50df567485b94b1332d867c41d3f7e46.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 U. S. History Chapter 11 Notes The Great Depression Begins
U. S. History Chapter 11 Notes The Great Depression Begins
 Section 1 The Nation’s Sick Economy
Section 1 The Nation’s Sick Economy
 Economic Troubles on the Horizon • Problems began threatening economic prosperity by the end of the 1920 s • Farm debt • Consumer debt - many people were buying goods on credit • More goods then buyers - prices rose faster than wages • Declining Trade – • Income disparity - Consumers & farmers went steadily deeper into debt
Economic Troubles on the Horizon • Problems began threatening economic prosperity by the end of the 1920 s • Farm debt • Consumer debt - many people were buying goods on credit • More goods then buyers - prices rose faster than wages • Declining Trade – • Income disparity - Consumers & farmers went steadily deeper into debt
 Industries in Trouble • Key industries like railroads, textiles, steel barely made profit • • Mining, lumbering expanded during were no longer in high demand • Boom industries - automobiles, construction, consumer goods weakened
Industries in Trouble • Key industries like railroads, textiles, steel barely made profit • • Mining, lumbering expanded during were no longer in high demand • Boom industries - automobiles, construction, consumer goods weakened
 Farm Troubles • International demand for U. S. grain declined after war - prices dropped by 40% or more • • Farm income declined & farmers defaulted on loans • • Congress attempted to pass the Mc. Nary- Haugen bill to help farmers - Price-supports -
Farm Troubles • International demand for U. S. grain declined after war - prices dropped by 40% or more • • Farm income declined & farmers defaulted on loans • • Congress attempted to pass the Mc. Nary- Haugen bill to help farmers - Price-supports -
 Consumers Problems • 1920 s - rich got richer & poor got poorer • • 70% of families earned less than minimum for decent standard of living - $2500 annually • • Many people had been purchasing goods on credit (buy now, pay later) • • Consumers had trouble paying off debt & cut back on spending
Consumers Problems • 1920 s - rich got richer & poor got poorer • • 70% of families earned less than minimum for decent standard of living - $2500 annually • • Many people had been purchasing goods on credit (buy now, pay later) • • Consumers had trouble paying off debt & cut back on spending
 OBJ #1 - Describe the CAUSES and SPARK of the Great Depression. How did Overproduction affect both farmers and industry? What system collapsed and caused millions to lose their savings? Explain how buying on Margin created the Spark. How did people lose money because of the spark? I. OBJ #1 - Cause & Spark of the Depression A. Causes of the Depression 1. Overproduction, ) a. Factory Workers begin to get layed-off b. Farmers Can’t Survive c. Supply & Demand- Prices Drop 2. Bank Failures a b. c. d.
OBJ #1 - Describe the CAUSES and SPARK of the Great Depression. How did Overproduction affect both farmers and industry? What system collapsed and caused millions to lose their savings? Explain how buying on Margin created the Spark. How did people lose money because of the spark? I. OBJ #1 - Cause & Spark of the Depression A. Causes of the Depression 1. Overproduction, ) a. Factory Workers begin to get layed-off b. Farmers Can’t Survive c. Supply & Demand- Prices Drop 2. Bank Failures a b. c. d.
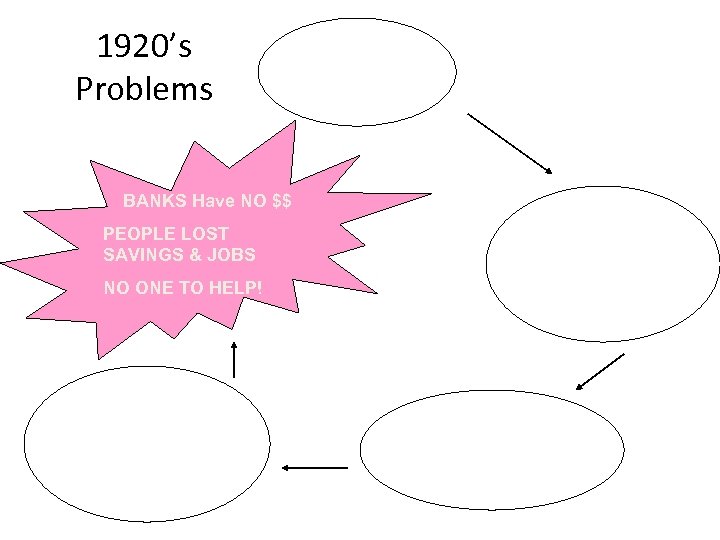 1920’s Problems BANKS Have NO $$ PEOPLE LOST SAVINGS & JOBS NO ONE TO HELP!
1920’s Problems BANKS Have NO $$ PEOPLE LOST SAVINGS & JOBS NO ONE TO HELP!
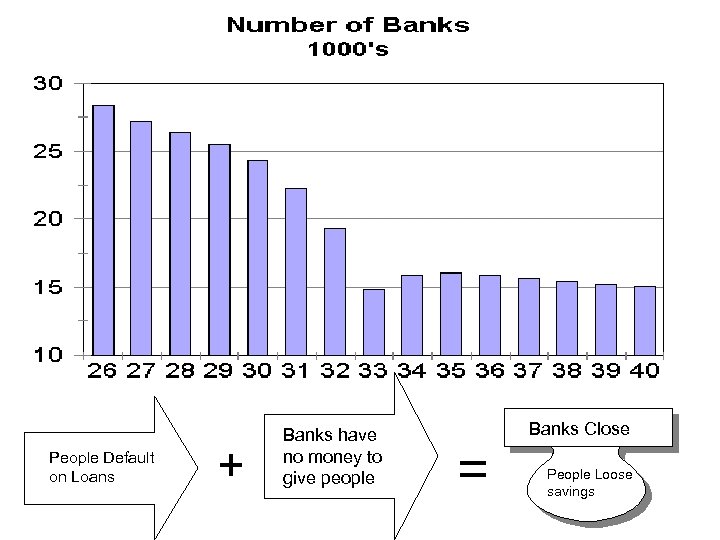 People Default on Loans + Banks have no money to give people Banks Close = People Loose savings
People Default on Loans + Banks have no money to give people Banks Close = People Loose savings
 The Election of 1928 • Democrat Alfred E. Smith four times governor of New York • Republican • U. S. had experienced prosperity under Republicans in 1920 s •
The Election of 1928 • Democrat Alfred E. Smith four times governor of New York • Republican • U. S. had experienced prosperity under Republicans in 1920 s •

 Dreams of Riches in the Stock Market • Late 1920 s – Some economist warning of weaknesses in the economy - Most Americans ignored them • • Dow Jones Industrial Average was used as barometer of the market’s health -
Dreams of Riches in the Stock Market • Late 1920 s – Some economist warning of weaknesses in the economy - Most Americans ignored them • • Dow Jones Industrial Average was used as barometer of the market’s health -
 Dreams of Riches in the Stock Market • 1920 s - stock prices rose steadily “Bull Market” •
Dreams of Riches in the Stock Market • 1920 s - stock prices rose steadily “Bull Market” •

 The Stock Market Crashes • September 1929 stock prices peaked & then fell • • October 24, 1929 Market took plunge & many panicked investors unloaded their shares
The Stock Market Crashes • September 1929 stock prices peaked & then fell • • October 24, 1929 Market took plunge & many panicked investors unloaded their shares
 The Stock Market Crashes • October 29, 1929 - Stock market crashed (Black Tuesday) -
The Stock Market Crashes • October 29, 1929 - Stock market crashed (Black Tuesday) -
 OBJ #1 - Cause & Sparks of Depression QUICK REVIEW: Causes: 1. 2. Spark: 1. Results: 1. 2.
OBJ #1 - Cause & Sparks of Depression QUICK REVIEW: Causes: 1. 2. Spark: 1. Results: 1. 2.
 Financial Collapse • Great Depression – • • • - lasted from After crash, people panicked & withdraw money from banks Banks 1929 to 1932 - gross national product was cut nearly in half - 90, 000 businesses went bankrupt 1933 Those with jobs received cuts in hours & pay
Financial Collapse • Great Depression – • • • - lasted from After crash, people panicked & withdraw money from banks Banks 1929 to 1932 - gross national product was cut nearly in half - 90, 000 businesses went bankrupt 1933 Those with jobs received cuts in hours & pay
 Worldwide Shock Waves • Great Depression limited U. S. ability to import European goods • • Other countries couldn’t earn American currency to buy U. S. goods - Many countries retaliated by raising their own tariffs •
Worldwide Shock Waves • Great Depression limited U. S. ability to import European goods • • Other countries couldn’t earn American currency to buy U. S. goods - Many countries retaliated by raising their own tariffs •
 Causes of the Great Depression • Factors leading to Great Depression: • Declining Trade – • Farm problems - Many farmers were forced to sell • Easy credit – Borrowed money to invest in market • Income disparity •
Causes of the Great Depression • Factors leading to Great Depression: • Declining Trade – • Farm problems - Many farmers were forced to sell • Easy credit – Borrowed money to invest in market • Income disparity •
 Section 2 Hardship and Suffering During the Depression
Section 2 Hardship and Suffering During the Depression
 The Depression Devastates People’s Lives • People lost jobs & were evicted from homes • Had to live in parks or sewer pipes • Shantytowns -
The Depression Devastates People’s Lives • People lost jobs & were evicted from homes • Had to live in parks or sewer pipes • Shantytowns -
 The Depression Devastates People’s Lives • People dug through garbage & begged - Soup kitchens offered free or low-cost food - Bread lines - people lined up for food from charities & public agencies • African Americans & Latinos had higher unemployment & lower pay • Minorities were also targets of violence (Lynching or deportation)
The Depression Devastates People’s Lives • People dug through garbage & begged - Soup kitchens offered free or low-cost food - Bread lines - people lined up for food from charities & public agencies • African Americans & Latinos had higher unemployment & lower pay • Minorities were also targets of violence (Lynching or deportation)
 The Depression in Rural Areas • Most farmers could grow food for their families •
The Depression in Rural Areas • Most farmers could grow food for their families •
 The Dust Bowl • Farmers in Great Plains exhausted land through overproduction • 1930 s - drought & windstorms scattered for hundreds of miles • Dust Bowl
The Dust Bowl • Farmers in Great Plains exhausted land through overproduction • 1930 s - drought & windstorms scattered for hundreds of miles • Dust Bowl




 The Dust Bowl • Many farm families migrated to Pacific Coast
The Dust Bowl • Many farm families migrated to Pacific Coast
 OBJ #3 - Describe the natural disaster that affected the U. S. during the Great Depression. What was the disaster’s nick-name? What caused the disaster? Where did the people go to try and escape their troubles and how were they treated (nicknames for these people)? III. OBJ. #3 - Natural Disaster “The DUST BOWL” A. Great Plains suffers a huge Drought (1931) 1. Causes: a b 2. Huge Dust storms cover ‘Great Plains B. Results 1. 2. , a. b.
OBJ #3 - Describe the natural disaster that affected the U. S. during the Great Depression. What was the disaster’s nick-name? What caused the disaster? Where did the people go to try and escape their troubles and how were they treated (nicknames for these people)? III. OBJ. #3 - Natural Disaster “The DUST BOWL” A. Great Plains suffers a huge Drought (1931) 1. Causes: a b 2. Huge Dust storms cover ‘Great Plains B. Results 1. 2. , a. b.

 Effects on the American Family • Family was source of strength for most Americans • Believed in traditional values and emphasized the importance of family unity • • Some families broke apart under strain of making ends meet
Effects on the American Family • Family was source of strength for most Americans • Believed in traditional values and emphasized the importance of family unity • • Some families broke apart under strain of making ends meet
 Men in the Streets • Many men used to working & supporting families had difficulty coping – Couldn’t find jobs – Many stopped trying • Some men even abandoned their families
Men in the Streets • Many men used to working & supporting families had difficulty coping – Couldn’t find jobs – Many stopped trying • Some men even abandoned their families
 Women Struggle to Survive • Women worked hard to help their families survive the adversity • • Women worked outside home & were resented by unemployed men
Women Struggle to Survive • Women worked hard to help their families survive the adversity • • Women worked outside home & were resented by unemployed men
 Women Struggle to Survive • Early 1930 s – Some cities refused to hire married schoolteachers • Many women
Women Struggle to Survive • Early 1930 s – Some cities refused to hire married schoolteachers • Many women
 Children Suffer Hardships • Poor diets & health care led to serious health problems in children • Teenagers left home & rode trains in search of work & adventure - Many died or were beaten
Children Suffer Hardships • Poor diets & health care led to serious health problems in children • Teenagers left home & rode trains in search of work & adventure - Many died or were beaten
 Social and Psychological Effects • 1928 to 1932 – • Admissions to state mental hospitals tripled • Put off marriage & children • Many people showed great kindness to strangers - Gave food, clothing & a place to stay
Social and Psychological Effects • 1928 to 1932 – • Admissions to state mental hospitals tripled • Put off marriage & children • Many people showed great kindness to strangers - Gave food, clothing & a place to stay
 Section 3 Hoover Struggles with the Depression
Section 3 Hoover Struggles with the Depression
 Hoover Tries to Reassure the Nation • President Herbert Hoover told Americans the economy was sound • Many experts believed depressions were normal part of business cycle - Believed that it was best to do nothing & let the economy fix itself • Hoover believed government
Hoover Tries to Reassure the Nation • President Herbert Hoover told Americans the economy was sound • Many experts believed depressions were normal part of business cycle - Believed that it was best to do nothing & let the economy fix itself • Hoover believed government
 Hoover Tries to Reassure the Nation • Many believed that people should succeed through their own efforts • People should take care of own families & not depend on government • Hoover
Hoover Tries to Reassure the Nation • Many believed that people should succeed through their own efforts • People should take care of own families & not depend on government • Hoover
 Hoover Takes Cautious Steps • Hoover called meeting of business, banking, labor leaders to solve problems - Asked them to work to together to solve the problems • Created organization to
Hoover Takes Cautious Steps • Hoover called meeting of business, banking, labor leaders to solve problems - Asked them to work to together to solve the problems • Created organization to
 Hoover Takes Cautious Steps • Hoover’s authorized the construction of the Boulder Dam on Colorado River w - later renamed Hoover Dam -
Hoover Takes Cautious Steps • Hoover’s authorized the construction of the Boulder Dam on Colorado River w - later renamed Hoover Dam -



 Democrats Win in 1930 Congressional Elections
Democrats Win in 1930 Congressional Elections
 Democrats Win in 1930 Congressional Elections • Farmers tried to create food shortages to raise prices
Democrats Win in 1930 Congressional Elections • Farmers tried to create food shortages to raise prices

 Hoover Takes Action • Hoover softened his stance on no government intervention in the economy • Hoover negotiates agreements among private entities • Backs - buy crops, keep off market until prices rise
Hoover Takes Action • Hoover softened his stance on no government intervention in the economy • Hoover negotiates agreements among private entities • Backs - buy crops, keep off market until prices rise
 Hoover Takes Action • Got large banks to establish - Loaned money to smaller banks to prevent bankruptcy • Late 1931 - Hoover persuaded Congress to pass measures reform banking, provide mortgage relief, & funnel federal money into business investment -
Hoover Takes Action • Got large banks to establish - Loaned money to smaller banks to prevent bankruptcy • Late 1931 - Hoover persuaded Congress to pass measures reform banking, provide mortgage relief, & funnel federal money into business investment -
 Hoover Takes Action • Reconstruction Finance Corporation – • Hoover’s measures didn’t improve economy before presidential election
Hoover Takes Action • Reconstruction Finance Corporation – • Hoover’s measures didn’t improve economy before presidential election
 Gassing the Bonus Army • 1932 – Incident with World War I veterans further damaged Hoover’s image & public morale • 1924 – -
Gassing the Bonus Army • 1932 – Incident with World War I veterans further damaged Hoover’s image & public morale • 1924 – -
 Gassing the Bonus Army • Bonus Army –
Gassing the Bonus Army • Bonus Army –
 Gassing the Bonus Army • Hoover opposed bill • Believed they were communists • He respected their right to protest (Provided food & supplies for shantytown) • June 17, 1932 – • Most veterans left Washington •
Gassing the Bonus Army • Hoover opposed bill • Believed they were communists • He respected their right to protest (Provided food & supplies for shantytown) • June 17, 1932 – • Most veterans left Washington •
 Gassing the Bonus Army • Hoover feared violence & called on U. S. Army to disband Bonus Army - Led by
Gassing the Bonus Army • Hoover feared violence & called on U. S. Army to disband Bonus Army - Led by
 Gassing the Bonus Army • Infantry tear gassed over 1, 000 people, including children • Many people were injured (11 month old baby died)
Gassing the Bonus Army • Infantry tear gassed over 1, 000 people, including children • Many people were injured (11 month old baby died)
 OBJ #2 -Describe how the Great Depression affected people. Who was the president when it started, and what did he do to help? Who tried to help the poor and what problems did they have? How did people try to escape the Great Depression? II. OBJ. #2 – Affects of the Depression A. Jobless / Homeless 1. 2. 3. B. Hatred for President Hoover 1. Say’s it is NOT Government’s job to fix the Poor a. b. PROBLEM 2. People name Poor Places after Hoover a b
OBJ #2 -Describe how the Great Depression affected people. Who was the president when it started, and what did he do to help? Who tried to help the poor and what problems did they have? How did people try to escape the Great Depression? II. OBJ. #2 – Affects of the Depression A. Jobless / Homeless 1. 2. 3. B. Hatred for President Hoover 1. Say’s it is NOT Government’s job to fix the Poor a. b. PROBLEM 2. People name Poor Places after Hoover a b
 OBJ #2 - Effects of the Great Depression Wizard C. Escaping the Depression 1. Radio 2. Moviesa. b. 3. Literature a. Steinbeck, of OZ
OBJ #2 - Effects of the Great Depression Wizard C. Escaping the Depression 1. Radio 2. Moviesa. b. 3. Literature a. Steinbeck, of OZ


