f5c588281de196b1cf68d31ee639d8ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

UBC Mechanics Based Modeling of the Dynamic Response of Wood Frame Building By Ricardo Foschi, Frank Lam, Helmut Prion, Carlos Ventura Henry He and Felix Yao University of B. C. CUREe-Caltech Woodframe Project Element 1 - Researchers Meeting University of California, San Diego January 2001

UBC Research Project: Reliability and Design of Innovative Wood Structures under Earthquake and Extreme Wind Conditions Combined analytical and experimental studies to evaluate the performance of wood frame structures l Reliability procedures to consider the randomness of loading and system response l Funded by Forest Renewal BC l Collaborations with CUREe-Caltech Woodframe Project l

UBC TEAM l Principal researchers: R. O. Foschi, F. Lam, H. Prion, & C. Ventura l F. Yao, H. Li, Y. T. Wang – Structural Analysis, Reliability H. He - Modeling and testing of simple 3 D structures M. Popovski - Glulam frames D. Moses, N. Allotey, A. Schreyer - Nail & bolted connections R. Mastschuch, B. Sjoberg - Reinforced bolted connections N. Richard, P. Welzel - Openings M. Stefanescu, G. Finckenstein - Japanese Post & Beam Frames Full scale shake table testing of 2 storey buildings l l l l
3 -D Model of Wall Systems l Develop and verify 3 D structural analysis model with mechanics based nail hysteresis subroutine – Model Development – Input Data – Full Scale Test Data Completed verification of static, cyclic and dynamic behaviour (2 D) l Completed verification of static behaviour (3 D) l – (PI: ROF, FL – HH)
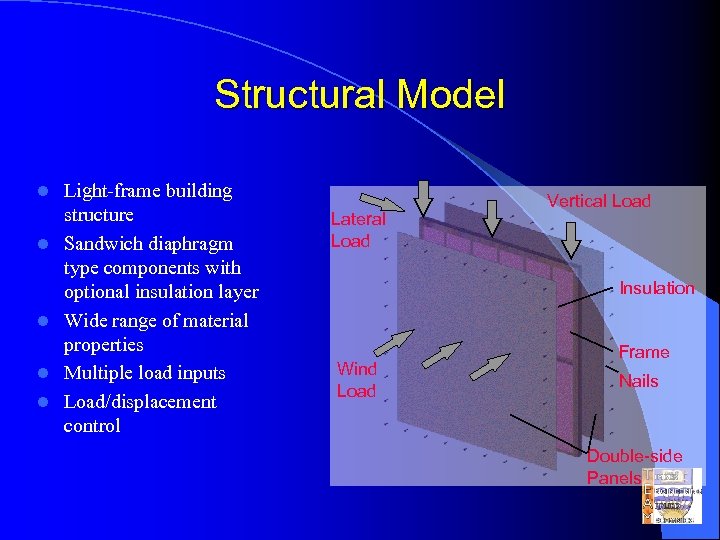
Structural Model l l Light-frame building structure Sandwich diaphragm type components with optional insulation layer Wide range of material properties Multiple load inputs Load/displacement control Lateral Load Vertical Load Insulation Wind Load Frame Nails Double-side Panels
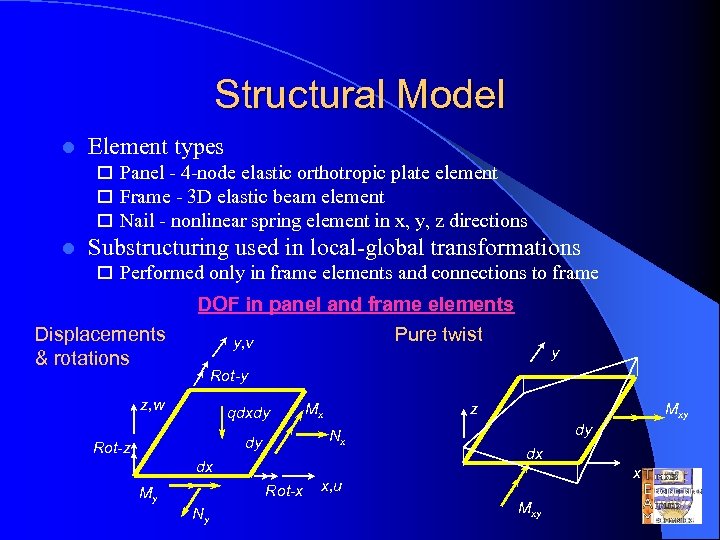
Structural Model l Element types o Panel - 4 -node elastic orthotropic plate element o Frame - 3 D elastic beam element o Nail - nonlinear spring element in x, y, z directions l Substructuring used in local-global transformations o Performed only in frame elements and connections to frame Displacements & rotations DOF in panel and frame elements Pure twist y, v y Rot-y z, w qdxdy z Nx dy Rot-z Mx dx Rot-x My Ny Mxy dy dx x x, u Mxy

Mechanics Based Nail Hysteresis l Beam elements (nail) on nonlinear foundations (panel and frame) l Basic material properties – Non-linear Stress Strain Behaviour of the steel – Non-linear Embedment Properties of the Wood l Hysteresis behaviour

Cyclic Behaviour Mechanics based nail model was implemented into 3 D program l Single nail case compared to test results l o Pinched and asymmetric hysteresis loops o Stiffness and strength degradations l Possible issues o Solution Stability o Model Calibration o Material Properties
Mechanics-Based Nail Model
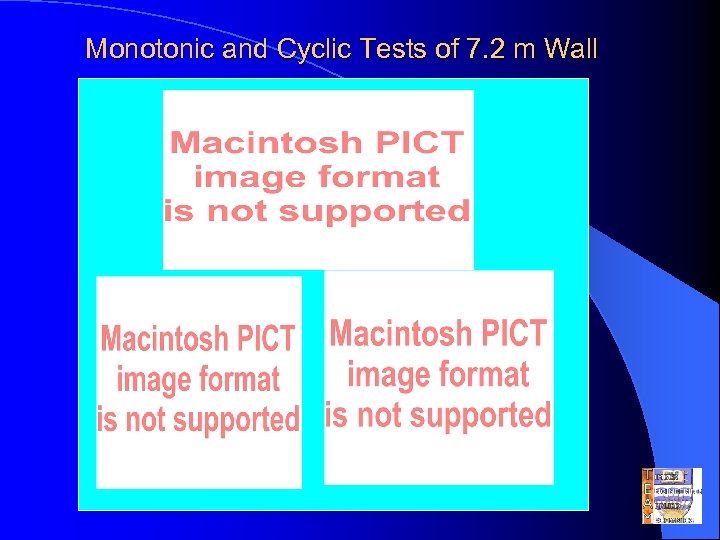
Monotonic and Cyclic Tests of 7. 2 m Wall
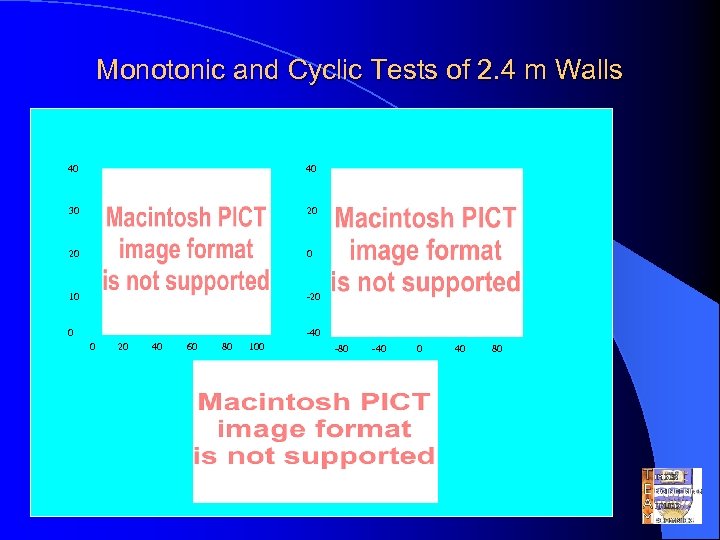
Monotonic and Cyclic Tests of 2. 4 m Walls 40 40 Wall 5 Cyclic Test 30 20 Wall 3 0 20 Wall 1 10 -20 0 Monotonic Test -40 0 20 40 60 80 100 -80 -40 0 40 80
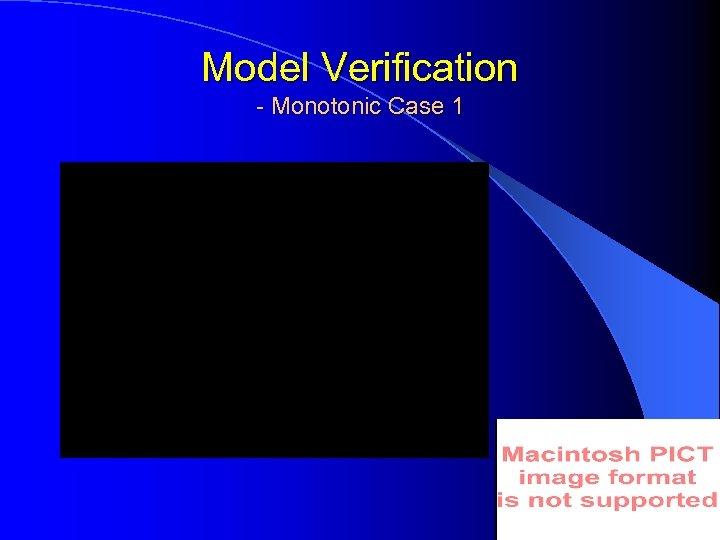
Model Verification - Monotonic Case 1
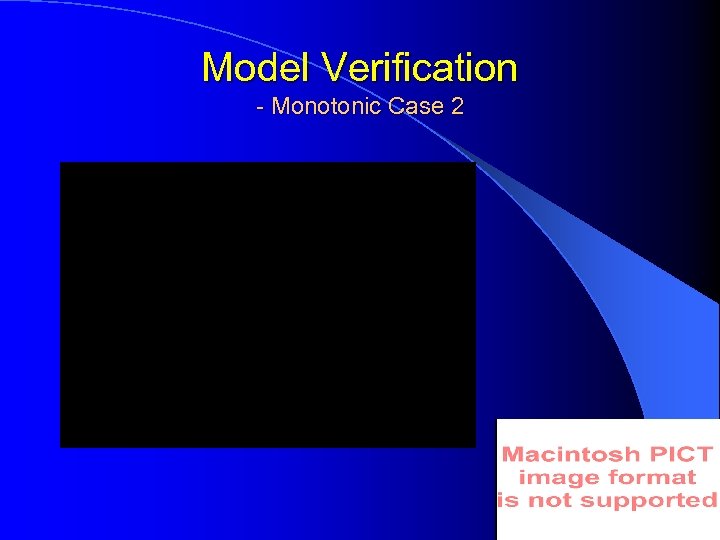
Model Verification - Monotonic Case 2
Model Verification - Cyclic Case 1
Model Verification - Cyclic Case 2

Model Predictions - Cyclic Case

Shake Table Test set up of 2. 4 wall Inertia masses Distribution beam Shear wall specimen Vertical actuators Support frame Shake table Longitudinal actuator
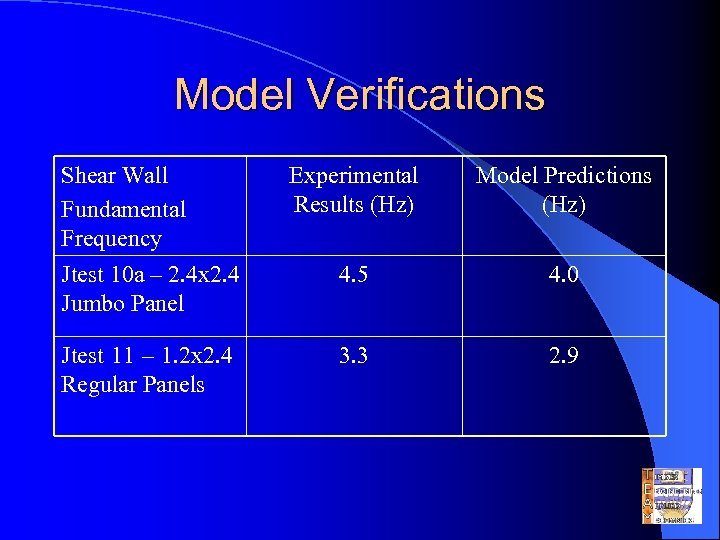
Model Verifications Shear Wall Fundamental Frequency Jtest 10 a – 2. 4 x 2. 4 Jumbo Panel Experimental Results (Hz) Model Predictions (Hz) 4. 5 4. 0 Jtest 11 – 1. 2 x 2. 4 Regular Panels 3. 3 2. 9
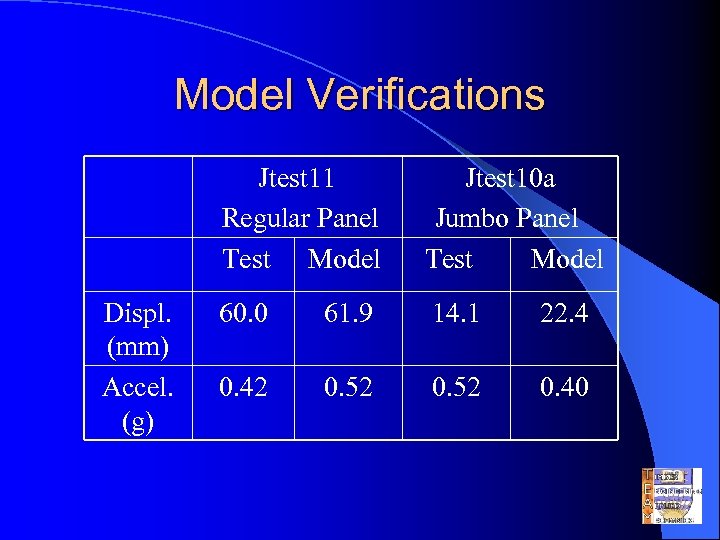
Model Verifications Displ. (mm) Accel. (g) Jtest 11 Regular Panel Test Model Jtest 10 a Jumbo Panel Test Model 60. 0 61. 9 14. 1 22. 4 0. 42 0. 52 0. 40
Model Verification - Dynamic Case 2 D

Model Predictions - 3 -D Static Response

Model of an Eccentric Structure

Specimen Details

Model Verification - Static Case 3 D
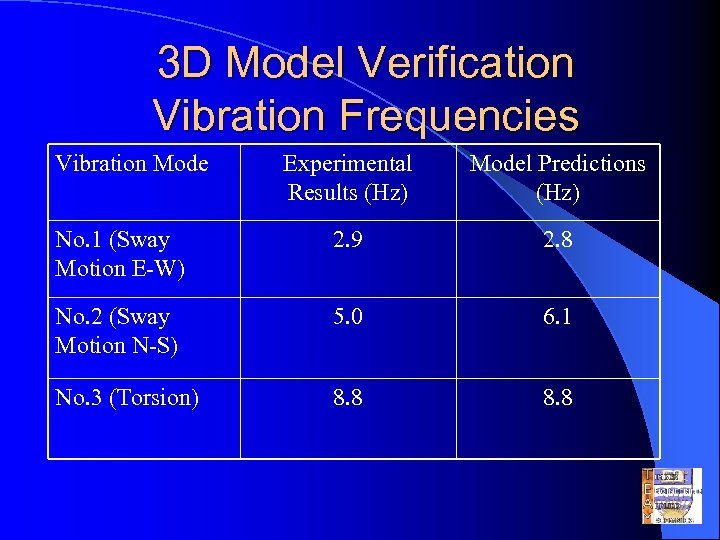
3 D Model Verification Vibration Frequencies Vibration Mode Experimental Results (Hz) Model Predictions (Hz) No. 1 (Sway Motion E-W) 2. 9 2. 8 No. 2 (Sway Motion N-S) 5. 0 6. 1 No. 3 (Torsion) 8. 8

Model Verification - Dynamic Case 3 D Single Component Shaking

Failed Shake Table Specimen

Failed Shake Table Specimen

3 D Simplified Model Test Observations Significant torsional response l Single Component Shaking (~0. 4 g pga) l – Damage initiated in the narrow wall – Adjacent long wall was also severely damaged – Significant softening after 1 st pulse l Two Component Shaking (~0. 26 g pga) – Two side walls were severely damaged – Significant softening after 1 st pulse
Summary on Model Development l Modeling/analytical procedures 1. Program calibrations and verification (Dynamic case) 2. Study of structural parameters and performance 1. Experimental procedures Ø Verification of 3 D finite element program ü Ø Static Dynamic l Reliability based design procedures 1. Response Surfaces Approaches
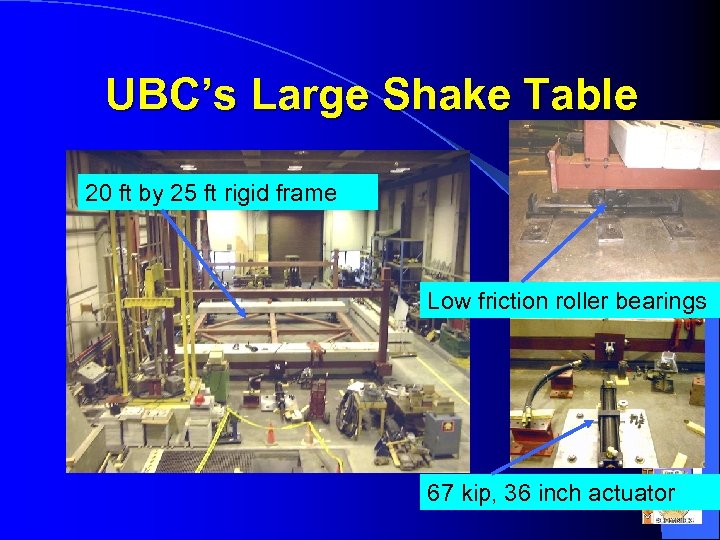
UBC’s Large Shake Table 20 ft by 25 ft rigid frame Low friction roller bearings 67 kip, 36 inch actuator

Subsystem testing Simulated weight of 2 nd floor

Two Storey House Test

f5c588281de196b1cf68d31ee639d8ba.ppt