6f0e4e28d1483b7f908951beb528b7aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Tuition fees and access to higher education John Rushforth Deputy Director
Tuition fees and access to higher education John Rushforth Deputy Director
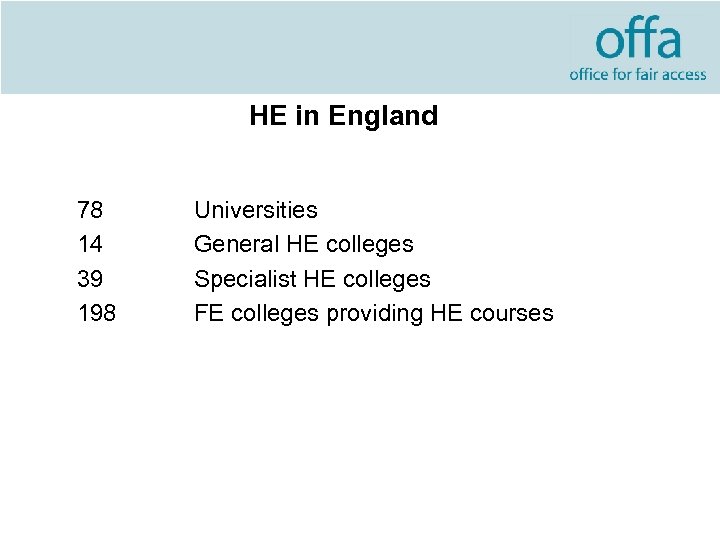 HE in England 78 14 39 198 Universities General HE colleges Specialist HE colleges FE colleges providing HE courses
HE in England 78 14 39 198 Universities General HE colleges Specialist HE colleges FE colleges providing HE courses
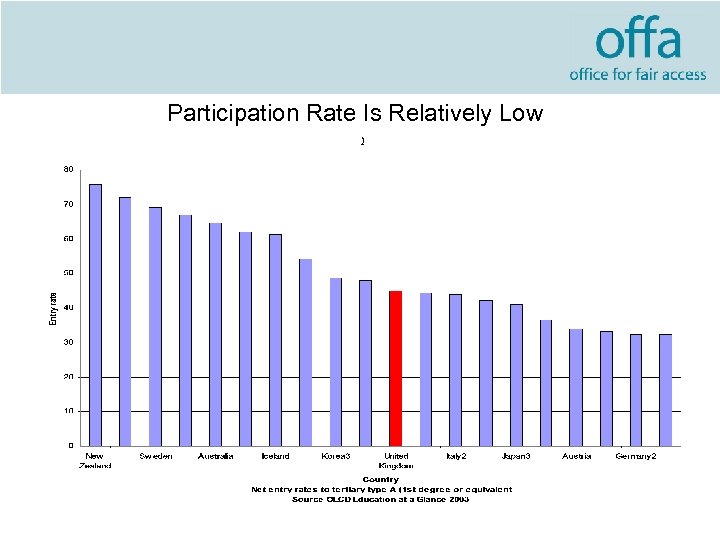 Participation Rate Is Relatively Low
Participation Rate Is Relatively Low
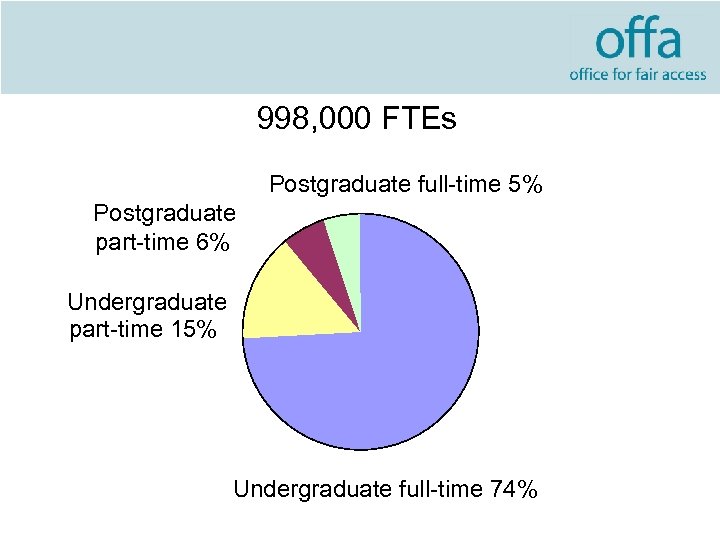 998, 000 FTEs Postgraduate full-time 5% Postgraduate part-time 6% Undergraduate part-time 15% Undergraduate full-time 74%
998, 000 FTEs Postgraduate full-time 5% Postgraduate part-time 6% Undergraduate part-time 15% Undergraduate full-time 74%
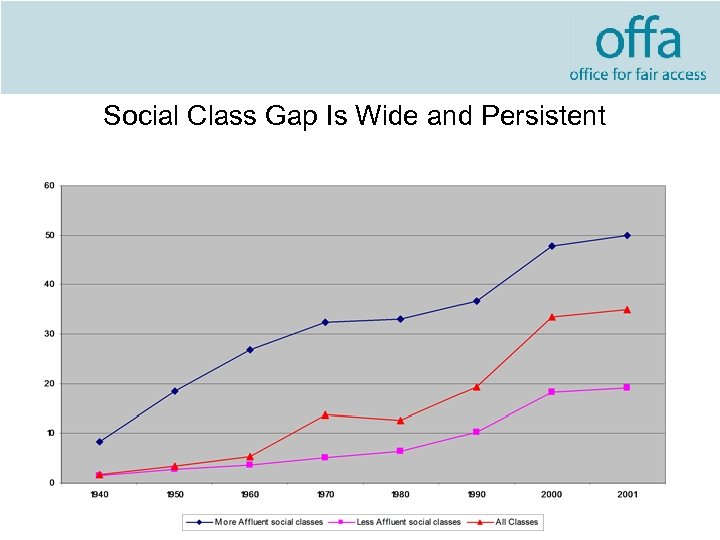 Social Class Gap Is Wide and Persistent
Social Class Gap Is Wide and Persistent
 From 2006 -07 • No up-front tuition fees • Government pays the tuition fee to the HE institution initially • Government recovers the fee after graduation • Tuition fees can vary from £ 0 to £ 3, 000
From 2006 -07 • No up-front tuition fees • Government pays the tuition fee to the HE institution initially • Government recovers the fee after graduation • Tuition fees can vary from £ 0 to £ 3, 000
 Repayments • Tuition fees repaid alongside any maintenance loan • Student maintenance loans – to £ 4000 • • Collected through the payroll, like tax Salary threshold increased to £ 15, 000 from 2005 -06 Repayment rate: 9% of excess income Zero real rate of interest • Students from low income families get £ 2700 grant
Repayments • Tuition fees repaid alongside any maintenance loan • Student maintenance loans – to £ 4000 • • Collected through the payroll, like tax Salary threshold increased to £ 15, 000 from 2005 -06 Repayment rate: 9% of excess income Zero real rate of interest • Students from low income families get £ 2700 grant
 Why do all this? • Put more income into HE • Fairer sharing of the cost between graduate, graduate’s family and the taxpayer • Increase influence of student demand on teaching quality • Put more control with institutions
Why do all this? • Put more income into HE • Fairer sharing of the cost between graduate, graduate’s family and the taxpayer • Increase influence of student demand on teaching quality • Put more control with institutions
 Why OFFA • Risk that potential students will – Be concerned about debt – Perceive that higher education is not affordable • Something needed to safeguard and promote access • An expectation that some variable fees will be invested in financial support for students
Why OFFA • Risk that potential students will – Be concerned about debt – Perceive that higher education is not affordable • Something needed to safeguard and promote access • An expectation that some variable fees will be invested in financial support for students
 What is OFFA for • Regulate the charging of higher tuition fees (but only FT UG) • Promote and safeguard fair access to HE • Identify good practice in the promotion of equality of access to higher education • But mustn’t interfere with academic freedom
What is OFFA for • Regulate the charging of higher tuition fees (but only FT UG) • Promote and safeguard fair access to HE • Identify good practice in the promotion of equality of access to higher education • But mustn’t interfere with academic freedom
 OFFA’s levers • Access agreement – – – • • Bursaries Outreach Financial Information Objectives Public documents Advice Publicity Fines Prohibition
OFFA’s levers • Access agreement – – – • • Bursaries Outreach Financial Information Objectives Public documents Advice Publicity Fines Prohibition
 OFFA • • • Requirements Expect more from those with furthest to go Additionality Ambitious milestones Collaborative outreach Monitoring Communication
OFFA • • • Requirements Expect more from those with furthest to go Additionality Ambitious milestones Collaborative outreach Monitoring Communication
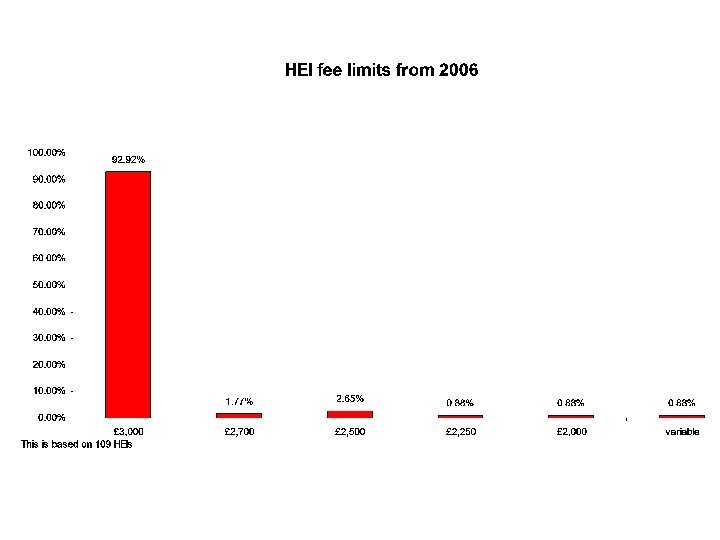
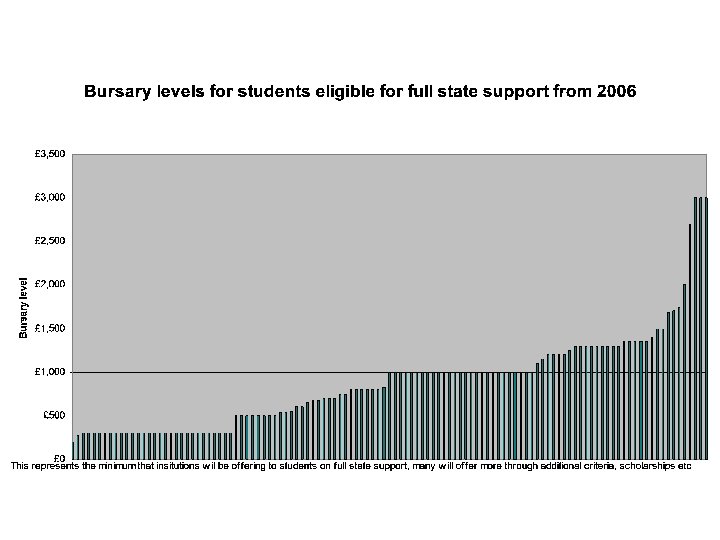
 What will impact of fees be • • • There is data on the fear of debt More generous student support package More places More communication More outreach Data on the initial introduction of tuition fees, and on the international experience, is encouraging
What will impact of fees be • • • There is data on the fear of debt More generous student support package More places More communication More outreach Data on the initial introduction of tuition fees, and on the international experience, is encouraging
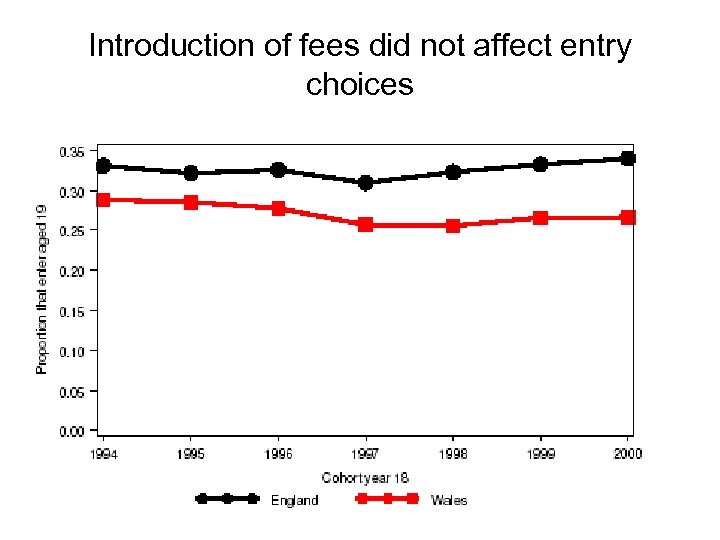 Introduction of fees did not affect entry choices
Introduction of fees did not affect entry choices
 Will this deliver fair access • Once prior attainment is sufficiently-well taken into account socio-economic background does not have an independent effect on HE participation. • The substantial social class inequality in HE occurs largely as a result of inequalities earlier in the education system.
Will this deliver fair access • Once prior attainment is sufficiently-well taken into account socio-economic background does not have an independent effect on HE participation. • The substantial social class inequality in HE occurs largely as a result of inequalities earlier in the education system.
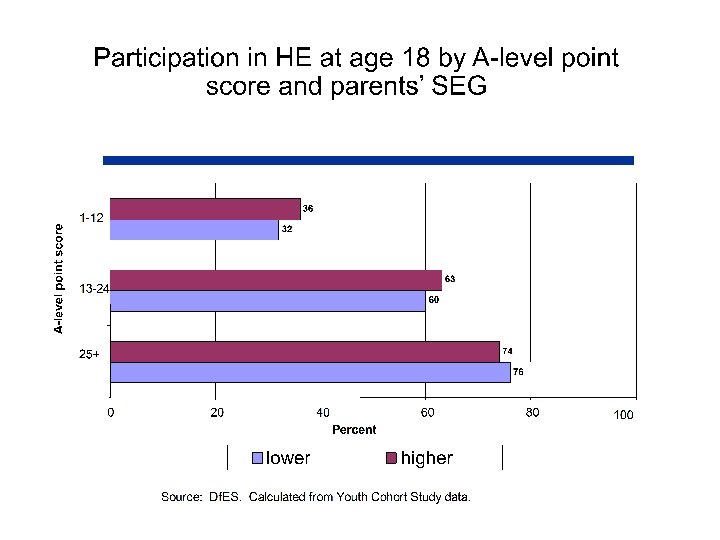
 Key Elements for Widening Participation • • Increased supply Effective outreach programme New modes of delivery Maintain retention rates Institutional strategies for widening participation Fair admissions Increased investment
Key Elements for Widening Participation • • Increased supply Effective outreach programme New modes of delivery Maintain retention rates Institutional strategies for widening participation Fair admissions Increased investment
 Funding • £ 282 million to institutions in 2005 -06: – £ 51 million outreach – £ 11 million for disabled students – £ 220 million for retention • Distributed on the basis of risk • £ 72 M for Aimhigher
Funding • £ 282 million to institutions in 2005 -06: – £ 51 million outreach – £ 11 million for disabled students – £ 220 million for retention • Distributed on the basis of risk • £ 72 M for Aimhigher
 Summary • English HE faces a long term complex problem • We have put in place a system which tries to balance the contributions of the state, students and parents • OFFA has provided assurance • We have a lot more to do before the profile of the HE student body fully reflects that of society at large
Summary • English HE faces a long term complex problem • We have put in place a system which tries to balance the contributions of the state, students and parents • OFFA has provided assurance • We have a lot more to do before the profile of the HE student body fully reflects that of society at large


