Лекция 12 Опухоли Общие вопросы 2011.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 «Tumors doctrine» Lecture
«Tumors doctrine» Lecture
 Tumors Synonyms – neoplasm, blastoma. - It is a pathological process, characterized by unrestrained (quick and constant) reproduction and growth of cells.
Tumors Synonyms – neoplasm, blastoma. - It is a pathological process, characterized by unrestrained (quick and constant) reproduction and growth of cells.
 Epidemiology o o Tumors take the 3 rd place among the mortality causes in Russia. 1 st place among men – carcinoma of lungs, among women – breast cancer, 2 nd place - carcinoma of stomach, 3 rd place – large intestine cancer.
Epidemiology o o Tumors take the 3 rd place among the mortality causes in Russia. 1 st place among men – carcinoma of lungs, among women – breast cancer, 2 nd place - carcinoma of stomach, 3 rd place – large intestine cancer.
 Tumors etiology. Тheories of their origin. 1. 2. 3. 4. Physicochemical theory (Virchow`s) Viral-genetic (Silber`s) Dysontogenetic (Cohnheim`s) Polyetiologic (Petrov`s)
Tumors etiology. Тheories of their origin. 1. 2. 3. 4. Physicochemical theory (Virchow`s) Viral-genetic (Silber`s) Dysontogenetic (Cohnheim`s) Polyetiologic (Petrov`s)
 Chemical oncogenes o o o Influence of cancerogenic substances Food-borne oncogenesis Hormonal oncogenesis
Chemical oncogenes o o o Influence of cancerogenic substances Food-borne oncogenesis Hormonal oncogenesis
 Cancerogenic substances: o o o o Polycyclic carbohydrates (soot /benzapilene/) Cigarette smoking (resins) Aromatic amines Cyclamate and saccharin Aflatoxin Nitrosamines (nitrites) Anticancer drugs (cyclophosphamide) Аsbestos
Cancerogenic substances: o o o o Polycyclic carbohydrates (soot /benzapilene/) Cigarette smoking (resins) Aromatic amines Cyclamate and saccharin Aflatoxin Nitrosamines (nitrites) Anticancer drugs (cyclophosphamide) Аsbestos
 Food-borne oncogenesis: o o Insufficiency of dietary fibers in the food allowance ―› Slowing down of food passage in the intestines ―› Reproduction of anaerobic bacteria ―› Anaerobic bacteria ferments cause the formation of cancerogenic substances
Food-borne oncogenesis: o o Insufficiency of dietary fibers in the food allowance ―› Slowing down of food passage in the intestines ―› Reproduction of anaerobic bacteria ―› Anaerobic bacteria ferments cause the formation of cancerogenic substances
 Hormonal oncogenesis: o o Estrogens (endometrial carcinoma) Estrogens (breast cancer in experimental mice) Diethylstilbestrol (vaginal carcinoma in descendants) Steroids (adenoma of the liver)
Hormonal oncogenesis: o o Estrogens (endometrial carcinoma) Estrogens (breast cancer in experimental mice) Diethylstilbestrol (vaginal carcinoma in descendants) Steroids (adenoma of the liver)
 Physical oncogenesis: o o o Ultraviolet radiation (cancer of the skin, melanoma) X-ray irradiation (cancer of the skin and leucosis in radiologists) Radioactive isotopes (radium – osteosarcoma, radioactive iodine – cancer of thyroid gland, radioactive thorium – liver carcinoma)
Physical oncogenesis: o o o Ultraviolet radiation (cancer of the skin, melanoma) X-ray irradiation (cancer of the skin and leucosis in radiologists) Radioactive isotopes (radium – osteosarcoma, radioactive iodine – cancer of thyroid gland, radioactive thorium – liver carcinoma)
 Viral oncogenesis: 1. Oncogenic RNA-viruses: o Tumors, connected with AIDSinfection (В-cell lymphoma) 2. Oncogenic DNA-viruses: o Papilloma virus o Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) o Hepatitis B virus
Viral oncogenesis: 1. Oncogenic RNA-viruses: o Tumors, connected with AIDSinfection (В-cell lymphoma) 2. Oncogenic DNA-viruses: o Papilloma virus o Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) o Hepatitis B virus
 Genetic oncogenesis: 1. Tumors with inheritance according to Мendel`s law: - Retinoblastoma - Wilms` tumor (nephroblastoma) - Familial intestinal polyposis 2. Tumors with polygenetic inheritance: - Breast cancer - Intestinal cancer
Genetic oncogenesis: 1. Tumors with inheritance according to Мendel`s law: - Retinoblastoma - Wilms` tumor (nephroblastoma) - Familial intestinal polyposis 2. Tumors with polygenetic inheritance: - Breast cancer - Intestinal cancer
 Tumors with polygenetic inheritance Relatives of the patients with breast cancer have higher probability to be affected this type of cancer
Tumors with polygenetic inheritance Relatives of the patients with breast cancer have higher probability to be affected this type of cancer
 Immediate causes of tumor development: Theory of genetic mutations can be realized as: o Theory of monoclonal origin or o «tumor field» theory. Moreover, o theory of immune surveillance failure is marked out. o
Immediate causes of tumor development: Theory of genetic mutations can be realized as: o Theory of monoclonal origin or o «tumor field» theory. Moreover, o theory of immune surveillance failure is marked out. o
 Tumors characteristic features: o o o Аtypism Growth (outward appearance) Tumor borders Recurrence Metastasis Influence on the organism
Tumors characteristic features: o o o Аtypism Growth (outward appearance) Tumor borders Recurrence Metastasis Influence on the organism
 Tumors atypism: It is a tumor acquiring of the new properties, uncharacteristic for the normal tissue. We distinguish the following atypism types: 1. Моrphological (tissue and cellular) 2. Functional 3. Antigenic 4. Меtabolic
Tumors atypism: It is a tumor acquiring of the new properties, uncharacteristic for the normal tissue. We distinguish the following atypism types: 1. Моrphological (tissue and cellular) 2. Functional 3. Antigenic 4. Меtabolic
 Tissue atypism: o o o Is characterized by derangement of: Size Form Tissue structures interaction
Tissue atypism: o o o Is characterized by derangement of: Size Form Tissue structures interaction
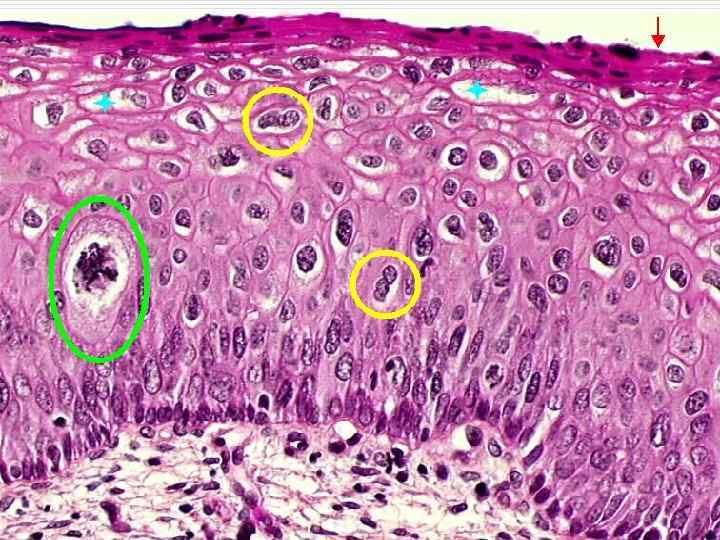
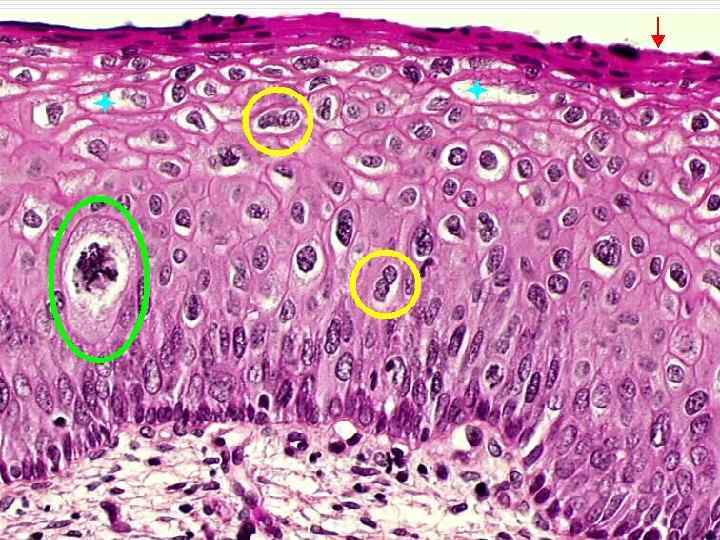
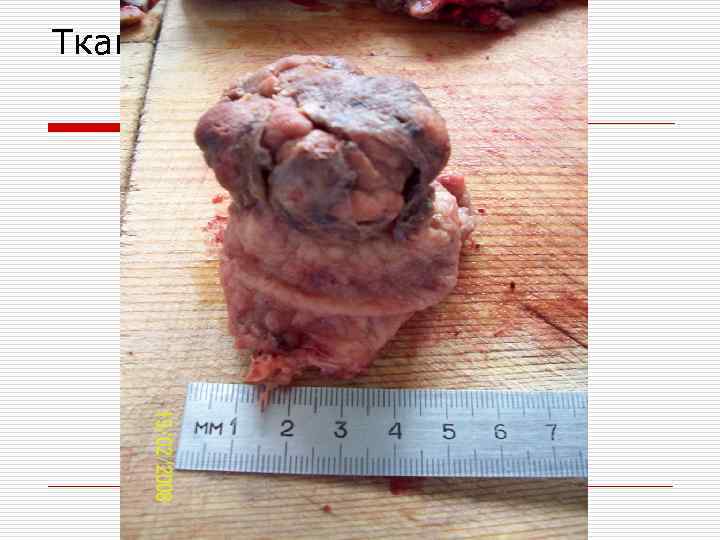 Тканевой атипизм
Тканевой атипизм
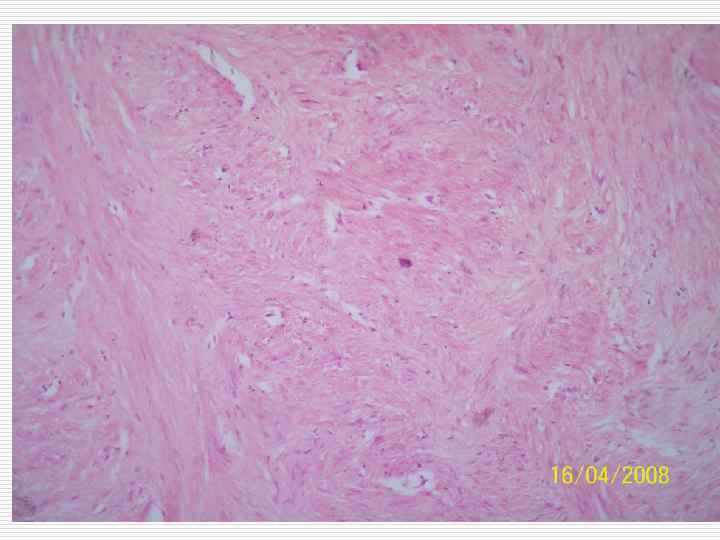
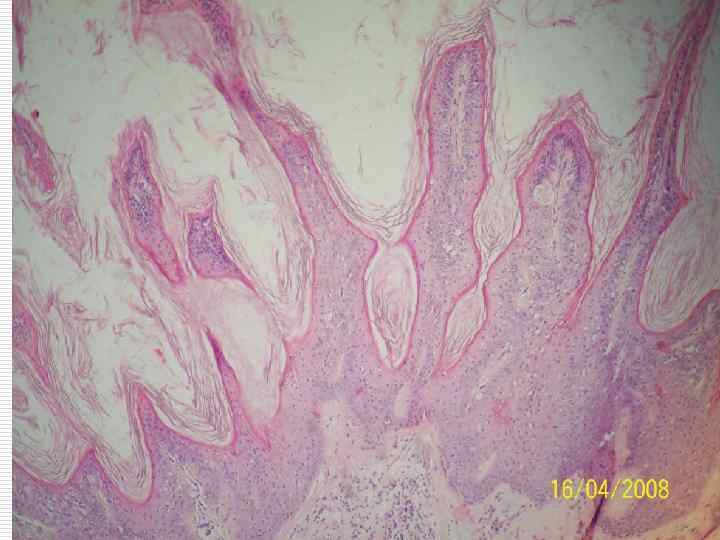
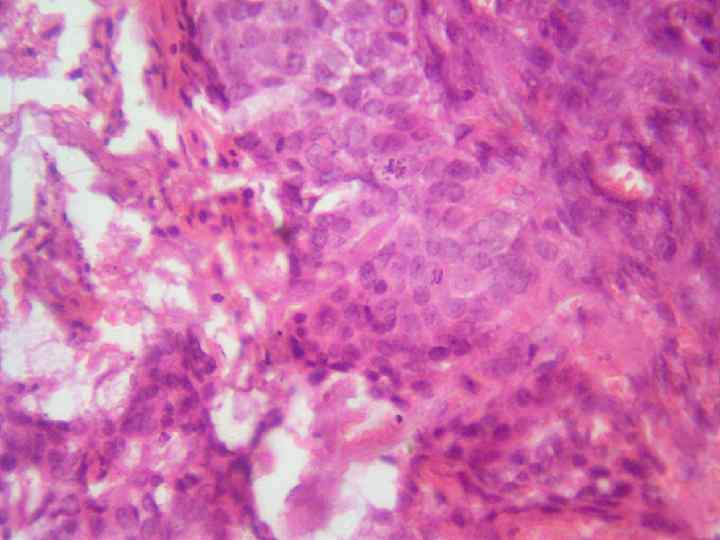
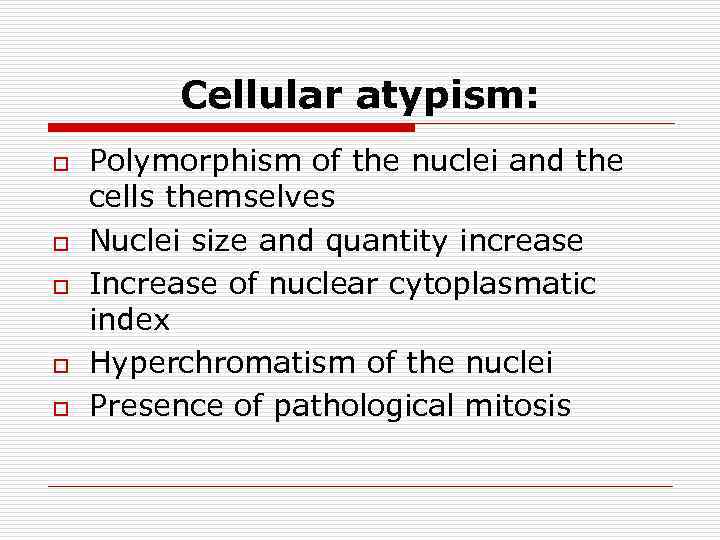 Cellular atypism: o o o Polymorphism of the nuclei and the cells themselves Nuclei size and quantity increase Increase of nuclear cytoplasmatic index Hyperchromatism of the nuclei Presence of pathological mitosis
Cellular atypism: o o o Polymorphism of the nuclei and the cells themselves Nuclei size and quantity increase Increase of nuclear cytoplasmatic index Hyperchromatism of the nuclei Presence of pathological mitosis
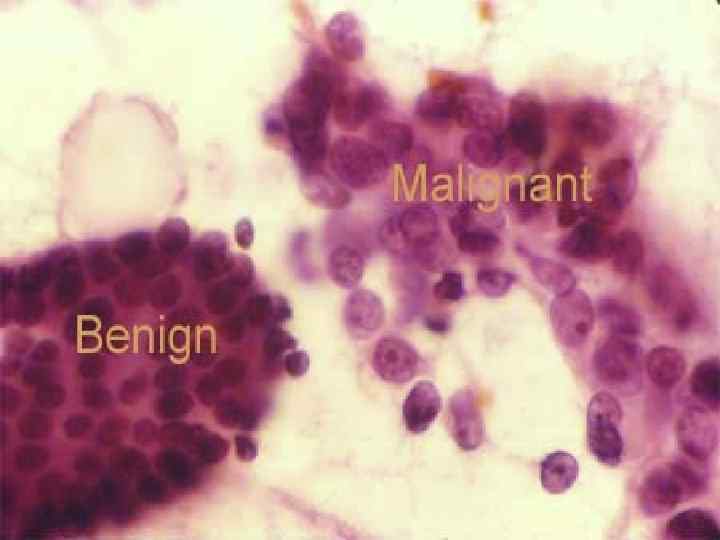

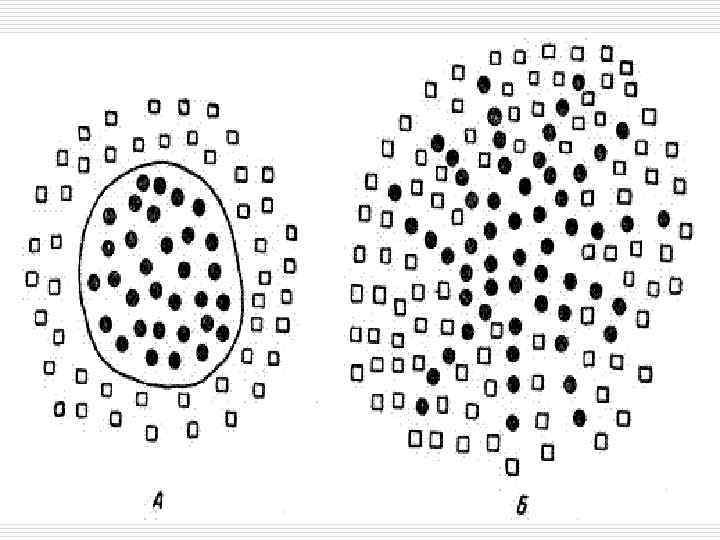
 Tumors growth and borders: 1. 2. Expansive growth – slow – the borders are distinct. Infiltrating growth (destruens) – fast (rapid) – the borders are indistinct.
Tumors growth and borders: 1. 2. Expansive growth – slow – the borders are distinct. Infiltrating growth (destruens) – fast (rapid) – the borders are indistinct.
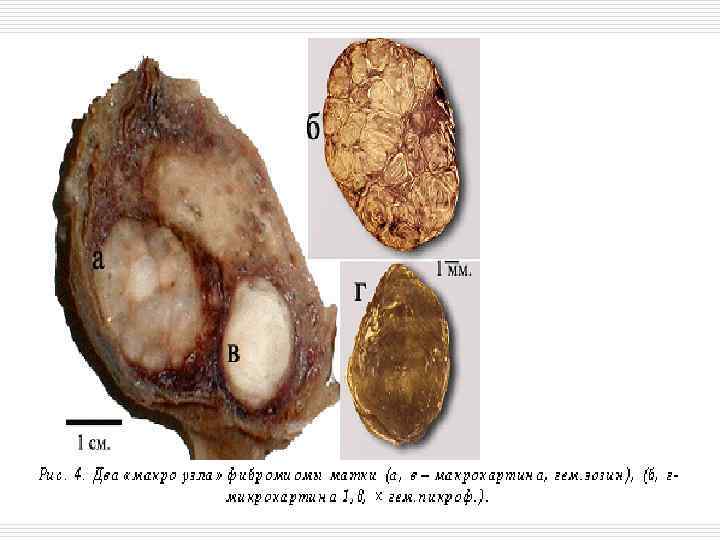
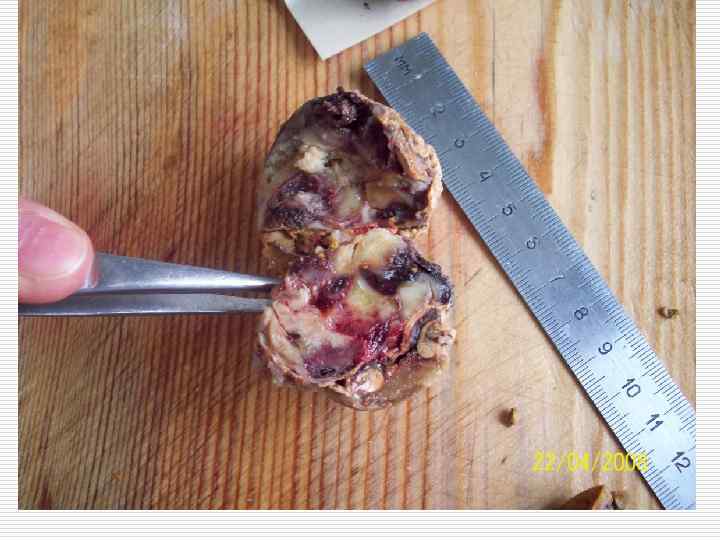
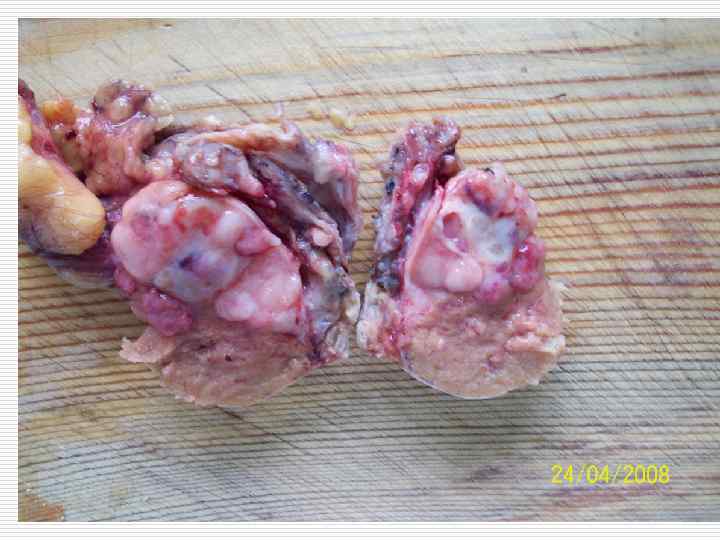
 Tumors outward appearance: o o Node Cyst Infiltrate Ulcer
Tumors outward appearance: o o Node Cyst Infiltrate Ulcer
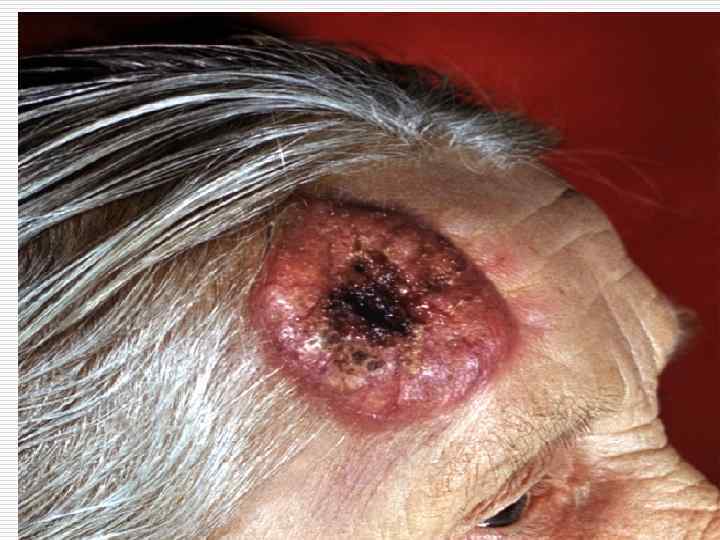
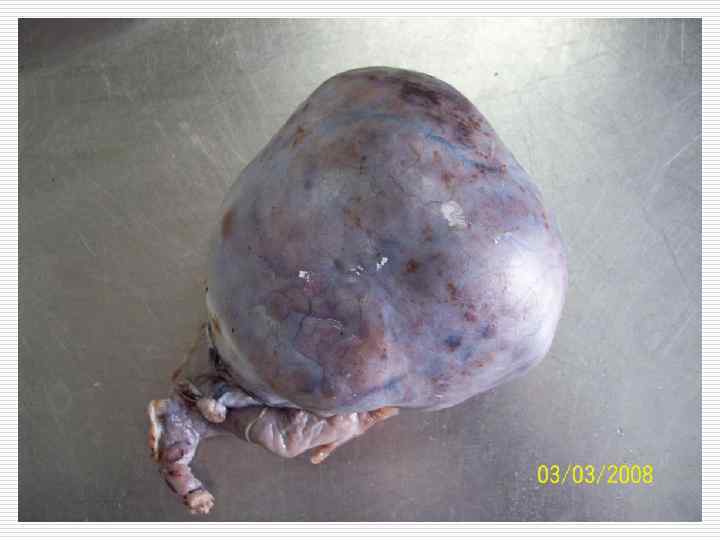
 With respect to the hollow organ lumen the tumors can be: o o Exophytic Endophytic
With respect to the hollow organ lumen the tumors can be: o o Exophytic Endophytic
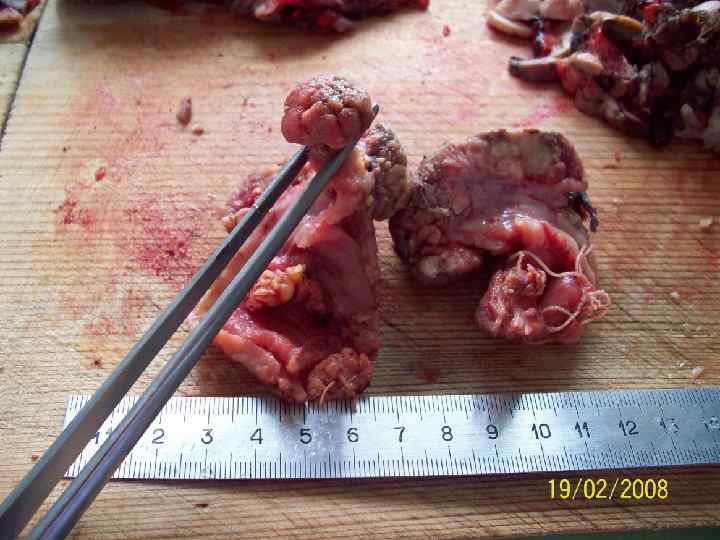
 Recurrence (relapse) - repeated appearance of the tumor after its excision (eradication) or radiotherapy.
Recurrence (relapse) - repeated appearance of the tumor after its excision (eradication) or radiotherapy.
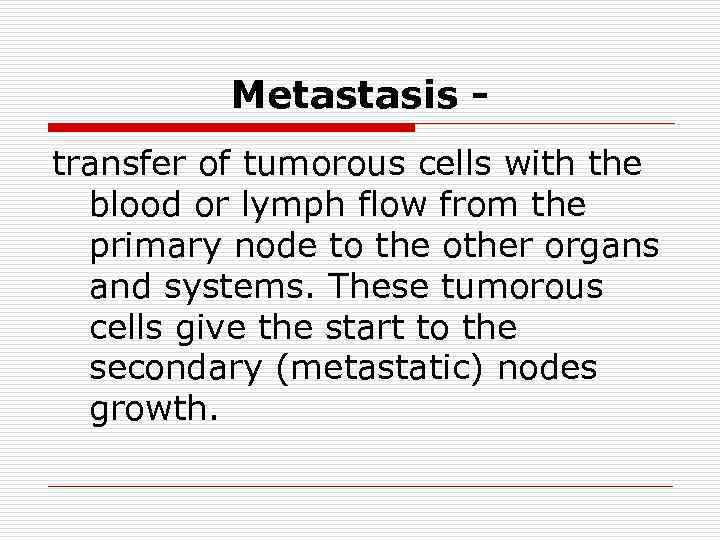 Metastasis transfer of tumorous cells with the blood or lymph flow from the primary node to the other organs and systems. These tumorous cells give the start to the secondary (metastatic) nodes growth.
Metastasis transfer of tumorous cells with the blood or lymph flow from the primary node to the other organs and systems. These tumorous cells give the start to the secondary (metastatic) nodes growth.
 Metastases can be: o o o Lymphogenic Hematogenic In the body cavities (dissemination).
Metastases can be: o o o Lymphogenic Hematogenic In the body cavities (dissemination).
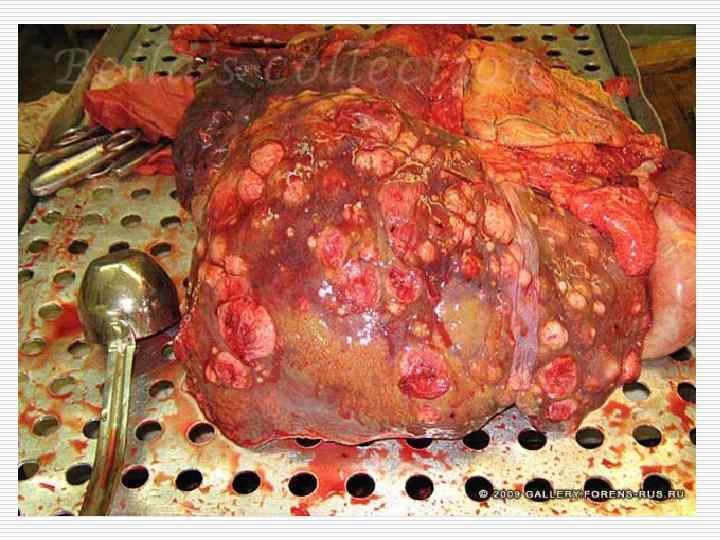
 Influence on the organism: o o Local (tumor compression of surrounding tissues – аtrophy, or tumor invasion into surrounding tissues with their destruction) General (intoxication)
Influence on the organism: o o Local (tumor compression of surrounding tissues – аtrophy, or tumor invasion into surrounding tissues with their destruction) General (intoxication)
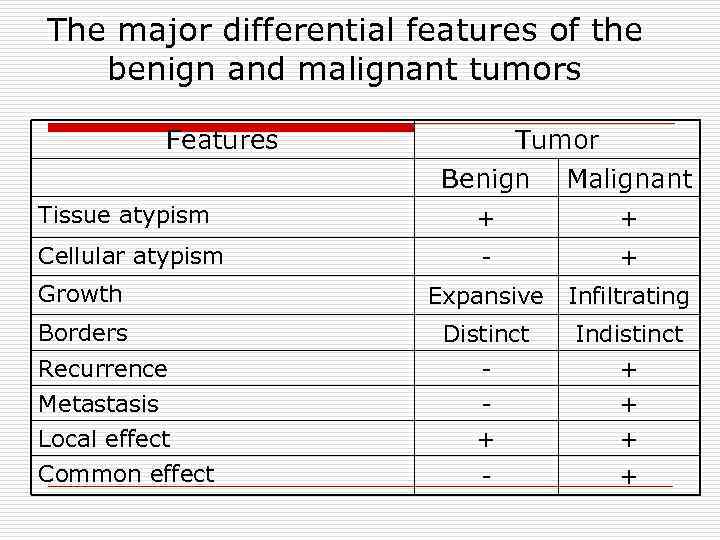 The major differential features of the benign and malignant tumors Features Tumor Benign Malignant Tissue atypism + + Cellular atypism - + Growth Expansive Infiltrating Borders Distinct Indistinct Recurrence - + Меtastasis - + Local effect + + Common effect - +
The major differential features of the benign and malignant tumors Features Tumor Benign Malignant Tissue atypism + + Cellular atypism - + Growth Expansive Infiltrating Borders Distinct Indistinct Recurrence - + Меtastasis - + Local effect + + Common effect - +
 Besides, the tumors with the local infiltrating growth (for example, basalioma) are distinguished.
Besides, the tumors with the local infiltrating growth (for example, basalioma) are distinguished.
 !!! The cancer must be differentiated from dysplasia o o In case of dysplasia the invasiveness is not present Dysplasia, even a severe one, can be reversible
!!! The cancer must be differentiated from dysplasia o o In case of dysplasia the invasiveness is not present Dysplasia, even a severe one, can be reversible
 Tumors nomenclature: o o o For benign tumors = name in Latin or Greek + oma For malignant epithelial tumors: + carcinoma or cancer For malignant mesenchymal tumors: + sarcoma For embryonal tumors: + blastoma Exclusions: melanoma, seminoma.
Tumors nomenclature: o o o For benign tumors = name in Latin or Greek + oma For malignant epithelial tumors: + carcinoma or cancer For malignant mesenchymal tumors: + sarcoma For embryonal tumors: + blastoma Exclusions: melanoma, seminoma.
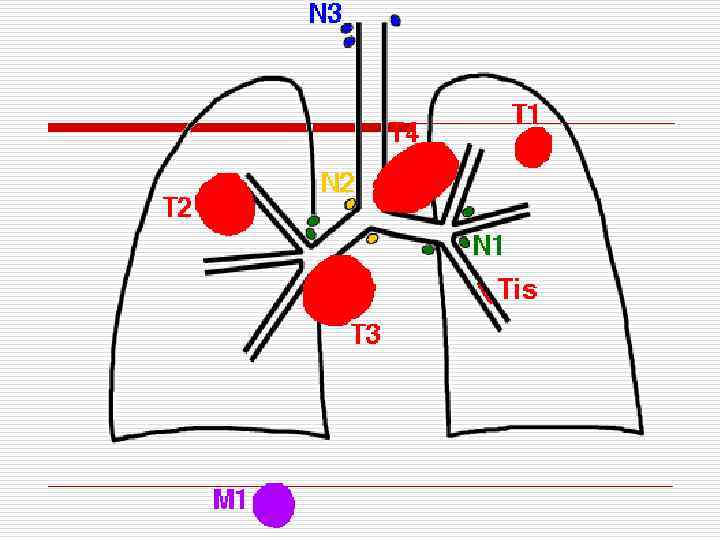
 Tumors classifications: According to the clinical course: Benign and malignant 2. According to the process dissemination (TNM): - Т – primary tumor, N – regional metastases, М – remote metastases. 1.
Tumors classifications: According to the clinical course: Benign and malignant 2. According to the process dissemination (TNM): - Т – primary tumor, N – regional metastases, М – remote metastases. 1.
 Tumors classifications: 3. According to histogenesis: - From the epithelial tissue - From the mesenchymal tissues - From the melanin-forming tissue - From the nervous system tissue - Tumors of the blood system - Teratomas
Tumors classifications: 3. According to histogenesis: - From the epithelial tissue - From the mesenchymal tissues - From the melanin-forming tissue - From the nervous system tissue - Tumors of the blood system - Teratomas
 Tumor description scheme: o o Localization Outward appearance (node, plaque etc. ) Маcroscopic description: size, form, consistency, borders, color on incision Мicroscopic description: characteristic of the tissue and/or cellular atypism.
Tumor description scheme: o o Localization Outward appearance (node, plaque etc. ) Маcroscopic description: size, form, consistency, borders, color on incision Мicroscopic description: characteristic of the tissue and/or cellular atypism.


