Tutorials_Microeconomics.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Tutorials for 20 points Microeconomics
Tutorials for 20 points Microeconomics
 Exercise 1 (2 points) The population demand function of a product Qd=7 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -5+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 3 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 1. 5 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
Exercise 1 (2 points) The population demand function of a product Qd=7 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -5+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 3 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 1. 5 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
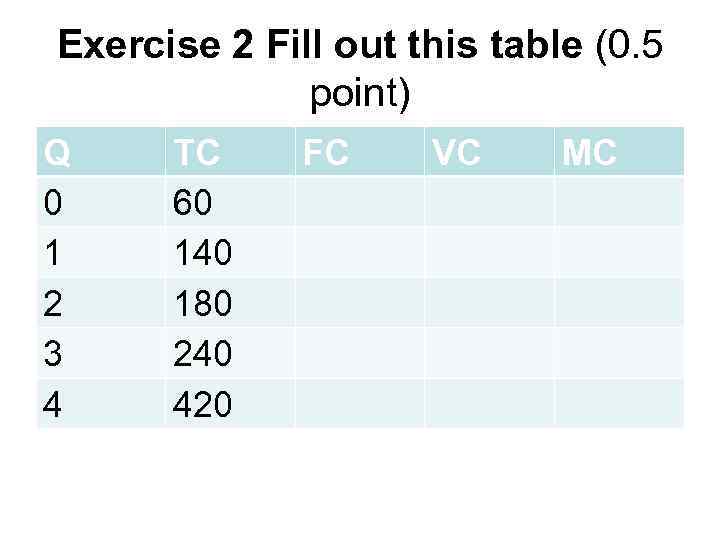 Exercise 2 Fill out this table (0. 5 point) Q 0 1 2 3 4 TC 60 140 180 240 420 FC VC MC
Exercise 2 Fill out this table (0. 5 point) Q 0 1 2 3 4 TC 60 140 180 240 420 FC VC MC
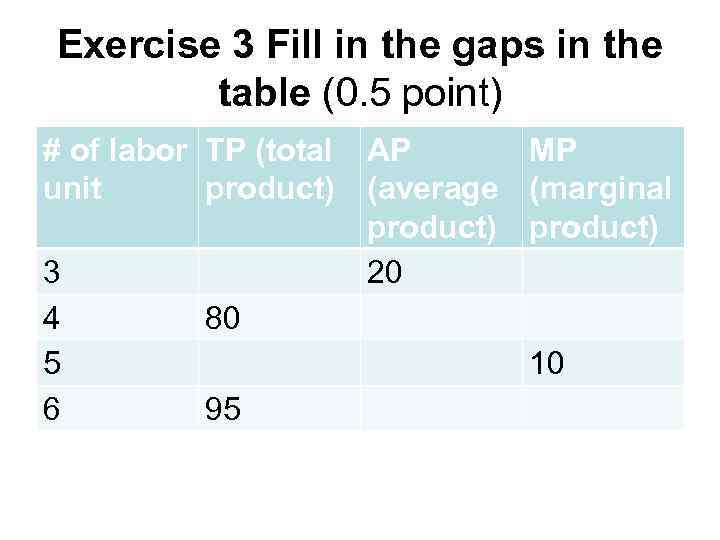 Exercise 3 Fill in the gaps in the table (0. 5 point) # of labor TP (total unit product) 3 4 5 6 AP MP (average (marginal product) 20 80 10 95
Exercise 3 Fill in the gaps in the table (0. 5 point) # of labor TP (total unit product) 3 4 5 6 AP MP (average (marginal product) 20 80 10 95
 Exercise 4 (0. 5 point) The function of company’s total cost is TC=100 Q – 2 Q^2 + 0. 04 Q^3 Find the amount of marginal cost in Q=12 units.
Exercise 4 (0. 5 point) The function of company’s total cost is TC=100 Q – 2 Q^2 + 0. 04 Q^3 Find the amount of marginal cost in Q=12 units.
 Exercise 5 (1 point) The function of TR (total revenue) is TR=10 Q – Q^2 + 2 Q^3. What is the amount of marginal revenue (MR) in output volume Q=5?
Exercise 5 (1 point) The function of TR (total revenue) is TR=10 Q – Q^2 + 2 Q^3. What is the amount of marginal revenue (MR) in output volume Q=5?
 Exercise 6 (2 points) The population demand function of a product Qd=8 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -4+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 4 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 2 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
Exercise 6 (2 points) The population demand function of a product Qd=8 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -4+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 4 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 2 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
 Exercise 7 Fill out this table (0. 5 point) Q 0 10 20 30 40 50 AFC VC - AC 20 MC - TC 100 11 390 5 420 2 14
Exercise 7 Fill out this table (0. 5 point) Q 0 10 20 30 40 50 AFC VC - AC 20 MC - TC 100 11 390 5 420 2 14
 Exercise 8 (1 point) • Assume that a technology of production is shown by the production function Q=√(KL). The firm’s cost is 36 cur. units in wage rate w=4 cur. units and rent rate r=6 cur. units. Find optimum production volume. Budget limitation of a company is C = w*L + r*K
Exercise 8 (1 point) • Assume that a technology of production is shown by the production function Q=√(KL). The firm’s cost is 36 cur. units in wage rate w=4 cur. units and rent rate r=6 cur. units. Find optimum production volume. Budget limitation of a company is C = w*L + r*K
 Exercise 9 (1 point) Fixed cost of a company is 55 cur. units. The function of company’s marginal cost is MC= 22 -8 Q + 3 Q^2 + 2 Q^3 Determine the function of total cost in Q=3 units.
Exercise 9 (1 point) Fixed cost of a company is 55 cur. units. The function of company’s marginal cost is MC= 22 -8 Q + 3 Q^2 + 2 Q^3 Determine the function of total cost in Q=3 units.
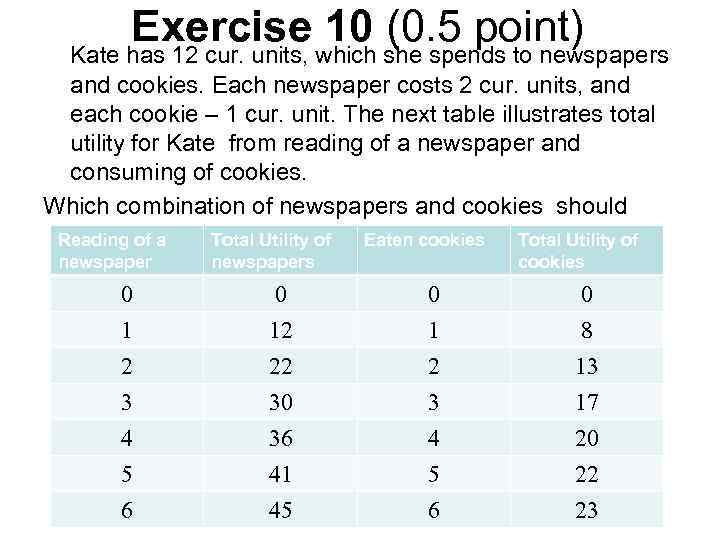 Exercise 10 (0. 5 point) Kate has 12 cur. units, which she spends to newspapers and cookies. Each newspaper costs 2 cur. units, and each cookie – 1 cur. unit. The next table illustrates total utility for Kate from reading of a newspaper and consuming of cookies. Which combination of newspapers and cookies should select Kate for total utility optimization. Reading of a Total Utility of Eaten cookies Total Utility of newspapers cookies 0 1 2 0 12 22 0 1 2 0 8 13 3 4 5 6 30 36 41 45 3 4 5 6 17 20 22 23
Exercise 10 (0. 5 point) Kate has 12 cur. units, which she spends to newspapers and cookies. Each newspaper costs 2 cur. units, and each cookie – 1 cur. unit. The next table illustrates total utility for Kate from reading of a newspaper and consuming of cookies. Which combination of newspapers and cookies should select Kate for total utility optimization. Reading of a Total Utility of Eaten cookies Total Utility of newspapers cookies 0 1 2 0 12 22 0 1 2 0 8 13 3 4 5 6 30 36 41 45 3 4 5 6 17 20 22 23
 Exercise 11 (0. 5 point) • Marginal utility of two products are given in the following table: # of portion Sweets (MU) Apple (MU) 1 60 150 2 40 120 3 20 90 Price of 1 kg sweets -80 cur. unit, and price of 1 kg apple– 160 cur. unit. Consumer budget is 400 cur. unit. Find optimal consumption volume of sweets and apple.
Exercise 11 (0. 5 point) • Marginal utility of two products are given in the following table: # of portion Sweets (MU) Apple (MU) 1 60 150 2 40 120 3 20 90 Price of 1 kg sweets -80 cur. unit, and price of 1 kg apple– 160 cur. unit. Consumer budget is 400 cur. unit. Find optimal consumption volume of sweets and apple.
 Exercise 12 (0. 5 point) The demand function of product X is Qdx=14 -Px + 0. 1 Py. The price of product X – 6 cur. unit, price of product Y – 10 cur. Unit. Find the ratio of cross elasticity of demand of producr X by price of product Y.
Exercise 12 (0. 5 point) The demand function of product X is Qdx=14 -Px + 0. 1 Py. The price of product X – 6 cur. unit, price of product Y – 10 cur. Unit. Find the ratio of cross elasticity of demand of producr X by price of product Y.
 Exercise 13 (0. 5 points) • The demand function of product is Qd=8 P, and supply function of product is Qs = 4 + 2 P. Assume , that tax was introduced as 20% of buyer’s price. Calculate the consumer surplus pre and post tax introduction.
Exercise 13 (0. 5 points) • The demand function of product is Qd=8 P, and supply function of product is Qs = 4 + 2 P. Assume , that tax was introduced as 20% of buyer’s price. Calculate the consumer surplus pre and post tax introduction.
 Exercise 14 ( 0. 5 point) The fixed cost of a company is 80 cur. unit. The function of marginal cost is MC = 30 – 10 Q + 6 Q^2 + 1. 6 Q^3 Find the function of company’s total cost and calculate this cost in output 3 product units.
Exercise 14 ( 0. 5 point) The fixed cost of a company is 80 cur. unit. The function of marginal cost is MC = 30 – 10 Q + 6 Q^2 + 1. 6 Q^3 Find the function of company’s total cost and calculate this cost in output 3 product units.
 Exercise 15 (0. 5 point) Demand function to product of monopoly is Qd=16 -P, and function of total cost TC =14+Q^2. What is the price of monopoly in order to maximize profit?
Exercise 15 (0. 5 point) Demand function to product of monopoly is Qd=16 -P, and function of total cost TC =14+Q^2. What is the price of monopoly in order to maximize profit?
 Exercise 16 (0. 5 point) The total cost function of monopoly is TC=30 + 20 Q; and demand function of monopoly in two markets are: P 1=40 -2 Q 1, P 2 = 80 – 10 Q 2. Determine sale volume and prices on two markets that maximize profit of monopoly.
Exercise 16 (0. 5 point) The total cost function of monopoly is TC=30 + 20 Q; and demand function of monopoly in two markets are: P 1=40 -2 Q 1, P 2 = 80 – 10 Q 2. Determine sale volume and prices on two markets that maximize profit of monopoly.
 Exercise 17 (0. 5 point) Demand function to product of monopoly is Qd=180 -2 P, and function of total cost TC =2 Q^2+90. What is the price of monopoly in order to maximize profit?
Exercise 17 (0. 5 point) Demand function to product of monopoly is Qd=180 -2 P, and function of total cost TC =2 Q^2+90. What is the price of monopoly in order to maximize profit?
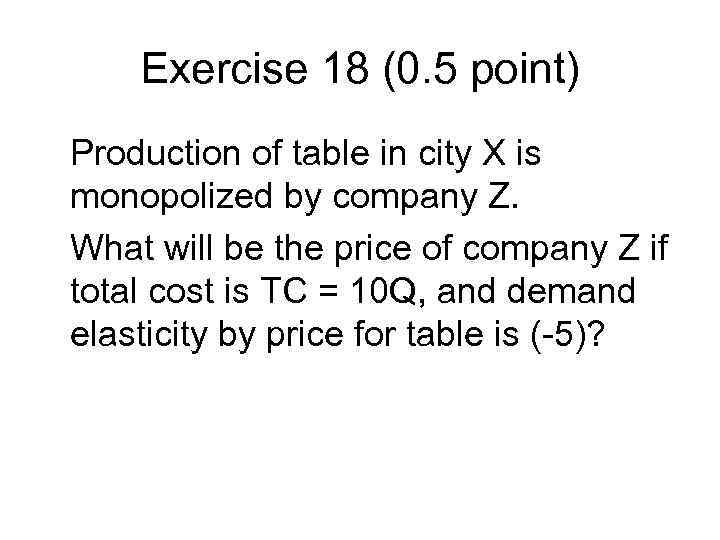 Exercise 18 (0. 5 point) Production of table in city X is monopolized by company Z. What will be the price of company Z if total cost is TC = 10 Q, and demand elasticity by price for table is (-5)?
Exercise 18 (0. 5 point) Production of table in city X is monopolized by company Z. What will be the price of company Z if total cost is TC = 10 Q, and demand elasticity by price for table is (-5)?
 Exercise 19 (0. 5 point) The total cost function of monopoly is TC=30000 + 50 Q, demand function of product is P=100 - 0. 01 Q. Find: a)Price in which profit is maximum, also this profit b)Price and profit in which tax in the amount of 10 cur. unit per product is paid c)Price and profit, if a company will pay tax for capital as amount of 200 cur. unit
Exercise 19 (0. 5 point) The total cost function of monopoly is TC=30000 + 50 Q, demand function of product is P=100 - 0. 01 Q. Find: a)Price in which profit is maximum, also this profit b)Price and profit in which tax in the amount of 10 cur. unit per product is paid c)Price and profit, if a company will pay tax for capital as amount of 200 cur. unit
 Exercise 20 (0. 5 point) Price Demand volume 9 0 8 1 7 2 6 3 5 4 4 5 3 6 2 7 1 8 0 9 The price of demand of monopoly is given in the table. a) calculate marginal revenue of monopoly b)What is output for profit maximization of monopoly in fixed marginal cost as 5 cur. unit.
Exercise 20 (0. 5 point) Price Demand volume 9 0 8 1 7 2 6 3 5 4 4 5 3 6 2 7 1 8 0 9 The price of demand of monopoly is given in the table. a) calculate marginal revenue of monopoly b)What is output for profit maximization of monopoly in fixed marginal cost as 5 cur. unit.
 Exercise 21 (0. 5 point) The population demand function of a product Qd=8 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -5+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 2 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 1 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
Exercise 21 (0. 5 point) The population demand function of a product Qd=8 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -5+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 2 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 1 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
 Exercise 22 (0. 5 point) • Assume, we have the following information about company’s activity, its marginal revenue is given by function MR = 1000 – 20 Q, marginal cost MC = 100 + 10 Q What is the amount of product and price if: a) a firm is acting as monopoly b) a firm is acting in conditions of perfect competition
Exercise 22 (0. 5 point) • Assume, we have the following information about company’s activity, its marginal revenue is given by function MR = 1000 – 20 Q, marginal cost MC = 100 + 10 Q What is the amount of product and price if: a) a firm is acting as monopoly b) a firm is acting in conditions of perfect competition
 Exercise 23 (0. 5 point) • The demand function of product is Qd=153 P, and supply function of product is Qs = -5 + 2 P. Assume , that tax was introduced as 20% of buyer’s price. Calculate the consumer surplus pre and post tax introduction.
Exercise 23 (0. 5 point) • The demand function of product is Qd=153 P, and supply function of product is Qs = -5 + 2 P. Assume , that tax was introduced as 20% of buyer’s price. Calculate the consumer surplus pre and post tax introduction.
 Exercise 24 (0. 5 point) The total cost function of monopoly is TC = 2 Q^2+90, and function of demand is Q=180 -2 P. Determine the price of profit maximization.
Exercise 24 (0. 5 point) The total cost function of monopoly is TC = 2 Q^2+90, and function of demand is Q=180 -2 P. Determine the price of profit maximization.
 Exercise 25 (0. 5 point) The population demand function of a product Qd=8 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -5+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 3 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 2 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
Exercise 25 (0. 5 point) The population demand function of a product Qd=8 -P. The supply function of the product is Qs= -5+2 P, where Qd and Qs – demand supply volumes in mln units per year, P – price in tg. 1) 2) 3) 4) Determine the equilibrium price and sales volume Assume that the fixed price is set 3 tg per unit. Determine sales volume and the volume of unsatisfied demand (deficit). Assume that a new tax paid by a seller in an amount of 2 tg per unit was introduced to this product. Find the equilibrium sales volume and prices for a customer (P+) and seller (P-). Determine surplus of a seller and buyer until and after tax introduction. Calculate the amount of tax revenues to budget. Estimate public losses from the tax introduction.
 Exercise 26 (0. 5 point) Cost 1000 tg Excise Duty 10% VAT 12% Selling price with VAT 4000 tg Wholeseller’s markup 10% Retailer’s markup 25% Find profit and retailing price. Also shw the structure of retailing price as a pie diagram.
Exercise 26 (0. 5 point) Cost 1000 tg Excise Duty 10% VAT 12% Selling price with VAT 4000 tg Wholeseller’s markup 10% Retailer’s markup 25% Find profit and retailing price. Also shw the structure of retailing price as a pie diagram.
 Exercise 27 (0. 5 point) A firm is producing cigarettes and acting in terms of monopolistic competition. The function of marginal revenue of firm is as MR = 10 -2 Q, and increasing part of long term marginal cost curve is LMC= 2 Q-2. If minimum meaning of long term average cost (LAC) is equal to 6, what is the surplus of production power for company?
Exercise 27 (0. 5 point) A firm is producing cigarettes and acting in terms of monopolistic competition. The function of marginal revenue of firm is as MR = 10 -2 Q, and increasing part of long term marginal cost curve is LMC= 2 Q-2. If minimum meaning of long term average cost (LAC) is equal to 6, what is the surplus of production power for company?
 Exercise 28 (0. 5 point) • Two firms are acting in industry, and marginal cost of them is same and equal to zero. Demand of indusry’s product is P=100 -Q. Determine price and production volume, if there is free competition in industry. Determine price and volume of production, if companies are incorporated into cartel.
Exercise 28 (0. 5 point) • Two firms are acting in industry, and marginal cost of them is same and equal to zero. Demand of indusry’s product is P=100 -Q. Determine price and production volume, if there is free competition in industry. Determine price and volume of production, if companies are incorporated into cartel.
 Exercise 29 (0. 5 point) Two firms are acting in industry, they divide market equally. Demand on product of this industry is P= 400 – 2 Q. Marginal cost of firm is fixed and equal to 10. How many products are produced by each firm and what is the market price?
Exercise 29 (0. 5 point) Two firms are acting in industry, they divide market equally. Demand on product of this industry is P= 400 – 2 Q. Marginal cost of firm is fixed and equal to 10. How many products are produced by each firm and what is the market price?
 Exercise 30 (0. 5 point) The company is a perfect competitor on factor market (labor). In determined capital the production function is Q=200 L – 5 L^2. The rate of wage (w) is 100 cur. units, amd product price (p) = 5 cur. units. 1)Determine the demand function of a firm by labor (Ld) 2) How many Labur is used by company?
Exercise 30 (0. 5 point) The company is a perfect competitor on factor market (labor). In determined capital the production function is Q=200 L – 5 L^2. The rate of wage (w) is 100 cur. units, amd product price (p) = 5 cur. units. 1)Determine the demand function of a firm by labor (Ld) 2) How many Labur is used by company?
 Exercise 31 (0. 5 point) Select the better option of getting income by interest rate I =10% 1)Whole life rent by amount of 2600 cur. unit in year 2)Getting revenue by the following chart: 5000 first year and 8000 at the end of second year and 20600 at the enf of third year.
Exercise 31 (0. 5 point) Select the better option of getting income by interest rate I =10% 1)Whole life rent by amount of 2600 cur. unit in year 2)Getting revenue by the following chart: 5000 first year and 8000 at the end of second year and 20600 at the enf of third year.
 Exercise 32 (0. 5 point) A firm is staying in terms of perfect competition on market of product and labor. Its production function is Q=120 L – 2 L^2. The wage rate is 40 cur units, product price is 10 cur. units. Determine optimal product output for the firm.
Exercise 32 (0. 5 point) A firm is staying in terms of perfect competition on market of product and labor. Its production function is Q=120 L – 2 L^2. The wage rate is 40 cur units, product price is 10 cur. units. Determine optimal product output for the firm.
 Exercise 33 (0. 5 point) A person is expecting to get the next revenues: 100 cur. unit in the first year, 150 in second, 200 in third, 250 cur. unit in fourth year. Interest rate 20 % annually. What is the today value for incomes in 4 years.
Exercise 33 (0. 5 point) A person is expecting to get the next revenues: 100 cur. unit in the first year, 150 in second, 200 in third, 250 cur. unit in fourth year. Interest rate 20 % annually. What is the today value for incomes in 4 years.


