0bc7ed48a8d353800d48f6730f94b94c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 176
 Types of Industry 1
Types of Industry 1
 Types of Industry You can divide the jobs and industries into 4 groups – n Primary n Secondary n Tertiary n Quaternary. 2
Types of Industry You can divide the jobs and industries into 4 groups – n Primary n Secondary n Tertiary n Quaternary. 2
 Quaternary Industries n Quaternary Industries - process ideas n e. g. computer programmers, accountants and university professors etc. 3
Quaternary Industries n Quaternary Industries - process ideas n e. g. computer programmers, accountants and university professors etc. 3
 Primary Industry n Primary industries – extract raw materials n e. g. iron, lumber, gold and the like 4
Primary Industry n Primary industries – extract raw materials n e. g. iron, lumber, gold and the like 4
 Secondary Industry n Secondary industry – uses materials from Primary Industry to create finished products n e. g. vehicles 5
Secondary Industry n Secondary industry – uses materials from Primary Industry to create finished products n e. g. vehicles 5
 Tertiary Industry Tertiary industries - services that support Primary and Secondary industries. n Tertiary and Quaternary industries employ 3 X more than Primary and Secondary combined. n 6
Tertiary Industry Tertiary industries - services that support Primary and Secondary industries. n Tertiary and Quaternary industries employ 3 X more than Primary and Secondary combined. n 6
 Basic Industries e. g. Miners receive their pay from sources beyond the boundaries of their local economy. n Their jobs are as the result of the customers who indirectly buy items that are produced from the metals/ores they extract. n 7
Basic Industries e. g. Miners receive their pay from sources beyond the boundaries of their local economy. n Their jobs are as the result of the customers who indirectly buy items that are produced from the metals/ores they extract. n 7
 Non-Basic Industry Non-Basic - does not bring new money into a local economy n $ is effectively recycled within a community n Basic Industries are crucial for growing and economy. n 8
Non-Basic Industry Non-Basic - does not bring new money into a local economy n $ is effectively recycled within a community n Basic Industries are crucial for growing and economy. n 8
 Question What Industry is important for the growth of an economy. a) Non-Basic b) Basic c) Primary c) Secondary 9
Question What Industry is important for the growth of an economy. a) Non-Basic b) Basic c) Primary c) Secondary 9
 Question Tertiary and Quaternary Industries employ ___ times more people than do Primary and Secondary Industries combined. a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 10
Question Tertiary and Quaternary Industries employ ___ times more people than do Primary and Secondary Industries combined. a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 10
 Question What industry is first in line? a) b) c) d) Quaternary Tertiary Secondary Primary 11
Question What industry is first in line? a) b) c) d) Quaternary Tertiary Secondary Primary 11
 Question Which industry recycles monies already in one’s local economy? a) b) c) d) Tertiary Non-basic Basic Primary 12
Question Which industry recycles monies already in one’s local economy? a) b) c) d) Tertiary Non-basic Basic Primary 12
 The World Community 13
The World Community 13
 Why the Increase in International Connections? More people are traveling to more places n International trade grows a great amount every year n Phoning and internet allow contact throughout the “Global Village” n 14
Why the Increase in International Connections? More people are traveling to more places n International trade grows a great amount every year n Phoning and internet allow contact throughout the “Global Village” n 14
 Grouping Countries n How do you group countries? n n n Similarities Comparing economic and social development Economic development is measured using Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita 15
Grouping Countries n How do you group countries? n n n Similarities Comparing economic and social development Economic development is measured using Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita 15
 Grouping Countries n Social development is measured by comparing factors like: n n n How long people live Health care they receive Education levels reached 16
Grouping Countries n Social development is measured by comparing factors like: n n n How long people live Health care they receive Education levels reached 16
 Three Levels of Development n Developed Countries n n Countries that have highest social and economic development Some characteristics of Developed Countries are having well developed: § § § Education Health care Banking Transportation Information technologies 17
Three Levels of Development n Developed Countries n n Countries that have highest social and economic development Some characteristics of Developed Countries are having well developed: § § § Education Health care Banking Transportation Information technologies 17
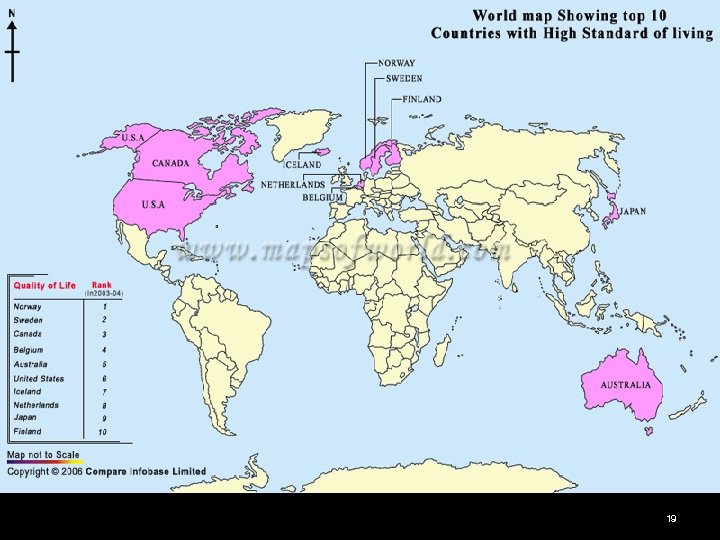
 Developed Countries n n People living in this type of country have the highest standards of living in the world The poorest people in these countries are well to do in comparison to average persons residing in developing countries 18
Developed Countries n n People living in this type of country have the highest standards of living in the world The poorest people in these countries are well to do in comparison to average persons residing in developing countries 18
 19
19
 Developed Countries Contain 20% of the World’s population n Use most of the World’s resources n Produce most of the World’s pollution n 20
Developed Countries Contain 20% of the World’s population n Use most of the World’s resources n Produce most of the World’s pollution n 20
 Developing Countries n Developing countries n n Have lowest levels of economic/social growth Are dominated by Primary industries and Agriculture Most citizens live their lives farming Most of the population does not have money to spend on telephones, banks, and schools 21
Developing Countries n Developing countries n n Have lowest levels of economic/social growth Are dominated by Primary industries and Agriculture Most citizens live their lives farming Most of the population does not have money to spend on telephones, banks, and schools 21
 Developing Countries n n n Citizens earn very little money Therefore they do not pay taxes Since no taxes are paid, governments in developing countries are unable to provide for: n n n Education Health Care Economic Development 22
Developing Countries n n n Citizens earn very little money Therefore they do not pay taxes Since no taxes are paid, governments in developing countries are unable to provide for: n n n Education Health Care Economic Development 22
 Newly Industrializing Countries n n n Countries that are becoming developed Undergoing enormous change Change in lifestyles and economy are occurring at a rapid speed 23
Newly Industrializing Countries n n n Countries that are becoming developed Undergoing enormous change Change in lifestyles and economy are occurring at a rapid speed 23
 Limits of Grouping Countries this way… n There are only 3 groups n n Countries can be very different from each other yet, still belong to the same group Wealth and resources are not necessarily distributed evenly or equitably 24
Limits of Grouping Countries this way… n There are only 3 groups n n Countries can be very different from each other yet, still belong to the same group Wealth and resources are not necessarily distributed evenly or equitably 24
 What determines the level of development? n Life expectancy n n Wealth n n How long people live GDP per capita is used to measure wealth Population Growth n How fast the population is growing 25
What determines the level of development? n Life expectancy n n Wealth n n How long people live GDP per capita is used to measure wealth Population Growth n How fast the population is growing 25
 What determines the level of development? § Education level § Determines literacy level of country n n Health care n Having effective health care is vital for development Food supply n How much food each country supplies its people 26
What determines the level of development? § Education level § Determines literacy level of country n n Health care n Having effective health care is vital for development Food supply n How much food each country supplies its people 26
 QUESTION What is meant by the term Global Village? a) “It takes a village to grow a child. ” b) Cities are becoming more diverse and have residents representing a wide variety of cultures. c) An organization that obtains and sells goods from third world countries in developed countries, to support artisans from developing countries. d) Communication by phone and internet resulting is more closely connected communities. 27
QUESTION What is meant by the term Global Village? a) “It takes a village to grow a child. ” b) Cities are becoming more diverse and have residents representing a wide variety of cultures. c) An organization that obtains and sells goods from third world countries in developed countries, to support artisans from developing countries. d) Communication by phone and internet resulting is more closely connected communities. 27
 QUESTION Which country is known to have the highest standard of living amongst its citizens? a) Brazil b) Norway c) Italy d) Spain 28
QUESTION Which country is known to have the highest standard of living amongst its citizens? a) Brazil b) Norway c) Italy d) Spain 28
 Question Which of the following produces most of the World’s pollution? a) Industrializing countries b) Developing countries c) Developed countries d) Third world countries 29
Question Which of the following produces most of the World’s pollution? a) Industrializing countries b) Developing countries c) Developed countries d) Third world countries 29
 Question How do we typically and frequently group countries? a) By differences and social development b) By differences and economic development c) By similarities and social and ecological development d) By similarities and social and economic development 30
Question How do we typically and frequently group countries? a) By differences and social development b) By differences and economic development c) By similarities and social and ecological development d) By similarities and social and economic development 30
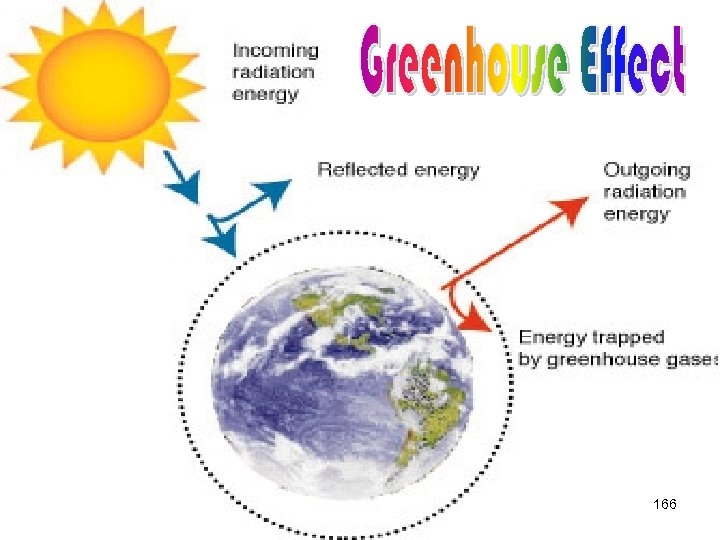
 Global Warming Living in the Greenhouse 31
Global Warming Living in the Greenhouse 31
 Global Warming an increase of the earth's temperature by a few degrees 32
Global Warming an increase of the earth's temperature by a few degrees 32
 What is happening? Gases trap more heat in the atmosphere than needed n Global temperatures are rising n 33
What is happening? Gases trap more heat in the atmosphere than needed n Global temperatures are rising n 33
 The Green House Effect 34
The Green House Effect 34
 Main Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide n Methane n Halocarbons n Water Vapour n 35
Main Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide n Methane n Halocarbons n Water Vapour n 35
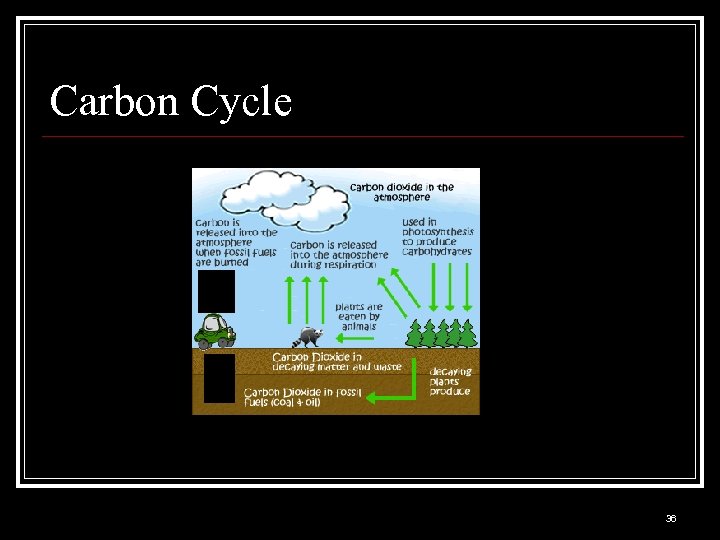 Carbon Cycle 36
Carbon Cycle 36
 Carbon Cycle n More carbon is being released n More people n n 1. 6 Billion 1888 6 Billion today Lifestyle requires more fossil fuels, clearing more forests Carbon locked away beneath Earth’s surface is now being added to atmosphere through fossil fuels 37
Carbon Cycle n More carbon is being released n More people n n 1. 6 Billion 1888 6 Billion today Lifestyle requires more fossil fuels, clearing more forests Carbon locked away beneath Earth’s surface is now being added to atmosphere through fossil fuels 37
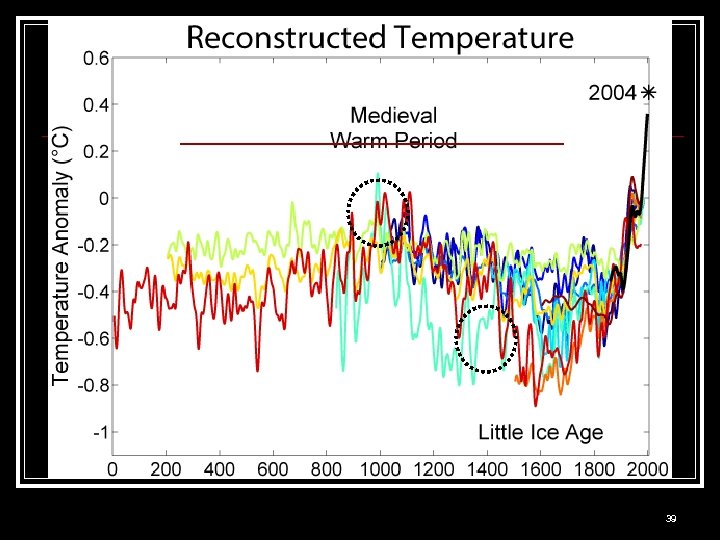
 Hoax Theory n The earth has gone through warming and cooling periods n n The Medieval Warming Period Global Warming is nothing to worry about 38
Hoax Theory n The earth has gone through warming and cooling periods n n The Medieval Warming Period Global Warming is nothing to worry about 38
 39
39
 Hoax Theory n During the Medieval warming period there were NOT… n n n Cars Factories 6 B people 40
Hoax Theory n During the Medieval warming period there were NOT… n n n Cars Factories 6 B people 40
 How will this effect us? Global temperatures are rising n Summer 2003 European Heat Wave n n n 35 000 people died Become more frequent 41
How will this effect us? Global temperatures are rising n Summer 2003 European Heat Wave n n n 35 000 people died Become more frequent 41
 How will this effect us? n Imbalance of precipitation n Alberta and Saskatchewan would suffer from this n Already driest area of Southern Canada 42
How will this effect us? n Imbalance of precipitation n Alberta and Saskatchewan would suffer from this n Already driest area of Southern Canada 42
 How will this effect us? n Increase of sea level by 1 m n n n Caused by melting glaciers and polar ice 80% of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific would be flooded Bangladesh would suffer devastating floods n n Population of 120 million 4 times that of Canada 43
How will this effect us? n Increase of sea level by 1 m n n n Caused by melting glaciers and polar ice 80% of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific would be flooded Bangladesh would suffer devastating floods n n Population of 120 million 4 times that of Canada 43
 How will this effect us? n The amount of “weather refugees” is increasing n There are now more of these refugees than political/war refugees n n n 25 million weather 23 million political/war Canada would be under a lot of pressure to accept these people 44
How will this effect us? n The amount of “weather refugees” is increasing n There are now more of these refugees than political/war refugees n n n 25 million weather 23 million political/war Canada would be under a lot of pressure to accept these people 44
 How will this effect us? Wealthy countries must provide at least $86 billion US to the world's poor by 2015 n help them cope with n n n floods droughts disease other negative effects from global warming 45
How will this effect us? Wealthy countries must provide at least $86 billion US to the world's poor by 2015 n help them cope with n n n floods droughts disease other negative effects from global warming 45
 What can/should we do? n We MUST reduce the amount of emissions n n n Carpool Walk Bike Plant a tree Use energy efficient devices 46
What can/should we do? n We MUST reduce the amount of emissions n n n Carpool Walk Bike Plant a tree Use energy efficient devices 46
 What can/should we do? n Use alternate fuel sources n n Electric Wind Solar Geothermal 47
What can/should we do? n Use alternate fuel sources n n Electric Wind Solar Geothermal 47
 The Tindo 48
The Tindo 48
 The Tindo n World’s first solar powered electric bus n Adelaide, Australia Free admission n 200 km range between charges n Charged with solar generated electricity n 49
The Tindo n World’s first solar powered electric bus n Adelaide, Australia Free admission n 200 km range between charges n Charged with solar generated electricity n 49
 Groups 1. In between n n 2. 3. Do nothing until there is clear proof Global warming is clear n 4. Willing to accept the problem Not willing to take the steps to solve it Take drastic action Gradually switch to cleaner energy and environmentally friendly lifestyles 50
Groups 1. In between n n 2. 3. Do nothing until there is clear proof Global warming is clear n 4. Willing to accept the problem Not willing to take the steps to solve it Take drastic action Gradually switch to cleaner energy and environmentally friendly lifestyles 50
 Question What percentage of the Marshall Islands would be flooded if the sea level rose 1 m? A. B. C. D. . 8% 24% 80% 95% 51
Question What percentage of the Marshall Islands would be flooded if the sea level rose 1 m? A. B. C. D. . 8% 24% 80% 95% 51
 Question Which of the following energy sources is the most environmentally friendly? A. B. C. D. Nuclear Geothermal Natural Gas Coal 52
Question Which of the following energy sources is the most environmentally friendly? A. B. C. D. Nuclear Geothermal Natural Gas Coal 52
 Question Which of the following would be the most environmentally friendly method of transportation? a. b. c. d. Carpool Taxi (alone) Bio-Diesel Vehicle Air 53
Question Which of the following would be the most environmentally friendly method of transportation? a. b. c. d. Carpool Taxi (alone) Bio-Diesel Vehicle Air 53
 Question What is the “Greenhouse Effect? ” A. B. C. D. Carbon dioxide trapped deep beneath the earth’s surface The thinning of our atmosphere Gases trap heat from the sun in our atmosphere Toxins from plastic factories damage our Ozone Layer that prevents solar radiation from escaping. 54
Question What is the “Greenhouse Effect? ” A. B. C. D. Carbon dioxide trapped deep beneath the earth’s surface The thinning of our atmosphere Gases trap heat from the sun in our atmosphere Toxins from plastic factories damage our Ozone Layer that prevents solar radiation from escaping. 54
 Water Resources 55
Water Resources 55
 Types of Fresh Water o There are four types of fresh water n n Surface water Sub-surface water Desalination Frozen water 56
Types of Fresh Water o There are four types of fresh water n n Surface water Sub-surface water Desalination Frozen water 56
 Surface Water o Surface water is water in lakes, rivers or wetlands. n o It is naturally replenished by rainfall, and lost to oceans and evaporation It is estimated that Canada has the largest amount of fresh water in the World 57
Surface Water o Surface water is water in lakes, rivers or wetlands. n o It is naturally replenished by rainfall, and lost to oceans and evaporation It is estimated that Canada has the largest amount of fresh water in the World 57
 Sub-surface water o o This water is located in the pore space of soil and rocks It shares many of the same characteristics of surface water, the main difference being its slow rate of turnover 58
Sub-surface water o o This water is located in the pore space of soil and rocks It shares many of the same characteristics of surface water, the main difference being its slow rate of turnover 58
 Desalination o o This is a process where saline water is converted to fresh water This is a expensive resource compared to others, and only satisfies a very small percentage of humans 59
Desalination o o This is a process where saline water is converted to fresh water This is a expensive resource compared to others, and only satisfies a very small percentage of humans 59
 Frozen water o o There have been a few plans made to turn ice burgs into a water source But so far it has only been used for novelty reasons, even though glacier runoff is considered to be fresh water 60
Frozen water o o There have been a few plans made to turn ice burgs into a water source But so far it has only been used for novelty reasons, even though glacier runoff is considered to be fresh water 60
 Uses of Water o o Canadians consume large quantities of water users Many of our personal, social and economic activities relate to water 61
Uses of Water o o Canadians consume large quantities of water users Many of our personal, social and economic activities relate to water 61
 Water Diversions o o o When there are water shortages - we often divert water from one drainage basin to another Can only be done over short distances Water is used to produce hydroelectricity 62
Water Diversions o o o When there are water shortages - we often divert water from one drainage basin to another Can only be done over short distances Water is used to produce hydroelectricity 62
 Wetlands o o o Wetlands are an important source of groundwater and can act as storage areas for flood water However they are starting to disappear Over 70% of S. Ontario’s wetlands have dried up 63
Wetlands o o o Wetlands are an important source of groundwater and can act as storage areas for flood water However they are starting to disappear Over 70% of S. Ontario’s wetlands have dried up 63
 Future Needs o Today Canadians have plenty water, but the demand is likely to grow as our population increases and our industries expand 64
Future Needs o Today Canadians have plenty water, but the demand is likely to grow as our population increases and our industries expand 64
 What kind of water is found in rivers, lakes and wetlands? a) b) c) d) Fresh water Saline water Sub-surface water Frozen water 65
What kind of water is found in rivers, lakes and wetlands? a) b) c) d) Fresh water Saline water Sub-surface water Frozen water 65
 Water Diversions ______ a) b) c) d) Are great for the eco-system Provide animals with a place to live Can be used to create hydro electricity b and c 66
Water Diversions ______ a) b) c) d) Are great for the eco-system Provide animals with a place to live Can be used to create hydro electricity b and c 66
 What percentage of Southern Ontario’s wetlands have dried up? a) b) c) d) 5% 30% 50% 70% 67
What percentage of Southern Ontario’s wetlands have dried up? a) b) c) d) 5% 30% 50% 70% 67
 Why is the demand for fresh water likely to grow in the future? a) b) c) d) Because of higher population It won’t Because of growth in industry a and c 68
Why is the demand for fresh water likely to grow in the future? a) b) c) d) Because of higher population It won’t Because of growth in industry a and c 68
 Canada’s Foreign Trade 69
Canada’s Foreign Trade 69
 Key Terms… n n n Imports Exports Trade surplus Net imports Net exports n n n Trade deficit Tariff Import substitution Protectionism Free trade 70
Key Terms… n n n Imports Exports Trade surplus Net imports Net exports n n n Trade deficit Tariff Import substitution Protectionism Free trade 70
 Exports vs. Imports n More exports than imports the difference is called trade surplus n More imports than exports it’s called trade deficit 71
Exports vs. Imports n More exports than imports the difference is called trade surplus n More imports than exports it’s called trade deficit 71
 Why Must Canada Export? The three main reasons are: 1. To pay for things that we import 2. To keep our economy healthy 3. To lower prices of Canadian-made goods for Canadians 72
Why Must Canada Export? The three main reasons are: 1. To pay for things that we import 2. To keep our economy healthy 3. To lower prices of Canadian-made goods for Canadians 72
 How do we benefit? n Canada benefits from exporting goods by simply selling them to other countries. n For a country to make money from trading they must export more goods than the import. 73
How do we benefit? n Canada benefits from exporting goods by simply selling them to other countries. n For a country to make money from trading they must export more goods than the import. 73
 You Should Know… A tariff is a tax charged on products coming into Canada to protect our industries. n It is applied to enforce protectionism. n 74
You Should Know… A tariff is a tax charged on products coming into Canada to protect our industries. n It is applied to enforce protectionism. n 74
 In Real Life Tariff and Protectionism… When you go to the States to shop, you will undoubtedly spend some of your money there. If you spend over $200, you will have to pay duty on your purchases at the border, and that’s a ‘royal pain’ in the butt. 75
In Real Life Tariff and Protectionism… When you go to the States to shop, you will undoubtedly spend some of your money there. If you spend over $200, you will have to pay duty on your purchases at the border, and that’s a ‘royal pain’ in the butt. 75
 Freedom! n Free trade is pretty much the type of trade we all think we want… n n Trade with no strings attached No hidden fees No duty at the border and of course no tariff barriers. 76
Freedom! n Free trade is pretty much the type of trade we all think we want… n n Trade with no strings attached No hidden fees No duty at the border and of course no tariff barriers. 76
 Another little tidbit… Import substitution is the process of replacing foreign goods with Canadian goods to support Canadian business. 77
Another little tidbit… Import substitution is the process of replacing foreign goods with Canadian goods to support Canadian business. 77
 IMPORT SUBSTITUTION n WHEN YOU CHOOSE TO USE A CANADIAN GROWN OR MADE PRODUCT YOU ARE SAVING CANADA FROM IMPORTING THAT PARTICULAR GOOD. THIS IS CALLED IMPORT SUBSTITUTION. 78
IMPORT SUBSTITUTION n WHEN YOU CHOOSE TO USE A CANADIAN GROWN OR MADE PRODUCT YOU ARE SAVING CANADA FROM IMPORTING THAT PARTICULAR GOOD. THIS IS CALLED IMPORT SUBSTITUTION. 78
 Canadian Import Substitution Canadian cars are quite different from European cars. They are generally less fuel efficient and not as economical. 79
Canadian Import Substitution Canadian cars are quite different from European cars. They are generally less fuel efficient and not as economical. 79
 However, people still feel compelled to purchase Canadian built cars to support our country’s vehicle production and its workers. 80
However, people still feel compelled to purchase Canadian built cars to support our country’s vehicle production and its workers. 80
 Statistics… n Every 1 in 5 jobs in Canada is tied to exports n Canada’s largest trading partner is the Unites States 81
Statistics… n Every 1 in 5 jobs in Canada is tied to exports n Canada’s largest trading partner is the Unites States 81
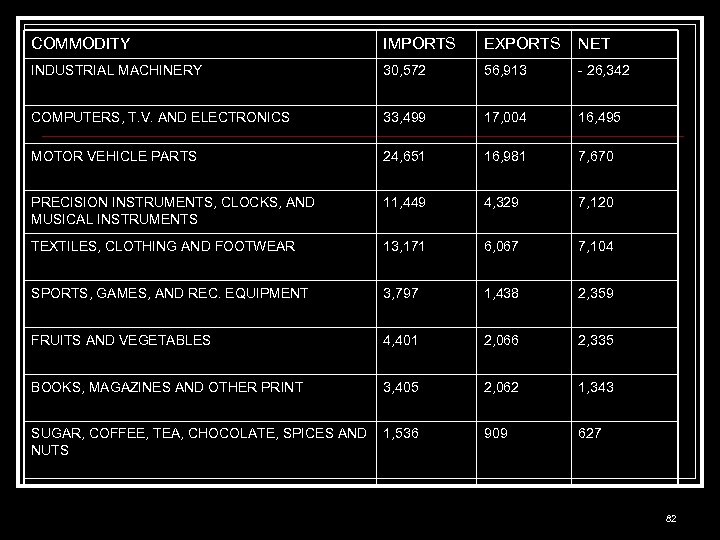 COMMODITY IMPORTS EXPORTS NET INDUSTRIAL MACHINERY 30, 572 56, 913 - 26, 342 COMPUTERS, T. V. AND ELECTRONICS 33, 499 17, 004 16, 495 MOTOR VEHICLE PARTS 24, 651 16, 981 7, 670 PRECISION INSTRUMENTS, CLOCKS, AND MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS 11, 449 4, 329 7, 120 TEXTILES, CLOTHING AND FOOTWEAR 13, 171 6, 067 7, 104 SPORTS, GAMES, AND REC. EQUIPMENT 3, 797 1, 438 2, 359 FRUITS AND VEGETABLES 4, 401 2, 066 2, 335 BOOKS, MAGAZINES AND OTHER PRINT 3, 405 2, 062 1, 343 SUGAR, COFFEE, TEA, CHOCOLATE, SPICES AND NUTS 1, 536 909 627 82
COMMODITY IMPORTS EXPORTS NET INDUSTRIAL MACHINERY 30, 572 56, 913 - 26, 342 COMPUTERS, T. V. AND ELECTRONICS 33, 499 17, 004 16, 495 MOTOR VEHICLE PARTS 24, 651 16, 981 7, 670 PRECISION INSTRUMENTS, CLOCKS, AND MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS 11, 449 4, 329 7, 120 TEXTILES, CLOTHING AND FOOTWEAR 13, 171 6, 067 7, 104 SPORTS, GAMES, AND REC. EQUIPMENT 3, 797 1, 438 2, 359 FRUITS AND VEGETABLES 4, 401 2, 066 2, 335 BOOKS, MAGAZINES AND OTHER PRINT 3, 405 2, 062 1, 343 SUGAR, COFFEE, TEA, CHOCOLATE, SPICES AND NUTS 1, 536 909 627 82
 NAFTA A movement that started in 1988 to have free trade in North American Free Trade Agreement 83
NAFTA A movement that started in 1988 to have free trade in North American Free Trade Agreement 83
 GATT An agreement including major trade countries that encourages Trade world wide. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade 84
GATT An agreement including major trade countries that encourages Trade world wide. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade 84
 Which of the following is an example of trade deficit? a) Canada gives USA 50 cows and does not receive any. b) China and Canada exchange 1, 000 lbs of grain and rice. c) Canada gives 6, 000 meters of material away and receives 5, 000 meters of material from another country d) Canada gives Russia 1, 000 cars and receives 2, 000 cars from Germany. 85
Which of the following is an example of trade deficit? a) Canada gives USA 50 cows and does not receive any. b) China and Canada exchange 1, 000 lbs of grain and rice. c) Canada gives 6, 000 meters of material away and receives 5, 000 meters of material from another country d) Canada gives Russia 1, 000 cars and receives 2, 000 cars from Germany. 85
 a) Import Substitution is when… b) c) d) Goods are imported and resold within another country When you purchase goods produced in your own country. Goods that are traded from one country to another. You are building a project and you use a different material than suggested. 86
a) Import Substitution is when… b) c) d) Goods are imported and resold within another country When you purchase goods produced in your own country. Goods that are traded from one country to another. You are building a project and you use a different material than suggested. 86
 87
87
![Key Terms n Ecological Footprint [ E. F. ] n Carrying Capacity n Sustainability Key Terms n Ecological Footprint [ E. F. ] n Carrying Capacity n Sustainability](https://present5.com/presentation/0bc7ed48a8d353800d48f6730f94b94c/image-88.jpg) Key Terms n Ecological Footprint [ E. F. ] n Carrying Capacity n Sustainability n Productive Land n Degraded Land n Energy land 88
Key Terms n Ecological Footprint [ E. F. ] n Carrying Capacity n Sustainability n Productive Land n Degraded Land n Energy land 88
 What is an ecological footprint? n An ecological footprint is the amount of space that is required to support an individual’s activities. 89
What is an ecological footprint? n An ecological footprint is the amount of space that is required to support an individual’s activities. 89
 What is an ecological footprint? n An ecological footprint is a measurement of the demands that we place on our environment 90
What is an ecological footprint? n An ecological footprint is a measurement of the demands that we place on our environment 90
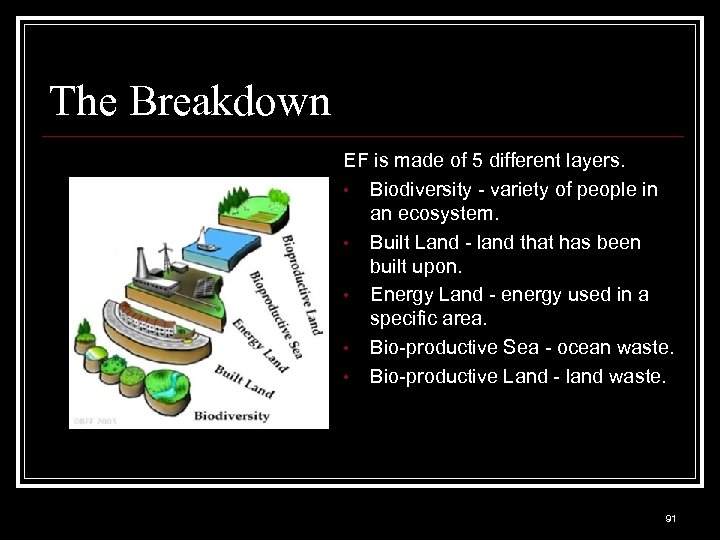 The Breakdown EF is made of 5 different layers. • Biodiversity - variety of people in an ecosystem. • Built Land - land that has been built upon. • Energy Land - energy used in a specific area. • Bio-productive Sea - ocean waste. • Bio-productive Land - land waste. 91
The Breakdown EF is made of 5 different layers. • Biodiversity - variety of people in an ecosystem. • Built Land - land that has been built upon. • Energy Land - energy used in a specific area. • Bio-productive Sea - ocean waste. • Bio-productive Land - land waste. 91
 Facts n The average global footprint is 21 global hectares person. n Unfortunately, the sustainable footprint is only approximately 15 hectares per capita. n Global Ecological Footprint Calculator 92
Facts n The average global footprint is 21 global hectares person. n Unfortunately, the sustainable footprint is only approximately 15 hectares per capita. n Global Ecological Footprint Calculator 92
 Reducing our Ecological Footprint n n Carpool Bike Walk, etc. Use energy saving lightbulbs, appliances, solar energy, etc. 93
Reducing our Ecological Footprint n n Carpool Bike Walk, etc. Use energy saving lightbulbs, appliances, solar energy, etc. 93
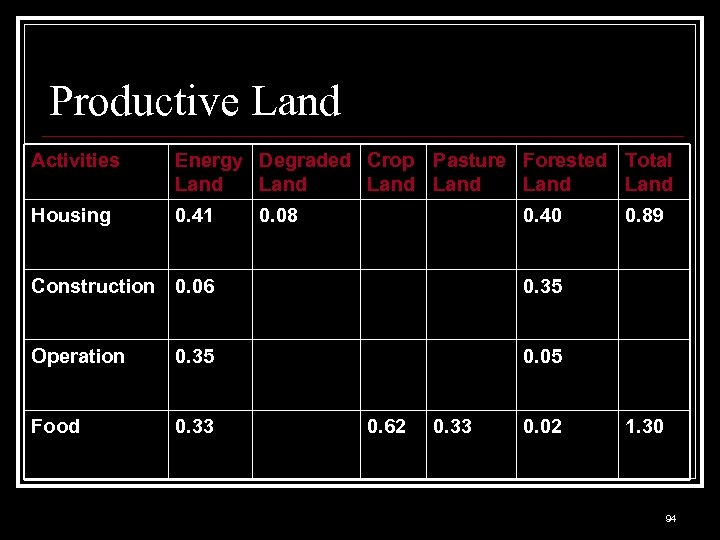 Productive Land Activities Energy Degraded Crop Pasture Forested Total Land Land Housing 0. 41 0. 08 0. 40 Construction 0. 06 0. 35 Operation 0. 35 0. 05 Food 0. 33 0. 89 0. 62 0. 33 0. 02 1. 30 94
Productive Land Activities Energy Degraded Crop Pasture Forested Total Land Land Housing 0. 41 0. 08 0. 40 Construction 0. 06 0. 35 Operation 0. 35 0. 05 Food 0. 33 0. 89 0. 62 0. 33 0. 02 1. 30 94
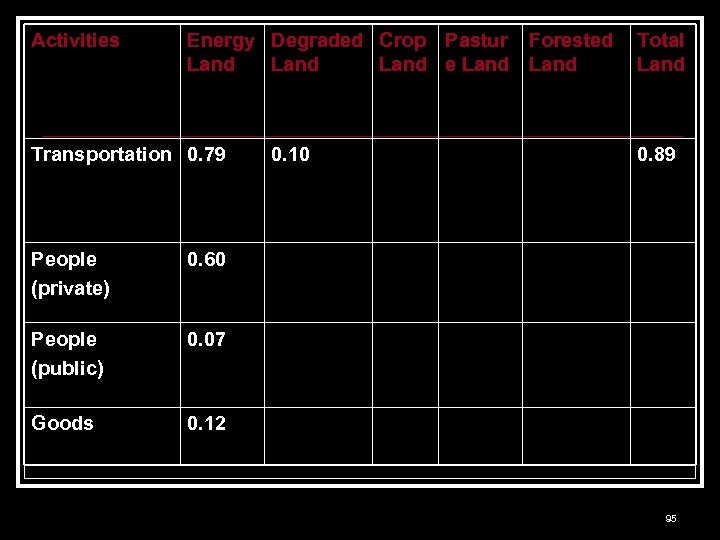 Activities Energy Degraded Crop Pastur Forested Land e Land Transportation 0. 79 People (private) 0. 07 Goods 0. 89 0. 60 People (public) 0. 10 Total Land 0. 12 95
Activities Energy Degraded Crop Pastur Forested Land e Land Transportation 0. 79 People (private) 0. 07 Goods 0. 89 0. 60 People (public) 0. 10 Total Land 0. 12 95
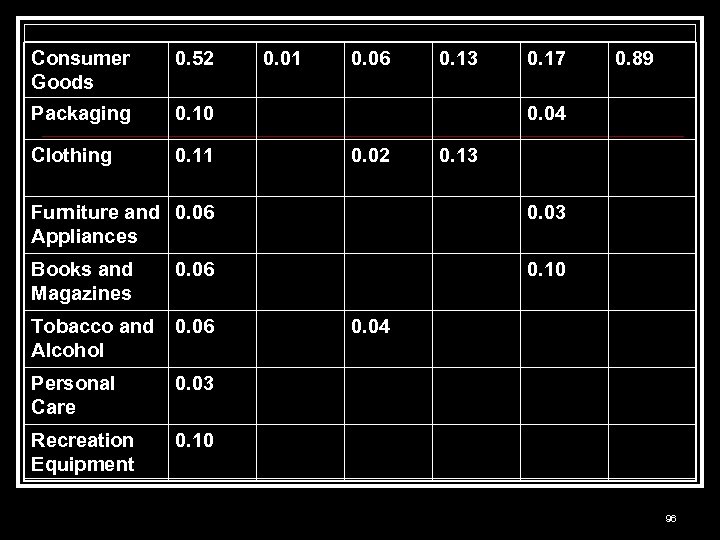 Consumer Goods 0. 52 Packaging 0. 10 Clothing 0. 11 0. 06 0. 13 0. 17 0. 89 0. 04 0. 02 0. 13 Furniture and 0. 06 Appliances 0. 03 Books and Magazines 0. 06 0. 10 Tobacco and Alcohol 0. 06 Personal Care 0. 03 Recreation Equipment 0. 10 0. 04 96
Consumer Goods 0. 52 Packaging 0. 10 Clothing 0. 11 0. 06 0. 13 0. 17 0. 89 0. 04 0. 02 0. 13 Furniture and 0. 06 Appliances 0. 03 Books and Magazines 0. 06 0. 10 Tobacco and Alcohol 0. 06 Personal Care 0. 03 Recreation Equipment 0. 10 0. 04 96
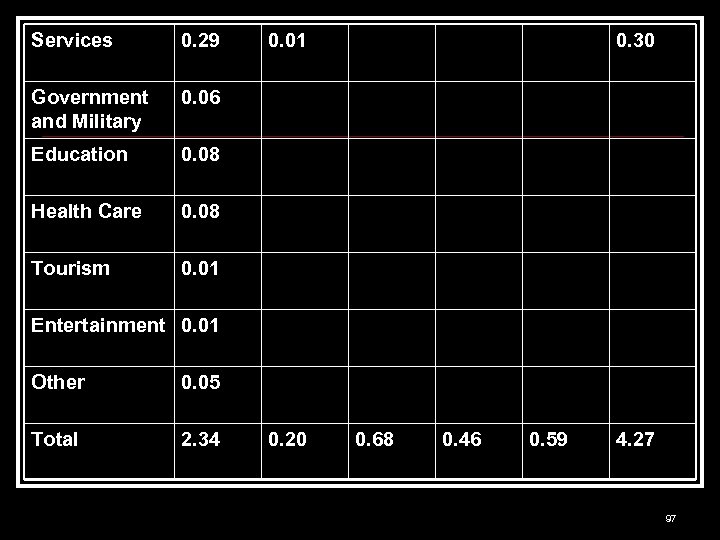 Services 0. 29 Government and Military 0. 06 Education 0. 08 Health Care 0. 08 Tourism 0. 01 0. 30 0. 01 Entertainment 0. 01 Other 0. 05 Total 2. 34 0. 20 0. 68 0. 46 0. 59 4. 27 97
Services 0. 29 Government and Military 0. 06 Education 0. 08 Health Care 0. 08 Tourism 0. 01 0. 30 0. 01 Entertainment 0. 01 Other 0. 05 Total 2. 34 0. 20 0. 68 0. 46 0. 59 4. 27 97
![QUESTION What is the average environmental footprint person? a] 12 hectares b] 15 hectares QUESTION What is the average environmental footprint person? a] 12 hectares b] 15 hectares](https://present5.com/presentation/0bc7ed48a8d353800d48f6730f94b94c/image-98.jpg) QUESTION What is the average environmental footprint person? a] 12 hectares b] 15 hectares c] 18 hectares d] 21 hectares 98
QUESTION What is the average environmental footprint person? a] 12 hectares b] 15 hectares c] 18 hectares d] 21 hectares 98
![QUESTION Ecological footprints measure… a] the average annual amount of Carbon Dioxide that we QUESTION Ecological footprints measure… a] the average annual amount of Carbon Dioxide that we](https://present5.com/presentation/0bc7ed48a8d353800d48f6730f94b94c/image-99.jpg) QUESTION Ecological footprints measure… a] the average annual amount of Carbon Dioxide that we emit into the atmosphere. b] the amount of greenhouse gases in the air c] the demand that we place on the environment d] your Ecological shoe size 99
QUESTION Ecological footprints measure… a] the average annual amount of Carbon Dioxide that we emit into the atmosphere. b] the amount of greenhouse gases in the air c] the demand that we place on the environment d] your Ecological shoe size 99
 100
100
![Key Terms n Ecological n Carrying Footprint [ E. F. ] n Productive Land Key Terms n Ecological n Carrying Footprint [ E. F. ] n Productive Land](https://present5.com/presentation/0bc7ed48a8d353800d48f6730f94b94c/image-101.jpg) Key Terms n Ecological n Carrying Footprint [ E. F. ] n Productive Land n Degraded Land n Energy Land Capacity n Fair Earthshare n Sustainability n Overshoot 101
Key Terms n Ecological n Carrying Footprint [ E. F. ] n Productive Land n Degraded Land n Energy Land Capacity n Fair Earthshare n Sustainability n Overshoot 101
 What is an ecological footprint? An ecological footprint is the amount of space that is required to support a person’s activities. 102
What is an ecological footprint? An ecological footprint is the amount of space that is required to support a person’s activities. 102
 What is an ecological footprint? The ecological footprint measures the demand that we place on our environment 103
What is an ecological footprint? The ecological footprint measures the demand that we place on our environment 103
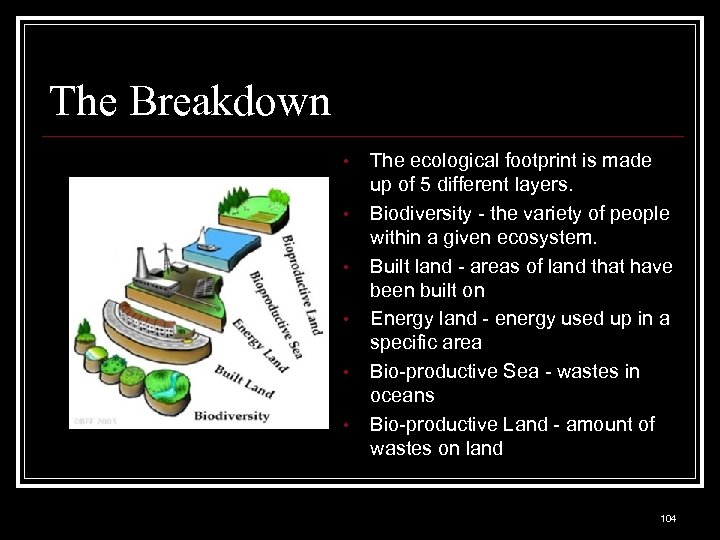 The Breakdown • • • The ecological footprint is made up of 5 different layers. Biodiversity - the variety of people within a given ecosystem. Built land - areas of land that have been built on Energy land - energy used up in a specific area Bio-productive Sea - wastes in oceans Bio-productive Land - amount of wastes on land 104
The Breakdown • • • The ecological footprint is made up of 5 different layers. Biodiversity - the variety of people within a given ecosystem. Built land - areas of land that have been built on Energy land - energy used up in a specific area Bio-productive Sea - wastes in oceans Bio-productive Land - amount of wastes on land 104
 Facts n n n The global average footprint is 21 global hectares person. The sustainable footprint is approx. 15 global hectares per capita. Global Ecological Footprint Calculator 105
Facts n n n The global average footprint is 21 global hectares person. The sustainable footprint is approx. 15 global hectares per capita. Global Ecological Footprint Calculator 105
 Reducing our Ecological Footprint n n Carpooling, biking, walking, etc. [exercise to save the environment] Use energy saving bulbs, appliances, solar energy, etc. 106
Reducing our Ecological Footprint n n Carpooling, biking, walking, etc. [exercise to save the environment] Use energy saving bulbs, appliances, solar energy, etc. 106
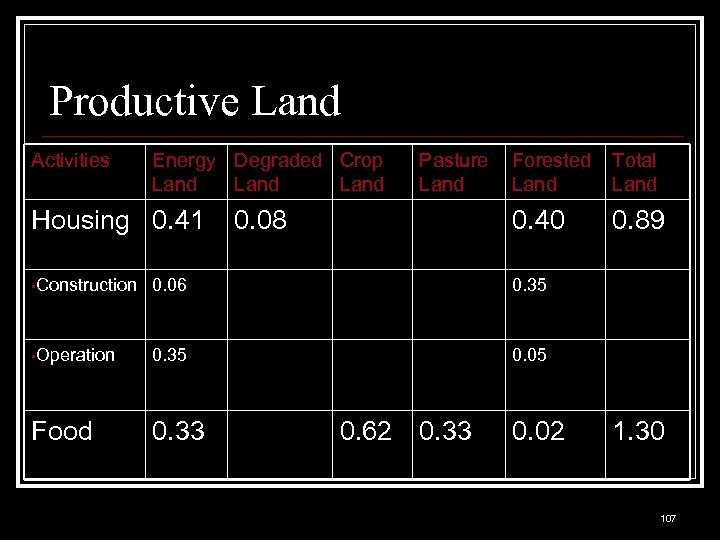 Productive Land Activities Energy Degraded Crop Land Housing 0. 41 Pasture Land Total Land 0. 40 0. 08 Forested Land 0. 89 • Construction 0. 06 0. 35 • Operation 0. 35 0. 05 Food 0. 33 0. 62 0. 33 0. 02 1. 30 107
Productive Land Activities Energy Degraded Crop Land Housing 0. 41 Pasture Land Total Land 0. 40 0. 08 Forested Land 0. 89 • Construction 0. 06 0. 35 • Operation 0. 35 0. 05 Food 0. 33 0. 62 0. 33 0. 02 1. 30 107
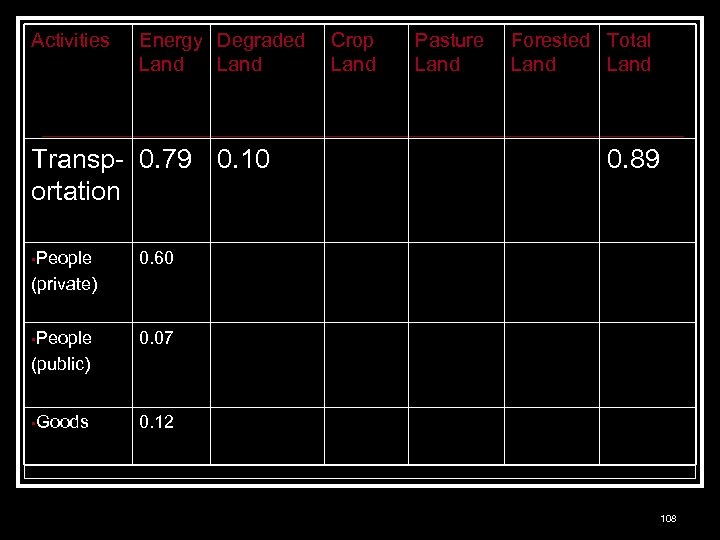 Activities Energy Degraded Land Transp- 0. 79 0. 10 ortation • People Crop Land Pasture Land Forested Total Land 0. 89 0. 60 (private) • People 0. 07 (public) • Goods 0. 12 108
Activities Energy Degraded Land Transp- 0. 79 0. 10 ortation • People Crop Land Pasture Land Forested Total Land 0. 89 0. 60 (private) • People 0. 07 (public) • Goods 0. 12 108
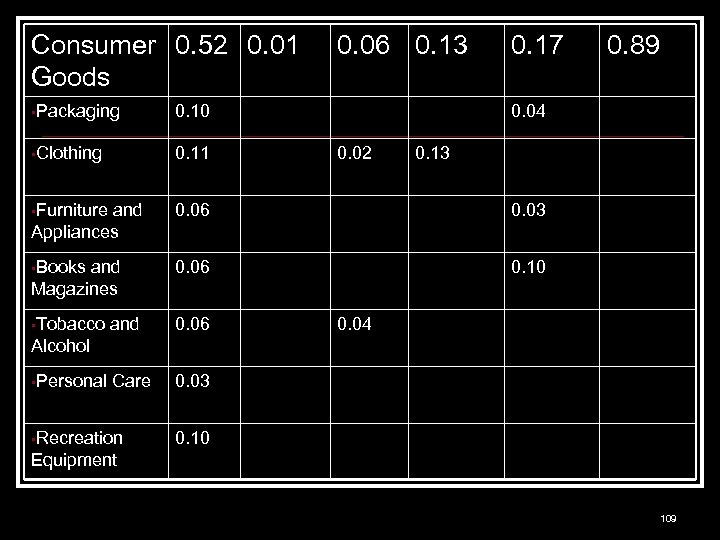 Consumer 0. 52 0. 01 Goods 0. 06 0. 13 0. 17 • Packaging 0. 10 • Clothing 0. 11 • Furniture and Appliances 0. 06 0. 03 • Books and Magazines 0. 06 0. 10 • Tobacco and 0. 06 Care 0. 89 0. 04 0. 03 0. 02 0. 13 0. 04 Alcohol • Personal • Recreation 0. 10 Equipment 109
Consumer 0. 52 0. 01 Goods 0. 06 0. 13 0. 17 • Packaging 0. 10 • Clothing 0. 11 • Furniture and Appliances 0. 06 0. 03 • Books and Magazines 0. 06 0. 10 • Tobacco and 0. 06 Care 0. 89 0. 04 0. 03 0. 02 0. 13 0. 04 Alcohol • Personal • Recreation 0. 10 Equipment 109
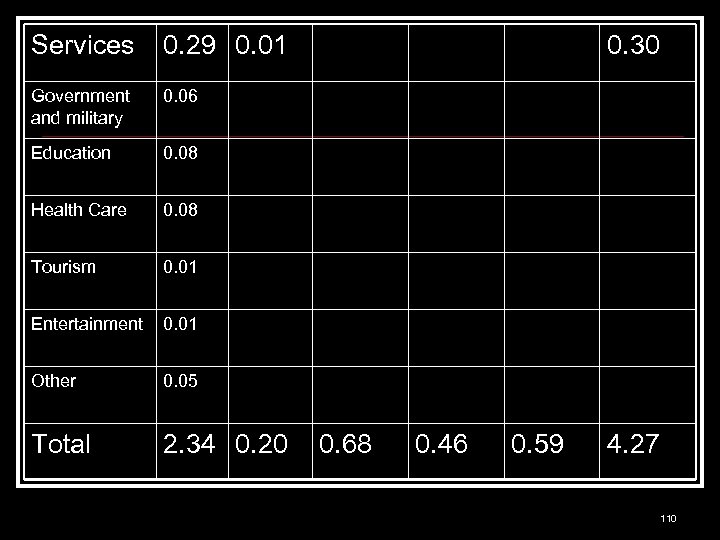 Services 0. 29 0. 01 Government and military 0. 06 Education 0. 08 Health Care 0. 08 Tourism 0. 01 Entertainment 0. 01 Other 0. 05 Total 2. 34 0. 20 0. 30 0. 68 0. 46 0. 59 4. 27 110
Services 0. 29 0. 01 Government and military 0. 06 Education 0. 08 Health Care 0. 08 Tourism 0. 01 Entertainment 0. 01 Other 0. 05 Total 2. 34 0. 20 0. 30 0. 68 0. 46 0. 59 4. 27 110
![QUESTION What is the average global footprint person? a]15 global hectares b]12 global hectares QUESTION What is the average global footprint person? a]15 global hectares b]12 global hectares](https://present5.com/presentation/0bc7ed48a8d353800d48f6730f94b94c/image-111.jpg) QUESTION What is the average global footprint person? a]15 global hectares b]12 global hectares c]18 global hectares d]21 global hectares 111
QUESTION What is the average global footprint person? a]15 global hectares b]12 global hectares c]18 global hectares d]21 global hectares 111
![QUESTION The Ecological Footprint measures… a] the circumference around MOTHER EARTH b] the amount QUESTION The Ecological Footprint measures… a] the circumference around MOTHER EARTH b] the amount](https://present5.com/presentation/0bc7ed48a8d353800d48f6730f94b94c/image-112.jpg) QUESTION The Ecological Footprint measures… a] the circumference around MOTHER EARTH b] the amount of greenhouse gases in the air c] the demand that we place on the environment d] your shoe size 112
QUESTION The Ecological Footprint measures… a] the circumference around MOTHER EARTH b] the amount of greenhouse gases in the air c] the demand that we place on the environment d] your shoe size 112
 113
113
 114
114
 What is the Global Village? 115
What is the Global Village? 115
 Ways to group countries… 116
Ways to group countries… 116
 Three Levels of Development 117
Three Levels of Development 117
 Three Levels of Development 118
Three Levels of Development 118
 Three Levels of Development 119
Three Levels of Development 119
 Limitations of Grouping Countries “Progress” & “Development” 3 Groups 120
Limitations of Grouping Countries “Progress” & “Development” 3 Groups 120
 How many different levels of country are there? A)3 B)4 C)5 121
How many different levels of country are there? A)3 B)4 C)5 121
 Most of the new development in the developed countries is focused on: A)Manufacturing B)Agriculture C)Farming 122
Most of the new development in the developed countries is focused on: A)Manufacturing B)Agriculture C)Farming 122
 Types of Industry 123
Types of Industry 123
 National Wealth & Branches of Industry l Wealth is generated from a combination of rich natural resources and labour of people. l There are 4 categories of Industry: l Primary l Secondary l Tertiary l Quaternary 124
National Wealth & Branches of Industry l Wealth is generated from a combination of rich natural resources and labour of people. l There are 4 categories of Industry: l Primary l Secondary l Tertiary l Quaternary 124
 Primary Industries § Extraction of raw materials § This area of the economy makes a huge contribution to Canada’s wealth. § These Industries are tied directly to natural resources, and are usually located close by. 125
Primary Industries § Extraction of raw materials § This area of the economy makes a huge contribution to Canada’s wealth. § These Industries are tied directly to natural resources, and are usually located close by. 125
 Secondary Industries n n n Secondary Industries are involved in the processing of primary industry products into finished goods. This may involve more than one step. The largest sector of secondary industry is manufacturing, which is responsible for making all the goods consumers need. 126
Secondary Industries n n n Secondary Industries are involved in the processing of primary industry products into finished goods. This may involve more than one step. The largest sector of secondary industry is manufacturing, which is responsible for making all the goods consumers need. 126
 Tertiary Industry • • • Provide services Without this sector, industry could not function This area employs most of the Canadians in industry • These are called service industries, which is where most of you work, if you work at all. 127
Tertiary Industry • • • Provide services Without this sector, industry could not function This area employs most of the Canadians in industry • These are called service industries, which is where most of you work, if you work at all. 127
 Basic & Non-Basic Industry o Basic jobs come from basic industries, and are paid indirectly by the consumer, like a logger in Thompson. o Non-Basic jobs are jobs that are paid directly by the consumer, and they are not needed to fully support the local economy, like a chef. 128
Basic & Non-Basic Industry o Basic jobs come from basic industries, and are paid indirectly by the consumer, like a logger in Thompson. o Non-Basic jobs are jobs that are paid directly by the consumer, and they are not needed to fully support the local economy, like a chef. 128
 Question Wealth is generated by: 1. 2. 3. 4. Labour Shrewd business practices Taxes Mechanical labour 129
Question Wealth is generated by: 1. 2. 3. 4. Labour Shrewd business practices Taxes Mechanical labour 129
 Which area of industry provides the most revenue for Canada? 1. 2. 3. 4. Primary Industry Secondary Industry Tertiary Industry Quaternary Industry 130
Which area of industry provides the most revenue for Canada? 1. 2. 3. 4. Primary Industry Secondary Industry Tertiary Industry Quaternary Industry 130
 A secondary industry does what? 1. 2. 3. 4. Provides jobs Processes products Helps the economy All of the above 131
A secondary industry does what? 1. 2. 3. 4. Provides jobs Processes products Helps the economy All of the above 131
 Which industry provides the greatest number of jobs? a. b. c. d. Manufacturing Tertiary Industry Mining a&c 132
Which industry provides the greatest number of jobs? a. b. c. d. Manufacturing Tertiary Industry Mining a&c 132
 Canada’s Foreign Trade 133
Canada’s Foreign Trade 133
 Why Do We Trade? o Countries depend on other countries for trading 134
Why Do We Trade? o Countries depend on other countries for trading 134
 Terms o Exporting more than importing = trade surplus o Importing more than exporting = trade deficit 135
Terms o Exporting more than importing = trade surplus o Importing more than exporting = trade deficit 135
 Who Do We Trade With? 136
Who Do We Trade With? 136
 The United States o America is our best friend whether we like it or not o By far most of our importing and exporting is done with the US 137
The United States o America is our best friend whether we like it or not o By far most of our importing and exporting is done with the US 137
 NAFTA The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) means North American countries can trade with each other without duty 138
NAFTA The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) means North American countries can trade with each other without duty 138
 The Softwood Lumber Dispute o Long ongoing problem 139
The Softwood Lumber Dispute o Long ongoing problem 139
 What is the Softwood Lumber Dispute? o Provincial government subsidizes o America charges a high tariff o Canada doesn’t get business from America 140
What is the Softwood Lumber Dispute? o Provincial government subsidizes o America charges a high tariff o Canada doesn’t get business from America 140
 What is happening now? o US lifted the tax in 2006 o Canada is still limited in their sales 141
What is happening now? o US lifted the tax in 2006 o Canada is still limited in their sales 141
 Our Imports o A lot of our imports are from tropical and 3 rd world countries 142
Our Imports o A lot of our imports are from tropical and 3 rd world countries 142
 143
143
 Our Exports 144
Our Exports 144
 o 20% of jobs in Canada are linked to exports 145
o 20% of jobs in Canada are linked to exports 145
 Should We Reduce Our Imports o Is it good we get our products for cheap in other countries? 146
Should We Reduce Our Imports o Is it good we get our products for cheap in other countries? 146
 What percent of Canadian Jobs are linked to Exports a. 30% b. 20% c. 50% d. 15% 147
What percent of Canadian Jobs are linked to Exports a. 30% b. 20% c. 50% d. 15% 147
 When a country imports more than it exports it is called a a. Trade surplus b. Import country c. Trade deficit d. All of the above 148
When a country imports more than it exports it is called a a. Trade surplus b. Import country c. Trade deficit d. All of the above 148
 Our closest trading partner is a. US b. China c. UK d. Japan 149
Our closest trading partner is a. US b. China c. UK d. Japan 149
 What does NAFTA stand for a. North American Foundation To Achieve b. North American Free Trial Alternative c. North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement d. North American Free Trade Agreement 150
What does NAFTA stand for a. North American Foundation To Achieve b. North American Free Trial Alternative c. North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement d. North American Free Trade Agreement 150
 Water Resources 151
Water Resources 151
 Water for Life Ø Humans need water more that any other physical thing. Ø On average, people need about 2. 5 L per day to stay healthy. Ø This is driven by the fact that over 2/3 of our bodies are composed of water. 152
Water for Life Ø Humans need water more that any other physical thing. Ø On average, people need about 2. 5 L per day to stay healthy. Ø This is driven by the fact that over 2/3 of our bodies are composed of water. 152
 Drinking Water n n n ¾ of the earth’s surface is covered in water. Of that, only 0. 6% can be consumed. Most of this drinkable water is found in Lakes, Rivers, and Aquifers. 153
Drinking Water n n n ¾ of the earth’s surface is covered in water. Of that, only 0. 6% can be consumed. Most of this drinkable water is found in Lakes, Rivers, and Aquifers. 153
 Pollution • Physical – Able to see, human presence • Chemical – Colourless & usually odourless pesticides/herbicides • Biological – Substances that harm the living organisms in the area 154
Pollution • Physical – Able to see, human presence • Chemical – Colourless & usually odourless pesticides/herbicides • Biological – Substances that harm the living organisms in the area 154
 Biological Magnification • BM is where an organism on the bottom of the food chain, like a plant that ingests chemicals or toxins, and when an animal eats 5 plants, it gets not only 1 x the amount of chemical, but 5 x, and so on up the food chain to us. 155
Biological Magnification • BM is where an organism on the bottom of the food chain, like a plant that ingests chemicals or toxins, and when an animal eats 5 plants, it gets not only 1 x the amount of chemical, but 5 x, and so on up the food chain to us. 155
 Drainage Basins Ø The Pacific Ø The Atlantic Ø The Arctic Ø Hudson Bay Ø Gulf of Mexico 156
Drainage Basins Ø The Pacific Ø The Atlantic Ø The Arctic Ø Hudson Bay Ø Gulf of Mexico 156
 Water Uses Power (Hydroelectricity) n Consumption n Industry n Irrigation (Classified as either instream or withdrawal use. ) n n Canada overall uses about 130 billion L/day, whereas it’s expected that by 2011, water use could jump to 180 billion L per day. 157
Water Uses Power (Hydroelectricity) n Consumption n Industry n Irrigation (Classified as either instream or withdrawal use. ) n n Canada overall uses about 130 billion L/day, whereas it’s expected that by 2011, water use could jump to 180 billion L per day. 157
 Sustainable Development “Our economic and environmental health today and in the future will depend in part on how we manage our water resources. We need to evaluate our behavior and lifestyles in order to sustain our high quality freshwater resources for future generations. If we do not take measures to protect our environment, the words from the poem The Ancient Mariner may predict our future: ‘Water, water everywhere, 158
Sustainable Development “Our economic and environmental health today and in the future will depend in part on how we manage our water resources. We need to evaluate our behavior and lifestyles in order to sustain our high quality freshwater resources for future generations. If we do not take measures to protect our environment, the words from the poem The Ancient Mariner may predict our future: ‘Water, water everywhere, 158
 Questions What percentage of earth’s surface water is actually drinkable? a. b. c. d. 0. 3% 0. 5% 0. 65% 159
Questions What percentage of earth’s surface water is actually drinkable? a. b. c. d. 0. 3% 0. 5% 0. 65% 159
 Which is not a drainage basin of Canada? a. b. c. d. The Pacific The St. Lawrence The Gulf of Mexico The Arctic 160
Which is not a drainage basin of Canada? a. b. c. d. The Pacific The St. Lawrence The Gulf of Mexico The Arctic 160
 On average, how many liters of water do Canadians use every day? a. b. c. d. 240 L 270 L 300 L 330 L 161
On average, how many liters of water do Canadians use every day? a. b. c. d. 240 L 270 L 300 L 330 L 161
 Which is not a type of water use? a. b. c. d. Biological Instream Withdrawal Hydroelectric 162
Which is not a type of water use? a. b. c. d. Biological Instream Withdrawal Hydroelectric 162
 163
163
 Global Warming is the idea that world temperatures are increasing. 164
Global Warming is the idea that world temperatures are increasing. 164
 165
165
 166
166
 Carbon dioxide is the most important greenhouse gas. It is made by animals breathing you are producing it right now as you breathe! It is made from the burning of any organic material like wood and grass. 167
Carbon dioxide is the most important greenhouse gas. It is made by animals breathing you are producing it right now as you breathe! It is made from the burning of any organic material like wood and grass. 167
 168
168
 THE IMPACT OF GLOBAL WARMING Scientists predict that average temperature in the next 100 years will increase by 1 to 3. 5 C. 169
THE IMPACT OF GLOBAL WARMING Scientists predict that average temperature in the next 100 years will increase by 1 to 3. 5 C. 169
 More on the impact on Global Warming. . The biggest increase will occur in polar areas, especially in the winter months. This warming would have a number of effects on the world and on Canada. 170
More on the impact on Global Warming. . The biggest increase will occur in polar areas, especially in the winter months. This warming would have a number of effects on the world and on Canada. 170
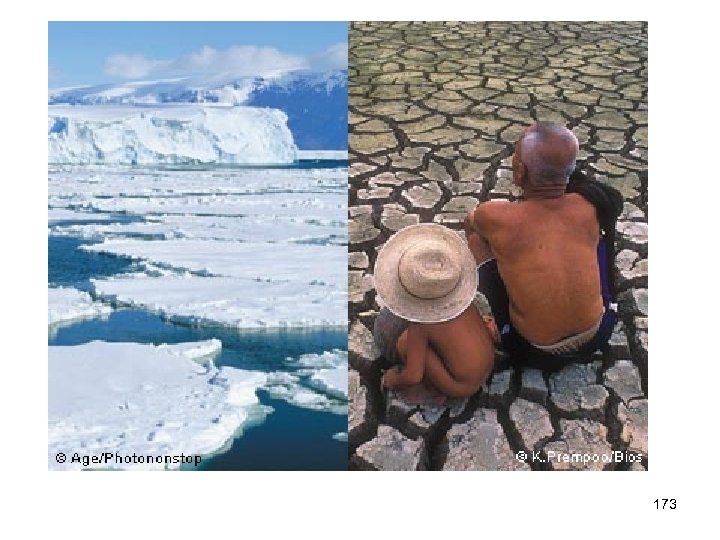
 One of the impacts of global warming is an increase in sea level of one meter, caused by melting glaciers and polar ice sheets. 171
One of the impacts of global warming is an increase in sea level of one meter, caused by melting glaciers and polar ice sheets. 171
 Glacier in the Peruvian Andes in 1980 and from the same position in 2002. Cordillera Blanca, Peru. 172
Glacier in the Peruvian Andes in 1980 and from the same position in 2002. Cordillera Blanca, Peru. 172
 173
173
 What animal was threatened under the U. S. endangered species act was announced, on May 14, 2008? ? !!? ? a. Black Bear b. Whale c. Dolphin d. Polar Bear e. Hummingbird 174
What animal was threatened under the U. S. endangered species act was announced, on May 14, 2008? ? !!? ? a. Black Bear b. Whale c. Dolphin d. Polar Bear e. Hummingbird 174
 What is the most important Greenhouse Gas? !? a. Methane b. Carbon Dioxide c. Oxygen d. Nitrous Oxide e. Water Vapor 175
What is the most important Greenhouse Gas? !? a. Methane b. Carbon Dioxide c. Oxygen d. Nitrous Oxide e. Water Vapor 175
 How much snow has the planet lost since the 1960’s? a. 12% b. 10% c. 11% d. 5% 176
How much snow has the planet lost since the 1960’s? a. 12% b. 10% c. 11% d. 5% 176


