b8c2150442b0636566b80796def27586.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

UBC’s e-Strategy: u. Portal and Open Source Applications Presented to Mc. Gill University Portal Executive Committee October 24, 2003 Ted Dodds, CIO, University of British Columbia
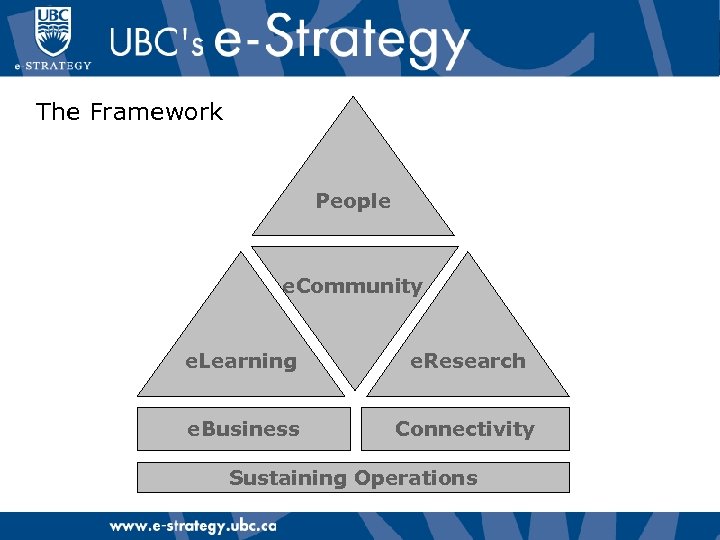
The Framework People e. Community e. Learning e. Research e. Business Connectivity Sustaining Operations

u. Portal at UBC Very early adopter – Partly defensive to “free” portal vendors of the day – u. Portal has outlasted initial competition Collaborative development – – Contracted with IBS in early 2000 Development and (Java) skills transfer Rebuild application development capacity in ITServices Regular multi-institution developers meetings ongoing

u. Portal at UBC “my. UBC” in production September 2000 – – u. Portal “ 0. 9” Main channels: web-mail, SIS, calendar Adoption targeted at incoming cohort (~5, 000) Use grew rapidly to 34, 000 users, primarily students First mover benefits – – UBC was early contributor to JA-SIG clearinghouse Continue to contribute Also seek to leverage contributions of others Upgraded to u. Portal 2. 0 rather recently
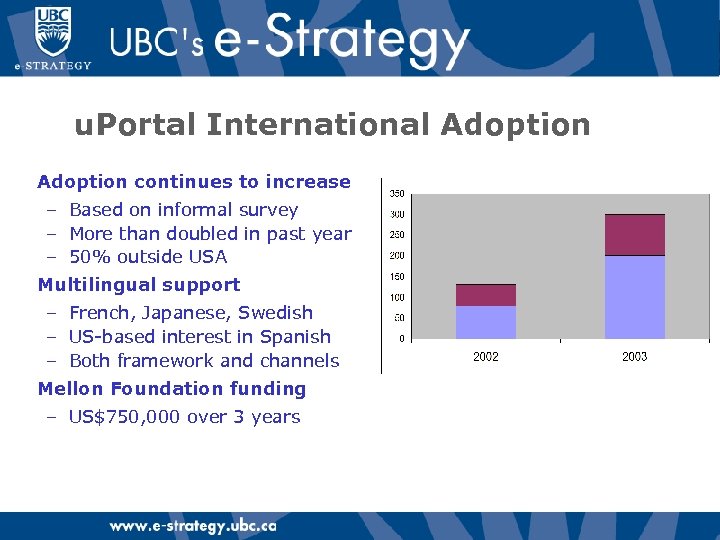
u. Portal International Adoption continues to increase – Based on informal survey – More than doubled in past year – 50% outside USA Multilingual support – French, Japanese, Swedish – US-based interest in Spanish – Both framework and channels Mellon Foundation funding – US$750, 000 over 3 years

u. Portal Current and Future Info. World Nov 7/2003 – Nominated for Top 100 software products Development plans for 3. 0 – JSR 168 enabled (standard portlets) – WSRP Remote Portlet Consumer (remote producer) – Delivery date TBA, possible mid-2004 JSR 168 “portlets” – Pluggable user interface components that provide a presentation layer to Information Systems
u. Portal and the “Portal Business” 1 Turning from portal software to – Adapters and connectors – Implementation expertise and services Portal frameworks becoming standard/commodity – Applications becoming focus, hence JSR 168 Risk of implementation failure – Primary cause: lack of content (“empty” portal) – Gartner: 20% is shelfware – Meta: 30% failure rate (better than IT average!) Source: Jim Farmer’s report on Enterprise Portals Conference, Chicago, Sept. 30/2003

u. Portal and the “Portal Business” u. Portal continues to compete favourably – User base, technology, open standards – SAKAI would augment u. Portal’s position in Higher Ed. Open Source can complement commercial – Luminous product based on u. Portal – Unicon (formerly IBS) continued engagement and commitment – Open really means open

SAKAI Project Five member consortium – – – Michigan MIT Indiana u. Portal OKI Purpose – – “Code mobility” through open source Overcome technical and timing challenges Portal and CMS – Fall 2004 Existing IP integrated – Fall 2005

Related Open Source Projects SAKAI institutions offer extensive code base – Institutional level commitment to open source – Belief that sharing provides greater value than individual attempts to commercialize local innovation Appications sampler – – – Course management (CHEF, Michigan) Content management (CUCMS, Columbia) Workflow (EDEN, Indiana) Personal information (Chandler, OSAF) Portal (u. Portal, JA-SIG) Identity management (CAS, Yale)

Institutional Collaboration SAKAI Model – More examples of collaboration in US than Canada – Networking a possible exception – UBC and UCB § Actively discussing joint projects Canadian Collaboration – Mc. Gill and UBC appear to have similar vision – Focusing on end-user (productivity, effectiveness, service) – Opportunity to explore common needs and collaboration possibilities
b8c2150442b0636566b80796def27586.ppt