 UML Component and Deployment Diagrams 1
UML Component and Deployment Diagrams 1
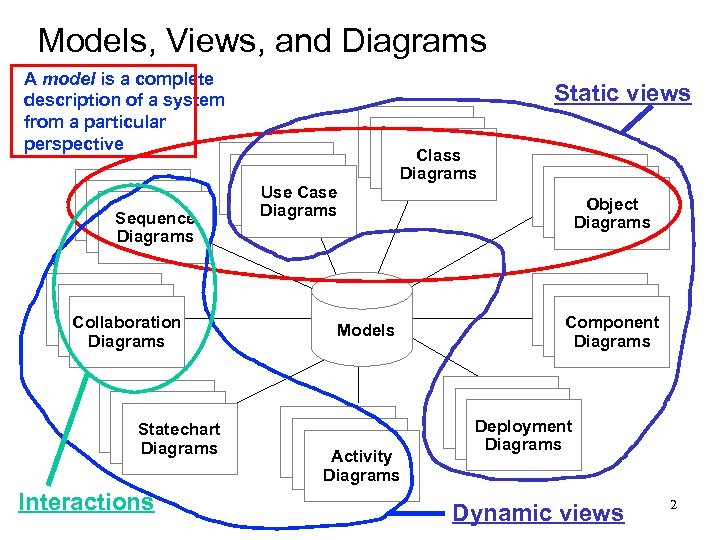 Models, Views, and Diagrams A model is a complete description of a system from a particular perspective Use Case Diagrams Sequence Diagrams Scenario Diagrams Collaboration Diagrams Scenario Diagrams Statechart Diagrams Interactions Static views Use Case Diagrams State Diagrams Class Diagrams Models State Diagrams Object Diagrams State Diagrams Component Diagrams Deployment Diagrams Activity Diagrams Dynamic views 2
Models, Views, and Diagrams A model is a complete description of a system from a particular perspective Use Case Diagrams Sequence Diagrams Scenario Diagrams Collaboration Diagrams Scenario Diagrams Statechart Diagrams Interactions Static views Use Case Diagrams State Diagrams Class Diagrams Models State Diagrams Object Diagrams State Diagrams Component Diagrams Deployment Diagrams Activity Diagrams Dynamic views 2
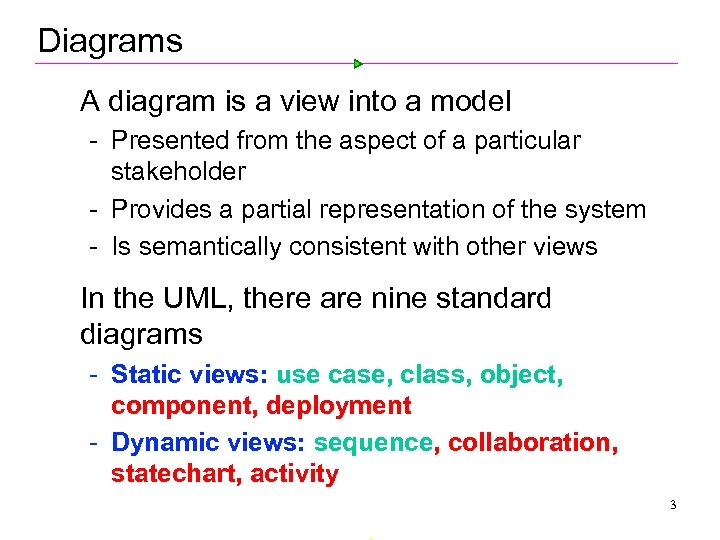 Diagrams Ø A diagram is a view into a model Presented from the aspect of a particular stakeholder Provides a partial representation of the system Is semantically consistent with other views Ø In the UML, there are nine standard diagrams Static views: use case, class, object, component, deployment Dynamic views: sequence, collaboration, statechart, activity 3
Diagrams Ø A diagram is a view into a model Presented from the aspect of a particular stakeholder Provides a partial representation of the system Is semantically consistent with other views Ø In the UML, there are nine standard diagrams Static views: use case, class, object, component, deployment Dynamic views: sequence, collaboration, statechart, activity 3
 4
4
 5
5
 6
6
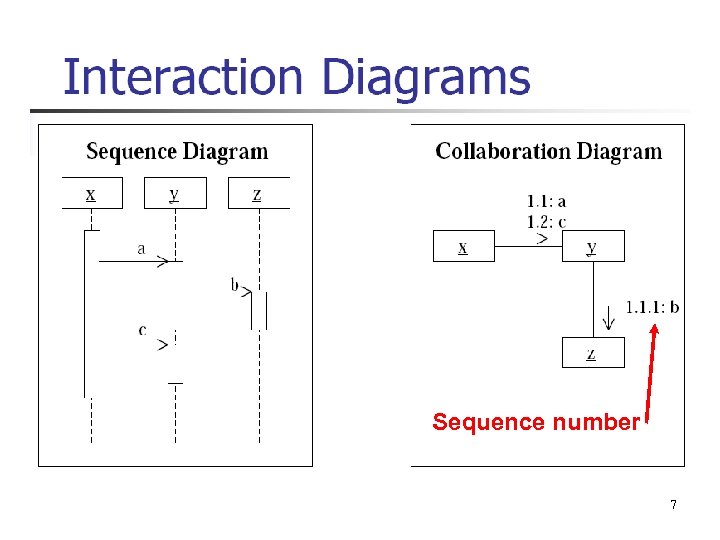 Sequence number 7
Sequence number 7
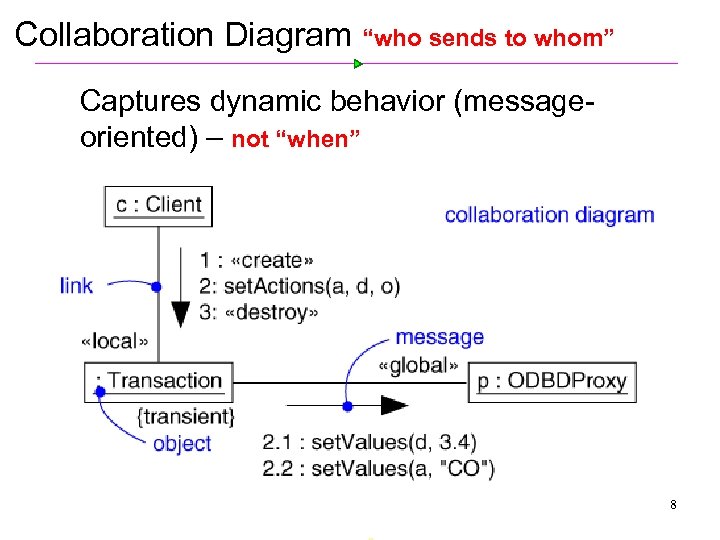 Collaboration Diagram “who sends to whom” Ø Captures dynamic behavior (message oriented) – not “when” 8
Collaboration Diagram “who sends to whom” Ø Captures dynamic behavior (message oriented) – not “when” 8
 Collaboration Diagram Ø Captures dynamic behavior (message oriented) Ø Purpose Model flow of control Illustrate coordination of object structure and control 9
Collaboration Diagram Ø Captures dynamic behavior (message oriented) Ø Purpose Model flow of control Illustrate coordination of object structure and control 9
 Example: Change Flight Itinerary (Use case description) 10
Example: Change Flight Itinerary (Use case description) 10
 11
11
 12
12
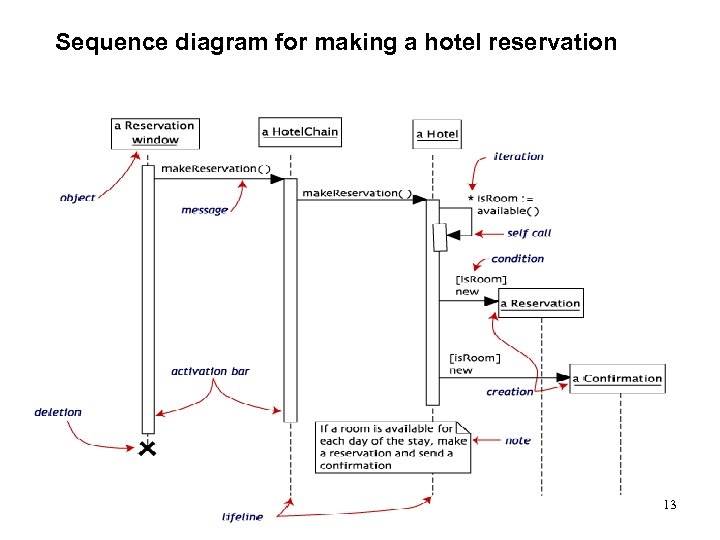 Sequence diagram for making a hotel reservation 13
Sequence diagram for making a hotel reservation 13
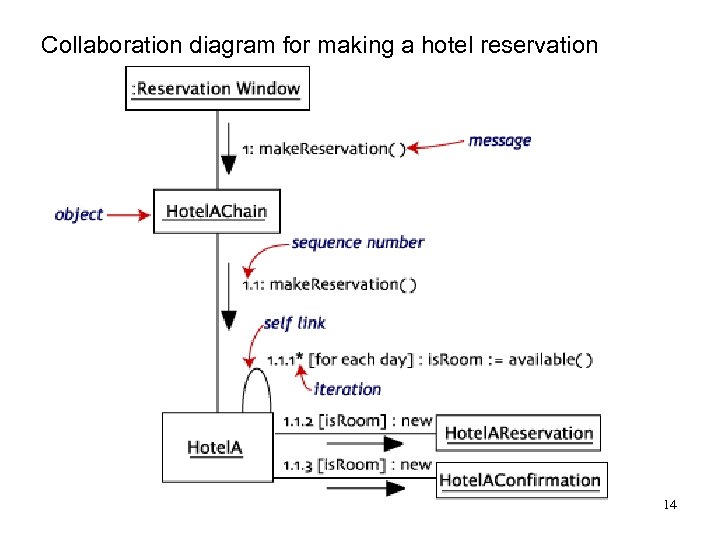 Collaboration diagram for making a hotel reservation 14
Collaboration diagram for making a hotel reservation 14
 UML Statechart Diagram Automata: 15
UML Statechart Diagram Automata: 15
 16
16
 17
17
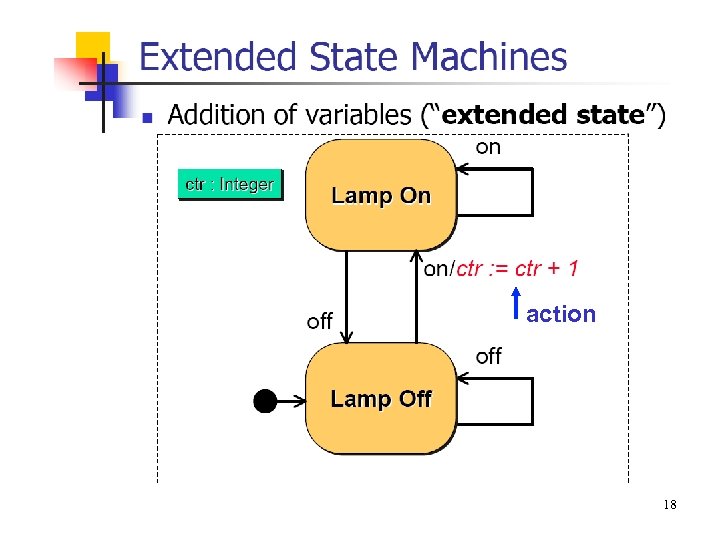 action 18
action 18
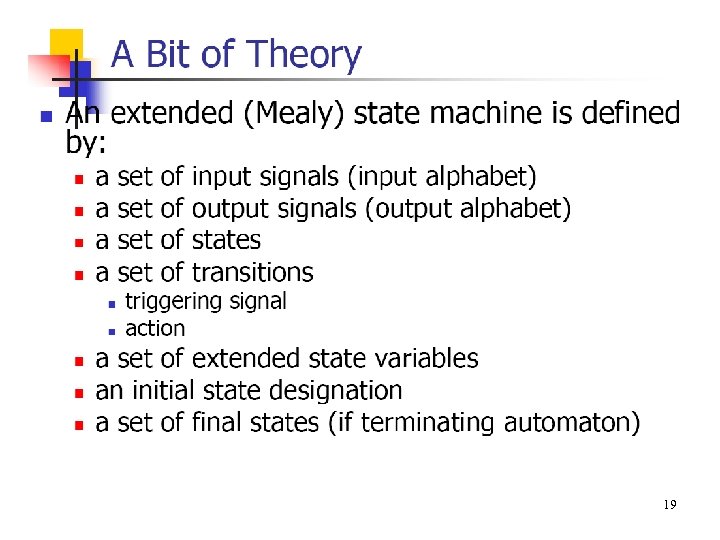 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
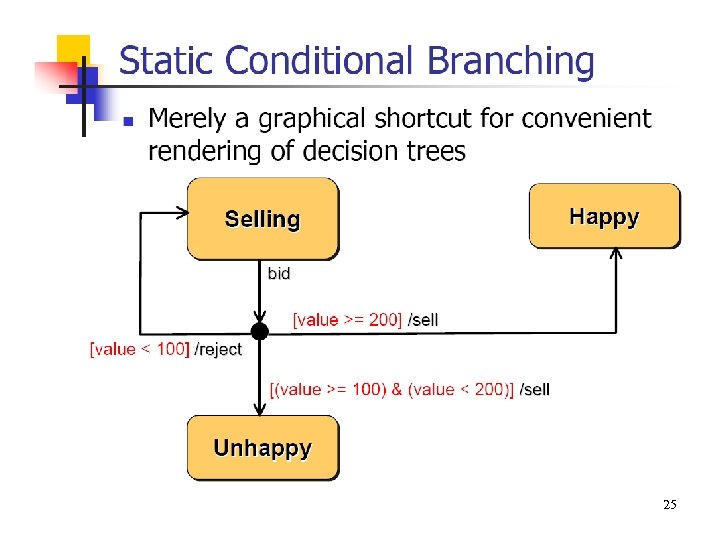 25
25
 26
26
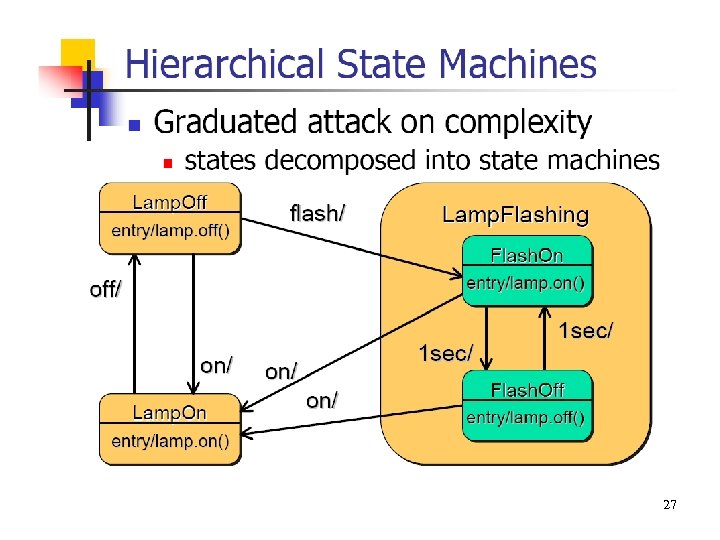 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
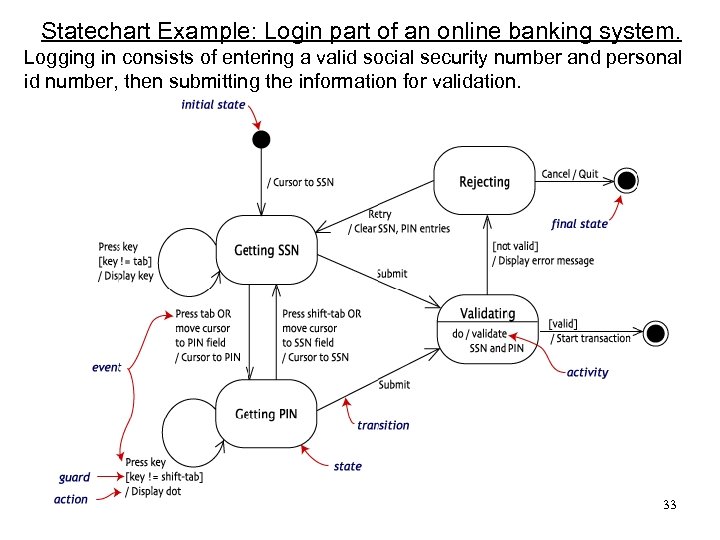 Statechart Example: Login part of an online banking system. Logging in consists of entering a valid social security number and personal id number, then submitting the information for validation. 33
Statechart Example: Login part of an online banking system. Logging in consists of entering a valid social security number and personal id number, then submitting the information for validation. 33
 34
34
 UML Activity Diagram 35
UML Activity Diagram 35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
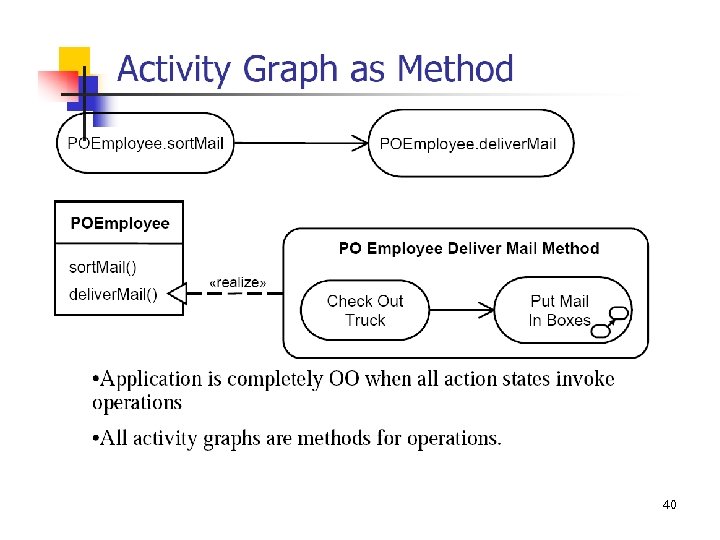 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
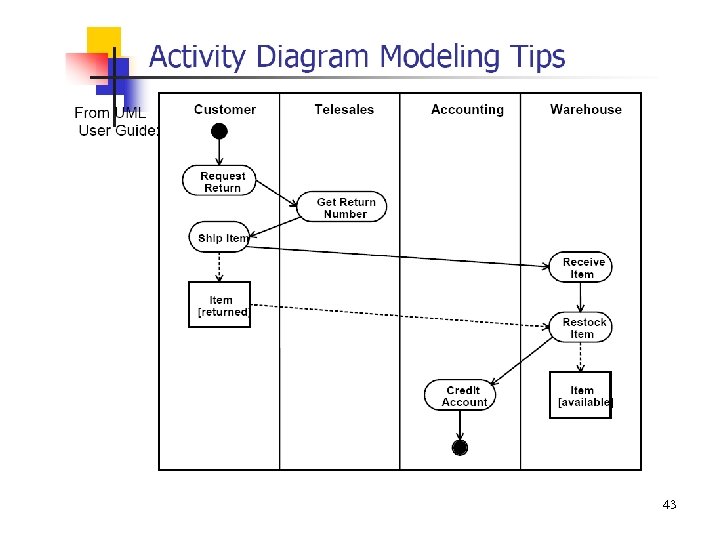 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
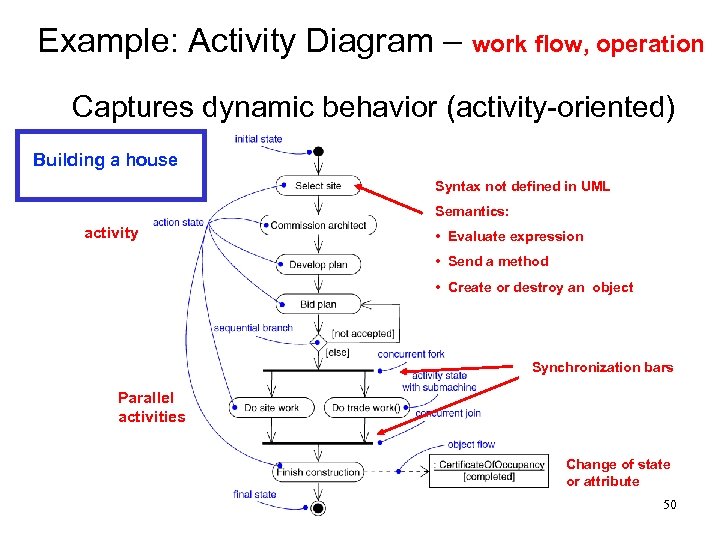 Example: Activity Diagram – work flow, operation Ø Captures dynamic behavior (activity oriented) Building a house Syntax not defined in UML Semantics: activity • Evaluate expression • Send a method • Create or destroy an object Synchronization bars Parallel activities Change of state or attribute 50
Example: Activity Diagram – work flow, operation Ø Captures dynamic behavior (activity oriented) Building a house Syntax not defined in UML Semantics: activity • Evaluate expression • Send a method • Create or destroy an object Synchronization bars Parallel activities Change of state or attribute 50
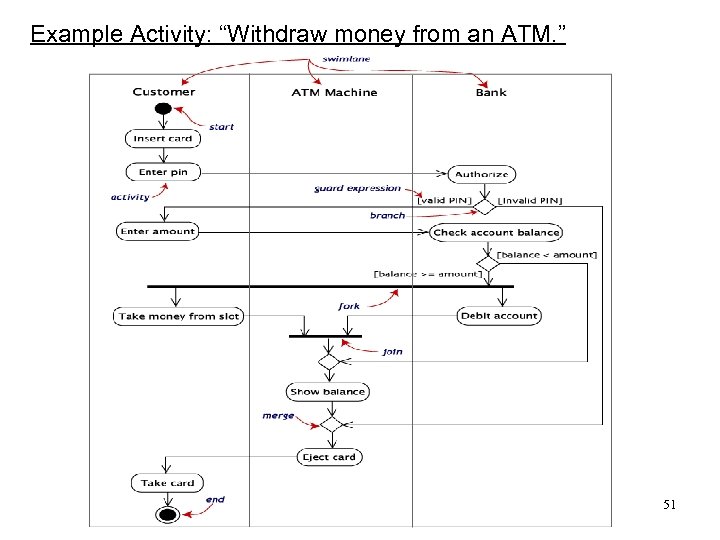 Example Activity: “Withdraw money from an ATM. ” 51
Example Activity: “Withdraw money from an ATM. ” 51
 52
52