7207ebb7f9ffaa967effcb8661947dca.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Methodologies for Web Information System Design Peter Barna p. barna@tue. nl /department of mathematics and computer science

TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Outline • • • Traditional IS and WIS Phases of the design cycle for WIS Navigation and Adaptation Methodologies Conclusion Questions /department of mathematics and computer science

TU/e Traditional IS and WIS eindhovenuniversity of technology Traditional IS • Work typically with well defined and closed data repository • Serve to well known and specific audience • Use dedicated SW and HW platforms WIS • Work typically with heterogeneous, dynamic and distributed data • Serve to diverse and large audience • Use web navigation with all its specifics /department of mathematics and computer science
TU/e Typical WIS design cycle eindhovenuniversity of technology • • • Requirements analysis delivers Requirement spec Conceptual design delivers Conceptual model Navigation design delivers Navigation model(s) Adaptation design delivers Adaptation model Presentation design delivers Presentation model Implementation delivers WIS /department of mathematics and computer science
TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Navigation • Good navigation structure of an application helps user to find relevant information fast and avoids him to be “lost” in hyperspace • Navigation model: – Abstracts from concrete platform (OS, hypertext protocol) as much as possible – Depends on CM, but is separated (multiple NM possible for one CM) /department of mathematics and computer science
TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Adaptation • Makes WIS more suitable for individual users • Based on different aspects: – User’s platform; since it does not change during browsing the adaptation is static (adaptability) – User’s preferences; since this also usually does not change during the adaptation is static – User’s behaviour; since it includes also browsing, the adaptation is dynamic (adaptivity) /department of mathematics and computer science
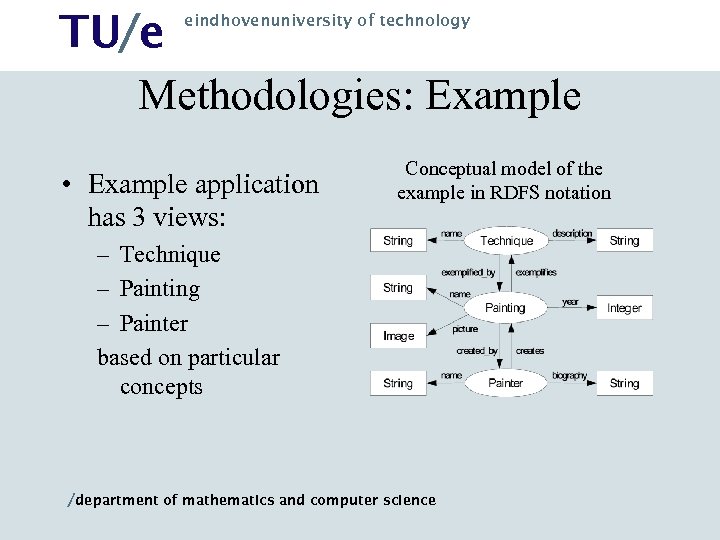
TU/e Methodologies: Example eindhovenuniversity of technology • Example application has 3 views: Conceptual model of the example in RDFS notation – Technique – Painting – Painter based on particular concepts /department of mathematics and computer science
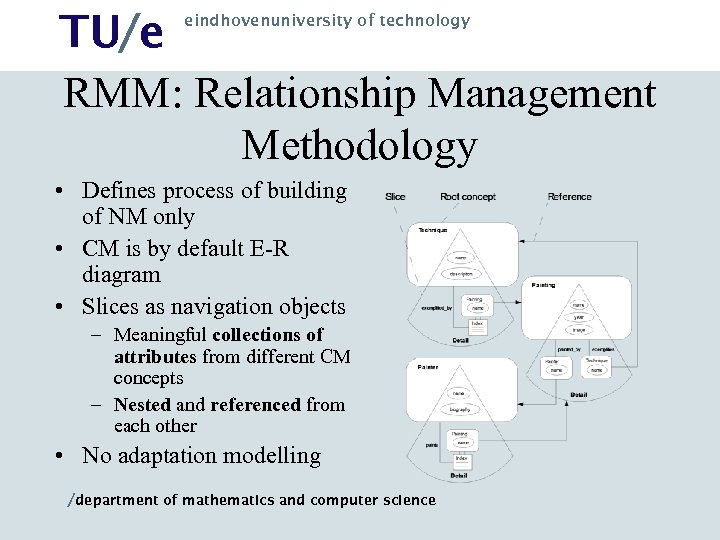
TU/e RMM: Relationship Management Methodology eindhovenuniversity of technology • Defines process of building of NM only • CM is by default E-R diagram • Slices as navigation objects – Meaningful collections of attributes from different CM concepts – Nested and referenced from each other • No adaptation modelling /department of mathematics and computer science
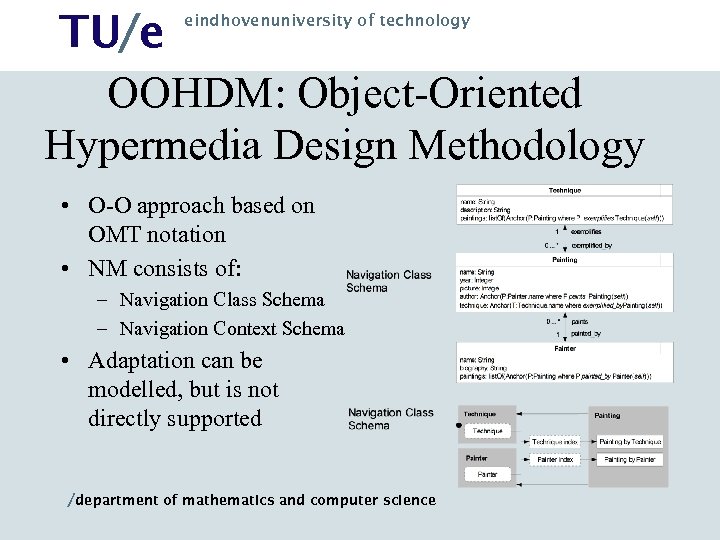
TU/e OOHDM: Object-Oriented Hypermedia Design Methodology eindhovenuniversity of technology • O-O approach based on OMT notation • NM consists of: – Navigation Class Schema – Navigation Context Schema • Adaptation can be modelled, but is not directly supported /department of mathematics and computer science
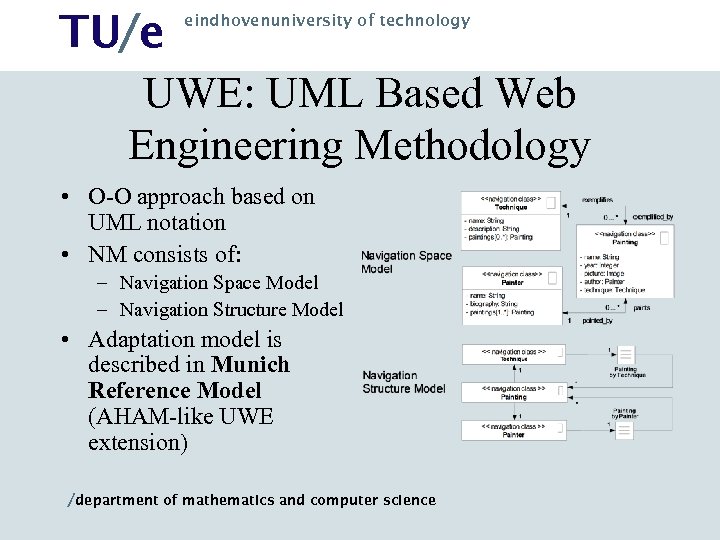
TU/e UWE: UML Based Web Engineering Methodology eindhovenuniversity of technology • O-O approach based on UML notation • NM consists of: – Navigation Space Model – Navigation Structure Model • Adaptation model is described in Munich Reference Model (AHAM-like UWE extension) /department of mathematics and computer science
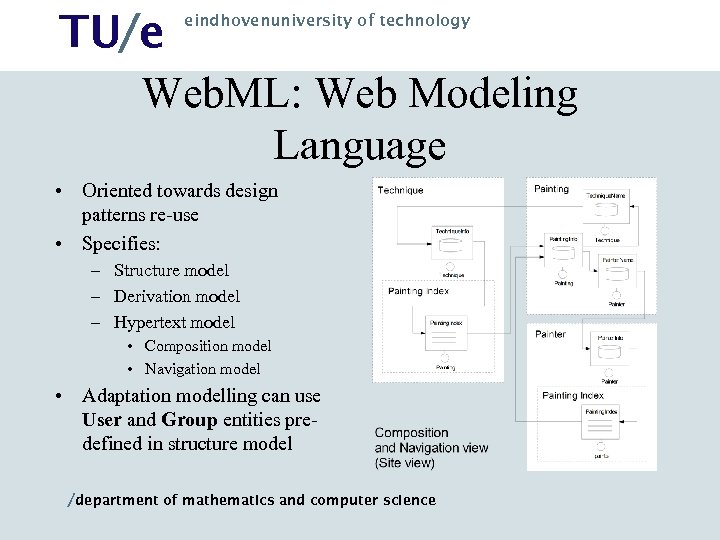
TU/e Web. ML: Web Modeling Language eindhovenuniversity of technology • Oriented towards design patterns re-use • Specifies: – Structure model – Derivation model – Hypertext model • Composition model • Navigation model • Adaptation modelling can use User and Group entities predefined in structure model /department of mathematics and computer science
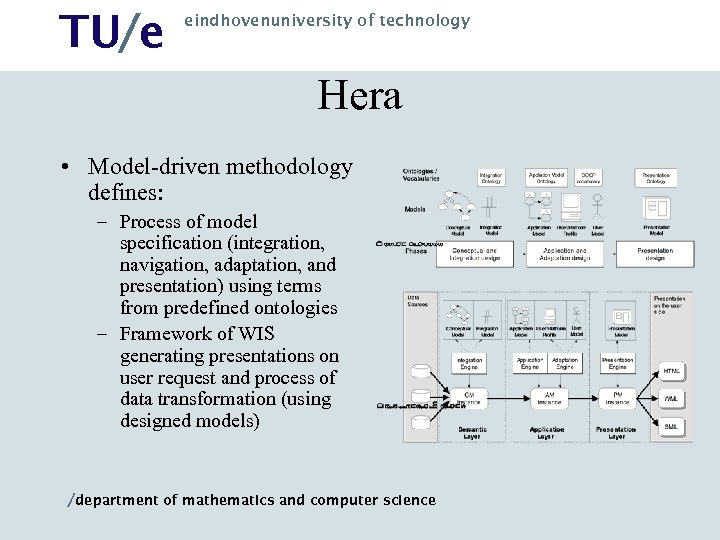
TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Hera • Model-driven methodology defines: – Process of model specification (integration, navigation, adaptation, and presentation) using terms from predefined ontologies – Framework of WIS generating presentations on user request and process of data transformation (using designed models) /department of mathematics and computer science
TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Hera • Navigation specification is RMM-like, it uses the slice concept • Adaptation in Hera: – Static (adaptability): based on platform profile and user’s preferences. The appearance of slices is decided during presentation generation – Dynamic (adaptivity): based on overview of concepts/slices visited by user during browsing. Hera uses the AHAM reference model. /department of mathematics and computer science

TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Conclusion • O-O methodologies facilitate specification of WIS with possible rich functionality, but the functionality specification is usually vague (the implementation of methods is left to programmers). • Many methodologies allow adaptation modeling in some ways, but just few really support it sufficiently. • Hera: allows automated presentation generation, supports adaptation modeling. • Future Hera research: extend it with techniques that would facilitate generation of presentations with functionality richer than only links following. /department of mathematics and computer science

TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Thank you for your attention… /department of mathematics and computer science

TU/e eindhovenuniversity of technology Questions… /department of mathematics and computer science
7207ebb7f9ffaa967effcb8661947dca.ppt