ccd19e312f603b8989bca39c6d87958e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58

TWISC’s Information Security Research Today and Tomorrow: Ubicomp, Usability and Sec. Urity D. T. Lee Director, IIS, Academia Sinica Director, TWISC IEEE SUTC 2006 Asia University, Taichung Jun. 5~7, 2006

Outline • Ubiquitous Computing – Usability – Security • • 2 TWISC & Secure Ubicomp Research & Activities in TWISC Cooperation & Collaboration: i. CAST Security Research in TWISC— 2006~2008

Ubiquitous Computing -- Ubicomp “Each person is continually interacting with hundreds of … interconnected computers” -- “Some computer science issues in Ubiquitous computing. ”, CACM, 1993. Everyware: The Dawing What is ubiquitous computing? Age of Ubicomp by Adam Greenfield >> Ubiquitous computing (ubicomp, or sometimes ubiqcomp) integrates computation into the environment, rather than having computers which are distinct objects -- Wikipedia which ideally “weave themselves into the fabric of everyday life until they are indistinguishable from it” 3 -- Mark Weiser, “The computer of the 21 st century. ”, Scientific American, 1991.
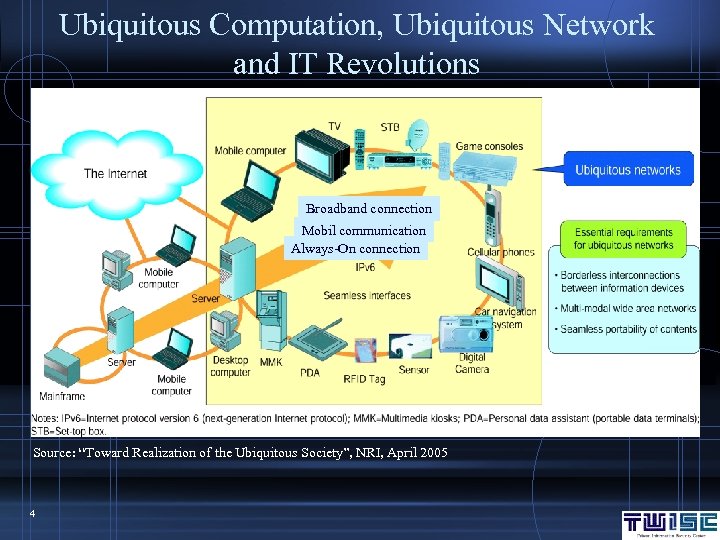
Ubiquitous Computation, Ubiquitous Network and IT Revolutions Broadband connection Mobil communication Always-On connection Source: “Toward Realization of the Ubiquitous Society”, NRI, April 2005 4

Everyday Computing: Things to be Considered • Dynamic, ad hoc and shared environment – Multiple activities operate concurrently – No clear beginning & end to all activities – Interruption is expected • Usability – Interface between human and Ubicomp (Ubiquitous computing) environment? – Human becomes the core of ubicomp environment. • Security – What are the changes in this new type of digital environment? – Effectiveness vs. Simplicity • How to secure new environment easily? 5

From Old School to New School Internet • Layer 3 & 4 attack • Virus, OS-level • Firewall and basic IDS 6 Mobile & Wireless • IPS, Application firewall • Google hacking • XML Security • Web Services & Web applications • Wireless Security • Vo. IP Security Everywhere computation • Past + Present • RFID & Sensor Network • Web 2. 0 & live personal content • Wireless anywhere • Security request in next generation?

Security & Privacy Issues • Old Model: – Places permanent firewall to secure traffic between intranet and internet – Requires a piece of running code to actively validate usage/access – Requires heavy computation resource to provide encryption/ decryption functionality – Presents weak protection in wireless environment • Not easy for people to secure their wireless data • Inadequate for Ubiquitous computing 7

Demo DST Tags by TI: (Steve Bono, et al. Johns Hopkins Univ. Jan. 2005) At left, an Exxon. Mobile Speed. Pass for electronic payment At right, an immobilizer equipped car key. The small chip is embedded into the plastic head of the key. Courtesy: http: //rfidanalysis. org ØScenario 1. Sniffing a DST tag in a victim's pocket. Active attack: scanning ØScenario 2. Cracking the key in a DST tag. Parallel cracker 16 -FPGAs. Sniffed data is entered using the keyboard, and results are read off the LEDs on each board. Equipment needed ØScenario 3. Starting a car using the DST simulator. 8 to clone a DST tag at close range. Passive attack: eavesdropping A microreader, laptop, & a serial cable.

Security and Privacy Issues • Characteristics relevant to Ubi. Comp security : – – Variability & capabilities of devices introduce complexities to security framework Heterogeneity of security & privacy 1) Ad-hoc device communication with different protocols - The technology of content encoding becomes critical – • Without good protection, the severity of security breach and data leakage would worsen!! – 9 Location-awareness in policy management Users would be forced to turn off ubicomp features because of lack of protection, thus the benefit of ubicomp environment diminishes
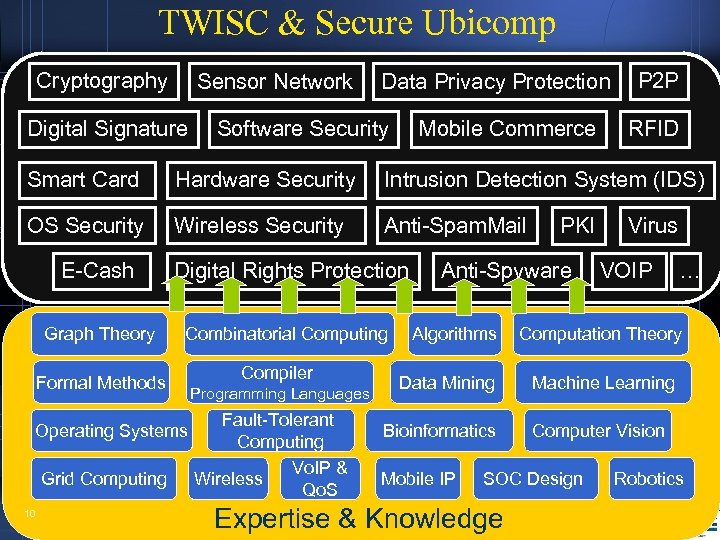
TWISC & Secure Ubicomp Cryptography Sensor Network Digital Signature Data Privacy Protection Software Security Mobile Commerce P 2 P RFID Smart Card Hardware Security Intrusion Detection System (IDS) OS Security Wireless Security Anti-Spam. Mail E-Cash Digital Rights Protection Graph Theory Combinatorial Computing Formal Methods Operating Systems Grid Computing 10 Compiler Programming Languages Fault-Tolerant Computing Vo. IP & Wireless Qo. S PKI Anti-Spyware Algorithms Data Mining Bioinformatics Mobile IP VOIP … Computation Theory Machine Learning Computer Vision SOC Design Expertise & Knowledge Virus Robotics

Introduction to TWISC http: //www. twisc. org/ • Officially founded on April 1 st, 2005 » Funded by the National Science Council, Taiwan • An integrated effort to boost research and development activities in information security, promote public awareness and foster partnership among government, academia and private sectors in information security. • The headquarters of TWISC is at the Info. Comm Research Center, Academia Sinica (soon-to-be established) • The first physical center in northern Taiwan has been established at National Taiwan University of Science and Technology (TWISC@NTUST) -- (TWISC@NCTU, TWISC@NCKU under way) 11

Objectives/Missions • Advance the research and development of technologies in information security and related areas. • Provide education and training, help build human resource capacity, and promote public awareness in information security. • Collaborate with private sector to enhance local information security industry in security management and applications software development. • Seek international collaborations to build a ubiquitous secure community. 12

Strategies • Integrate resources and expertise among government, industry and academia to make comprehensive plans on how to foster security-related research effort, and help promote public awareness and capacitybuilding in information security • Strive for excellence in research and development of technologies in information security & keep abreast with the top-notch leading research institutions worldwide • Serve as a bridge for partnership among government, industry and academia, and as a catalyst of technology transfer in information security sector, and promote university-industry cooperative research in securityrelated applications • Build a framework for national/international collaboration, including exchange of scholars, researchers and students, and hosting of workshops and conferences 13
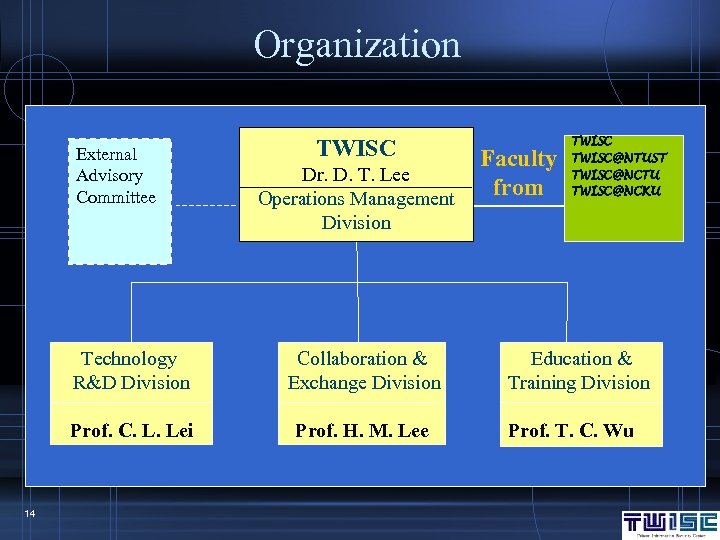
Organization External Advisory Committee TWISC Dr. D. T. Lee Operations Management Division Technology R&D Division Prof. C. L. Lei 14 Collaboration & Exchange Division Prof. H. M. Lee Faculty from TWISC@NTUST TWISC@NCTU TWISC@NCKU Education & Training Division Prof. T. C. Wu

Principal Investigators • Dr. Der-Tsai Lee 李德財 Director, Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica Director of TWISC E-mail: dtlee@iis. sinica. edu. tw • Professor Tzong-Chen Wu 吳宗成 Department of Information Management National Taiwan University of Science & Technology CEO, TWISC@NTUST and Director, Div. Education & Training E-mail: tcwu@cs. ntust. edu. tw • Professor Hahn-Ming Lee 李漢銘 Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan University of Science & Technology Director, Div. Exchange & Collaboration, TWISC@NTUST E-mail: hmlee@mail. ntust. edu. tw • Professor Chin-Laung Lei 雷欽隆 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Director, Div. Technology Research & Development, TWISC@NTUST E-mail: lei@cc. ee. ntu. edu. tw 15

Technology R&D Division Headed by Professor Chin-Laung Lei 雷欽隆 EE, National Taiwan University • To do advanced research in information security • To develop information security technologies and applications software for research and education • To plan and conduct university-industry cooperative research • To help realize technology transfer to industry 16
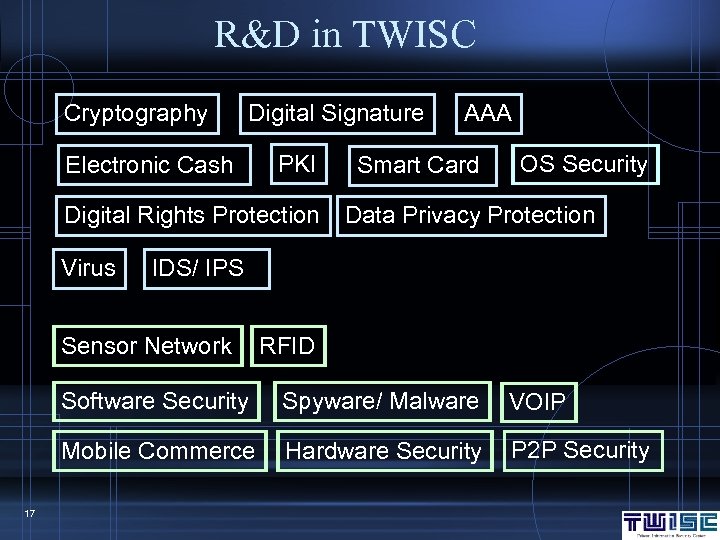
R&D in TWISC Cryptography Digital Signature Electronic Cash PKI Digital Rights Protection Virus AAA Smart Card OS Security Data Privacy Protection IDS/ IPS Sensor Network RFID Software Security VOIP Mobile Commerce 17 Spyware/ Malware Hardware Security P 2 P Security

Foundation of Cryptography • Collaborators: – Dr. Chi-Jen Lu, et al. , IIS, Academia Sinica • Motivation: To invent randomness research tools with applications to cryptography • Publications in – Journal of Cryptology – Theoretical Computer Science – IEEE Transactions on Information Theory • Major results: – Efficient construction of randomness extractors • Extract almost perfect randomness from slightly random sources – Application of randomness extractors in cryptography 18 • Achieve encryption with everlasting security against adversaries of bounded storage

Multivariate Public-Key Cryptosystems • Collaborators: – Dr. Bo-Ying Yang, Dr. Jiun-Ming Chen, TKU, Dr. L-C. Wang, NDHU; Messrs Y-H Chen, S-H Kao, Y-H Hu, NTU • Motivation: Find a more robust and efficient alternative to PKCs – RSA depends on infeasibility of factoring a large integer – ECC depends on difficulty of taking Discrete Log – But both of RSA and ECC can be solved efficiently by Shor’s Quantum Computing Algorithm • Multivariate PKCs – An alternative PKC whose public key is represented by multivariate polynomials over a finite field • Provides much more solid system that can’t be broken in poly-time by Quantum Computer • Also very efficient to handle key generation/authentication • Publications 19 – A "Medium-Field" Multivariate Public-Key Encryption Scheme, Cryptographer Track, RSA 2006 (Feb. 13 -17, 2006) – Another in 3 rd conference in Security in Pervasive Computing (York, Apr. 18 -21, 2006).

Low Resource PKCs • Collaborators: – Dr. Bo-Ying Yang, Dr. Jiun-Ming Chen, Y-H Chen, Sam Tsai (NTU), Doug Cheng (Harvard) • Motivation: Implement PKCs efficiently to facilitate pervasive / ubiquitous computing – Traditional PKCs on embedded systems • • Very slow and require dedicated hardware e. g. A lab in Austria is trying to implement ECC on a low-cost RFID – They are unable to satisfy the low power requirements – RSA would be hopeless • TTS and similar schemes are being ported to sensors and small ASICs (for RFID use). – High Speed Signatures on Low-Cost Smart Cards 20
Digital Signature and Its Applications • Collaborators: – Dr. Tzong-Chen Wu et al. , NTUST • Motivation: – To improve the performance of verifying digital signatures • Achievements: – T. C. Wu and Y. C. Lin, “Self-certified Approach for Authenticated Key Agreement, " Book Chapter, in Computer Security in the 21 st Century, Lee, D. T. ; Shieh, S. P. ; Tygar, J. D. (Eds. ), Springer, 2005. – Lin, C. Y. , Wu, T. C. , Zhang, F. , and Hwang, J. J. , “New identitybased society oriented signature schemes from pairings on elliptic curves”, Applied Mathematics and Computation, Vol. 160, 2005, pp. 245 -260. (SCI, EI) – Patent: 21 • The method of wording correctness output for anti-forgery of e-document, Patent No. 108925 • Centralized self-certified mark, Patent No. I 255627 • The secure subscribing system of e-publications, Pub. Notice No. 200417220
Database Privacy Protection 2 • Collaborators (1998 - ): – Da-Wei Wang, Tsan-sheng Hsu, Churn-Jung Liau, IIS, Academia Sinica • Funding: Academia Sinica, NSC, National Health Insurance Bureau • Motivation: – How to release data while protecting individual privacy – Database privacy protection of National Health Insurance Bureau(健保局) • Representative Achievements: – A logic framework for data privacy protection – Quantifying privacy leakage – Cell. Secu: a prototype privacy gateway – A logic framework for knowledge acquisition 22
Database Privacy Protection 1 • A logic framework for data privacy protection – Privacy breach formally defined • Quantifying privacy leakage – It’s important to address potential tradeoffs between privacy leakage and computational complexity – Quantify privacy leakage by economic model, information theory framework, etc. • Cell. Secu: a prototype privacy gateway – Queries to the database can be automatically checked for privacy compliance – Built on our logic framework with quantitative measurements of privacy leakage incorporated • A logic framework for knowledge acquisition - From the scenario of one static query to the knowledge acquisition process via database queries 23

Hardware Security • Collaborators: – Dr. Jung-Hui Chiu, Yuan-Hung Lien, Sung-Shiou Shen, Li. Lun Lin, Sheng-Ho Lin • Motivation: – New testing techniques for Smart Card SPA/DFA attacks • Contribution to industry/ academia: – Smart Card Protection : • A balancing and masking method to prevent from timing attacks and SPA/DFA attacks – Secure GPRS/3 G/WLAN authentication : • A feasible SIM/USIM reconnection authentication via the current built-in hash functions 24

Intrusion Detection & Prevention System • Collaborators: – Hahn-Ming Lee, Yuh-Jye Lee, Hsing-Kuo Pao, Wei-Chung Teng, Tien-Ruey Hsiang, Lin-Kuei Yang, Kuo-Hua Yang, Yu-Shan Hsu • Representative Achievements: – A new detection/ prevention technique based on Data Mining and Neural Networks – Performance outperforms #1 of KDD Cup and – Low false positive and low false negative rates for detecting Do. S and RS 21 attacks • Contribution: – An efficient cascading intrusion detection framework that combines OCSVM with SSVM. – Chunking technique was introduced to deal with massive dataset in the training process • Low Memory Usage! 25

Web Application Security • Collaborators: – Dr. D. T. Lee, Yao-Wen Huang, Chung-Hung Tsai, Fang-Yu, Christian Hang, Sy-Yen Kuo, Shih-Kun-Huang, Tsung-Po Lin • Motivation: – Build systematic and automatic mechanisms for detecting/protecting web application vulnerability • Representative Achievements: – WAVES (Web Application Vulnerability and Error Scanner): • • Remote, dynamic, black-box testing (PT) Found bugs in Furtune 500 websites WWW 2003 Best Paper Finalist Appeared in Journal of Computer Networks special issue on web and network security, 2005 – Web. SSARI (Web Application Security via Static Analysis and Runtime Inspection): • to perform compile-time verification and runtime enforcement of web application security • Downloaded and verified 230 open source Web applications from Source. Forge. net. • Identified 69 as vulnerable; 38 projects ack’d our findings 26 • WWW 2004 Best Paper Finalist
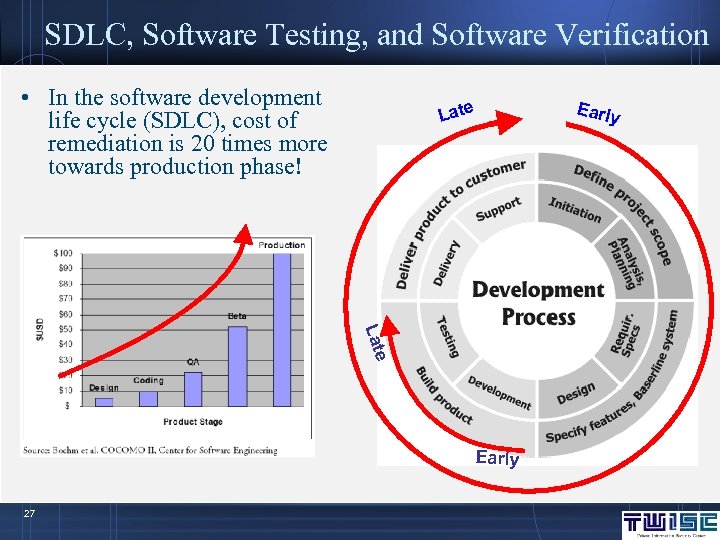
SDLC, Software Testing, and Software Verification • In the software development life cycle (SDLC), cost of remediation is 20 times more towards production phase! Early Late e Lat Early 27

Vo. IP Qo. S and Security • Collaborators: – Dr. Chin Laung Lei, Dr. Wen Shenq Juang, Dr. Ren Junn Hwang, Kuan Ta Chen • Motivation: Study the security and Qo. S issues of the Vo. IP system – – • 28 Analyze Skype packet trace Propose sophisticated Qo. S and User Satisfaction Model Analyze the security system and possible weaknesses of Skype system Develop technique to attack Skype system Publication: – "Quantifying Skype User Satisfaction, “ to appear in ACM SIGCOMM 2006 (Sept. 2006)

Content & Digital Rights Protection 5 • Collaborators: – Mark Hong-Yuan Liao, C. S. Lu, C. C. Shih, G. J. Yu, IIS • Funding (1998 - ): Academia Sinica, NSC • Motivation: – Protect IP rights of multimedia (images and video) – National Digital Archives Program NSC (2002 -2006) • Representative Achievements: – Watermarking algorithms – Patent & Tech. Transfer 29
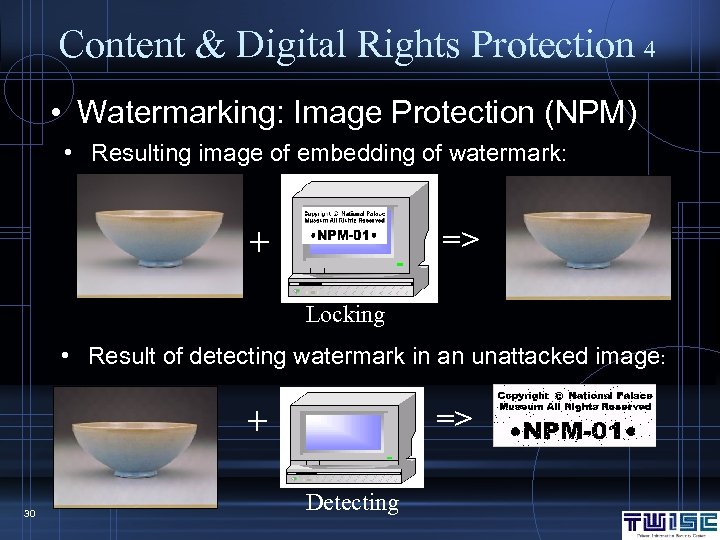
Content & Digital Rights Protection 4 • Watermarking: Image Protection (NPM) • Resulting image of embedding of watermark: => + Locking • Result of detecting watermark in an unattacked image: => + 30 Detecting

Content & Digital Rights Protection 3 • Visible watermark is plainly visible across the body of the image or situated on the side 31
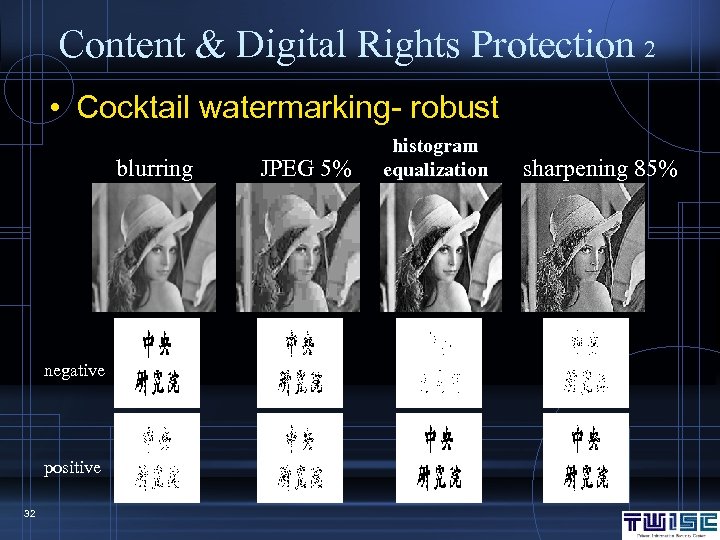
Content & Digital Rights Protection 2 • Cocktail watermarking- robust blurring negative positive 32 JPEG 5% histogram equalization sharpening 85%

Content & Digital Rights Protection 1 Invisible watermarking- Fragile original image watermarked image altered image What you see is NOT what it really is. 2 nd level 33 3 rd level 4 th level

More Active Research Topics • Algebraic Cryptanalysis • Identification and Authentication Schemes and related applications • Qo. S for IPSec VPN • RFID Security • Wireless & Sensor Network Security • Remote Authentication 34

Collaboration & Exchange Division Headed by Professor Hahn-Ming Lee 李漢銘 CSIE, NTUST • To draft technology and scholar exchange plans • To establish information security-alliance program among local universities and with international organizations • To establish channels for exchange of researchers and students between collaboration partners • To host international workshops and conferences in information security and related areas • To organize Distinguished Lecture Series, Workshops on Advanced Information Security Technology, and Information Security Summer School (Aug. 2006, coming soon) 35

Host International Workshops and Conferences - SADFE 2005 (First International Workshop on Systematic Approaches to Digital Forensic Engineering) Nov. 7 -10, 2005, Taipei, Taiwan http: //conf. ncku. edu. tw/sadfe/ Invited Speakers: – Prof. George Mohay , Queensland University of Technology – Prof. Steve Schroeder , Seattle University, a pioneer in Cyber crime law enforcement – Dr. Ming-Yuh Huang: Boeing Associate Technical Fellow 36

Host International Workshops and Conferences - Asia. CCS'06 • ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security (Asia. CCS'06) March 21 -23, 2006, Taipei, Taiwan http: //www. iis. sinica. edu. tw/asiaccs 06/ 37

Distinguished Lecture Series 3 • Date: 2005/10/27 • Prof. Kentaro Kato CHUO University • Topic: Y-00 protocol: Quantum Cryptography for Optical Fiber Networks • Date: 2005/12/16 • Professor Hideki IMAI, Information and Systems Dept. of Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo • Topic: Trends and Challenges for Securer Cryptography 38

Distinguished Lecture Series 2 Date: 2006/3/20 Topics: (1) Open problems and promising approaches in computer security (Prof. Tygar) (2) Software Security and Solutions : A Stony Brook Perspective ( Prof. Chiueh) Prof. Tzi-cker Chiueh Computer Science Department State University of New York at Stony Brook 39 Prof. Doug Tygar Computer Science Department UC Berkeley

Distinguished Lecture Series 1 Date: 2006/5/1 in NTUST Topic: General Method for Enhancing Security of Multivariate Public Key Cryptosystems Prof. TSUJII Shigeo, President, Institute of Information Security Japan Date: 2006/6/1 in NCKU and NTUST Topic: Security Challenges in Ubiquitous Society Prof. Kwangjo Kim Director, International Research Center of Information Security Information and Communications University Korea 40

Workshop on Advanced Information Security Technology Date: 2006/01/20 -21 at NTUST Topic: Multivariate PKC Prof. Jintai Ding, University Prof. Christopher Wolf, Ecole of Cincinnati, USA Normal Superieure, France 41 Prof. Bo-Yin Yang, Tamkang University Taiwan

Information Security Summer School (ISSS) July-Aug. 2006 • Lectures: Prof. Tzong-Chen Wu (NTUST), Prof. Chi-Sung Laih (NCKU), Prof. Bo-Yin Yang (TKU), and Prof. Dawn Song (CMU, USA), Prof. Adrian Perrig (CMU), Prof. Rajkumar (CMU), Dr. Mayes (ISG, UK), Prof. Mitchell … and many known scholars in Information Security • Date: 2006/7~2006/8 • Venue: National Taiwan University of Science and Technology (NTUST) • For more information see http: //www. twisc. org 42

International Collaboration for Advancing Security Technology (i. CAST) Security Technologies & Applications in Wireless Sensor Networks Investigation on Intrusion Detection/Prevention Information Security and Privacy Protection Technology in RFID Applications Static Analysis/Software Verification System Research & Development of High Security Remote Authentication Technology 43 High Speed IDS Expert System and Privacypreserving Information Protection Management
International Collaboration in TWISC 44

Education & Training Division Headed by Professor Tzong-Chen Wu 吳宗成 Computer Science, NTUST 45 • To organize and prepare curricula or educational programs for information security • To offer training courses and promote information sharing and public awareness of information security • To provide incentives for researchers/faculty members in terms of awards, recognition, and promotion • To host training workshops in information security for academic and industrial professionals

TWISC@NTUST • TWISC established its first physical center on Nov. 10, 2005 at the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology (TWISC@NTUST) in northern Taiwan • Motivation: – Integrate the resources and expertise scattered among the universities and research institutes in northern Taiwan – Promote public awareness and foster partnership among government, academia and private sector in information security • Core Members: – More than 20 professors and 30 Ph. D/MS students – Tzong-Chen Wu, Hahn-Ming Lee, Chin-Laung Lei, Da-Wei Wang, Wei-Hua He, Chi-Jen Lu, Chien-Lung Hsu, Bo-Yin Yang, Churn-Jung Liau, Feipei Lai, Yuh-Jye Lee, Tyng-Ruey Chuang, Tien-Ruey Hsiang, Chuan-Kai Yang, Wei-Chung Teng, Hsing. Kuo Pao, Nai-Wei Lo, Wei-Hua He, Jung-Hui Chiu, Shi-Jinn Horng, Tsan-Sheng Hsu, Chien-Lung Hsu, Yuan-Cheng Lai 46

TWISC@NTUST • Research Topics: – Security technologies and applications for low-resource devices • Wireless network security • Sensor network security • RFID security – Quantum cryptography • Post-Quantum cryptography • Multivariate Public Key Cryptography – Web application security assessment • Software security • Formal verification – Visual cryptography • Data hiding • Multimedia protection – Intrusion detection and prevention • Firewall • Intrusion detection • Anti-virus, anti-spam or anti-spyware • 47 Major Activies: – Integrate all academia and research institutes in northern Taiwan – Hold weekly seminars and monthly distinguished lecture series in information security – Promoted information security awareness – Research advanced information security topics

TWISC@NCTU • TWISC at National Chiao-Tung University • Former group founded by RDEC in 1997 to establish GSNCERT (Government Service Network – Computer Emergency Response Team) : Protect Taiwan government’s network and websites • Physical center (TWISC@NCTU) is to be established in Sept. 2006, involving academia and research institutions in central Taiwan including Hsinchu Science Park and Central Taiwan Science Park. • Research Topics: – Wireless network security – Intrusion detection/prevention – Computer and information security – Cryptography 48

TWISC@NCTU • Core members: – More than 16 professors and 30 Ph. D/MS students – Shiuhpyng Shieh, Wen-Guey Tseng, Rong-Jae Chen, Shih-Kun-Huang, Yi-Shiung Yeh, S. J. Tsai, Y. D. Lin, Yu-Lun Huang, T. Y. Hsu, John Zao, Wen-Nun Tsai, H. M. Sun, J. K. Jan, M. S. Hwang, C. H. Lin • Major Accomplishments: – Designed and developed intrusion detection system (A-IDS), remote security scanner (R-SCAN) – Served over 3, 000 government agencies, and scanned over 200, 000 computers in a week 49

TWISC@NCKU • TWISC at National Cheng-Kung University • The physical center (TWISC@NCKU) is to be established in August 2006, involving academia and research institutions in southern Taiwan, including Southern Taiwan Science Park. • Facilities and Objectives: – A well established security testbed for Taiwan information security research – Prevent attacks in IPv 6 network, e. g. : 6 to 4 DDo. S – Protect SIP-based application • Traditional firewall/IDS can’t fully provide the protection • Research Topics: – Network Security Testbed – IPv 6 -Enabled IDS – IPS for SIP Vo. IP System – DNS Server Protection • Core members: – C. S. Laih, L. M. Tseng, C. H. Lee, D. M. Ko, C. H. Cheng, W. K. Kuo, P. Z Cheng , W. Z. Kuo, L. Tsen 50

TWISC@NCKU 51 • Major Accomplishments: – Testbed: • An Internet topology close to real world • More than 290 tools • More than 20 testing scenarios • Integrate Eurecom Honeypot network security statistics database – IPv 6 IDS: • Taiwan’s first IPv 6 IDS that supports 6 to 4 and tunnel broker • Immune to Nmap Finger. Printing • Ready for technology transfer – Protection mechanism for SIP-based applications: • Won an award in CC 2005, Ministry of Education • Ready for technology transfer
TWISC & Ubicomp Security Cryptography Sensor Network P 2 P Data Privacy Protection IIS, NTUST NTU Digital Signature Academia Sinica. Software Security Mobile Commerce RFID Smart Card Hardware Security Intrusion Detection System (IDS) OS Security Wireless Security Anti-Spam. Mail TKU SCU E-Cash Digital Rights Protection Graph Theory Combinatorial Computing Formal Methods PKI Anti-Spyware Algorithms CGU Virus VOIP … Computation Theory Compiler Members. Programming Languages Data Mining institutions from other universities and Machine Learning Fault-Tolerant / NCKU/ … NCTU Operating Systems Bioinformatics Computer Vision Computing TWISC@NCTU, TWISC@NCKU Grid Computing 52 Wireless VOIP Mobile IP SOC Design Expertise & Knowledge Robotics

Security Research in TWISC— 2006~2008 Wireless Security RFID Cryptography Intrusion Detection System (IDS) /IPS Smart Card E-Cash Software Security Mobile Commerce Virus Anti-Spyware Digital Signature Digital Right Protection PKI AAA Data Privacy Protection Anti-Spam. Mail Hardware Security P 2 P OS Security Sensor Network Cryptographic Protocol Design 53 4

Security Research in TWISC— 2006~2008 Wireless Security RFID Cryptography Intrusion Detection System (IDS) /IPS Smart Card E-Cash Software Security Mobile Commerce Virus Anti-Spyware AAA Data Privacy Protection Anti-Spam. Mail Hardware Security P 2 P/ Web Security 54 Digital Signature Digital Right Protection PKI 3 OS Security Sensor Network

Security Research in TWISC— 2006~2008 Cryptography Digital Signature Intrusion Detection System (IDS) /IPS Smart Card E-Cash Software Security Mobile Commerce 55 Virus Anti-Spyware Wireless Security 2 RFID Digital Rights Protection AAA PKI Data Privacy Protection Anti-Spam. Mail Hardware Security P 2 P Software Protection OS Security Sensor Network

Security Research in TWISC— 2006~2008 Cryptography Digital Signature Intrusion Detection System (IDS) /IPS Smart Card E-Cash Software Security Mobile Commerce Virus Anti-Spyware Wireless Security AAA Data Privacy Protection Anti-Spam. Mail Hardware Security P 2 P Any Possibility! New Opportunity! 56 RFID Digital Right Protection PKI 1 OS Security Sensor Network

Conclusion • In Ubicomp environment, sec. Urity will be KEY toward Usability • TWISC is to serve as an R&D resource center to enhance technical competence, including Ubicomp security • TWISC is to enlarge human resource capacity and promote public awareness in information security • TWISC is to be a window for university-industry partnership and international collaboration in information security • TWISC represents integrated research capabilities in Taiwan, aiming to establish itself as a power house in information security, working closely with other renowned centers or laboratories worldwide. 57

Thank you for your attention 58
ccd19e312f603b8989bca39c6d87958e.ppt