 TYPES OF RELATIONS
TYPES OF RELATIONS
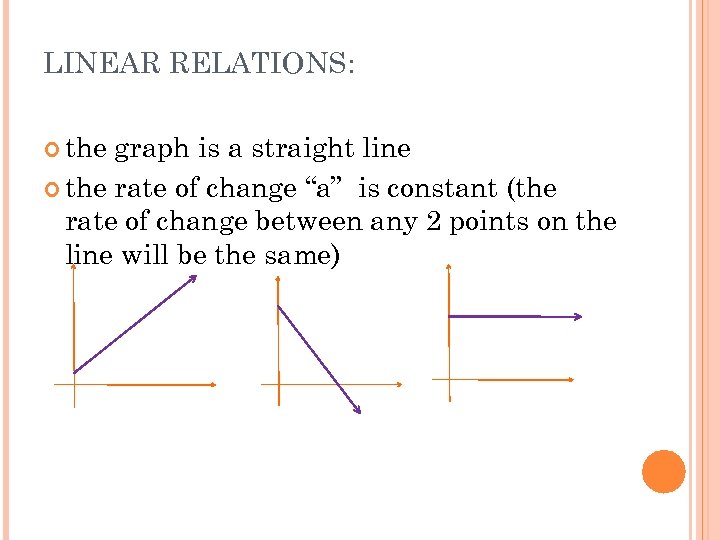 LINEAR RELATIONS: the graph is a straight line the rate of change “a” is constant (the rate of change between any 2 points on the line will be the same)
LINEAR RELATIONS: the graph is a straight line the rate of change “a” is constant (the rate of change between any 2 points on the line will be the same)
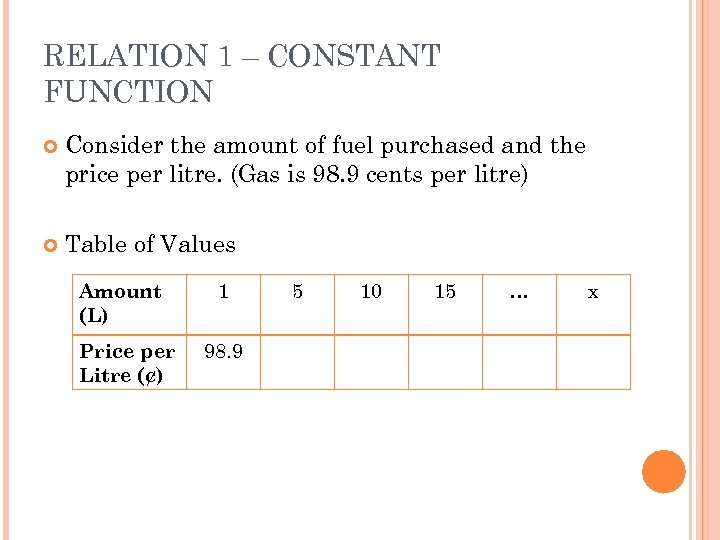 RELATION 1 – CONSTANT FUNCTION Consider the amount of fuel purchased and the price per litre. (Gas is 98. 9 cents per litre) Table of Values Amount (L) Price per Litre (¢) 1 98. 9 5 10 15 … x
RELATION 1 – CONSTANT FUNCTION Consider the amount of fuel purchased and the price per litre. (Gas is 98. 9 cents per litre) Table of Values Amount (L) Price per Litre (¢) 1 98. 9 5 10 15 … x
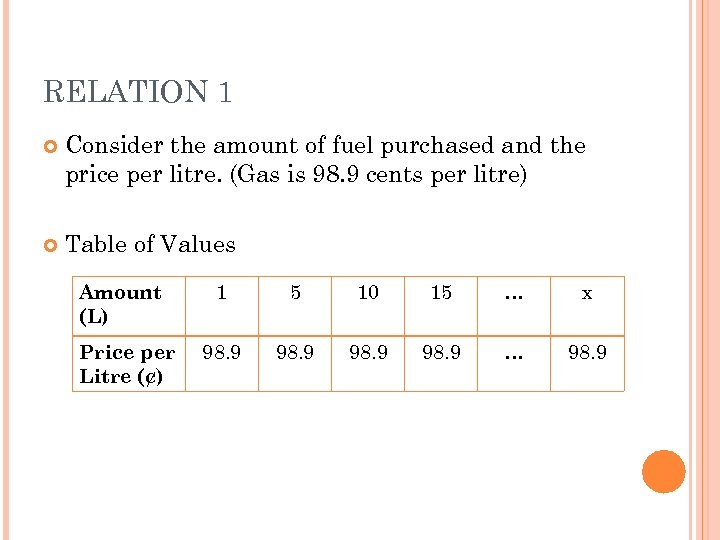 RELATION 1 Consider the amount of fuel purchased and the price per litre. (Gas is 98. 9 cents per litre) Table of Values Amount (L) Price per Litre (¢) 1 5 10 15 … x 98. 9 … 98. 9
RELATION 1 Consider the amount of fuel purchased and the price per litre. (Gas is 98. 9 cents per litre) Table of Values Amount (L) Price per Litre (¢) 1 5 10 15 … x 98. 9 … 98. 9
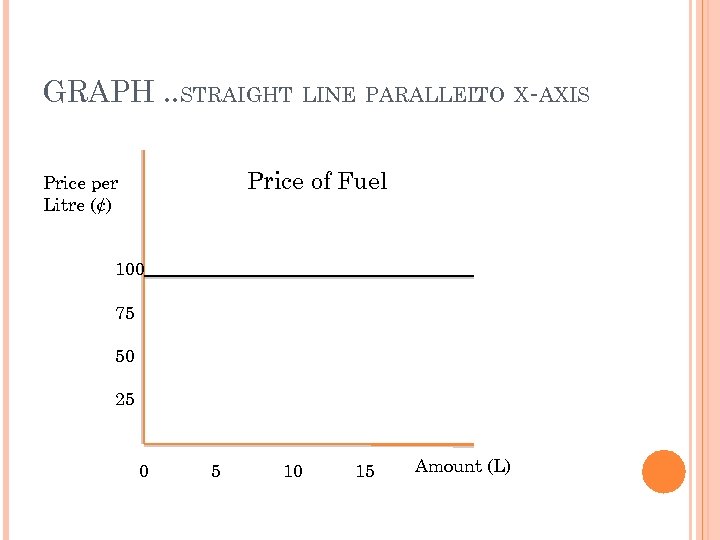 GRAPH. . STRAIGHT LINE PARALLELTO X-AXIS Price of Fuel Price per Litre (¢) 100 75 50 25 0 5 10 15 Amount (L)
GRAPH. . STRAIGHT LINE PARALLELTO X-AXIS Price of Fuel Price per Litre (¢) 100 75 50 25 0 5 10 15 Amount (L)
 RULE The rule is: cost per litre = 98. 9 ¢ The rule is y = 98. 9 ¢ Table of Values No matter what the x value is. . the y value always stays the SAME
RULE The rule is: cost per litre = 98. 9 ¢ The rule is y = 98. 9 ¢ Table of Values No matter what the x value is. . the y value always stays the SAME
 The cost per litre is constant The rate of change is zero (a = 0) We call this a ZERO VARIATION relation The rule is: y = b (constant value) y = 98. 9
The cost per litre is constant The rate of change is zero (a = 0) We call this a ZERO VARIATION relation The rule is: y = b (constant value) y = 98. 9
 DO. . WORKBOOK PAGE 107 -108 ACTIVITY 2 COST OF BUS RIDE DO. . A, B, C, D, E, F PAGE 116 #8 PAGE 143 #2 TEXTBOOK #1 PAGE 153 #4 BRING TEXTBOOK #2 FROM NOW ON
DO. . WORKBOOK PAGE 107 -108 ACTIVITY 2 COST OF BUS RIDE DO. . A, B, C, D, E, F PAGE 116 #8 PAGE 143 #2 TEXTBOOK #1 PAGE 153 #4 BRING TEXTBOOK #2 FROM NOW ON
 RELATION 2 – DIRECT VARIATION The cost of apples is $2. 50 per kg. Independent variable: number of kg you buy Dependent variable: cost of buying apples
RELATION 2 – DIRECT VARIATION The cost of apples is $2. 50 per kg. Independent variable: number of kg you buy Dependent variable: cost of buying apples
 RELATION 2 – DIRECT VARIATION The cost of apples is $2. 50 per kg. Independent variable: # of kg of apples Dependent variable: cost ($)
RELATION 2 – DIRECT VARIATION The cost of apples is $2. 50 per kg. Independent variable: # of kg of apples Dependent variable: cost ($)
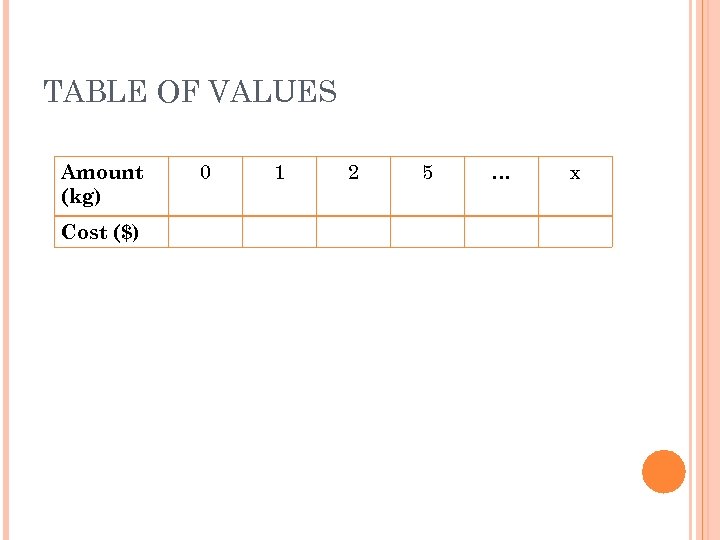 TABLE OF VALUES Amount (kg) Cost ($) 0 1 2 5 … x
TABLE OF VALUES Amount (kg) Cost ($) 0 1 2 5 … x
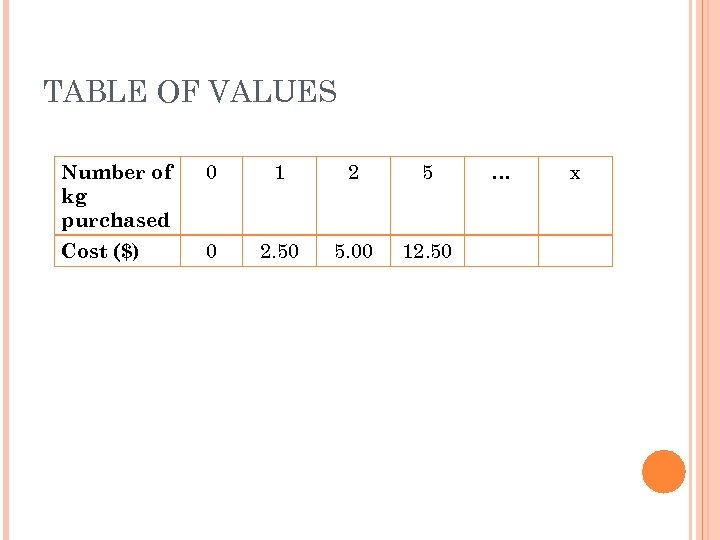 TABLE OF VALUES Number of kg purchased 0 1 2 5 Cost ($) 0 2. 50 5. 00 12. 50 … x
TABLE OF VALUES Number of kg purchased 0 1 2 5 Cost ($) 0 2. 50 5. 00 12. 50 … x
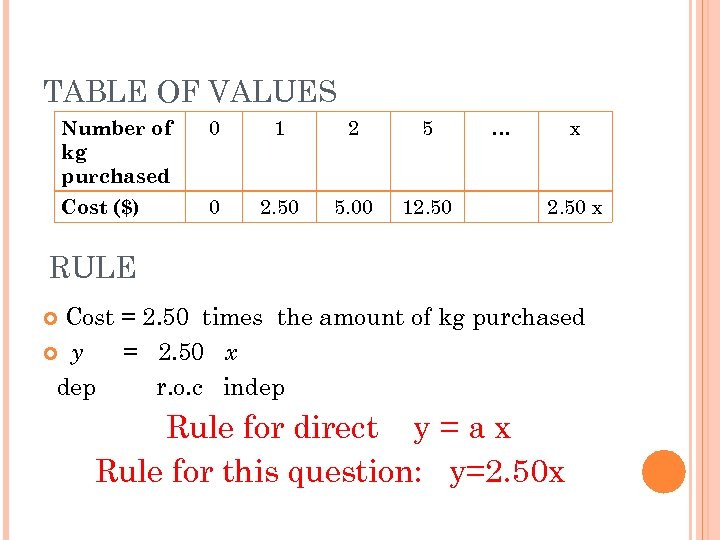 TABLE OF VALUES Number of kg purchased 0 1 2 5 Cost ($) 0 2. 50 5. 00 12. 50 … x 2. 50 x RULE Cost = 2. 50 times the amount of kg purchased y = 2. 50 x dep r. o. c indep Rule for direct y = a x Rule for this question: y=2. 50 x
TABLE OF VALUES Number of kg purchased 0 1 2 5 Cost ($) 0 2. 50 5. 00 12. 50 … x 2. 50 x RULE Cost = 2. 50 times the amount of kg purchased y = 2. 50 x dep r. o. c indep Rule for direct y = a x Rule for this question: y=2. 50 x
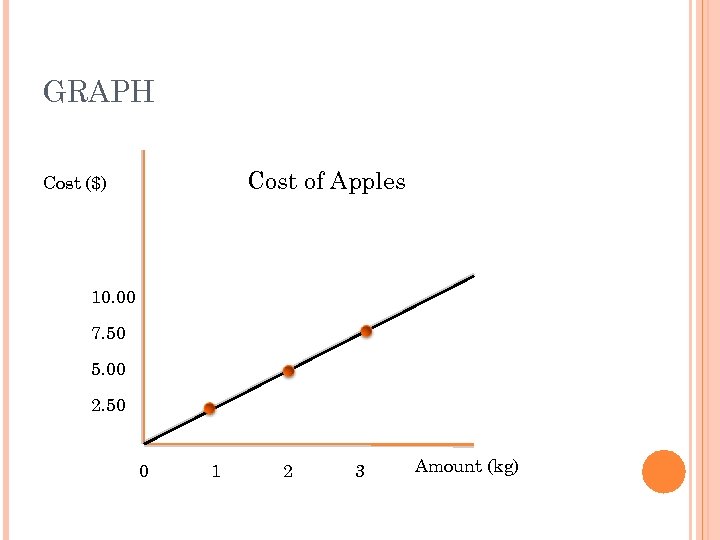 GRAPH Cost of Apples Cost ($) 10. 00 7. 50 5. 00 2. 50 0 1 2 3 Amount (kg)
GRAPH Cost of Apples Cost ($) 10. 00 7. 50 5. 00 2. 50 0 1 2 3 Amount (kg)
 DIRECT VARIATION There is no initial fee (start-up cost) Values are proportional (you can cross multiply and always get the same answer) The rule is y = ax (“a” is the rate of change) y is dep var, x is indep. var The graph is a straight line that passes through the origin
DIRECT VARIATION There is no initial fee (start-up cost) Values are proportional (you can cross multiply and always get the same answer) The rule is y = ax (“a” is the rate of change) y is dep var, x is indep. var The graph is a straight line that passes through the origin
 WORK ON ZERO AND DIRECT RELATIONS Workbook Page 116 #8, 9 Text #2 Page 101 #1 Page 102 #4 a-h, #5 Page 103 #6, 7 Page 104 #9 (find the rate of change first then write it in the rule y = ax
WORK ON ZERO AND DIRECT RELATIONS Workbook Page 116 #8, 9 Text #2 Page 101 #1 Page 102 #4 a-h, #5 Page 103 #6, 7 Page 104 #9 (find the rate of change first then write it in the rule y = ax
 QUIZ ON RATE OF CHANGE…TAKE OUT A PIECE OF PAPER. . PUT YOUR NAME ON IT… Calculate the rate of change…write coordinates, label, write the formula, solve for the r. o. c 1(2, 10) (6, 30) a =5 2 - (-2, 4) (5, -2) a= -6/7 3. - ( 1, 8) a= o 4 - (26, 12) (102, 50) a= 38/76 or 1/2 5 - (24, 4) a= -4/12 or -1/3 (8, 8) (12, 8)
QUIZ ON RATE OF CHANGE…TAKE OUT A PIECE OF PAPER. . PUT YOUR NAME ON IT… Calculate the rate of change…write coordinates, label, write the formula, solve for the r. o. c 1(2, 10) (6, 30) a =5 2 - (-2, 4) (5, -2) a= -6/7 3. - ( 1, 8) a= o 4 - (26, 12) (102, 50) a= 38/76 or 1/2 5 - (24, 4) a= -4/12 or -1/3 (8, 8) (12, 8)