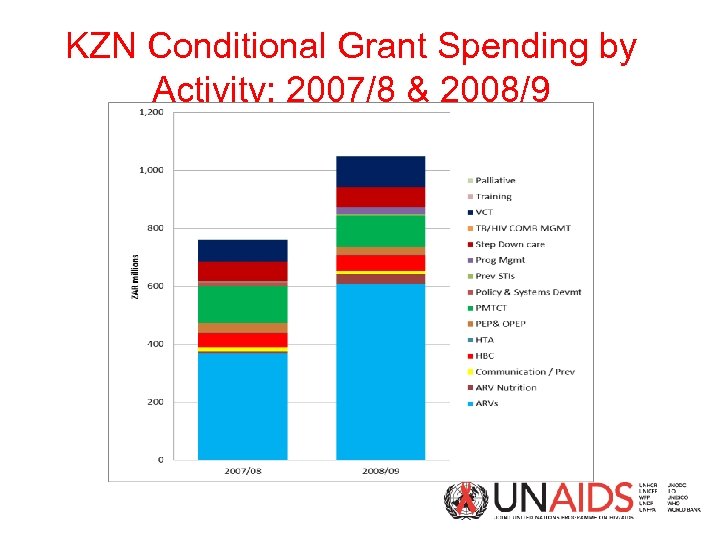 KZN Conditional Grant Spending by Activity: 2007/8 & 2008/9
KZN Conditional Grant Spending by Activity: 2007/8 & 2008/9
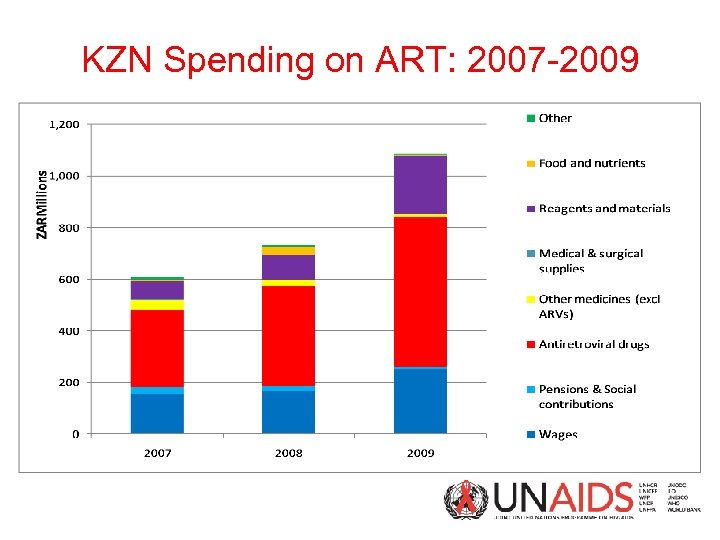 KZN Spending on ART: 2007 -2009
KZN Spending on ART: 2007 -2009
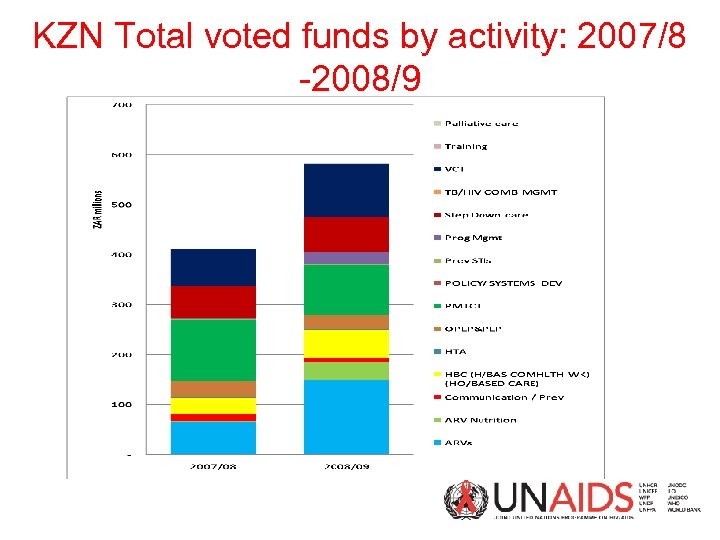 KZN Total voted funds by activity: 2007/8 -2008/9
KZN Total voted funds by activity: 2007/8 -2008/9
 VISION ZERO NEW HIV INFECTIONS. ZERO DISCRIMINATION. ZERO AIDS-RELATED DEATHS.
VISION ZERO NEW HIV INFECTIONS. ZERO DISCRIMINATION. ZERO AIDS-RELATED DEATHS.


