001eea6c2eca12e93109e419b7235262.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 U. S. Coast Guard Maritime Security Risk Analysis Model (MSRAM) “Balancing resources to risk” Presentation for the Critical Infrastructure Protection Workshop The Center for Homeland Defense and Security June 2008 Presented by LCDR Brady Downs, USCG Domestic Port Security Evaluations Division (CG-5142) Directorate of Assessment, Integration and Risk Management US Coast Guard Headquarters, Washington, D. C. 1
U. S. Coast Guard Maritime Security Risk Analysis Model (MSRAM) “Balancing resources to risk” Presentation for the Critical Infrastructure Protection Workshop The Center for Homeland Defense and Security June 2008 Presented by LCDR Brady Downs, USCG Domestic Port Security Evaluations Division (CG-5142) Directorate of Assessment, Integration and Risk Management US Coast Guard Headquarters, Washington, D. C. 1
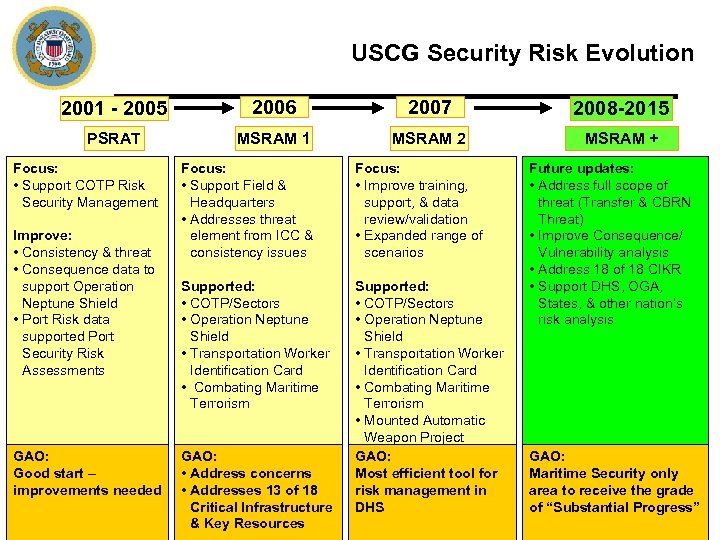 USCG Security Risk Evolution 2001 - 2005 2006 2007 2008 -2015 PSRAT MSRAM 1 MSRAM 2 MSRAM + Focus: • Support COTP Risk Security Management Improve: • Consistency & threat • Consequence data to support Operation Neptune Shield • Port Risk data supported Port Security Risk Assessments GAO: Good start – improvements needed Focus: • Support Field & Headquarters • Addresses threat element from ICC & consistency issues Focus: • Improve training, support, & data review/validation • Expanded range of scenarios Supported: • COTP/Sectors • Operation Neptune Shield • Transportation Worker Identification Card • Combating Maritime Terrorism • Mounted Automatic Weapon Project GAO: Most efficient tool for risk management in DHS GAO: • Address concerns • Addresses 13 of 18 Critical Infrastructure & Key Resources Future updates: • Address full scope of threat (Transfer & CBRN Threat) • Improve Consequence/ Vulnerability analysis • Address 18 of 18 CIKR • Support DHS, OGA, States, & other nation’s risk analysis GAO: Maritime Security only area to receive the grade of “Substantial Progress” 2
USCG Security Risk Evolution 2001 - 2005 2006 2007 2008 -2015 PSRAT MSRAM 1 MSRAM 2 MSRAM + Focus: • Support COTP Risk Security Management Improve: • Consistency & threat • Consequence data to support Operation Neptune Shield • Port Risk data supported Port Security Risk Assessments GAO: Good start – improvements needed Focus: • Support Field & Headquarters • Addresses threat element from ICC & consistency issues Focus: • Improve training, support, & data review/validation • Expanded range of scenarios Supported: • COTP/Sectors • Operation Neptune Shield • Transportation Worker Identification Card • Combating Maritime Terrorism • Mounted Automatic Weapon Project GAO: Most efficient tool for risk management in DHS GAO: • Address concerns • Addresses 13 of 18 Critical Infrastructure & Key Resources Future updates: • Address full scope of threat (Transfer & CBRN Threat) • Improve Consequence/ Vulnerability analysis • Address 18 of 18 CIKR • Support DHS, OGA, States, & other nation’s risk analysis GAO: Maritime Security only area to receive the grade of “Substantial Progress” 2
 OUR MISSION o Prevent terrorist attacks within the United States - (PREVENT) o Reduce America’s vulnerability to terrorism - (PROTECT) o Minimize the resulting damage if prevention fails - (RESPOND) o Recover from attacks that do occur- Ensure economic security - (RECOVER) Homeland Security Act of 2002 3
OUR MISSION o Prevent terrorist attacks within the United States - (PREVENT) o Reduce America’s vulnerability to terrorism - (PROTECT) o Minimize the resulting damage if prevention fails - (RESPOND) o Recover from attacks that do occur- Ensure economic security - (RECOVER) Homeland Security Act of 2002 3
 MSRAM Analysis Crosses DHS Sectors The complexity of the marine transportation system and the maritime domain creates a unique opportunity for the Coast Guard due to the vast array of critical infrastructure, assets, key resources, systems, & networks that make up our nation’s riverports, seaports and the maritime domain. Maritime domain is a microcosm of the national economy. Risk crosses all 18 DHS Sectors Similar situation for Localities, Cities, State, National, International risk analysis 4
MSRAM Analysis Crosses DHS Sectors The complexity of the marine transportation system and the maritime domain creates a unique opportunity for the Coast Guard due to the vast array of critical infrastructure, assets, key resources, systems, & networks that make up our nation’s riverports, seaports and the maritime domain. Maritime domain is a microcosm of the national economy. Risk crosses all 18 DHS Sectors Similar situation for Localities, Cities, State, National, International risk analysis 4
 MSRAM Risk Calculator The MSRAM was designed to enhance security and reduce the risk of terrorism by identifying and prioritizing critical infrastructure, key resources and high consequence transits and events across sectors using a common risk methodology, taxonomy and metrics to measure security risk at the local, regional, and national levels. Support Senior Leadership risk based decision making process 5
MSRAM Risk Calculator The MSRAM was designed to enhance security and reduce the risk of terrorism by identifying and prioritizing critical infrastructure, key resources and high consequence transits and events across sectors using a common risk methodology, taxonomy and metrics to measure security risk at the local, regional, and national levels. Support Senior Leadership risk based decision making process 5
 MSRAM Security Risk Concept Threat Vulnerability Consequence X Threat = Capability X Intent (with confidence) ICC Strategic Threat X Vulnerability = Achievability X System Security X Target Hardness Mitigated by Interdiction Capability = Risk Consequence = Death and Injury, Primary and Secondary Economic, Environment , National security, Symbolic Impacts X (Less Response Capability) And Secondary Economic Impact Mitigated by Response Capability 6
MSRAM Security Risk Concept Threat Vulnerability Consequence X Threat = Capability X Intent (with confidence) ICC Strategic Threat X Vulnerability = Achievability X System Security X Target Hardness Mitigated by Interdiction Capability = Risk Consequence = Death and Injury, Primary and Secondary Economic, Environment , National security, Symbolic Impacts X (Less Response Capability) And Secondary Economic Impact Mitigated by Response Capability 6
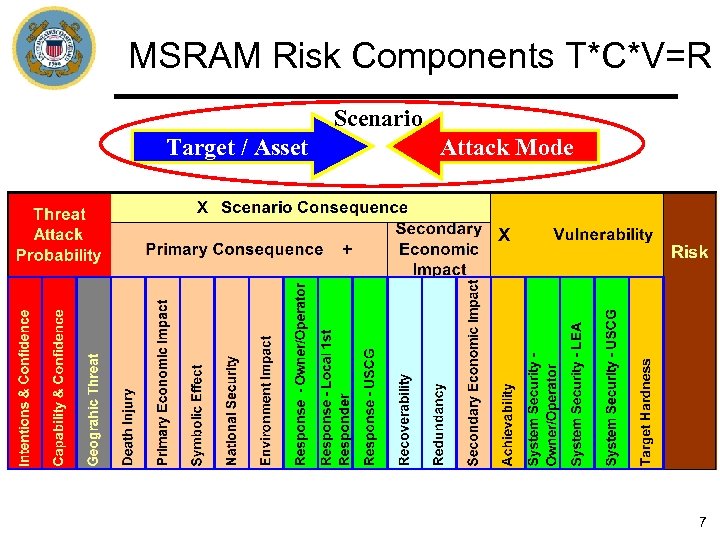 MSRAM Risk Components T*C*V=R Scenario Target / Asset Attack Mode 7
MSRAM Risk Components T*C*V=R Scenario Target / Asset Attack Mode 7
 Breadth of MSRAM Risk Information 644, 000 Data Points Target Factors Scenario Factors (Scenarios = Target +Attack Mode) q Target name q Threat q Target Class o Intent q Availability o Capability q Maximum Consequence q USCG Role (Lead, Support, Other) o Death/Injury q Maritime Transportation Security Act o Primary Economic Regulated o Secondary Economic (Recoverability/Redundancy) q Area o Environmental q Captain of the Port o National Security q CG Station o Symbolic q Port o Response Capability (Owner/Operator, 1 st Responders, USCG) q Waterway q Latitude / Longitude q Vulnerability q County (link to FEMA regions) o Achievability q River Mile Marker o System Security (Owner/Operator, LE, USCG) o Target Hardness q DHS MCI/KR sector q DHS Grant Port q Risk q o Ability to additional DOD target factors as necessary o o o Organic: 24 hour, steady state owner/operator response Mitigated: risk including impact of USCG & LEA Primary: primary economic impact only Total: risk including secondary economic 8
Breadth of MSRAM Risk Information 644, 000 Data Points Target Factors Scenario Factors (Scenarios = Target +Attack Mode) q Target name q Threat q Target Class o Intent q Availability o Capability q Maximum Consequence q USCG Role (Lead, Support, Other) o Death/Injury q Maritime Transportation Security Act o Primary Economic Regulated o Secondary Economic (Recoverability/Redundancy) q Area o Environmental q Captain of the Port o National Security q CG Station o Symbolic q Port o Response Capability (Owner/Operator, 1 st Responders, USCG) q Waterway q Latitude / Longitude q Vulnerability q County (link to FEMA regions) o Achievability q River Mile Marker o System Security (Owner/Operator, LE, USCG) o Target Hardness q DHS MCI/KR sector q DHS Grant Port q Risk q o Ability to additional DOD target factors as necessary o o o Organic: 24 hour, steady state owner/operator response Mitigated: risk including impact of USCG & LEA Primary: primary economic impact only Total: risk including secondary economic 8
 Depth of MSRAM Risk Information Over 74, 000 Judgements Target Categories/Classes Attack Modes q q q Barge o 10 classes Facility o 14 classes Infrastructure o 7 classes Key Asset o 8 classes Other o 2 classes o High Population o Events Vessel o 21 classes MSRAM target classes link to DHS sectors q q q Attack by Hijacked Vessel Boat Bomb (while vessel is present) Car/Truck Bomb Hijacking of Vessel Passenger/Passerby Explosives/Improvised Explosive Devices Sabotage Standoff Weapon Launched from Water and Land (including Man-Portable Air Defense Weapon) Swimmer/Diver/Underwater Delivery Systems Terrorist Assault Team (Hostage Taking) Attack by Hijacked Large Aircraft Small Suicide Aircraft Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear Cyber Attack Mines (Aquatic) & Mines (Land) Transfer of Terrorist, weapons/materials Ability to additional DOD attack modes as necessary 9
Depth of MSRAM Risk Information Over 74, 000 Judgements Target Categories/Classes Attack Modes q q q Barge o 10 classes Facility o 14 classes Infrastructure o 7 classes Key Asset o 8 classes Other o 2 classes o High Population o Events Vessel o 21 classes MSRAM target classes link to DHS sectors q q q Attack by Hijacked Vessel Boat Bomb (while vessel is present) Car/Truck Bomb Hijacking of Vessel Passenger/Passerby Explosives/Improvised Explosive Devices Sabotage Standoff Weapon Launched from Water and Land (including Man-Portable Air Defense Weapon) Swimmer/Diver/Underwater Delivery Systems Terrorist Assault Team (Hostage Taking) Attack by Hijacked Large Aircraft Small Suicide Aircraft Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear Cyber Attack Mines (Aquatic) & Mines (Land) Transfer of Terrorist, weapons/materials Ability to additional DOD attack modes as necessary 9
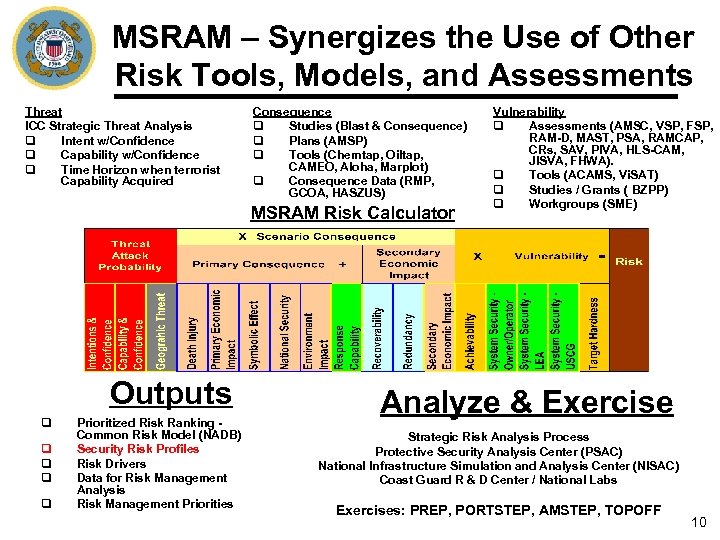 MSRAM – Synergizes the Use of Other Risk Tools, Models, and Assessments Threat ICC Strategic Threat Analysis q Intent w/Confidence q Capability w/Confidence q Time Horizon when terrorist Capability Acquired Consequence q Studies (Blast & Consequence) q Plans (AMSP) q Tools (Chemtap, Oiltap, CAMEO, Aloha, Marplot) q Consequence Data (RMP, GCOA, HASZUS) MSRAM Risk Calculator Outputs q q q Prioritized Risk Ranking Common Risk Model (NADB) Security Risk Profiles Risk Drivers Data for Risk Management Analysis Risk Management Priorities Vulnerability q Assessments (AMSC, VSP, FSP, RAM-D, MAST, PSA, RAMCAP, CRs, SAV, PIVA, HLS-CAM, JISVA, FHWA). q Tools (ACAMS, Vi. SAT) q Studies / Grants ( BZPP) q Workgroups (SME) Analyze & Exercise Strategic Risk Analysis Process Protective Security Analysis Center (PSAC) National Infrastructure Simulation and Analysis Center (NISAC) Coast Guard R & D Center / National Labs Exercises: PREP, PORTSTEP, AMSTEP, TOPOFF 10
MSRAM – Synergizes the Use of Other Risk Tools, Models, and Assessments Threat ICC Strategic Threat Analysis q Intent w/Confidence q Capability w/Confidence q Time Horizon when terrorist Capability Acquired Consequence q Studies (Blast & Consequence) q Plans (AMSP) q Tools (Chemtap, Oiltap, CAMEO, Aloha, Marplot) q Consequence Data (RMP, GCOA, HASZUS) MSRAM Risk Calculator Outputs q q q Prioritized Risk Ranking Common Risk Model (NADB) Security Risk Profiles Risk Drivers Data for Risk Management Analysis Risk Management Priorities Vulnerability q Assessments (AMSC, VSP, FSP, RAM-D, MAST, PSA, RAMCAP, CRs, SAV, PIVA, HLS-CAM, JISVA, FHWA). q Tools (ACAMS, Vi. SAT) q Studies / Grants ( BZPP) q Workgroups (SME) Analyze & Exercise Strategic Risk Analysis Process Protective Security Analysis Center (PSAC) National Infrastructure Simulation and Analysis Center (NISAC) Coast Guard R & D Center / National Labs Exercises: PREP, PORTSTEP, AMSTEP, TOPOFF 10
 MSRAM Data Review Process Local, Regional and National HQ Assessment, Review & 4 Analysis Provide consistency/ normalization between Areas 2 1 District Review Provide consistency/normalization between Sectors COTP/Sector Assessment with AMSC Input - Identifies risk profile for individual targets Green = Data is at the Security Sensitive Information level Review and Direction 3 Area Review Provide consistency/normalization between Districts RED = Data is at the Secret level 11
MSRAM Data Review Process Local, Regional and National HQ Assessment, Review & 4 Analysis Provide consistency/ normalization between Areas 2 1 District Review Provide consistency/normalization between Sectors COTP/Sector Assessment with AMSC Input - Identifies risk profile for individual targets Green = Data is at the Security Sensitive Information level Review and Direction 3 Area Review Provide consistency/normalization between Districts RED = Data is at the Secret level 11
 Previous Consequence-Based Approach Cruise Ship Freight Ship Oil Tanker Nuclear Power Plant Bridge Refinery Waterway Ferry CDC Barge LOW Consequence Chemical Defense Plant Facility HIGH Consequence One Dimension Consequence Scale 12
Previous Consequence-Based Approach Cruise Ship Freight Ship Oil Tanker Nuclear Power Plant Bridge Refinery Waterway Ferry CDC Barge LOW Consequence Chemical Defense Plant Facility HIGH Consequence One Dimension Consequence Scale 12
 MSRAM creates a Risk-Based Risk-Informed Security Profile Likelihood (Threat * Vulnerability) HIGH Bridge - Boat Bomb High Capacity Ferry Terminal- Car/Truck Bomb Ferry 150 1000 – Boat Bomb High Capacity Ferry – Boat Bomb Cruise Terminal – Car/Truck Bomb National Icon – Boat Bomb Petroleum Refinery – Car/Truck Bomb High Capacity Ferry Car/Truck Bomb Oil Tanker – Boat Bomb Cruise Ship Boat Bomb LPG Tanker - Boat Bomb Nuclear Power Plant – Car/Truck Bomb CDC Facility – Car/Truck Bomb Cruise Ship - Car/Truck Bomb Cruise Ship – Attack By Hijacked Vessel LPG Tanker – Stand. Off Weapon LOW Bridge – Attack By Hijacked Vessel LOW Consequence HIGH Consequence 13
MSRAM creates a Risk-Based Risk-Informed Security Profile Likelihood (Threat * Vulnerability) HIGH Bridge - Boat Bomb High Capacity Ferry Terminal- Car/Truck Bomb Ferry 150 1000 – Boat Bomb High Capacity Ferry – Boat Bomb Cruise Terminal – Car/Truck Bomb National Icon – Boat Bomb Petroleum Refinery – Car/Truck Bomb High Capacity Ferry Car/Truck Bomb Oil Tanker – Boat Bomb Cruise Ship Boat Bomb LPG Tanker - Boat Bomb Nuclear Power Plant – Car/Truck Bomb CDC Facility – Car/Truck Bomb Cruise Ship - Car/Truck Bomb Cruise Ship – Attack By Hijacked Vessel LPG Tanker – Stand. Off Weapon LOW Bridge – Attack By Hijacked Vessel LOW Consequence HIGH Consequence 13
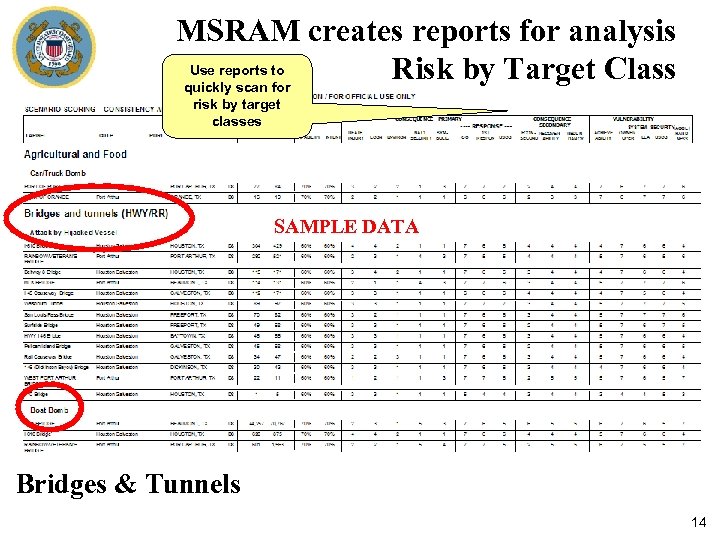 MSRAM creates reports for analysis Use reports to Risk by Target Class quickly scan for risk by target classes SAMPLE DATA Bridges & Tunnels 14
MSRAM creates reports for analysis Use reports to Risk by Target Class quickly scan for risk by target classes SAMPLE DATA Bridges & Tunnels 14
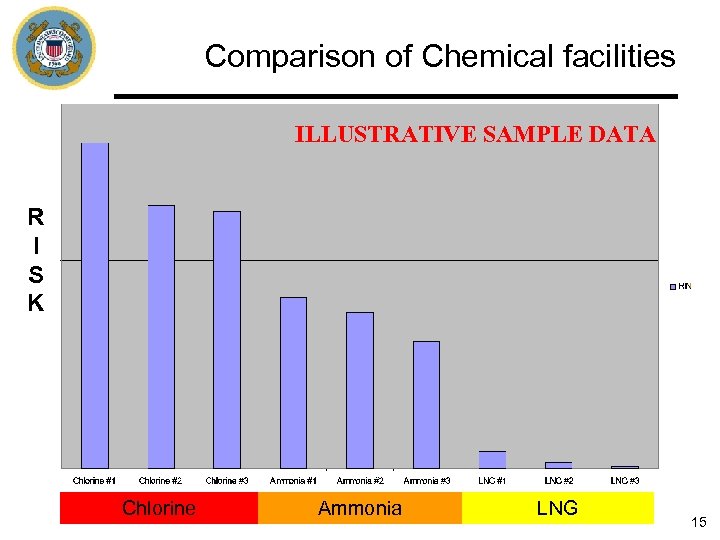 Comparison of Chemical facilities ILLUSTRATIVE SAMPLE DATA R I S K Chlorine Ammonia LNG 15
Comparison of Chemical facilities ILLUSTRATIVE SAMPLE DATA R I S K Chlorine Ammonia LNG 15
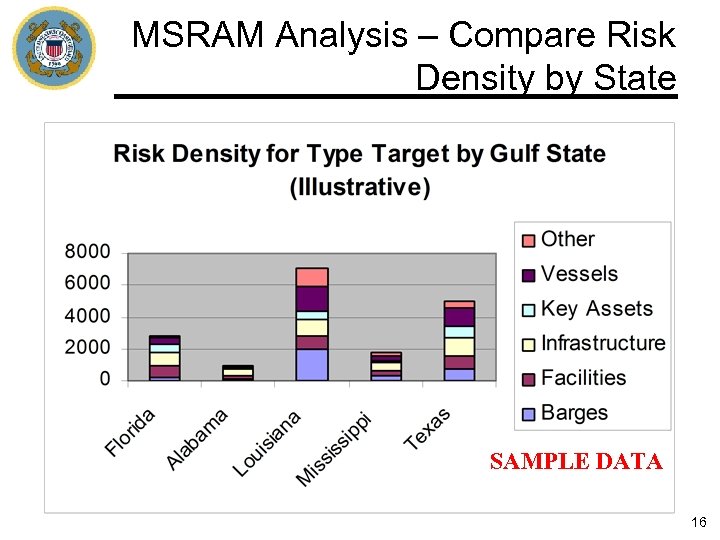 MSRAM Analysis – Compare Risk Density by State SAMPLE DATA 16
MSRAM Analysis – Compare Risk Density by State SAMPLE DATA 16
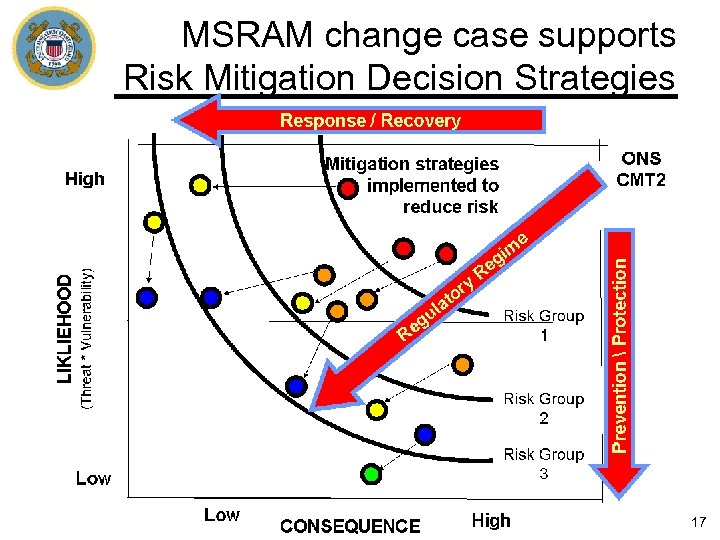 MSRAM change case supports Risk Mitigation Decision Strategies 17
MSRAM change case supports Risk Mitigation Decision Strategies 17
 MSRAM National Risk Profile Response/Recovery LIKELIHOOD (Threat * Vulnerability) X# target represent top 40% of the total risk e im ry u g Re o lat eg R X# target represent top 60% of the total risk 18, 000+ targets represent 100 % of the total risk Prevention/Protection X# target represent top 20% of the total risk CONSEQUENCE 18
MSRAM National Risk Profile Response/Recovery LIKELIHOOD (Threat * Vulnerability) X# target represent top 40% of the total risk e im ry u g Re o lat eg R X# target represent top 60% of the total risk 18, 000+ targets represent 100 % of the total risk Prevention/Protection X# target represent top 20% of the total risk CONSEQUENCE 18
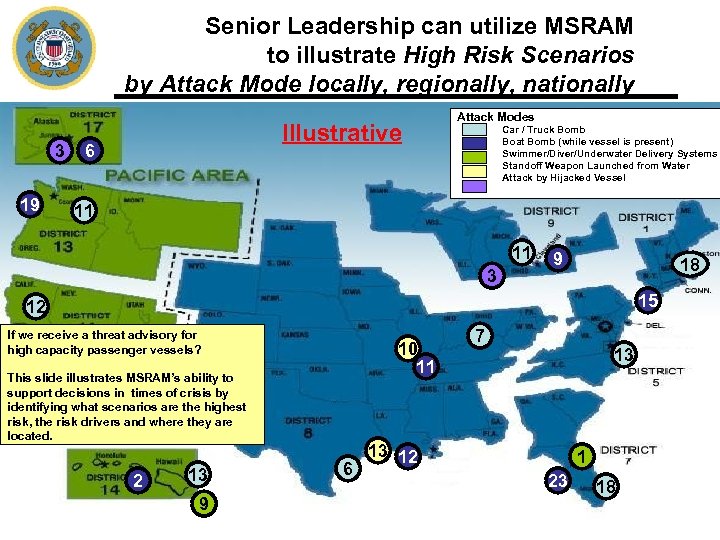 Senior Leadership can utilize MSRAM to illustrate High Risk Scenarios by Attack Mode locally, regionally, nationally 3 19 Illustrative 6 Attack Modes Car / Truck Bomb Boat Bomb (while vessel is present) Swimmer/Diver/Underwater Delivery Systems Standoff Weapon Launched from Water Attack by Hijacked Vessel 11 11 3 9 18 15 12 If we receive a threat advisory for high capacity passenger vessels? 10 11 This slide illustrates MSRAM’s ability to support decisions in times of crisis by identifying what scenarios are the highest risk, the risk drivers and where they are located. 2 13 9 6 7 13 13 12 1 23 18 19
Senior Leadership can utilize MSRAM to illustrate High Risk Scenarios by Attack Mode locally, regionally, nationally 3 19 Illustrative 6 Attack Modes Car / Truck Bomb Boat Bomb (while vessel is present) Swimmer/Diver/Underwater Delivery Systems Standoff Weapon Launched from Water Attack by Hijacked Vessel 11 11 3 9 18 15 12 If we receive a threat advisory for high capacity passenger vessels? 10 11 This slide illustrates MSRAM’s ability to support decisions in times of crisis by identifying what scenarios are the highest risk, the risk drivers and where they are located. 2 13 9 6 7 13 13 12 1 23 18 19
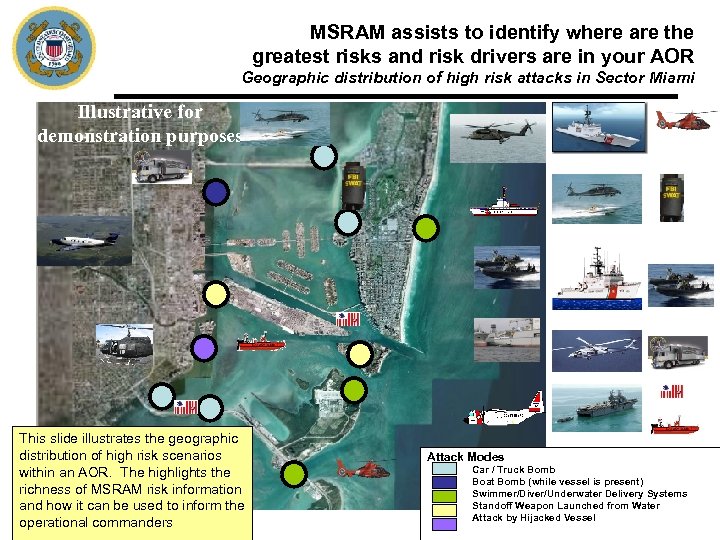 MSRAM assists to identify where are the greatest risks and risk drivers are in your AOR Geographic distribution of high risk attacks in Sector Miami Illustrative for demonstration purposes This slide illustrates the geographic distribution of high risk scenarios within an AOR. The highlights the richness of MSRAM risk information and how it can be used to inform the operational commanders Attack Modes Car / Truck Bomb Boat Bomb (while vessel is present) Swimmer/Diver/Underwater Delivery Systems Standoff Weapon Launched from Water Attack by Hijacked Vessel 20
MSRAM assists to identify where are the greatest risks and risk drivers are in your AOR Geographic distribution of high risk attacks in Sector Miami Illustrative for demonstration purposes This slide illustrates the geographic distribution of high risk scenarios within an AOR. The highlights the richness of MSRAM risk information and how it can be used to inform the operational commanders Attack Modes Car / Truck Bomb Boat Bomb (while vessel is present) Swimmer/Diver/Underwater Delivery Systems Standoff Weapon Launched from Water Attack by Hijacked Vessel 20
 MSRAM supports Local, Regional and National applications q Strategic Uses o Provides an understanding of: • the types of targets and attacks that present the highest risk • the risk-based distribution of targets regionally (Risk Density) o o o o q Operational Uses o o q Strategic planning outcomes measure Support of Strategic planning effort-Combating Maritime Terrorism (CMT) Transportation Worker Identification Credential (TWIC) implementation DHS Port Security Grant Process (risk formula and grant evaluation) National Maritime Security Risk Assessment (NMSRA) National Maritime Threat Assessment Methodology Strategic Operational Planning Process (SOPP) Operation Neptune Shield Geospatial Risk Map Area Maritime Security Plans (AMSP) / Action Plans / Contingency plans Mounted Automatic Weapon allocation project Tactical Uses o o Incident Command System (ICS) risk management cycle National Special Security Event (NSSE) Communication tool amongst stakeholders-AMS Committee Supports updates to NVIC 09 -02 AMSPs and 03 -03 Facility security plans 21
MSRAM supports Local, Regional and National applications q Strategic Uses o Provides an understanding of: • the types of targets and attacks that present the highest risk • the risk-based distribution of targets regionally (Risk Density) o o o o q Operational Uses o o q Strategic planning outcomes measure Support of Strategic planning effort-Combating Maritime Terrorism (CMT) Transportation Worker Identification Credential (TWIC) implementation DHS Port Security Grant Process (risk formula and grant evaluation) National Maritime Security Risk Assessment (NMSRA) National Maritime Threat Assessment Methodology Strategic Operational Planning Process (SOPP) Operation Neptune Shield Geospatial Risk Map Area Maritime Security Plans (AMSP) / Action Plans / Contingency plans Mounted Automatic Weapon allocation project Tactical Uses o o Incident Command System (ICS) risk management cycle National Special Security Event (NSSE) Communication tool amongst stakeholders-AMS Committee Supports updates to NVIC 09 -02 AMSPs and 03 -03 Facility security plans 21
 Global Supply Chain Security Risk MSRAM can assist in determining the risk & interdiction capability along critical nodes CBP Booking 24 Hour Advance Information CTPAT Shipment Notice International Ship & 96 Hour Port Facility Notice of Arrival Compliance Container Security Initiative DNDO, Deep Water, Domain Awareness Entry State / Local Carrier Movements Factory Truck, Rail, Distribution Truck, Rail, Barge Center Transport DR. Lewis Port of Lading Trans. Water shipment Conveyance Port Air Conveyance Port of Entry Truck, Rail, Distribution Barge Center Transport MSRAM CFR Critical Network Transportation Analysis Security Risk Analysis Regulatory Regime Enforcement 22
Global Supply Chain Security Risk MSRAM can assist in determining the risk & interdiction capability along critical nodes CBP Booking 24 Hour Advance Information CTPAT Shipment Notice International Ship & 96 Hour Port Facility Notice of Arrival Compliance Container Security Initiative DNDO, Deep Water, Domain Awareness Entry State / Local Carrier Movements Factory Truck, Rail, Distribution Truck, Rail, Barge Center Transport DR. Lewis Port of Lading Trans. Water shipment Conveyance Port Air Conveyance Port of Entry Truck, Rail, Distribution Barge Center Transport MSRAM CFR Critical Network Transportation Analysis Security Risk Analysis Regulatory Regime Enforcement 22
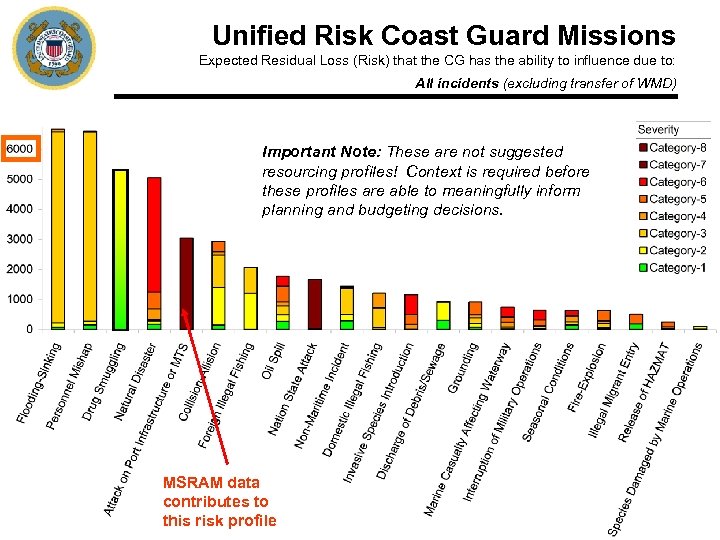 Unified Risk Coast Guard Missions Expected Residual Loss (Risk) that the CG has the ability to influence due to: All incidents (excluding transfer of WMD) Important Note: These are not suggested resourcing profiles! Context is required before these profiles are able to meaningfully inform planning and budgeting decisions. MSRAM data contributes to this risk profile 23
Unified Risk Coast Guard Missions Expected Residual Loss (Risk) that the CG has the ability to influence due to: All incidents (excluding transfer of WMD) Important Note: These are not suggested resourcing profiles! Context is required before these profiles are able to meaningfully inform planning and budgeting decisions. MSRAM data contributes to this risk profile 23
 Maritime Security Risk Analysis Model Support Senior Leadership risk based/informed decision making process “In the absence of emotion and Political influence Risk is where risk is. ” Quote by LCDR Brady Downs, USCG during Congressional briefing 2007 Questions? Topics for Discussion! 24
Maritime Security Risk Analysis Model Support Senior Leadership risk based/informed decision making process “In the absence of emotion and Political influence Risk is where risk is. ” Quote by LCDR Brady Downs, USCG during Congressional briefing 2007 Questions? Topics for Discussion! 24


