94371b0774627224a24b2b238976a164.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 UHS, Inc. ICD-10 -CM/PCS Physician Education Neurology and Neurosurgery 1
UHS, Inc. ICD-10 -CM/PCS Physician Education Neurology and Neurosurgery 1
 ICD-10 Implementation • October 1, 2015 – Compliance date for implementation of ICD-10 -CM (diagnoses) and ICD-10 -PCS (procedures) – Ambulatory and physician services provided on or after 10/1/15 – Inpatient discharges occurring on or after 10/1/15 • ICD-10 -CM (diagnoses) will be used by all providers in every health care setting • ICD-10 -PCS (procedures) will be used only for hospital claims for inpatient hospital procedures – ICD-10 -PCS will not be used on physician claims, even those for inpatient visits 2
ICD-10 Implementation • October 1, 2015 – Compliance date for implementation of ICD-10 -CM (diagnoses) and ICD-10 -PCS (procedures) – Ambulatory and physician services provided on or after 10/1/15 – Inpatient discharges occurring on or after 10/1/15 • ICD-10 -CM (diagnoses) will be used by all providers in every health care setting • ICD-10 -PCS (procedures) will be used only for hospital claims for inpatient hospital procedures – ICD-10 -PCS will not be used on physician claims, even those for inpatient visits 2
 Why ICD-10 Current ICD-9 Code Set is: – Outdated: 30 years old – Current code structure limits amount of new codes that can be created – Has obsolete groupings of disease families – Lacks specificity and detail to support: • Accurate anatomical positions • Differentiation of risk & severity • Key parameters to differentiate disease manifestations 3
Why ICD-10 Current ICD-9 Code Set is: – Outdated: 30 years old – Current code structure limits amount of new codes that can be created – Has obsolete groupings of disease families – Lacks specificity and detail to support: • Accurate anatomical positions • Differentiation of risk & severity • Key parameters to differentiate disease manifestations 3
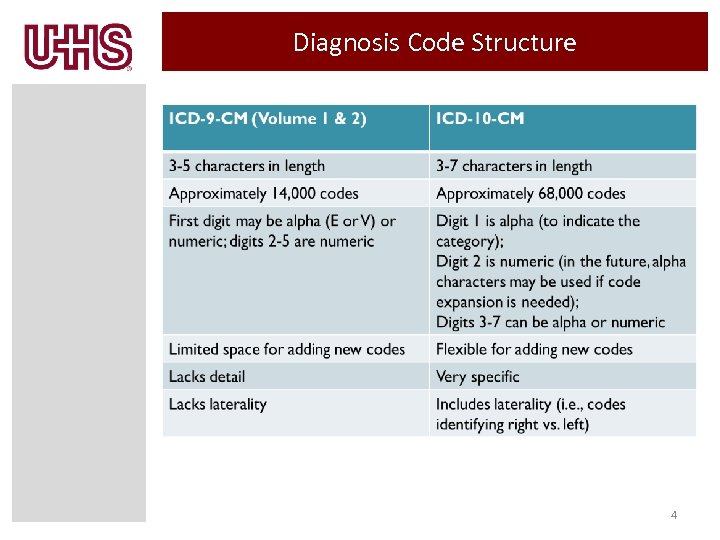 Diagnosis Code Structure 4
Diagnosis Code Structure 4
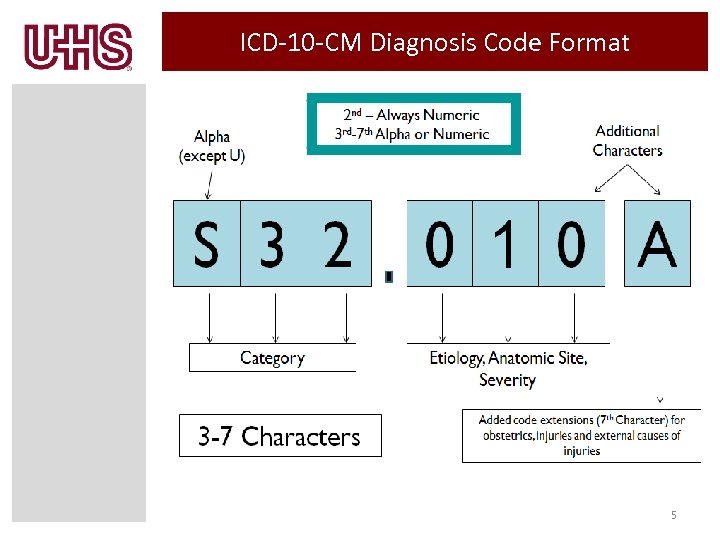 ICD-10 -CM Diagnosis Code Format 5
ICD-10 -CM Diagnosis Code Format 5
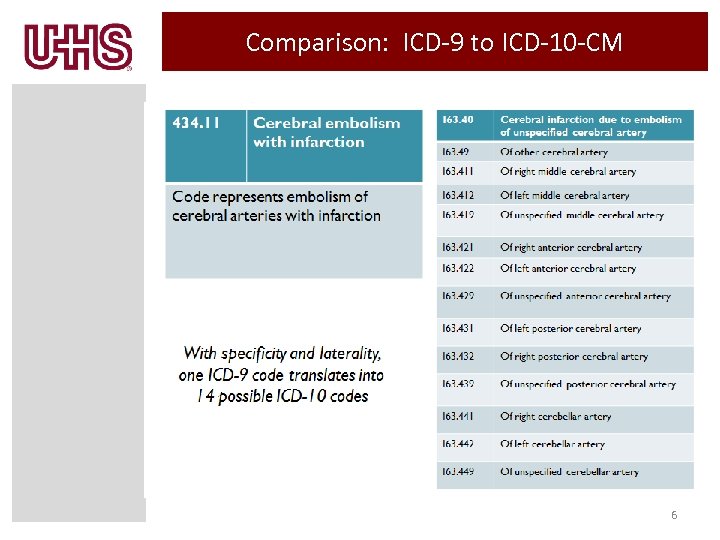 Comparison: ICD-9 to ICD-10 -CM 6
Comparison: ICD-9 to ICD-10 -CM 6
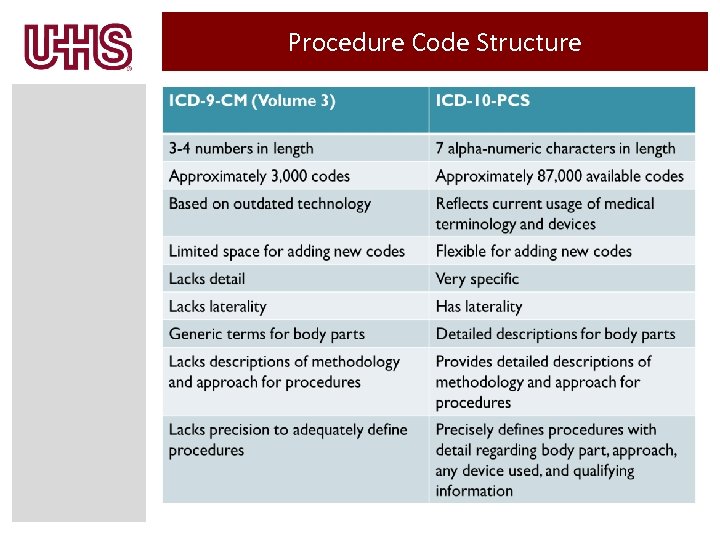 Procedure Code Structure
Procedure Code Structure
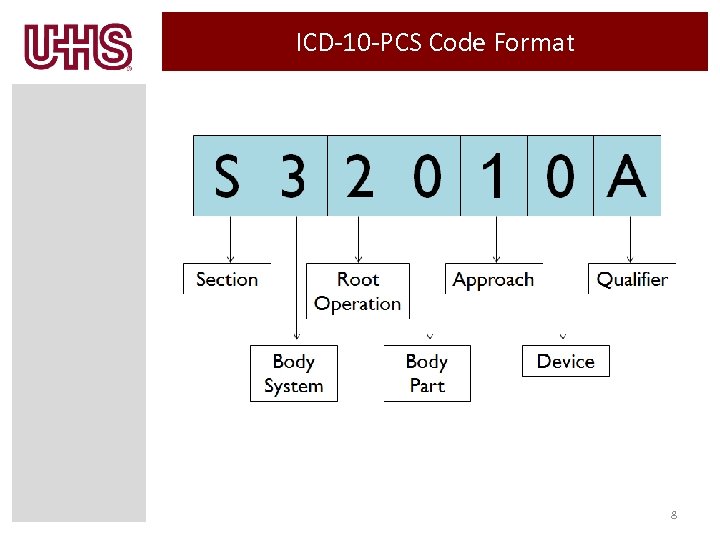 ICD-10 -PCS Code Format 8
ICD-10 -PCS Code Format 8
 ICD-10 Changes Everything! • ICD-10 is a Business Function Change, not just another code set change. • ICD-10 Implementation will impact everyone: – Registration, Nurses, Managers, Lab, Clinical Areas, Billing, Physicians, and Coding • How is ICD-10 going to change what you do? 9
ICD-10 Changes Everything! • ICD-10 is a Business Function Change, not just another code set change. • ICD-10 Implementation will impact everyone: – Registration, Nurses, Managers, Lab, Clinical Areas, Billing, Physicians, and Coding • How is ICD-10 going to change what you do? 9
 ICD-10 -CM/PCS Documentation Tips 10
ICD-10 -CM/PCS Documentation Tips 10
 ICD-10 Provider Impact • Clinical documentation is the foundation of successful ICD 10 Implementation • Golden Rule of Documentation – If it isn’t documented by the physician, it didn’t happen – If it didn’t happen, it can’t be billed • The purpose in documentation is to tell the story of what was performed and what is diagnosed accurately and thoroughly reflecting the condition of the patient – what services were rendered and what is the severity of illness • The key word is SPECIFICITY – Granularity – Laterality • Complete and concise documentation allows for accurate coding and reimbursement 11
ICD-10 Provider Impact • Clinical documentation is the foundation of successful ICD 10 Implementation • Golden Rule of Documentation – If it isn’t documented by the physician, it didn’t happen – If it didn’t happen, it can’t be billed • The purpose in documentation is to tell the story of what was performed and what is diagnosed accurately and thoroughly reflecting the condition of the patient – what services were rendered and what is the severity of illness • The key word is SPECIFICITY – Granularity – Laterality • Complete and concise documentation allows for accurate coding and reimbursement 11
 Gold Standard Documentation Practices 1. Always document diagnoses that contributed to the reason for admission, not just the presenting symptoms 2. Document diagnoses, rather that descriptors 3. Indicate acuity/severity of all diagnoses 4. Link all diseases/diagnoses to their underlying cause 5. Indicate “suspected”, “possible”, or “likely” when treating a condition empirically 6. Use supporting documentation from the dietician / wound care to accurately document nutritional disorders and pressure ulcers 7. Clarify diagnoses that are present on admission 8. Clearly indicate what has been ruled out 9. Avoid the use of arrows and symbols 10. Clarify the significance of diagnostic tests 12
Gold Standard Documentation Practices 1. Always document diagnoses that contributed to the reason for admission, not just the presenting symptoms 2. Document diagnoses, rather that descriptors 3. Indicate acuity/severity of all diagnoses 4. Link all diseases/diagnoses to their underlying cause 5. Indicate “suspected”, “possible”, or “likely” when treating a condition empirically 6. Use supporting documentation from the dietician / wound care to accurately document nutritional disorders and pressure ulcers 7. Clarify diagnoses that are present on admission 8. Clearly indicate what has been ruled out 9. Avoid the use of arrows and symbols 10. Clarify the significance of diagnostic tests 12
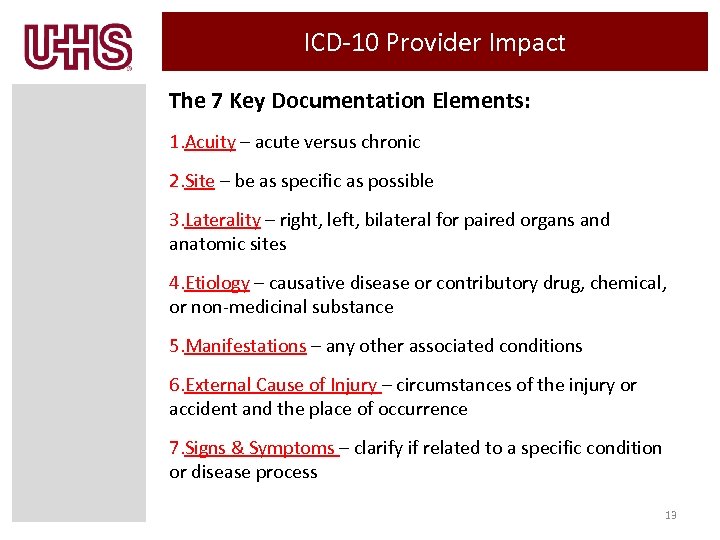 ICD-10 Provider Impact The 7 Key Documentation Elements: 1. Acuity – acute versus chronic 2. Site – be as specific as possible 3. Laterality – right, left, bilateral for paired organs and anatomic sites 4. Etiology – causative disease or contributory drug, chemical, or non-medicinal substance 5. Manifestations – any other associated conditions 6. External Cause of Injury – circumstances of the injury or accident and the place of occurrence 7. Signs & Symptoms – clarify if related to a specific condition or disease process 13
ICD-10 Provider Impact The 7 Key Documentation Elements: 1. Acuity – acute versus chronic 2. Site – be as specific as possible 3. Laterality – right, left, bilateral for paired organs and anatomic sites 4. Etiology – causative disease or contributory drug, chemical, or non-medicinal substance 5. Manifestations – any other associated conditions 6. External Cause of Injury – circumstances of the injury or accident and the place of occurrence 7. Signs & Symptoms – clarify if related to a specific condition or disease process 13
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Do not use symbols to indicate a disease. For example “↑lipids” means that a laboratory result indicates the lipids are elevated – or “↑BP” means that a blood pressure reading is high These are not the same as hyperlipidemia or hypertension 14
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Do not use symbols to indicate a disease. For example “↑lipids” means that a laboratory result indicates the lipids are elevated – or “↑BP” means that a blood pressure reading is high These are not the same as hyperlipidemia or hypertension 14
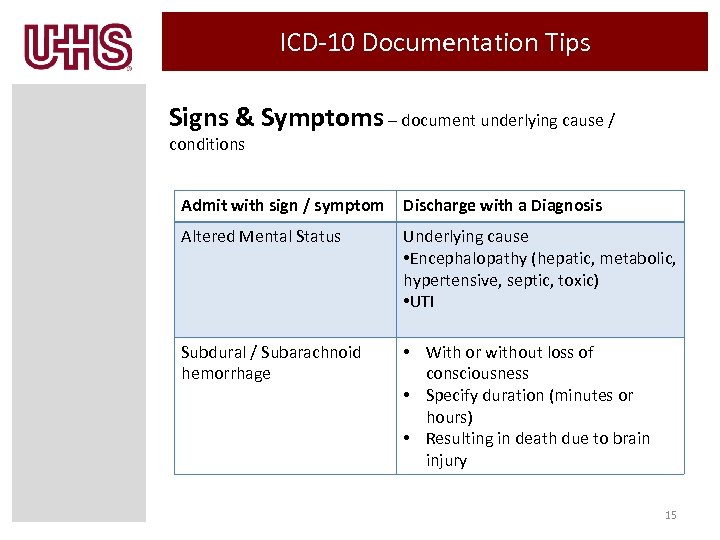 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Signs & Symptoms – document underlying cause / conditions Admit with sign / symptom Discharge with a Diagnosis Altered Mental Status Underlying cause • Encephalopathy (hepatic, metabolic, hypertensive, septic, toxic) • UTI Subdural / Subarachnoid hemorrhage • With or without loss of consciousness • Specify duration (minutes or hours) • Resulting in death due to brain injury 15
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Signs & Symptoms – document underlying cause / conditions Admit with sign / symptom Discharge with a Diagnosis Altered Mental Status Underlying cause • Encephalopathy (hepatic, metabolic, hypertensive, septic, toxic) • UTI Subdural / Subarachnoid hemorrhage • With or without loss of consciousness • Specify duration (minutes or hours) • Resulting in death due to brain injury 15
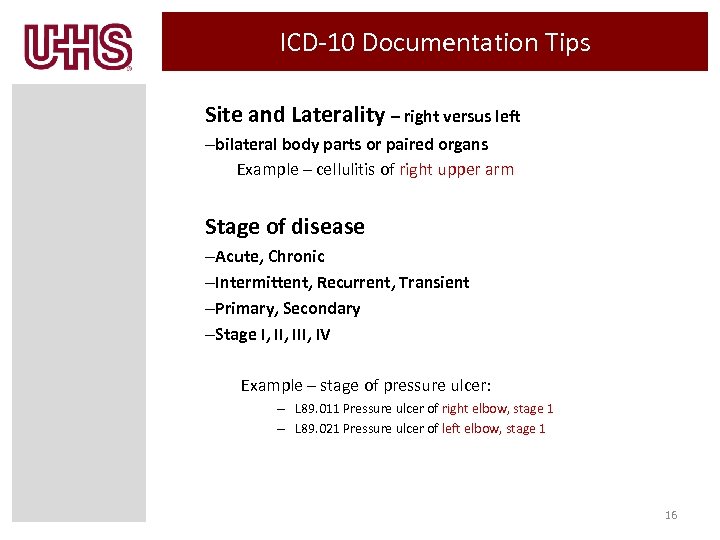 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Site and Laterality – right versus left –bilateral body parts or paired organs Example – cellulitis of right upper arm Stage of disease –Acute, Chronic –Intermittent, Recurrent, Transient –Primary, Secondary –Stage I, III, IV Example – stage of pressure ulcer: – L 89. 011 Pressure ulcer of right elbow, stage 1 – L 89. 021 Pressure ulcer of left elbow, stage 1 16
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Site and Laterality – right versus left –bilateral body parts or paired organs Example – cellulitis of right upper arm Stage of disease –Acute, Chronic –Intermittent, Recurrent, Transient –Primary, Secondary –Stage I, III, IV Example – stage of pressure ulcer: – L 89. 011 Pressure ulcer of right elbow, stage 1 – L 89. 021 Pressure ulcer of left elbow, stage 1 16
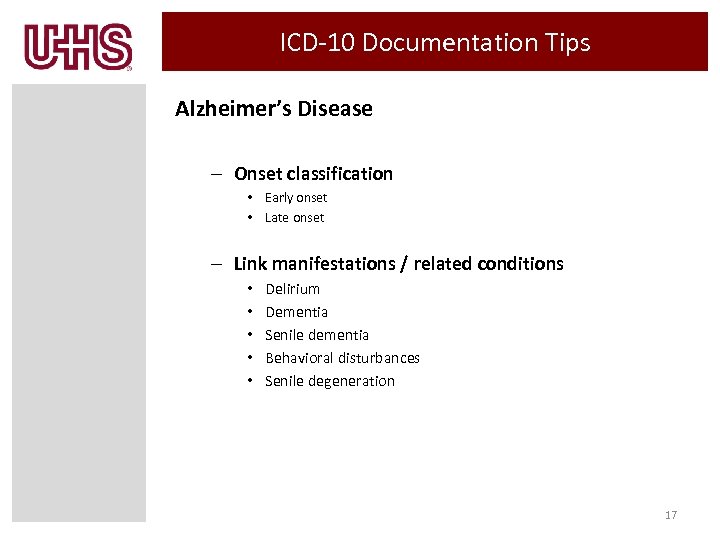 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Alzheimer’s Disease – Onset classification • Early onset • Late onset – Link manifestations / related conditions • • • Delirium Dementia Senile dementia Behavioral disturbances Senile degeneration 17
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Alzheimer’s Disease – Onset classification • Early onset • Late onset – Link manifestations / related conditions • • • Delirium Dementia Senile dementia Behavioral disturbances Senile degeneration 17
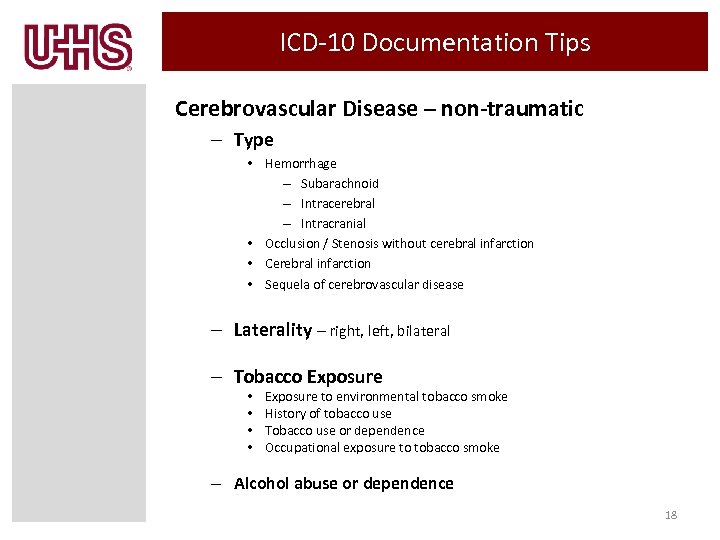 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebrovascular Disease – non-traumatic – Type • Hemorrhage – Subarachnoid – Intracerebral – Intracranial • Occlusion / Stenosis without cerebral infarction • Cerebral infarction • Sequela of cerebrovascular disease – Laterality – right, left, bilateral – Tobacco Exposure • • Exposure to environmental tobacco smoke History of tobacco use Tobacco use or dependence Occupational exposure to tobacco smoke – Alcohol abuse or dependence 18
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebrovascular Disease – non-traumatic – Type • Hemorrhage – Subarachnoid – Intracerebral – Intracranial • Occlusion / Stenosis without cerebral infarction • Cerebral infarction • Sequela of cerebrovascular disease – Laterality – right, left, bilateral – Tobacco Exposure • • Exposure to environmental tobacco smoke History of tobacco use Tobacco use or dependence Occupational exposure to tobacco smoke – Alcohol abuse or dependence 18
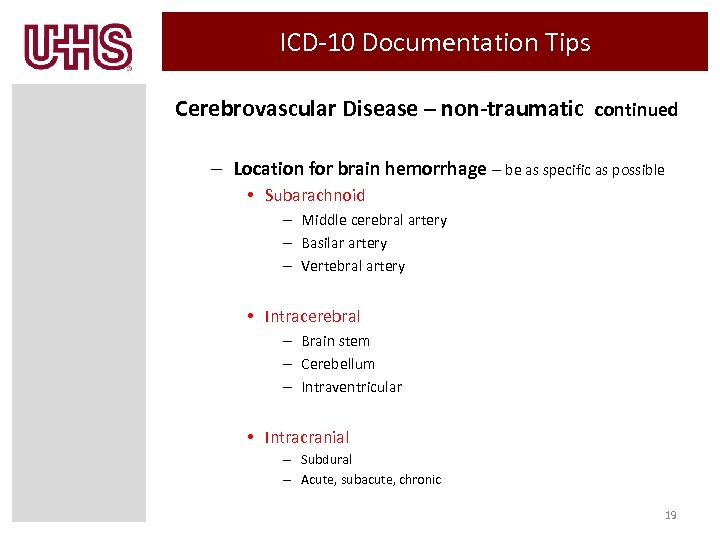 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebrovascular Disease – non-traumatic continued – Location for brain hemorrhage – be as specific as possible • Subarachnoid – Middle cerebral artery – Basilar artery – Vertebral artery • Intracerebral – Brain stem – Cerebellum – Intraventricular • Intracranial – Subdural – Acute, subacute, chronic 19
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebrovascular Disease – non-traumatic continued – Location for brain hemorrhage – be as specific as possible • Subarachnoid – Middle cerebral artery – Basilar artery – Vertebral artery • Intracerebral – Brain stem – Cerebellum – Intraventricular • Intracranial – Subdural – Acute, subacute, chronic 19
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebral Artery Infarction / Stroke Specify the location or source of the hemorrhage and laterality –Document cause – thrombosis, embolism, stenosis –Sites – be as specific as possible • Precerebral – right and left vertebral, basilar, right and left carotid • Cerebral – right and left middle, right and left anterior, right and left posterior, right and left cerebellar –Laterality – right, left, bilateral 20
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebral Artery Infarction / Stroke Specify the location or source of the hemorrhage and laterality –Document cause – thrombosis, embolism, stenosis –Sites – be as specific as possible • Precerebral – right and left vertebral, basilar, right and left carotid • Cerebral – right and left middle, right and left anterior, right and left posterior, right and left cerebellar –Laterality – right, left, bilateral 20
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebral Artery Infarction / Stroke – Document dominant verses non-dominant side • for all paralytic syndromes such as hemiplegia, monoplegia and hemiparesis and for residual effects Example: previous cerebral infarction 6 months ago with residual left-sided hemiparesis on his nondominant side. – Did the patient receive t. PA at a different facility within the 24 hours prior to admission? 21
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Cerebral Artery Infarction / Stroke – Document dominant verses non-dominant side • for all paralytic syndromes such as hemiplegia, monoplegia and hemiparesis and for residual effects Example: previous cerebral infarction 6 months ago with residual left-sided hemiparesis on his nondominant side. – Did the patient receive t. PA at a different facility within the 24 hours prior to admission? 21
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Epilepsy – Epilepsy Type • Idiopathic or symptomatic • Simple or complex partial seizures • Generalized – If intractable, include clarification • • Poorly controlled Pharmacoresistant Treatment resistant Refractory – Document with or without status epilepticus – Seizure - classify as • Febrile, convulsions, new onset, single or hysterical 22
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Epilepsy – Epilepsy Type • Idiopathic or symptomatic • Simple or complex partial seizures • Generalized – If intractable, include clarification • • Poorly controlled Pharmacoresistant Treatment resistant Refractory – Document with or without status epilepticus – Seizure - classify as • Febrile, convulsions, new onset, single or hysterical 22
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Parkinson’s Disease – Type – primary versus secondary • If secondary, specify underlying cause – Malignant neuroleptic – Neuroleptic-induced – Postencephalitic – Vascular – Syphilis – Drug-induced, specify drug – Link manifestations • Dementia • Behavioral disturbance 23
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Parkinson’s Disease – Type – primary versus secondary • If secondary, specify underlying cause – Malignant neuroleptic – Neuroleptic-induced – Postencephalitic – Vascular – Syphilis – Drug-induced, specify drug – Link manifestations • Dementia • Behavioral disturbance 23
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Polyneuropathy – Type • • Hereditary Idiopathic Inflammatory Sequelae – Document underlying cause • • • Diabetes Amyloidosis Radiation-induced Drug-induced, specify the drug Alcohol-induced 24
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Polyneuropathy – Type • • Hereditary Idiopathic Inflammatory Sequelae – Document underlying cause • • • Diabetes Amyloidosis Radiation-induced Drug-induced, specify the drug Alcohol-induced 24
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Glasgow Coma – ICD-10 -CM coding will need the score from each of the assessment areas – Eye opening – Verbal response – Motor response » » R 40. 211 Coma scale, eyes open never R 40. 212 Coma scale, eyes open to pain R 40. 213 Coma scale, eyes open to sound R 40. 214 Coma scale, eyes open spontaneously – Report the Glasgow coma scale total score » R 40. 241 Glasgow coma scale score 13 – 15 » R 40. 242 Glasgow coma scale score 9 - 12 » R 40. 243 Glasgow coma scale score 3 – 8 25
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Glasgow Coma – ICD-10 -CM coding will need the score from each of the assessment areas – Eye opening – Verbal response – Motor response » » R 40. 211 Coma scale, eyes open never R 40. 212 Coma scale, eyes open to pain R 40. 213 Coma scale, eyes open to sound R 40. 214 Coma scale, eyes open spontaneously – Report the Glasgow coma scale total score » R 40. 241 Glasgow coma scale score 13 – 15 » R 40. 242 Glasgow coma scale score 9 - 12 » R 40. 243 Glasgow coma scale score 3 – 8 25
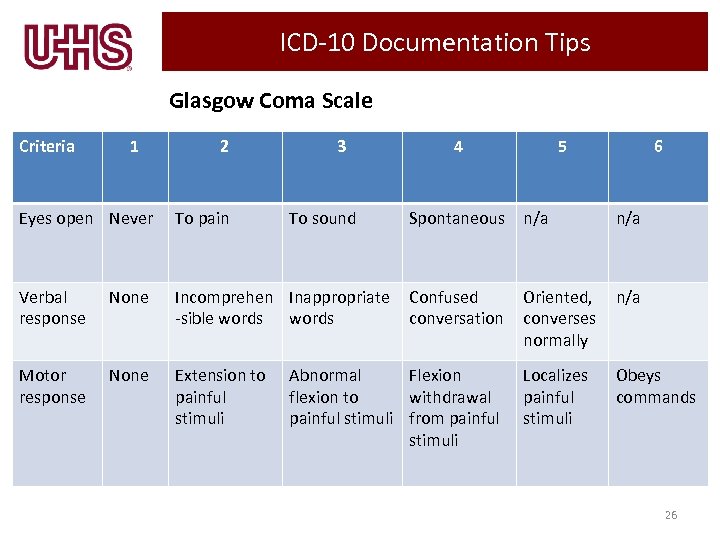 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Glasgow Coma Scale Criteria 1 2 3 Eyes open Never To pain To sound Verbal response None Incomprehen Inappropriate -sible words Motor response None Extension to painful stimuli 4 5 6 Spontaneous n/a Confused conversation Oriented, converses normally n/a Localizes painful stimuli Obeys commands Abnormal Flexion flexion to withdrawal painful stimuli from painful stimuli 26
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Glasgow Coma Scale Criteria 1 2 3 Eyes open Never To pain To sound Verbal response None Incomprehen Inappropriate -sible words Motor response None Extension to painful stimuli 4 5 6 Spontaneous n/a Confused conversation Oriented, converses normally n/a Localizes painful stimuli Obeys commands Abnormal Flexion flexion to withdrawal painful stimuli from painful stimuli 26
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Drug Under-dosing is a new code in ICD-10 -CM. – It identifies situations in which a patient has taken less of a medication than prescribed by the physician. • Intentional versus unintentional – Documentation requirements include: • The medical condition • The patient’s reason for not taking the medication – example – financial reason – Z 91. 120 – Patient’s intentional underdosing of medication due to financial hardship 27
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Drug Under-dosing is a new code in ICD-10 -CM. – It identifies situations in which a patient has taken less of a medication than prescribed by the physician. • Intentional versus unintentional – Documentation requirements include: • The medical condition • The patient’s reason for not taking the medication – example – financial reason – Z 91. 120 – Patient’s intentional underdosing of medication due to financial hardship 27
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Codes for postoperative complications have been expanded and a distinction made between intraoperative complications and postprocedural disorders • The provider must clearly document the relationship between the condition and the procedure – Example: • D 78. 01 –Intraoperative hemorrhage and hematoma of spleen complicating a procedure on the spleen • D 78. 21 –Post-procedural hemorrhage and hematoma of spleen following a procedure on the spleen 28
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Codes for postoperative complications have been expanded and a distinction made between intraoperative complications and postprocedural disorders • The provider must clearly document the relationship between the condition and the procedure – Example: • D 78. 01 –Intraoperative hemorrhage and hematoma of spleen complicating a procedure on the spleen • D 78. 21 –Post-procedural hemorrhage and hematoma of spleen following a procedure on the spleen 28
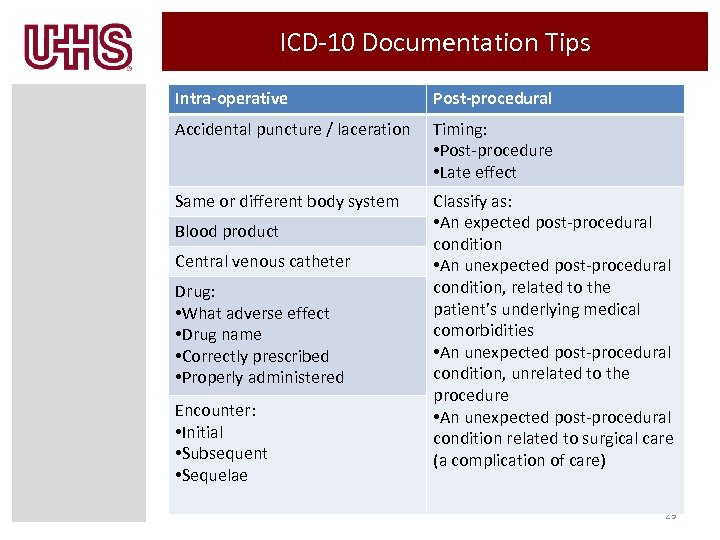 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Intra-operative Post-procedural Accidental puncture / laceration Timing: • Post-procedure • Late effect Same or different body system Classify as: • An expected post-procedural condition • An unexpected post-procedural condition, related to the patient’s underlying medical comorbidities • An unexpected post-procedural condition, unrelated to the procedure • An unexpected post-procedural condition related to surgical care (a complication of care) Blood product Central venous catheter Drug: • What adverse effect • Drug name • Correctly prescribed • Properly administered Encounter: • Initial • Subsequent • Sequelae 29
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Intra-operative Post-procedural Accidental puncture / laceration Timing: • Post-procedure • Late effect Same or different body system Classify as: • An expected post-procedural condition • An unexpected post-procedural condition, related to the patient’s underlying medical comorbidities • An unexpected post-procedural condition, unrelated to the procedure • An unexpected post-procedural condition related to surgical care (a complication of care) Blood product Central venous catheter Drug: • What adverse effect • Drug name • Correctly prescribed • Properly administered Encounter: • Initial • Subsequent • Sequelae 29
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips ICD-10 -PCS does not allow for unspecified procedures, clearly document: • Body System – general physiological system / anatomic region • Root Operation – objective of the procedure • Body Part – specific anatomical site • Approach – technique used to reach the site of the procedure • Device – Devices left at the operative site
ICD-10 Documentation Tips ICD-10 -PCS does not allow for unspecified procedures, clearly document: • Body System – general physiological system / anatomic region • Root Operation – objective of the procedure • Body Part – specific anatomical site • Approach – technique used to reach the site of the procedure • Device – Devices left at the operative site
 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Example – spinal fusion • Root Operation –Fusion • Body Part –Thoracic vertebral joints 2 - 7 • Approach – Open (anterior/posterior) and Column (anterior/posterior) • Device –Autologous tissue substitute
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Example – spinal fusion • Root Operation –Fusion • Body Part –Thoracic vertebral joints 2 - 7 • Approach – Open (anterior/posterior) and Column (anterior/posterior) • Device –Autologous tissue substitute
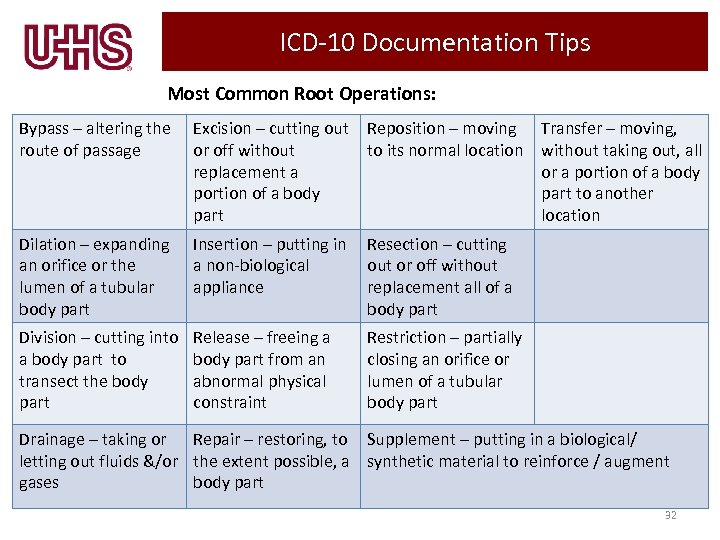 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Most Common Root Operations: Bypass – altering the route of passage Excision – cutting out or off without replacement a portion of a body part Reposition – moving Transfer – moving, to its normal location without taking out, all or a portion of a body part to another location Dilation – expanding an orifice or the lumen of a tubular body part Insertion – putting in a non-biological appliance Resection – cutting out or off without replacement all of a body part Division – cutting into a body part to transect the body part Release – freeing a body part from an abnormal physical constraint Restriction – partially closing an orifice or lumen of a tubular body part Drainage – taking or Repair – restoring, to Supplement – putting in a biological/ letting out fluids &/or the extent possible, a synthetic material to reinforce / augment gases body part 32
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Most Common Root Operations: Bypass – altering the route of passage Excision – cutting out or off without replacement a portion of a body part Reposition – moving Transfer – moving, to its normal location without taking out, all or a portion of a body part to another location Dilation – expanding an orifice or the lumen of a tubular body part Insertion – putting in a non-biological appliance Resection – cutting out or off without replacement all of a body part Division – cutting into a body part to transect the body part Release – freeing a body part from an abnormal physical constraint Restriction – partially closing an orifice or lumen of a tubular body part Drainage – taking or Repair – restoring, to Supplement – putting in a biological/ letting out fluids &/or the extent possible, a synthetic material to reinforce / augment gases body part 32
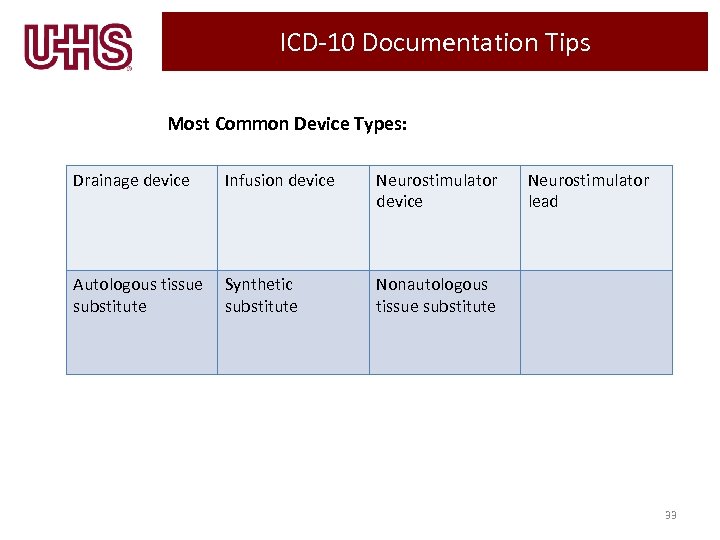 ICD-10 Documentation Tips Most Common Device Types: Drainage device Infusion device Neurostimulator device Autologous tissue substitute Synthetic substitute Neurostimulator lead Nonautologous tissue substitute 33
ICD-10 Documentation Tips Most Common Device Types: Drainage device Infusion device Neurostimulator device Autologous tissue substitute Synthetic substitute Neurostimulator lead Nonautologous tissue substitute 33
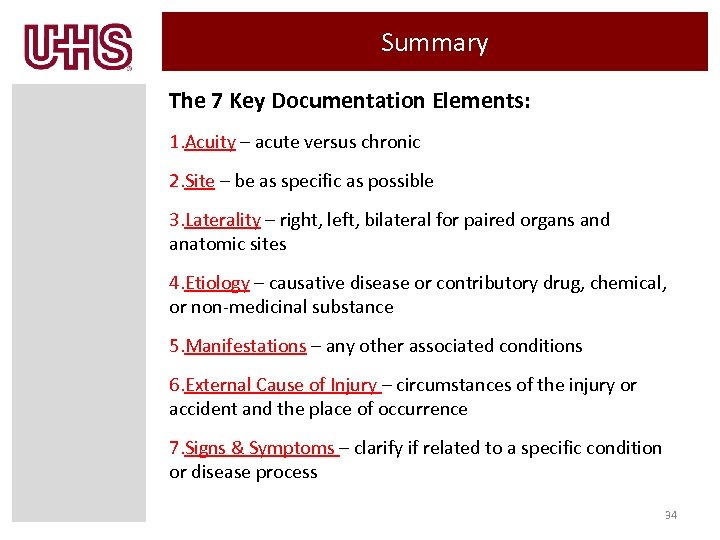 Summary The 7 Key Documentation Elements: 1. Acuity – acute versus chronic 2. Site – be as specific as possible 3. Laterality – right, left, bilateral for paired organs and anatomic sites 4. Etiology – causative disease or contributory drug, chemical, or non-medicinal substance 5. Manifestations – any other associated conditions 6. External Cause of Injury – circumstances of the injury or accident and the place of occurrence 7. Signs & Symptoms – clarify if related to a specific condition or disease process 34
Summary The 7 Key Documentation Elements: 1. Acuity – acute versus chronic 2. Site – be as specific as possible 3. Laterality – right, left, bilateral for paired organs and anatomic sites 4. Etiology – causative disease or contributory drug, chemical, or non-medicinal substance 5. Manifestations – any other associated conditions 6. External Cause of Injury – circumstances of the injury or accident and the place of occurrence 7. Signs & Symptoms – clarify if related to a specific condition or disease process 34


