46a381b391dfd0c09f56928fee0cb5d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Two Methods for Improving Text Classification when Training Data is Sparse Andrew Mc. Callum mccallum@cs. cmu. edu Just Research (formerly JPRC) Carnegie Mellon University For more detail see http: //www. cs. cmu. edu/~mccallum Improving Text Classification by Shrinkage in a Hierarchy of Classes (Sub. to ICML-98) Mc. Callum, Rosenfeld, Mitchell, Ng Learning to Classify. Text from Labeled and Unlabeled Documents (AAAI-98) Nigam, Mc. Callum, Thrun, Mitchell
Two Methods for Improving Text Classification when Training Data is Sparse Andrew Mc. Callum mccallum@cs. cmu. edu Just Research (formerly JPRC) Carnegie Mellon University For more detail see http: //www. cs. cmu. edu/~mccallum Improving Text Classification by Shrinkage in a Hierarchy of Classes (Sub. to ICML-98) Mc. Callum, Rosenfeld, Mitchell, Ng Learning to Classify. Text from Labeled and Unlabeled Documents (AAAI-98) Nigam, Mc. Callum, Thrun, Mitchell
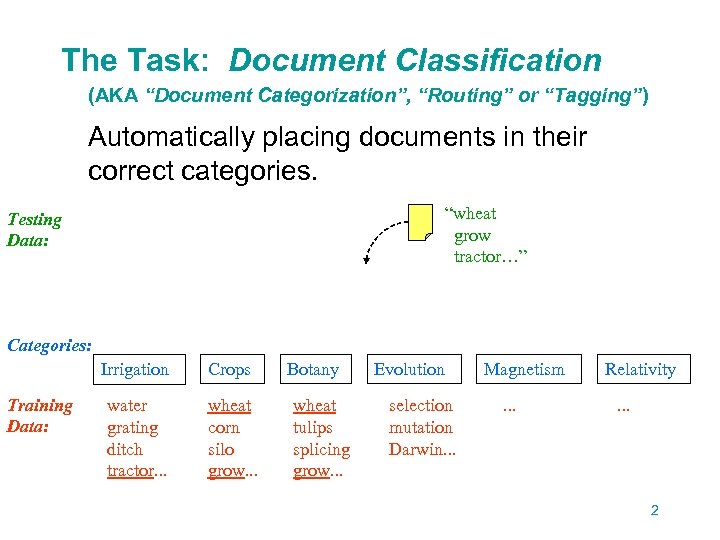 The Task: Document Classification (AKA “Document Categorization”, “Routing” or “Tagging”) Automatically placing documents in their correct categories. “wheat grow tractor…” Testing Data: Categories: Irrigation Training Data: Crops water grating ditch tractor. . . wheat corn silo grow. . . Botany wheat tulips splicing grow. . . Evolution selection mutation Darwin. . . Magnetism. . . Relativity. . . 2
The Task: Document Classification (AKA “Document Categorization”, “Routing” or “Tagging”) Automatically placing documents in their correct categories. “wheat grow tractor…” Testing Data: Categories: Irrigation Training Data: Crops water grating ditch tractor. . . wheat corn silo grow. . . Botany wheat tulips splicing grow. . . Evolution selection mutation Darwin. . . Magnetism. . . Relativity. . . 2
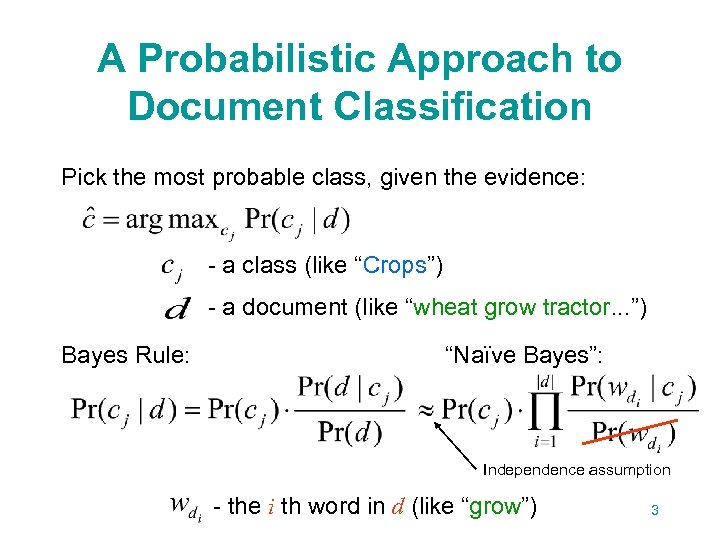 A Probabilistic Approach to Document Classification Pick the most probable class, given the evidence: - a class (like “Crops”) - a document (like “wheat grow tractor. . . ”) Bayes Rule: “Naïve Bayes”: Independence assumption - the i th word in d (like “grow”) 3
A Probabilistic Approach to Document Classification Pick the most probable class, given the evidence: - a class (like “Crops”) - a document (like “wheat grow tractor. . . ”) Bayes Rule: “Naïve Bayes”: Independence assumption - the i th word in d (like “grow”) 3
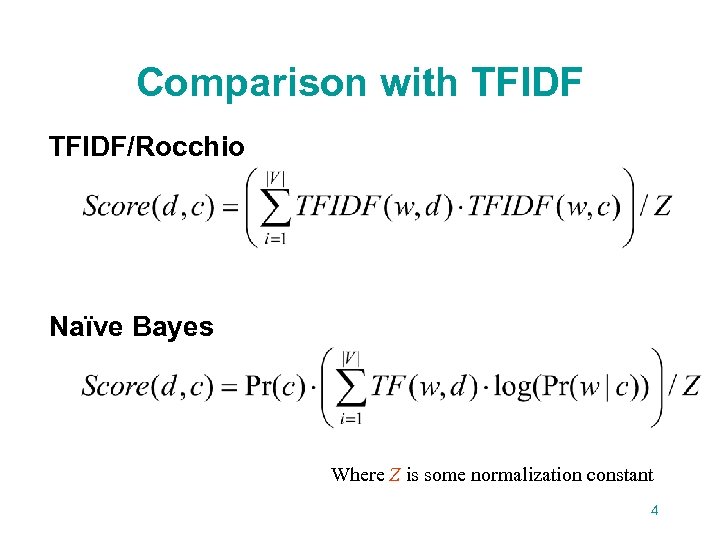 Comparison with TFIDF/Rocchio Naïve Bayes Where Z is some normalization constant 4
Comparison with TFIDF/Rocchio Naïve Bayes Where Z is some normalization constant 4
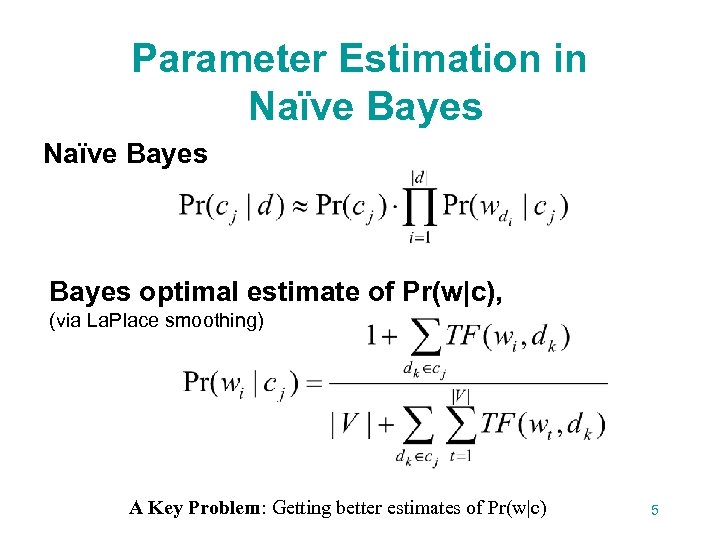 Parameter Estimation in Naïve Bayes optimal estimate of Pr(w|c), (via La. Place smoothing) A Key Problem: Getting better estimates of Pr(w|c) 5
Parameter Estimation in Naïve Bayes optimal estimate of Pr(w|c), (via La. Place smoothing) A Key Problem: Getting better estimates of Pr(w|c) 5
 Document Classification in a Hierarchy of Classes Andrew Mc. Callum Roni Rosenfeld Tom Mitchell Andrew Ng
Document Classification in a Hierarchy of Classes Andrew Mc. Callum Roni Rosenfeld Tom Mitchell Andrew Ng
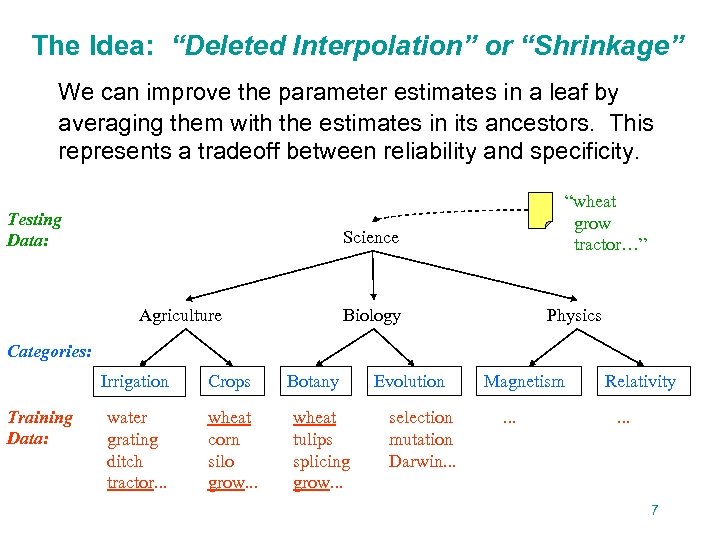 The Idea: “Deleted Interpolation” or “Shrinkage” We can improve the parameter estimates in a leaf by averaging them with the estimates in its ancestors. This represents a tradeoff between reliability and specificity. Testing Data: “wheat grow tractor…” Science Agriculture Biology Physics Categories: Irrigation Training Data: Crops water grating ditch tractor. . . wheat corn silo grow. . . Botany wheat tulips splicing grow. . . Evolution selection mutation Darwin. . . Magnetism. . . Relativity. . . 7
The Idea: “Deleted Interpolation” or “Shrinkage” We can improve the parameter estimates in a leaf by averaging them with the estimates in its ancestors. This represents a tradeoff between reliability and specificity. Testing Data: “wheat grow tractor…” Science Agriculture Biology Physics Categories: Irrigation Training Data: Crops water grating ditch tractor. . . wheat corn silo grow. . . Botany wheat tulips splicing grow. . . Evolution selection mutation Darwin. . . Magnetism. . . Relativity. . . 7
![“Deleted Interpolation” or “Shrinkage” [Jelinek and Mercer, 1980], [James and Stein, 1961] “Deleted Interpolation” “Deleted Interpolation” or “Shrinkage” [Jelinek and Mercer, 1980], [James and Stein, 1961] “Deleted Interpolation”](https://present5.com/presentation/46a381b391dfd0c09f56928fee0cb5d8/image-8.jpg) “Deleted Interpolation” or “Shrinkage” [Jelinek and Mercer, 1980], [James and Stein, 1961] “Deleted Interpolation” in N-gram space: “Deleted Interpolation” in class hierarchy space: Learn the l’s via EM, performing the E-step with leave-one-out cross-validation. 8
“Deleted Interpolation” or “Shrinkage” [Jelinek and Mercer, 1980], [James and Stein, 1961] “Deleted Interpolation” in N-gram space: “Deleted Interpolation” in class hierarchy space: Learn the l’s via EM, performing the E-step with leave-one-out cross-validation. 8
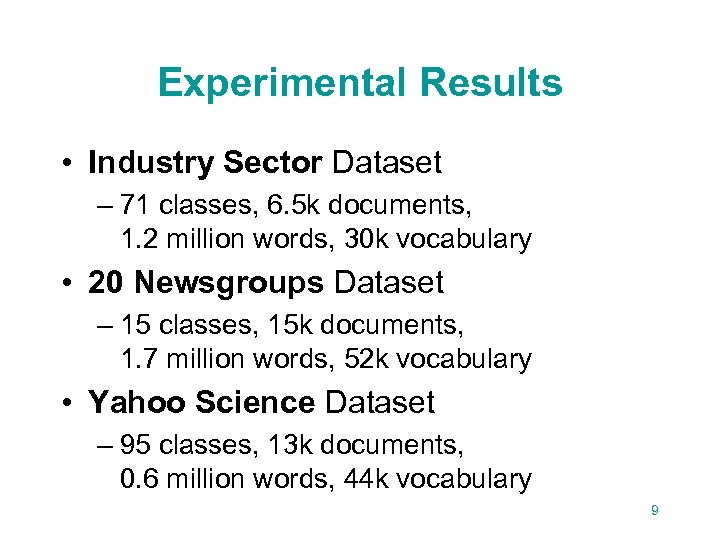 Experimental Results • Industry Sector Dataset – 71 classes, 6. 5 k documents, 1. 2 million words, 30 k vocabulary • 20 Newsgroups Dataset – 15 classes, 15 k documents, 1. 7 million words, 52 k vocabulary • Yahoo Science Dataset – 95 classes, 13 k documents, 0. 6 million words, 44 k vocabulary 9
Experimental Results • Industry Sector Dataset – 71 classes, 6. 5 k documents, 1. 2 million words, 30 k vocabulary • 20 Newsgroups Dataset – 15 classes, 15 k documents, 1. 7 million words, 52 k vocabulary • Yahoo Science Dataset – 95 classes, 13 k documents, 0. 6 million words, 44 k vocabulary 9
 Learning to Classify Text from Labeled and Unlabeled Documents Kamal Nigam Andrew Mc. Callum Sebastian Thrun Tom Mitchell
Learning to Classify Text from Labeled and Unlabeled Documents Kamal Nigam Andrew Mc. Callum Sebastian Thrun Tom Mitchell
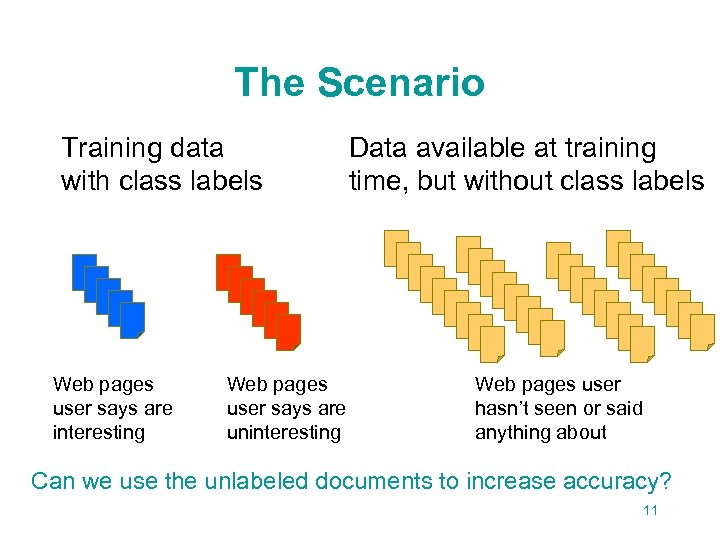 The Scenario Training data with class labels Web pages user says are interesting Web pages user says are uninteresting Data available at training time, but without class labels Web pages user hasn’t seen or said anything about Can we use the unlabeled documents to increase accuracy? 11
The Scenario Training data with class labels Web pages user says are interesting Web pages user says are uninteresting Data available at training time, but without class labels Web pages user hasn’t seen or said anything about Can we use the unlabeled documents to increase accuracy? 11
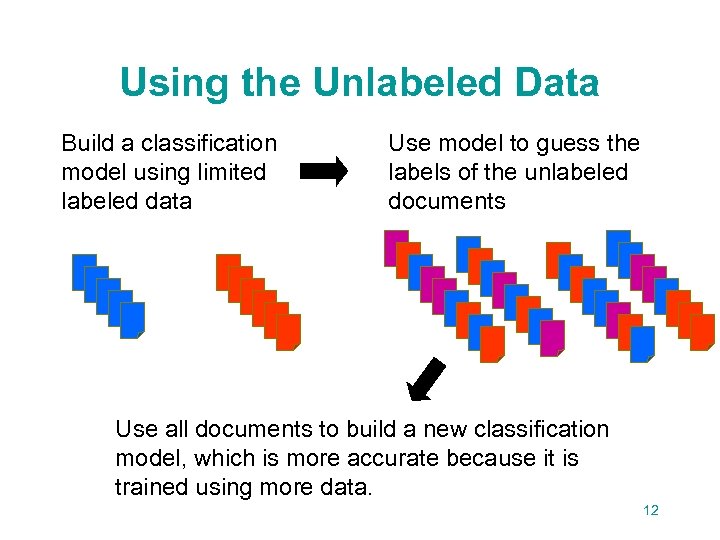 Using the Unlabeled Data Build a classification model using limited labeled data Use model to guess the labels of the unlabeled documents Use all documents to build a new classification model, which is more accurate because it is trained using more data. 12
Using the Unlabeled Data Build a classification model using limited labeled data Use model to guess the labels of the unlabeled documents Use all documents to build a new classification model, which is more accurate because it is trained using more data. 12
![Expectation Maximization [Dempster, Laird, Rubin 1977] Applies when there are two inter-dependent unknowns. (1) Expectation Maximization [Dempster, Laird, Rubin 1977] Applies when there are two inter-dependent unknowns. (1)](https://present5.com/presentation/46a381b391dfd0c09f56928fee0cb5d8/image-13.jpg) Expectation Maximization [Dempster, Laird, Rubin 1977] Applies when there are two inter-dependent unknowns. (1) The word probabilities for each class (2) The class labels of the unlabeled doc’s. • E-step: Use current “guess” of (1) to estimate value of (2) – Use classification model built from limited training data to assign probabilistic labels to unlabeled documents • M-step: Use probabilistic estimates of (2) to update (1). – Use probabilistic class labels on unlabeled documents to build a more accurate classification model. • Repeat E- and M-steps until convergence. 13
Expectation Maximization [Dempster, Laird, Rubin 1977] Applies when there are two inter-dependent unknowns. (1) The word probabilities for each class (2) The class labels of the unlabeled doc’s. • E-step: Use current “guess” of (1) to estimate value of (2) – Use classification model built from limited training data to assign probabilistic labels to unlabeled documents • M-step: Use probabilistic estimates of (2) to update (1). – Use probabilistic class labels on unlabeled documents to build a more accurate classification model. • Repeat E- and M-steps until convergence. 13
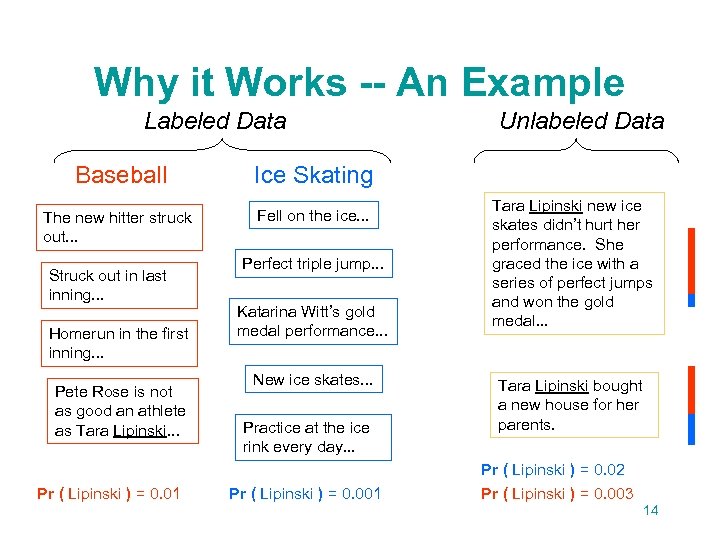 Why it Works -- An Example Labeled Data Baseball Ice Skating The new hitter struck out. . . Fell on the ice. . . Unlabeled Data Struck out in last inning. . . Homerun in the first inning. . . Pete Rose is not as good an athlete as Tara Lipinski. . . Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 01 Perfect triple jump. . . Katarina Witt’s gold medal performance. . . New ice skates. . . Practice at the ice rink every day. . . Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 001 Tara Lipinski new ice skates didn’t hurt her performance. She graced the ice with a series of perfect jumps and won the gold medal. . . Tara Lipinski bought a new house for her parents. Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 02 Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 003 14
Why it Works -- An Example Labeled Data Baseball Ice Skating The new hitter struck out. . . Fell on the ice. . . Unlabeled Data Struck out in last inning. . . Homerun in the first inning. . . Pete Rose is not as good an athlete as Tara Lipinski. . . Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 01 Perfect triple jump. . . Katarina Witt’s gold medal performance. . . New ice skates. . . Practice at the ice rink every day. . . Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 001 Tara Lipinski new ice skates didn’t hurt her performance. She graced the ice with a series of perfect jumps and won the gold medal. . . Tara Lipinski bought a new house for her parents. Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 02 Pr ( Lipinski ) = 0. 003 14
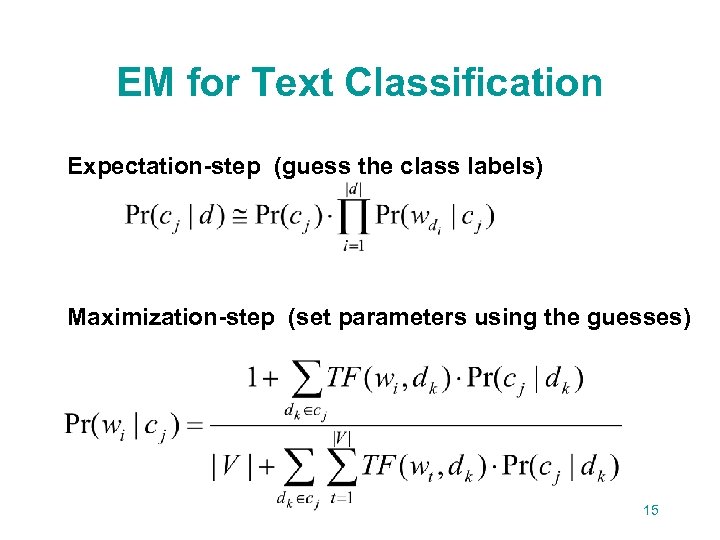 EM for Text Classification Expectation-step (guess the class labels) Maximization-step (set parameters using the guesses) 15
EM for Text Classification Expectation-step (guess the class labels) Maximization-step (set parameters using the guesses) 15
 Experimental Results -- The Data • Four classes of Web pages – Student, Faculty, Course, Project – 4199 Web pages total • Twenty newsgroups from Use. Net – several of religion, politics, sports, comp. * – 1000 articles per class • New articles from Reuters – 90 different categories – 12902 articles total 16
Experimental Results -- The Data • Four classes of Web pages – Student, Faculty, Course, Project – 4199 Web pages total • Twenty newsgroups from Use. Net – several of religion, politics, sports, comp. * – 1000 articles per class • New articles from Reuters – 90 different categories – 12902 articles total 16
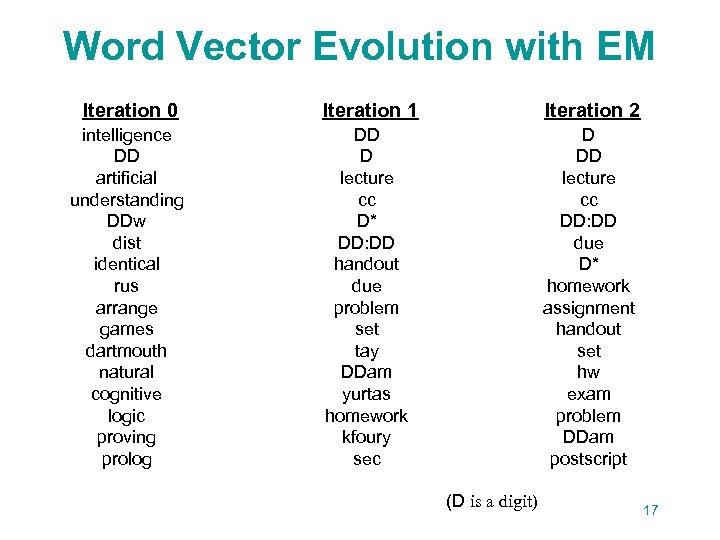 Word Vector Evolution with EM Iteration 0 Iteration 1 Iteration 2 intelligence DD artificial understanding DDw dist identical rus arrange games dartmouth natural cognitive logic proving prolog DD D lecture cc D* DD: DD handout due problem set tay DDam yurtas homework kfoury sec D DD lecture cc DD: DD due D* homework assignment handout set hw exam problem DDam postscript (D is a digit) 17
Word Vector Evolution with EM Iteration 0 Iteration 1 Iteration 2 intelligence DD artificial understanding DDw dist identical rus arrange games dartmouth natural cognitive logic proving prolog DD D lecture cc D* DD: DD handout due problem set tay DDam yurtas homework kfoury sec D DD lecture cc DD: DD due D* homework assignment handout set hw exam problem DDam postscript (D is a digit) 17
 Related Work • Using EM to reduce the need for training examples: – [Miller and Uyar 1997] [Shahshahani and Landgrebe 1994] • Auto. Class - unsupervised EM with Naïve Bayes: – [Cheeseman 1988] • Using EM to fill in missing values – [Ghahramani and Jordan 1995] 18
Related Work • Using EM to reduce the need for training examples: – [Miller and Uyar 1997] [Shahshahani and Landgrebe 1994] • Auto. Class - unsupervised EM with Naïve Bayes: – [Cheeseman 1988] • Using EM to fill in missing values – [Ghahramani and Jordan 1995] 18


