da74ecece6f767efe0ca3439ca42aadd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 U. S. Export Controls Nancy Wood Outsource Trade Group, LLC Managing Director Svtronics, Inc March 24, 2014
U. S. Export Controls Nancy Wood Outsource Trade Group, LLC Managing Director Svtronics, Inc March 24, 2014
 Export Control Regulations Ø International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) Ø Ø 22 CFR Parts 120 -130 Controls on Defense Articles, Technology and Services (Munitions Items) Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) Arms Export Control Act (AECA) Ø Export Administration Regulations (EAR) Ø 15 CFR Parts 730 -774 Ø Controls on Dual-Use Goods and Technology (Items with a commercial and military utility) and purely commercial items Ø Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) Ø Export Administration Act (EAA) 2
Export Control Regulations Ø International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) Ø Ø 22 CFR Parts 120 -130 Controls on Defense Articles, Technology and Services (Munitions Items) Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) Arms Export Control Act (AECA) Ø Export Administration Regulations (EAR) Ø 15 CFR Parts 730 -774 Ø Controls on Dual-Use Goods and Technology (Items with a commercial and military utility) and purely commercial items Ø Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) Ø Export Administration Act (EAA) 2
 Overview: Scope of Export Controls What is an Export? • Any item sent from the United States to a foreign destination • An “item” includes commodities (products, test equipment, production equipment, computers, spare parts), software, technology (design drawings, technical specifications, production data, technical assistance) • Technology is “deemed” to be exported when provided to non-U. S. nationals within the United States • How an item leaves the United States does not matter for export control purposes – Hand carry – Air/ocean – Electronic – In person • Transfers or shipments to non-U. S. affiliates/parent company are exports 3
Overview: Scope of Export Controls What is an Export? • Any item sent from the United States to a foreign destination • An “item” includes commodities (products, test equipment, production equipment, computers, spare parts), software, technology (design drawings, technical specifications, production data, technical assistance) • Technology is “deemed” to be exported when provided to non-U. S. nationals within the United States • How an item leaves the United States does not matter for export control purposes – Hand carry – Air/ocean – Electronic – In person • Transfers or shipments to non-U. S. affiliates/parent company are exports 3
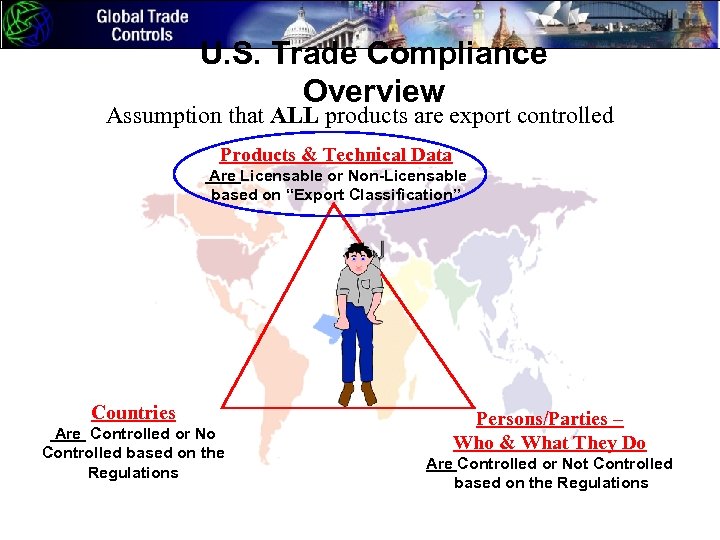 U. S. Trade Compliance Overview Assumption that ALL products are export controlled Products & Technical Data Are Licensable or Non-Licensable based on “Export Classification” Countries Are Controlled or No Controlled based on the Regulations Persons/Parties – Who & What They Do Are Controlled or Not Controlled based on the Regulations
U. S. Trade Compliance Overview Assumption that ALL products are export controlled Products & Technical Data Are Licensable or Non-Licensable based on “Export Classification” Countries Are Controlled or No Controlled based on the Regulations Persons/Parties – Who & What They Do Are Controlled or Not Controlled based on the Regulations
 Svtronics, Inc Article: OMAP versions, Panda Board, Rackmount client work terminal Classification of Articles: 5 A 002. a 1 License Exception: ENC for private sector end-uses Jurisdiction: Department of Commerce, Export Administration Regulations Controls: Sudan, Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Syria and Entity List/Denied Part List http: //export. gov/ecr/eg_main_023148. asp
Svtronics, Inc Article: OMAP versions, Panda Board, Rackmount client work terminal Classification of Articles: 5 A 002. a 1 License Exception: ENC for private sector end-uses Jurisdiction: Department of Commerce, Export Administration Regulations Controls: Sudan, Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Syria and Entity List/Denied Part List http: //export. gov/ecr/eg_main_023148. asp
 • SUPPLEMENT NO. 3 TO PART 740 - LICENSE EXCEPTION ENC FAVORABLE • TREATMENT COUNTRIES • Australia • Austria • Belgium • Bulgaria • Canada • Cyprus • Czech Republic • Denmark • Estonia • Finland • France • Germany • Greece • Hungary • Iceland • Ireland • Italy • Japan • Latvia • Lithuania • Luxembourg • Malta • Netherlands • New Zealand • Norway • Poland • Portugal • Romania • Slovakia • Slovenia • Spain • Sweden • Switzerland • Turkey • United Kingdom
• SUPPLEMENT NO. 3 TO PART 740 - LICENSE EXCEPTION ENC FAVORABLE • TREATMENT COUNTRIES • Australia • Austria • Belgium • Bulgaria • Canada • Cyprus • Czech Republic • Denmark • Estonia • Finland • France • Germany • Greece • Hungary • Iceland • Ireland • Italy • Japan • Latvia • Lithuania • Luxembourg • Malta • Netherlands • New Zealand • Norway • Poland • Portugal • Romania • Slovakia • Slovenia • Spain • Sweden • Switzerland • Turkey • United Kingdom
 International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) 7
International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) 7
 International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) • Administered by the U. S. Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) • Enforced by Homeland Security, Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and the FBI • Control the temporary and permanent export to ALL countries of defense articles (including technical data and software) • Control temporary imports of defense articles (including technical data and software) 8 • Control the provision of defense services
International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) • Administered by the U. S. Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) • Enforced by Homeland Security, Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and the FBI • Control the temporary and permanent export to ALL countries of defense articles (including technical data and software) • Control temporary imports of defense articles (including technical data and software) 8 • Control the provision of defense services
 ITAR • Anyone who manufactures or exports defense articles, provides defense services or brokers defense articles must register with the DDTC • Registration alone does not satisfy license/prior approval requirements • Brokering defense articles and defense services is also controlled – U. S. persons acting as an agent for the transfer or sale of defense articles or services, both foreign and U. S. – Foreign persons acting as an agent for the transfer or sale of U. S. origin defense articles or services 9
ITAR • Anyone who manufactures or exports defense articles, provides defense services or brokers defense articles must register with the DDTC • Registration alone does not satisfy license/prior approval requirements • Brokering defense articles and defense services is also controlled – U. S. persons acting as an agent for the transfer or sale of defense articles or services, both foreign and U. S. – Foreign persons acting as an agent for the transfer or sale of U. S. origin defense articles or services 9
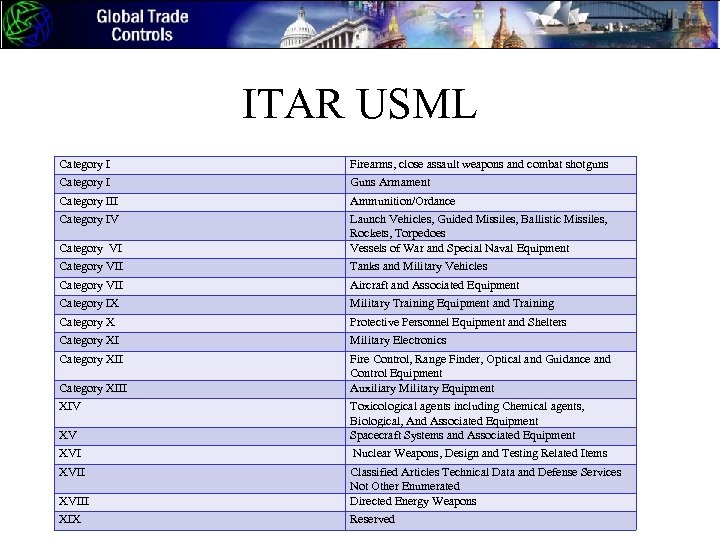 ITAR USML Category I Firearms, close assault weapons and combat shotguns Category I Guns Armament Category III Ammunition/Ordance Category IV Category VI Launch Vehicles, Guided Missiles, Ballistic Missiles, Rockets, Torpedoes Vessels of War and Special Naval Equipment Category VII Tanks and Military Vehicles Category VII Aircraft and Associated Equipment Category IX Military Training Equipment and Training Category X Protective Personnel Equipment and Shelters Category XI Military Electronics Category XII Fire Control, Range Finder, Optical and Guidance and Control Equipment Auxiliary Military Equipment Category XIII XIV XV Toxicological agents including Chemical agents, Biological, And Associated Equipment Spacecraft Systems and Associated Equipment XVI Nuclear Weapons, Design and Testing Related Items XVIII Classified Articles Technical Data and Defense Services Not Other Enumerated Directed Energy Weapons XIX Reserved
ITAR USML Category I Firearms, close assault weapons and combat shotguns Category I Guns Armament Category III Ammunition/Ordance Category IV Category VI Launch Vehicles, Guided Missiles, Ballistic Missiles, Rockets, Torpedoes Vessels of War and Special Naval Equipment Category VII Tanks and Military Vehicles Category VII Aircraft and Associated Equipment Category IX Military Training Equipment and Training Category X Protective Personnel Equipment and Shelters Category XI Military Electronics Category XII Fire Control, Range Finder, Optical and Guidance and Control Equipment Auxiliary Military Equipment Category XIII XIV XV Toxicological agents including Chemical agents, Biological, And Associated Equipment Spacecraft Systems and Associated Equipment XVI Nuclear Weapons, Design and Testing Related Items XVIII Classified Articles Technical Data and Defense Services Not Other Enumerated Directed Energy Weapons XIX Reserved
 ITAR Definition: Technical Data • § 120. 10: information which is required for the design, development, production, manufacture, assembly, operation, repair, testing, maintenance or modification of defense articles – Also includes software as defined by § 121. 8(f) directly related to defense articles – Includes: information in the form of blueprints, drawings, photographs, plans, instructions or documentation – Excludes: basic marketing information, public domain information, and fundamental research • Be careful! Marketing activities can quickly slip into the provision of technical data. 11
ITAR Definition: Technical Data • § 120. 10: information which is required for the design, development, production, manufacture, assembly, operation, repair, testing, maintenance or modification of defense articles – Also includes software as defined by § 121. 8(f) directly related to defense articles – Includes: information in the form of blueprints, drawings, photographs, plans, instructions or documentation – Excludes: basic marketing information, public domain information, and fundamental research • Be careful! Marketing activities can quickly slip into the provision of technical data. 11
 ITAR Definition: Defense Service • § 120. 9: – (1) the furnishing of assistance (including training) to foreign persons, whether in the U. S. or abroad in the design, development, engineering, manufacture, production, assembly, testing, repair, maintenance, modification, operations, demilitarization, destruction, processing or use of defense articles • Does not require the transmission of ITARcontrolled technical data • Assistance involving public domain information or information subject to the EAR can still be a defense service if the assistance relates to a defense article 12
ITAR Definition: Defense Service • § 120. 9: – (1) the furnishing of assistance (including training) to foreign persons, whether in the U. S. or abroad in the design, development, engineering, manufacture, production, assembly, testing, repair, maintenance, modification, operations, demilitarization, destruction, processing or use of defense articles • Does not require the transmission of ITARcontrolled technical data • Assistance involving public domain information or information subject to the EAR can still be a defense service if the assistance relates to a defense article 12
 ITAR Definition: Defense Service • § 120. 9 (cont. ): – (2) the furnishing to foreign persons of any technical data controlled under this subchapter (§ 120. 10) whether in the U. S. or abroad – (3) military training of foreign units and forces, regular and irregular, including formal or informal instruction of foreign persons in the U. S. or abroad or by correspondence courses, technical, educational, or information publications and media of all kinds, training aid, orientation, training exercise, and military advice • Remember: You cannot have a defense service without a foreign person 13
ITAR Definition: Defense Service • § 120. 9 (cont. ): – (2) the furnishing to foreign persons of any technical data controlled under this subchapter (§ 120. 10) whether in the U. S. or abroad – (3) military training of foreign units and forces, regular and irregular, including formal or informal instruction of foreign persons in the U. S. or abroad or by correspondence courses, technical, educational, or information publications and media of all kinds, training aid, orientation, training exercise, and military advice • Remember: You cannot have a defense service without a foreign person 13
 ITAR: Types of Licenses for Export or Temporary Import • DSP-5: Permanent export of unclassified defense articles or technology. *New submitting Agreements • DSP-73: Temporary export of unclassified defense articles or technology • DSP-61: Temporary import of unclassified defense articles or technology • DSP-85: Permanent or temporary export of classified defense articles or technology – Duration for all: 4 years or when total authorized quantity or dollar value has been shipped, whichever occurs first. 14
ITAR: Types of Licenses for Export or Temporary Import • DSP-5: Permanent export of unclassified defense articles or technology. *New submitting Agreements • DSP-73: Temporary export of unclassified defense articles or technology • DSP-61: Temporary import of unclassified defense articles or technology • DSP-85: Permanent or temporary export of classified defense articles or technology – Duration for all: 4 years or when total authorized quantity or dollar value has been shipped, whichever occurs first. 14
 ITAR: Types of Licenses • Technical Assistance Agreements (TAA) • An agreement for the performance of a defense service or the disclosure of technical data, as opposed to an agreement granting a right or license to manufacture defense articles. Authorization for the assembly of defense articles can be included, provided production rights or manufacturing know-how are not conveyed. Duration defined in TAA, up to 10 years. • Manufacturing License Agreements (MLA) • An agreement whereby a U. S. person grants to a foreign person authorization to manufacture defense articles abroad and which involves the export of technical data or defense articles or the performance of a defense service; or the use by the foreign person of technical data or defense articles previously exported by the U. S. person. Duration defined in MLA, up to 10 years. • Warehouse and Distribution Agreements (WDA) • An agreement to establish a warehouse or distribution point outside the United States for onward distribution within an approved sales territory of defense articles exported from the United States. Duration defined in WDA, up to 10 years. 15
ITAR: Types of Licenses • Technical Assistance Agreements (TAA) • An agreement for the performance of a defense service or the disclosure of technical data, as opposed to an agreement granting a right or license to manufacture defense articles. Authorization for the assembly of defense articles can be included, provided production rights or manufacturing know-how are not conveyed. Duration defined in TAA, up to 10 years. • Manufacturing License Agreements (MLA) • An agreement whereby a U. S. person grants to a foreign person authorization to manufacture defense articles abroad and which involves the export of technical data or defense articles or the performance of a defense service; or the use by the foreign person of technical data or defense articles previously exported by the U. S. person. Duration defined in MLA, up to 10 years. • Warehouse and Distribution Agreements (WDA) • An agreement to establish a warehouse or distribution point outside the United States for onward distribution within an approved sales territory of defense articles exported from the United States. Duration defined in WDA, up to 10 years. 15
 Export Administration Regulations 16
Export Administration Regulations 16
 Export Administration Regulations (EAR) • Administered by the U. S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) • Enforced by Commerce Department, Office of Export Enforcement (OEE), Homeland Security, Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and the FBI • Control the export and reexport of commercial and “dualuse” items (products, equipment, materials, software, technology) • Restrict activities of U. S. persons with respect to proliferation activities 17
Export Administration Regulations (EAR) • Administered by the U. S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) • Enforced by Commerce Department, Office of Export Enforcement (OEE), Homeland Security, Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) and the FBI • Control the export and reexport of commercial and “dualuse” items (products, equipment, materials, software, technology) • Restrict activities of U. S. persons with respect to proliferation activities 17
 EAR Definition: Technology • Specific information necessary for the “development”, “production”, or “use” of a product • The information takes the form of “technical data” or “technical assistance” • Technical assistance may take the form of instruction, skills training, working knowledge, or consulting services, among others • Servicing a product is considered to be a transfer of technology under the EAR 18
EAR Definition: Technology • Specific information necessary for the “development”, “production”, or “use” of a product • The information takes the form of “technical data” or “technical assistance” • Technical assistance may take the form of instruction, skills training, working knowledge, or consulting services, among others • Servicing a product is considered to be a transfer of technology under the EAR 18
 EAR Definition: Software • A collection of one or more “programs” or “microprograms” fixed in any tangible medium of expression • Controlled under the EAR if it is specially designed or modified for the “development”, “production”, or “use” of items commodities controlled identified on the CCL 19
EAR Definition: Software • A collection of one or more “programs” or “microprograms” fixed in any tangible medium of expression • Controlled under the EAR if it is specially designed or modified for the “development”, “production”, or “use” of items commodities controlled identified on the CCL 19
 Commerce Control List (CCL) Category 0 – Nuclear Materials, Facilities, and Equipment [and Miscellaneous Items] Category 1 – Materials, Chemicals, “Microorganisms, ” and Toxins Category 2 – Materials Processing Category 3 – Electronics Category 4 – Computers Category 5 – Telecommunications and “Information Security” Category 6 – Sensors and Lasers Category 7 – Navigation and Avionics Category 8 – Marine Category 9 – Propulsion Systems, Space Vehicles and Related Equipment EAR 99 - Items that do not fall into any of the above categories • Each Category controls: A. Systems, Equipment and Components, B. Test, Inspection and Production Equipment, C. Materials, D. Software and E. Technology. Each entry describes the controlled items in very technical terms. All products (including spare parts), software and technical data must be classified to determine licensing requirements. 20
Commerce Control List (CCL) Category 0 – Nuclear Materials, Facilities, and Equipment [and Miscellaneous Items] Category 1 – Materials, Chemicals, “Microorganisms, ” and Toxins Category 2 – Materials Processing Category 3 – Electronics Category 4 – Computers Category 5 – Telecommunications and “Information Security” Category 6 – Sensors and Lasers Category 7 – Navigation and Avionics Category 8 – Marine Category 9 – Propulsion Systems, Space Vehicles and Related Equipment EAR 99 - Items that do not fall into any of the above categories • Each Category controls: A. Systems, Equipment and Components, B. Test, Inspection and Production Equipment, C. Materials, D. Software and E. Technology. Each entry describes the controlled items in very technical terms. All products (including spare parts), software and technical data must be classified to determine licensing requirements. 20
 EAR: License Determination Process • Determine classification – Check CCL for goods, technology, software for ECCN – If not on CCL, use EAR 99 • Destination – Embargoed destination? – If on CCL, check country chart – If going to specific aircraft/helicopter, also check. • End user • End use • If a license requirement exists, review license exceptions to see if may proceed without a license under a particular license exception 21
EAR: License Determination Process • Determine classification – Check CCL for goods, technology, software for ECCN – If not on CCL, use EAR 99 • Destination – Embargoed destination? – If on CCL, check country chart – If going to specific aircraft/helicopter, also check. • End user • End use • If a license requirement exists, review license exceptions to see if may proceed without a license under a particular license exception 21
 • Export Control Compliance: For your Business 22
• Export Control Compliance: For your Business 22
 ITAR: Foreign Person • A foreign person is defined in ITAR § 120. 16 as: – Any natural person who is not a lawful permanent resident of the United States, or – Any natural person who is not a protected individual • U. S. citizens and green card holders are U. S. persons • A company must have authorization from DDTC to provide access to defense articles or services to a foreign person employee or visitor • DDTC considers country of origin (birth) to be part of a person’s nationality • DDTC considers dual nationalities relevant 23
ITAR: Foreign Person • A foreign person is defined in ITAR § 120. 16 as: – Any natural person who is not a lawful permanent resident of the United States, or – Any natural person who is not a protected individual • U. S. citizens and green card holders are U. S. persons • A company must have authorization from DDTC to provide access to defense articles or services to a foreign person employee or visitor • DDTC considers country of origin (birth) to be part of a person’s nationality • DDTC considers dual nationalities relevant 23
 EAR: Foreign National • A foreign national is: – A person who is not lawfully admitted for permanent residence in the United States, or – A person who is not a protected individual • A company must have authorization from BIS to provide access to technology to a foreign national if an export of that technology to the individual’s home country would require a license • BIS considers “last in time” nationality; BIS does not treat individuals as dual nationals • BIS does not currently consider country of origin (birth) to be relevant as a separate factor 24
EAR: Foreign National • A foreign national is: – A person who is not lawfully admitted for permanent residence in the United States, or – A person who is not a protected individual • A company must have authorization from BIS to provide access to technology to a foreign national if an export of that technology to the individual’s home country would require a license • BIS considers “last in time” nationality; BIS does not treat individuals as dual nationals • BIS does not currently consider country of origin (birth) to be relevant as a separate factor 24
 Human Resources/Security • ITAR and EAR consider it an export to transfer controlled technical data/technology to a foreign person, even when that person is located IN THE UNITED STATES • Identify foreign nationals present at the Company – New Hires – Existing employees – Seconded employees (long or short term) – Contract employees – Visitors 25
Human Resources/Security • ITAR and EAR consider it an export to transfer controlled technical data/technology to a foreign person, even when that person is located IN THE UNITED STATES • Identify foreign nationals present at the Company – New Hires – Existing employees – Seconded employees (long or short term) – Contract employees – Visitors 25
 HR/Security • Visitors to facility – Not exempt from export control restrictions because duration of stay is more than a day, week, month or because it is a repeat visitor – Plan ahead! • Screen all visitors against Restricted Parties Lists • Determine whether the visitor will require access to controlled data or articles and inquire about nationality as needed to satisfy export control requirements • Obtain an export license, as needed • Implement a Technology Control Plan 26
HR/Security • Visitors to facility – Not exempt from export control restrictions because duration of stay is more than a day, week, month or because it is a repeat visitor – Plan ahead! • Screen all visitors against Restricted Parties Lists • Determine whether the visitor will require access to controlled data or articles and inquire about nationality as needed to satisfy export control requirements • Obtain an export license, as needed • Implement a Technology Control Plan 26
 Information Systems • System administrator and system maintenance personnel must be U. S. persons • Software safeguards – e. g. , Location and security of backup file copies • Know the classification of all software on the system, particularly any software installed on Company laptop computers with which employees may travel 27
Information Systems • System administrator and system maintenance personnel must be U. S. persons • Software safeguards – e. g. , Location and security of backup file copies • Know the classification of all software on the system, particularly any software installed on Company laptop computers with which employees may travel 27
 Program/Contract Management • Be aware of foreign national employees involved in the program – Ensure all appropriate export authorizations are in place and being followed – Encourage compliance with any relevant Technology Control Plans – Must take into consideration all of these issues 28
Program/Contract Management • Be aware of foreign national employees involved in the program – Ensure all appropriate export authorizations are in place and being followed – Encourage compliance with any relevant Technology Control Plans – Must take into consideration all of these issues 28
 Product Engineering • Role in export compliance generally – Assist with product classification – Identify and mark controlled technical data • Be aware of export controls on technical data and defense services in all you do • If you are using existing drawings/specifications as a starting point for a new product, understand the export 29 classification of the initial data
Product Engineering • Role in export compliance generally – Assist with product classification – Identify and mark controlled technical data • Be aware of export controls on technical data and defense services in all you do • If you are using existing drawings/specifications as a starting point for a new product, understand the export 29 classification of the initial data
 Product Engineering • Outsourcing engineering drawing support • Transfers of data/drawings to customers during design phase – Meetings with customers – Presentations to customers • Transfers of hardware as samples/prototypes/etc. • Hand-off of drawings/product specifications to purchasing/sourcing team requires a clear communication of export control status 30
Product Engineering • Outsourcing engineering drawing support • Transfers of data/drawings to customers during design phase – Meetings with customers – Presentations to customers • Transfers of hardware as samples/prototypes/etc. • Hand-off of drawings/product specifications to purchasing/sourcing team requires a clear communication of export control status 30
 Purchasing • Ensure you understand the export control status of the items to be purchased – Mark the drawings/specifications so your supplier is aware, too • Low level or common parts: Bundling ITAR data on single drawing or specification • Domestic sourcing – If supplying ITAR-controlled items, is the supplier registered with DDTC? – If controlled technical data will be provided, determine if any foreign nationals are involved and work with supplier to obtain any necessary export authorizations – Be cognizant of export control status of items procured on behalf of foreign affiliates: even foreign origin data is controlled under U. S. export controls when it is in the United States! – Ensure suppliers/subcontractors fulfill responsibilities under applicable regulations and report on the status of their products and associated commodities regarding export restrictions 31
Purchasing • Ensure you understand the export control status of the items to be purchased – Mark the drawings/specifications so your supplier is aware, too • Low level or common parts: Bundling ITAR data on single drawing or specification • Domestic sourcing – If supplying ITAR-controlled items, is the supplier registered with DDTC? – If controlled technical data will be provided, determine if any foreign nationals are involved and work with supplier to obtain any necessary export authorizations – Be cognizant of export control status of items procured on behalf of foreign affiliates: even foreign origin data is controlled under U. S. export controls when it is in the United States! – Ensure suppliers/subcontractors fulfill responsibilities under applicable regulations and report on the status of their products and associated commodities regarding export restrictions 31
 Purchasing • Global sourcing – Be conscious of countries and parties with whom you deal – Screen all potential suppliers against Restricted Parties List – If suppliers have access to database/extranet, ensure adequate controls exist to limit access to controlled technical data – Consider export control status of any drawings/specifications that must be provided to supplier – If working with supplier to design, modify, integrate parts for your purposes, determine if any controlled defense services or technical assistance – Ensure suppliers/subcontractors fulfill responsibilities under applicable regulations and report on the status of their products and associated commodities regarding export restrictions • Dealing with a buying agent? Beware of possible brokering under the ITAR 32
Purchasing • Global sourcing – Be conscious of countries and parties with whom you deal – Screen all potential suppliers against Restricted Parties List – If suppliers have access to database/extranet, ensure adequate controls exist to limit access to controlled technical data – Consider export control status of any drawings/specifications that must be provided to supplier – If working with supplier to design, modify, integrate parts for your purposes, determine if any controlled defense services or technical assistance – Ensure suppliers/subcontractors fulfill responsibilities under applicable regulations and report on the status of their products and associated commodities regarding export restrictions • Dealing with a buying agent? Beware of possible brokering under the ITAR 32
 Marketing & Sales • Temporary exports for trade shows or other demonstrations – Temporary exports under the EAR: TMP license exception – Temporary exports under the ITAR: need a license— plan ahead • Make sales contingent upon receiving any required export authorizations • Ensure customer is aware of possible end-user/end-use limitations and retransfer or reexport restrictions • Is an agent or sales representative involved? Beware of brokering under the ITAR 33
Marketing & Sales • Temporary exports for trade shows or other demonstrations – Temporary exports under the EAR: TMP license exception – Temporary exports under the ITAR: need a license— plan ahead • Make sales contingent upon receiving any required export authorizations • Ensure customer is aware of possible end-user/end-use limitations and retransfer or reexport restrictions • Is an agent or sales representative involved? Beware of brokering under the ITAR 33
 Customer Support • Exemption for repair/replacement of ITAR-controlled hardware – ITAR § 123. 4(a)(1) – Repairs only; does not authorize the supply of upgraded or otherwise improved items – Must return to country from which imported – Specific documentation requirements at the time of import and export – Use § 126. 5(a) for temporary imports from Canada for repair and/or replacement • Does not authorize transfers of technical data or defense services for the repair of items overseas – ITAR § 124. 2(a) provides exemption for provision of training in the basic operation and maintenance of defense articles lawfully exported or authorized for export to the same recipient 34
Customer Support • Exemption for repair/replacement of ITAR-controlled hardware – ITAR § 123. 4(a)(1) – Repairs only; does not authorize the supply of upgraded or otherwise improved items – Must return to country from which imported – Specific documentation requirements at the time of import and export – Use § 126. 5(a) for temporary imports from Canada for repair and/or replacement • Does not authorize transfers of technical data or defense services for the repair of items overseas – ITAR § 124. 2(a) provides exemption for provision of training in the basic operation and maintenance of defense articles lawfully exported or authorized for export to the same recipient 34
 Shipping • Ensure you are aware of the export classification and export license requirements for all items to be shipped from the Company – Request additional information from shipping requestor to determine export control requirements – Coordinate with ECO as necessary • For controlled goods, confirm a valid license or exemption authorizes the shipment – Properly document the export on all required export documentation – Ensure proper destination control statement is included on shipment • For exports of technical data, ensure adequate information is provided in export documentation (especially if using online shipping software for express delivery services) • Do not release shipments that lack proper export authorization 35
Shipping • Ensure you are aware of the export classification and export license requirements for all items to be shipped from the Company – Request additional information from shipping requestor to determine export control requirements – Coordinate with ECO as necessary • For controlled goods, confirm a valid license or exemption authorizes the shipment – Properly document the export on all required export documentation – Ensure proper destination control statement is included on shipment • For exports of technical data, ensure adequate information is provided in export documentation (especially if using online shipping software for express delivery services) • Do not release shipments that lack proper export authorization 35
 Thank You Q&A If you have any questions in the future please do not hesitate to contact: Nancy Wood Outsource Trade Group, LLC Nancy. wood@outsourcetradegroup. com Or View your company online database at: http: //www. outsourcetradegroup. com
Thank You Q&A If you have any questions in the future please do not hesitate to contact: Nancy Wood Outsource Trade Group, LLC Nancy. wood@outsourcetradegroup. com Or View your company online database at: http: //www. outsourcetradegroup. com


