5943c0ccfc36e019e56076397258f28e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 UFCEKP-20 -2 Client Server Programming Jin Sa http: //www. cems. uwe. ac. uk/~jsa/Client. Server 08/ Julia Dawson http: //squanderette. co. uk/ufcekp/ 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 1
UFCEKP-20 -2 Client Server Programming Jin Sa http: //www. cems. uwe. ac. uk/~jsa/Client. Server 08/ Julia Dawson http: //squanderette. co. uk/ufcekp/ 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 1
 What is this module about? • Aim of the module, what you should be able to do by the end of module • Content of the module • How is the module delivered • How are you assessed • Where can you find resources 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 2
What is this module about? • Aim of the module, what you should be able to do by the end of module • Content of the module • How is the module delivered • How are you assessed • Where can you find resources 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 2
 Aim of the module • By the end of the module you should be able to develop programs that implement simple network applications based on some protocols using a number of techniques. • This leads to these questions: – What do we mean by network applications and protocols? – What are the implementation techniques? – What programming language do we use? 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 3
Aim of the module • By the end of the module you should be able to develop programs that implement simple network applications based on some protocols using a number of techniques. • This leads to these questions: – What do we mean by network applications and protocols? – What are the implementation techniques? – What programming language do we use? 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 3
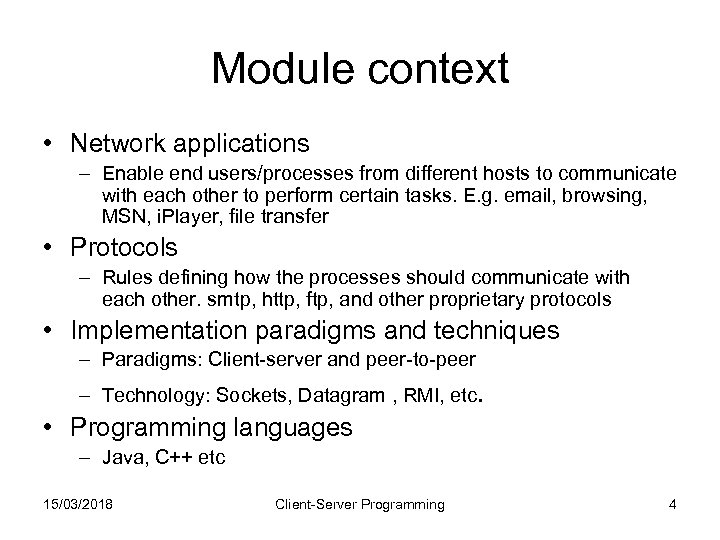 Module context • Network applications – Enable end users/processes from different hosts to communicate with each other to perform certain tasks. E. g. email, browsing, MSN, i. Player, file transfer • Protocols – Rules defining how the processes should communicate with each other. smtp, http, ftp, and other proprietary protocols • Implementation paradigms and techniques – Paradigms: Client-server and peer-to-peer – Technology: Sockets, Datagram , RMI, etc. • Programming languages – Java, C++ etc 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 4
Module context • Network applications – Enable end users/processes from different hosts to communicate with each other to perform certain tasks. E. g. email, browsing, MSN, i. Player, file transfer • Protocols – Rules defining how the processes should communicate with each other. smtp, http, ftp, and other proprietary protocols • Implementation paradigms and techniques – Paradigms: Client-server and peer-to-peer – Technology: Sockets, Datagram , RMI, etc. • Programming languages – Java, C++ etc 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 4
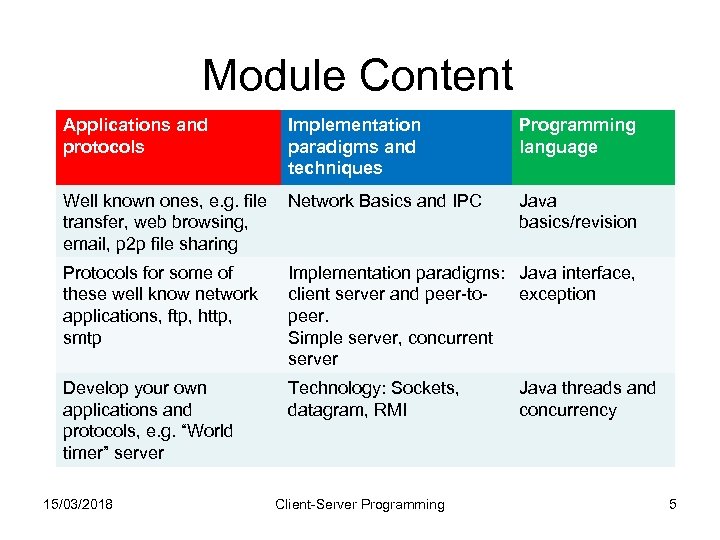 Module Content Applications and protocols Implementation paradigms and techniques Well known ones, e. g. file Network Basics and IPC transfer, web browsing, email, p 2 p file sharing Programming language Java basics/revision Protocols for some of these well know network applications, ftp, http, smtp Implementation paradigms: Java interface, client server and peer-toexception peer. Simple server, concurrent server Develop your own applications and protocols, e. g. “World timer” server Technology: Sockets, datagram, RMI 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming Java threads and concurrency 5
Module Content Applications and protocols Implementation paradigms and techniques Well known ones, e. g. file Network Basics and IPC transfer, web browsing, email, p 2 p file sharing Programming language Java basics/revision Protocols for some of these well know network applications, ftp, http, smtp Implementation paradigms: Java interface, client server and peer-toexception peer. Simple server, concurrent server Develop your own applications and protocols, e. g. “World timer” server Technology: Sockets, datagram, RMI 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming Java threads and concurrency 5
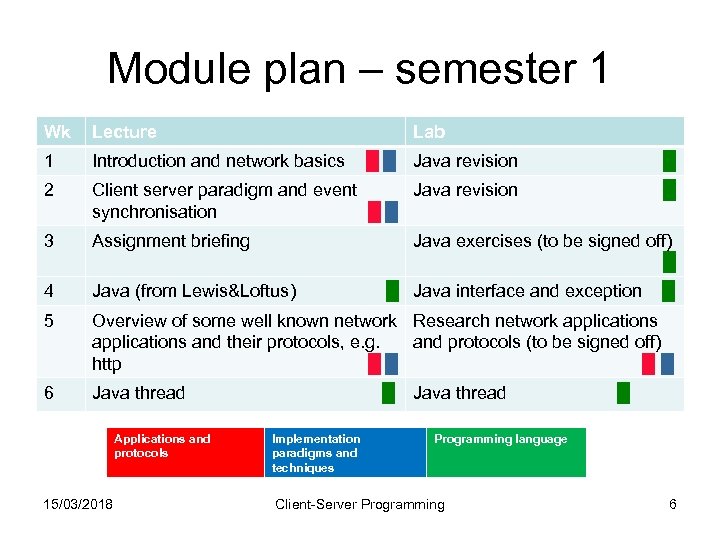 Module plan – semester 1 Wk Lecture 1 Introduction and network basics █ █ Java revision █ 2 Client server paradigm and event Java revision █ synchronisation █ █ 3 Assignment briefing 4 Java (from Lewis&Loftus) █ Java interface and exception █ 5 Overview of some well known network Research network applications and their protocols, e. g. and protocols (to be signed off) http █ █ 6 Java thread █ Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 Lab Java exercises (to be signed off) █ Implementation paradigms and techniques Java thread █ Programming language Client-Server Programming 6
Module plan – semester 1 Wk Lecture 1 Introduction and network basics █ █ Java revision █ 2 Client server paradigm and event Java revision █ synchronisation █ █ 3 Assignment briefing 4 Java (from Lewis&Loftus) █ Java interface and exception █ 5 Overview of some well known network Research network applications and their protocols, e. g. and protocols (to be signed off) http █ █ 6 Java thread █ Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 Lab Java exercises (to be signed off) █ Implementation paradigms and techniques Java thread █ Programming language Client-Server Programming 6
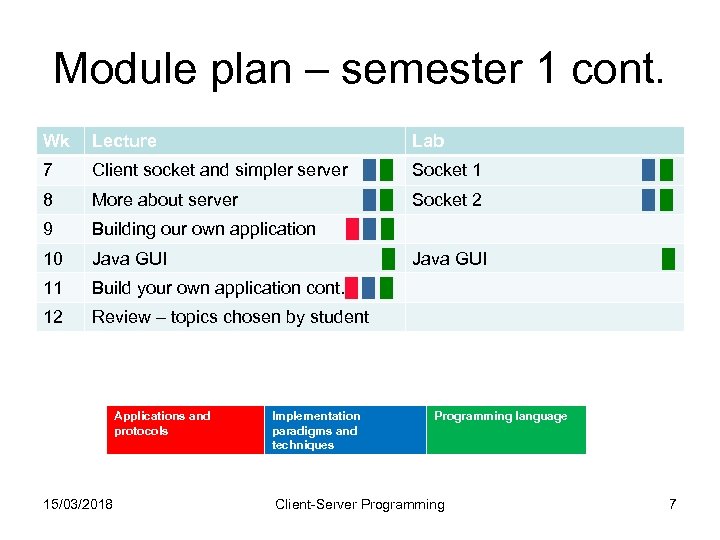 Module plan – semester 1 cont. Wk Lecture 7 Client socket and simpler server █ █ Socket 1 █ █ 8 More about server █ █ Socket 2 █ █ 9 Building our own application █ █ █ 10 Java GUI █ Java GUI █ 11 Build your own application cont. █ █ █ 12 Review – topics chosen by student Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 Lab Implementation paradigms and techniques Programming language Client-Server Programming 7
Module plan – semester 1 cont. Wk Lecture 7 Client socket and simpler server █ █ Socket 1 █ █ 8 More about server █ █ Socket 2 █ █ 9 Building our own application █ █ █ 10 Java GUI █ Java GUI █ 11 Build your own application cont. █ █ █ 12 Review – topics chosen by student Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 Lab Implementation paradigms and techniques Programming language Client-Server Programming 7
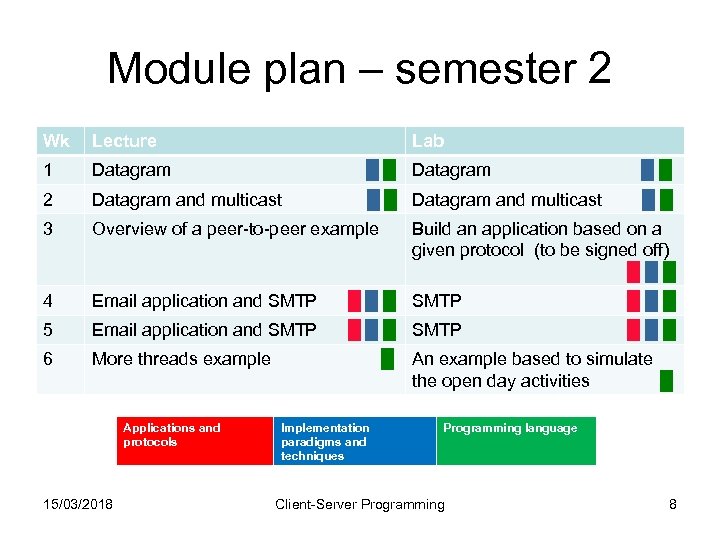 Module plan – semester 2 Wk Lecture 1 Datagram █ █ Datagram █ █ 2 Datagram and multicast █ █ Datagram and multicast █ █ 3 Overview of a peer-to-peer example 4 Email application and SMTP █ █ █ SMTP █ █ █ 5 Email application and SMTP █ █ █ SMTP █ █ █ 6 More threads example █ Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 Lab Implementation paradigms and techniques Build an application based on a given protocol (to be signed off) █ █ █ An example based to simulate the open day activities █ Programming language Client-Server Programming 8
Module plan – semester 2 Wk Lecture 1 Datagram █ █ Datagram █ █ 2 Datagram and multicast █ █ Datagram and multicast █ █ 3 Overview of a peer-to-peer example 4 Email application and SMTP █ █ █ SMTP █ █ █ 5 Email application and SMTP █ █ █ SMTP █ █ █ 6 More threads example █ Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 Lab Implementation paradigms and techniques Build an application based on a given protocol (to be signed off) █ █ █ An example based to simulate the open day activities █ Programming language Client-Server Programming 8
 Module plan – semester 2 cont. Wk Lecture Lab 7 RMI █ █ 8 RMI cont. █ █ RMI █ █ 9 Revision 10 CSP in context – related issues Easter break 11 Assignment feedback 12 Review – topics chosen by student Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 More applications Implementation paradigms and techniques Programming language Client-Server Programming 9
Module plan – semester 2 cont. Wk Lecture Lab 7 RMI █ █ 8 RMI cont. █ █ RMI █ █ 9 Revision 10 CSP in context – related issues Easter break 11 Assignment feedback 12 Review – topics chosen by student Applications and protocols 15/03/2018 More applications Implementation paradigms and techniques Programming language Client-Server Programming 9
 Delivery and Assessment • One lecture and one practical per week • Assessment consists of one exam (50%) and one assignment (50%). 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 10
Delivery and Assessment • One lecture and one practical per week • Assessment consists of one exam (50%) and one assignment (50%). 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 10
 Resources • “Java Network Programming”, 3 rd edition, by Elliotte Rusty Harold, published by O‘Reilly • “Computer Networking: A top-down approach”, Fourth edition, by Kurose and Ross, published by Pearson Addison Wesley, chapter 1 Computer network and the Internet, chapter 2 Application layer • Some of the tutorials from http: //java. sun. com/docs/books/tutorial/networking/ • Some of the tutorials from http: //java. sun. com/docs/books/tutorial/essential/ • “Distributed Systems Concepts and Design”, 4 th edition, by Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg, published by Addison Wesley. Chapter 4 Interprocess comminucations • “Java Software Solutions”, 5 th (International) ed, Lewis and Loftus (2006). Addison-Wesley 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 11
Resources • “Java Network Programming”, 3 rd edition, by Elliotte Rusty Harold, published by O‘Reilly • “Computer Networking: A top-down approach”, Fourth edition, by Kurose and Ross, published by Pearson Addison Wesley, chapter 1 Computer network and the Internet, chapter 2 Application layer • Some of the tutorials from http: //java. sun. com/docs/books/tutorial/networking/ • Some of the tutorials from http: //java. sun. com/docs/books/tutorial/essential/ • “Distributed Systems Concepts and Design”, 4 th edition, by Coulouris, Dollimore and Kindberg, published by Addison Wesley. Chapter 4 Interprocess comminucations • “Java Software Solutions”, 5 th (International) ed, Lewis and Loftus (2006). Addison-Wesley 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 11
 Basic network concepts and the Internet • Outline of the rest of the unit – – – – Distributed system Types of networks Internet provides services to network applications Protocols Network architecture TCP/IP protocols suite Connection-oriented and connectionless communications – Network resources – Addressing a process running on a host 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 12
Basic network concepts and the Internet • Outline of the rest of the unit – – – – Distributed system Types of networks Internet provides services to network applications Protocols Network architecture TCP/IP protocols suite Connection-oriented and connectionless communications – Network resources – Addressing a process running on a host 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 12
 Distributed system • In Coulouris et al “We define a distributed system as one in which hardware or software components located at networked computers communicate and coordinate their actions only by passing messages. ” 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 13
Distributed system • In Coulouris et al “We define a distributed system as one in which hardware or software components located at networked computers communicate and coordinate their actions only by passing messages. ” 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 13
 Types of network • • Local area networks (LAN), e. g. Ethernet Wide area network (WAN) Internetwork, e. g. Internet Wireless local area network (WLAN), e. g. Wi. Fi • Etc. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 14
Types of network • • Local area networks (LAN), e. g. Ethernet Wide area network (WAN) Internetwork, e. g. Internet Wireless local area network (WLAN), e. g. Wi. Fi • Etc. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 14
 A typical intranet 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 15
A typical intranet 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 15
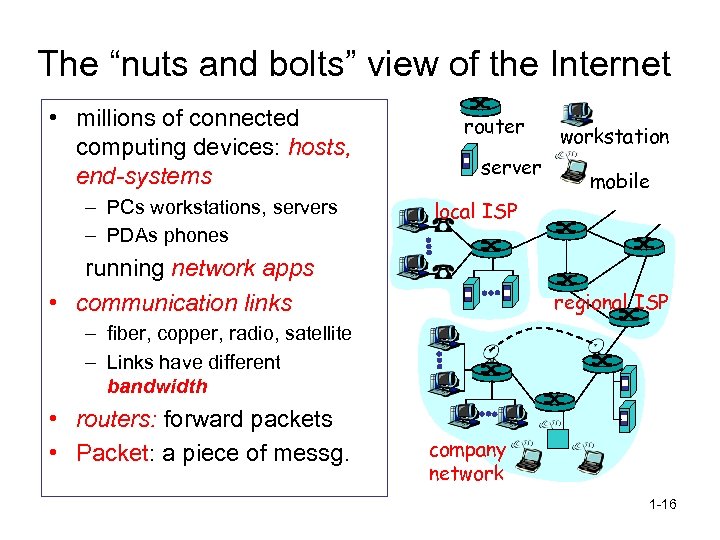 The “nuts and bolts” view of the Internet • millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems – PCs workstations, servers – PDAs phones router server workstation mobile local ISP running network apps • communication links regional ISP – fiber, copper, radio, satellite – Links have different bandwidth • routers: forward packets • Packet: a piece of messg. company network 1 -16
The “nuts and bolts” view of the Internet • millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end-systems – PCs workstations, servers – PDAs phones router server workstation mobile local ISP running network apps • communication links regional ISP – fiber, copper, radio, satellite – Links have different bandwidth • routers: forward packets • Packet: a piece of messg. company network 1 -16
 Internet provides services to network applications • Applications: email, web surfing, instant messaging, Vo. IP, distributed games, P 2 P file sharing, remote login etc. • Applications are distributed involving multiple end systems exchanging data with each other. • End systems provide services defined as Application Programming Interface (API) • So the Internet is an infrastructure for providing services to network applications. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 17
Internet provides services to network applications • Applications: email, web surfing, instant messaging, Vo. IP, distributed games, P 2 P file sharing, remote login etc. • Applications are distributed involving multiple end systems exchanging data with each other. • End systems provide services defined as Application Programming Interface (API) • So the Internet is an infrastructure for providing services to network applications. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 17
 Network standards and protocols • When two or more processes communicate with each other, in order to accomplish a task, they need to follow some rules that decide how and when they can communicate with each other. • Such rules, called protocols, specify such matters as the formatting and semantics of data, flow control. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 18
Network standards and protocols • When two or more processes communicate with each other, in order to accomplish a task, they need to follow some rules that decide how and when they can communicate with each other. • Such rules, called protocols, specify such matters as the formatting and semantics of data, flow control. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 18
 Protocol (taken from Wiki) • In computing, a protocol is a convention or standard that controls or enables the connection, communication, and data transfer between two computing endpoints. In its simplest form, a protocol can be defined as the rules governing the syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 19
Protocol (taken from Wiki) • In computing, a protocol is a convention or standard that controls or enables the connection, communication, and data transfer between two computing endpoints. In its simplest form, a protocol can be defined as the rules governing the syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 19
 Example Protocols • Network applications need to have protocols associated with them. Examples are: – Email: SMTP – Web surfing: HTTP – File transfer: FTP – Getting the daytime: Daytime protocol • Protocols are defined in layers 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 20
Example Protocols • Network applications need to have protocols associated with them. Examples are: – Email: SMTP – Web surfing: HTTP – File transfer: FTP – Getting the daytime: Daytime protocol • Protocols are defined in layers 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 20
 Network architecture The division of the layers is conceptual: the implementation of the functionalities need not be clearly divided. The conceptual division serves at least two useful purposes : 1. it allows protocols to be specified systematically 2. it allows programs to be written in terms of logical data flow 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 21
Network architecture The division of the layers is conceptual: the implementation of the functionalities need not be clearly divided. The conceptual division serves at least two useful purposes : 1. it allows protocols to be specified systematically 2. it allows programs to be written in terms of logical data flow 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 21
 Protocol layers in the ISO model 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 22
Protocol layers in the ISO model 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 22
 The TCP/IP protocol suite • The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol suite is a set of network protocols which supports the following network architecture. • It is currently the protocol suite employed on the Internet. • Java’s network classes are based on the TCP/IP protocol 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 23
The TCP/IP protocol suite • The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol suite is a set of network protocols which supports the following network architecture. • It is currently the protocol suite employed on the Internet. • Java’s network classes are based on the TCP/IP protocol 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 23
 The TCP/IP protocol suite • The Internet layer implements the Internet Protocol, which provides the functionalities for allowing data to be transmitted between any two hosts on the Internet. • The Application layer gives an application access to the communication environment. Examples of protocols found at this layer are Telnet, FTP, HTTP and SMTP • The Transport layer provides delivery services for the application layer. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are at the transport layer • The internetwork layer is responsible for the routing and delivery of data across networks. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 24
The TCP/IP protocol suite • The Internet layer implements the Internet Protocol, which provides the functionalities for allowing data to be transmitted between any two hosts on the Internet. • The Application layer gives an application access to the communication environment. Examples of protocols found at this layer are Telnet, FTP, HTTP and SMTP • The Transport layer provides delivery services for the application layer. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are at the transport layer • The internetwork layer is responsible for the routing and delivery of data across networks. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 24
 TCP and UDP • TCP is a reliable, connection-oriented protocol that provides error checking and flow control through a virtual link. This gives a reliable service, therefore TCP would be utilized, for example, by file transfer and email delivery. • UDP is an unreliable, connectionless protocol that provides data transport with lower network traffic overheads than TCP - UDP does not error check or offer any flow control, this is left to the application process. Applications such as short transaction and Vo. IP use UDP. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 25
TCP and UDP • TCP is a reliable, connection-oriented protocol that provides error checking and flow control through a virtual link. This gives a reliable service, therefore TCP would be utilized, for example, by file transfer and email delivery. • UDP is an unreliable, connectionless protocol that provides data transport with lower network traffic overheads than TCP - UDP does not error check or offer any flow control, this is left to the application process. Applications such as short transaction and Vo. IP use UDP. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 25
 Connection-oriented and connectionless communication Connection-oriented connectionless Addressing At connection time With each packet Connection Establishing connection N/A Data delivery Maintain order Protocols 15/03/2018 Difficult to main order TCP: Exchange large UDP: Small amount of stream and/or number of data in limited rounds of data, e. g. file exchanges, Vo. IP transfer Client-Server Programming 26
Connection-oriented and connectionless communication Connection-oriented connectionless Addressing At connection time With each packet Connection Establishing connection N/A Data delivery Maintain order Protocols 15/03/2018 Difficult to main order TCP: Exchange large UDP: Small amount of stream and/or number of data in limited rounds of data, e. g. file exchanges, Vo. IP transfer Client-Server Programming 26
 How does this module fits • In this module, we will be concerned with developing applications at the Application layer using the services provided at the Transport layer (and the layers below). • The Java network classes are based on the TCP/IP protocols. Hence we can use the APIs provided in these classes to write Java programs for the application layer. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 27
How does this module fits • In this module, we will be concerned with developing applications at the Application layer using the services provided at the Transport layer (and the layers below). • The Java network classes are based on the TCP/IP protocols. Hence we can use the APIs provided in these classes to write Java programs for the application layer. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 27
 Network resources • Network resources are resources available to the participants of a distributed computing community. • Network resources include hardware such as computers and equipment, and software such as processes, emailboxes, files, web documents. • An important class of network resources is network services such as the Web and file transfer, which are provided by specific processes running on computers. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 28
Network resources • Network resources are resources available to the participants of a distributed computing community. • Network resources include hardware such as computers and equipment, and software such as processes, emailboxes, files, web documents. • An important class of network resources is network services such as the Web and file transfer, which are provided by specific processes running on computers. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 28
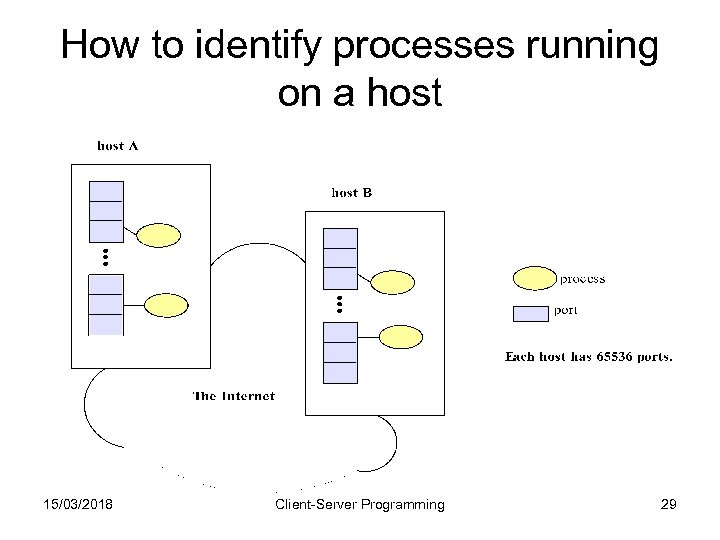 How to identify processes running on a host 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 29
How to identify processes running on a host 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 29
 Identifying processes with ports • Domain names (or IP addresses) locate computers (hosts) • The logical entity port is used to identify a process running on a host • In the transport layer, both TCP and UDP use ports on each host for dispatching data to processes • A process that wishes to exchange data with another process must be assigned a port • To send data to a process associated with port p on host H, an applicatin programm must address the data to (H, p) in the code. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 30
Identifying processes with ports • Domain names (or IP addresses) locate computers (hosts) • The logical entity port is used to identify a process running on a host • In the transport layer, both TCP and UDP use ports on each host for dispatching data to processes • A process that wishes to exchange data with another process must be assigned a port • To send data to a process associated with port p on host H, an applicatin programm must address the data to (H, p) in the code. 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 30
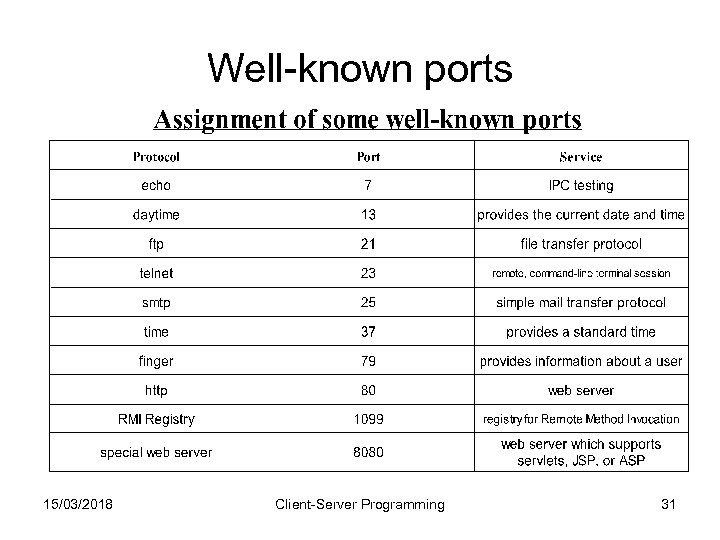 Well-known ports 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 31
Well-known ports 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 31
 Review questions • • • What is a network application? What is a protocol? What is the TCP/IP protocol? What are TCP and UDP? Explain the concepts of connection-oriented communication and connectionless communication • Understand how to address Internet host; how to address a running process 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 32
Review questions • • • What is a network application? What is a protocol? What is the TCP/IP protocol? What are TCP and UDP? Explain the concepts of connection-oriented communication and connectionless communication • Understand how to address Internet host; how to address a running process 15/03/2018 Client-Server Programming 32


