b6cb83632cce5084edcaaff7fa78ccf3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 U. S. Drug Law & FDA Chung Keel Lee, Ph. D. Advisor Korea Food & Drug Administration Adjunct Professor Korea University Consultant Pan American Health Organization, WHO
U. S. Drug Law & FDA Chung Keel Lee, Ph. D. Advisor Korea Food & Drug Administration Adjunct Professor Korea University Consultant Pan American Health Organization, WHO
 I. Drug Law History • 1906 The Pure Food & Drugs Act – Purity • 1938 The Federal Food, Drug & Cosmetic Act(FDCA) – Safety – Pre-market Notification • 1962 The Kefauver-Harris Amendments – Pre-market Approval – Effectiveness ( & Safety) – GMP • 1970 Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) – Clinical & Pharmacologic studies not required
I. Drug Law History • 1906 The Pure Food & Drugs Act – Purity • 1938 The Federal Food, Drug & Cosmetic Act(FDCA) – Safety – Pre-market Notification • 1962 The Kefauver-Harris Amendments – Pre-market Approval – Effectiveness ( & Safety) – GMP • 1970 Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) – Clinical & Pharmacologic studies not required
 I. Drug Law History (continued) • 1978 Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) – Update GMP • 1992 Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) – Renew 1 x / 5 years • 2002 Pharmaceutical CGMP for 21 st Century – Risk-based Approach – Quality System Approach
I. Drug Law History (continued) • 1978 Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) – Update GMP • 1992 Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) – Renew 1 x / 5 years • 2002 Pharmaceutical CGMP for 21 st Century – Risk-based Approach – Quality System Approach
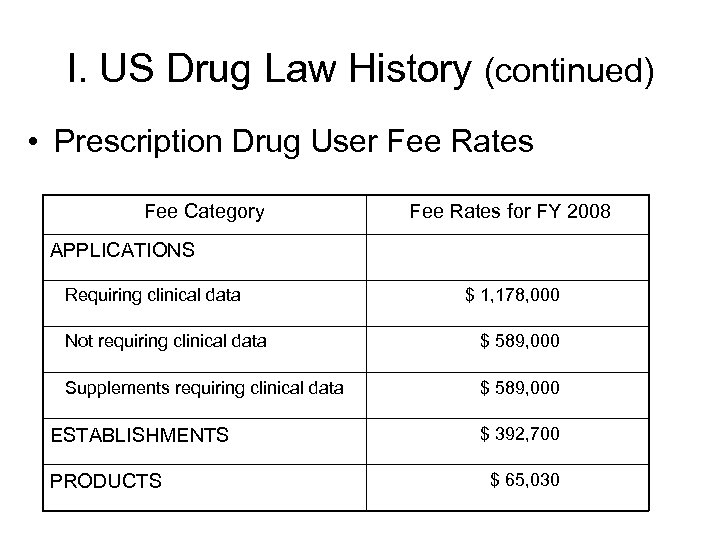 I. US Drug Law History (continued) • Prescription Drug User Fee Rates Fee Category Fee Rates for FY 2008 APPLICATIONS Requiring clinical data $ 1, 178, 000 Not requiring clinical data $ 589, 000 Supplements requiring clinical data $ 589, 000 ESTABLISHMENTS PRODUCTS $ 392, 700 $ 65, 030
I. US Drug Law History (continued) • Prescription Drug User Fee Rates Fee Category Fee Rates for FY 2008 APPLICATIONS Requiring clinical data $ 1, 178, 000 Not requiring clinical data $ 589, 000 Supplements requiring clinical data $ 589, 000 ESTABLISHMENTS PRODUCTS $ 392, 700 $ 65, 030
 II. Laws, Regulations & Guidances • United States Codes (USC) • Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) • Guidances – Agency’s current thinking – Means of communication – Recommendations
II. Laws, Regulations & Guidances • United States Codes (USC) • Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) • Guidances – Agency’s current thinking – Means of communication – Recommendations
 III. Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) ex). CGMP → 21 CFR 211 • Title : Broad Areas ex). Title 3 : The President Title 21 : Food & Drugs Title 40 : Protection of Environment • Chapter : Issuing Agent ex). Title 21 : Food & Drugs Chapter I : FDA, DOHHS Chapter II : DEA, DOJ • Part : Specific Regulatory Areas ex). CGMP for Drugs → 21 CFR 211 GLP for Drugs → 21 CFR 58 • Section : ex). 21 CFR 211. 44
III. Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) ex). CGMP → 21 CFR 211 • Title : Broad Areas ex). Title 3 : The President Title 21 : Food & Drugs Title 40 : Protection of Environment • Chapter : Issuing Agent ex). Title 21 : Food & Drugs Chapter I : FDA, DOHHS Chapter II : DEA, DOJ • Part : Specific Regulatory Areas ex). CGMP for Drugs → 21 CFR 211 GLP for Drugs → 21 CFR 58 • Section : ex). 21 CFR 211. 44
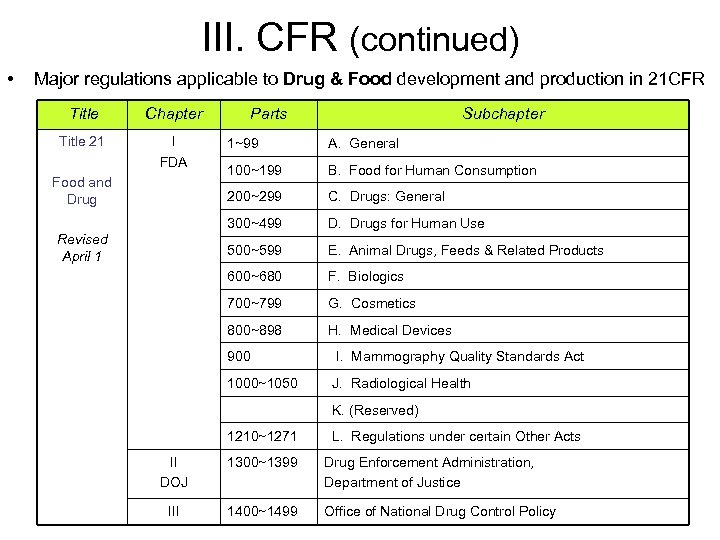 III. CFR (continued) • Major regulations applicable to Drug & Food development and production in 21 CFR Title Chapter Title 21 I FDA Parts Subchapter 100~199 B. Food for Human Consumption C. Drugs: General 300~499 D. Drugs for Human Use 500~599 E. Animal Drugs, Feeds & Related Products 600~680 F. Biologics 700~799 G. Cosmetics 800~898 Revised April 1 A. General 200~299 Food and Drug 1~99 H. Medical Devices 900 I. Mammography Quality Standards Act 1000~1050 J. Radiological Health K. (Reserved) 1210~1271 L. Regulations under certain Other Acts II DOJ 1300~1399 Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice III 1400~1499 Office of National Drug Control Policy
III. CFR (continued) • Major regulations applicable to Drug & Food development and production in 21 CFR Title Chapter Title 21 I FDA Parts Subchapter 100~199 B. Food for Human Consumption C. Drugs: General 300~499 D. Drugs for Human Use 500~599 E. Animal Drugs, Feeds & Related Products 600~680 F. Biologics 700~799 G. Cosmetics 800~898 Revised April 1 A. General 200~299 Food and Drug 1~99 H. Medical Devices 900 I. Mammography Quality Standards Act 1000~1050 J. Radiological Health K. (Reserved) 1210~1271 L. Regulations under certain Other Acts II DOJ 1300~1399 Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice III 1400~1499 Office of National Drug Control Policy
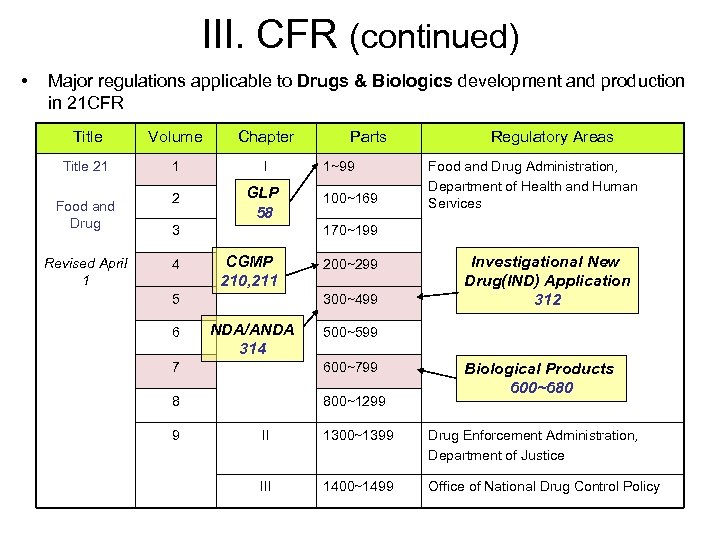 III. CFR (continued) • Major regulations applicable to Drugs & Biologics development and production in 21 CFR Title Volume Chapter Title 21 1 I 2 GLP 58 Food and Drug Revised April 1 3 4 1~99 100~169 CGMP 210, 211 200~299 300~499 NDA/ANDA 314 Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services Investigational New Drug(IND) Application 312 500~599 7 600~799 8 800~1299 9 Regulatory Areas 170~199 5 6 Parts Biological Products 600~680 II 1300~1399 Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice III 1400~1499 Office of National Drug Control Policy
III. CFR (continued) • Major regulations applicable to Drugs & Biologics development and production in 21 CFR Title Volume Chapter Title 21 1 I 2 GLP 58 Food and Drug Revised April 1 3 4 1~99 100~169 CGMP 210, 211 200~299 300~499 NDA/ANDA 314 Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services Investigational New Drug(IND) Application 312 500~599 7 600~799 8 800~1299 9 Regulatory Areas 170~199 5 6 Parts Biological Products 600~680 II 1300~1399 Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice III 1400~1499 Office of National Drug Control Policy
 III. CFR (continued) • Revised Annually – – Title 1 ~ 16 January 1 Title 17 ~27 April 1 Title 28 ~41 July 1 Title 42 ~50 October 1 • Federal Register (FR) – ex). 65 FR 52018, Aug. 28, 2000
III. CFR (continued) • Revised Annually – – Title 1 ~ 16 January 1 Title 17 ~27 April 1 Title 28 ~41 July 1 Title 42 ~50 October 1 • Federal Register (FR) – ex). 65 FR 52018, Aug. 28, 2000
 III. CFR (continued) • Major CGMPS – – – Drug / Biologics : 21 CFR 210 & 211 Blood & Blood Components : 21 CFR 606 Human Food : 21 CFR 110 Medical Device : 21 CFR 820 Cellular & Tissue-based Products : 21 CFR 1271
III. CFR (continued) • Major CGMPS – – – Drug / Biologics : 21 CFR 210 & 211 Blood & Blood Components : 21 CFR 606 Human Food : 21 CFR 110 Medical Device : 21 CFR 820 Cellular & Tissue-based Products : 21 CFR 1271
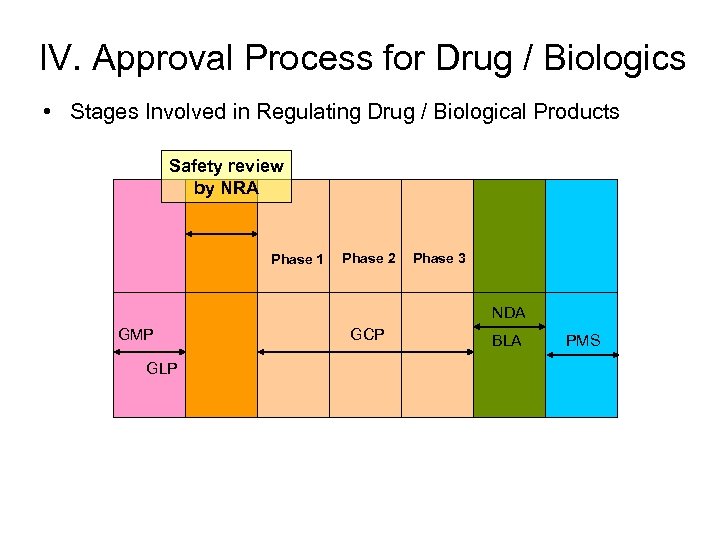 IV. Approval Process for Drug / Biologics • Stages Involved in Regulating Drug / Biological Products Safety review by NRA Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 NDA GMP GLP GCP BLA PMS
IV. Approval Process for Drug / Biologics • Stages Involved in Regulating Drug / Biological Products Safety review by NRA Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 NDA GMP GLP GCP BLA PMS
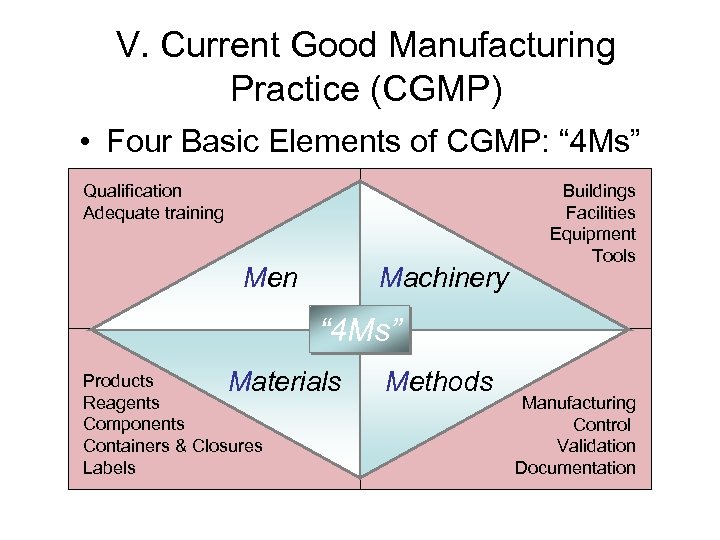 V. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) • Four Basic Elements of CGMP: “ 4 Ms” Qualification Adequate training Men Machinery Buildings Facilities Equipment Tools “ 4 Ms” Products Materials Reagents Components Containers & Closures Labels Methods Manufacturing Control Validation Documentation
V. Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) • Four Basic Elements of CGMP: “ 4 Ms” Qualification Adequate training Men Machinery Buildings Facilities Equipment Tools “ 4 Ms” Products Materials Reagents Components Containers & Closures Labels Methods Manufacturing Control Validation Documentation
 V. CGMP (continued) • Critical Areas to be Inspected – – – – Buildings, facilities and equipment Personnel training, qualifications and Experience Components Manufacturing operations Laboratory controls Packaging and labeling operations Records and reports Qualification / Validation
V. CGMP (continued) • Critical Areas to be Inspected – – – – Buildings, facilities and equipment Personnel training, qualifications and Experience Components Manufacturing operations Laboratory controls Packaging and labeling operations Records and reports Qualification / Validation
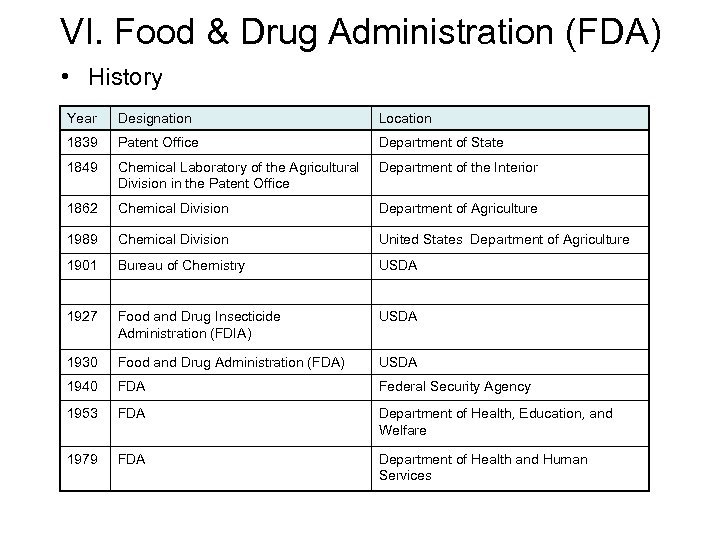 VI. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) • History Year Designation Location 1839 Patent Office Department of State 1849 Chemical Laboratory of the Agricultural Division in the Patent Office Department of the Interior 1862 Chemical Division Department of Agriculture 1989 Chemical Division United States Department of Agriculture 1901 Bureau of Chemistry USDA 1927 Food and Drug Insecticide Administration (FDIA) USDA 1930 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) USDA 1940 FDA Federal Security Agency 1953 FDA Department of Health, Education, and Welfare 1979 FDA Department of Health and Human Services
VI. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) • History Year Designation Location 1839 Patent Office Department of State 1849 Chemical Laboratory of the Agricultural Division in the Patent Office Department of the Interior 1862 Chemical Division Department of Agriculture 1989 Chemical Division United States Department of Agriculture 1901 Bureau of Chemistry USDA 1927 Food and Drug Insecticide Administration (FDIA) USDA 1930 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) USDA 1940 FDA Federal Security Agency 1953 FDA Department of Health, Education, and Welfare 1979 FDA Department of Health and Human Services
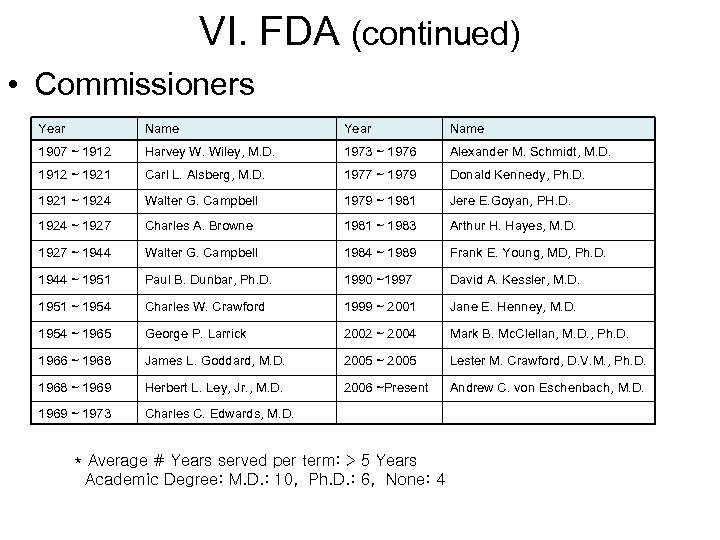 VI. FDA (continued) • Commissioners Year Name 1907 ~ 1912 Harvey W. Wiley, M. D. 1973 ~ 1976 Alexander M. Schmidt, M. D. 1912 ~ 1921 Carl L. Alsberg, M. D. 1977 ~ 1979 Donald Kennedy, Ph. D. 1921 ~ 1924 Walter G. Campbell 1979 ~ 1981 Jere E. Goyan, PH. D. 1924 ~ 1927 Charles A. Browne 1981 ~ 1983 Arthur H. Hayes, M. D. 1927 ~ 1944 Walter G. Campbell 1984 ~ 1989 Frank E. Young, MD, Ph. D. 1944 ~ 1951 Paul B. Dunbar, Ph. D. 1990 ~1997 David A. Kessler, M. D. 1951 ~ 1954 Charles W. Crawford 1999 ~ 2001 Jane E. Henney, M. D. 1954 ~ 1965 George P. Larrick 2002 ~ 2004 Mark B. Mc. Clellan, M. D. , Ph. D. 1966 ~ 1968 James L. Goddard, M. D. 2005 ~ 2005 Lester M. Crawford, D. V. M. , Ph. D. 1968 ~ 1969 Herbert L. Ley, Jr. , M. D. 2006 ~Present Andrew C. von Eschenbach, M. D. 1969 ~ 1973 Charles C. Edwards, M. D. * Average # Years served per term: > 5 Years Academic Degree: M. D. : 10, Ph. D. : 6, None: 4
VI. FDA (continued) • Commissioners Year Name 1907 ~ 1912 Harvey W. Wiley, M. D. 1973 ~ 1976 Alexander M. Schmidt, M. D. 1912 ~ 1921 Carl L. Alsberg, M. D. 1977 ~ 1979 Donald Kennedy, Ph. D. 1921 ~ 1924 Walter G. Campbell 1979 ~ 1981 Jere E. Goyan, PH. D. 1924 ~ 1927 Charles A. Browne 1981 ~ 1983 Arthur H. Hayes, M. D. 1927 ~ 1944 Walter G. Campbell 1984 ~ 1989 Frank E. Young, MD, Ph. D. 1944 ~ 1951 Paul B. Dunbar, Ph. D. 1990 ~1997 David A. Kessler, M. D. 1951 ~ 1954 Charles W. Crawford 1999 ~ 2001 Jane E. Henney, M. D. 1954 ~ 1965 George P. Larrick 2002 ~ 2004 Mark B. Mc. Clellan, M. D. , Ph. D. 1966 ~ 1968 James L. Goddard, M. D. 2005 ~ 2005 Lester M. Crawford, D. V. M. , Ph. D. 1968 ~ 1969 Herbert L. Ley, Jr. , M. D. 2006 ~Present Andrew C. von Eschenbach, M. D. 1969 ~ 1973 Charles C. Edwards, M. D. * Average # Years served per term: > 5 Years Academic Degree: M. D. : 10, Ph. D. : 6, None: 4
 VI. FDA (continued) • Commemorative Stamps 1956 Commemorative Stamp honoring Dr. Harvey W. Wiley 1998 Stamp Commemorates Food & Drugs Act
VI. FDA (continued) • Commemorative Stamps 1956 Commemorative Stamp honoring Dr. Harvey W. Wiley 1998 Stamp Commemorates Food & Drugs Act
 VI. FDA (Continued) • Mission Statement – To protect the public health by assuring • Safety, Efficacy & Security of – – – human & veterinary drugs biological products medical devices food supply cosmetics products emitting radiation – To advance the public health by helping • To speed innovations • The public get the accurate, science-based information
VI. FDA (Continued) • Mission Statement – To protect the public health by assuring • Safety, Efficacy & Security of – – – human & veterinary drugs biological products medical devices food supply cosmetics products emitting radiation – To advance the public health by helping • To speed innovations • The public get the accurate, science-based information
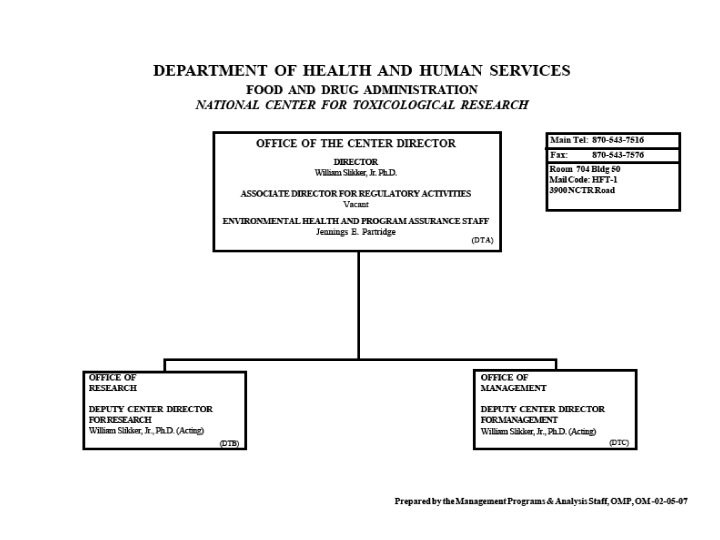
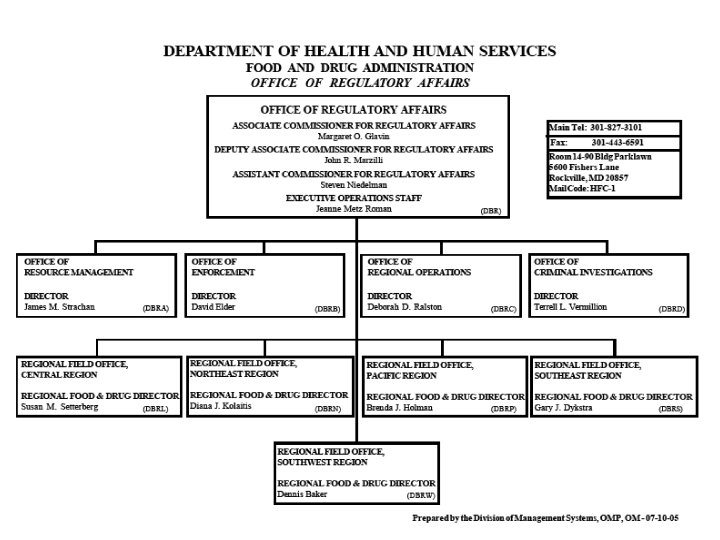
 VI. FDA (Continued) • Organization Charts See the Charts!
VI. FDA (Continued) • Organization Charts See the Charts!
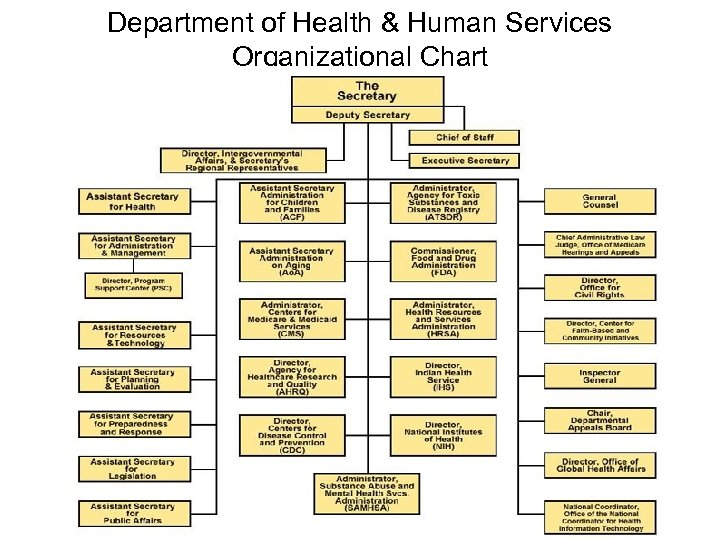 Department of Health & Human Services Organizational Chart
Department of Health & Human Services Organizational Chart
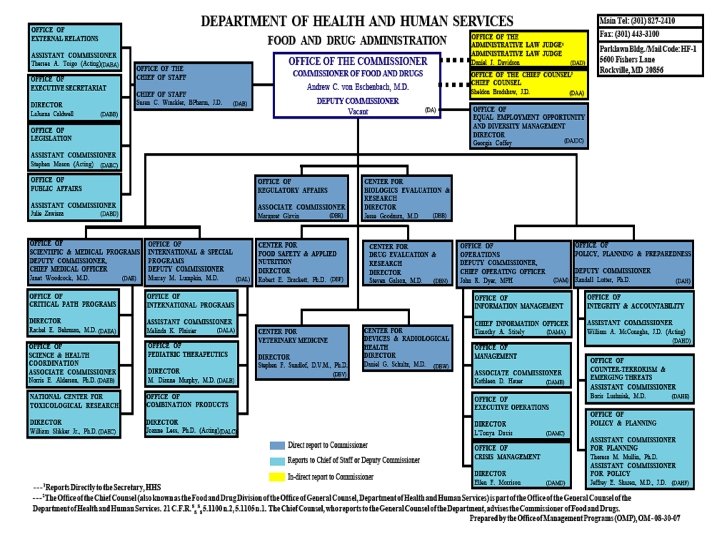
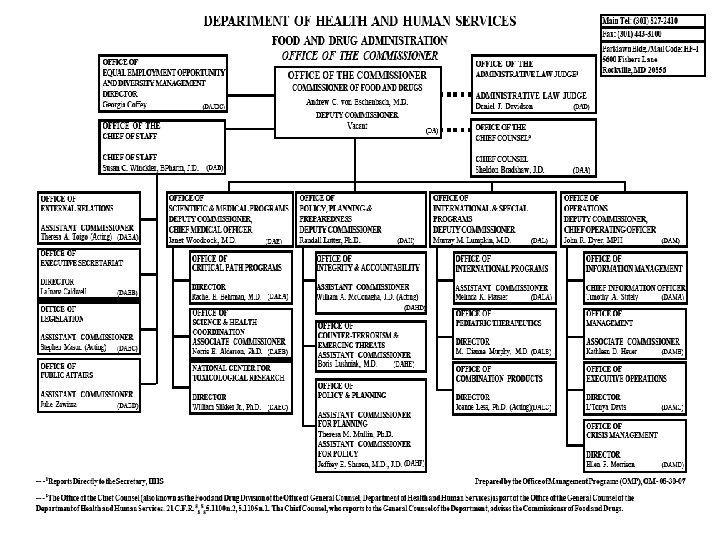
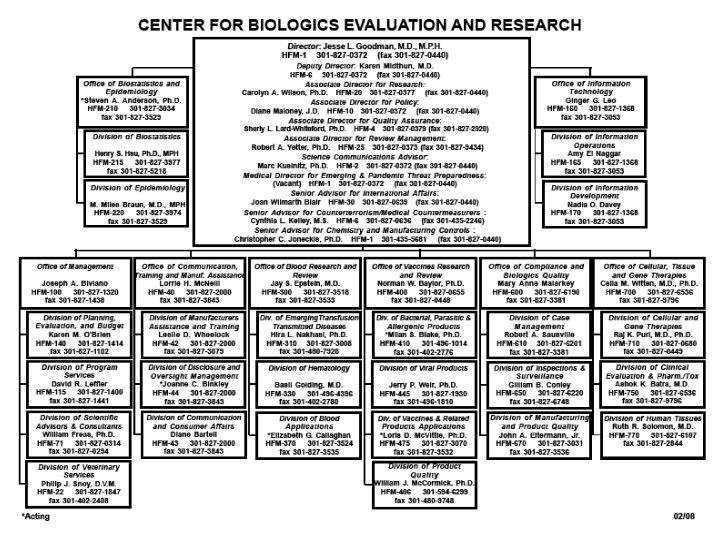
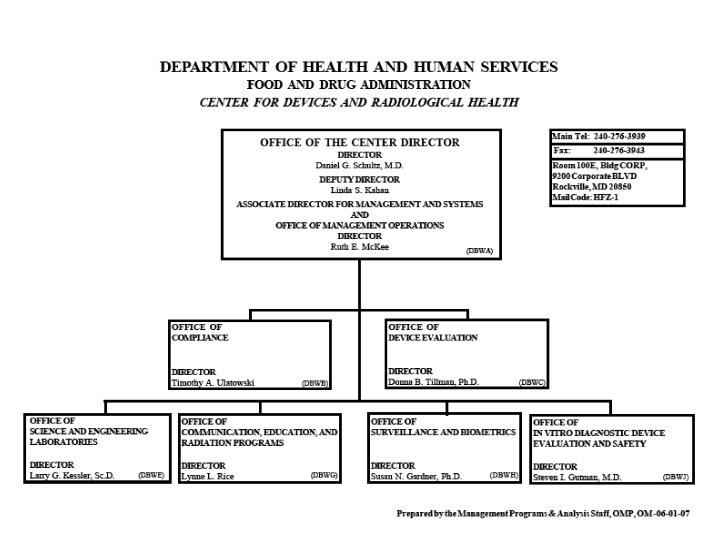
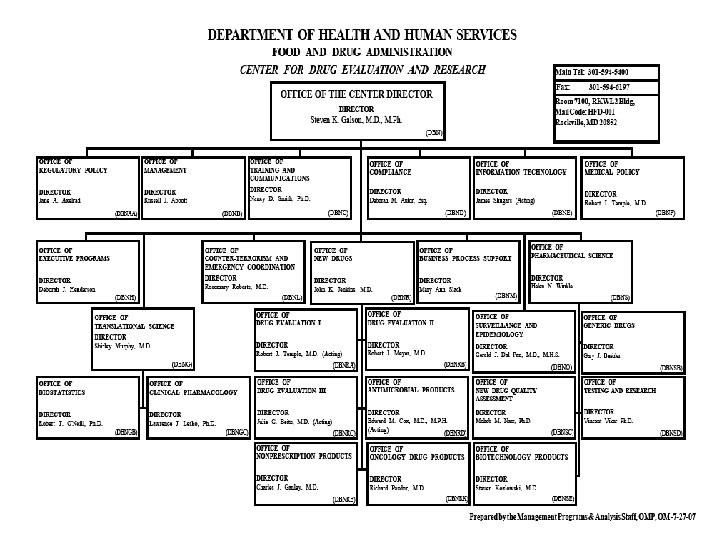
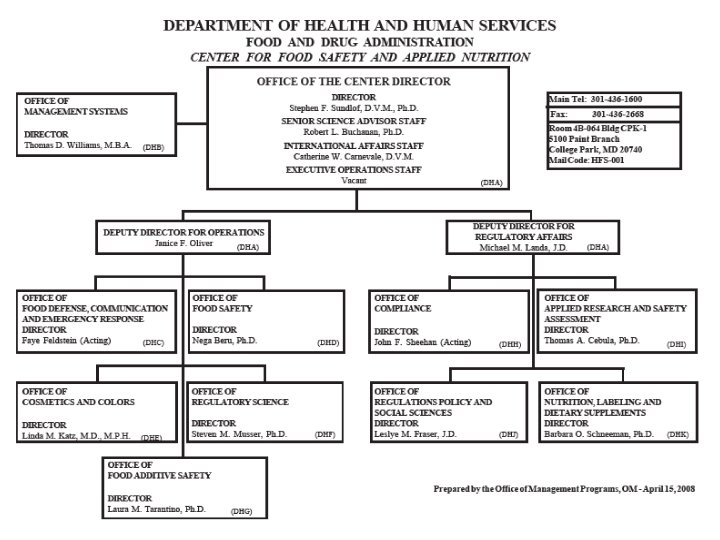
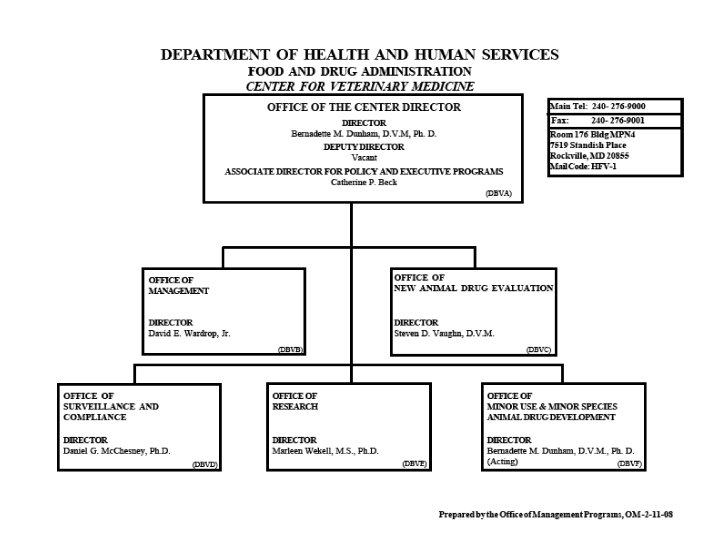
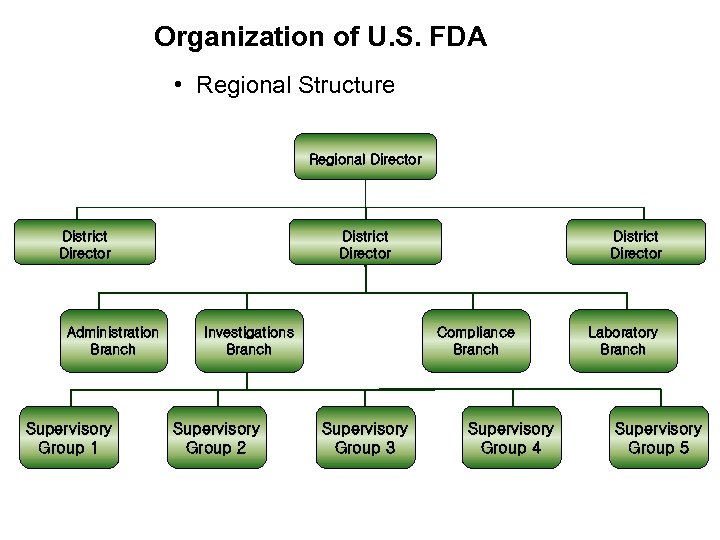 Organization of U. S. FDA • Regional Structure Regional Director District Director Administration Branch Supervisory Group 1 District Director Investigations Branch Supervisory Group 2 District Director Compliance Branch Supervisory Group 3 Supervisory Group 4 Laboratory Branch Supervisory Group 5
Organization of U. S. FDA • Regional Structure Regional Director District Director Administration Branch Supervisory Group 1 District Director Investigations Branch Supervisory Group 2 District Director Compliance Branch Supervisory Group 3 Supervisory Group 4 Laboratory Branch Supervisory Group 5
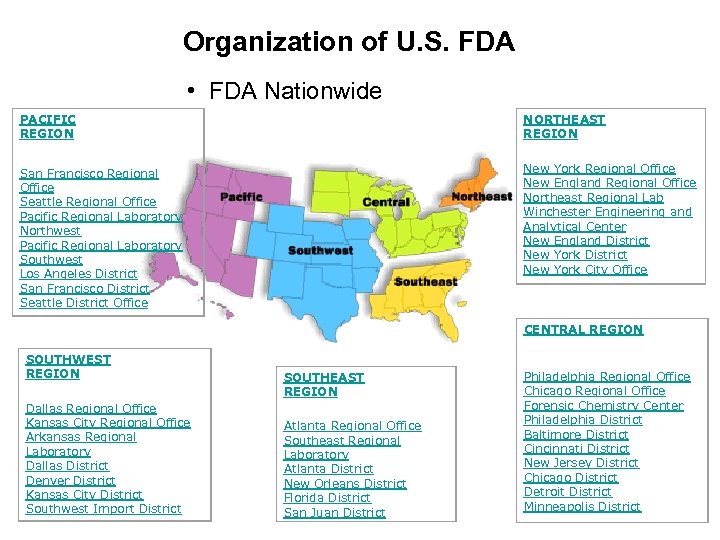 Organization of U. S. FDA • FDA Nationwide PACIFIC REGION NORTHEAST REGION San Francisco Regional Office Seattle Regional Office Pacific Regional Laboratory Northwest Pacific Regional Laboratory Southwest Los Angeles District San Francisco District Seattle District Office New York Regional Office New England Regional Office Northeast Regional Lab Winchester Engineering and Analytical Center New England District New York City Office CENTRAL REGION SOUTHWEST REGION Dallas Regional Office Kansas City Regional Office Arkansas Regional Laboratory Dallas District Denver District Kansas City District Southwest Import District SOUTHEAST REGION Atlanta Regional Office Southeast Regional Laboratory Atlanta District New Orleans District Florida District San Juan District Philadelphia Regional Office Chicago Regional Office Forensic Chemistry Center Philadelphia District Baltimore District Cincinnati District New Jersey District Chicago District Detroit District Minneapolis District
Organization of U. S. FDA • FDA Nationwide PACIFIC REGION NORTHEAST REGION San Francisco Regional Office Seattle Regional Office Pacific Regional Laboratory Northwest Pacific Regional Laboratory Southwest Los Angeles District San Francisco District Seattle District Office New York Regional Office New England Regional Office Northeast Regional Lab Winchester Engineering and Analytical Center New England District New York City Office CENTRAL REGION SOUTHWEST REGION Dallas Regional Office Kansas City Regional Office Arkansas Regional Laboratory Dallas District Denver District Kansas City District Southwest Import District SOUTHEAST REGION Atlanta Regional Office Southeast Regional Laboratory Atlanta District New Orleans District Florida District San Juan District Philadelphia Regional Office Chicago Regional Office Forensic Chemistry Center Philadelphia District Baltimore District Cincinnati District New Jersey District Chicago District Detroit District Minneapolis District
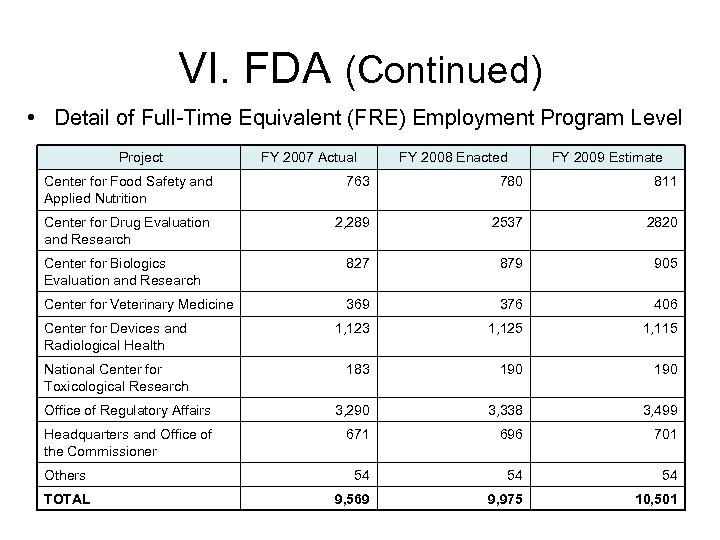 VI. FDA (Continued) • Detail of Full-Time Equivalent (FRE) Employment Program Level Project FY 2007 Actual FY 2008 Enacted FY 2009 Estimate Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition 763 780 811 Center for Drug Evaluation and Research 2, 289 2537 2820 Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research 827 879 905 Center for Veterinary Medicine 369 376 406 Center for Devices and Radiological Health 1, 123 1, 125 1, 115 National Center for Toxicological Research 183 190 Office of Regulatory Affairs 3, 290 3, 338 3, 499 Headquarters and Office of the Commissioner 671 696 701 54 54 54 9, 569 9, 975 10, 501 Others TOTAL
VI. FDA (Continued) • Detail of Full-Time Equivalent (FRE) Employment Program Level Project FY 2007 Actual FY 2008 Enacted FY 2009 Estimate Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition 763 780 811 Center for Drug Evaluation and Research 2, 289 2537 2820 Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research 827 879 905 Center for Veterinary Medicine 369 376 406 Center for Devices and Radiological Health 1, 123 1, 125 1, 115 National Center for Toxicological Research 183 190 Office of Regulatory Affairs 3, 290 3, 338 3, 499 Headquarters and Office of the Commissioner 671 696 701 54 54 54 9, 569 9, 975 10, 501 Others TOTAL
 Vll. Statement of Dr. Andrew C. von Eschenbach before U. S. House of Representatives on “ FDA’s Foreign Drug Inspection Program” Nov. 1, 2007 • General – > 200 foreign drug manufacturing inspections per year – Foreign drug inspection • usually for 5 days • 3 days for a control testing lab • up to 2 weeks for a sterile product – 800 FDA investigators trained foreign inspections • 355 for drug inspections – 3 consecutive 5 -day inspections by 1 investigator
Vll. Statement of Dr. Andrew C. von Eschenbach before U. S. House of Representatives on “ FDA’s Foreign Drug Inspection Program” Nov. 1, 2007 • General – > 200 foreign drug manufacturing inspections per year – Foreign drug inspection • usually for 5 days • 3 days for a control testing lab • up to 2 weeks for a sterile product – 800 FDA investigators trained foreign inspections • 355 for drug inspections – 3 consecutive 5 -day inspections by 1 investigator
 Vll. Statement of Dr. Andrew C. von Eschenbach before U. S. House of Representatives on “ FDA’s Foreign Drug Inspection Program” Nov. 1, 2007 (continued) • Drug Ingredient Safety – Foreign drug counterfeiting & contamination • glycerin contaminated with diethylene glycol (DEG) – 100 children killed in Haiti • glycerin contaminated with DEG from China – 20 deaths in Panama (2006) • toothpaste contaminated with DEG from China • FDA guidance issued – Foreign intermediaries involved in the supply channel
Vll. Statement of Dr. Andrew C. von Eschenbach before U. S. House of Representatives on “ FDA’s Foreign Drug Inspection Program” Nov. 1, 2007 (continued) • Drug Ingredient Safety – Foreign drug counterfeiting & contamination • glycerin contaminated with diethylene glycol (DEG) – 100 children killed in Haiti • glycerin contaminated with DEG from China – 20 deaths in Panama (2006) • toothpaste contaminated with DEG from China • FDA guidance issued – Foreign intermediaries involved in the supply channel
 Vll. Statement of Dr. Andrew C. von Eschenbach before U. S. House of Representatives on “ FDA’s Foreign Drug Inspection Program” Nov. 1, 2007 (continued) • Improving the Oversight of Foreign Manufactured Drugs – Information Technology (IT) enhancements – International efforts. • Cooperative relationship with foreign regulators - Cooperation under FTA - Memorandum of understanding (MOU) - Letter-exchanging • Exchanges “ inspectional information” (MRA) - 3 -year transition period - EU-US bilateral agreement • FDA applied for joining PIC/S • Educational workshop
Vll. Statement of Dr. Andrew C. von Eschenbach before U. S. House of Representatives on “ FDA’s Foreign Drug Inspection Program” Nov. 1, 2007 (continued) • Improving the Oversight of Foreign Manufactured Drugs – Information Technology (IT) enhancements – International efforts. • Cooperative relationship with foreign regulators - Cooperation under FTA - Memorandum of understanding (MOU) - Letter-exchanging • Exchanges “ inspectional information” (MRA) - 3 -year transition period - EU-US bilateral agreement • FDA applied for joining PIC/S • Educational workshop



