0348d5b16ce2ab3099ea2d4be346913d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 190

U. S. Census Bureau Foreign Trade Division Understanding Foreign Trade Data May 16, 2007

U. S. Census Bureau Overview of Imports and Exports Carol Aristone Commodity Analysis Branch Carol. Ann. Aristone@census. gov

What do the statistics measure? The physical movement of goods between: • United States, Puerto Rico, U. S. Virgin Islands • Foreign countries. 3

Coverage Movement of goods into & out of: • • U. S. Customs Territory U. S. Virgin Islands Bonded Warehouses Foreign Trade Zones (FTZs) 4

Coverage • Goods not included: • U. S. trade with U. S. territories • Trade between foreign countries and U. S. territories (other than PR and VI) • In transit merchandise through the U. S. 5

What’s not Covered in Statistics? • • Monetary gold & silver U. S. government to U. S. government Imports of articles repaired under warranty Intangibles Personal and household effects Low valued transactions Consult the Guide to Foreign Trade Statistics 6

The Harmonized System (HS) Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the U. S. Annotated for Statistical Reporting Purposes (HTSUSA) Statistical Classification of Domestic and Foreign Commodities Exported from the U. S. (Schedule B) 7

The HS System 17, 000+ HTSUSA & 8, 000+ Schedule B codes • Periodically revised • Structure: • 2 digit Chapter • 4 digit Heading • 6 digit sub heading • 8 digit legal • 10 digit statistical 8
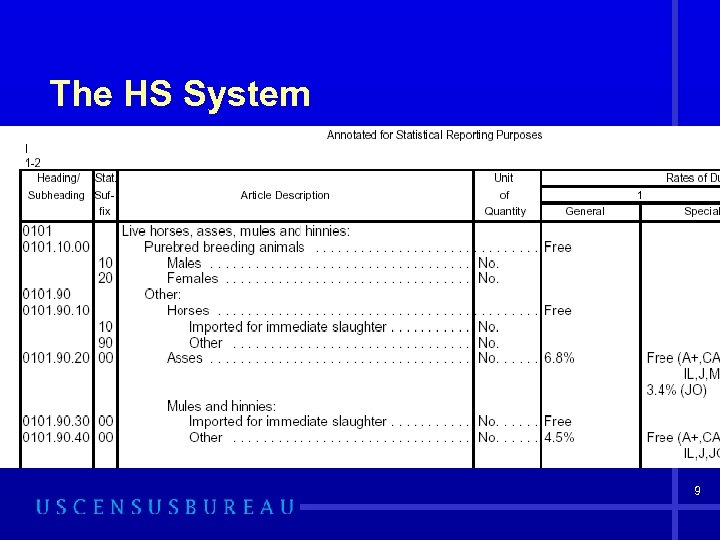
The HS System 9
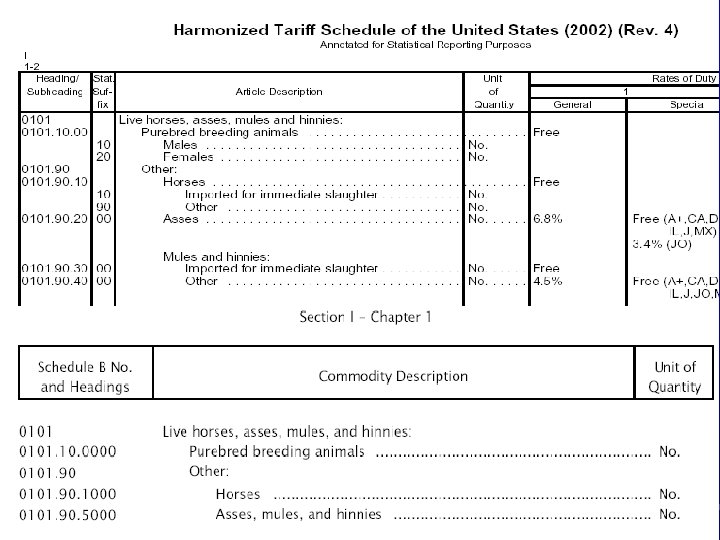
The HS System 10

What is the difference? Export codes (Schedule B) are maintained by the U. S. Census Bureau. Import codes are administered by the U. S. International Trade Commission (USITC). Import Codes CAN be used to classify Exports, but Exports codes CAN NOT be used to classify goods for import (Imports has a lot more detail!!) 11
Changes to the HTSUSA & Schedule B Changes occur three different ways: • WCO changes affect the HS (4 or 6 digit) level • Legislation – affects the legal (8 -digit) level • Imports only • 484(f) committee – affects the statistical (10 -digit) level 12

Partner Country • Exports – Country of Ultimate Destination • Imports – Country of Origin – Where goods are grown, mined or manufactured – Use country of shipment if origin unknown for re-imports 13

Exports

Related vs. Non-related Statistics cover the physical movement of goods, regardless of if item is sold When a U. S. manufacturer exports merchandise to their company in France or to a non-related purchaser in Russia, both are counted as trade 15

Valuation F. A. S. Export Value (free alongside ship) • Value of export at port based on transaction price, including inland freight, insurance other charges incurred (before loaded) • Excludes international freight, cost of loading merchandise and any other charges/costs beyond port of export 16

Leases If merchandise exported for <12 months • Non-stat Consignment - Temp. lease with option to buy • Stat • Examples: artwork or aircraft 17

Repairs – Exports Exporting items for repair • Report Ch. 1 -97 HS number of item • Non-stat • AES exemption code TR (temporary export for repair) Exporting items repaired in U. S. • Report HS 9801 and value of repair 18

Imports

Foreign Trade Zones – Imports • Duties not required until goods withdrawn for consumption • Importer has choice to pay at the rate of the original foreign materials or the finished product • Can result in $3, 000 new car 20

Bonded Warehouses – Imports Duty payment deferred No duty if re-exported to foreign countries 21
General vs. Consumption General Imports – measures flow of goods across U. S. border • Imports for direct consumption • Bonded warehouse entries and FTZ admissions • Most widely used measure of imports 22

General vs. Consumption (cont. ) Imports for Consumption – goods cleared through Customs • Imports for direct consumption • Bonded warehouse and FTZ withdrawals 23

Valuation Customs Value • Generally, price actually paid excluding: • Duties • Freight • Insurance and other charges • Relationship b/w parties should not influence value 24
Valuation (cont. ) CIF (cost, insurance, freight) • CIF = Customs Value + Import Charges • Excludes U. S. import duties 25

Valuation (cont. ) Dutiable Value • Customs value of foreign goods subject to duty • Where merchandise is a combination of U. S. and foreign goods, duty is applied only to the foreign value added 26

Valuation (cont. ) To determine the dutiable value of a combination of U. S. and foreign goods: • Example: 9802 provision • U. S. value is included in statistics § Value is total of domestic + foreign values • U. S. Goods indicators show that a portion of the import is domestic materials • Publication IM 146 A 27

Valuation (cont. ) Duty • Collected by CBP • Reported on the Automated Commercial System (ACS) • FTD generally uses duty as reported on ACS 28

Country Sub-Codes (CSC) Indicates a special program allowing for free or reduced duty • Examples: GSP, US-Chile Free Trade Agreement, NAFTA • CSC used: • • 00 = no special programs claimed CA = Goods marked for Canada (NAFTA) MX = Goods marked for Mexico (NAFTA) Full list available on our website 29
Rate Provision (RP) codes • RP codes indicate free or dutiable status • Used in conjunction with goods imported using Ch. 98 or 99 code • RP code can relate back to Ch. 98 or 99 • Assigned by FTD 30

Rate Provisions (cont. ) Examples of RP codes: • RP 17 = Free as articles imported for the handicapped. Imported under HTS subheadings 9817. 00. 92, 9817. 00. 94 & 9817. 00. 96 • RP 69 = Dutiable at rate prescribed in Rate of Duty columns of HTS Ch. 99. Duty reported • Full list available on our website 31

Special Provisions Chapter 98 & 99 for National use • Ch 98 - duty free/reduction • Ch 99 - legislation, executive and administrative actions 32

Special Provisions (cont. ) 9801 - U. S. goods exported and returned not advanced or improved • U. S. origin • Previously exported from U. S. 33

Special Provisions (cont. ) 9802 – Goods with components of U. S. origin • U. S. goods assembled abroad • Importers deduct value of U. S. goods from total Customs value 34

Dual Reporting of Codes Report 10 -digit statistical reporting number • Chapter 1 -97 Followed by special provision • Chapter 98 UQ from Ch 1 -97 35

Dual Reporting of Codes 9817. 85. 01 • Prototypes for development, testing, evaluation • Free 8422. 11. 0000 • Dishwasher, household • 2. 4% 8422. 19. 0000 • Dishwasher, other • Free 36

Special Provisions (cont. ) Chapter 99 • Quotas • Additional duties • Temporary reductions 37
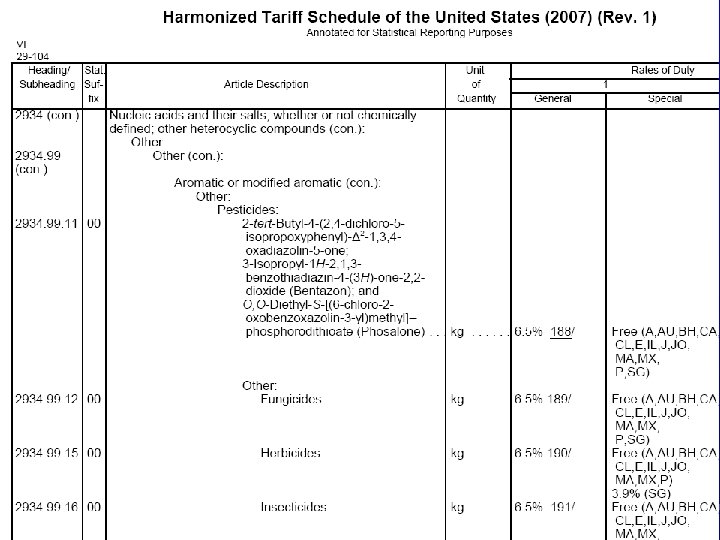
38

Dual Reporting of Codes • Footnote 189 - See headings 9902. 01. 19, 9902. 12, 9902. 12. 54, etc. • Reduced or duty free rates • 9902. 01. 19 Vinclozolin • Report 9902. 01. 19 - 2934. 99. 1200 39

Repairs – Imports Importing repaired item • Report Ch. 98 number and value of repair • If under warranty – non-stat • If Non-warranty – stat § Also report Ch. 1 -97 HS in order to determine duty Importing item for repair • Temporary imports 40

Internet References FTD • http: //www. census. gov/trade Guide to Foreign Trade Statistics • http: //www. census. gov/foreigntrade/guide/index. html 41

Internet References (con. ) Schedule B • http: //www. census. gov/scheduleb HTSUSA • http: //www. usitc. gov/tata/hts/bychapter/index. htm 42

Internet References (con. ) CSC • http: //www. census. gov/foreigntrade/reference/codes/csc. html RP • http: //www. census. gov/foreigntrade/reference/codes/rp. html 43

Any Questions? 44

Processing and Editing May 16, 2007 Andrew Jennings Methods Research and Quality Assurance Andrew. S. Jennings@census. gov

Introduction • The Foreign Trade Division processes over 6 million import and export transactions a month • Publish the official merchandise trade statistics on a monthly basis • Ensure that published statistics are accurate • Published data may appear different than what can be seen on the electronic systems 46

Outline Sources of Data Processing Data Categories Differences 47
Sources of Import Data Imports • The Automated Commercial System (ACS) • Automated Foreign Trade Zones (AFTZ) • Paper Documents • Canadian Gas and Electricity • Estimates 48
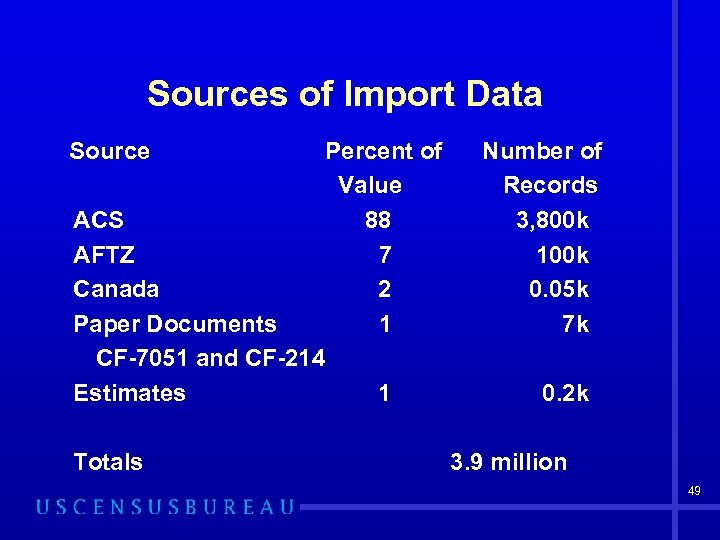
Sources of Import Data Source ACS AFTZ Canada Paper Documents CF-7051 and CF-214 Estimates Totals Percent of Value 88 7 2 1 1 Number of Records 3, 800 k 100 k 0. 05 k 7 k 0. 2 k 3. 9 million 49

Sources of Export Data Exports • Automated Export System (AES) • Canadian Data Exchange • Shippers Export Declarations (SED) • Estimates 50
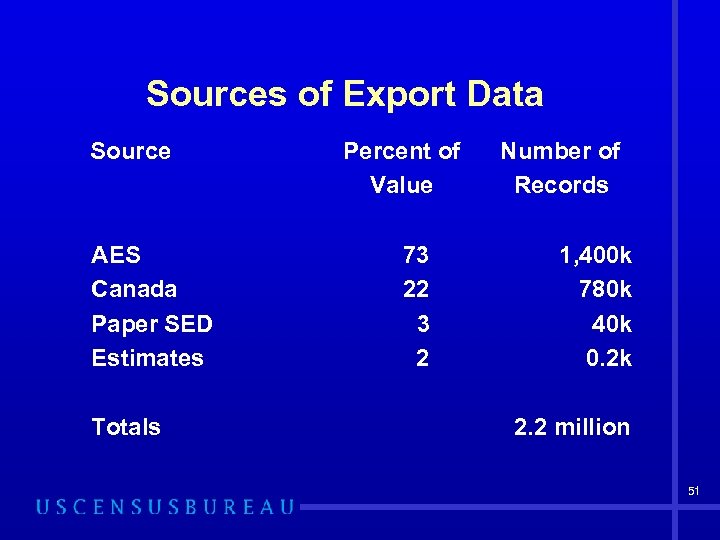
Sources of Export Data Source AES Canada Paper SED Estimates Totals Percent of Value 73 22 3 2 Number of Records 1, 400 k 780 k 40 k 0. 2 k 2. 2 million 51

Sources of Data Editing at point of collection • Data are edited at point of collection • Ensures best quality data • Subset of what is edited post collection 52

Processing Overview • Prepare for editing • Edit • Resolve errors • Categorize and aggregate the data 53

Prepare Records for Editing Combine Sources • Reformat data to uniform structure • Identify Non-statistical transactions • Low value records • Non-extractable entries 54

Prepare Records for Editing Statistical time periods • Imports - Release date • Exports - Clearance date • Statistical month • Carryover 55

Prepare Records for Editing Preliminary Alterations • Recode commodities as necessary • Convert quantities • Convert Schedule B from HTS (exports only) • Prorate shipping weight (exports only) 56

Prepare Records for Editing Apply Corrections to Data • Customs corrections • Filer corrections 57

Editing Overview • Code Validations • Ratio Edits • Maximums and Minimums 58

Editing Code Validations • Harmonized System commodity • Country of origin • Foreign port • U. S. port • Special Programs Indicators (imports) 59

Editing Code Validations • We validate codes with lookup tables that are updated monthly as changes are made • Commodity-specific consistency checks Example: import bananas from Greenland • Check exports shipped by vessel are processed through a vessel port, not an airport 60

Editing Ratio Edits • Verify numeric data by computing ratios • Check ratios against commodity-specific ranges • Several types of ratio edits o Quantity to value o Quantity to shipping weight/value to shipping weight o First quantity to second quantity for shipments requiring two quantities 61

Editing Ratio Edits • Unit price example - Fireworks – We edit the quantity using unit price parameters of 0. 663966/kg and $30. 165/kg – We expect a $40, 000 shipment of fireworks from China to have a quantity between 1, 326 kg and 60, 244 kg • $10, 000 / 10, 000 kg 62

Editing Maximums and Minimums • General Maximums o Shipping weight exceeds what the mode of transportation carry • Commodity-specific maximums o Maximum shipping weights – Example: 20 kilograms of diamonds unlikely o Maximum values • Maximum quantities 63

Editing Commodity Specific Parameters • 2. 7 million parameters • Files containing editing parameters by commodity • Flexible – can easily make necessary changes to parameters 64

Editing Error resolution • Cannot review every erroneous record • Analysts review records that have the most impact • Edit programs impute insignificant records 65

Editing Imputation • Impute a new quantity or shipping weight from a factor and value or previously edited field • Unit price example 1, 000 kg of fireworks valued at $40, 000 would reject our edit. Using an imputation factor of $4. 51/kg, the edit program would change quantity to 8, 853 kg. 66

Editing Analyst review • Contact the filer • Ensure correct classification • Bypass the edits 67

Editing Analyst Review • Review data by grouping individual records • Aggregate by commodity to determine if total values and quantities are reasonable • Utilize control files • Compare measures to previous months – look for missing or misreported data and identify processing problems 68
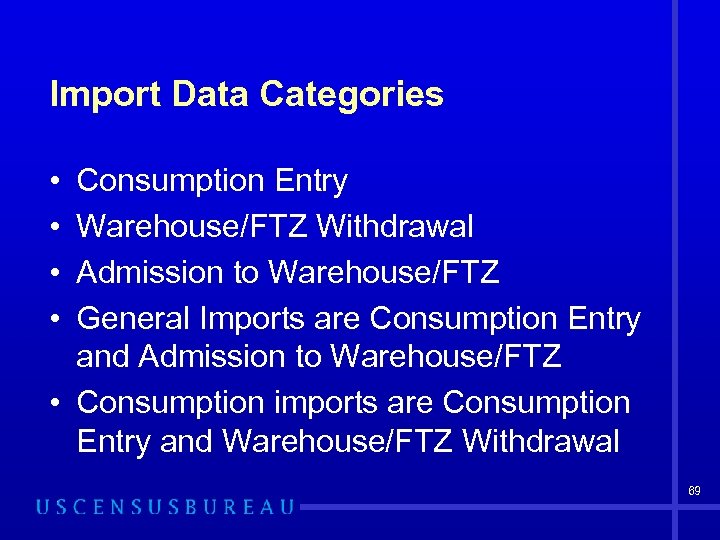
Import Data Categories • • Consumption Entry Warehouse/FTZ Withdrawal Admission to Warehouse/FTZ General Imports are Consumption Entry and Admission to Warehouse/FTZ • Consumption imports are Consumption Entry and Warehouse/FTZ Withdrawal 69
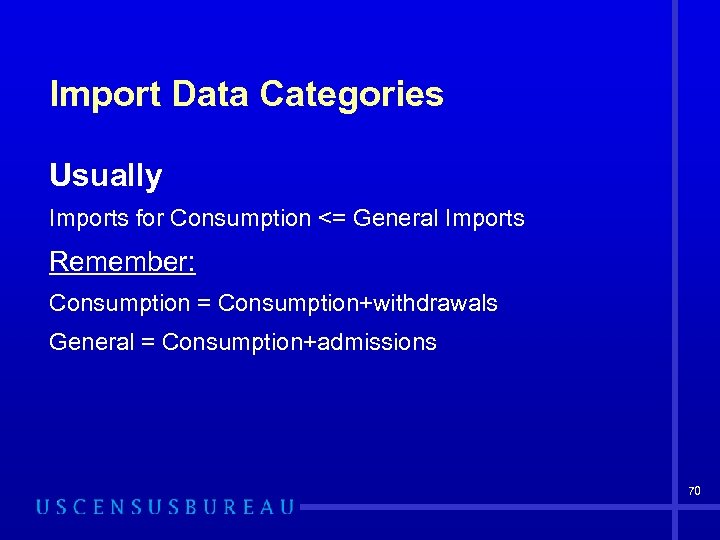
Import Data Categories Usually Imports for Consumption <= General Imports Remember: Consumption = Consumption+withdrawals General = Consumption+admissions 70

Why would Consumption be greater than General Imports? Goods processed in a FTZ Example: Petroleum entered in FTZ § General import stats would show Ch 27 when goods admitted to FTZ § Petroleum is processed in the zone, creating byproducts classified in Ch 25 § Therefore imports for consumption are based on what EXITS the zone (Ch 25) 71

Why would Consumption be greater than General Imports? Petroleum processed in a FTZ could result in: Chapter 27 General import stats > Consumption stats Chapter 25 General Import stats < Consumption stats 72

Export Data Categories Domestic – Merchandise grown, produced or manufactured in the U. S. – Foreign merchandise changed in the U. S. Foreign (re-export) – Foreign merchandise, entered for consumption or into a warehouse or FTZ, that is unchanged at the time of export Published exports are domestic exports and foreign exports 73

Data Categories Noncontiguous trade – PR and VI trade with U. S. are Noncontiguous exports 74
Raw Data Versus Published Statistics Why is the data on the portal different from published statistics? – Several sources of data We pull data from several different sources, including estimating low value shipments. – The data are categorized Double counting trade into and out of warehouses and Foreign Trade Zones – We make changes to the data during processing Non-statistical Data, Data Corrections, Alteration of Data – Time periods 75

Data Processing and Editing Questions please! Andrew. S. Jennings@census. gov (301)763 -7041 76

Process Coordination Staff The United States – Canada Data Exchange

What is the United States – Canada Data Exchange? Agreement between the governments of the United States and Canada 78

Reasons for Data Exchange? ? • Rise in undercoverage of export statistics in the ’ 70 s and ’ 80 s • Increasing operating costs to process Shipper’s Export Declarations • Eliminate reporting burden of exporters • Greater scrutiny of import statistics • Geographical location of both countries 79

Who’s Involved ? United States • Census Bureau (Census) • Customs & Border Protection (CBP) Canada • Statistics Canada (STC) • Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) 80

What Happens? The U. S. Census Bureau and Statistics Canada exchange each other’s import statistics to publish their export statistics.

When Canadian Imports Arrive at Census • STC transmits files twice per month • Adjustments are required 82

• Freight Adjustments • Currency Conversion • U. S. Exports of Foreign Goods to Canada • Exports of U. S. goods to Canada from other countries • Revisions 83
Inland Freight • Exclusion of inland freight charges in Canadian imports • Inclusion of inland freight charges in U. S. exports • Census adds inland freight charges to compensate for the difference in valuation 84

Currency Conversion • U. S. Federal Reserve’s monthly exchange rate • STC converts to U. S. Dollars and transmits data to Census 85

Exports of Foreign Goods to Canada • Census counts these goods as U. S. exports to Canada • STC does not count these goods as imports from the U. S. • The Data Exchange accounts for this difference by adding these goods to the U. S. export statistics 86

Exports of U. S. Goods to Canada from Other Countries • STC counts these goods as imports from the U. S. • Census does not count these goods as U. S. exports • The Data Exchange accounts for this difference by excluding these goods from the U. S. export statistics 87

Revisions • Estimates for Late Arrivals • Corrections from STC • Corrections Made by Census 88

Estimates for Late Arrivals • STC sends Census estimates for late arrivals • The estimates are replaced with actual values the following month in the FT 900 press release only 89

Corrections from STC • STC sends corrections to data transmissions • Census receives the corrections and applies them to the export statistics 90
Corrections Made By Census • Census applies manual corrections based on data verification • Census verifies corrections with STC counterpart • These corrections occur prior to publication when possible 91

Other U. S. /Canada Issues • Railcar Data • Data Conversions • In-transit Shipments • U. S. Exports Shipped from Canadian Ports 92

Railcar Data • Duty-free railcars and locomotives are exempt from import filing requirements 93
Data Conversions • HS Recodes • Quantity Conversions 94

In-transit Shipments • Import filing issue • Effect on data 95

U. S. Exports Shipped from Canadian Ports • Filing compliance issue • Possible source of undercoverage 96

Questions? ? ? Questions ? ? Questions ? ? 97

U. S. Census Bureau Foreign Trade Division Trade with Partner Countries Earle Patrick May 16, 2007 U. S. Census Bureau

Trade with Partner Countries Major reasons for discrepancies • • • Trade Involving a third country In-transit goods Different trade systems 99

Trade with Partner Countries Other reasons for discrepancies • • Re-import of goods Insurance and Freight charges Treatment of low-value shipments Puerto Rico and U. S. Virgin Islands 100

Trade with Partner Countries 1. 2. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is considered an export ? Domestically produced merchandise sold to a foreign country Foreign goods resold to a foreign country Parts exported for further processing or incorporation into a more advanced product Capital equipment shipped to a foreign assembly or manufacturing location Charitable goods 101

Trade with Partner Countries UN guidelines for imports • Grown, mined, or produced • Substantially transformed • U. S. Customs determines origin when necessary 102

Trade with Partner Countries Trade involving a third country • China exports to India • India resells product to U. S. • China is still country of origin 103

Trade with Partner Countries In-transit goods • Definition of in-transit goods • Administrative requirements • Shippers send goods as normal imports to U. S. 104

Trade with Partner Countries Re-import of goods • Chapters 1 – 97 • Chapter 98 – heading 9801 105

Trade with Partner Countries Different trade systems • General trade system • Special trade system 106

Trade with Partner Countries Insurance and Freight Charges • Customs value • Cost, Insurance, and Freight 107

Trade with Partner Countries Miscellaneous Reasons • Low-value shipments • Puerto Rico and the U. S. Virgin Islands 108

Trade with Partner Countries Any questions ? 109
Methods Research & Quality Assurance Branch Port and Mode of Transportation Data Lee Stefanis May 16, 2007 U. S. Census Bureau 110
Introduction District/Port Data Definitions: Ø District of Exportation Ø Vessel or Air – Custom’s district where merchandise is loaded and taken out of the country Ø Overland – Custom’s district where merchandise crosses the U. S. Border into foreign territory Ø First 2 digits of port code 111

Introduction Ø Import District of Entry Ø The district in which merchandise clears Customs for entry into consumption channels, bonded warehouses, or Foreign Trade Zones. Ø Import District of Unlading Ø The district where merchandise is unloaded from the importing vessel or aircraft. 112

Introduction Method of Transportation: Ø Transportation Statistics Categories Ø Vessel, Air, and Other Methods Ø Based on the method of transportation by which the merchandise arrives in or departs from the United States Ø We obtain this information from the documentation the filers provide Ø Other methods are available for certain publication (i. e. rail vs. truck) 113
Introduction Method of Transportation: ØEntering/Departing through Canada & Mexico ØRecorded under the method of transportation by which they enter or depart the U. S. regardless of the transportation mode for the rest of their journey 114

How does a truck get here from China? Ø Method of Transportation is identified by the method of conveyance that is used when the shipment crosses the border into the U. S. Ø Example: China Canada on vessel, then Canada U. S. on truck Ø Over 5% of goods arriving over land originate in countries other than Canada and Mexico. 115
Reporting of District/Port Data Quality Issues: Ø Filing Ø Imports – data captured at time of entry summary Ø Exports – port where shipment is expected to ship from Ø Knowledge of Filer Ø Airports and Seaports Ø Correcting the obsolete/incorrect codes 116

Mail, Pipeline and Other Unknowns U. S. Mail ØFor exports via U. S. Mail, filers can report any code, but the Census Bureau changes the code to ‘ 8000’ ØThe Census Bureau corrects some export shipments that are incorrectly reported as mail (e. g. fire trucks) 117

Mail, Pipeline and Other Unknowns Pipeline ØFor shipments by pipeline, exporters file with the port having jurisdiction for the pipeline 118

Mail, Pipeline and Other Unknowns ØIn some cases a commodity, such as cattle, can cross the border anywhere, so the reported port may not be the location of movement into or out of the U. S. 119

User-Fee Ports and Nearby Ports ØA lot of couriers have their own port codes ØRecoding of courier port codes 120

Canadian Data Exchange ØQuality Issue ØWe take Canada’s imports for our exports which can lead to inaccurate port code information 121

Questions? Lee Stefanis Lee. H. Stefanis@census. gov (301) 763 -3150 122

U. S. Census Bureau Foreign Trade Division Quality Issues Alison Gajcowski May 16, 2007 U. S. Census Bureau

Sources of Errors – Nonfiling of documentation – Transiting goods – Underestimation of low value transactions – Late filing – Reporting errors – Data capture errors 124

Nonfiling of Export Documentation – Example: • If exporting to Canada, no documentation of export is required • BUT if shipping through Canada to Spain documentation is required – FTZ withdrawals for export 125
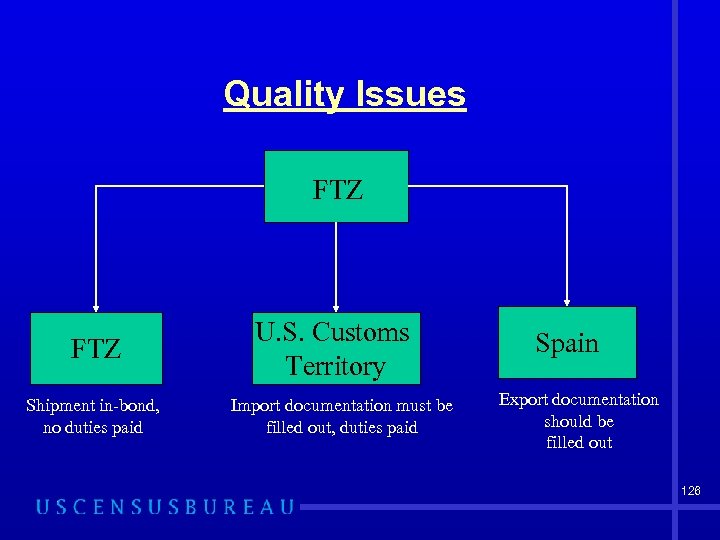
Quality Issues FTZ Shipment in-bond, no duties paid U. S. Customs Territory Import documentation must be filled out, duties paid Spain Export documentation should be filled out 126

Nonfiling of Export Documentation Cont’d – Increased electronic filing • Reduces the instances of nonfiling • Less export paper documents are lost 127

Nonfiling of Import Documentation – Rail cars • By law importers of rail cars are not required to report their shipments 128

Classification – Exports and duty free imports are not scrutinized as closely for proper classification – 80% of imports are duty free 129

Reasons for Misclassification – Typos – Duty avoidance – Not understanding the classification system * ABI and AES utilize edits to detect misreporting and send error messages to the filers* 130

Low Value Estimation – Value of these shipments is estimated – Factors based on ratios of low valued shipments to individual country total for past periods – The factors used may no longer be effective and FTD is in the process of improving the estimation methods 131

Charges – If a charge (such as invoiced freight, insurance, or other charges) is included in the invoice price, then all must be included in the customs value – If an importer does not know the exact value of all charges, than they must be estimated – To have an item excluded, must provide documentation – Result is that actual value of goods may be overstated for some commodities 132

Carryover – Term used to identify the trade records received and/or processed too late for inclusion with records that transaction month – Current carryover rate (2006 avg) • 0. 35% exports • 0. 94% imports 133

Carryover – Each month in the FT 900, the total import, export, trade balance and “end-use” totals for the prior month are adjusted for carryover • SITC (Standard International Trade Classification) and country detail reports not revised – Annual revision takes place each June • SITC and country detail reports are revised 134

Revisions – Every June of the current year, FTD publishes an annual revision of the previous year • Carryover correction • Corrections resulting from data investigations • Customs and Canadian revisions 135
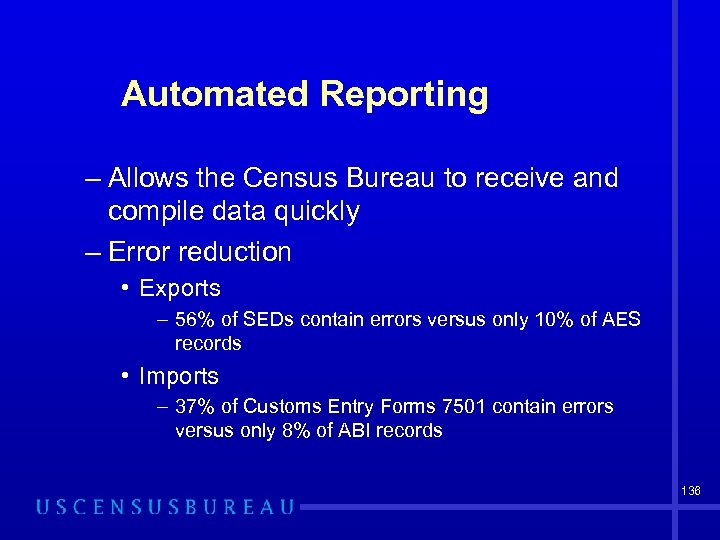
Automated Reporting – Allows the Census Bureau to receive and compile data quickly – Error reduction • Exports – 56% of SEDs contain errors versus only 10% of AES records • Imports – 37% of Customs Entry Forms 7501 contain errors versus only 8% of ABI records 136
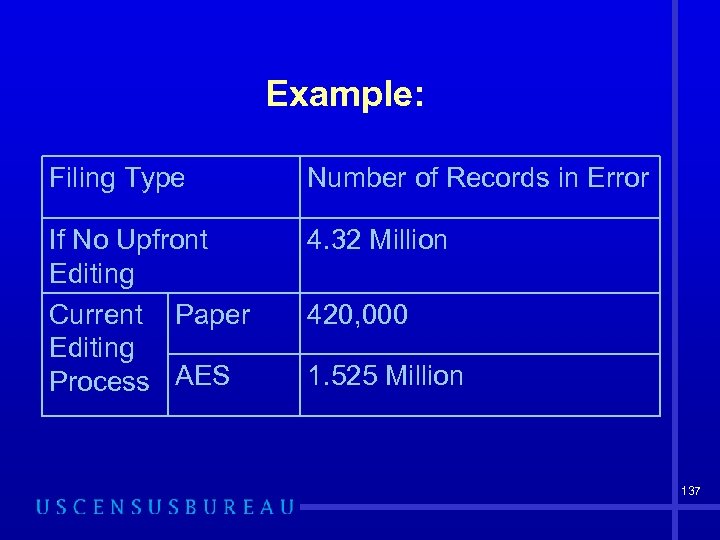
Example: Filing Type Number of Records in Error If No Upfront Editing Current Paper Editing Process AES 4. 32 Million 420, 000 1. 525 Million 137

Automated Reporting – ABI and AES intercept data problems and return error messages to the broker or filer for resolution – Census Bureau edits also reside in the Statistics Canada import processing system – Internal Census Bureau edits are used to prepare the data for dissemination 138

Quality Issues Any Questions? Alison. Gajcowski@census. gov (301)763 -7043 139

U. S. Census Bureau Foreign Trade Division Origin of Movement Export State Origin State, ZIP Code & Sub-state Data John Chantis May 16, 2007 Economic Research Service Washington, DC

Background: Origin of Movement (OM) State – Based on Origin State § Available 1987 – Present § On our monthly FT 900 Press Release, Supplement, exhibit 2 Origin of Movement (OM) – ZIP Code Based § Available on website starting with January 2006 statistics 141

Based on Origin State: § Available 1987 -Present § Based on the state in which the goods begin their journey to the port of export § Does not represent the production origin of U. S. export merchandise 142

Origin State examples: § Goods warehoused in GA transported to a FL port to be shipped to a foreign country. OM state is……GA § Auto parts produced from many states are consolidated in TX to be exported to Mexico. OM state is…… TX. 143

Origin of Movement (OM) State Series – § Available in our monthly FT 900 Press Release, supplement, exhibit 2 § Web address: http: //www. census. gov/foreign-trade/Press. Release/current_press_release/exh 2 s. pdf § Screen image follows 144
145

Other available state data products: § FTD - Quarterly and Annual OM state data on CDROM. Please call our Current Systems Programming Branch on 301 -763 -2214. Available in three options…. Option 1: State by 3 -Digit NAICS Commodity by Country (Total, Air and Vessel). Option 2: Region by 4 -Digit SITC, District/Port of Exit, & Country (Total, Air & Vessel). Option 3: State by District/Port of Exit, & Country (Total, Air & Vessel)- No Commodity Detail 146

Other products … § Global Trade Information Services (GTIS) WORLD TRADE ATLAS * U. S. State Export Edition Online. http: //www. gtis. com § Manufacturing and Construction Division (MCD) - Gives exports by state, NAICS and major economic sector. Available online at http: //www. census. gov/mcd. 147

Based on ZIP Code: § Available January 2006 - Present § The ZIP Code of the USPPI, the party in the US that receives the primary benefit from the shipment § Does not necessarily represent the location of the USPPI 148

ZIP Code State examples: § Goods warehoused in GA transported to a FL port to be shipped to a foreign country. ZIP state is. . . GA § For shipments with multiple origins, report the address from which the commodity with the greatest value begins its journey. 149

ZIP Code Based report: § Similar to OM supplement, exhibit 2 press release; available on our website: http: //www. census. gov/foreigntrade/statistics/state/zip/index. html § FTD - Quarterly and Annual ZIP state data on CDROM. Please call our Current Systems Programming Branch on 301 -7632214. Available in the same three options. 150
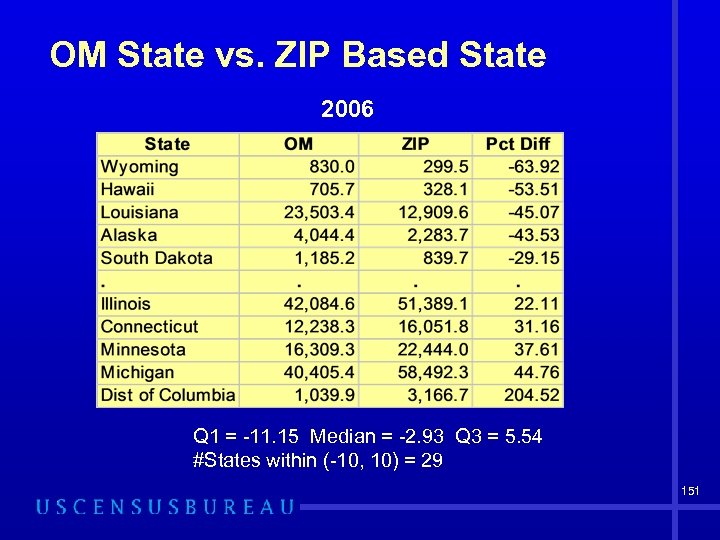
OM State vs. ZIP Based State 2006 Q 1 = -11. 15 Median = -2. 93 Q 3 = 5. 54 #States within (-10, 10) = 29 151
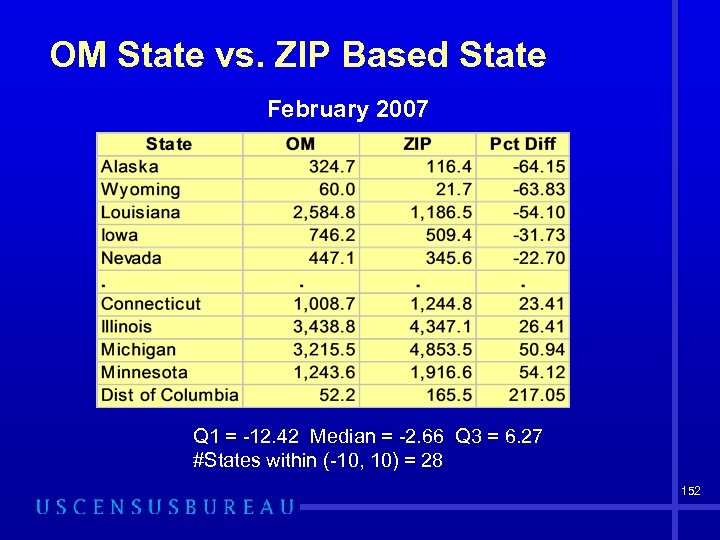
OM State vs. ZIP Based State February 2007 Q 1 = -12. 42 Median = -2. 66 Q 3 = 6. 27 #States within (-10, 10) = 28 152

Sub-State Data § Data historically based on Metropolitan Area (MA). § MA’s are now called Core Based Statistical Area (CBSA) by Office of Management & Budget (OMB). § New definitions for CBSA’s were announced by OMB on June 2003. 153
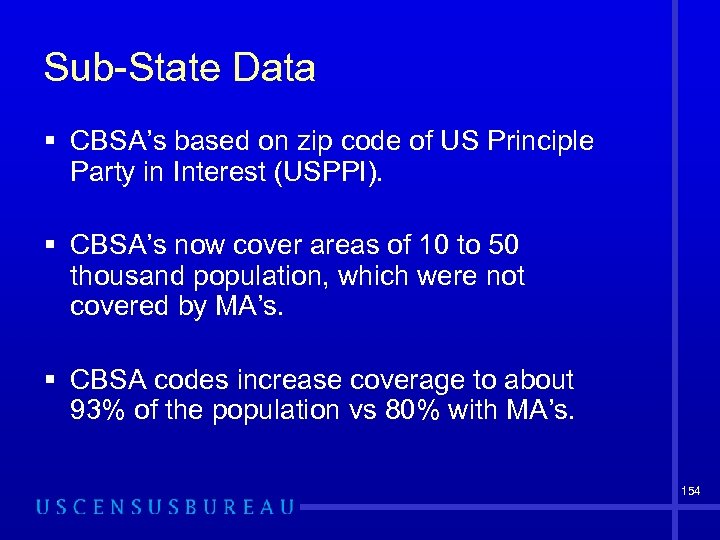
Sub-State Data § CBSA’s based on zip code of US Principle Party in Interest (USPPI). § CBSA’s now cover areas of 10 to 50 thousand population, which were not covered by MA’s. § CBSA codes increase coverage to about 93% of the population vs 80% with MA’s. 154

Sub-State Data § In 2006 completed a quality review and disclosure analysis of 3 -digit ZIP Codes, CBSA Metro, and other tables based on 2005 data § As historically, under contract, we have produced data for ITA which they release § Last year we provided 3 -digit ZIP Code & CBSA Metro totals for 2005 Export data to ITA 155

Future Goal… Have started preliminary work to provide data to ITA based on 2006 trade. • The current contract calls for CBSA by 3 -digit NAICS, CBSA by Destination, CBSA by 3 digit NAICS by Destination, and other tables of trade totals. • 2006 CBSA data will be available mid to late 2007. 156

For more information: John. Chantis@Census. gov Special Projects Branch Foreign Trade Division (301) 763 -3251 www. census. gov/foreign-trade/www/ 157

158

U. S. Census Bureau Foreign Trade Division Profile of U. S. Exporting Companies 2004 -2005 Jeff Mc. Hugh May 16, 2007 U. S. Census Bureau

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Released January 10, 2007 Available on FTD Website back to 1996 http: //www. census. gov/foreign-trade/aip/index. html#profile 160

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 $ Partially ponsored by the International Trade Administration (ITA) Produced by the Special Projects Branch Produced by linking export records to the Census Business Register, which contains employment, company types, & company locations 161
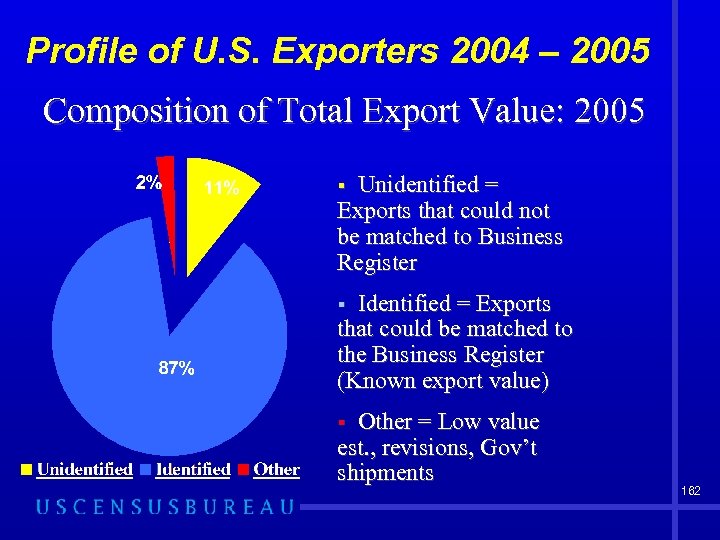
Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Composition of Total Export Value: 2005 Unidentified = Exports that could not be matched to Business Register § Identified = Exports that could be matched to the Business Register (Known export value) § Other = Low value est. , revisions, Gov’t shipments § 162

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 The Profile can answer questions such as: Õ Value that can be attributed to large manufacturers in 2005 Õ Canada’s known export value that can be attributed to companies with 1 to 19 employees Õ Number of companies that exported from Maryland in 2005 and how much known value was exported 163

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Profile Provides Data Users: Õ Exporting community’s employment sizes, types of companies, & major foreign markets Õ Top 25 U. S. export countries and multiple country groupings Õ Export value and number of exporters for each state (OM State) Õ Number of employees of identified exporting companies 164

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 The profile report provides information on 2 main characteristics: ÕCompany type – NAICS based (North American Industry Classification System) ÕCompany size - # of employees Small (0 -99 employees) Medium (100 -499 employees) Large (500 or more employees) 165
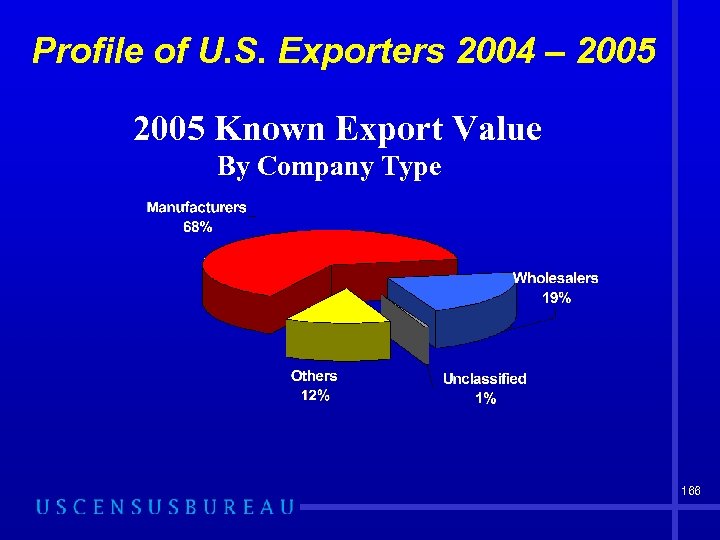
Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Known Export Value By Company Type 166
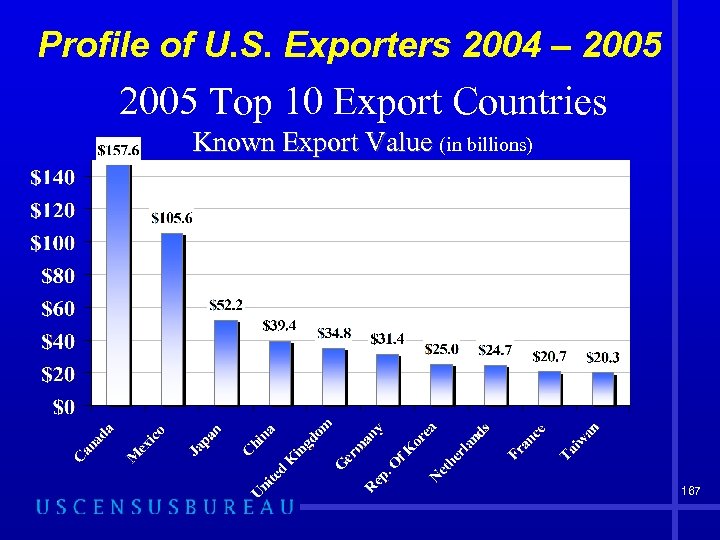
Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Top 10 Export Countries Known Export Value (in billions) 167
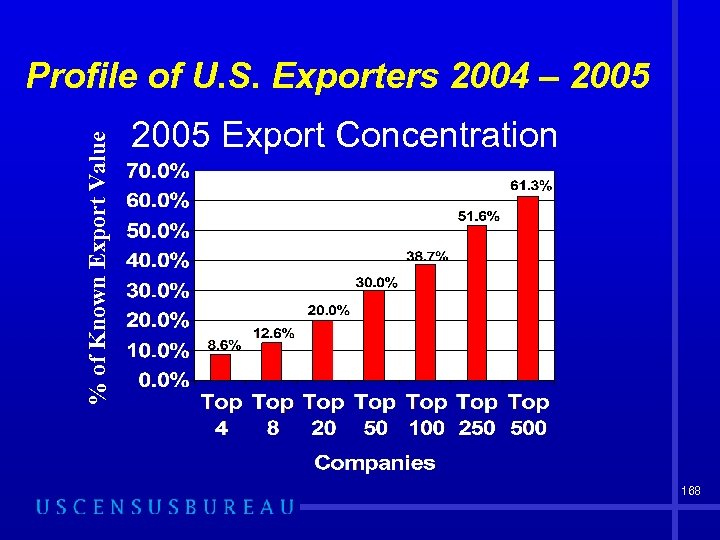
% of Known Export Value Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Export Concentration 168
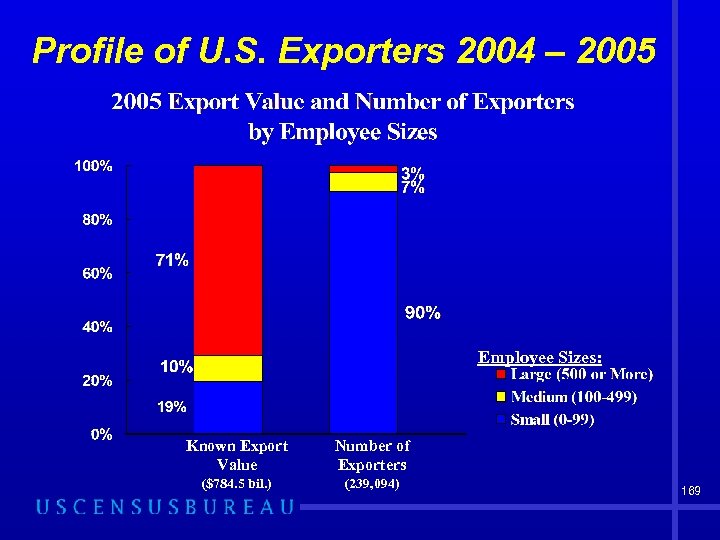
Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Employee Sizes: Known Export Value Number of Exporters ($784. 5 bil. ) (239, 094) 169

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 How is our data valuable to data users? Example: A data user wants to know how many Large sized companies (500+ Employees) export to OPEC countries and how much value is exported. 170

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 Special requests for data: If there is a special tabulation that is not included in the Profile, we may be able to provide it to you for a cost. Example: A data user wanted to know the number of U. S. companies that exported to Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) countries in a given year. Table 5 a of the Profile did not provide export data on these CAFTA countries, so we compiled the data and gave it to the data user for a cost. 171

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 The EDB Team Kristen Corwin Jeff Mc. Hugh Chris Farmer (301)763 -3629 172

Profile of U. S. Exporters 2004 – 2005 173

Data Dissemination Branch Understanding and Using Foreign Trade Data Seminar May 16, 2007 174

Press Releases • FT-900: U. S. International Trade In Goods and Services • FT-900 A: U. S. Imports for Consumption of Steel Products • Profile of U. S. Exporting Companies • Related Party Trade www. census. gov/trade 175

Data Reports • Softwood Lumber Imports from Canada • FT 920: U. S. Merchandise Trade: Selected Highlights www. census. gov/trade 176

Trade Statistics Commodity Advanced Technology Products, End-Use, NAICS, SITC Country Top Trading Partners Trade in Goods by Country Trade with Puerto Rico and U. S. Possessions Special Reports Textile Imports www. census. gov/trade 177

State Export Data • U. S. Exports of Goods by State Origin of Movement NAICS - Product Groupings • State Exports by Top 25 Commodities & Countries www. census. gov/trade 178

U. S. Imports and Exports of Merchandise Trade Data Monthly • Entire FTD Data Base • HS Detail - All Commodities • Value, Quantity, Shipping Weight • Country, District • Method of Transportation www. census. gov/trade 179

U. S. Imports and Exports of Merchandise Trade Data Monthly continued • Monthly and Year-to-Date Statistics • Concordance • Look-up Software Five Year History • Annual Revisions www. census. gov/trade 180

Other Data Products • Selected Commodity Subscription Service (1 to 10 Reports) • Data Banks • Port HS • Customized Reports www. census. gov/trade 181

USATrade Online • Exports and Imports • Harmonized System (HS) Classification • Country and District level • Monthly and Year-to-Date data 2002 - present • Annual data from 1992 – present http: //www. usatradeonlinegov/. 182

Port Data on USATrade Online • District, Port, and Country • Monthly, YTD, and Annual from 2003 – Present • 2 -, 4 -, and 6 -Digit HS • Imports and Exports http: //www. usatradeonlinegov/. 183

Port Data on USATrade Online • Total Value • Vessel Shipping Weight • Air Value • Air Shipping Weight • Containerized Vessel Value • Containerized Vessel Shipping Weight http: //www. usatradeonlinegov/. 184

USATrade Online Features • Search by word or code • Drill down by HS level • Print, Chart, Download reports • Create and save custom reports • Standard reports http: //www. usatradeonlinegov/. 185

USATrade Online Features • Rank • Highlight • Graph • Calculate • Sort • Suppress • Drag and Drop http: //www. usatradeonlinegov/. 186

Coming Soon to USATrade Online • NAICS – Imports • NAICS – Exports • State Exports by 2 -, 4 -, and 6 -Digit HS 2 -, 3 -, and 4 -Digit NAICS http: //www. usatradeonlinegov/. 187

FTD Website - Features • Search Index, Map, and Search • FTD Web News • FTD Links Release Dates, Announcements www. census. gov/trade 188

FTD Website - References • Schedule B Search Engine Browse, Search or Download Schedule B Book • Information Concordance Files Obsolete to New Codes Notices, Guides, Papers Classifications Codes Staff Directories www. census. gov/trade 189
Data Dissemination Branch Customized Reports (301) 763 - 2311 (301) 457 -4615 (Fax) General Inquiries (301) 763 -2227 (301) 457 -2647 (Fax) ftd. data. dissemination@census. gov www. census. gov/trade/ 190
0348d5b16ce2ab3099ea2d4be346913d.ppt