320d0e7b9c64c55c44243aba3fad7d6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

 U. S. Congress (Ch. 10) • U. S. Congress - U. S. National Legislature • Bicameralism - two house legislature -Senate -House of Representatives
U. S. Congress (Ch. 10) • U. S. Congress - U. S. National Legislature • Bicameralism - two house legislature -Senate -House of Representatives
 National Legislature • Reasons for Bicameralism -History - Framers knew it well British Parliament bicameral since 1300’s -Practical - Framers created 2 houses to settle conflict between large states and small states
National Legislature • Reasons for Bicameralism -History - Framers knew it well British Parliament bicameral since 1300’s -Practical - Framers created 2 houses to settle conflict between large states and small states
 National Legislature -Theoretical - Framers wanted 2 houses in order for one house to check on another • Terms of Congress -2 years in length -20 th Amendment -current term of Congress - noon Jan. 3, 2017 to Jan 3, 2019 (115 th Congress) -Terms of Congress once began on March 4 th
National Legislature -Theoretical - Framers wanted 2 houses in order for one house to check on another • Terms of Congress -2 years in length -20 th Amendment -current term of Congress - noon Jan. 3, 2017 to Jan 3, 2019 (115 th Congress) -Terms of Congress once began on March 4 th
 National Legislature -each term divided into 2 sessions -Congress in session year round • Special Session of Congress -only called by President -called in emergency situations -highly unlikely to happen again
National Legislature -each term divided into 2 sessions -Congress in session year round • Special Session of Congress -only called by President -called in emergency situations -highly unlikely to happen again
 House of Representatives • House of Reps § 435 members – (currently 241 R’s – 194 D’s ) § Each state gets at least one (AK, DE, MT, ND, SD, VT, WY) § U. S. Territories have one member but no vote § Reps are elected to two-year terms - this makes them pay close attention to constituents § No term limits
House of Representatives • House of Reps § 435 members – (currently 241 R’s – 194 D’s ) § Each state gets at least one (AK, DE, MT, ND, SD, VT, WY) § U. S. Territories have one member but no vote § Reps are elected to two-year terms - this makes them pay close attention to constituents § No term limits


 House of Representatives • House of Reps § Seats each state gets apportioned according to population § Constitution - Congress shall reapportion House seats after each census § As the nation grew- so did the House of Reps - 435 seats by 1910
House of Representatives • House of Reps § Seats each state gets apportioned according to population § Constitution - Congress shall reapportion House seats after each census § As the nation grew- so did the House of Reps - 435 seats by 1910
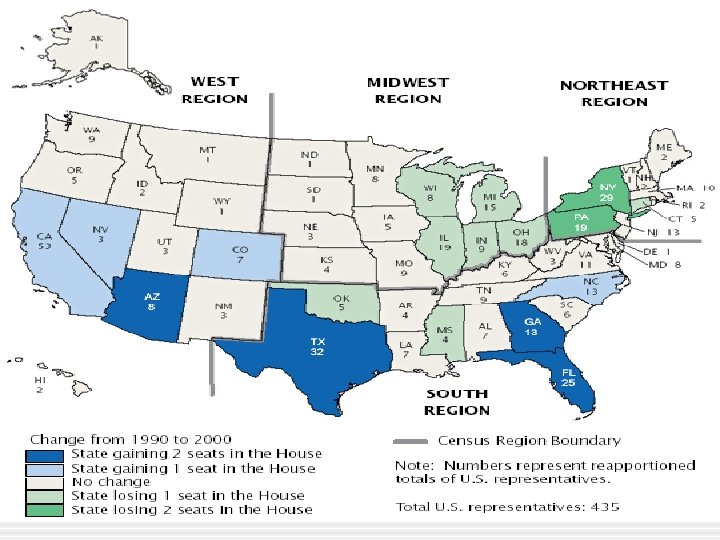
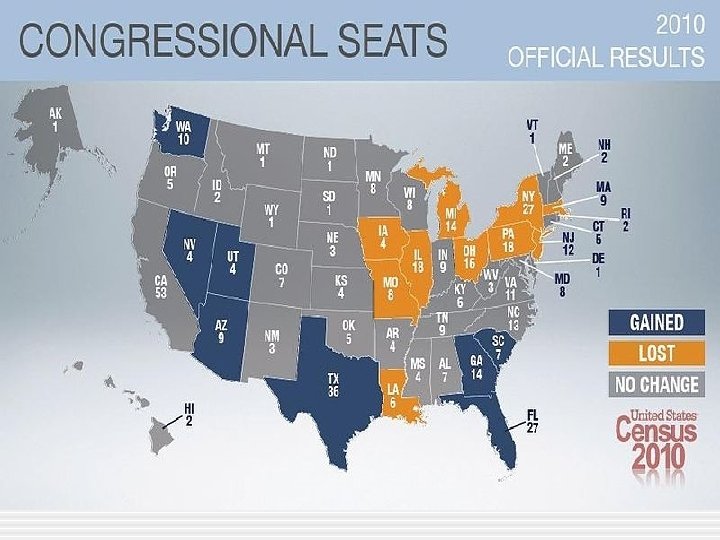
 House of Representatives • Reapportionment Act of 1929 § Permanent size of House is 435 - 1 seat for every about 710, 000 people § Following census - Census Bureau determines number of seats each state should have § Plan is sent to Congress for approval § Congress still has the power but Census Bureau does the work § Next reapportionment will be based on the 2020 Census - it will take effect before the 2022 elections
House of Representatives • Reapportionment Act of 1929 § Permanent size of House is 435 - 1 seat for every about 710, 000 people § Following census - Census Bureau determines number of seats each state should have § Plan is sent to Congress for approval § Congress still has the power but Census Bureau does the work § Next reapportionment will be based on the 2020 Census - it will take effect before the 2022 elections
 Congressional Elections • Congressional Elections § Same day in every state § Off year elections -Congressional elections that occur in nonpresidential election years (2006, 2010, 2014) § Party in power usually loses seats in off-year elections.
Congressional Elections • Congressional Elections § Same day in every state § Off year elections -Congressional elections that occur in nonpresidential election years (2006, 2010, 2014) § Party in power usually loses seats in off-year elections.
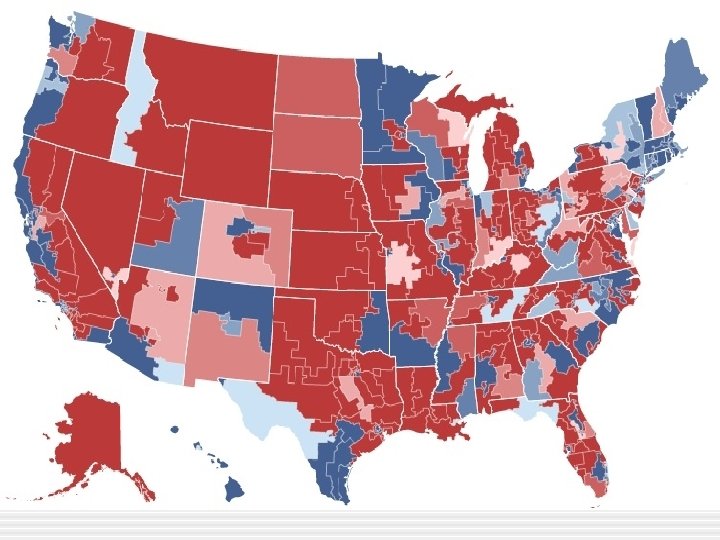
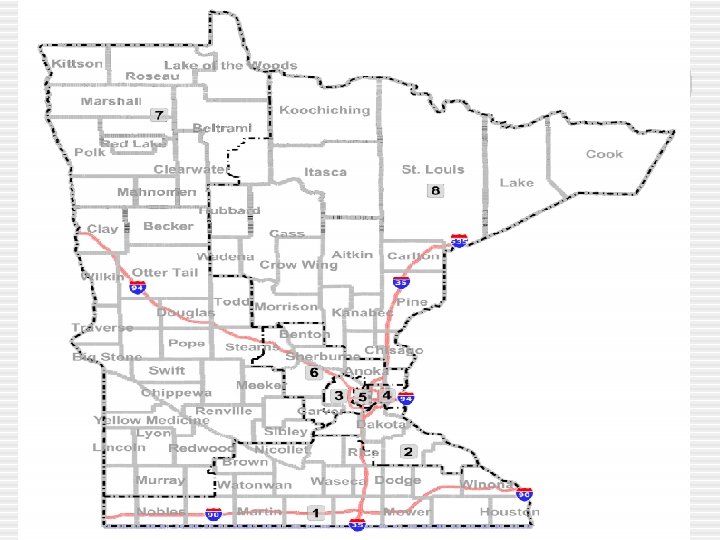
 Congressional Elections • Congressional Elections § Districts - 435 seats in House - 435 separate Congressional Districts - Single member district - voters in district elect one representative for that district - ND is 1 district - State legislatures are responsible for drawing congressional districts in their state (Re-district every 10 years)
Congressional Elections • Congressional Elections § Districts - 435 seats in House - 435 separate Congressional Districts - Single member district - voters in district elect one representative for that district - ND is 1 district - State legislatures are responsible for drawing congressional districts in their state (Re-district every 10 years)
 House of Representatives • Gerrymandering § How it’s done - concentrate oppositions voters in one or a few districts - Spread opposition among several districts
House of Representatives • Gerrymandering § How it’s done - concentrate oppositions voters in one or a few districts - Spread opposition among several districts
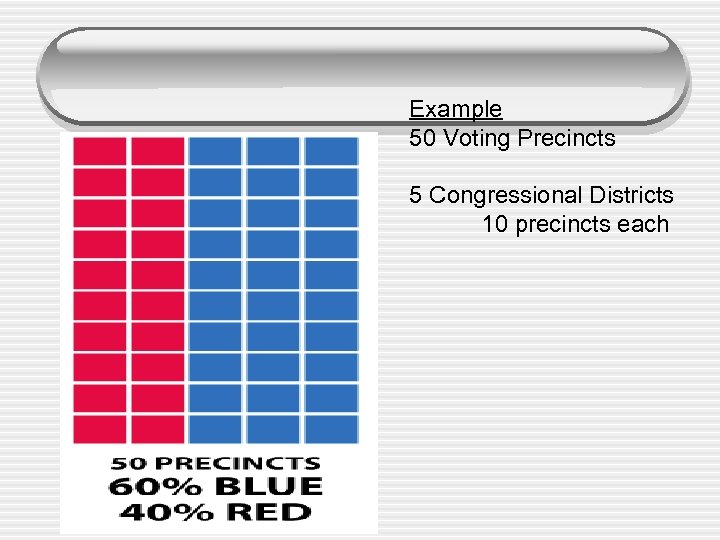 Example 50 Voting Precincts 5 Congressional Districts 10 precincts each
Example 50 Voting Precincts 5 Congressional Districts 10 precincts each
 House of Representatives • Wesberry v. Sanders, 1964 § Supreme Court ended population differences among districts § As much as possible, one persons vote must be worth as much an another’s
House of Representatives • Wesberry v. Sanders, 1964 § Supreme Court ended population differences among districts § As much as possible, one persons vote must be worth as much an another’s
 House of Representatives • Formal Qualifications 1. must be at least 25 years old 2. citizen of U. S. for at least 7 years 3. inhabitant of state from which elected - The House can punish members - (majority vote) House can expel members (2/3 vote) House cannot exclude those meeting qualifications What happens if house seat is vacant?
House of Representatives • Formal Qualifications 1. must be at least 25 years old 2. citizen of U. S. for at least 7 years 3. inhabitant of state from which elected - The House can punish members - (majority vote) House can expel members (2/3 vote) House cannot exclude those meeting qualifications What happens if house seat is vacant?
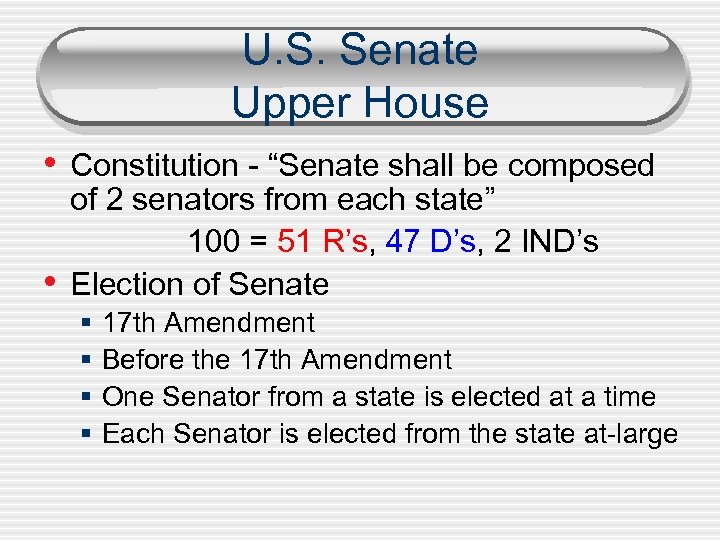 U. S. Senate Upper House • Constitution - “Senate shall be composed • of 2 senators from each state” 100 = 51 R’s, 47 D’s, 2 IND’s Election of Senate § § 17 th Amendment Before the 17 th Amendment One Senator from a state is elected at a time Each Senator is elected from the state at-large
U. S. Senate Upper House • Constitution - “Senate shall be composed • of 2 senators from each state” 100 = 51 R’s, 47 D’s, 2 IND’s Election of Senate § § 17 th Amendment Before the 17 th Amendment One Senator from a state is elected at a time Each Senator is elected from the state at-large
 House of Representatives • Informal Qualifications § Vary from state to state, time to time, and district to district § Based on vote-getting abilities (ex - party I. D. )
House of Representatives • Informal Qualifications § Vary from state to state, time to time, and district to district § Based on vote-getting abilities (ex - party I. D. )


 U. S. Senate election of Senate § What happens if Senate seat is vacant? • Terms of Senators - 6 years § Strom Thurmond (48) / Robert Byrd (50) § Terms are staggered - only 1/3 of terms expire every two years § Continuous Body - all seats never up for election at same time
U. S. Senate election of Senate § What happens if Senate seat is vacant? • Terms of Senators - 6 years § Strom Thurmond (48) / Robert Byrd (50) § Terms are staggered - only 1/3 of terms expire every two years § Continuous Body - all seats never up for election at same time
 U. S. Senate • Upper House § § § Good source of candidate for President 1/3 of Senators once served in House Smaller membership Larger constituencies More national media attention More of a national politician than House members § Longer terms
U. S. Senate • Upper House § § § Good source of candidate for President 1/3 of Senators once served in House Smaller membership Larger constituencies More national media attention More of a national politician than House members § Longer terms
 U. S. Senate • Qualifications 1. Must by at least 30 years old 2. Citizen of U. S. for at least 9 years 3. Inhabitant of state from which elected -can punish and expel members same as House
U. S. Senate • Qualifications 1. Must by at least 30 years old 2. Citizen of U. S. for at least 9 years 3. Inhabitant of state from which elected -can punish and expel members same as House
 Members of Congress • Representatives of the people § Casting votes -Trustee - votes decided on merit -Delegate - vote the way they think constituents would want -Partisan - vote allegiance to party. This is a leading factor in determining votes -Politicos - Try to balance conflicting factors when voting
Members of Congress • Representatives of the people § Casting votes -Trustee - votes decided on merit -Delegate - vote the way they think constituents would want -Partisan - vote allegiance to party. This is a leading factor in determining votes -Politicos - Try to balance conflicting factors when voting
 Members of Congress Committees and Laws • How Congress makes laws -anyone can propose laws -must be introduced by member of Congress (hopper) -co-sponsors may help -Known as a bill before it becomes a law -bill is assigned to a committee for debate, research, and revision -committees specialize in different topics
Members of Congress Committees and Laws • How Congress makes laws -anyone can propose laws -must be introduced by member of Congress (hopper) -co-sponsors may help -Known as a bill before it becomes a law -bill is assigned to a committee for debate, research, and revision -committees specialize in different topics
 Committees and Laws -committees hold congressional hearings to gather information on bill -committee recommends passage then sends to full body of House or Senate for vote -most bills don’t make it to the floor -if bill passes one house, it must pass the other (majority)
Committees and Laws -committees hold congressional hearings to gather information on bill -committee recommends passage then sends to full body of House or Senate for vote -most bills don’t make it to the floor -if bill passes one house, it must pass the other (majority)
 Committees and Laws - after bill passes Congress it goes to the President - President, special-interest groups, lobbyists, can affect the passage of a bill - If veto, Congress can override
Committees and Laws - after bill passes Congress it goes to the President - President, special-interest groups, lobbyists, can affect the passage of a bill - If veto, Congress can override
 Committees and Laws • Committees - Congress divides much of its work into - committees Both houses have committees Standing committees, subcommittees, special committees, conference committees
Committees and Laws • Committees - Congress divides much of its work into - committees Both houses have committees Standing committees, subcommittees, special committees, conference committees
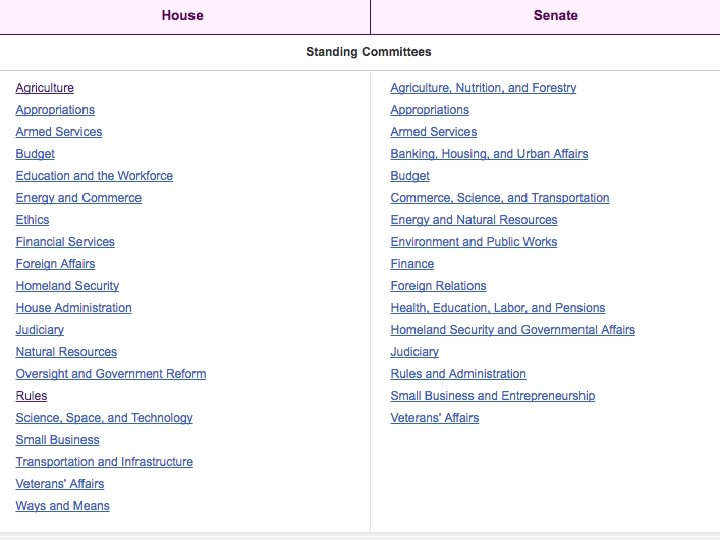 Committees and Laws *Senate committees -agriculture, nutrition, and forestry -appropriations -armed services -foreign relations -budget *House committees -appropriations -agriculture -armed services -education & work -ways and means
Committees and Laws *Senate committees -agriculture, nutrition, and forestry -appropriations -armed services -foreign relations -budget *House committees -appropriations -agriculture -armed services -education & work -ways and means
 Committees and Laws - oversight function - Select Congressional Committees review actions of executive branch and some parts of society
Committees and Laws - oversight function - Select Congressional Committees review actions of executive branch and some parts of society
 Leadership in Congress *House Presiding officer - Speaker of the House Party officers - Majority Floor Leader Majority Whip Minority Floor Leader Minority Whip
Leadership in Congress *House Presiding officer - Speaker of the House Party officers - Majority Floor Leader Majority Whip Minority Floor Leader Minority Whip
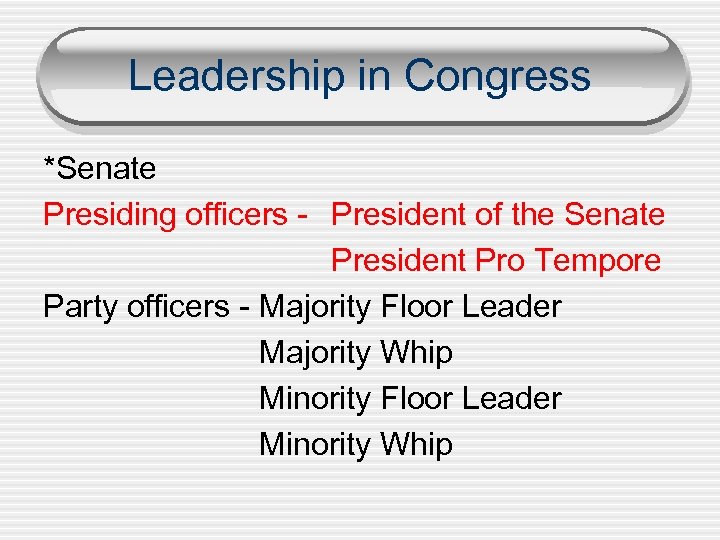 Leadership in Congress *Senate Presiding officers - President of the Senate President Pro Tempore Party officers - Majority Floor Leader Majority Whip Minority Floor Leader Minority Whip
Leadership in Congress *Senate Presiding officers - President of the Senate President Pro Tempore Party officers - Majority Floor Leader Majority Whip Minority Floor Leader Minority Whip
 Members of Congress Compensation • Constitution - Congress fixes • • • compensation for members 27 th Amendment - not ‘til after next Congressional election Voter backlash Non-salary compensation (fringe benefits) -special tax deduction - for 2 residencies -travel allowances
Members of Congress Compensation • Constitution - Congress fixes • • • compensation for members 27 th Amendment - not ‘til after next Congressional election Voter backlash Non-salary compensation (fringe benefits) -special tax deduction - for 2 residencies -travel allowances
 Members of Congress Compensation -generous retirement -offices & staff in D. C. and home state -free parking at Capitol building and airports -Franking privilege -High Salaries - make public service more appealing to qualified people
Members of Congress Compensation -generous retirement -offices & staff in D. C. and home state -free parking at Capitol building and airports -Franking privilege -High Salaries - make public service more appealing to qualified people


