d0d01d659ee5f1c5f15c9c2b088c6c0c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 UIR Alert Agent : An alert system for identifying suspicious web-site browsing leading to unintended information revelation(UIR) Rohini K. Srihari State University of New York at Buffalo May 6, 2003 FAA Workshop May 2003
UIR Alert Agent : An alert system for identifying suspicious web-site browsing leading to unintended information revelation(UIR) Rohini K. Srihari State University of New York at Buffalo May 6, 2003 FAA Workshop May 2003
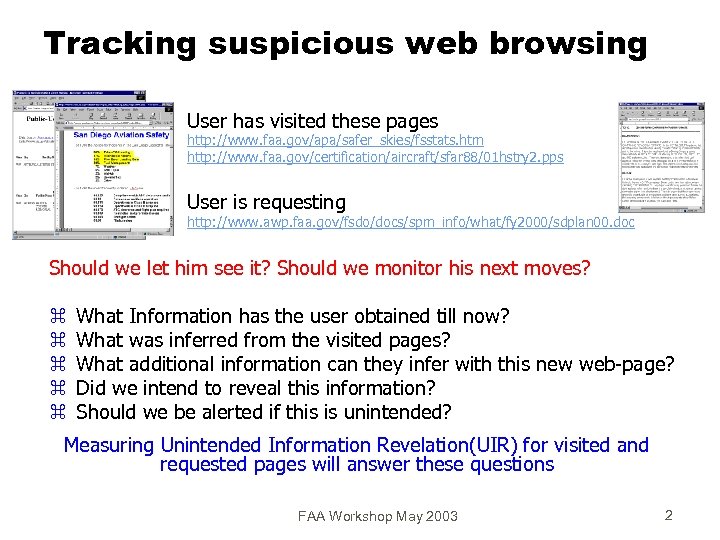 Tracking suspicious web browsing User has visited these pages http: //www. faa. gov/apa/safer_skies/fsstats. htm http: //www. faa. gov/certification/aircraft/sfar 88/01 hstry 2. pps User is requesting http: //www. awp. faa. gov/fsdo/docs/spm_info/what/fy 2000/sdplan 00. doc Should we let him see it? Should we monitor his next moves? z z z What Information has the user obtained till now? What was inferred from the visited pages? What additional information can they infer with this new web-page? Did we intend to reveal this information? Should we be alerted if this is unintended? Measuring Unintended Information Revelation(UIR) for visited and requested pages will answer these questions FAA Workshop May 2003 2
Tracking suspicious web browsing User has visited these pages http: //www. faa. gov/apa/safer_skies/fsstats. htm http: //www. faa. gov/certification/aircraft/sfar 88/01 hstry 2. pps User is requesting http: //www. awp. faa. gov/fsdo/docs/spm_info/what/fy 2000/sdplan 00. doc Should we let him see it? Should we monitor his next moves? z z z What Information has the user obtained till now? What was inferred from the visited pages? What additional information can they infer with this new web-page? Did we intend to reveal this information? Should we be alerted if this is unintended? Measuring Unintended Information Revelation(UIR) for visited and requested pages will answer these questions FAA Workshop May 2003 2
 Outline z Unintended Information Revelation z Problem Definition y Solutions with Existing Technology z Proposed Solution y UIR System Architecture y Extracting Concepts and Associations y Creating Concept Chain Graphs (CCG) y Mining and visualization of CCGs z Evaluation Methodology z Preliminary Results z Summary FAA Workshop May 2003 3
Outline z Unintended Information Revelation z Problem Definition y Solutions with Existing Technology z Proposed Solution y UIR System Architecture y Extracting Concepts and Associations y Creating Concept Chain Graphs (CCG) y Mining and visualization of CCGs z Evaluation Methodology z Preliminary Results z Summary FAA Workshop May 2003 3
 User’s previous request Fact Sheet: Aviation Accident Statistics http: //www. faa. gov/apa/safer_skies/fsstats. htm Important Concepts z safer skies, fatal accidents, runway incursions, hijack, etc. Interesting Information z Number and percentage of Fatal Accidents in 1996 y Runway Incursions y Ice/Snow y In-Flight fire FAA Workshop May 2003 4
User’s previous request Fact Sheet: Aviation Accident Statistics http: //www. faa. gov/apa/safer_skies/fsstats. htm Important Concepts z safer skies, fatal accidents, runway incursions, hijack, etc. Interesting Information z Number and percentage of Fatal Accidents in 1996 y Runway Incursions y Ice/Snow y In-Flight fire FAA Workshop May 2003 4
 User’s current request Fuel tank ignition events http: //www. faa. gov/certification/aircraft/sfar 88/01 hstry 2. pps Important Concepts z fatalities, fuel tank ignition, hull loss, electrostatics, etc. Interesting Information z. Identifies causes for fuel tank ignition accidents y Small bomb y Faulty Wiring y Pump Faults FAA Workshop May 2003 5
User’s current request Fuel tank ignition events http: //www. faa. gov/certification/aircraft/sfar 88/01 hstry 2. pps Important Concepts z fatalities, fuel tank ignition, hull loss, electrostatics, etc. Interesting Information z. Identifies causes for fuel tank ignition accidents y Small bomb y Faulty Wiring y Pump Faults FAA Workshop May 2003 5
 Synthesized Information z In-flight fire can cause accidents z Fuel-tank ignitions caused by small bombs, faulty pumps/wirings, etc. z Domain Knowledge: In-flight fires and fuel-tank ignitions are aviation hazards. z Inference: faulty wirings can cause in-flight fires FAA Workshop May 2003 6
Synthesized Information z In-flight fire can cause accidents z Fuel-tank ignitions caused by small bombs, faulty pumps/wirings, etc. z Domain Knowledge: In-flight fires and fuel-tank ignitions are aviation hazards. z Inference: faulty wirings can cause in-flight fires FAA Workshop May 2003 6
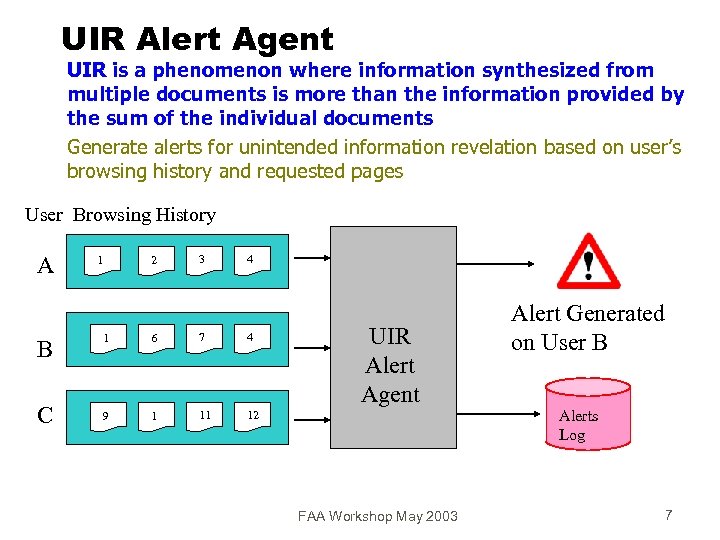 UIR Alert Agent UIR is a phenomenon where information synthesized from multiple documents is more than the information provided by the sum of the individual documents Generate alerts for unintended information revelation based on user’s browsing history and requested pages User Browsing History A B C 1 2 3 4 1 6 7 4 9 1 11 UIR Alert Agent 12 FAA Workshop May 2003 Alert Generated on User B Alerts Log 7
UIR Alert Agent UIR is a phenomenon where information synthesized from multiple documents is more than the information provided by the sum of the individual documents Generate alerts for unintended information revelation based on user’s browsing history and requested pages User Browsing History A B C 1 2 3 4 1 6 7 4 9 1 11 UIR Alert Agent 12 FAA Workshop May 2003 Alert Generated on User B Alerts Log 7
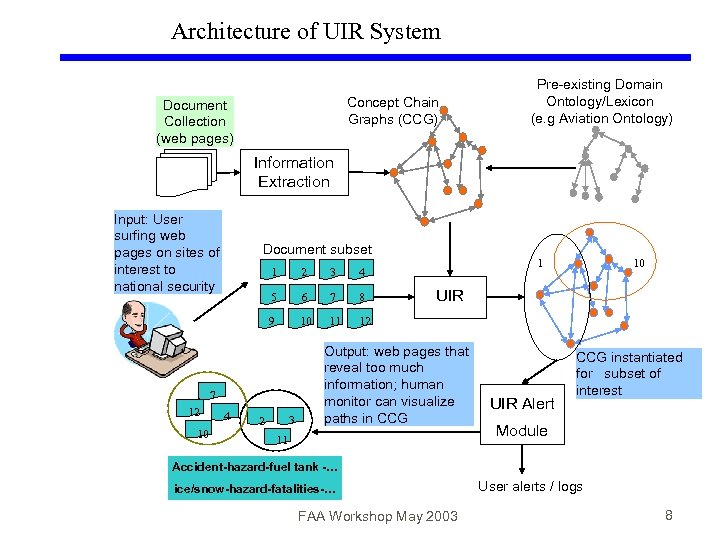 Architecture of UIR System Concept Chain Graphs (CCG) Document Collection (web pages) Pre-existing Domain Ontology/Lexicon (e. g Aviation Ontology) Information Extraction Input: User surfing web pages on sites of interest to national security Document subset 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 10 4 10 12 7 12 1 4 3 2 UIR Output: web pages that reveal too much information; human monitor can visualize paths in CCG 11 UIR Alert CCG instantiated for subset of interest Module Accident-hazard-fuel tank -… ice/snow-hazard-fatalities-… FAA Workshop May 2003 User alerts / logs 8
Architecture of UIR System Concept Chain Graphs (CCG) Document Collection (web pages) Pre-existing Domain Ontology/Lexicon (e. g Aviation Ontology) Information Extraction Input: User surfing web pages on sites of interest to national security Document subset 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 10 4 10 12 7 12 1 4 3 2 UIR Output: web pages that reveal too much information; human monitor can visualize paths in CCG 11 UIR Alert CCG instantiated for subset of interest Module Accident-hazard-fuel tank -… ice/snow-hazard-fatalities-… FAA Workshop May 2003 User alerts / logs 8
 Proposed Solution Step 1: Determine significant concepts and associations in target domain (offline, semi-automatic) y use of existing ontologies such as DAML ontology on aviation y use of information extraction to automatically extract concepts and associations from representative document collection Step 2: Create Concept Chain Graph (CCG) y consolidates underlying domain knowledge, specific documents y weights concepts and associations using both domain weights, individual document weights Step 3: Visualization and text mining operations on CCG Step 4: UIR Alert agent invoked y tracking user surfing patterns y what-if scenarios FAA Workshop May 2003 9
Proposed Solution Step 1: Determine significant concepts and associations in target domain (offline, semi-automatic) y use of existing ontologies such as DAML ontology on aviation y use of information extraction to automatically extract concepts and associations from representative document collection Step 2: Create Concept Chain Graph (CCG) y consolidates underlying domain knowledge, specific documents y weights concepts and associations using both domain weights, individual document weights Step 3: Visualization and text mining operations on CCG Step 4: UIR Alert agent invoked y tracking user surfing patterns y what-if scenarios FAA Workshop May 2003 9
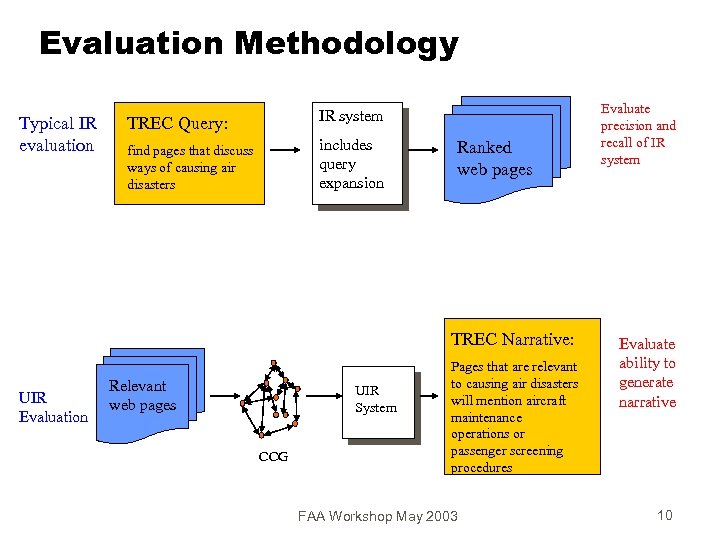 Evaluation Methodology Typical IR evaluation IR system TREC Query: includes query expansion find pages that discuss ways of causing air disasters Ranked web pages TREC Narrative: UIR Evaluation Relevant web pages UIR System CCG Pages that are relevant to causing air disasters will mention aircraft maintenance operations or passenger screening procedures FAA Workshop May 2003 Evaluate precision and recall of IR system Evaluate ability to generate narrative 10
Evaluation Methodology Typical IR evaluation IR system TREC Query: includes query expansion find pages that discuss ways of causing air disasters Ranked web pages TREC Narrative: UIR Evaluation Relevant web pages UIR System CCG Pages that are relevant to causing air disasters will mention aircraft maintenance operations or passenger screening procedures FAA Workshop May 2003 Evaluate precision and recall of IR system Evaluate ability to generate narrative 10
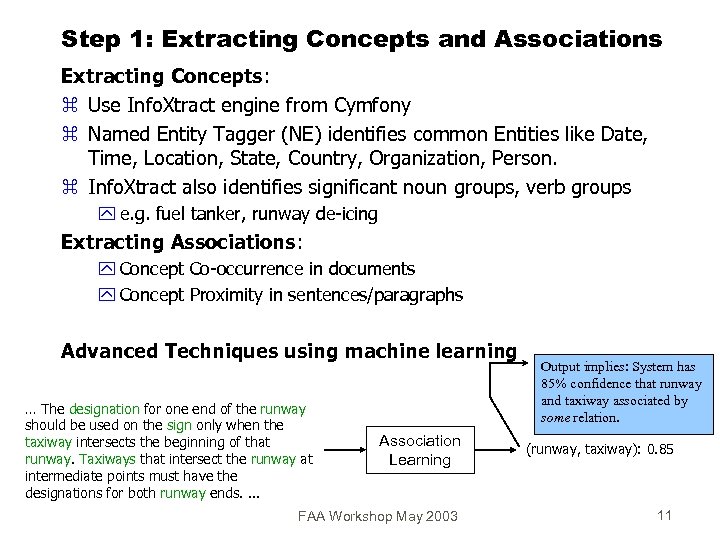 Step 1: Extracting Concepts and Associations Extracting Concepts: z Use Info. Xtract engine from Cymfony z Named Entity Tagger (NE) identifies common Entities like Date, Time, Location, State, Country, Organization, Person. z Info. Xtract also identifies significant noun groups, verb groups y e. g. fuel tanker, runway de-icing Extracting Associations: y Concept Co-occurrence in documents y Concept Proximity in sentences/paragraphs Advanced Techniques using machine learning … The designation for one end of the runway should be used on the sign only when the taxiway intersects the beginning of that runway. Taxiways that intersect the runway at intermediate points must have the designations for both runway ends. . Output implies: System has 85% confidence that runway and taxiway associated by some relation. Association Learning (runway, taxiway): 0. 85 FAA Workshop May 2003 11
Step 1: Extracting Concepts and Associations Extracting Concepts: z Use Info. Xtract engine from Cymfony z Named Entity Tagger (NE) identifies common Entities like Date, Time, Location, State, Country, Organization, Person. z Info. Xtract also identifies significant noun groups, verb groups y e. g. fuel tanker, runway de-icing Extracting Associations: y Concept Co-occurrence in documents y Concept Proximity in sentences/paragraphs Advanced Techniques using machine learning … The designation for one end of the runway should be used on the sign only when the taxiway intersects the beginning of that runway. Taxiways that intersect the runway at intermediate points must have the designations for both runway ends. . Output implies: System has 85% confidence that runway and taxiway associated by some relation. Association Learning (runway, taxiway): 0. 85 FAA Workshop May 2003 11
 Sample Information Extraction output Concepts and Named Entities are marked up during information extraction DATE: October 23, 1992 NO. 92 -03 TO: AIRPORT CERTIFICATION PROGRAM INSPECTORS TOPIC: Effects Of Type II Deicing Fluid On Runway Friction The FAA's Technical Center in conjunction with the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey conducted tests to determine the effects of Type II aircraft deicing fluids on runway friction. The tests were conducted this past July and August at La Guardia and John F. Kennedy International Airports on grooved asphaltic pavement. Since the tests were conducted in the summer no attempt was made to simulate ice or snow on the pavement surface. (See future test programs. ) Two specially instrumented B-727's and two Saab friction devices were used to measure the runway friction. The purpose of this effort was to test the premise that Type II deicing fluid deposited on a runway poses a hazard to aircraft landing on the runway. At the present time it is unknown to what extent Type II actually falls off a departing aircraft and what portion of it is deposited on the runway. (See future test programs. ) FAA Workshop May 2003 12
Sample Information Extraction output Concepts and Named Entities are marked up during information extraction DATE: October 23, 1992 NO. 92 -03 TO: AIRPORT CERTIFICATION PROGRAM INSPECTORS TOPIC: Effects Of Type II Deicing Fluid On Runway Friction The FAA's Technical Center in conjunction with the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey conducted tests to determine the effects of Type II aircraft deicing fluids on runway friction. The tests were conducted this past July and August at La Guardia and John F. Kennedy International Airports on grooved asphaltic pavement. Since the tests were conducted in the summer no attempt was made to simulate ice or snow on the pavement surface. (See future test programs. ) Two specially instrumented B-727's and two Saab friction devices were used to measure the runway friction. The purpose of this effort was to test the premise that Type II deicing fluid deposited on a runway poses a hazard to aircraft landing on the runway. At the present time it is unknown to what extent Type II actually falls off a departing aircraft and what portion of it is deposited on the runway. (See future test programs. ) FAA Workshop May 2003 12
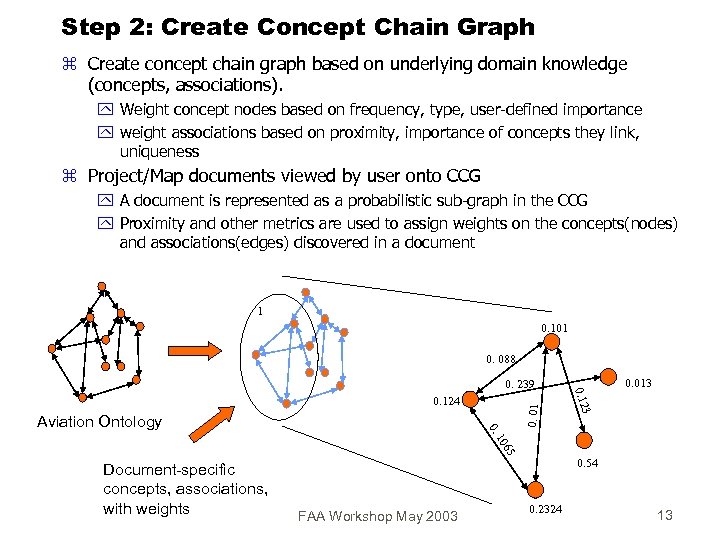 Step 2: Create Concept Chain Graph z Create concept chain graph based on underlying domain knowledge (concepts, associations). y Weight concept nodes based on frequency, type, user-defined importance y weight associations based on proximity, importance of concepts they link, uniqueness z Project/Map documents viewed by user onto CCG y A document is represented as a probabilistic sub-graph in the CCG y Proximity and other metrics are used to assign weights on the concepts(nodes) and associations(edges) discovered in a document 1 0. 101 0. 088 0. Aviation Ontology 0. 01 0. 124 3 0. 12 0. 239 0. 013 65 10 Document-specific concepts, associations, with weights 0. 54 FAA Workshop May 2003 0. 2324 13
Step 2: Create Concept Chain Graph z Create concept chain graph based on underlying domain knowledge (concepts, associations). y Weight concept nodes based on frequency, type, user-defined importance y weight associations based on proximity, importance of concepts they link, uniqueness z Project/Map documents viewed by user onto CCG y A document is represented as a probabilistic sub-graph in the CCG y Proximity and other metrics are used to assign weights on the concepts(nodes) and associations(edges) discovered in a document 1 0. 101 0. 088 0. Aviation Ontology 0. 01 0. 124 3 0. 12 0. 239 0. 013 65 10 Document-specific concepts, associations, with weights 0. 54 FAA Workshop May 2003 0. 2324 13
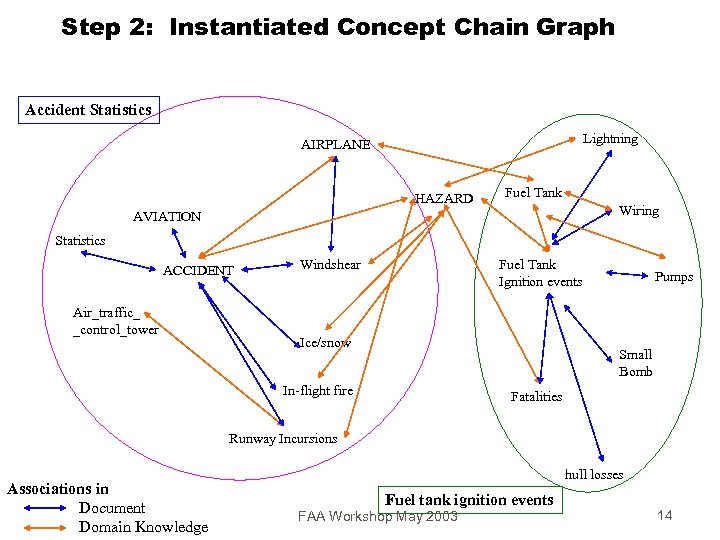 Step 2: Instantiated Concept Chain Graph Accident Statistics Lightning AIRPLANE HAZARD Fuel Tank Wiring AVIATION Statistics ACCIDENT Air_traffic_ _control_tower Windshear Fuel Tank Ignition events Ice/snow Pumps Small Bomb In-flight fire Fatalities Runway Incursions Associations in Document Domain Knowledge hull losses Fuel tank ignition events FAA Workshop May 2003 14
Step 2: Instantiated Concept Chain Graph Accident Statistics Lightning AIRPLANE HAZARD Fuel Tank Wiring AVIATION Statistics ACCIDENT Air_traffic_ _control_tower Windshear Fuel Tank Ignition events Ice/snow Pumps Small Bomb In-flight fire Fatalities Runway Incursions Associations in Document Domain Knowledge hull losses Fuel tank ignition events FAA Workshop May 2003 14
 Step 3: Mining the CCG z Goals y detecting information-rich concept chains xe. g. air disaster - onboard explosion - fuel tanker y quantifying information revealed xissue alerts when too much information is revealed x“what-if” scenarios to enable dissemination of benign information z Graph traversal y generate CCG representing documents viewed by user y start with explicit query/search terms as seed concepts; could be multiple terms y strategies: xtry to find best paths/chains that connect “seed” concepts; could generate multiple chains xtry to find best subgraph y various graph traversal algorithms are suitable FAA Workshop May 2003 15
Step 3: Mining the CCG z Goals y detecting information-rich concept chains xe. g. air disaster - onboard explosion - fuel tanker y quantifying information revealed xissue alerts when too much information is revealed x“what-if” scenarios to enable dissemination of benign information z Graph traversal y generate CCG representing documents viewed by user y start with explicit query/search terms as seed concepts; could be multiple terms y strategies: xtry to find best paths/chains that connect “seed” concepts; could generate multiple chains xtry to find best subgraph y various graph traversal algorithms are suitable FAA Workshop May 2003 15
 Graph Traversal Techniques z minimum cover techniques y INSTANCE: Graph G = {V, E} y SOLUTION: A vertex cover for G, i. e. , a subset V’ V such that, for each edge (u, v) E, at least one of u and v belongs to V'. y MEASURE: Cardinality of the vertex cover, i. e. , |V’ |. z Flow networks y given a network (G, s, t, c) where G = (V, E) is a directed graph with n vertices and m edges, s and t are two vertices (source and sink), and c: E-> R+ is a function that defines capacities of edges y find maximum flow from s to t that satisfies capacity constraints z Energy minimization (used in image processing) y active contours (e. g. snakes) used for tracking various shapes, including road detection y dynamic programming solutions available FAA Workshop May 2003 16
Graph Traversal Techniques z minimum cover techniques y INSTANCE: Graph G = {V, E} y SOLUTION: A vertex cover for G, i. e. , a subset V’ V such that, for each edge (u, v) E, at least one of u and v belongs to V'. y MEASURE: Cardinality of the vertex cover, i. e. , |V’ |. z Flow networks y given a network (G, s, t, c) where G = (V, E) is a directed graph with n vertices and m edges, s and t are two vertices (source and sink), and c: E-> R+ is a function that defines capacities of edges y find maximum flow from s to t that satisfies capacity constraints z Energy minimization (used in image processing) y active contours (e. g. snakes) used for tracking various shapes, including road detection y dynamic programming solutions available FAA Workshop May 2003 16
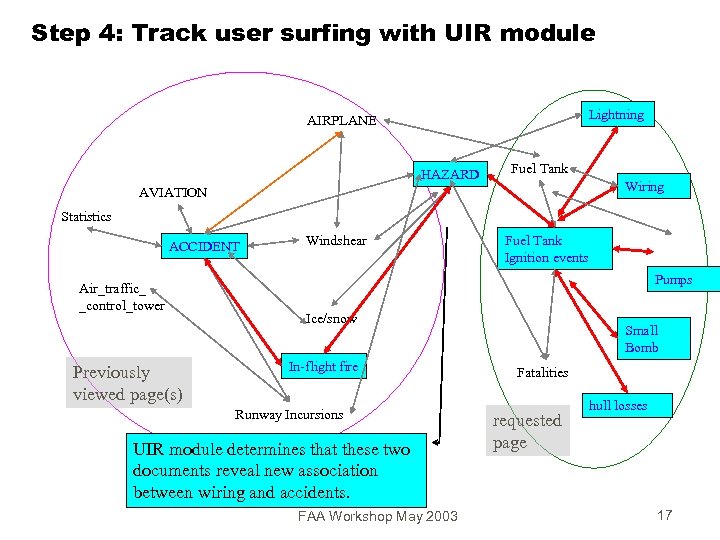 Step 4: Track user surfing with UIR module Lightning AIRPLANE HAZARD Fuel Tank Wiring AVIATION Statistics ACCIDENT Air_traffic_ _control_tower Previously viewed page(s) Windshear Fuel Tank Ignition events Pumps Ice/snow In-flight fire Runway Incursions UIR module determines that these two documents reveal new association between wiring and accidents. FAA Workshop May 2003 Small Bomb Fatalities requested page hull losses 17
Step 4: Track user surfing with UIR module Lightning AIRPLANE HAZARD Fuel Tank Wiring AVIATION Statistics ACCIDENT Air_traffic_ _control_tower Previously viewed page(s) Windshear Fuel Tank Ignition events Pumps Ice/snow In-flight fire Runway Incursions UIR module determines that these two documents reveal new association between wiring and accidents. FAA Workshop May 2003 Small Bomb Fatalities requested page hull losses 17
 Preliminary Experiments FAA Workshop May 2003 18
Preliminary Experiments FAA Workshop May 2003 18
 Summary Benefits to FAA z Automated monitoring information acquired by users of the FAA website and alert mechanism for unintentionally revealed information. z Shortlist and identify documents and concepts seen by the user that reveal unintended information z Domain map visualization tool facilitates concept and association based queries Claims z new, richer representation for information retrieval that combines keyword statistics (bag-of-words model) with NLP-based information extraction z Solution is general to any domain; only domain map needs to be customized/retrained z Experts can intervene, guide the process, if desired; tools provided FAA Workshop May 2003 19
Summary Benefits to FAA z Automated monitoring information acquired by users of the FAA website and alert mechanism for unintentionally revealed information. z Shortlist and identify documents and concepts seen by the user that reveal unintended information z Domain map visualization tool facilitates concept and association based queries Claims z new, richer representation for information retrieval that combines keyword statistics (bag-of-words model) with NLP-based information extraction z Solution is general to any domain; only domain map needs to be customized/retrained z Experts can intervene, guide the process, if desired; tools provided FAA Workshop May 2003 19


