Acid Base Indicators_ Titration curves.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 46

Tutorial on Indicators and Salt Hydrolysis. Prepared by Lawrence Kok http: //lawrencekok. blogspot. com
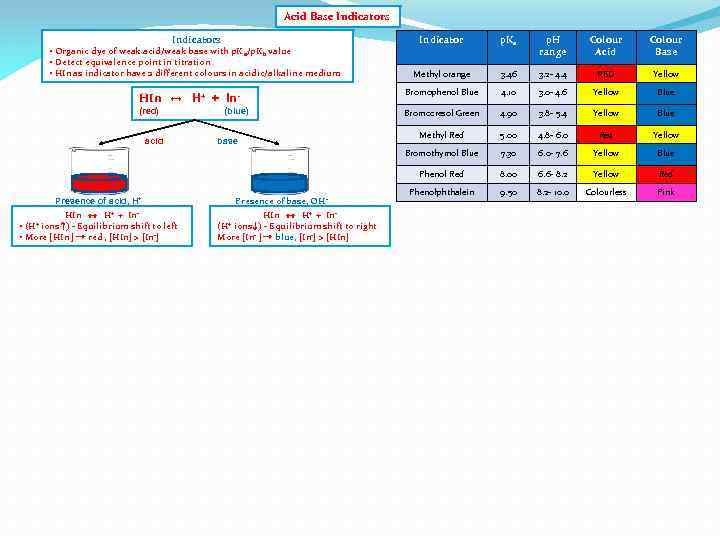
Acid Base Indicators Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow HIn ↔ H+ + In- Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue (red) Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink • Organic dye of weak acid/weak base with p. K a/p. Kb value • Detect equivalence point in titration • HIn as indicator have 2 different colours in acidic/alkaline medium acid (blue) base Presence of base, OH - Presence of acid, H+ HIn ↔ H+ + In • ions ↑) - Equilibrium shift to left • More [HIn ] → red , [HIn] > [In-] (H+ HIn ↔ H+ + Inions ↓) - Equilibrium shift to right More [In- ] → blue, [In-] > [HIn] (H+
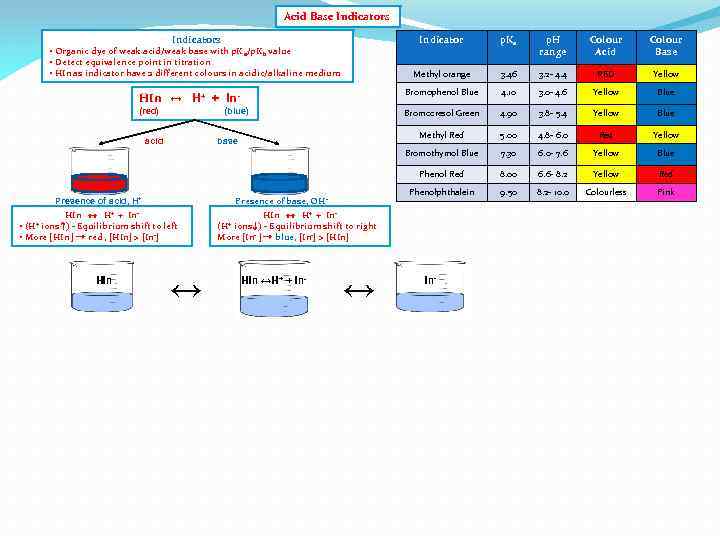
Acid Base Indicators Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow HIn ↔ H+ + In- Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue (red) Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink • Organic dye of weak acid/weak base with p. K a/p. Kb value • Detect equivalence point in titration • HIn as indicator have 2 different colours in acidic/alkaline medium (blue) acid base Presence of base, OH - Presence of acid, H+ HIn ↔ H+ + In • ions ↑) - Equilibrium shift to left • More [HIn ] → red , [HIn] > [In-] (H+ HIn ↔ H+ + Inions ↓) - Equilibrium shift to right More [In- ] → blue, [In-] > [HIn] (H+ HIn ↔H+ + In- ↔ In-
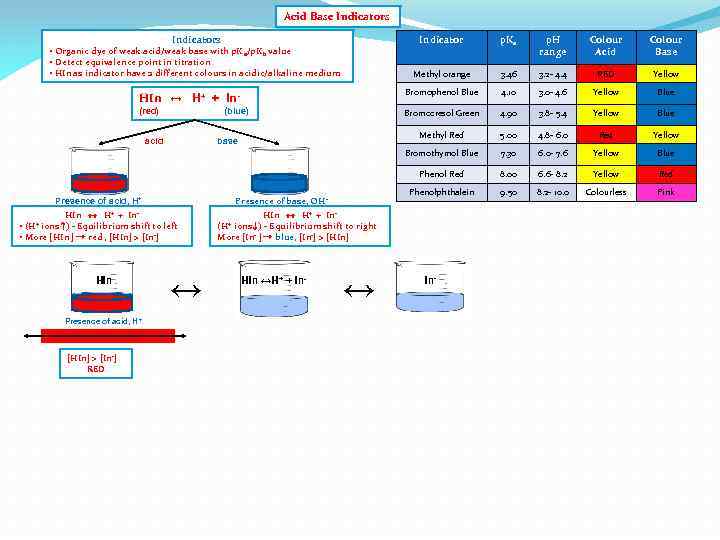
Acid Base Indicators Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow HIn ↔ H+ + In- Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue (red) Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink • Organic dye of weak acid/weak base with p. K a/p. Kb value • Detect equivalence point in titration • HIn as indicator have 2 different colours in acidic/alkaline medium (blue) acid base Presence of base, OH - Presence of acid, H+ HIn ↔ H+ + In • ions ↑) - Equilibrium shift to left • More [HIn ] → red , [HIn] > [In-] (H+ HIn Presence of acid, H + [HIn] > [In-] RED ↔ HIn ↔ H+ + Inions ↓) - Equilibrium shift to right More [In- ] → blue, [In-] > [HIn] (H+ HIn ↔H+ + In- ↔ In-
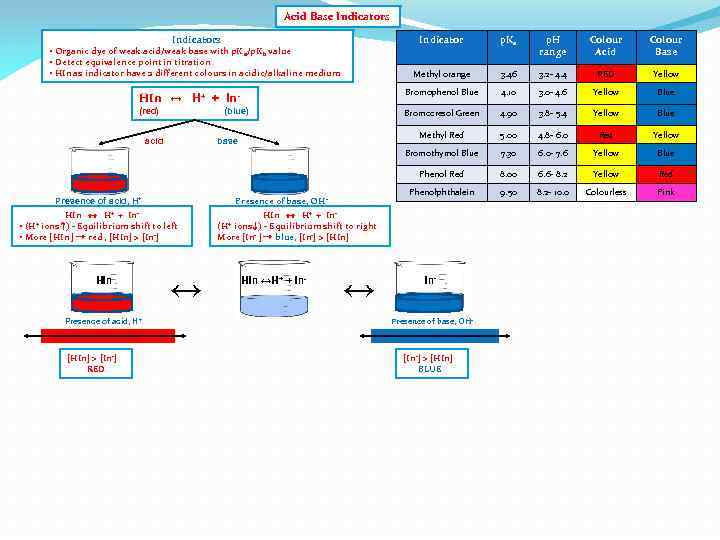
Acid Base Indicators Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow HIn ↔ H+ + In- Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue (red) Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink • Organic dye of weak acid/weak base with p. K a/p. Kb value • Detect equivalence point in titration • HIn as indicator have 2 different colours in acidic/alkaline medium (blue) acid base Presence of base, OH - Presence of acid, H+ HIn ↔ H+ + In • ions ↑) - Equilibrium shift to left • More [HIn ] → red , [HIn] > [In-] (H+ HIn Presence of acid, H + [HIn] > [In-] RED ↔ HIn ↔ H+ + Inions ↓) - Equilibrium shift to right More [In- ] → blue, [In-] > [HIn] (H+ HIn ↔H+ + In- ↔ In- Presence of base, OH- [In-] > [HIn] BLUE
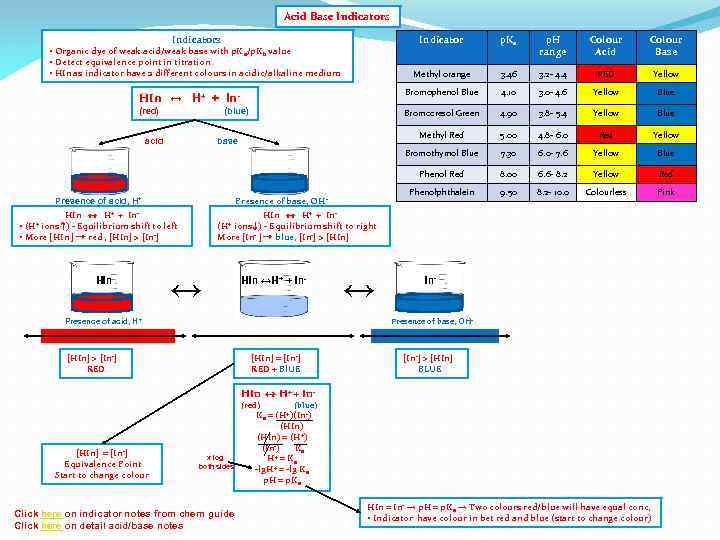
Acid Base Indicators Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow HIn ↔ H+ + In- Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue (red) Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink • Organic dye of weak acid/weak base with p. K a/p. Kb value • Detect equivalence point in titration • HIn as indicator have 2 different colours in acidic/alkaline medium (blue) acid base Presence of base, OH - Presence of acid, H+ HIn ↔ H+ + In • ions ↑) - Equilibrium shift to left • More [HIn ] → red , [HIn] > [In-] HIn ↔ H+ + Inions ↓) - Equilibrium shift to right More [In- ] → blue, [In-] > [HIn] (H+ HIn (H+ ↔ HIn ↔H+ + In- ↔ In- Presence of base, OH- Presence of acid, H + [HIn] > [In-] RED [HIn] = [In-] RED + Bl. UE [In-] > [HIn] BLUE HIn ↔ H+ + In(red) [HIn] = [In-] Equivalence Point Start to change colour x log both sides Click here on indicator notes from chem guide Click here on detail acid/base notes (blue) Ka = (H+)(In-) (HIn) = (H+) (In-) Ka H+ = Ka -lg. H+ = -lg Ka p. H = p. Ka HIn = In- → p. H = p. Ka → Two colours red/blue will have equal conc, • Indicator have colour in bet red and blue (start to change colour)
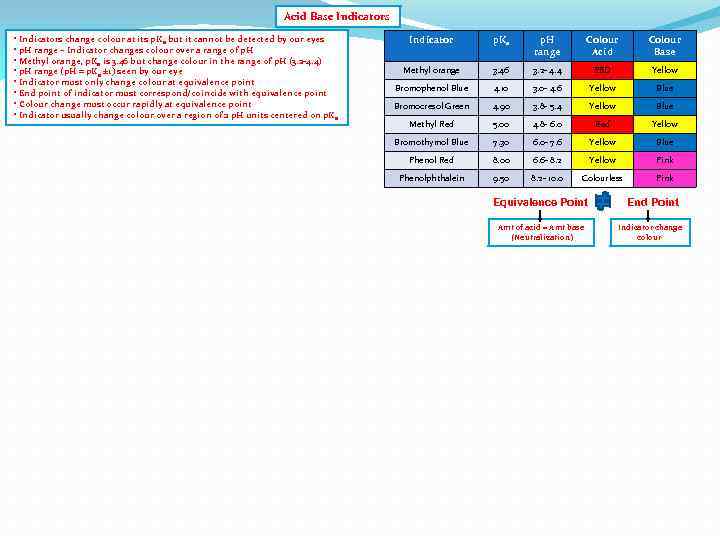
Acid Base Indicators • Indicators change colour at its p. Ka but it cannot be detected by our eyes • p. H range – Indicator changes colour over a range of p. H • Methyl orange, p. Ka is 3. 46 but change colour in the range of p. H (3. 2 -4. 4) • p. H range (p. H = p. Ka ± 1) seen by our eye • Indicator must only change colour at equivalence point • End point of indicator must correspond/coincide with equivalence point • Colour change must occur rapidly at equivalence point • Indicator usually change colour over a region of 2 p. H units centered on p. Ka Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Pink Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Equivalence Point Amt of acid = Amt base (Neutralization) End Point Indicator change colour
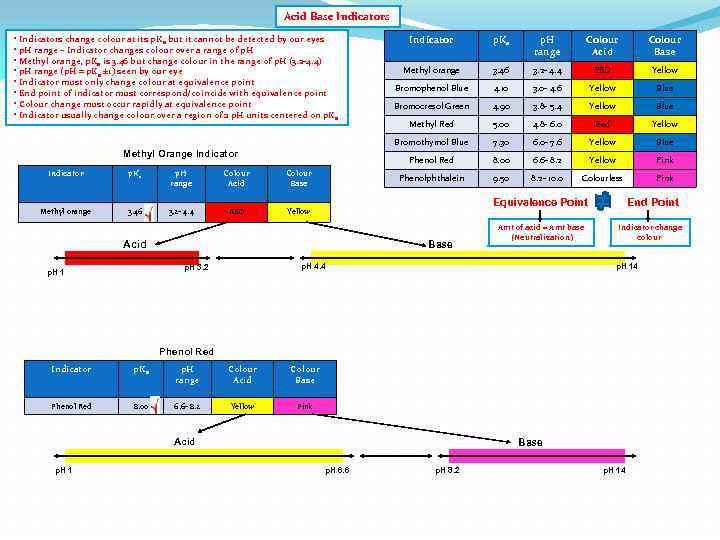
Acid Base Indicators • Indicators change colour at its p. Ka but it cannot be detected by our eyes • p. H range – Indicator changes colour over a range of p. H • Methyl orange, p. Ka is 3. 46 but change colour in the range of p. H (3. 2 -4. 4) • p. H range (p. H = p. Ka ± 1) seen by our eye • Indicator must only change colour at equivalence point • End point of indicator must correspond/coincide with equivalence point • Colour change must occur rapidly at equivalence point • Indicator usually change colour over a region of 2 p. H units centered on p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Pink Phenolphthalein Colour Base p. H range Phenol Red Indicator p. Ka Bromothymol Blue Methyl Orange Indicator 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Yellow Equivalence Point Acid Base p. H 4. 4 p. H 3. 2 p. H 1 Amt of acid = Amt base (Neutralization) End Point Indicator change colour p. H 14 Phenol Red Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Pink Acid p. H 1 Base p. H 6. 6 p. H 8. 2 p. H 14
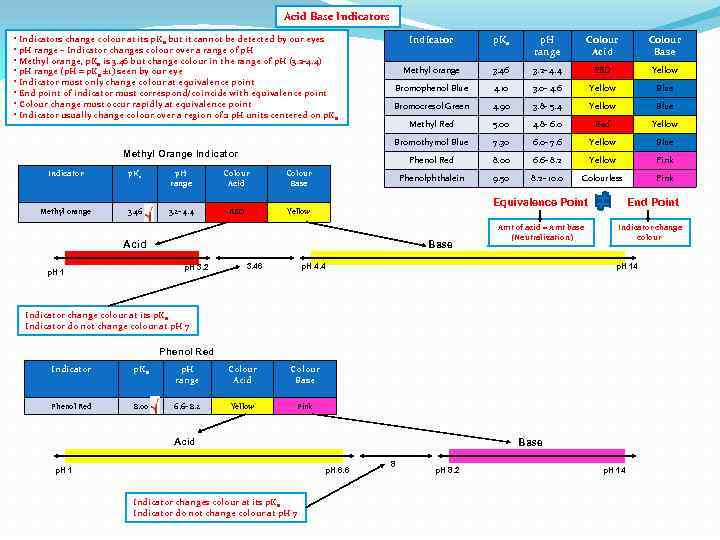
Acid Base Indicators • Indicators change colour at its p. Ka but it cannot be detected by our eyes • p. H range – Indicator changes colour over a range of p. H • Methyl orange, p. Ka is 3. 46 but change colour in the range of p. H (3. 2 -4. 4) • p. H range (p. H = p. Ka ± 1) seen by our eye • Indicator must only change colour at equivalence point • End point of indicator must correspond/coincide with equivalence point • Colour change must occur rapidly at equivalence point • Indicator usually change colour over a region of 2 p. H units centered on p. Ka Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Pink Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Methyl Orange Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Equivalence Point Acid Base p. H 3. 2 p. H 1 3. 46 Amt of acid = Amt base (Neutralization) p. H 4. 4 End Point Indicator change colour p. H 14 Indicator change colour at its p. Ka Indicator do not change colour at p. H 7 Phenol Red Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Pink Acid p. H 1 Base p. H 6. 6 Indicator changes colour at its p. Ka Indicator do not change colour at p. H 7 8 p. H 8. 2 p. H 14
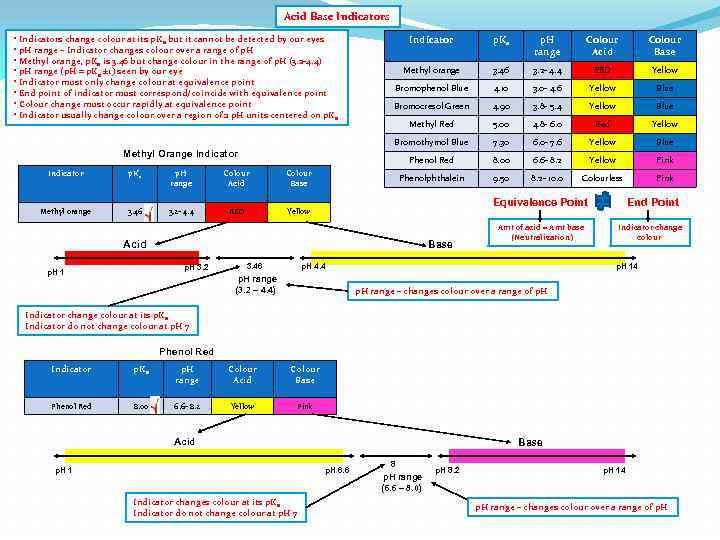
Acid Base Indicators • Indicators change colour at its p. Ka but it cannot be detected by our eyes • p. H range – Indicator changes colour over a range of p. H • Methyl orange, p. Ka is 3. 46 but change colour in the range of p. H (3. 2 -4. 4) • p. H range (p. H = p. Ka ± 1) seen by our eye • Indicator must only change colour at equivalence point • End point of indicator must correspond/coincide with equivalence point • Colour change must occur rapidly at equivalence point • Indicator usually change colour over a region of 2 p. H units centered on p. Ka Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Pink Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Methyl Orange Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Equivalence Point Acid Base p. H 3. 2 p. H 1 3. 46 Amt of acid = Amt base (Neutralization) p. H 4. 4 p. H range (3. 2 – 4. 4) End Point Indicator change colour p. H 14 p. H range – changes colour over a range of p. H Indicator change colour at its p. Ka Indicator do not change colour at p. H 7 Phenol Red Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Colour Base Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 2 Yellow Pink Acid p. H 1 Base p. H 6. 6 Indicator changes colour at its p. Ka Indicator do not change colour at p. H 7 8 p. H range (6. 6 – 8. 0) p. H 8. 2 p. H 14 p. H range – changes colour over a range of p. H
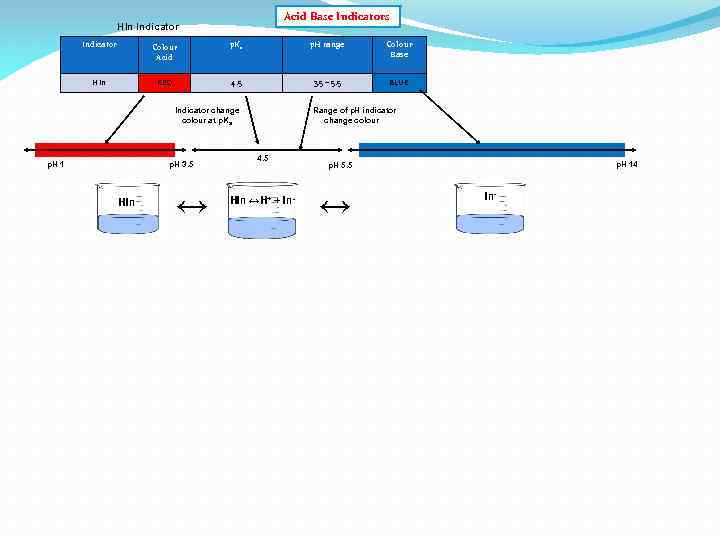
Acid Base Indicators HIn Indicator Colour Acid p. Ka p. H range Colour Base HIn RED 4. 5 3. 5 – 5. 5 BLUE Indicator change colour at p. Ka p. H 1 p. H 3. 5 HIn ↔ Range of p. H indicator change colour 4. 5 HIn ↔H+ + In- p. H 14 p. H 5. 5 ↔ In-
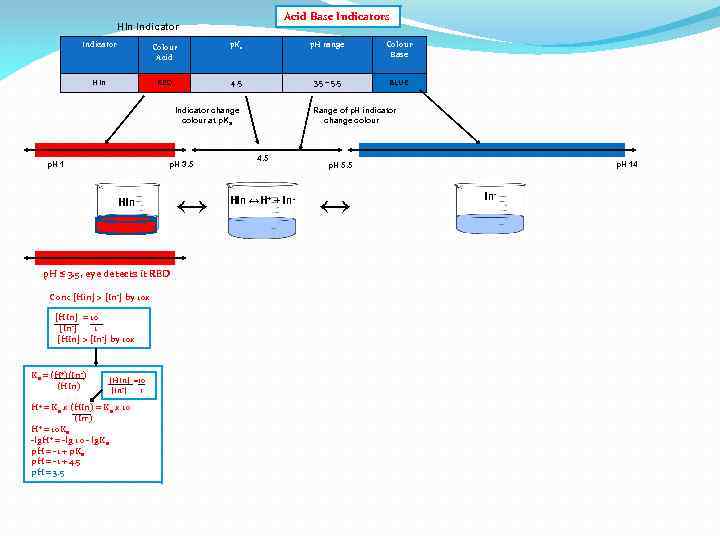
Acid Base Indicators HIn Indicator Colour Acid p. Ka p. H range Colour Base HIn RED 4. 5 3. 5 – 5. 5 BLUE Indicator change colour at p. Ka p. H 1 p. H 3. 5 HIn p. H ≤ 3. 5, eye detects it RED Conc [Hin] > [In-] by 10 x [HIn] = 10 [In-] 1 [HIn] > [In-] by 10 x Ka = (H+)(In-) (HIn) [HIn] =10 [In-] 1 H+ = Ka x (HIn) = Ka x 10 (In-) + = 10 K H a -lg. H+ = -lg 10 - lg. Ka p. H = -1 + p. Ka p. H = -1 + 4. 5 p. H = 3. 5 ↔ Range of p. H indicator change colour 4. 5 HIn ↔H+ + In- p. H 14 p. H 5. 5 ↔ In-
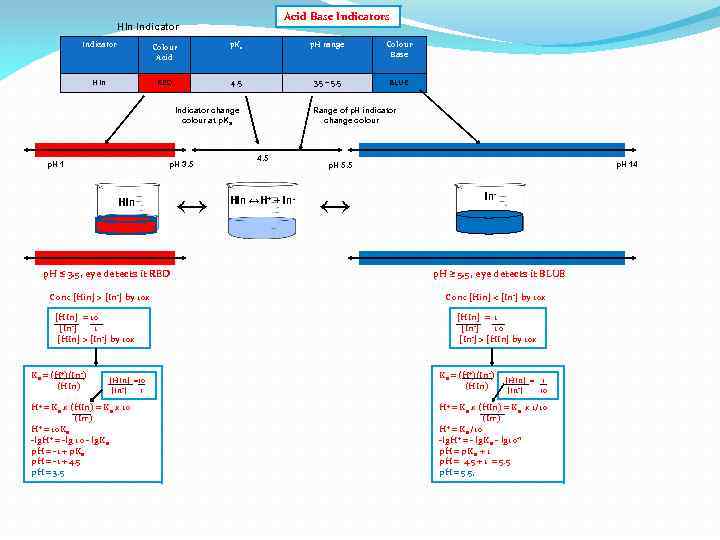
Acid Base Indicators HIn Indicator Colour Acid p. Ka p. H range Colour Base HIn RED 4. 5 3. 5 – 5. 5 BLUE Indicator change colour at p. Ka p. H 1 p. H 3. 5 HIn p. H ≤ 3. 5, eye detects it RED Conc [Hin] > [In-] by 10 x [HIn] = 10 [In-] 1 [HIn] > [In-] by 10 x Ka = (H+)(In-) (HIn) [HIn] =10 [In-] 1 H+ = Ka x (HIn) = Ka x 10 (In-) + = 10 K H a -lg. H+ = -lg 10 - lg. Ka p. H = -1 + p. Ka p. H = -1 + 4. 5 p. H = 3. 5 ↔ Range of p. H indicator change colour 4. 5 HIn ↔H+ + In- p. H 14 p. H 5. 5 ↔ In- p. H ≥ 5. 5, eye detects it BLUE Conc [Hin] < [In-] by 10 x [HIn] = 1 [In-] 10 [In-] > [HIn] by 10 x Ka = (H+)(In-) (HIn) [HIn] = 1 [In-] 10 H+ = Ka x (HIn) = Ka x 1/10 (In-) + = K /10 H a -lg. H+ = - lg. Ka - lg 10 -1 p. H = p. Ka + 1 p. H = 4. 5 + 1 = 5. 5 p. H = 5. 5,
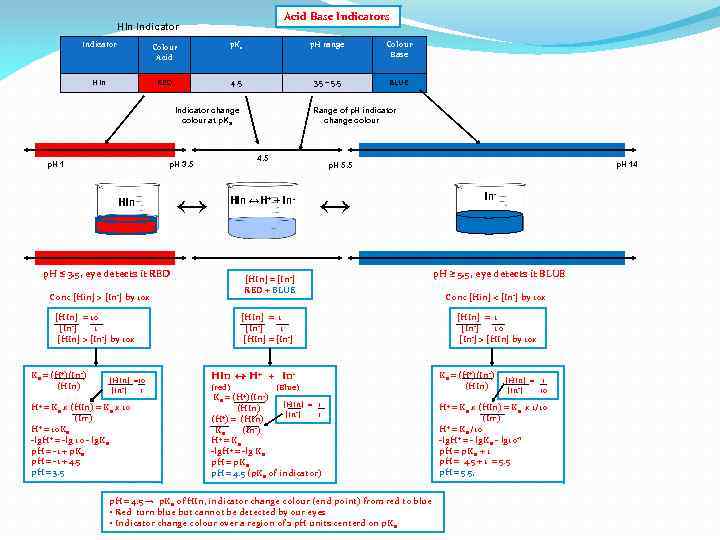
Acid Base Indicators HIn Indicator Colour Acid p. Ka p. H range Colour Base HIn RED 4. 5 3. 5 – 5. 5 BLUE Indicator change colour at p. Ka p. H 1 4. 5 p. H 3. 5 HIn ↔ [HIn] = 10 [In-] 1 [HIn] > [In-] by 10 x [HIn] =10 [In-] 1 H+ = Ka x (HIn) = Ka x 10 (In-) + = 10 K H a -lg. H+ = -lg 10 - lg. Ka p. H = -1 + p. Ka p. H = -1 + 4. 5 p. H = 3. 5 ↔ [HIn] = [In-] RED + BLUE Conc [Hin] > [In-] by 10 x [HIn] = 1 [In-] 1 [HIn] = [In-] HIn ↔ H+ + In(red) p. H 14 p. H 5. 5 HIn ↔H+ + In- p. H ≤ 3. 5, eye detects it RED Ka = (H+)(In-) (HIn) Range of p. H indicator change colour (Blue) Ka = (H+)(In-) [HIn] = 1 (HIn) [In-] 1 +) = (HIn) (H -) Ka (In H+ = Ka -lg. H+ = -lg Ka p. H = p. Ka p. H = 4. 5 (p. Ka of indicator) p. H = 4. 5 → p. Ka of HIn, indicator change colour (end point) from red to blue • Red turn blue but cannot be detected by our eyes • Indicator change colour over a region of 2 p. H units centerd on p. Ka In- p. H ≥ 5. 5, eye detects it BLUE Conc [Hin] < [In-] by 10 x [HIn] = 1 [In-] 10 [In-] > [HIn] by 10 x Ka = (H+)(In-) (HIn) [HIn] = 1 [In-] 10 H+ = Ka x (HIn) = Ka x 1/10 (In-) + = K /10 H a -lg. H+ = - lg. Ka - lg 10 -1 p. H = p. Ka + 1 p. H = 4. 5 + 1 = 5. 5 p. H = 5. 5,
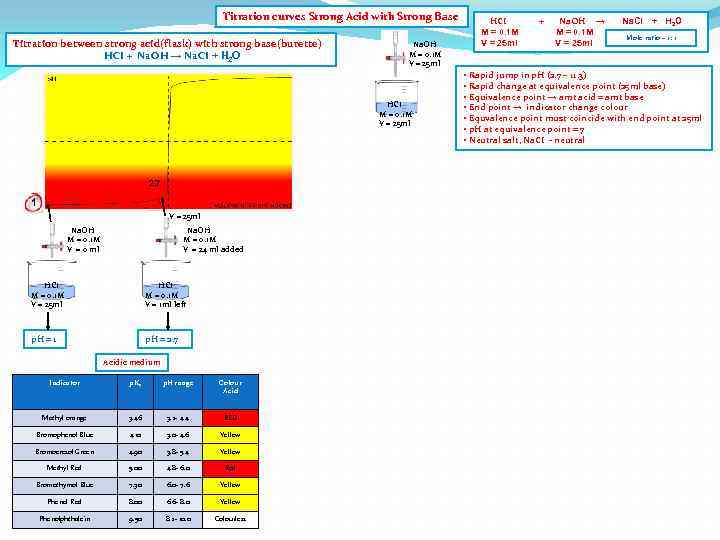
Titration curves Strong Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) HCI + Na. OH → Na. CI + H 2 O Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 2. 7 1 V = 25 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 1 p. H = 2. 7 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + Na. OH → M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Na. CI + H 2 O Mole ratio – 1: 1 • Rapid jump in p. H (2. 7 – 11. 3) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator change colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 7 • Neutral salt, Na. CI - neutral
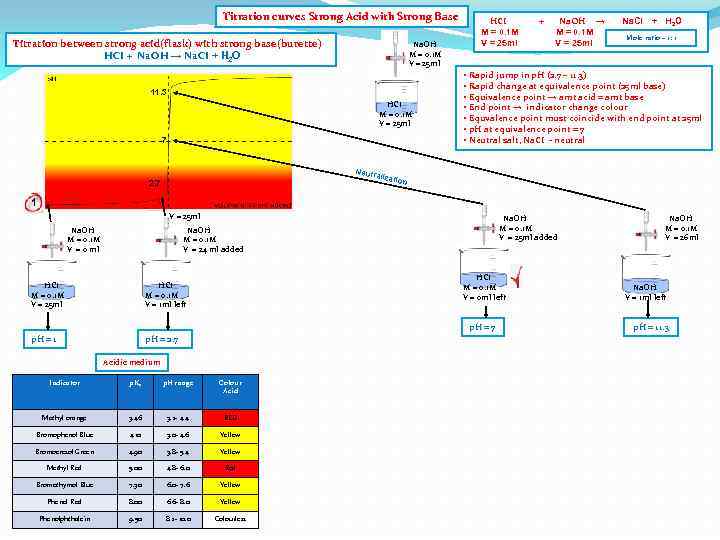
Titration curves Strong Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) HCI + Na. OH → Na. CI + H 2 O Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 11. 3 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7 Neutr 2. 7 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + Na. OH → M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Na. CI + H 2 O Mole ratio – 1: 1 • Rapid jump in p. H (2. 7 – 11. 3) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator change colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 7 • Neutral salt, Na. CI - neutral alizat ion 1 V = 25 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. H = 1 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 2. 7 p. H = 7 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml Na. OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 11. 3
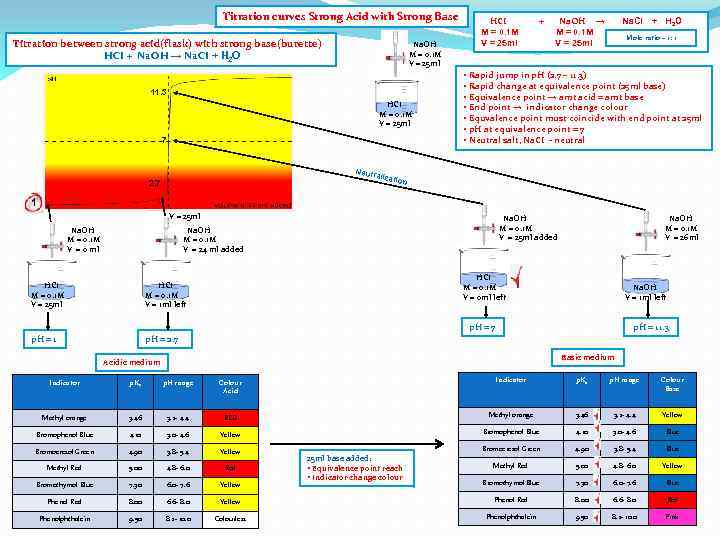
Titration curves Strong Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) HCI + Na. OH → Na. CI + H 2 O Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 11. 3 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7 Neutr 2. 7 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + Na. OH → M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Na. CI + H 2 O Mole ratio – 1: 1 • Rapid jump in p. H (2. 7 – 11. 3) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator change colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 7 • Neutral salt, Na. CI - neutral alizat ion 1 V = 25 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 1 Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml p. H = 2. 7 Na. OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 7 p. H = 11. 3 Basic medium Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Pink 25 ml base added: • Equivalence point reach • Indicator change colour
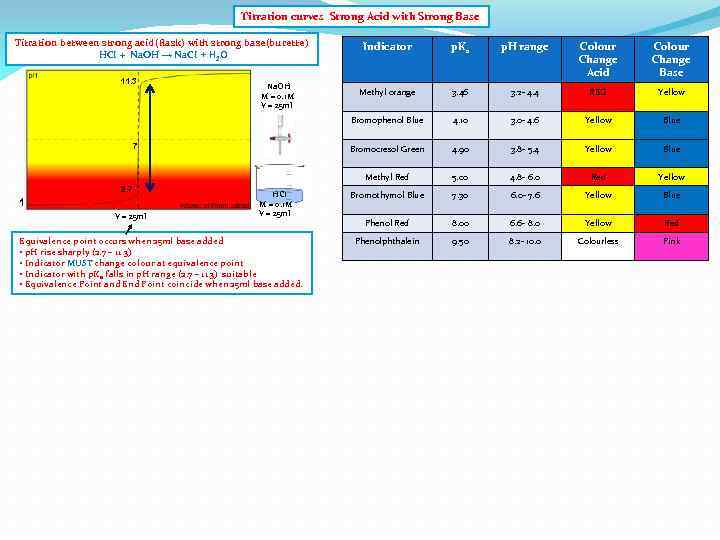
Titration curves Strong Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) HCI + Na. OH → Na. CI + H 2 O 2. 7 1 V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 7 p. H range Bromocresol Green Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromophenol Blue 11. 3 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink
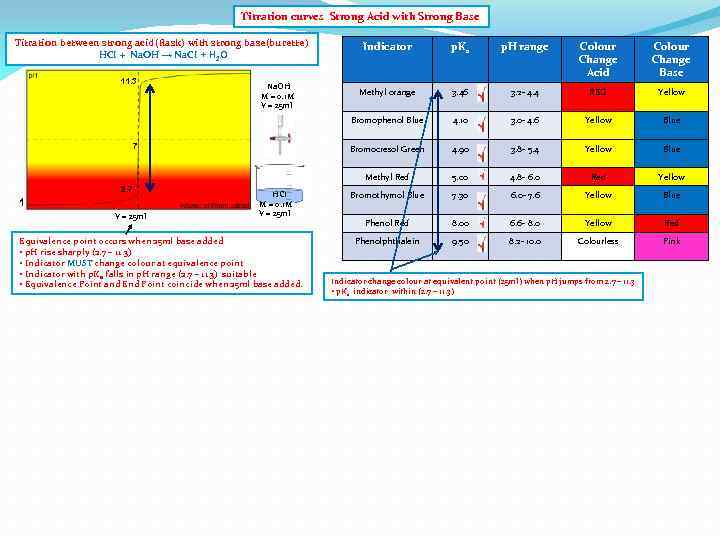
Titration curves Strong Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) HCI + Na. OH → Na. CI + H 2 O 2. 7 1 V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 7 p. H range Bromocresol Green Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromophenol Blue 11. 3 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml) when p. H jumps from 2. 7 – 11. 3 • p. Ka indicator within (2. 7 – 11. 3)
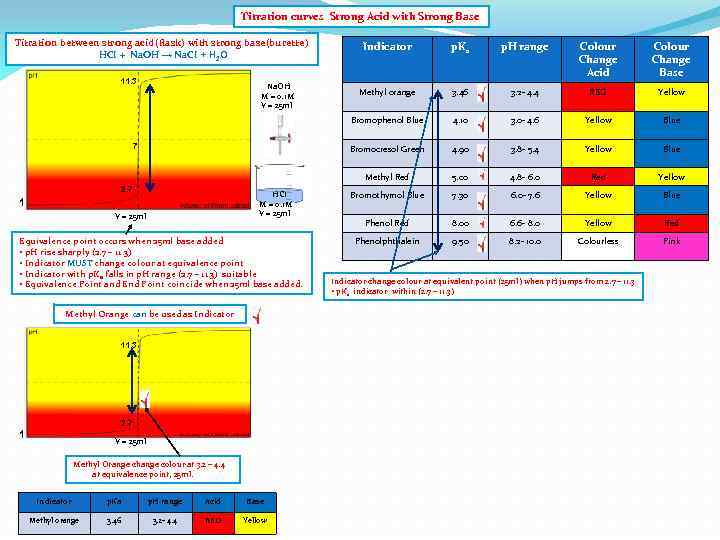
Titration curves Strong Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) HCI + Na. OH → Na. CI + H 2 O 2. 7 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 1 V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. Methyl Orange can be used as Indicator 11. 3 2. 7 1 V = 25 ml Methyl Orange change colour at 3. 2 – 4. 4 at equivalence point, 25 ml. Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 7 p. H range Bromocresol Green Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromophenol Blue 11. 3 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml) when p. H jumps from 2. 7 – 11. 3 • p. Ka indicator within (2. 7 – 11. 3)
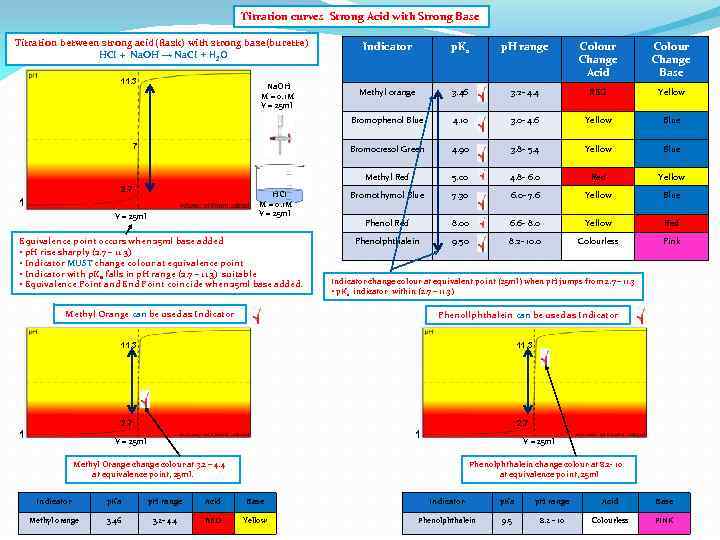
Titration curves Strong Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) HCI + Na. OH → Na. CI + H 2 O 2. 7 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 1 V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 7 p. H range Bromocresol Green Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromophenol Blue 11. 3 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml) when p. H jumps from 2. 7 – 11. 3 • p. Ka indicator within (2. 7 – 11. 3) Methyl Orange can be used as Indicator Phenollphthalein can be used as Indicator 11. 3 2. 7 1 V = 25 ml Methyl Orange change colour at 3. 2 – 4. 4 at equivalence point, 25 ml. Phenolphthalein change colour at 8. 2 - 10 at equivalence point, 25 ml Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 5 8. 2 - 10 Colourless PINK
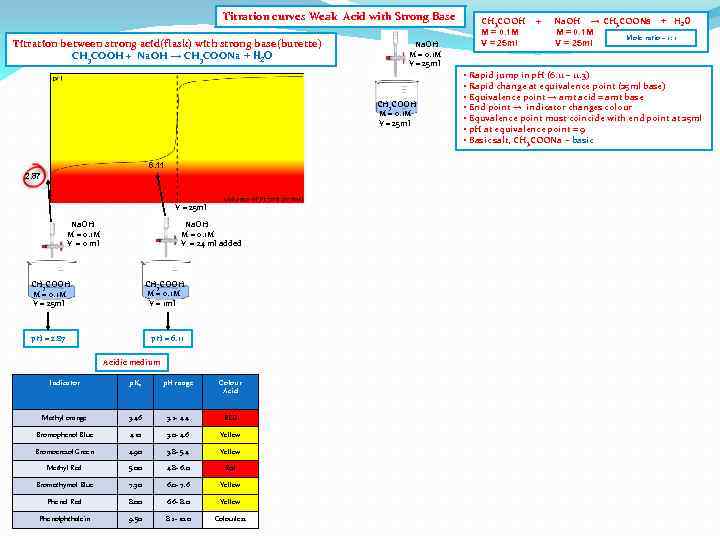
Titration curves Weak Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) CH 3 COOH + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. H = 2. 87 p. H = 6. 11 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O M = 0. 1 M Mole ratio – 1: 1 V = 25 ml • Rapid jump in p. H (6. 11 – 11. 3) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator changes colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 9 • Basic salt, CH 3 COONa - basic
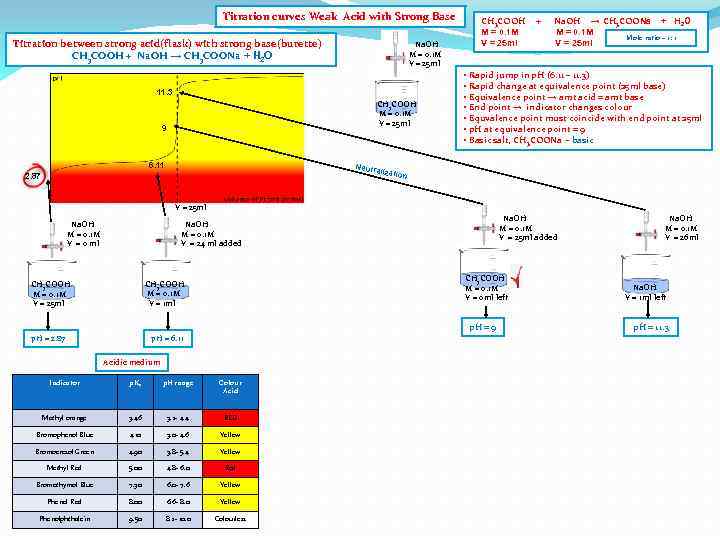
Titration curves Weak Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) CH 3 COOH + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 11. 3 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 9 6. 11 Neutr 2. 87 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O M = 0. 1 M Mole ratio – 1: 1 V = 25 ml • Rapid jump in p. H (6. 11 – 11. 3) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator changes colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 9 • Basic salt, CH 3 COONa - basic alizat ion V = 25 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. H = 9 p. H = 2. 87 p. H = 6. 11 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml Na. OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 11. 3
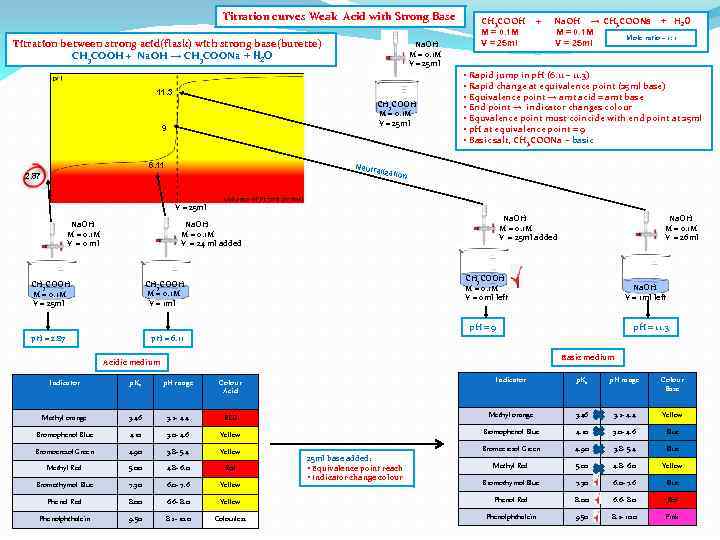
Titration curves Weak Acid with Strong Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with strong base(burette) CH 3 COOH + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 11. 3 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 9 6. 11 Neutr 2. 87 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O M = 0. 1 M Mole ratio – 1: 1 V = 25 ml • Rapid jump in p. H (6. 11 – 11. 3) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator changes colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 9 • Basic salt, CH 3 COONa - basic alizat ion V = 25 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml Na. OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 9 p. H = 2. 87 p. H = 11. 3 p. H = 6. 11 Basic medium Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Pink 25 ml base added: • Equivalence point reach • Indicator change colour
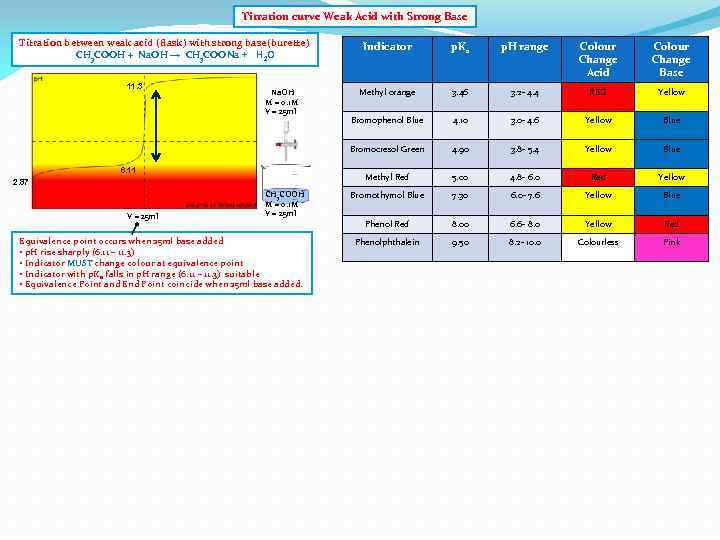
Titration curve Weak Acid with Strong Base Titration between weak acid (flask) with strong base(burette) CH 3 COOH + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (6. 11 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (6. 11 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromocresol Green 11. 3 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink
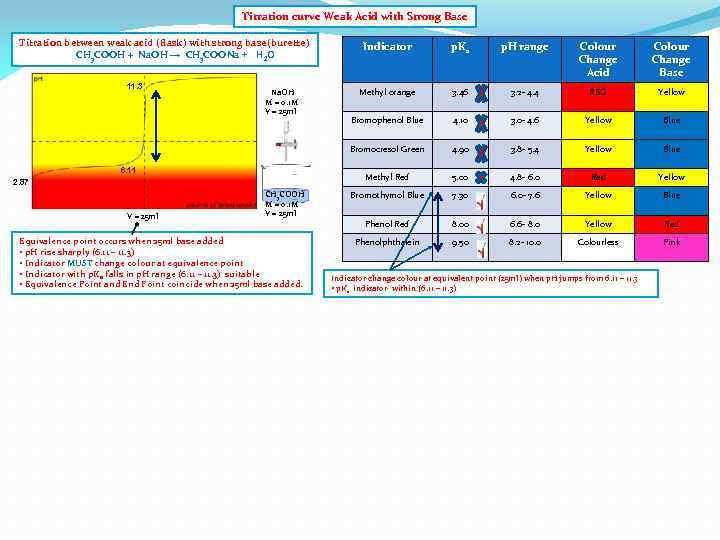
Titration curve Weak Acid with Strong Base Titration between weak acid (flask) with strong base(burette) CH 3 COOH + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (6. 11 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (6. 11 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromocresol Green 11. 3 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml) when p. H jumps from 6. 11 – 11. 3 • p. Ka indicator within (6. 11 – 11. 3)
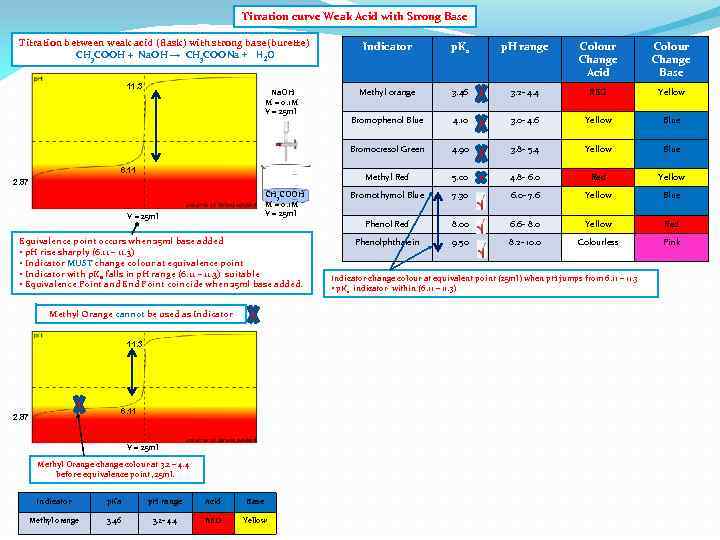
Titration curve Weak Acid with Strong Base Titration between weak acid (flask) with strong base(burette) CH 3 COOH + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (6. 11 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (6. 11 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. Methyl Orange cannot be used as Indicator 11. 3 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml Methyl Orange change colour at 3. 2 – 4. 4 before equivalence point, 25 ml. Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 6. 11 2. 87 p. H range Methyl Red Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromocresol Green 11. 3 Indicator 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml) when p. H jumps from 6. 11 – 11. 3 • p. Ka indicator within (6. 11 – 11. 3)
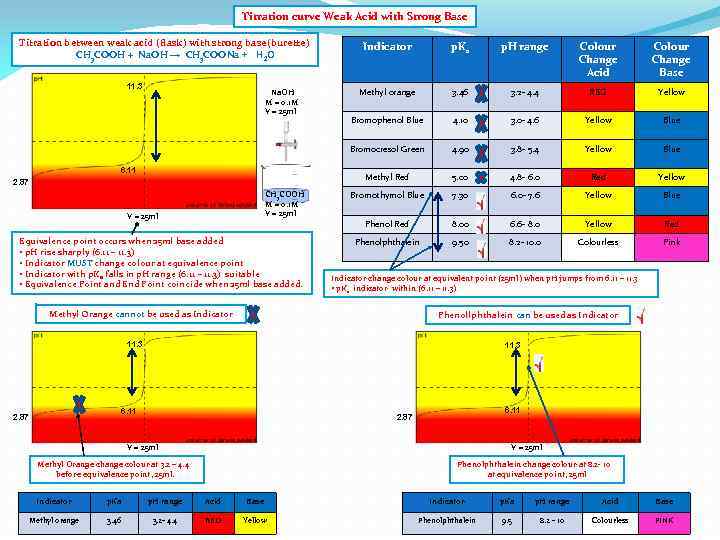
Titration curve Weak Acid with Strong Base Titration between weak acid (flask) with strong base(burette) CH 3 COOH + Na. OH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (6. 11 – 11. 3) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (6. 11 – 11. 3) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added. Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 6. 11 2. 87 p. H range Methyl Red Na. OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka Bromocresol Green 11. 3 Indicator 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml) when p. H jumps from 6. 11 – 11. 3 • p. Ka indicator within (6. 11 – 11. 3) Methyl Orange cannot be used as Indicator Phenollphthalein can be used as Indicator 11. 3 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml Methyl Orange change colour at 3. 2 – 4. 4 before equivalence point, 25 ml. Phenolphthalein change colour at 8. 2 - 10 at equivalence point, 25 ml Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 5 8. 2 - 10 Colourless PINK
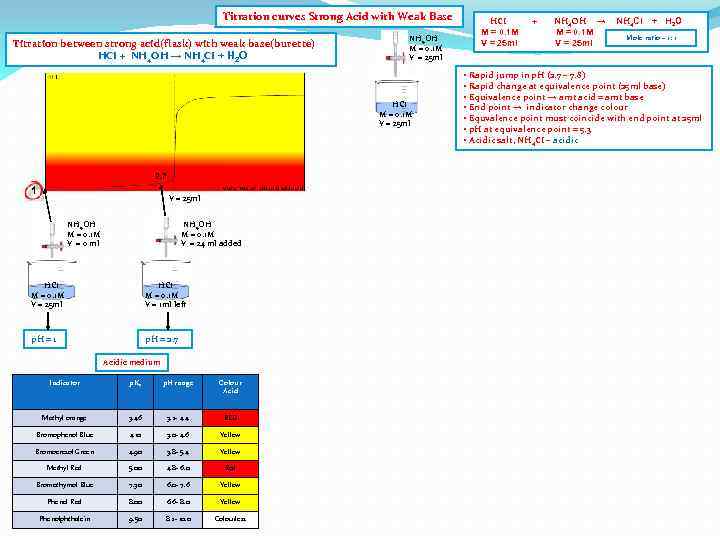
Titration curves Strong Acid with Weak Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with weak base(burette) HCI + NH 4 OH → NH 4 CI + H 2 O NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 2. 7 1 V = 25 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 1 p. H = 2. 7 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + NH 4 OH → M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml NH 4 CI + H 2 O Mole ratio – 1: 1 • Rapid jump in p. H (2. 7 – 7. 8) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator change colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 5. 3 • Acidic salt, NH 4 CI – acidic
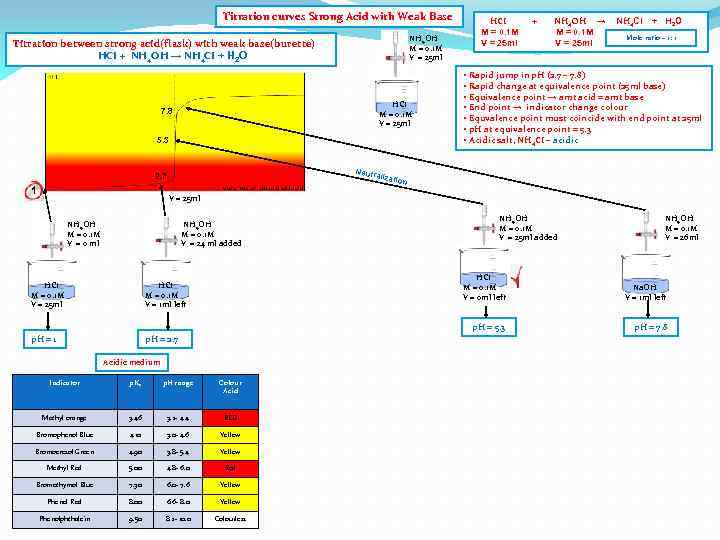
Titration curves Strong Acid with Weak Base NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Titration between strong acid(flask) with weak base(burette) HCI + NH 4 OH → NH 4 CI + H 2 O HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7. 8 5. 3 Neutr 2. 7 1 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + NH 4 OH → M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml NH 4 CI + H 2 O Mole ratio – 1: 1 • Rapid jump in p. H (2. 7 – 7. 8) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator change colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 5. 3 • Acidic salt, NH 4 CI – acidic alizat ion V = 25 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 1 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left p. H = 2. 7 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Na. OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 5. 3 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. H = 7. 8
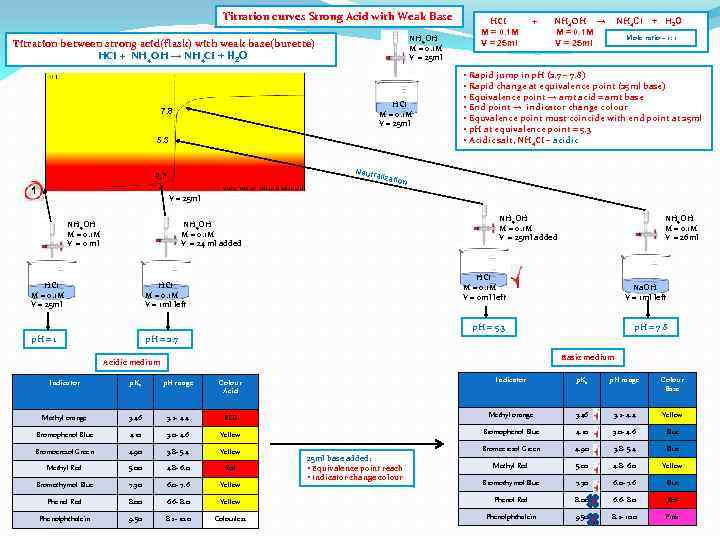
Titration curves Strong Acid with Weak Base NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Titration between strong acid(flask) with weak base(burette) HCI + NH 4 OH → NH 4 CI + H 2 O HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7. 8 5. 3 Neutr 2. 7 1 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + NH 4 OH → M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml NH 4 CI + H 2 O Mole ratio – 1: 1 • Rapid jump in p. H (2. 7 – 7. 8) • Rapid change at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator change colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 5. 3 • Acidic salt, NH 4 CI – acidic alizat ion V = 25 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 1 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left Na. OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 5. 3 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. H = 7. 8 p. H = 2. 7 Basic medium Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Pink 25 ml base added: • Equivalence point reach • Indicator change colour
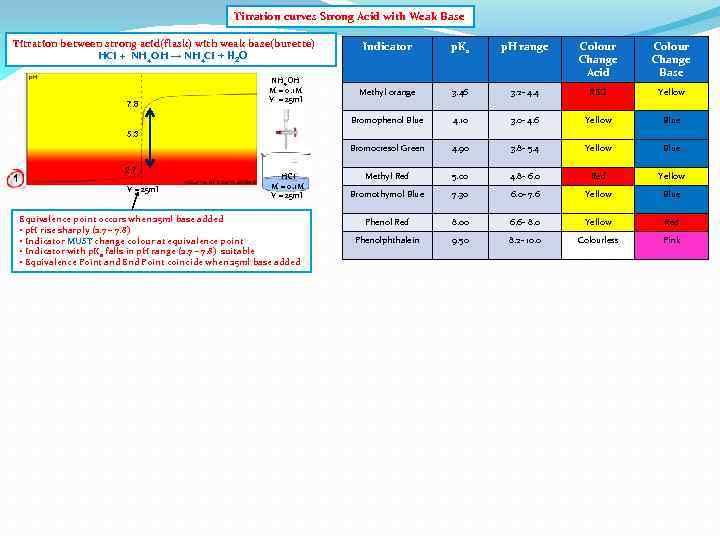
Titration curves Strong Acid with Weak Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with weak base(burette) HCI + NH 4 OH → NH 4 CI + H 2 O p. Ka p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 7. 8 NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Indicator 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 5. 3 1 2. 7 V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 7. 8) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 7. 8) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added
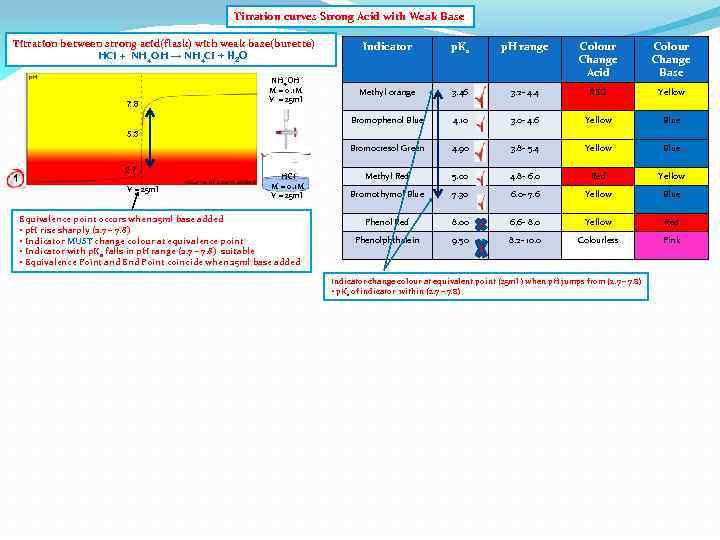
Titration curves Strong Acid with Weak Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with weak base(burette) HCI + NH 4 OH → NH 4 CI + H 2 O p. Ka p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 7. 8 NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Indicator 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 5. 3 1 2. 7 V = 25 ml HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 7. 8) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 7. 8) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml ) when p. H jumps from (2. 7 – 7. 8) • p. Ka of indicator within (2. 7 – 7. 8)
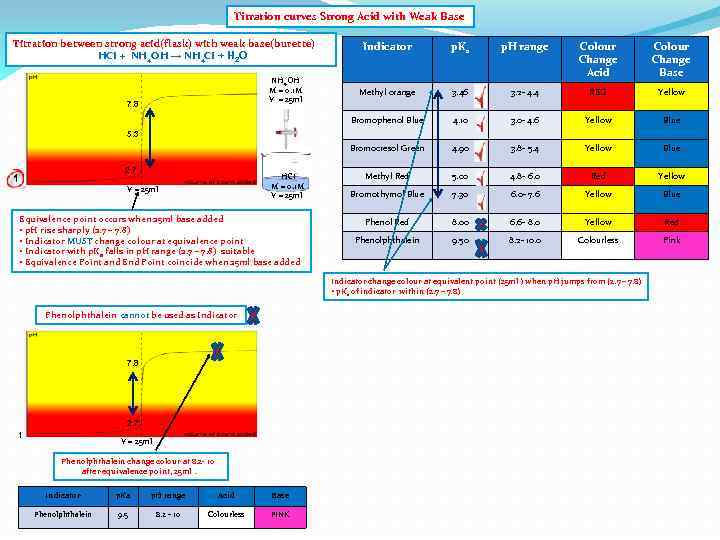
Titration curves Strong Acid with Weak Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with weak base(burette) HCI + NH 4 OH → NH 4 CI + H 2 O p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 7. 8 p. Ka Bromophenol Blue NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Indicator 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 5. 3 2. 7 1 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 7. 8) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 7. 8) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml ) when p. H jumps from (2. 7 – 7. 8) • p. Ka of indicator within (2. 7 – 7. 8) Phenolphthalein cannot be used as Indicator 7. 8 2. 7 1 V = 25 ml Phenolphthalein change colour at 8. 2 - 10 after equivalence point, 25 ml. Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Phenolphthalein 9. 5 8. 2 - 10 Colourless PINK
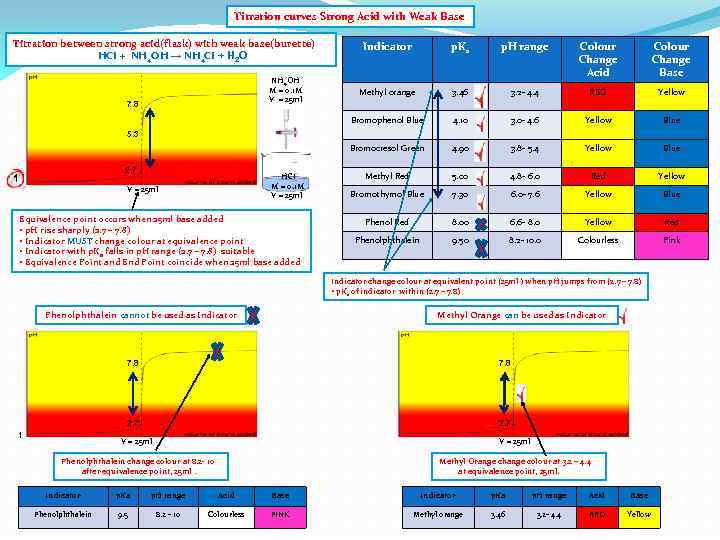
Titration curves Strong Acid with Weak Base Titration between strong acid(flask) with weak base(burette) HCI + NH 4 OH → NH 4 CI + H 2 O p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green 7. 8 p. Ka Bromophenol Blue NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Indicator 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 5. 3 2. 7 1 HCI M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • p. H rise sharply (2. 7 – 7. 8) • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • Indicator with p. Ka falls in p. H range (2. 7 – 7. 8) suitable • Equivalence Point and End Point coincide when 25 ml base added Indicator change colour at equivalent point (25 ml ) when p. H jumps from (2. 7 – 7. 8) • p. Ka of indicator within (2. 7 – 7. 8) Phenolphthalein cannot be used as Indicator Methyl Orange can be used as Indicator 7. 8 2. 7 1 7. 8 2. 7 V = 25 ml Phenolphthalein change colour at 8. 2 - 10 after equivalence point, 25 ml. Methyl Orange change colour at 3. 2 – 4. 4 at equivalence point, 25 ml. Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Phenolphthalein 9. 5 8. 2 - 10 Colourless PINK Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow
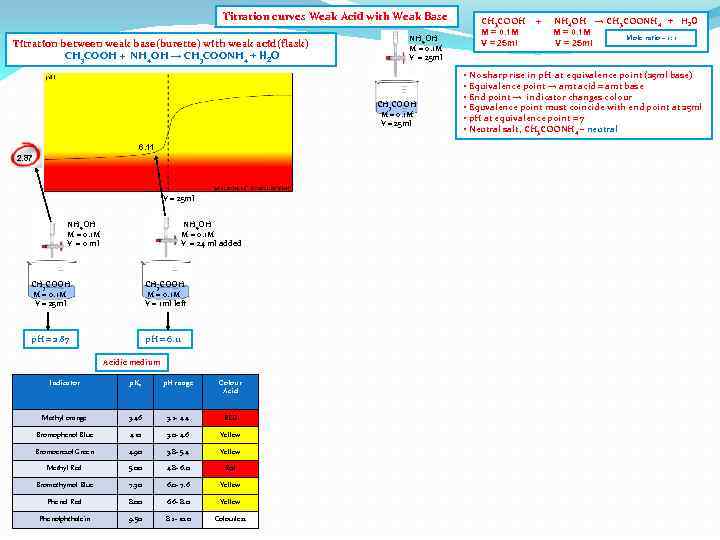
Titration curves Weak Acid with Weak Base Titration between weak base(burette) with weak acid(flask) CH 3 COOH + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 2. 87 p. H = 6. 11 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O M = 0. 1 M Mole ratio – 1: 1 V = 25 ml • No sharp rise in p. H at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator changes colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 7 • Neutral salt, CH 3 COONH 4 – neutral
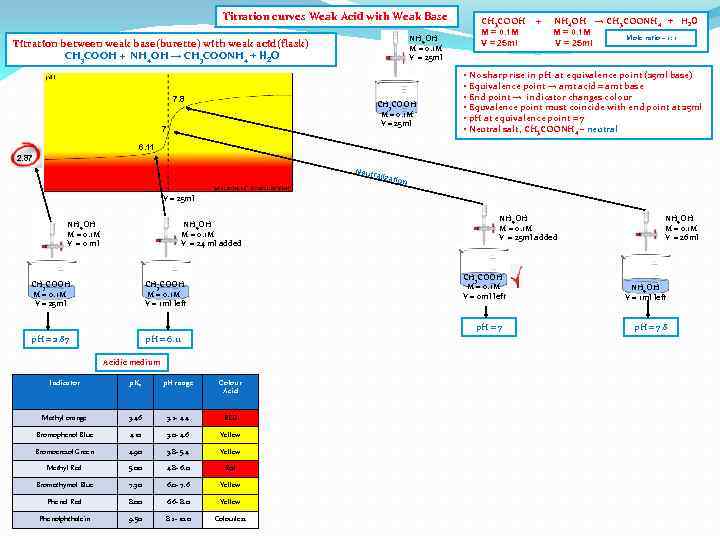
Titration curves Weak Acid with Weak Base NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Titration between weak base(burette) with weak acid(flask) CH 3 COOH + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O 7. 8 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O M = 0. 1 M Mole ratio – 1: 1 V = 25 ml • No sharp rise in p. H at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator changes colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 7 • Neutral salt, CH 3 COONH 4 – neutral 6. 11 2. 87 Neutr alizat ion V = 25 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 2. 87 NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added p. H = 6. 11 p. H = 7 Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml NH 4 OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 7. 8
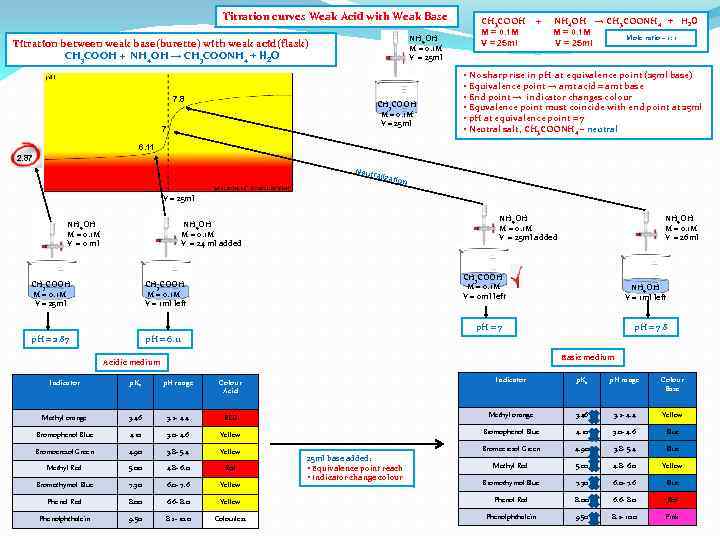
Titration curves Weak Acid with Weak Base NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Titration between weak base(burette) with weak acid(flask) CH 3 COOH + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O 7. 8 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O M = 0. 1 M Mole ratio – 1: 1 V = 25 ml • No sharp rise in p. H at equivalence point (25 ml base) • Equivalence point → amt acid = amt base • End point → indicator changes colour • Equvalence point must coincide with end point at 25 ml • p. H at equivalence point = 7 • Neutral salt, CH 3 COONH 4 – neutral 6. 11 2. 87 Neutr alizat ion V = 25 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml added NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 24 ml added CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 0 ml left CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 1 ml left p. H = 2. 87 NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 26 ml p. H = 6. 11 NH 4 OH V = 1 ml left p. H = 7. 8 Basic medium Acidic medium Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Acid Indicator p. Ka p. H range Colour Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Blue Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Bromocresol Green 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Blue Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Methyl Red 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Pink 25 ml base added: • Equivalence point reach • Indicator change colour
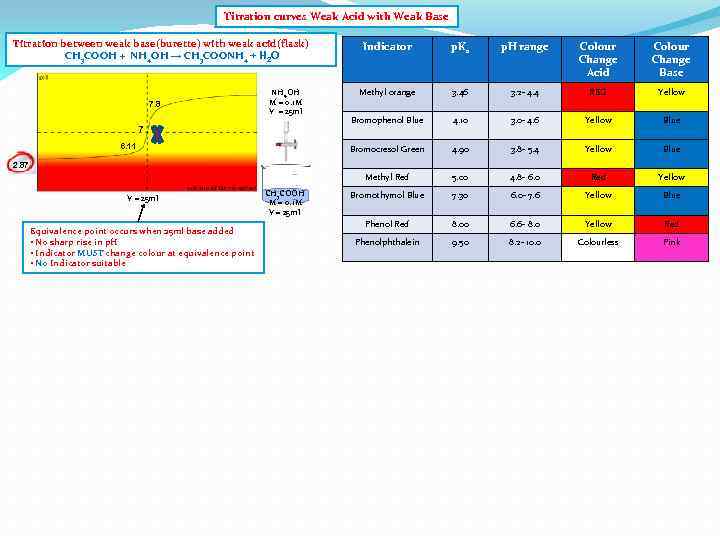
Titration curves Weak Acid with Weak Base Titration between weak base(burette) with weak acid(flask) CH 3 COOH + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O 7 6. 11 p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 7. 8 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 2. 87 V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • No sharp rise in p. H • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • No Indicator suitable CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml
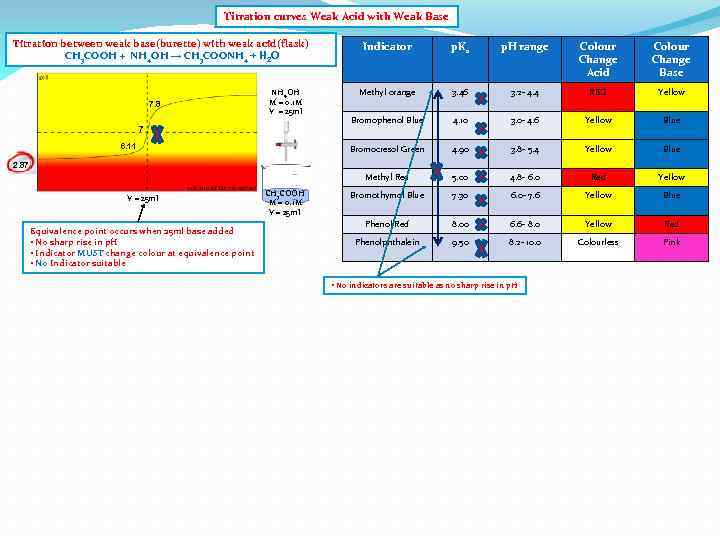
Titration curves Weak Acid with Weak Base Titration between weak base(burette) with weak acid(flask) CH 3 COOH + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O 7 6. 11 p. H range Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue Bromocresol Green NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml p. Ka 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue Methyl Red 7. 8 Indicator 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 2. 87 V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • No sharp rise in p. H • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • No Indicator suitable CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml • No indicators are suitable as no sharp rise in p. H
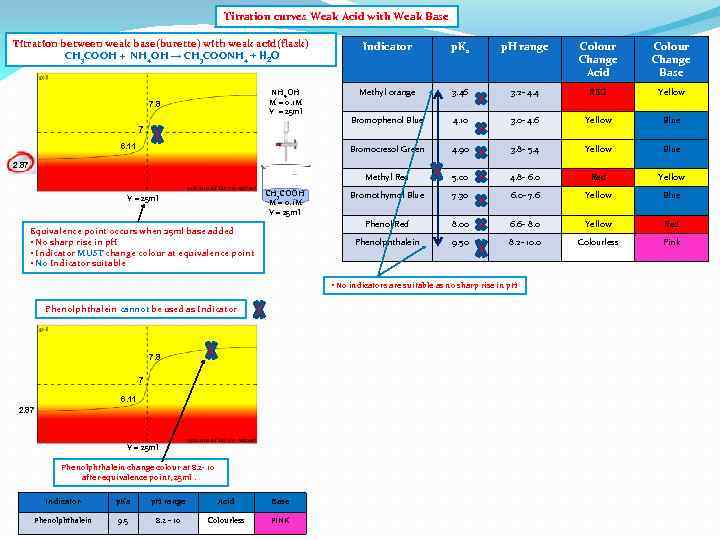
Titration curves Weak Acid with Weak Base Titration between weak base(burette) with weak acid(flask) CH 3 COOH + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 6. 11 p. H range Methyl Red 7 p. Ka Bromocresol Green NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7. 8 Indicator 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 2. 87 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • No sharp rise in p. H • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • No Indicator suitable • No indicators are suitable as no sharp rise in p. H Phenolphthalein cannot be used as Indicator 7. 8 7 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml Phenolphthalein change colour at 8. 2 - 10 after equivalence point, 25 ml. Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Phenolphthalein 9. 5 8. 2 - 10 Colourless PINK
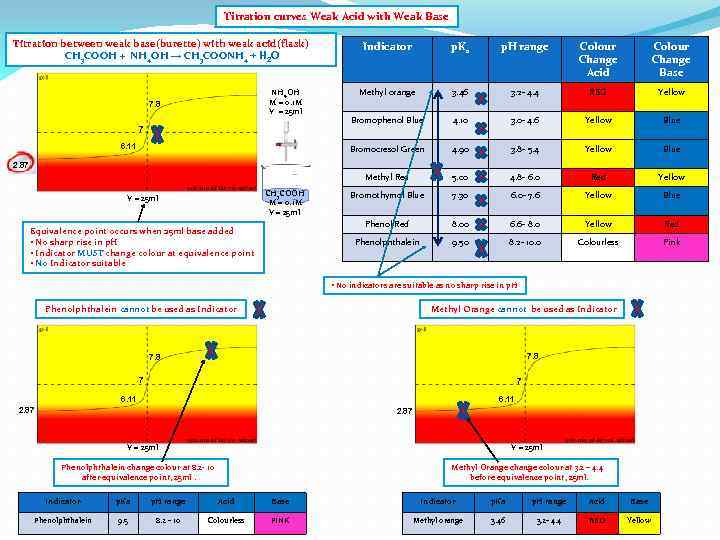
Titration curves Weak Acid with Weak Base Titration between weak base(burette) with weak acid(flask) CH 3 COOH + NH 4 OH → CH 3 COONH 4 + H 2 O Colour Change Acid Colour Change Base Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow Bromophenol Blue 4. 10 3. 0 - 4. 6 Yellow Blue 4. 90 3. 8 - 5. 4 Yellow Blue 5. 00 4. 8 - 6. 0 Red Yellow Bromothymol Blue 7. 30 6. 0 - 7. 6 Yellow Blue Phenol Red 8. 00 6. 6 - 8. 0 Yellow Red Phenolphthalein 6. 11 p. H range Methyl Red 7 p. Ka Bromocresol Green NH 4 OH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml 7. 8 Indicator 9. 50 8. 2 - 10. 0 Colourless Pink 2. 87 CH 3 COOH M = 0. 1 M V = 25 ml Equivalence point occurs when 25 ml base added • No sharp rise in p. H • Indicator MUST change colour at equivalence point • No Indicator suitable • No indicators are suitable as no sharp rise in p. H Phenolphthalein cannot be used as Indicator Methyl Orange cannot be used as Indicator 7. 8 7 7 6. 11 2. 87 V = 25 ml Phenolphthalein change colour at 8. 2 - 10 after equivalence point, 25 ml. Methyl Orange change colour at 3. 2 – 4. 4 before equivalence point, 25 ml. Indicator p. Ka p. H range Acid Base Phenolphthalein 9. 5 8. 2 - 10 Colourless PINK Methyl orange 3. 46 3. 2 - 4. 4 RED Yellow
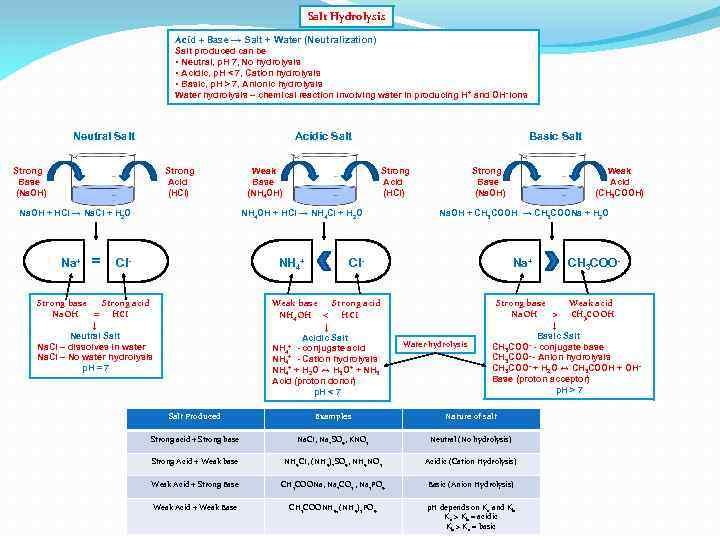
Salt Hydrolysis Acid + Base → Salt + Water (Neutralization) Salt produced can be • Neutral, p. H 7, No hydrolysis • Acidic, p. H < 7, Cation hydrolysis • Basic, p. H > 7, Anionic hydrolysis Water hydrolysis – chemical reaction involving water in producing H+ and OH- ions Neutral Salt Acidic Salt Strong Base (Na. OH) Strong Acid (HCI) Na. OH + HCI → Na. CI + H 2 O Na+ = Weak Base (NH 4 OH) Basic Salt Strong Acid (HCI) NH 4 OH + HCI → NH 4 CI + H 2 O CI- NH 4+ Strong base Strong acid Na. OH = HCI ↓ Neutral Salt Na. CI – dissolves in water Na. CI – No water hydrolysis p. H = 7 Strong Base (Na. OH) Na. OH + CH 3 COOH → CH 3 COONa + H 2 O CI- Weak base Strong acid NH 4 OH < HCI ↓ Acidic Salt NH 4+ - conjugate acid NH 4+ - Cation hydrolysis NH 4+ + H 2 O ↔ H 3 O+ + NH 3 Acid (proton donor) p. H < 7 Weak Acid (CH 3 COOH) Na+ Water hydrolysis CH 3 COO- Strong base Weak acid Na. OH > CH 3 COOH ↓ Basic Salt CH 3 COO- - conjugate base CH 3 COO- - Anion hydrolysis CH 3 COO- + H 2 O ↔ CH 3 COOH + OHBase (proton acceptor) p. H > 7 Salt Produced Examples Nature of salt Strong acid + Strong base Na. CI, Na 2 SO 4, KNO 3 Neutral (No hydrolysis) Strong Acid + Weak base NH 4 CI, (NH 4)2 SO 4, NH 4 NO 3 Acidic (Cation Hydrolysis) Weak Acid + Strong Base CH 3 COONa, Na 2 CO 3 , Na 3 PO 4 Basic (Anion Hydrolysis) Weak Acid + Weak Base CH 3 COONH 4, (NH 4)3 PO 4 p. H depends on Ka and Kb Ka > Kb = acidic Kb > Ka = basic
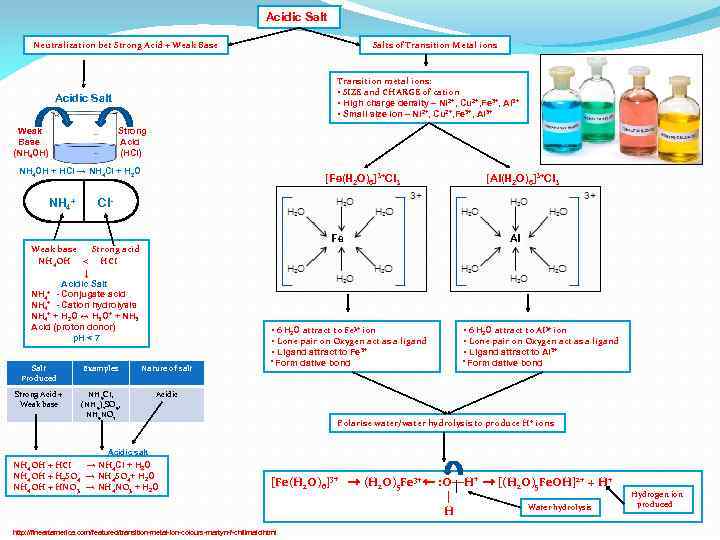
Acidic Salt Neutralization bet Strong Acid + Weak Base Salts of Transition Metal ions Transition metal ions: • SIZE and CHARGE of cation • High charge density – Ni 2+, Cu 2+, Fe 3+, Al 3+ • Small size ion – Ni 2+, Cu 2+, Fe 3+, Al 3+ Acidic Salt Weak Base (NH 4 OH) Strong Acid (HCI) NH 4 OH + HCI → NH 4 CI + H 2 O NH 4+ [Fe(H 2 O)6]3+CI 3 [AI(H 2 O)6]3+CI 3 CIFe Weak base Strong acid NH 4 OH < HCI ↓ Acidic Salt NH 4+ - Conjugate acid NH 4+ - Cation hydrolysis NH 4+ + H 2 O ↔ H 3 O+ + NH 3 Acid (proton donor) p. H < 7 AI • 6 H 2 O attract to Fe 3+ ion • Lone pair on Oxygen act as a ligand • Ligand attract to Fe 3+ Salt Produced Examples Nature of salt Strong Acid + Weak base NH 4 CI, (NH 4)2 SO 4, NH 4 NO 3 • 6 H 2 O attract to AI 3+ ion • Lone pair on Oxygen act as a ligand • Ligand attract to AI 3+ • Form dative bond Acidic Polarise water/water hydrolysis to produce H + ions Acidic salt NH 4 OH + HCI → NH 4 CI + H 2 O NH 4 OH + H 2 SO 4 → NH 4 SO 4+ H 2 O NH 4 OH + HNO 3 → NH 4 NO 3 + H 2 O [Fe(H 2 O)6]3+ → (H 2 O)5 Fe 3+ ← : O―H+ → [(H 2 O)5 Fe. OH]2+ + H+ | Water hydrolysis H http: //fineartamerica. com/featured/transition-metal-ion-colours-martyn-f-chillmaid. html Hydrogen ion produced
Simulation and Animation on Buffer and Titrations Click here titration animation Click here titration simulation Click here salt hydrolysis animation Click here on acid base indicator Click here on universal indicator Click here for videos from Khan Academy Click here acidic buffer animation Click here on universal indicator

Acknowledgements Thanks to source of pictures and video used in this presentation Thanks to Creative Commons for excellent contribution on licenses http: //creativecommons. org/licenses/ Prepared by Lawrence Kok Check out more video tutorials from my site and hope you enjoy this tutorial http: //lawrencekok. blogspot. com
Acid Base Indicators_ Titration curves.pptx