e6c47d075ff8d29847ac930f9df30fb9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 “Tutorial on Technical Challenges Associated with the Evolution to Vo. IP” Presented by: Susan Spradley – President, Wireline Networks Alan Stoddard – General Manager, Carrier Next Generation Networks FCC Office of Engineering and Technology September 22, 2003 FCC – Office of Engineering and Technology
“Tutorial on Technical Challenges Associated with the Evolution to Vo. IP” Presented by: Susan Spradley – President, Wireline Networks Alan Stoddard – General Manager, Carrier Next Generation Networks FCC Office of Engineering and Technology September 22, 2003 FCC – Office of Engineering and Technology
 Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 2
Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 2
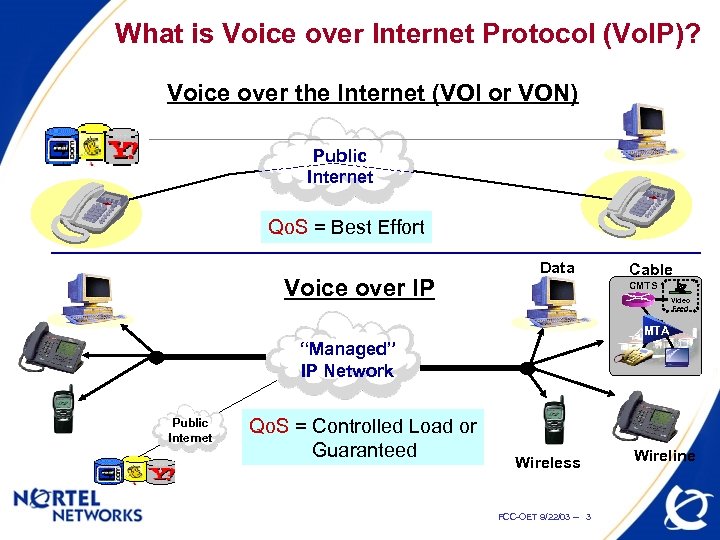 What is Voice over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP)? Voice over the Internet (VOI or VON) Public Internet Qo. S = Best Effort Voice over IP Data Cable CMTS Video Feed MTA “Managed” IP Network Public Internet Qo. S = Controlled Load or Guaranteed Wireless FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 3 Wireline
What is Voice over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP)? Voice over the Internet (VOI or VON) Public Internet Qo. S = Best Effort Voice over IP Data Cable CMTS Video Feed MTA “Managed” IP Network Public Internet Qo. S = Controlled Load or Guaranteed Wireless FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 3 Wireline
 Telecommunication Network Transitions Analog to Digital to Packet POTS SS 7, CLASS features Multimedia, Personalization Service Drivers BETTY JONES 919 -992 -1295 Large Offices Operation Drivers Regulation & Standards 1: 05 Office Consolidation Network Consolidation Voice Data Video One Chief Clear Regulation/Standards Evolving Regulations Multiple Forums Driving Standards Packet conversion, like Digital conversion, driven by Business Case FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 4
Telecommunication Network Transitions Analog to Digital to Packet POTS SS 7, CLASS features Multimedia, Personalization Service Drivers BETTY JONES 919 -992 -1295 Large Offices Operation Drivers Regulation & Standards 1: 05 Office Consolidation Network Consolidation Voice Data Video One Chief Clear Regulation/Standards Evolving Regulations Multiple Forums Driving Standards Packet conversion, like Digital conversion, driven by Business Case FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 4
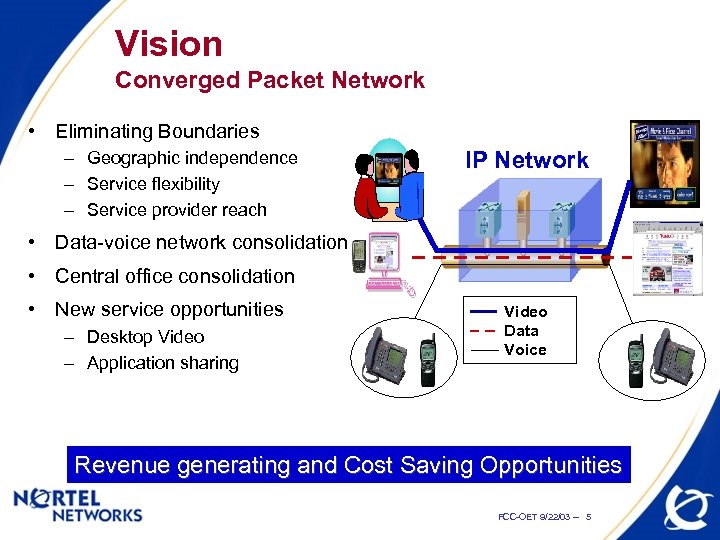 Vision Converged Packet Network • Eliminating Boundaries – Geographic independence – Service flexibility – Service provider reach IP Network • Data-voice network consolidation • Central office consolidation • New service opportunities – Desktop Video – Application sharing Video Data Voice Revenue generating and Cost Saving Opportunities FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 5
Vision Converged Packet Network • Eliminating Boundaries – Geographic independence – Service flexibility – Service provider reach IP Network • Data-voice network consolidation • Central office consolidation • New service opportunities – Desktop Video – Application sharing Video Data Voice Revenue generating and Cost Saving Opportunities FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 5
 Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 6
Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 6
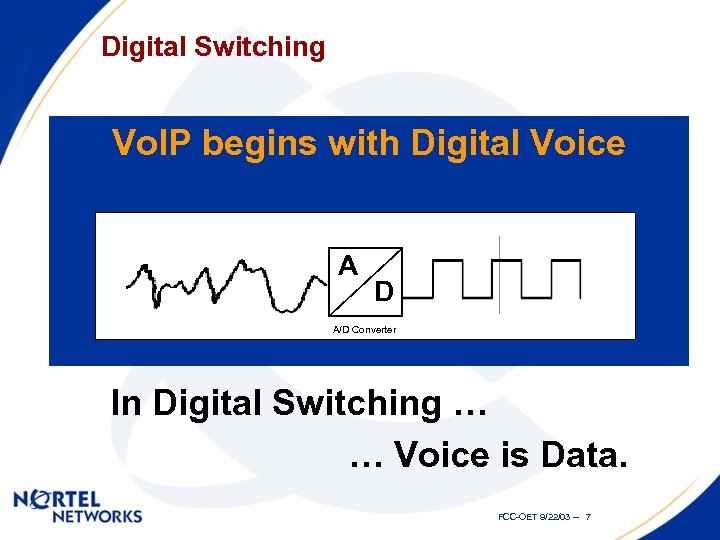 Digital Switching Vo. IP begins with Digital Voice A D A/D Converter In Digital Switching … … Voice is Data. FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 7
Digital Switching Vo. IP begins with Digital Voice A D A/D Converter In Digital Switching … … Voice is Data. FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 7
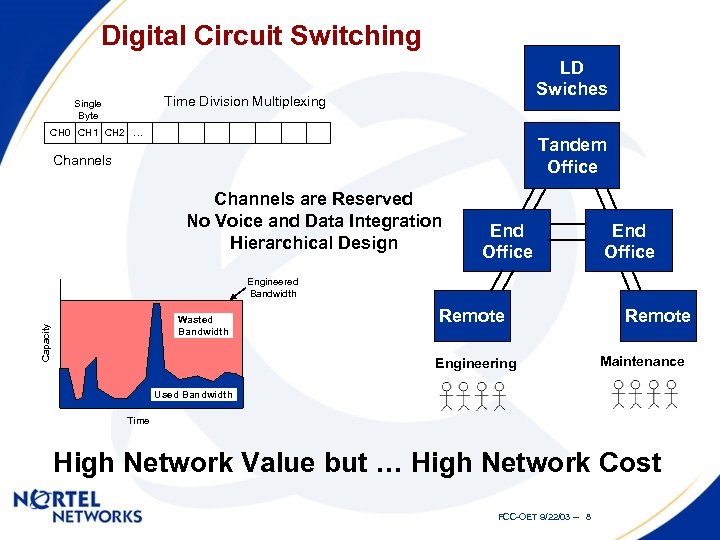 Digital Circuit Switching LD Swiches Time Division Multiplexing Single Byte CH 0 CH 1 CH 2 … Tandem Office Channels are Reserved No Voice and Data Integration Hierarchical Design End Office Engineered Bandwidth Capacity Wasted Bandwidth Remote Engineering Remote Maintenance Used Bandwidth Time High Network Value but … High Network Cost FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 8
Digital Circuit Switching LD Swiches Time Division Multiplexing Single Byte CH 0 CH 1 CH 2 … Tandem Office Channels are Reserved No Voice and Data Integration Hierarchical Design End Office Engineered Bandwidth Capacity Wasted Bandwidth Remote Engineering Remote Maintenance Used Bandwidth Time High Network Value but … High Network Cost FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 8
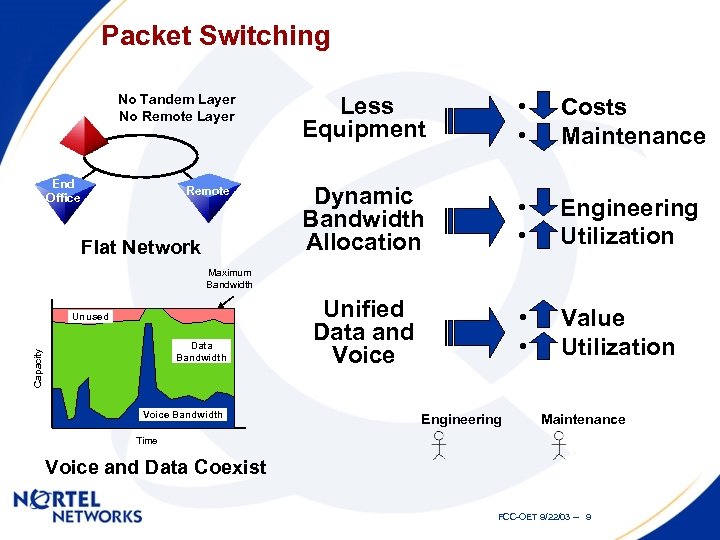 Packet Switching No Tandem Layer No Remote Layer End Office Remote Flat Network Less Equipment • • Costs Maintenance Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation • • Engineering Utilization Unified Data and Voice • • Value Utilization Maximum Bandwidth Unused Capacity Data Bandwidth Voice Bandwidth Engineering Maintenance Time Voice and Data Coexist FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 9
Packet Switching No Tandem Layer No Remote Layer End Office Remote Flat Network Less Equipment • • Costs Maintenance Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation • • Engineering Utilization Unified Data and Voice • • Value Utilization Maximum Bandwidth Unused Capacity Data Bandwidth Voice Bandwidth Engineering Maintenance Time Voice and Data Coexist FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 9
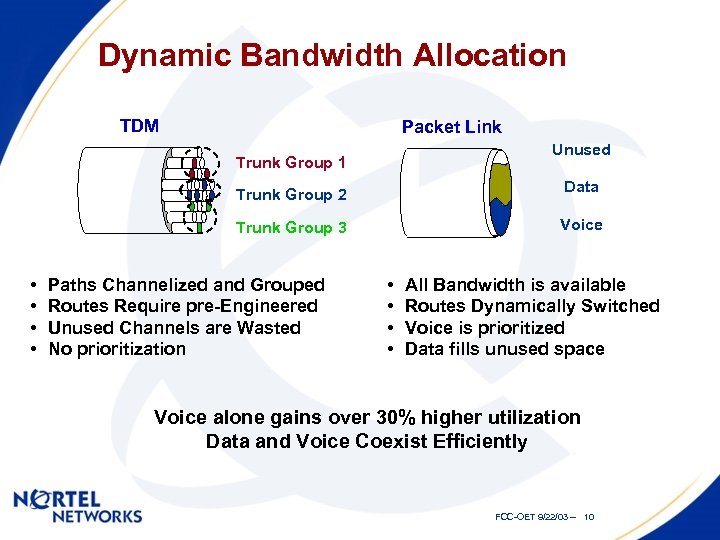 Value Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation TDM Packet Link Unused Trunk Group 1 Data Trunk Group 2 Voice Trunk Group 3 • • Paths Channelized and Grouped Routes Require pre-Engineered Unused Channels are Wasted No prioritization • • All Bandwidth is available Routes Dynamically Switched Voice is prioritized Data fills unused space Voice alone gains over 30% higher utilization Data and Voice Coexist Efficiently FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 10
Value Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation TDM Packet Link Unused Trunk Group 1 Data Trunk Group 2 Voice Trunk Group 3 • • Paths Channelized and Grouped Routes Require pre-Engineered Unused Channels are Wasted No prioritization • • All Bandwidth is available Routes Dynamically Switched Voice is prioritized Data fills unused space Voice alone gains over 30% higher utilization Data and Voice Coexist Efficiently FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 10
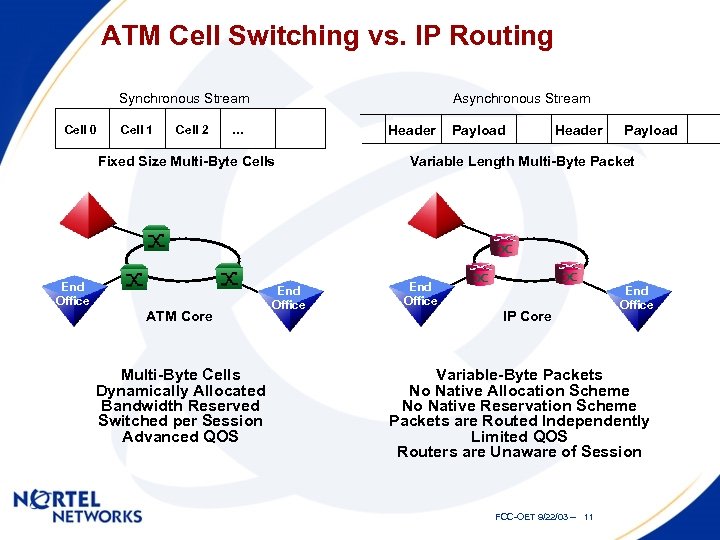 ATM Cell Switching vs. IP Routing Synchronous Stream Cell 0 Cell 1 Cell 2 Asynchronous Stream Header … Fixed Size Multi-Byte Cells End Office ATM Core Multi-Byte Cells Dynamically Allocated Bandwidth Reserved Switched per Session Advanced QOS End Office Payload Header Payload Variable Length Multi-Byte Packet End Office IP Core End Office Variable-Byte Packets No Native Allocation Scheme No Native Reservation Scheme Packets are Routed Independently Limited QOS Routers are Unaware of Session FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 11
ATM Cell Switching vs. IP Routing Synchronous Stream Cell 0 Cell 1 Cell 2 Asynchronous Stream Header … Fixed Size Multi-Byte Cells End Office ATM Core Multi-Byte Cells Dynamically Allocated Bandwidth Reserved Switched per Session Advanced QOS End Office Payload Header Payload Variable Length Multi-Byte Packet End Office IP Core End Office Variable-Byte Packets No Native Allocation Scheme No Native Reservation Scheme Packets are Routed Independently Limited QOS Routers are Unaware of Session FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 11
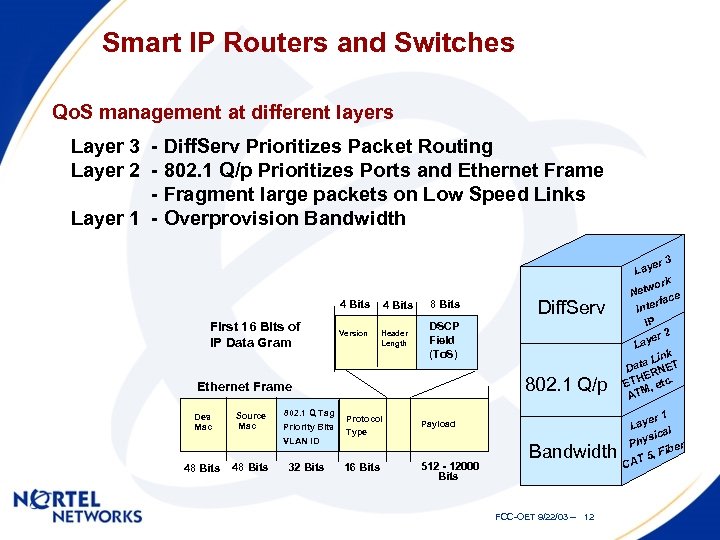 Smart IP Routers and Switches Qo. S management at different layers Layer 3 - Diff. Serv Prioritizes Packet Routing Layer 2 - 802. 1 Q/p Prioritizes Ports and Ethernet Frame - Fragment large packets on Low Speed Links Layer 1 - Overprovision Bandwidth 4 Bits First 16 Bits of IP Data Gram 4 Bits 8 Bits Version Header Length DSCP Field (To. S) 802. 1 Q/p Ethernet Frame Des Mac t Source Mac 802. 1 Q Tag • Priority Bits • VLAN ID 48 Bits 32 Bits Diff. Serv Protocol Type Payload 16 Bits 512 - 12000 Bits Bandwidth FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 12 er 3 Lay k wor Net face nter I IP er 2 Lay k Lin ata NET D ER ETH , etc. ATM er 1 Lay l sica Phy r Fibe T 5, CA
Smart IP Routers and Switches Qo. S management at different layers Layer 3 - Diff. Serv Prioritizes Packet Routing Layer 2 - 802. 1 Q/p Prioritizes Ports and Ethernet Frame - Fragment large packets on Low Speed Links Layer 1 - Overprovision Bandwidth 4 Bits First 16 Bits of IP Data Gram 4 Bits 8 Bits Version Header Length DSCP Field (To. S) 802. 1 Q/p Ethernet Frame Des Mac t Source Mac 802. 1 Q Tag • Priority Bits • VLAN ID 48 Bits 32 Bits Diff. Serv Protocol Type Payload 16 Bits 512 - 12000 Bits Bandwidth FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 12 er 3 Lay k wor Net face nter I IP er 2 Lay k Lin ata NET D ER ETH , etc. ATM er 1 Lay l sica Phy r Fibe T 5, CA
 Speech Codecs G. 711: “uncompressed” TDM coding: PSTN standard Compression (reduction in required bit-rate, e. g. , G. 729) • Accommodate access link speed (e. g. , wireless) • Reduce bandwidth needed in core: − trade off compression against cost Concerns • • Baseline voice quality will be lower for lower bit-rates Increased end-to-end delay Reduced performance with expected packet loss rates Transcoding − are there other compression codecs in the network? − how often will multiple transcodings occur in a complicated path? − frequency of use for features requiring transcoding conferencing, voice mail FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 13
Speech Codecs G. 711: “uncompressed” TDM coding: PSTN standard Compression (reduction in required bit-rate, e. g. , G. 729) • Accommodate access link speed (e. g. , wireless) • Reduce bandwidth needed in core: − trade off compression against cost Concerns • • Baseline voice quality will be lower for lower bit-rates Increased end-to-end delay Reduced performance with expected packet loss rates Transcoding − are there other compression codecs in the network? − how often will multiple transcodings occur in a complicated path? − frequency of use for features requiring transcoding conferencing, voice mail FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 13
 Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 14
Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 14
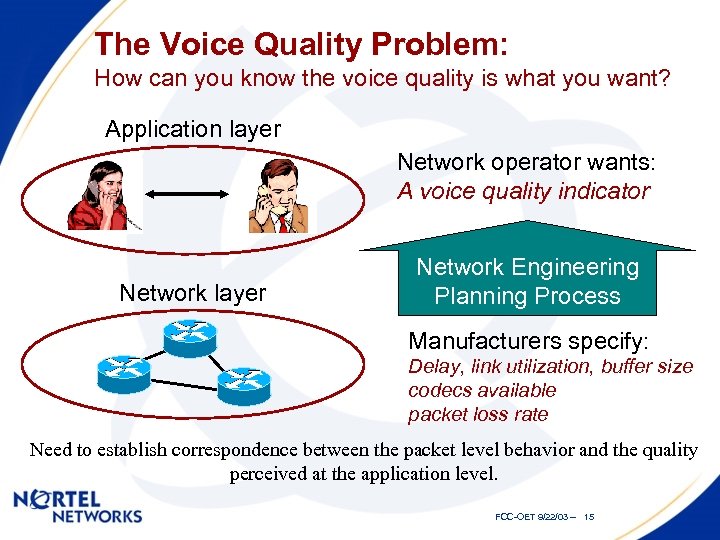 The Voice Quality Problem: How can you know the voice quality is what you want? Application layer Network operator wants: A voice quality indicator Network layer Network Engineering Planning Process Manufacturers specify: Delay, link utilization, buffer size codecs available packet loss rate Need to establish correspondence between the packet level behavior and the quality perceived at the application level. FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 15
The Voice Quality Problem: How can you know the voice quality is what you want? Application layer Network operator wants: A voice quality indicator Network layer Network Engineering Planning Process Manufacturers specify: Delay, link utilization, buffer size codecs available packet loss rate Need to establish correspondence between the packet level behavior and the quality perceived at the application level. FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 15
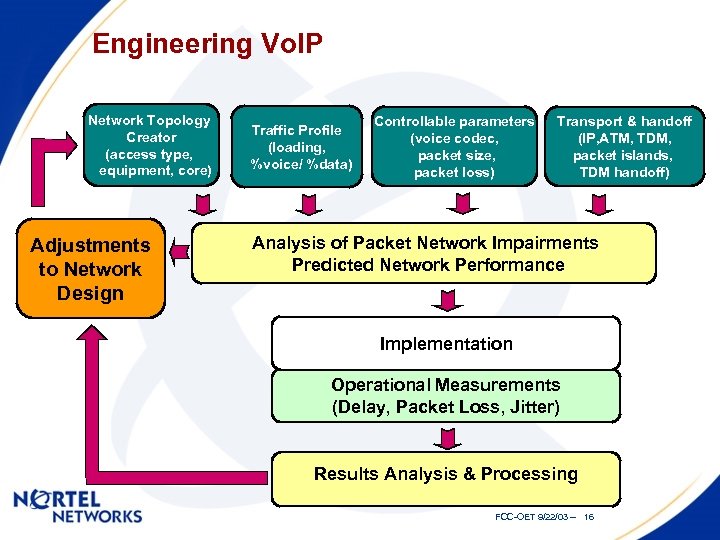 Engineering Vo. IP Network Topology Creator (access type, equipment, core) Adjustments to Network Design Traffic Profile (loading, %voice/ %data) Controllable parameters (voice codec, packet size, packet loss) Transport & handoff (IP, ATM, TDM, packet islands, TDM handoff) Analysis of Packet Network Impairments Predicted Network Performance Implementation Operational Measurements (Delay, Packet Loss, Jitter) Results Analysis & Processing FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 16
Engineering Vo. IP Network Topology Creator (access type, equipment, core) Adjustments to Network Design Traffic Profile (loading, %voice/ %data) Controllable parameters (voice codec, packet size, packet loss) Transport & handoff (IP, ATM, TDM, packet islands, TDM handoff) Analysis of Packet Network Impairments Predicted Network Performance Implementation Operational Measurements (Delay, Packet Loss, Jitter) Results Analysis & Processing FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 16
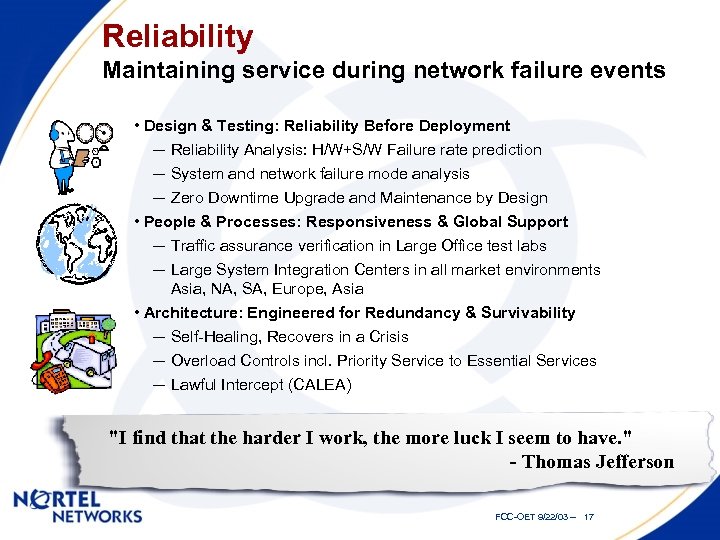 Reliability Maintaining service during network failure events • Design & Testing: Reliability Before Deployment ─ Reliability Analysis: H/W+S/W Failure rate prediction ─ System and network failure mode analysis ─ Zero Downtime Upgrade and Maintenance by Design • People & Processes: Responsiveness & Global Support ─ Traffic assurance verification in Large Office test labs ─ Large System Integration Centers in all market environments Asia, NA, SA, Europe, Asia • Architecture: Engineered for Redundancy & Survivability ─ Self-Healing, Recovers in a Crisis ─ Overload Controls incl. Priority Service to Essential Services ─ Lawful Intercept (CALEA) "I find that the harder I work, the more luck I seem to have. " - Thomas Jefferson FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 17
Reliability Maintaining service during network failure events • Design & Testing: Reliability Before Deployment ─ Reliability Analysis: H/W+S/W Failure rate prediction ─ System and network failure mode analysis ─ Zero Downtime Upgrade and Maintenance by Design • People & Processes: Responsiveness & Global Support ─ Traffic assurance verification in Large Office test labs ─ Large System Integration Centers in all market environments Asia, NA, SA, Europe, Asia • Architecture: Engineered for Redundancy & Survivability ─ Self-Healing, Recovers in a Crisis ─ Overload Controls incl. Priority Service to Essential Services ─ Lawful Intercept (CALEA) "I find that the harder I work, the more luck I seem to have. " - Thomas Jefferson FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 17
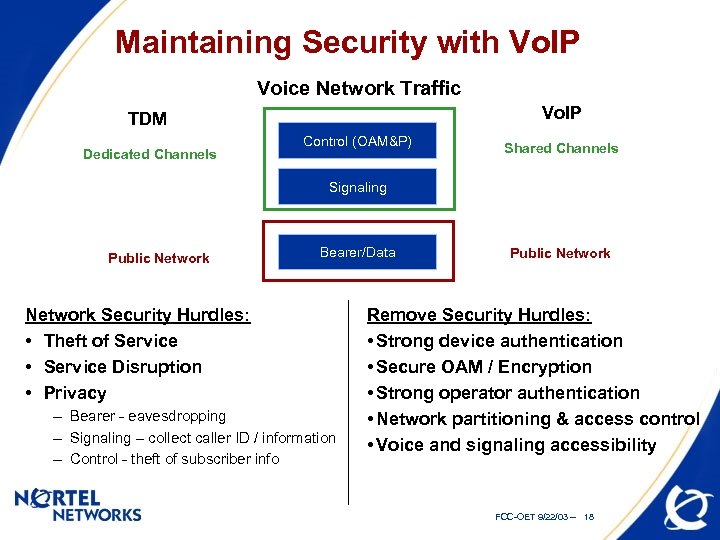 Maintaining Security with Vo. IP Voice Network Traffic Vo. IP TDM Dedicated Channels Control (OAM&P) Shared Channels Signaling Public Network Bearer/Data Network Security Hurdles: • Theft of Service • Service Disruption • Privacy – Bearer - eavesdropping – Signaling – collect caller ID / information – Control - theft of subscriber info Public Network Remove Security Hurdles: • Strong device authentication • Secure OAM / Encryption • Strong operator authentication • Network partitioning & access control • Voice and signaling accessibility FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 18
Maintaining Security with Vo. IP Voice Network Traffic Vo. IP TDM Dedicated Channels Control (OAM&P) Shared Channels Signaling Public Network Bearer/Data Network Security Hurdles: • Theft of Service • Service Disruption • Privacy – Bearer - eavesdropping – Signaling – collect caller ID / information – Control - theft of subscriber info Public Network Remove Security Hurdles: • Strong device authentication • Secure OAM / Encryption • Strong operator authentication • Network partitioning & access control • Voice and signaling accessibility FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 18
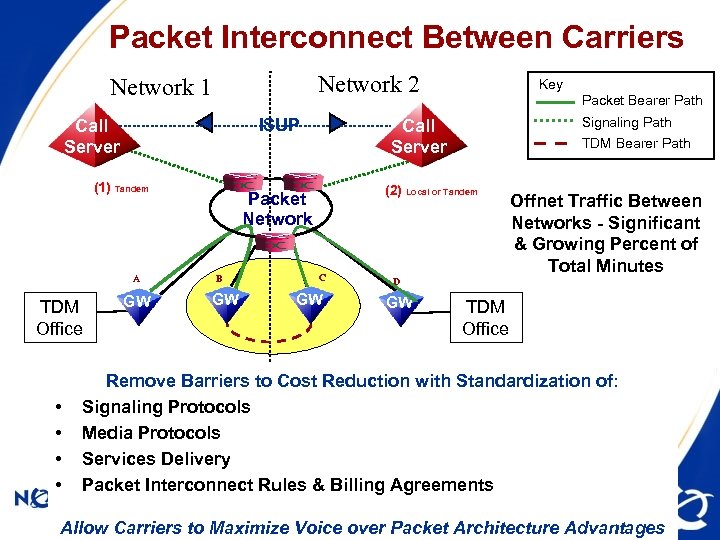 Packet Interconnect Between Carriers Network 2 Network 1 ISUP Call Server (1) Tandem A TDM Office • • GW GW Packet Bearer Path Signaling Path Call Server TDM Bearer Path (2) Local or Tandem Packet Network B Key C GW Offnet Traffic Between Networks - Significant & Growing Percent of Total Minutes D GW TDM Office Remove Barriers to Cost Reduction with Standardization of: Signaling Protocols Media Protocols Services Delivery Packet Interconnect Rules & Billing Agreements FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 19 Allow Carriers to Maximize Voice over Packet Architecture Advantages
Packet Interconnect Between Carriers Network 2 Network 1 ISUP Call Server (1) Tandem A TDM Office • • GW GW Packet Bearer Path Signaling Path Call Server TDM Bearer Path (2) Local or Tandem Packet Network B Key C GW Offnet Traffic Between Networks - Significant & Growing Percent of Total Minutes D GW TDM Office Remove Barriers to Cost Reduction with Standardization of: Signaling Protocols Media Protocols Services Delivery Packet Interconnect Rules & Billing Agreements FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 19 Allow Carriers to Maximize Voice over Packet Architecture Advantages
 Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 20
Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 20
 Technical Transition Models • Enterprise Networks – IP PBX – Hosted Services – Vo. IP VPNs • LD Networks • Local Networks • Beyond Voice -- Multimedia Networks FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 21
Technical Transition Models • Enterprise Networks – IP PBX – Hosted Services – Vo. IP VPNs • LD Networks • Local Networks • Beyond Voice -- Multimedia Networks FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 21
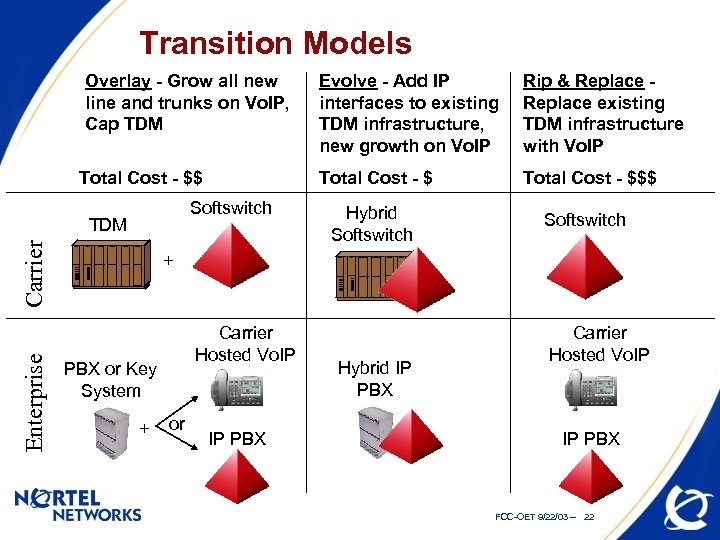 Transition Models Overlay - Grow all new line and trunks on Vo. IP, Cap TDM Carrier Enterprise Softswitch TDM Rip & Replace existing TDM infrastructure with Vo. IP Total Cost - $$ Evolve - Add IP interfaces to existing TDM infrastructure, new growth on Vo. IP Total Cost - $$$ Hybrid Softswitch + Carrier Hosted Vo. IP PBX or Key System + or IP PBX Hybrid IP PBX Carrier Hosted Vo. IP IP PBX FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 22
Transition Models Overlay - Grow all new line and trunks on Vo. IP, Cap TDM Carrier Enterprise Softswitch TDM Rip & Replace existing TDM infrastructure with Vo. IP Total Cost - $$ Evolve - Add IP interfaces to existing TDM infrastructure, new growth on Vo. IP Total Cost - $$$ Hybrid Softswitch + Carrier Hosted Vo. IP PBX or Key System + or IP PBX Hybrid IP PBX Carrier Hosted Vo. IP IP PBX FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 22
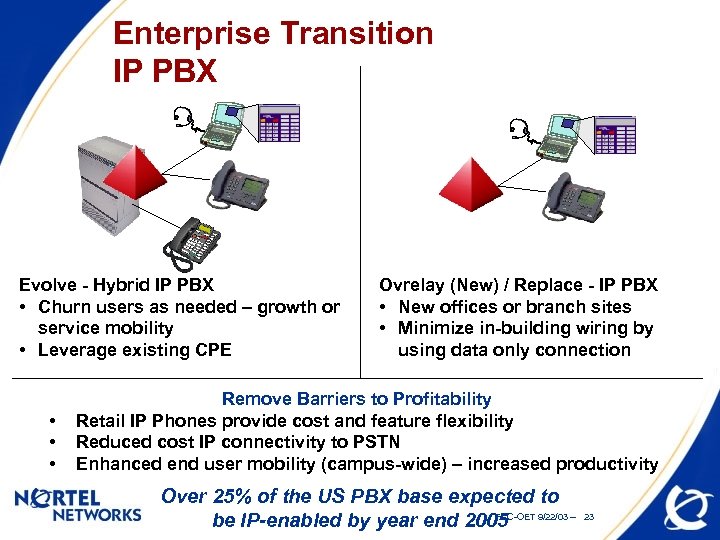 Enterprise Transition IP PBX Evolve - Hybrid IP PBX • Churn users as needed – growth or service mobility • Leverage existing CPE • • • Ovrelay (New) / Replace - IP PBX • New offices or branch sites • Minimize in-building wiring by using data only connection Remove Barriers to Profitability Retail IP Phones provide cost and feature flexibility Reduced cost IP connectivity to PSTN Enhanced end user mobility (campus-wide) – increased productivity Over 25% of the US PBX base expected to FCC-OET be IP-enabled by year end 2005 9/22/03 -- 23
Enterprise Transition IP PBX Evolve - Hybrid IP PBX • Churn users as needed – growth or service mobility • Leverage existing CPE • • • Ovrelay (New) / Replace - IP PBX • New offices or branch sites • Minimize in-building wiring by using data only connection Remove Barriers to Profitability Retail IP Phones provide cost and feature flexibility Reduced cost IP connectivity to PSTN Enhanced end user mobility (campus-wide) – increased productivity Over 25% of the US PBX base expected to FCC-OET be IP-enabled by year end 2005 9/22/03 -- 23
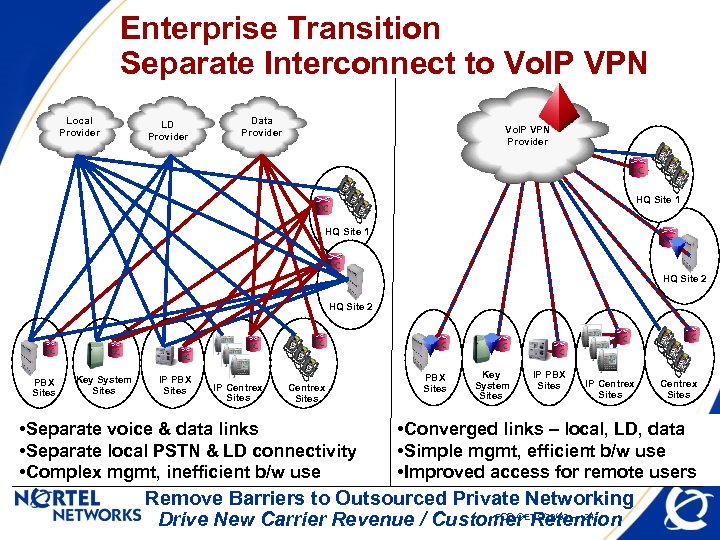 Enterprise Transition Separate Interconnect to Vo. IP VPN Local Provider LD Provider Data Provider Vo. IP VPN Provider HQ Site 1 HQ Site 2 PBX Sites Key System Sites IP PBX Sites IP Centrex Sites • Separate voice & data links • Separate local PSTN & LD connectivity • Complex mgmt, inefficient b/w use PBX Sites Key System Sites IP PBX Sites IP Centrex Sites • Converged links – local, LD, data • Simple mgmt, efficient b/w use • Improved access for remote users Remove Barriers to Outsourced Private Networking FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 24 Drive New Carrier Revenue / Customer Retention
Enterprise Transition Separate Interconnect to Vo. IP VPN Local Provider LD Provider Data Provider Vo. IP VPN Provider HQ Site 1 HQ Site 2 PBX Sites Key System Sites IP PBX Sites IP Centrex Sites • Separate voice & data links • Separate local PSTN & LD connectivity • Complex mgmt, inefficient b/w use PBX Sites Key System Sites IP PBX Sites IP Centrex Sites • Converged links – local, LD, data • Simple mgmt, efficient b/w use • Improved access for remote users Remove Barriers to Outsourced Private Networking FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 24 Drive New Carrier Revenue / Customer Retention
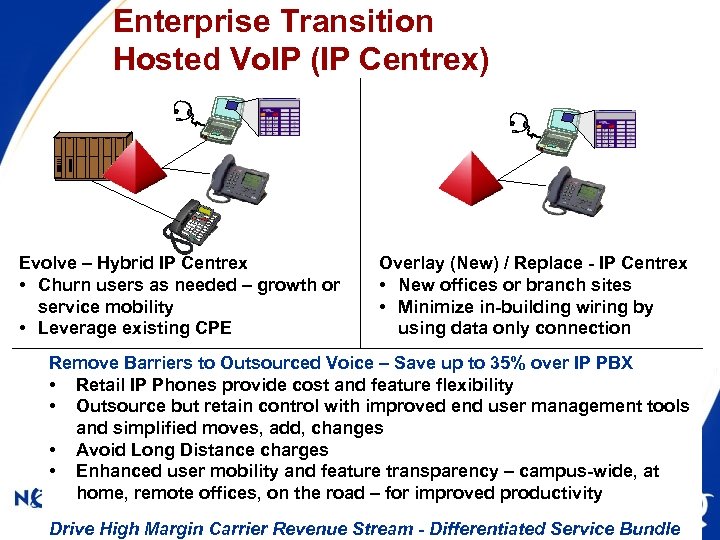 Enterprise Transition Hosted Vo. IP (IP Centrex) Evolve – Hybrid IP Centrex • Churn users as needed – growth or service mobility • Leverage existing CPE Overlay (New) / Replace - IP Centrex • New offices or branch sites • Minimize in-building wiring by using data only connection Remove Barriers to Outsourced Voice – Save up to 35% over IP PBX • Retail IP Phones provide cost and feature flexibility • Outsource but retain control with improved end user management tools and simplified moves, add, changes • Avoid Long Distance charges • Enhanced user mobility and feature transparency – campus-wide, at home, remote offices, on the road – for improved productivity FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 25 Drive High Margin Carrier Revenue Stream - Differentiated Service Bundle
Enterprise Transition Hosted Vo. IP (IP Centrex) Evolve – Hybrid IP Centrex • Churn users as needed – growth or service mobility • Leverage existing CPE Overlay (New) / Replace - IP Centrex • New offices or branch sites • Minimize in-building wiring by using data only connection Remove Barriers to Outsourced Voice – Save up to 35% over IP PBX • Retail IP Phones provide cost and feature flexibility • Outsource but retain control with improved end user management tools and simplified moves, add, changes • Avoid Long Distance charges • Enhanced user mobility and feature transparency – campus-wide, at home, remote offices, on the road – for improved productivity FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 25 Drive High Margin Carrier Revenue Stream - Differentiated Service Bundle
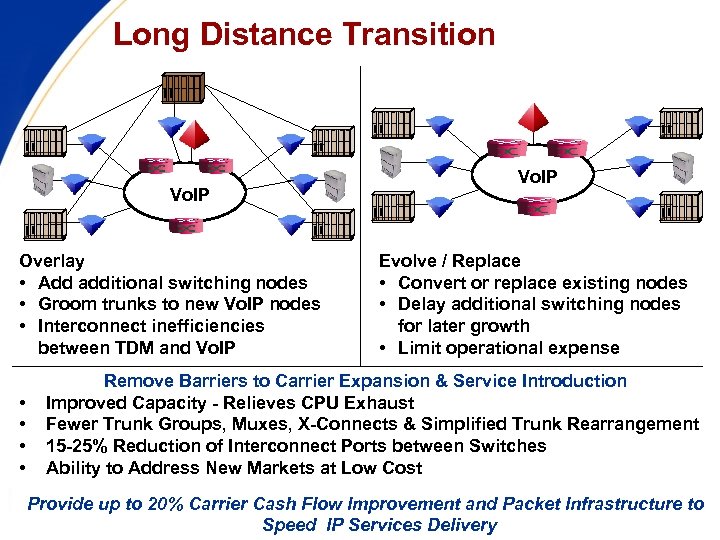 Long Distance Transition Vo. IP Overlay • Add additional switching nodes • Groom trunks to new Vo. IP nodes • Interconnect inefficiencies between TDM and Vo. IP • • Vo. IP Evolve / Replace • Convert or replace existing nodes • Delay additional switching nodes for later growth • Limit operational expense Remove Barriers to Carrier Expansion & Service Introduction Improved Capacity - Relieves CPU Exhaust Fewer Trunk Groups, Muxes, X-Connects & Simplified Trunk Rearrangement 15 -25% Reduction of Interconnect Ports between Switches Ability to Address New Markets at Low Cost Provide up to 20% Carrier Cash Flow Improvement and Packet Infrastructure to FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 26 Speed IP Services Delivery
Long Distance Transition Vo. IP Overlay • Add additional switching nodes • Groom trunks to new Vo. IP nodes • Interconnect inefficiencies between TDM and Vo. IP • • Vo. IP Evolve / Replace • Convert or replace existing nodes • Delay additional switching nodes for later growth • Limit operational expense Remove Barriers to Carrier Expansion & Service Introduction Improved Capacity - Relieves CPU Exhaust Fewer Trunk Groups, Muxes, X-Connects & Simplified Trunk Rearrangement 15 -25% Reduction of Interconnect Ports between Switches Ability to Address New Markets at Low Cost Provide up to 20% Carrier Cash Flow Improvement and Packet Infrastructure to FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 26 Speed IP Services Delivery
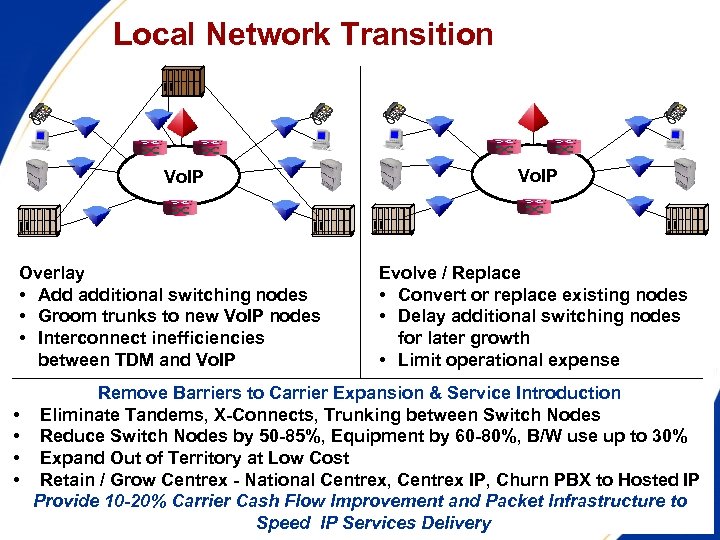 Local Network Transition Vo. IP Overlay • Add additional switching nodes • Groom trunks to new Vo. IP nodes • Interconnect inefficiencies between TDM and Vo. IP • • Vo. IP Evolve / Replace • Convert or replace existing nodes • Delay additional switching nodes for later growth • Limit operational expense Remove Barriers to Carrier Expansion & Service Introduction Eliminate Tandems, X-Connects, Trunking between Switch Nodes Reduce Switch Nodes by 50 -85%, Equipment by 60 -80%, B/W use up to 30% Expand Out of Territory at Low Cost Retain / Grow Centrex - National Centrex, Centrex IP, Churn PBX to Hosted IP Provide 10 -20% Carrier Cash Flow Improvement and Packet Infrastructure to Speed IP Services Delivery FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 27
Local Network Transition Vo. IP Overlay • Add additional switching nodes • Groom trunks to new Vo. IP nodes • Interconnect inefficiencies between TDM and Vo. IP • • Vo. IP Evolve / Replace • Convert or replace existing nodes • Delay additional switching nodes for later growth • Limit operational expense Remove Barriers to Carrier Expansion & Service Introduction Eliminate Tandems, X-Connects, Trunking between Switch Nodes Reduce Switch Nodes by 50 -85%, Equipment by 60 -80%, B/W use up to 30% Expand Out of Territory at Low Cost Retain / Grow Centrex - National Centrex, Centrex IP, Churn PBX to Hosted IP Provide 10 -20% Carrier Cash Flow Improvement and Packet Infrastructure to Speed IP Services Delivery FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 27
 Beyond Voice – Multimedia Transition Multimedia Overlay (New) / Replace • IP phone required • Softclient flexibility – PDAs and PCs become phones • Voice becomes a subset of data services bundle – delivered over DSL or data connection Existing Phone Evolve - Converged Desktop • Traditional voice services maintained with new multimedia add-ons • Existing desktop retained - new phone upgrades at end user driven pace • Utilizes existing TDM SIMRING or IN • Enables ubiquitous service delivery Remove Barriers to New Service Introduction • Simplify communications – Personal Communications Mgr, Unified Messaging • Enhance productivity – Video Calling & Conferencing, Web-Push / Co-Browsing FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 28 Provide New Carrier Revenue Stream & Differentiate Service Set
Beyond Voice – Multimedia Transition Multimedia Overlay (New) / Replace • IP phone required • Softclient flexibility – PDAs and PCs become phones • Voice becomes a subset of data services bundle – delivered over DSL or data connection Existing Phone Evolve - Converged Desktop • Traditional voice services maintained with new multimedia add-ons • Existing desktop retained - new phone upgrades at end user driven pace • Utilizes existing TDM SIMRING or IN • Enables ubiquitous service delivery Remove Barriers to New Service Introduction • Simplify communications – Personal Communications Mgr, Unified Messaging • Enhance productivity – Video Calling & Conferencing, Web-Push / Co-Browsing FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 28 Provide New Carrier Revenue Stream & Differentiate Service Set
 Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 29
Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 29
 Business Transition Network separate from Service Network Transition • Competitive Local: Cable, W-, CLEC – Cities/Municipalities? • More Competitive LD: IXC vs LEC • Data Access: – Res: DSL vs Cable – Biz: LEC vs IXC • Emerging Acccess Implications? – Wireless LANs – Fiber to the Home (FTTH) Services Transition • Voice: LECs to Cable, W-, CLEC • Video: Cable Broadband • IM: Yahoo, AOL to ASP • Client Based Services – SIP Clients – Peer to Peer – Napster Model • Service Provider Based Service – Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, Apple – Business specific Companies – Bring your own broadband Separating Service & Network permits Service ubiquity independent of access FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 30
Business Transition Network separate from Service Network Transition • Competitive Local: Cable, W-, CLEC – Cities/Municipalities? • More Competitive LD: IXC vs LEC • Data Access: – Res: DSL vs Cable – Biz: LEC vs IXC • Emerging Acccess Implications? – Wireless LANs – Fiber to the Home (FTTH) Services Transition • Voice: LECs to Cable, W-, CLEC • Video: Cable Broadband • IM: Yahoo, AOL to ASP • Client Based Services – SIP Clients – Peer to Peer – Napster Model • Service Provider Based Service – Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, Apple – Business specific Companies – Bring your own broadband Separating Service & Network permits Service ubiquity independent of access FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 30
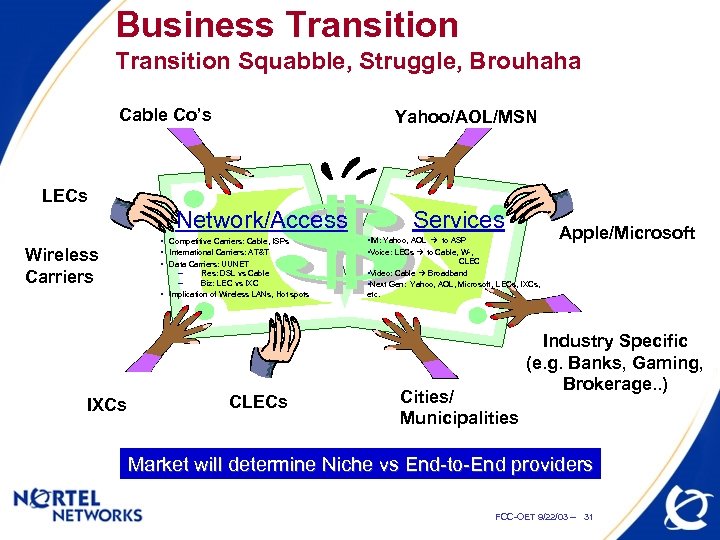 Business Transition Squabble, Struggle, Brouhaha Cable Co’s Yahoo/AOL/MSN LECs Services Network/Access Wireless Carriers IXCs • Competitive Carriers: Cable, ISPs • International Carriers: AT&T • Data Carriers: UUNET – Res: DSL vs Cable – Biz: LEC vs IXC • Implication of Wireless LANs, Hot spots CLECs Apple/Microsoft • IM: Yahoo, AOL to ASP • Voice: LECs to Cable, W-, CLEC • Video: Cable Broadband • Next Gen: Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, LECs, IXCs, etc. Cities/ Municipalities Industry Specific (e. g. Banks, Gaming, Brokerage. . ) Market will determine Niche vs End-to-End providers FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 31
Business Transition Squabble, Struggle, Brouhaha Cable Co’s Yahoo/AOL/MSN LECs Services Network/Access Wireless Carriers IXCs • Competitive Carriers: Cable, ISPs • International Carriers: AT&T • Data Carriers: UUNET – Res: DSL vs Cable – Biz: LEC vs IXC • Implication of Wireless LANs, Hot spots CLECs Apple/Microsoft • IM: Yahoo, AOL to ASP • Voice: LECs to Cable, W-, CLEC • Video: Cable Broadband • Next Gen: Yahoo, AOL, Microsoft, LECs, IXCs, etc. Cities/ Municipalities Industry Specific (e. g. Banks, Gaming, Brokerage. . ) Market will determine Niche vs End-to-End providers FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 31
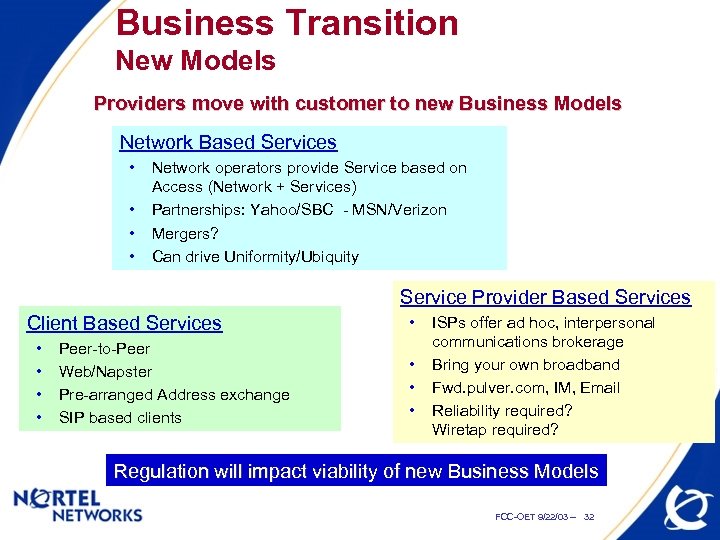 Business Transition New Models Providers move with customer to new Business Models Network Based Services • • Network operators provide Service based on Access (Network + Services) Partnerships: Yahoo/SBC - MSN/Verizon Mergers? Can drive Uniformity/Ubiquity Service Provider Based Services Client Based Services • • Peer-to-Peer Web/Napster Pre-arranged Address exchange SIP based clients • • ISPs offer ad hoc, interpersonal communications brokerage Bring your own broadband Fwd. pulver. com, IM, Email Reliability required? Wiretap required? Regulation will impact viability of new Business Models FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 32
Business Transition New Models Providers move with customer to new Business Models Network Based Services • • Network operators provide Service based on Access (Network + Services) Partnerships: Yahoo/SBC - MSN/Verizon Mergers? Can drive Uniformity/Ubiquity Service Provider Based Services Client Based Services • • Peer-to-Peer Web/Napster Pre-arranged Address exchange SIP based clients • • ISPs offer ad hoc, interpersonal communications brokerage Bring your own broadband Fwd. pulver. com, IM, Email Reliability required? Wiretap required? Regulation will impact viability of new Business Models FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 32
 Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 33
Agenda Introduction IP Telephony Overview Technical Considerations Technical Transition Models Business Transition Models Conclusions FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 33
 Conclusions • Technology is decoupling Service from Access • Users desire ubiquitous service access, personalization and the freedom of mobility • There are technology challenges that need to be considered in developing and deploying IP Telephony • There are both technical transition and business transition models to consider FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 34
Conclusions • Technology is decoupling Service from Access • Users desire ubiquitous service access, personalization and the freedom of mobility • There are technology challenges that need to be considered in developing and deploying IP Telephony • There are both technical transition and business transition models to consider FCC-OET 9/22/03 -- 34


