6862a3392d001a80b01e8aff73f769ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

UK Disability Inclusion Training: Education Sector

Workshop Outcomes By the end of the workshop, participants should be able to: • Recognise the influence of perceptions and experiences • Identify techniques for good inclusive practice • Recognise appropriate coaching implications • Identify potential challenges to participation and identify possible solutions • Appreciate the importance of effective communication in inclusive practice • Identify sources of additional information and guidance relevant to disability sport and coaches and volunteers

Workshop Principles • Focus on ability rather than disability • Influence and deliver good practice to suit all involved • Communicate appropriately and effectively • Support the inclusion of disabled people in sport and physical activity • Understand how to challenge real and perceived barriers • Where to go to for further information

Section 1 Perceptions and Experiences By the end of this section candidates should be able to • Recognise the influence of Curriculum for Excellence regarding inclusion training • Recognise the influence of perceptions and experiences

Curriculum for Excellence Focussed on the needs of the Child & Young person and designed to enable them to develop the four capacities. Curriculum for Excellence should lead to improved quality of learning and teaching and increased attainment & achievement for all children and young people in Scotland
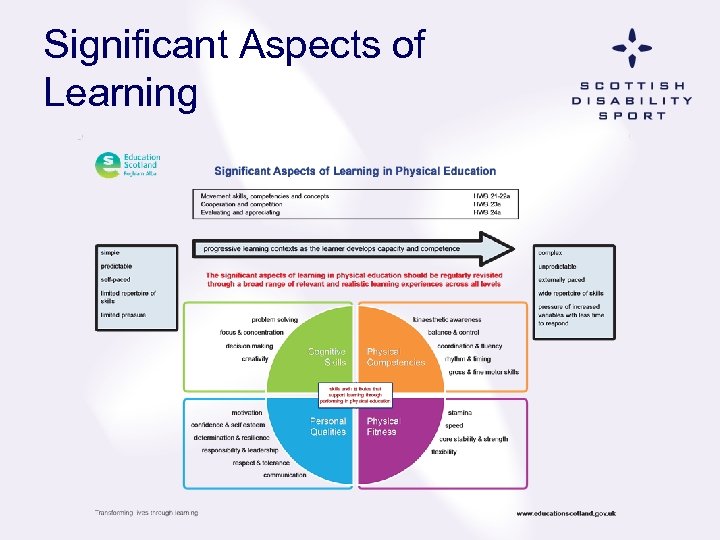
Significant Aspects of Learning

Curriculum for Excellence & UKDIT Curriculum for Excellence Focussed on the needs of the Child & Young person Coherent & Inclusive curriculum Health & well being Outcomes • Building physical competency & skills • Improving aspects of fitness • Develop personal & interpersonal skills • Open up opportunities to participate & perform at highest level UK Disability Inclusion Training Focussed on the needs of Children & young people Inclusion of children & young people with a disability UKDIT Outcomes Building the skills & physical competencies of those with a disability Improving the fitness of young disabled people Developing personal & interpersonal skills of young disabled people Creating opportunities to perform at the highest level

Perceptions & Experiences Why do children, athletes and players with a physical, sensory or learning disability participate in sport?

Perceptions & Experiences “People only see what they are prepared to see” (R. W. Emerson, 1803 -1882)





Section 2 Understanding the Participant By the end of this section candidates should be able to • Recognise appropriate coaching implications • Identify potential challenges to participation and identify possible solutions

Activity Task 1 • Make a list of different impairments/health conditions Task 2 • Create 3 – 4 groups of similar impairments/health conditions

Categories in Disability Sport Children, athletes and players with a physical impairment • ambulant • use a wheelchair for sports Children, athletes and players with a learning disability Children, athletes and players with a sensory impairment • Blind or partially sighted • Deaf or hard of hearing

Physical • Cerebral Palsy • Amputation • Spinal Injury • Dwarfism/Restricted Growth may be ambulant, a wheelchair user, or use a wheelchair for sport What are the practical implications?

Learning • Intelligence Quotient (IQ) of less than 75 e. g. Down’s Syndrome, Fragile X Syndrome What are the practical implications? NB: No sporting pathway exists specifically for those on the Autistic Spectrum. Autism is NOT necessarily a Learning Disability

Sensory • Visual Blind Partially Sighted • Hearing Profoundly deaf Hard of Hearing What are the practical implications?

Functional Approach • Considers the functional ability of the athlete – What is the participant ABLE to do rather than unable to do? • Assesses the impact of the impairment and environment on an individuals ability to master specific sport skills • Consider how the participant moves – observe upper and lower extremities and trunk

Impairment Considerations Minimal Congenital Severe or Acquired Progressive or Non-progressive

Key Messages 1. Be proactive rather than reactive • Talk to the people involved • Anticipate potential challenges 2. Be aware of your environment • Be realistic but constructively critical 3. YOU are important • Remember you CAN make a difference • Changes do not have to cost money – a short return to the drawing board may suffice • Small changes can have large impacts

Section 3: Models of Inclusion By the end of this section candidates should be able to • Identify techniques for good inclusive practice
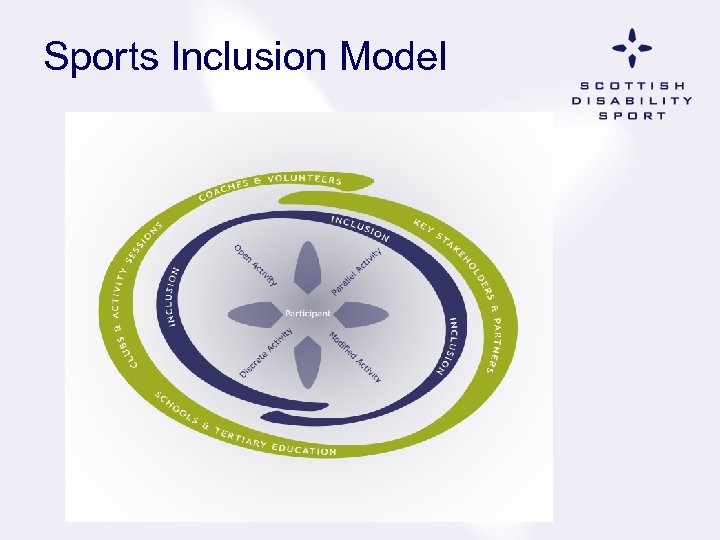
Sports Inclusion Model

Open Activity: Requires no alteration

Modified Activity: Uses adaptation and modification

STEPS How can I change? S pace – where the activity is happening T ask – what is happening E quipment – what is being used P eople – who is involved S peed – pace of the activity

Parallel Activity: Uses differentiation

Discrete/Specific Activity: targeted sport for particular groups
Group A Al-sayed ahmed Danah Anderson Gillian Anderson Sarah Blackstock Emma Briggs Charlotte Carson Callum Cheshire Calum Cleland Katie Collins Steven Crawford Jennifer Duffie Stephen Evans Lauren Ferns Kieran Forbes Daisy Forbes Sara Fox Naomi Galbraith Ellie Gallagher Matthew Mac. Kay Holly O'donohue Amy Group B Fox Geary Gordon Graham Grant Graves Harley Hayworth Helyer Hesford Hickson Hodgson Holmes Johnston Kennard Kenney Kershaw Kirkwood Lanigan Law Mac. Arthur Louise June Holly Rebecca Rory Danny Lucy Craig Liam Vicky Erin Jack Shaun Iona Natalie Rachel Crawford Charlotte Lucy Georgia Cara Laura
Group C Cook Gibson Mackenzie Mackinnon Mac. Sween Martin Mc. Cracken Mc. Ginn Mc. Gregor Mc. Hugh Mc. Vey Miller Mitchell Moreland Murphy Neilson Rahimian Shearer Slavin Stavert Sam Calum Hannah Christy Isla Katie Claire Rebecca Shonagh Niamh Kieran Kara Stacey Louise Jade Hannah Holly Lewis Ali Calum Andrew Group D Longley Patrick Printer Stevenson Stewart Sutherland Swinney Taylor Travers Walker Watt Whyte Wilson Wood Tom Chrissy Elise Rebecca Anna Niamh Allan Joanne Andrew Jasmin Rachel Katheryn Thomas Brogan Ciaran Chris Amelia Ciaran

Practical • Please make your way up to the Games Hall at the Pleasance to put theory of the Sports Inclusion Model and STEPS into practice

Section 4: Communication By the end of this section you should be able to use communication to: • Identify techniques for good inclusive practice • Recognise appropriate teaching implications • Appreciate the importance of effective communication in inclusive practice

Communication • The way we transfer information is very important • Every individual takes in information differently • We need to tailor our delivery style to suit the needs of the learners • Interpretation • Communication is about: Giving Information Receiving Information

Positive Behaviour • Respect individual participants • Challenging the social norms to ensure behaviour and interaction with disabled people are appropriate • THINK about your behaviour and how it might make other people feel

Thinking about what we do • Using Worksheet: Positive Behaviour • individually identify whether you think the statement are; True or False • In small groups, compare your answers, and discuss any differences.

Section 5 Further information Assessment By the end of this section candidates should be able to • Identify sources of additional information and guidance relevant to disability sport • Complete assessment

Scottish Disability Sport: Strategic Plan Overview 2012 - 2017 WHAT WE WILL DO Improving Sports Performance HOW WE ARE GOING TO MAKE IT HAPPEN Branch, Local and Regional sporting opportunities Education & Coaching Developing Talent and Performance Governance and Infrastructure Communication and Leadership People - Partnerships - Pathways Safeguarding in sport Inclusive Sports Equity Developing Sports Opportunities

Contacts Scottish Disability Sport • Caledonia House • South Gyle Edinburgh EH 12 9 DQ Tel: 0131 317 1130 Email: admin@scottishdisabilitysport. com Website: www. scottishdisabilitysport. com Local branch contact Regional Development Manager

Assessment

Workshop Outcomes By the end of the workshop, participants should be able to: • Recognise the influence of perceptions and experiences • Identify techniques for good inclusive practice • Recognise appropriate teaching implications • Identify potential challenges to participation and identify possible solutions • Appreciate the importance of effective communication in inclusive practice • Understand key aspects of legislation • Recognise pathways within disability sport • Appreciate classification in disability sport • Identify sources of additional information and guidance relevant to disability sport & PE
6862a3392d001a80b01e8aff73f769ee.ppt