b3495b15d53744d8ed60516b6cc01deb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 U. S. Department of Agriculture e. Government Program e. Government Smart Choice Web-based Supply Chain Management Kick Off Meeting May 20, 2003
U. S. Department of Agriculture e. Government Program e. Government Smart Choice Web-based Supply Chain Management Kick Off Meeting May 20, 2003
 USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 2
USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 2
 USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 3
USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 3
 USDA e. Government Program WBSCM is strategically important to USDA Project Rationale § The WBSCM Initiative supports several key programs and goals of USDA: • WBSCM comprises 1 of 5 strategic “Smart Choice” initiatives contained in USDA e. Government Strategic Plan FY 2002 -2006 • WBSCM will assist in supporting the President’s Management Agenda and the Secretary’s Agriculture Vision for improving the food aid program • A WBSCM system will enhance USDA’s capabilities to achieve its missions while reducing costs to USDA, MARAD, USAID, business partners, and citizens § This current project will significantly advance the WBSCM Initiative by: • Identifying the business/functional and technology requirements (supply chain value opportunities) • Defining what activities need to be completed in order to capture the supply chain opportunities and identifying the new enabling technologies • Justifying the funding required to support the WBSCM investment • Defining an implementation plan for building the system and describing the process changes required to build and support it 4
USDA e. Government Program WBSCM is strategically important to USDA Project Rationale § The WBSCM Initiative supports several key programs and goals of USDA: • WBSCM comprises 1 of 5 strategic “Smart Choice” initiatives contained in USDA e. Government Strategic Plan FY 2002 -2006 • WBSCM will assist in supporting the President’s Management Agenda and the Secretary’s Agriculture Vision for improving the food aid program • A WBSCM system will enhance USDA’s capabilities to achieve its missions while reducing costs to USDA, MARAD, USAID, business partners, and citizens § This current project will significantly advance the WBSCM Initiative by: • Identifying the business/functional and technology requirements (supply chain value opportunities) • Defining what activities need to be completed in order to capture the supply chain opportunities and identifying the new enabling technologies • Justifying the funding required to support the WBSCM investment • Defining an implementation plan for building the system and describing the process changes required to build and support it 4
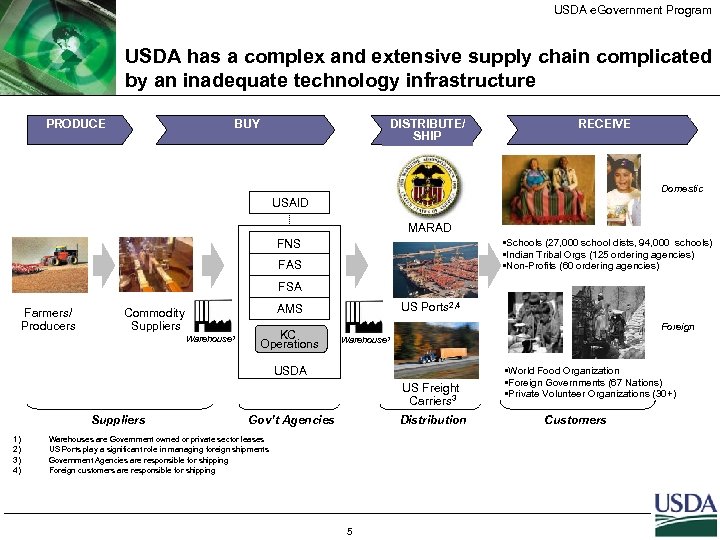 USDA e. Government Program USDA has a complex and extensive supply chain complicated by an inadequate technology infrastructure PRODUCE BUY DISTRIBUTE/ SHIP RECEIVE Domestic USAID MARAD §Schools (27, 000 school dists, 94, 000 schools) §Indian Tribal Orgs (125 ordering agencies) §Non-Profits (60 ordering agencies) FNS FAS FSA Farmers/ Producers Commodity Suppliers Warehouse 1 US Ports 2, 4 AMS KC Operations Foreign Warehouse 1 USDA US Freight Carriers 3 Suppliers 1) 2) 3) 4) Gov’t Agencies Distribution Warehouses are Government owned or private sector leases US Ports play a significant role in managing foreign shipments Government Agencies are responsible for shipping Foreign customers are responsible for shipping 5 §World Food Organization §Foreign Governments (67 Nations) §Private Volunteer Organizations (30+) Customers
USDA e. Government Program USDA has a complex and extensive supply chain complicated by an inadequate technology infrastructure PRODUCE BUY DISTRIBUTE/ SHIP RECEIVE Domestic USAID MARAD §Schools (27, 000 school dists, 94, 000 schools) §Indian Tribal Orgs (125 ordering agencies) §Non-Profits (60 ordering agencies) FNS FAS FSA Farmers/ Producers Commodity Suppliers Warehouse 1 US Ports 2, 4 AMS KC Operations Foreign Warehouse 1 USDA US Freight Carriers 3 Suppliers 1) 2) 3) 4) Gov’t Agencies Distribution Warehouses are Government owned or private sector leases US Ports play a significant role in managing foreign shipments Government Agencies are responsible for shipping Foreign customers are responsible for shipping 5 §World Food Organization §Foreign Governments (67 Nations) §Private Volunteer Organizations (30+) Customers
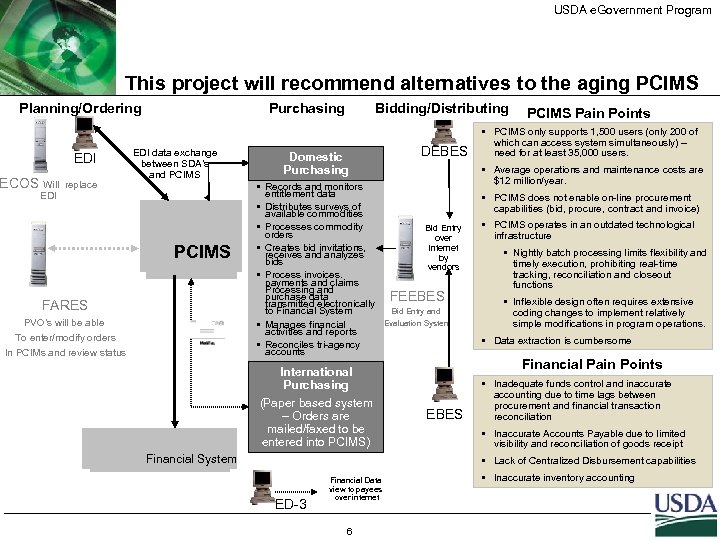 USDA e. Government Program This project will recommend alternatives to the aging PCIMS Planning/Ordering EDI ECOS Will replace Purchasing EDI data exchange between SDA’s and PCIMS EDI PCIMS FARES PVO’s will be able To enter/modify orders In PCIMs and review status Bidding/Distributing Domestic Purchasing § Records and monitors entitlement data § Distributes surveys of available commodities § Processes commodity orders § Creates bid invitations, receives and analyzes bids § Process invoices. payments and claims Processing and purchase data transmitted electronically to Financial System § Manages financial activities and reports § Reconciles tri-agency accounts International Purchasing (Paper based system – Orders are mailed/faxed to be entered into PCIMS) Financial System DEBES PCIMS Pain Points § PCIMS only supports 1, 500 users (only 200 of which can access system simultaneously) – need for at least 35, 000 users. § Average operations and maintenance costs are $12 million/year. § PCIMS does not enable on-line procurement capabilities (bid, procure, contract and invoice) Bid Entry over internet by vendors FEEBES Bid Entry and Evaluation System § PCIMS operates in an outdated technological infrastructure § Nightly batch processing limits flexibility and timely execution, prohibiting real-time tracking, reconciliation and closeout functions § Inflexible design often requires extensive coding changes to implement relatively simple modifications in program operations. § Data extraction is cumbersome Financial Pain Points EBES § Inadequate funds control and inaccurate accounting due to time lags between procurement and financial transaction reconciliation § Inaccurate Accounts Payable due to limited visibility and reconciliation of goods receipt § Lack of Centralized Disbursement capabilities ED-3 Financial Data view to payees over internet 6 § Inaccurate inventory accounting
USDA e. Government Program This project will recommend alternatives to the aging PCIMS Planning/Ordering EDI ECOS Will replace Purchasing EDI data exchange between SDA’s and PCIMS EDI PCIMS FARES PVO’s will be able To enter/modify orders In PCIMs and review status Bidding/Distributing Domestic Purchasing § Records and monitors entitlement data § Distributes surveys of available commodities § Processes commodity orders § Creates bid invitations, receives and analyzes bids § Process invoices. payments and claims Processing and purchase data transmitted electronically to Financial System § Manages financial activities and reports § Reconciles tri-agency accounts International Purchasing (Paper based system – Orders are mailed/faxed to be entered into PCIMS) Financial System DEBES PCIMS Pain Points § PCIMS only supports 1, 500 users (only 200 of which can access system simultaneously) – need for at least 35, 000 users. § Average operations and maintenance costs are $12 million/year. § PCIMS does not enable on-line procurement capabilities (bid, procure, contract and invoice) Bid Entry over internet by vendors FEEBES Bid Entry and Evaluation System § PCIMS operates in an outdated technological infrastructure § Nightly batch processing limits flexibility and timely execution, prohibiting real-time tracking, reconciliation and closeout functions § Inflexible design often requires extensive coding changes to implement relatively simple modifications in program operations. § Data extraction is cumbersome Financial Pain Points EBES § Inadequate funds control and inaccurate accounting due to time lags between procurement and financial transaction reconciliation § Inaccurate Accounts Payable due to limited visibility and reconciliation of goods receipt § Lack of Centralized Disbursement capabilities ED-3 Financial Data view to payees over internet 6 § Inaccurate inventory accounting
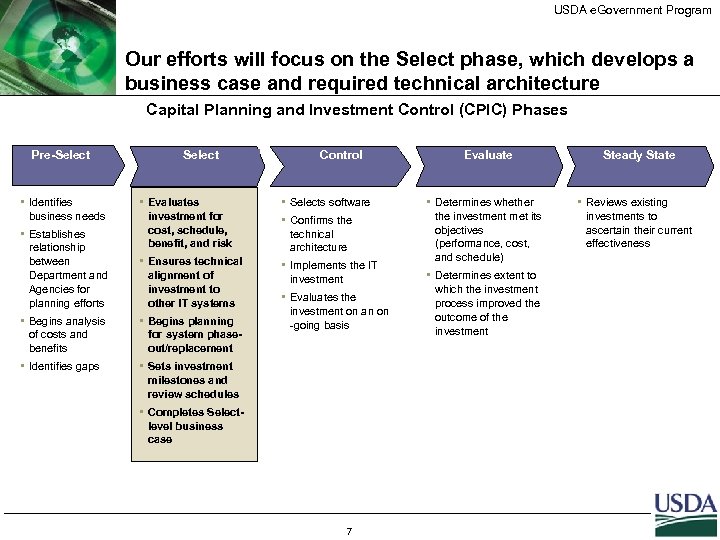 USDA e. Government Program Our efforts will focus on the Select phase, which develops a business case and required technical architecture Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) Phases Pre-Select • Identifies business needs • Establishes relationship between Department and Agencies for planning efforts Select Control • Evaluates investment for cost, schedule, benefit, and risk • Selects software • Ensures technical alignment of investment to other IT systems • Implements the IT investment • Begins analysis of costs and benefits • Begins planning for system phaseout/replacement • Identifies gaps • Confirms the technical architecture • Evaluates the investment on an on -going basis • Sets investment milestones and review schedules • Completes Selectlevel business case 7 Evaluate Steady State • Determines whether the investment met its objectives (performance, cost, and schedule) • Reviews existing investments to ascertain their current effectiveness • Determines extent to which the investment process improved the outcome of the investment
USDA e. Government Program Our efforts will focus on the Select phase, which develops a business case and required technical architecture Capital Planning and Investment Control (CPIC) Phases Pre-Select • Identifies business needs • Establishes relationship between Department and Agencies for planning efforts Select Control • Evaluates investment for cost, schedule, benefit, and risk • Selects software • Ensures technical alignment of investment to other IT systems • Implements the IT investment • Begins analysis of costs and benefits • Begins planning for system phaseout/replacement • Identifies gaps • Confirms the technical architecture • Evaluates the investment on an on -going basis • Sets investment milestones and review schedules • Completes Selectlevel business case 7 Evaluate Steady State • Determines whether the investment met its objectives (performance, cost, and schedule) • Reviews existing investments to ascertain their current effectiveness • Determines extent to which the investment process improved the outcome of the investment
 USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 8
USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 8
 USDA e. Government Program This project will build on the work of the Pre-select Business Case conducted in 2002 Results of the Pre-select Business Case • Identified how the WBSCM Initiative will support Agency and Departmental goals • Developed a preliminary vision for the WBSCM system • Defined the WBSCM value proposition and estimated potential costs and benefits • Identified significant potential savings, based on assumptions, that would result from a WBSCM system • Provided justification for the investment of time and resources to conduct the current project and its Select-level Business Case 9
USDA e. Government Program This project will build on the work of the Pre-select Business Case conducted in 2002 Results of the Pre-select Business Case • Identified how the WBSCM Initiative will support Agency and Departmental goals • Developed a preliminary vision for the WBSCM system • Defined the WBSCM value proposition and estimated potential costs and benefits • Identified significant potential savings, based on assumptions, that would result from a WBSCM system • Provided justification for the investment of time and resources to conduct the current project and its Select-level Business Case 9
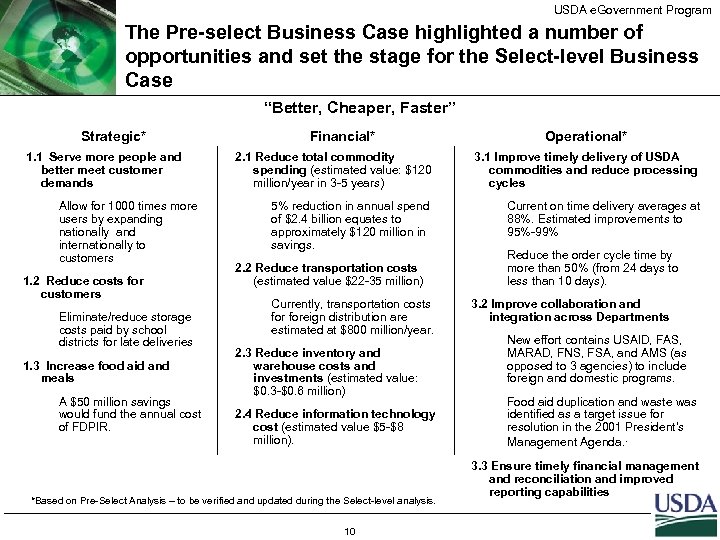 USDA e. Government Program The Pre-select Business Case highlighted a number of opportunities and set the stage for the Select-level Business Case “Better, Cheaper, Faster” Strategic* 1. 1 Serve more people and better meet customer demands Allow for 1000 times more users by expanding nationally and internationally to customers 1. 2 Reduce costs for customers Eliminate/reduce storage costs paid by school districts for late deliveries 1. 3 Increase food aid and meals A $50 million savings would fund the annual cost of FDPIR. Financial* Operational* 2. 1 Reduce total commodity spending (estimated value: $120 million/year in 3 -5 years) 3. 1 Improve timely delivery of USDA commodities and reduce processing cycles 5% reduction in annual spend of $2. 4 billion equates to approximately $120 million in savings. Current on time delivery averages at 88%. Estimated improvements to 95%-99% 2. 2 Reduce transportation costs (estimated value $22 -35 million) Currently, transportation costs foreign distribution are estimated at $800 million/year. 2. 3 Reduce inventory and warehouse costs and investments (estimated value: $0. 3 -$0. 6 million) 2. 4 Reduce information technology cost (estimated value $5 -$8 million). *Based on Pre-Select Analysis – to be verified and updated during the Select-level analysis. 10 Reduce the order cycle time by more than 50% (from 24 days to less than 10 days). 3. 2 Improve collaboration and integration across Departments New effort contains USAID, FAS, MARAD, FNS, FSA, and AMS (as opposed to 3 agencies) to include foreign and domestic programs. Food aid duplication and waste was identified as a target issue for resolution in the 2001 President's Management Agenda. · 3. 3 Ensure timely financial management and reconciliation and improved reporting capabilities
USDA e. Government Program The Pre-select Business Case highlighted a number of opportunities and set the stage for the Select-level Business Case “Better, Cheaper, Faster” Strategic* 1. 1 Serve more people and better meet customer demands Allow for 1000 times more users by expanding nationally and internationally to customers 1. 2 Reduce costs for customers Eliminate/reduce storage costs paid by school districts for late deliveries 1. 3 Increase food aid and meals A $50 million savings would fund the annual cost of FDPIR. Financial* Operational* 2. 1 Reduce total commodity spending (estimated value: $120 million/year in 3 -5 years) 3. 1 Improve timely delivery of USDA commodities and reduce processing cycles 5% reduction in annual spend of $2. 4 billion equates to approximately $120 million in savings. Current on time delivery averages at 88%. Estimated improvements to 95%-99% 2. 2 Reduce transportation costs (estimated value $22 -35 million) Currently, transportation costs foreign distribution are estimated at $800 million/year. 2. 3 Reduce inventory and warehouse costs and investments (estimated value: $0. 3 -$0. 6 million) 2. 4 Reduce information technology cost (estimated value $5 -$8 million). *Based on Pre-Select Analysis – to be verified and updated during the Select-level analysis. 10 Reduce the order cycle time by more than 50% (from 24 days to less than 10 days). 3. 2 Improve collaboration and integration across Departments New effort contains USAID, FAS, MARAD, FNS, FSA, and AMS (as opposed to 3 agencies) to include foreign and domestic programs. Food aid duplication and waste was identified as a target issue for resolution in the 2001 President's Management Agenda. · 3. 3 Ensure timely financial management and reconciliation and improved reporting capabilities
 USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-Select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 11
USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-Select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 11
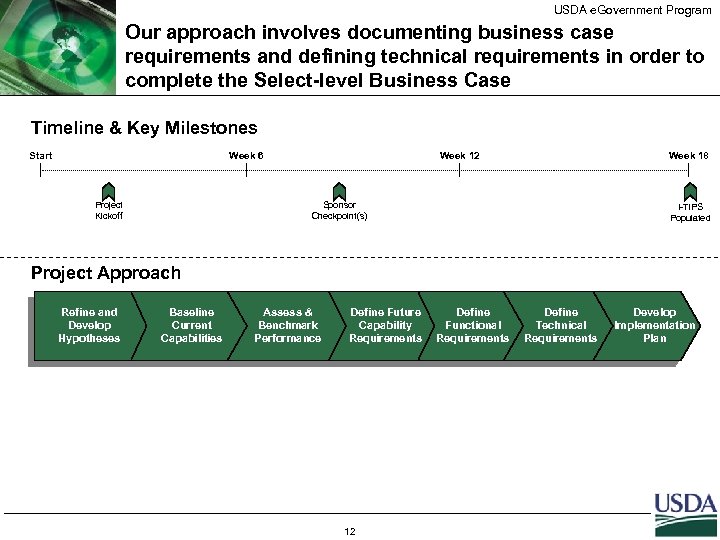 USDA e. Government Program Our approach involves documenting business case requirements and defining technical requirements in order to complete the Select-level Business Case Timeline & Key Milestones Start Week 6 Project Kickoff Week 12 Sponsor Checkpoint(s) Week 18 I-TIPS Populated Project Approach Refine and Develop Hypotheses Baseline Assess & Define Develop Define Future Define Analyze Current Determine Desired Define Value Determine Conduct Alternatives Current Benchmark Technical Implementation Capability Functional Capability Proposition Impact on USDA Analysis Capabilities Performance Plan Requirements 12
USDA e. Government Program Our approach involves documenting business case requirements and defining technical requirements in order to complete the Select-level Business Case Timeline & Key Milestones Start Week 6 Project Kickoff Week 12 Sponsor Checkpoint(s) Week 18 I-TIPS Populated Project Approach Refine and Develop Hypotheses Baseline Assess & Define Develop Define Future Define Analyze Current Determine Desired Define Value Determine Conduct Alternatives Current Benchmark Technical Implementation Capability Functional Capability Proposition Impact on USDA Analysis Capabilities Performance Plan Requirements 12
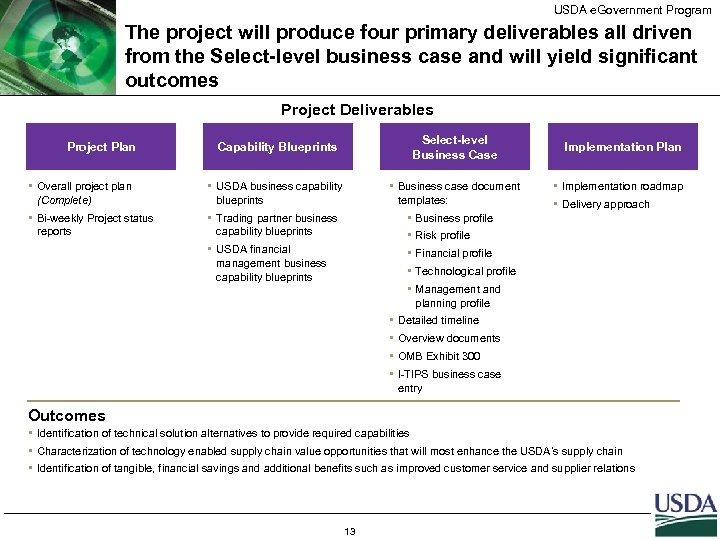 USDA e. Government Program The project will produce four primary deliverables all driven from the Select-level business case and will yield significant outcomes Project Deliverables Capability Blueprints Select-level Business Case • Overall project plan (Complete) • USDA business capability blueprints • Business case document templates: • Bi-weekly Project status reports • Trading partner business capability blueprints • Business profile • USDA financial management business capability blueprints • Financial profile Project Plan Implementation Plan • Implementation roadmap • Delivery approach • Risk profile • Technological profile • Management and planning profile • Detailed timeline • Overview documents • OMB Exhibit 300 • I-TIPS business case entry Outcomes • Identification of technical solution alternatives to provide required capabilities • Characterization of technology enabled supply chain value opportunities that will most enhance the USDA’s supply chain • Identification of tangible, financial savings and additional benefits such as improved customer service and supplier relations 13
USDA e. Government Program The project will produce four primary deliverables all driven from the Select-level business case and will yield significant outcomes Project Deliverables Capability Blueprints Select-level Business Case • Overall project plan (Complete) • USDA business capability blueprints • Business case document templates: • Bi-weekly Project status reports • Trading partner business capability blueprints • Business profile • USDA financial management business capability blueprints • Financial profile Project Plan Implementation Plan • Implementation roadmap • Delivery approach • Risk profile • Technological profile • Management and planning profile • Detailed timeline • Overview documents • OMB Exhibit 300 • I-TIPS business case entry Outcomes • Identification of technical solution alternatives to provide required capabilities • Characterization of technology enabled supply chain value opportunities that will most enhance the USDA’s supply chain • Identification of tangible, financial savings and additional benefits such as improved customer service and supplier relations 13
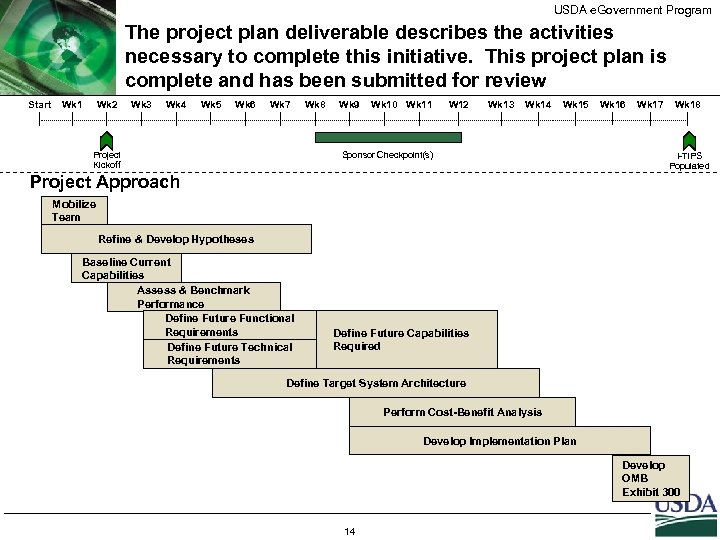 USDA e. Government Program The project plan deliverable describes the activities necessary to complete this initiative. This project plan is complete and has been submitted for review Start Wk 1 Wk 2 Wk 3 Wk 4 Wk 5 Wk 6 Wk 7 Project Kickoff Wk 8 Wk 9 Wk 10 Wk 11 W 12 Wk 13 Wk 14 Wk 15 Sponsor Checkpoint(s) Wk 16 Wk 17 Wk 18 I-TIPS Populated Project Approach Mobilize Team Refine & Develop Hypotheses Baseline Current Capabilities Assess & Benchmark Performance Define Future Functional Requirements Define Future Technical Requirements Define Future Capabilities Required Define Target System Architecture Perform Cost-Benefit Analysis Develop Implementation Plan Develop OMB Exhibit 300 14
USDA e. Government Program The project plan deliverable describes the activities necessary to complete this initiative. This project plan is complete and has been submitted for review Start Wk 1 Wk 2 Wk 3 Wk 4 Wk 5 Wk 6 Wk 7 Project Kickoff Wk 8 Wk 9 Wk 10 Wk 11 W 12 Wk 13 Wk 14 Wk 15 Sponsor Checkpoint(s) Wk 16 Wk 17 Wk 18 I-TIPS Populated Project Approach Mobilize Team Refine & Develop Hypotheses Baseline Current Capabilities Assess & Benchmark Performance Define Future Functional Requirements Define Future Technical Requirements Define Future Capabilities Required Define Target System Architecture Perform Cost-Benefit Analysis Develop Implementation Plan Develop OMB Exhibit 300 14
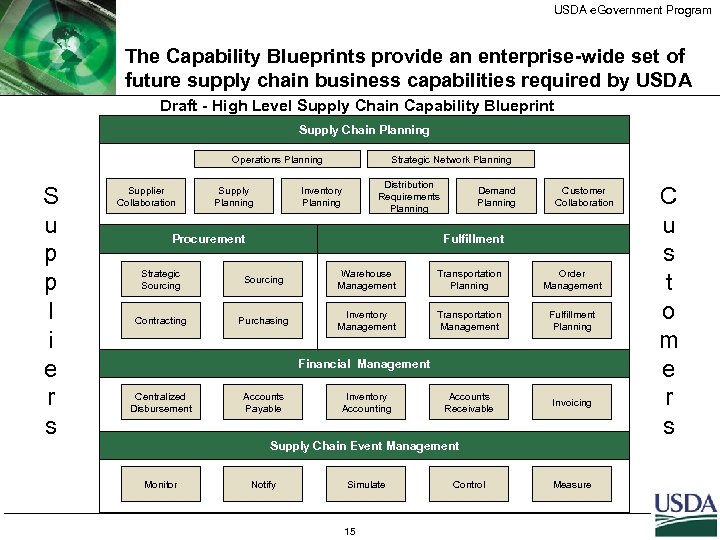 USDA e. Government Program The Capability Blueprints provide an enterprise-wide set of future supply chain business capabilities required by USDA Draft - High Level Supply Chain Capability Blueprint Supply Chain Planning Operations Planning S u p p l i e r s Supplier Collaboration Supply Planning Strategic Network Planning Distribution Requirements Planning Inventory Planning Procurement Demand Planning Customer Collaboration Fulfillment Strategic Sourcing Warehouse Management Transportation Planning Order Management Contracting Purchasing Inventory Management Transportation Management Fulfillment Planning Accounts Receivable Invoicing Financial Management Centralized Disbursement Accounts Payable Inventory Accounting Supply Chain Event Management Monitor Notify Simulate 15 Control Measure C u s t o m e r s
USDA e. Government Program The Capability Blueprints provide an enterprise-wide set of future supply chain business capabilities required by USDA Draft - High Level Supply Chain Capability Blueprint Supply Chain Planning Operations Planning S u p p l i e r s Supplier Collaboration Supply Planning Strategic Network Planning Distribution Requirements Planning Inventory Planning Procurement Demand Planning Customer Collaboration Fulfillment Strategic Sourcing Warehouse Management Transportation Planning Order Management Contracting Purchasing Inventory Management Transportation Management Fulfillment Planning Accounts Receivable Invoicing Financial Management Centralized Disbursement Accounts Payable Inventory Accounting Supply Chain Event Management Monitor Notify Simulate 15 Control Measure C u s t o m e r s
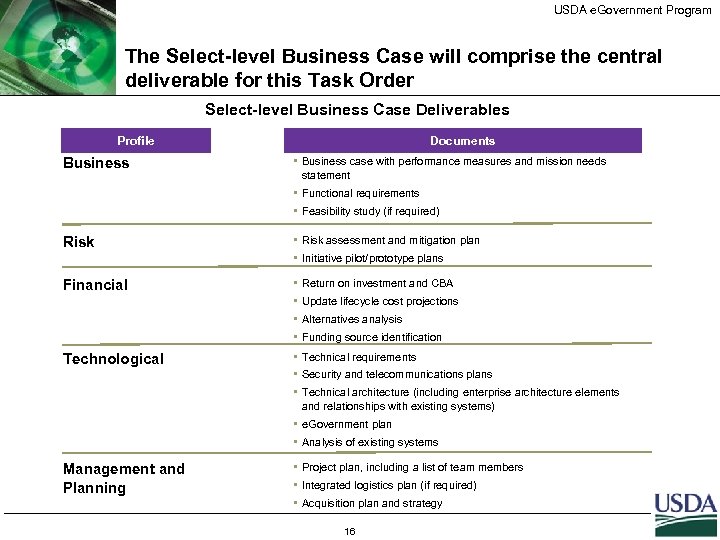 USDA e. Government Program The Select-level Business Case will comprise the central deliverable for this Task Order Select-level Business Case Deliverables Profile Business Documents • Business case with performance measures and mission needs statement • Functional requirements • Feasibility study (if required) Risk • Risk assessment and mitigation plan • Initiative pilot/prototype plans Financial • Return on investment and CBA • Update lifecycle cost projections • Alternatives analysis • Funding source identification Technological • Technical requirements • Security and telecommunications plans • Technical architecture (including enterprise architecture elements and relationships with existing systems) • e. Government plan • Analysis of existing systems Management and Planning • Project plan, including a list of team members • Integrated logistics plan (if required) • Acquisition plan and strategy 16
USDA e. Government Program The Select-level Business Case will comprise the central deliverable for this Task Order Select-level Business Case Deliverables Profile Business Documents • Business case with performance measures and mission needs statement • Functional requirements • Feasibility study (if required) Risk • Risk assessment and mitigation plan • Initiative pilot/prototype plans Financial • Return on investment and CBA • Update lifecycle cost projections • Alternatives analysis • Funding source identification Technological • Technical requirements • Security and telecommunications plans • Technical architecture (including enterprise architecture elements and relationships with existing systems) • e. Government plan • Analysis of existing systems Management and Planning • Project plan, including a list of team members • Integrated logistics plan (if required) • Acquisition plan and strategy 16
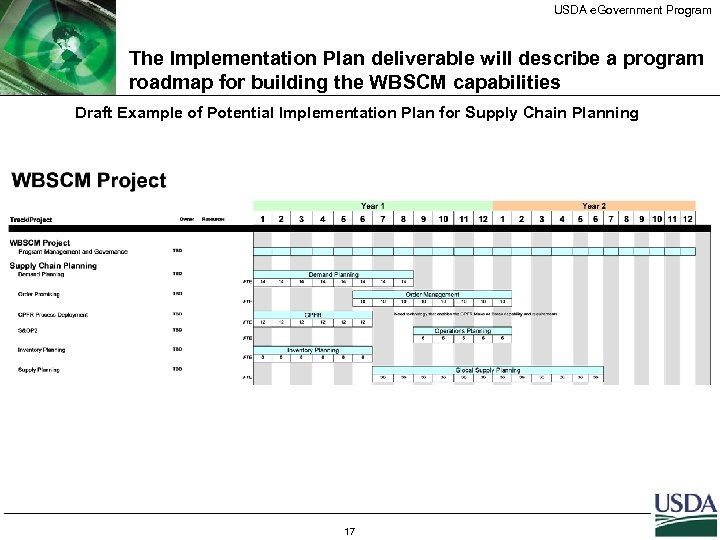 USDA e. Government Program The Implementation Plan deliverable will describe a program roadmap for building the WBSCM capabilities Draft Example of Potential Implementation Plan for Supply Chain Planning 17
USDA e. Government Program The Implementation Plan deliverable will describe a program roadmap for building the WBSCM capabilities Draft Example of Potential Implementation Plan for Supply Chain Planning 17
 USDA e. Government Program The four deliverables define the scope of this project, indicating there areas that this project will not address “What We are Not Going to Do” • Business Process Reengineering (BPR) • Organizational consolidation • Software vendor assessment and selection • Finalize technical architectures or systems 18
USDA e. Government Program The four deliverables define the scope of this project, indicating there areas that this project will not address “What We are Not Going to Do” • Business Process Reengineering (BPR) • Organizational consolidation • Software vendor assessment and selection • Finalize technical architectures or systems 18
 USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 19
USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 19
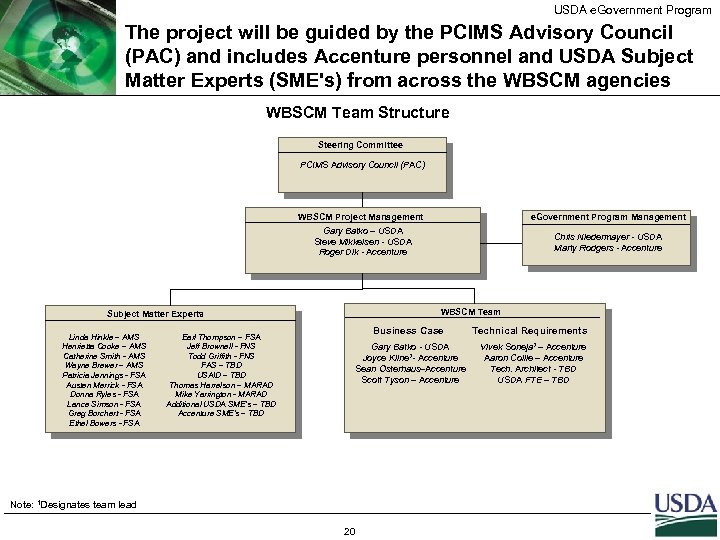 USDA e. Government Program The project will be guided by the PCIMS Advisory Council (PAC) and includes Accenture personnel and USDA Subject Matter Experts (SME's) from across the WBSCM agencies WBSCM Team Structure Steering Committee PCIMS Advisory Council (PAC) WBSCM Project Management e. Government Program Management Gary Batko – USDA Steve Mikkelsen - USDA Roger Dik - Accenture Chris Niedermayer - USDA Marty Rodgers - Accenture WBSCM Team Subject Matter Experts Linda Hinkle – AMS Henrietta Cooke – AMS Catherine Smith - AMS Wayne Brewer – AMS Patricia Jennings - FSA Austen Merrick - FSA Donna Ryles - FSA Lance Simson - FSA Greg Borchert - FSA Ethel Bowers - FSA Earl Thompson – FSA Jeff Brownell - FNS Todd Griffith - FNS FAS – TBD USAID – TBD Thomas Harrelson – MARAD Mike Yarrington - MARAD Additional USDA SME’s – TBD Accenture SME’s – TBD Business Case Gary Batko - USDA Joyce Kline 1 - Accenture Sean Osterhaus–Accenture Scott Tyson – Accenture Note: 1 Designates team lead 20 Technical Requirements Vivek Soneja 1 – Accenture Aaron Collie – Accenture Tech. Architect - TBD USDA FTE – TBD
USDA e. Government Program The project will be guided by the PCIMS Advisory Council (PAC) and includes Accenture personnel and USDA Subject Matter Experts (SME's) from across the WBSCM agencies WBSCM Team Structure Steering Committee PCIMS Advisory Council (PAC) WBSCM Project Management e. Government Program Management Gary Batko – USDA Steve Mikkelsen - USDA Roger Dik - Accenture Chris Niedermayer - USDA Marty Rodgers - Accenture WBSCM Team Subject Matter Experts Linda Hinkle – AMS Henrietta Cooke – AMS Catherine Smith - AMS Wayne Brewer – AMS Patricia Jennings - FSA Austen Merrick - FSA Donna Ryles - FSA Lance Simson - FSA Greg Borchert - FSA Ethel Bowers - FSA Earl Thompson – FSA Jeff Brownell - FNS Todd Griffith - FNS FAS – TBD USAID – TBD Thomas Harrelson – MARAD Mike Yarrington - MARAD Additional USDA SME’s – TBD Accenture SME’s – TBD Business Case Gary Batko - USDA Joyce Kline 1 - Accenture Sean Osterhaus–Accenture Scott Tyson – Accenture Note: 1 Designates team lead 20 Technical Requirements Vivek Soneja 1 – Accenture Aaron Collie – Accenture Tech. Architect - TBD USDA FTE – TBD
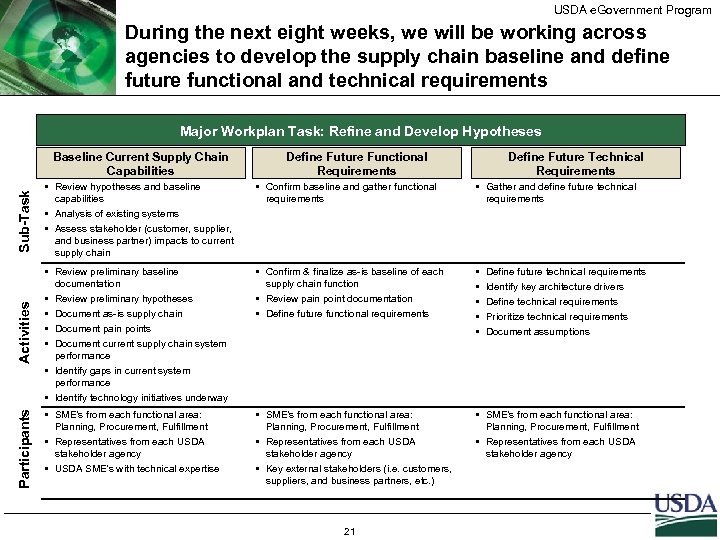 USDA e. Government Program During the next eight weeks, we will be working across agencies to develop the supply chain baseline and define future functional and technical requirements Major Workplan Task: Refine and Develop Hypotheses Define Future Technical Requirements • Review hypotheses and baseline capabilities • Analysis of existing systems • Assess stakeholder (customer, supplier, and business partner) impacts to current supply chain • Confirm baseline and gather functional requirements • Gather and define future technical requirements • Review preliminary baseline documentation • Review preliminary hypotheses • Document as-is supply chain • Document pain points • Document current supply chain system performance • Identify gaps in current system performance • Identify technology initiatives underway • Confirm & finalize as-is baseline of each supply chain function • Review pain point documentation • Define future functional requirements • • • SME’s from each functional area: Planning, Procurement, Fulfillment • Representatives from each USDA stakeholder agency • USDA SME's with technical expertise • SME’s from each functional area: Planning, Procurement, Fulfillment • Representatives from each USDA stakeholder agency • Key external stakeholders (i. e. customers, suppliers, and business partners, etc. ) • SME’s from each functional area: Planning, Procurement, Fulfillment • Representatives from each USDA stakeholder agency Participants Sub-Task Define Future Functional Requirements Activities Baseline Current Supply Chain Capabilities 21 Define future technical requirements Identify key architecture drivers Define technical requirements Prioritize technical requirements Document assumptions
USDA e. Government Program During the next eight weeks, we will be working across agencies to develop the supply chain baseline and define future functional and technical requirements Major Workplan Task: Refine and Develop Hypotheses Define Future Technical Requirements • Review hypotheses and baseline capabilities • Analysis of existing systems • Assess stakeholder (customer, supplier, and business partner) impacts to current supply chain • Confirm baseline and gather functional requirements • Gather and define future technical requirements • Review preliminary baseline documentation • Review preliminary hypotheses • Document as-is supply chain • Document pain points • Document current supply chain system performance • Identify gaps in current system performance • Identify technology initiatives underway • Confirm & finalize as-is baseline of each supply chain function • Review pain point documentation • Define future functional requirements • • • SME’s from each functional area: Planning, Procurement, Fulfillment • Representatives from each USDA stakeholder agency • USDA SME's with technical expertise • SME’s from each functional area: Planning, Procurement, Fulfillment • Representatives from each USDA stakeholder agency • Key external stakeholders (i. e. customers, suppliers, and business partners, etc. ) • SME’s from each functional area: Planning, Procurement, Fulfillment • Representatives from each USDA stakeholder agency Participants Sub-Task Define Future Functional Requirements Activities Baseline Current Supply Chain Capabilities 21 Define future technical requirements Identify key architecture drivers Define technical requirements Prioritize technical requirements Document assumptions
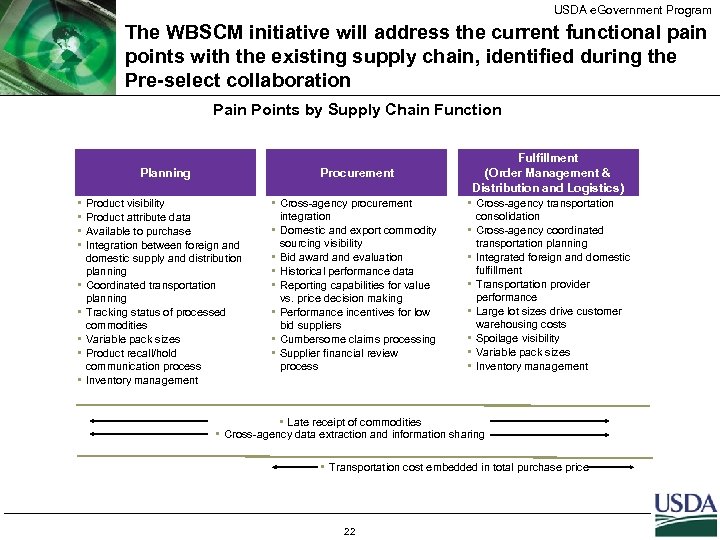 USDA e. Government Program The WBSCM initiative will address the current functional pain points with the existing supply chain, identified during the Pre-select collaboration Pain Points by Supply Chain Function Planning • • • Procurement Fulfillment (Order Management & Distribution and Logistics) Product visibility Product attribute data Available to purchase Integration between foreign and domestic supply and distribution planning Coordinated transportation planning Tracking status of processed commodities Variable pack sizes Product recall/hold communication process Inventory management • Cross-agency procurement integration • Domestic and export commodity sourcing visibility • Bid award and evaluation • Historical performance data • Reporting capabilities for value vs. price decision making • Performance incentives for low bid suppliers • Cumbersome claims processing • Supplier financial review process • Cross-agency transportation consolidation • Cross-agency coordinated transportation planning • Integrated foreign and domestic fulfillment • Transportation provider performance • Large lot sizes drive customer warehousing costs • Spoilage visibility • Variable pack sizes • Inventory management • Late receipt of commodities • Cross-agency data extraction and information sharing • Transportation cost embedded in total purchase price 22
USDA e. Government Program The WBSCM initiative will address the current functional pain points with the existing supply chain, identified during the Pre-select collaboration Pain Points by Supply Chain Function Planning • • • Procurement Fulfillment (Order Management & Distribution and Logistics) Product visibility Product attribute data Available to purchase Integration between foreign and domestic supply and distribution planning Coordinated transportation planning Tracking status of processed commodities Variable pack sizes Product recall/hold communication process Inventory management • Cross-agency procurement integration • Domestic and export commodity sourcing visibility • Bid award and evaluation • Historical performance data • Reporting capabilities for value vs. price decision making • Performance incentives for low bid suppliers • Cumbersome claims processing • Supplier financial review process • Cross-agency transportation consolidation • Cross-agency coordinated transportation planning • Integrated foreign and domestic fulfillment • Transportation provider performance • Large lot sizes drive customer warehousing costs • Spoilage visibility • Variable pack sizes • Inventory management • Late receipt of commodities • Cross-agency data extraction and information sharing • Transportation cost embedded in total purchase price 22
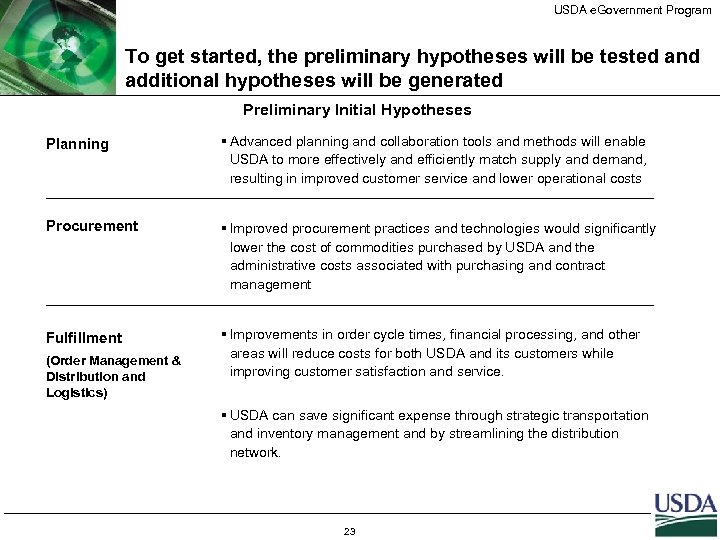 USDA e. Government Program To get started, the preliminary hypotheses will be tested and additional hypotheses will be generated Preliminary Initial Hypotheses Planning § Advanced planning and collaboration tools and methods will enable USDA to more effectively and efficiently match supply and demand, resulting in improved customer service and lower operational costs Procurement § Improved procurement practices and technologies would significantly lower the cost of commodities purchased by USDA and the administrative costs associated with purchasing and contract management Fulfillment § Improvements in order cycle times, financial processing, and other areas will reduce costs for both USDA and its customers while improving customer satisfaction and service. (Order Management & Distribution and Logistics) § USDA can save significant expense through strategic transportation and inventory management and by streamlining the distribution network. 23
USDA e. Government Program To get started, the preliminary hypotheses will be tested and additional hypotheses will be generated Preliminary Initial Hypotheses Planning § Advanced planning and collaboration tools and methods will enable USDA to more effectively and efficiently match supply and demand, resulting in improved customer service and lower operational costs Procurement § Improved procurement practices and technologies would significantly lower the cost of commodities purchased by USDA and the administrative costs associated with purchasing and contract management Fulfillment § Improvements in order cycle times, financial processing, and other areas will reduce costs for both USDA and its customers while improving customer satisfaction and service. (Order Management & Distribution and Logistics) § USDA can save significant expense through strategic transportation and inventory management and by streamlining the distribution network. 23
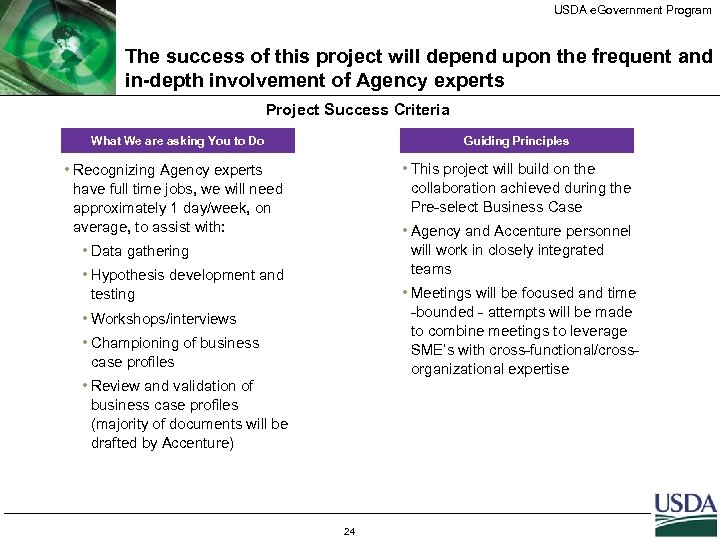 USDA e. Government Program The success of this project will depend upon the frequent and in-depth involvement of Agency experts Project Success Criteria What We are asking You to Do Guiding Principles • Recognizing Agency experts have full time jobs, we will need approximately 1 day/week, on average, to assist with: • This project will build on the collaboration achieved during the Pre-select Business Case • Agency and Accenture personnel will work in closely integrated teams • Data gathering • Hypothesis development and testing • Meetings will be focused and time -bounded - attempts will be made to combine meetings to leverage SME’s with cross-functional/crossorganizational expertise • Workshops/interviews • Championing of business case profiles • Review and validation of business case profiles (majority of documents will be drafted by Accenture) 24
USDA e. Government Program The success of this project will depend upon the frequent and in-depth involvement of Agency experts Project Success Criteria What We are asking You to Do Guiding Principles • Recognizing Agency experts have full time jobs, we will need approximately 1 day/week, on average, to assist with: • This project will build on the collaboration achieved during the Pre-select Business Case • Agency and Accenture personnel will work in closely integrated teams • Data gathering • Hypothesis development and testing • Meetings will be focused and time -bounded - attempts will be made to combine meetings to leverage SME’s with cross-functional/crossorganizational expertise • Workshops/interviews • Championing of business case profiles • Review and validation of business case profiles (majority of documents will be drafted by Accenture) 24
 USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 25
USDA e. Government Program Agenda Welcome and Introductions Project Overview Building on the Pre-select Approach and Deliverables Team Structure and Initial Activities Next Steps 25
 USDA e. Government Program The following list identifies the next steps to launch this project Next Steps • Provide your calendar of activities to Gary • Confirm team workspace • Schedule meetings with SME’s • Agree on dates for first trip to Kansas City • Initiate data collection per revised data request • Confirm project plan • Begin scheduling interviews with customers and suppliers 26
USDA e. Government Program The following list identifies the next steps to launch this project Next Steps • Provide your calendar of activities to Gary • Confirm team workspace • Schedule meetings with SME’s • Agree on dates for first trip to Kansas City • Initiate data collection per revised data request • Confirm project plan • Begin scheduling interviews with customers and suppliers 26
 USDA e. Government Program Questions 27
USDA e. Government Program Questions 27
 USDA e. Government Program Appendix 28
USDA e. Government Program Appendix 28
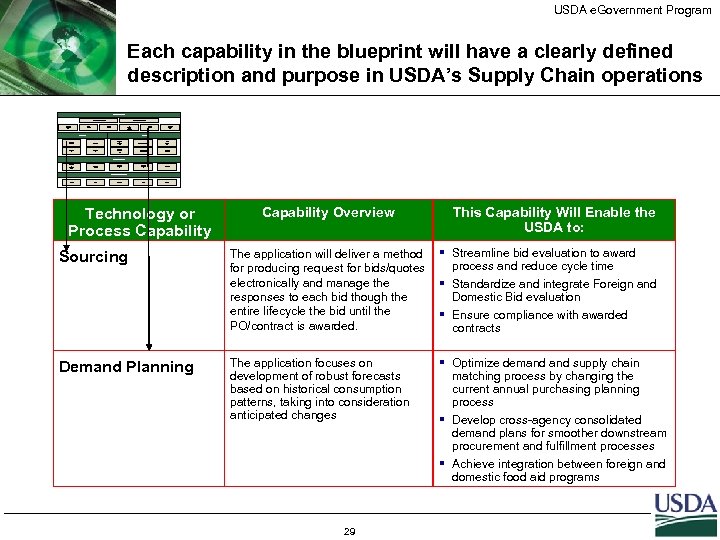 USDA e. Government Program Each capability in the blueprint will have a clearly defined description and purpose in USDA’s Supply Chain operations Supply Chain Planning Sales & Operations Planning Supplier Collabora tion Supply Planning Strategic Network Planning Distributi on Requirem ents Planning Inventory Planning Procurement Demand Planning Customer Collabora tion Fulfillment Strategic Sourcing Warehou se Managem ent Transportation Planning Order Managem ent Contracti ng Purchasin g Inventory Managem ent Transportation Management Fulfillmen t Planning Accounts Receivabl e Invoicing Control Measure Financial Management Centraliz ed Disburse ment Accounts Payable Inventory Accountin g Supply Chain Event Management Monitor Notify Simulate Technology or Process Capability Overview This Capability Will Enable the USDA to: Sourcing The application will deliver a method § Streamline bid evaluation to award process and reduce cycle time for producing request for bids/quotes electronically and manage the § Standardize and integrate Foreign and Domestic Bid evaluation responses to each bid though the entire lifecycle the bid until the § Ensure compliance with awarded PO/contract is awarded. contracts Demand Planning The application focuses on development of robust forecasts based on historical consumption patterns, taking into consideration anticipated changes 29 § Optimize demand supply chain matching process by changing the current annual purchasing planning process § Develop cross-agency consolidated demand plans for smoother downstream procurement and fulfillment processes § Achieve integration between foreign and domestic food aid programs
USDA e. Government Program Each capability in the blueprint will have a clearly defined description and purpose in USDA’s Supply Chain operations Supply Chain Planning Sales & Operations Planning Supplier Collabora tion Supply Planning Strategic Network Planning Distributi on Requirem ents Planning Inventory Planning Procurement Demand Planning Customer Collabora tion Fulfillment Strategic Sourcing Warehou se Managem ent Transportation Planning Order Managem ent Contracti ng Purchasin g Inventory Managem ent Transportation Management Fulfillmen t Planning Accounts Receivabl e Invoicing Control Measure Financial Management Centraliz ed Disburse ment Accounts Payable Inventory Accountin g Supply Chain Event Management Monitor Notify Simulate Technology or Process Capability Overview This Capability Will Enable the USDA to: Sourcing The application will deliver a method § Streamline bid evaluation to award process and reduce cycle time for producing request for bids/quotes electronically and manage the § Standardize and integrate Foreign and Domestic Bid evaluation responses to each bid though the entire lifecycle the bid until the § Ensure compliance with awarded PO/contract is awarded. contracts Demand Planning The application focuses on development of robust forecasts based on historical consumption patterns, taking into consideration anticipated changes 29 § Optimize demand supply chain matching process by changing the current annual purchasing planning process § Develop cross-agency consolidated demand plans for smoother downstream procurement and fulfillment processes § Achieve integration between foreign and domestic food aid programs
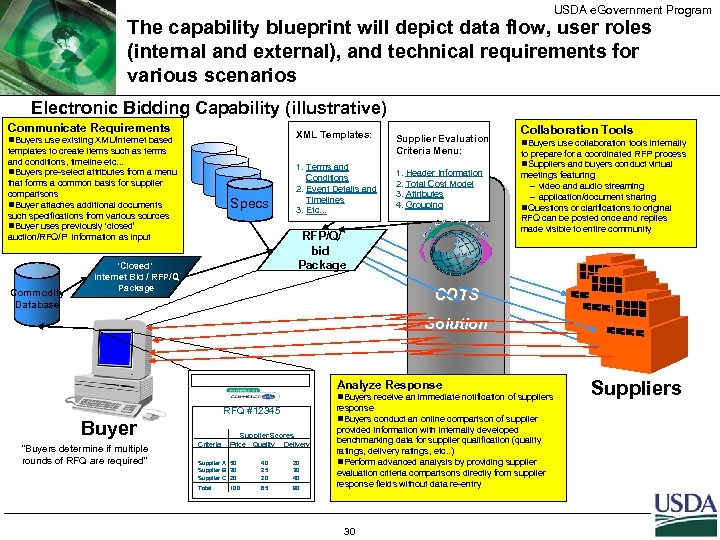 USDA e. Government Program The capability blueprint will depict data flow, user roles (internal and external), and technical requirements for various scenarios Electronic Bidding Capability (illustrative) Communicate Requirements XML Templates: n. Buyers use existing XML/internet based templates to create items such as terms and conditions, timeline etc. . . n. Buyers pre-select attributes from a menu that forms a common basis for supplier comparisons n. Buyer attaches additional documents such specifications from various sources n. Buyer uses previously ‘closed’ auction/RFQ/P information as input Commodity Database Specs 1. Terms and Conditions 2. Event Details and Timelines 3. Etc. . . Supplier Evaluation Criteria Menu: 1. Header Information 2. Total Cost Model 3. Attributes 4. Grouping RFP/Q/ bid Package ‘Closed’ Internet Bid / RFP/Q Package Collaboration Tools n. Buyers use collaboration tools internally to prepare for a coordinated RFP process n. Suppliers and buyers conduct virtual meetings featuring - video and audio streaming - application/document sharing n. Questions or clarifications to original RFQ can be posted once and replies made visible to entire community COTS Solution Analyze Response n. Buyers receive an immediate notification of suppliers RFQ #12345 Buyer “Buyers determine if multiple rounds of RFQ are required” Criteria Supplier Scores Price Quality Delivery Supplier A 50 Supplier B 30 Supplier C 20 40 25 20 20 30 40 Total 85 90 100 response n. Buyers conduct an online comparison of supplier provided information with internally developed benchmarking data for supplier qualification (quality ratings, delivery ratings, etc. . ) n. Perform advanced analysis by providing supplier evaluation criteria comparisons directly from supplier response fields without data re-entry 30 Suppliers
USDA e. Government Program The capability blueprint will depict data flow, user roles (internal and external), and technical requirements for various scenarios Electronic Bidding Capability (illustrative) Communicate Requirements XML Templates: n. Buyers use existing XML/internet based templates to create items such as terms and conditions, timeline etc. . . n. Buyers pre-select attributes from a menu that forms a common basis for supplier comparisons n. Buyer attaches additional documents such specifications from various sources n. Buyer uses previously ‘closed’ auction/RFQ/P information as input Commodity Database Specs 1. Terms and Conditions 2. Event Details and Timelines 3. Etc. . . Supplier Evaluation Criteria Menu: 1. Header Information 2. Total Cost Model 3. Attributes 4. Grouping RFP/Q/ bid Package ‘Closed’ Internet Bid / RFP/Q Package Collaboration Tools n. Buyers use collaboration tools internally to prepare for a coordinated RFP process n. Suppliers and buyers conduct virtual meetings featuring - video and audio streaming - application/document sharing n. Questions or clarifications to original RFQ can be posted once and replies made visible to entire community COTS Solution Analyze Response n. Buyers receive an immediate notification of suppliers RFQ #12345 Buyer “Buyers determine if multiple rounds of RFQ are required” Criteria Supplier Scores Price Quality Delivery Supplier A 50 Supplier B 30 Supplier C 20 40 25 20 20 30 40 Total 85 90 100 response n. Buyers conduct an online comparison of supplier provided information with internally developed benchmarking data for supplier qualification (quality ratings, delivery ratings, etc. . ) n. Perform advanced analysis by providing supplier evaluation criteria comparisons directly from supplier response fields without data re-entry 30 Suppliers


