70fe4b260a98fd5458f0e0c52f7313f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from Message Sequence Charts Michael Ebner Institute for Informatics · University of Göttingen · Germany ISSRE 2004 - WITUL
TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from Message Sequence Charts Michael Ebner Institute for Informatics · University of Göttingen · Germany ISSRE 2004 - WITUL
 Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 2
Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 2
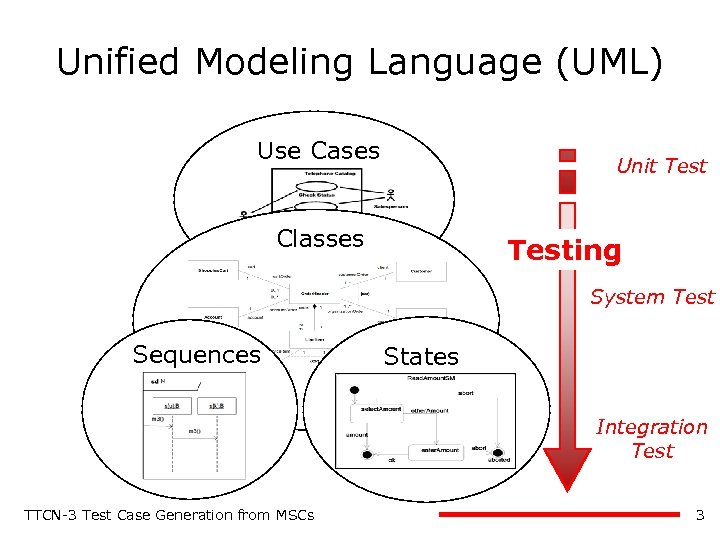 Unified Modeling Language (UML) Use Cases Unit Test Classes Testing System Test Sequences States Integration Test TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 3
Unified Modeling Language (UML) Use Cases Unit Test Classes Testing System Test Sequences States Integration Test TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 3
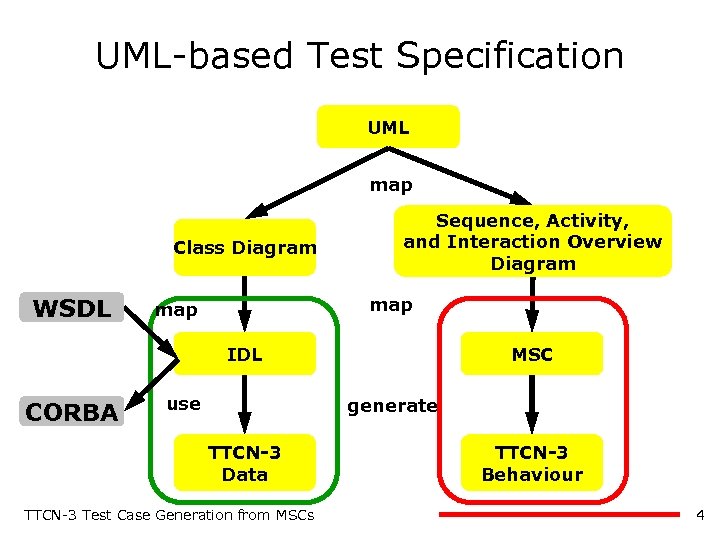 UML-based Test Specification UML map Class Diagram WSDL Sequence, Activity, and Interaction Overview Diagram map IDL CORBA use MSC generate TTCN-3 Data TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TTCN-3 Behaviour 4
UML-based Test Specification UML map Class Diagram WSDL Sequence, Activity, and Interaction Overview Diagram map IDL CORBA use MSC generate TTCN-3 Data TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TTCN-3 Behaviour 4
 Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 5
Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 5
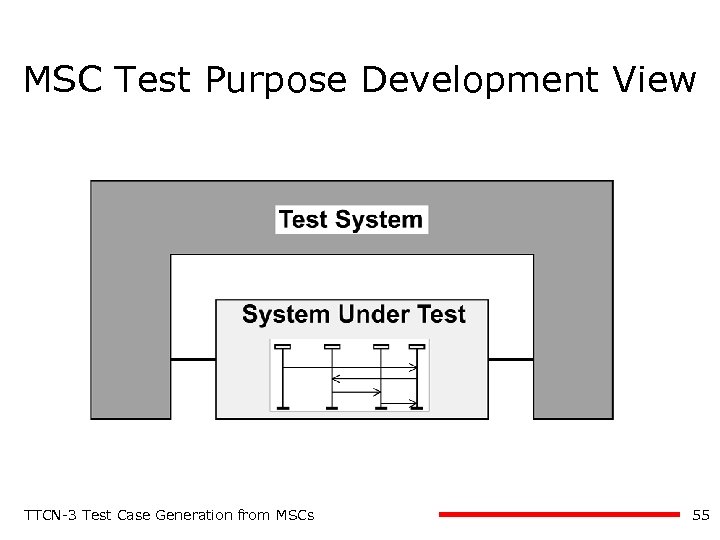
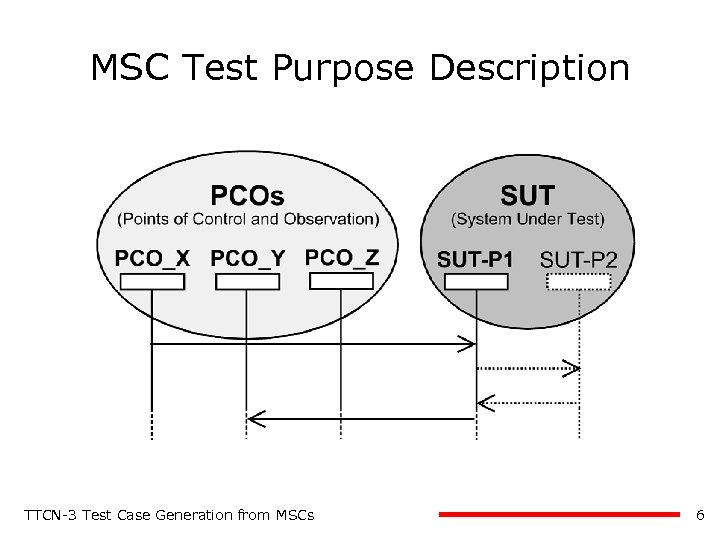 MSC Test Purpose Description TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 6
MSC Test Purpose Description TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 6
![Message Descriptions <message type> <message value> q [<message type>] <template reference> Matching mechanisms are Message Descriptions <message type> <message value> q [<message type>] <template reference> Matching mechanisms are](https://present5.com/presentation/70fe4b260a98fd5458f0e0c52f7313f3/image-7.jpg) Message Descriptions
Message Descriptions
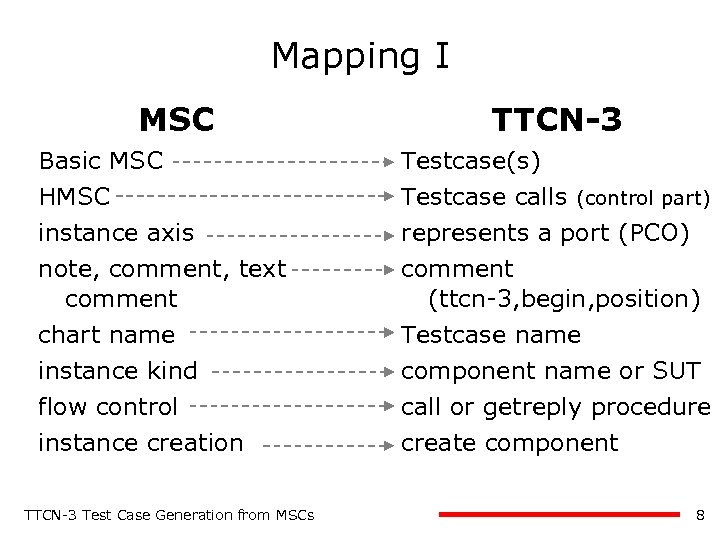 Mapping I MSC TTCN-3 Basic MSC HMSC instance axis note, comment, text comment chart name Testcase(s) Testcase calls (control part) represents a port (PCO) comment (ttcn-3, begin, position) Testcase name instance kind component name or SUT flow control call or getreply procedure instance creation create component TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 8
Mapping I MSC TTCN-3 Basic MSC HMSC instance axis note, comment, text comment chart name Testcase(s) Testcase calls (control part) represents a port (PCO) comment (ttcn-3, begin, position) Testcase name instance kind component name or SUT flow control call or getreply procedure instance creation create component TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 8
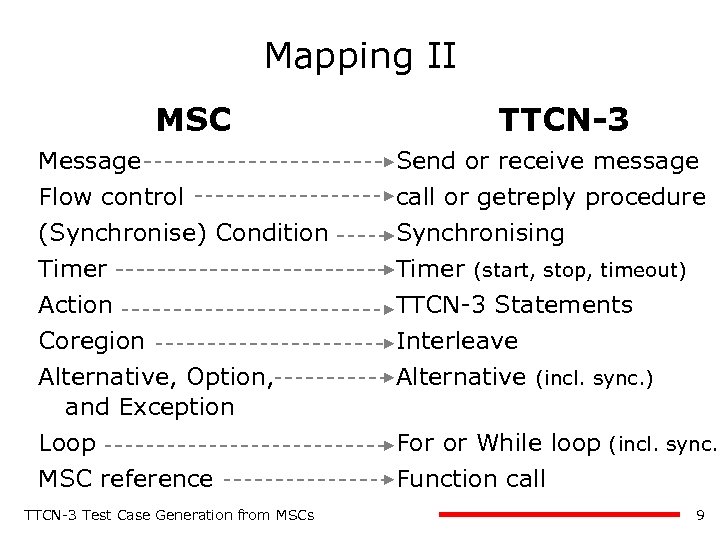 Mapping II MSC TTCN-3 Message Flow control (Synchronise) Condition Timer Action Coregion Send or receive message call or getreply procedure Synchronising Timer (start, stop, timeout) TTCN-3 Statements Interleave Alternative, Option, and Exception Alternative (incl. sync. ) Loop For or While loop (incl. sync. ) MSC reference Function call TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 9
Mapping II MSC TTCN-3 Message Flow control (Synchronise) Condition Timer Action Coregion Send or receive message call or getreply procedure Synchronising Timer (start, stop, timeout) TTCN-3 Statements Interleave Alternative, Option, and Exception Alternative (incl. sync. ) Loop For or While loop (incl. sync. ) MSC reference Function call TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 9
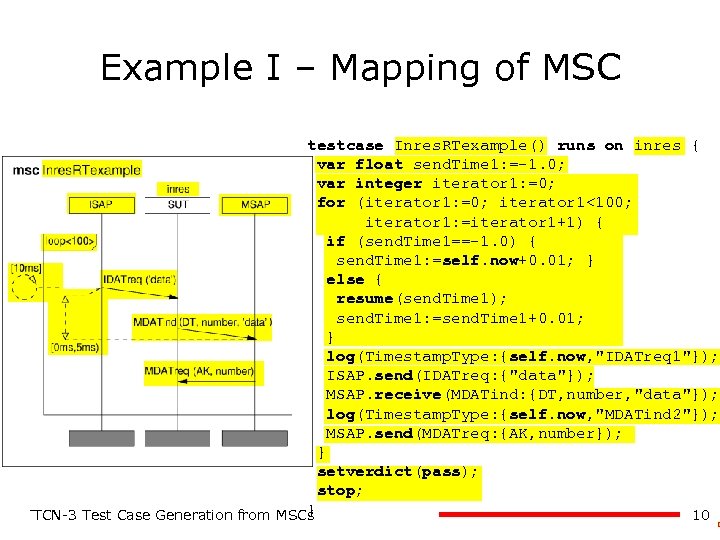 Example I – Mapping of MSC testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres { var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } 10 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs
Example I – Mapping of MSC testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres { var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } 10 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs
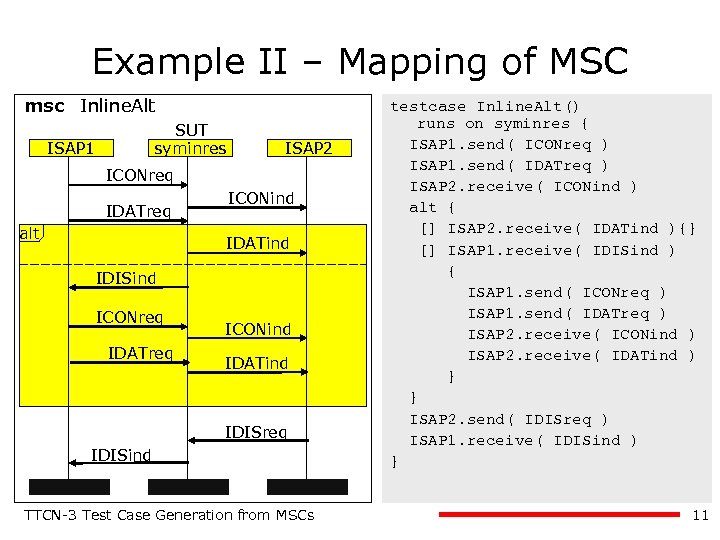 Example II – Mapping of MSC msc Inline. Alt SUT syminres ISAP 1 ISAP 2 ICONreq IDATreq alt ICONind IDATind IDISind ICONreq IDATreq ICONind IDATind IDISreq IDISind TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs testcase Inline. Alt() runs on syminres { ISAP 1. send( ICONreq ) ISAP 1. send( IDATreq ) ISAP 2. receive( ICONind ) alt { [] ISAP 2. receive( IDATind ){} [] ISAP 1. receive( IDISind ) { ISAP 1. send( ICONreq ) ISAP 1. send( IDATreq ) ISAP 2. receive( ICONind ) ISAP 2. receive( IDATind ) } } ISAP 2. send( IDISreq ) ISAP 1. receive( IDISind ) } 11
Example II – Mapping of MSC msc Inline. Alt SUT syminres ISAP 1 ISAP 2 ICONreq IDATreq alt ICONind IDATind IDISind ICONreq IDATreq ICONind IDATind IDISreq IDISind TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs testcase Inline. Alt() runs on syminres { ISAP 1. send( ICONreq ) ISAP 1. send( IDATreq ) ISAP 2. receive( ICONind ) alt { [] ISAP 2. receive( IDATind ){} [] ISAP 1. receive( IDISind ) { ISAP 1. send( ICONreq ) ISAP 1. send( IDATreq ) ISAP 2. receive( ICONind ) ISAP 2. receive( IDATind ) } } ISAP 2. send( IDISreq ) ISAP 1. receive( IDISind ) } 11
 Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 12
Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 12
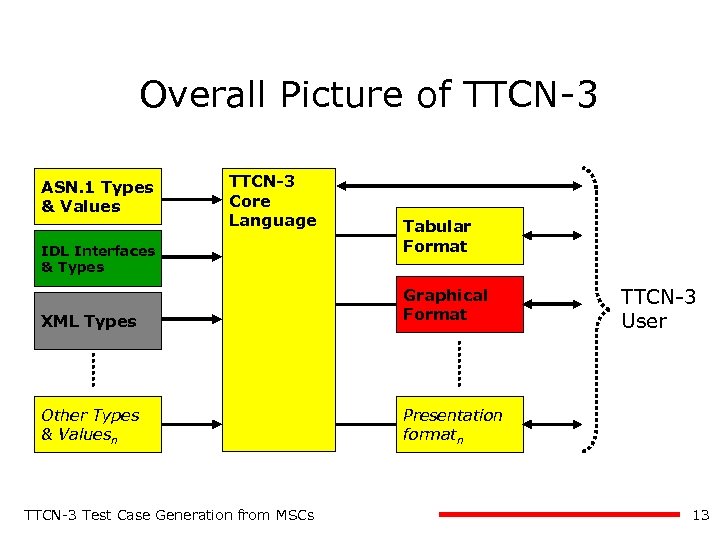 Overall Picture of TTCN-3 ASN. 1 Types & Values TTCN-3 Core Language IDL Interfaces & Types Tabular Format XML Types Graphical Format Other Types & Valuesn TTCN-3 User Presentation formatn TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 13
Overall Picture of TTCN-3 ASN. 1 Types & Values TTCN-3 Core Language IDL Interfaces & Types Tabular Format XML Types Graphical Format Other Types & Valuesn TTCN-3 User Presentation formatn TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 13
 GFT I § Provides a test specific profile for MSC-2000 § Defines generic extensions Ø Value returning GFT References Ø Hyper GFT Ø Hybrid GFT § Defines test specific extensions, e. g. Ø Port instances Ø Special Messages for instance handling Ø Type and Template definition for messages Ø Trigger and check message Ø Verdicts as special conditions Ø Defaults TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 14
GFT I § Provides a test specific profile for MSC-2000 § Defines generic extensions Ø Value returning GFT References Ø Hyper GFT Ø Hybrid GFT § Defines test specific extensions, e. g. Ø Port instances Ø Special Messages for instance handling Ø Type and Template definition for messages Ø Trigger and check message Ø Verdicts as special conditions Ø Defaults TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 14
 GFT II § Does not use ØGates ØGeneral Ordering ØTime Concepts ØMSC Reference Expression ØInstance Decomposition § Assumed data types are TTCN-3 data types TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 15
GFT II § Does not use ØGates ØGeneral Ordering ØTime Concepts ØMSC Reference Expression ØInstance Decomposition § Assumed data types are TTCN-3 data types TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 15
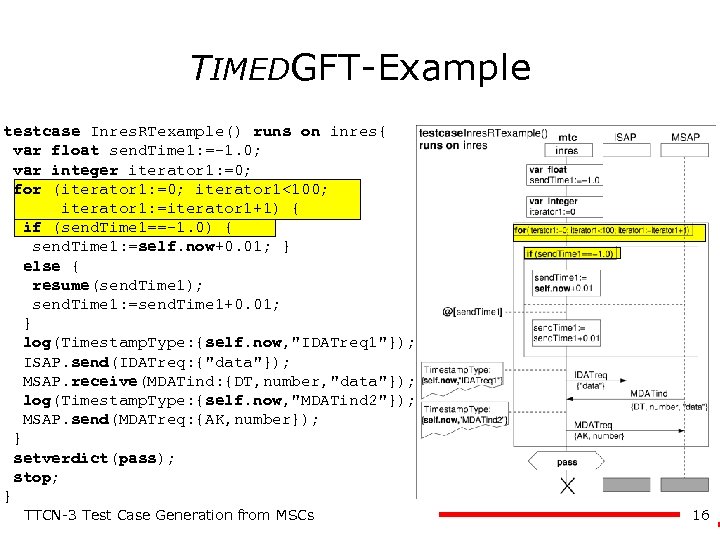 TIMEDGFT-Example testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres{ var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 16
TIMEDGFT-Example testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres{ var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 16
 Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 17
Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 17
 The UML 2. 0 Testing Profile (UTP) § Profile: UML extension mechanism § Initiated late 2001 § Make UML applicable for SW testing by enhancing UML with test concepts § Enhances reuse of design model § Adopted by OMG in June 2003 and since April 2004 standardized § Allow automated test generation with UML TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 18
The UML 2. 0 Testing Profile (UTP) § Profile: UML extension mechanism § Initiated late 2001 § Make UML applicable for SW testing by enhancing UML with test concepts § Enhances reuse of design model § Adopted by OMG in June 2003 and since April 2004 standardized § Allow automated test generation with UML TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 18
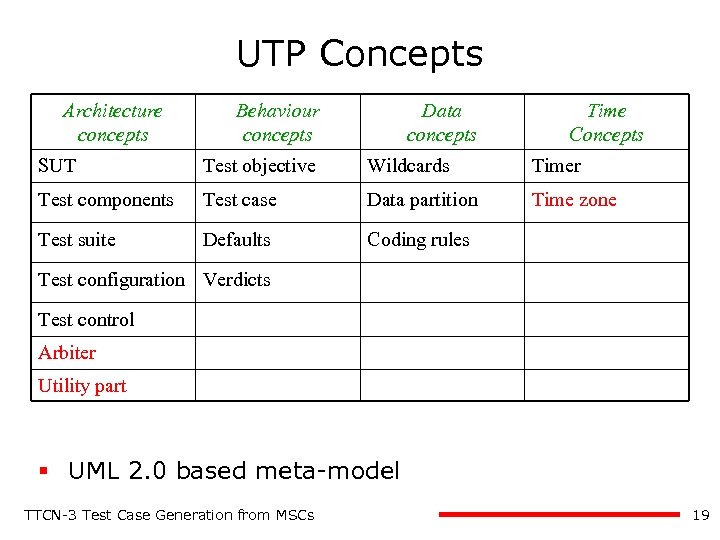 UTP Concepts Architecture concepts Behaviour concepts Data concepts Time Concepts SUT Test objective Wildcards Timer Test components Test case Data partition Time zone Test suite Defaults Coding rules Test configuration Verdicts Test control Arbiter Utility part § UML 2. 0 based meta-model TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 19
UTP Concepts Architecture concepts Behaviour concepts Data concepts Time Concepts SUT Test objective Wildcards Timer Test components Test case Data partition Time zone Test suite Defaults Coding rules Test configuration Verdicts Test control Arbiter Utility part § UML 2. 0 based meta-model TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 19
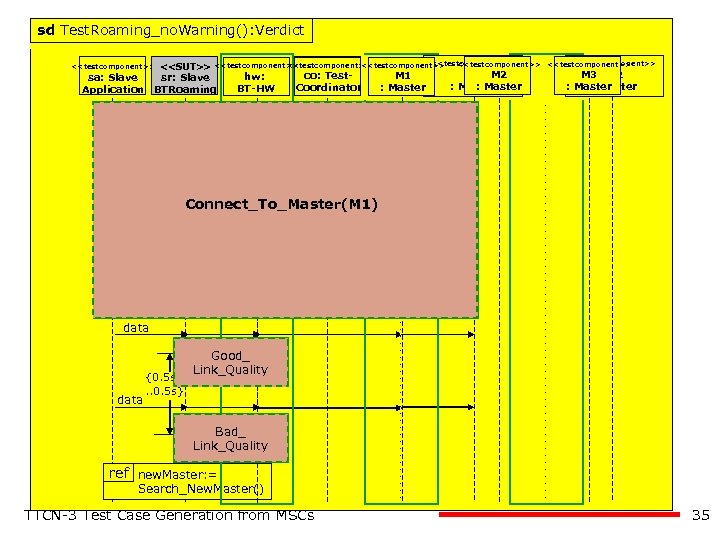
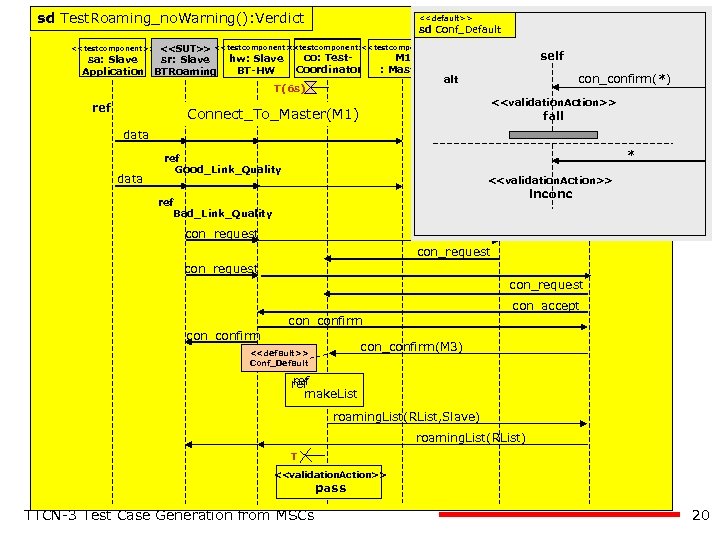 sd Test. Roaming_no. Warning(): Verdict sd BT-Roaming <
sd Test. Roaming_no. Warning(): Verdict sd BT-Roaming <
 UTP Outlook § Upcoming tool support: Ø Ø IBM/Rational: Eclipse Project Hyades Telelogic: Tau G 2 Microsoft: Visual Studio Daimler/FOKUS/Nokia/Testing. Tech: ITEA-Project TT-Medal TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 21
UTP Outlook § Upcoming tool support: Ø Ø IBM/Rational: Eclipse Project Hyades Telelogic: Tau G 2 Microsoft: Visual Studio Daimler/FOKUS/Nokia/Testing. Tech: ITEA-Project TT-Medal TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 21
 Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 22
Overview § Concept § Mapping of MSC to TTCN-3 § Related Concepts ØGraphical Format of TTCN-3 (GFT) ØUML Testing Profile (UTP) ØComparison § Summary TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 22
 Comparison I § all three concepts were based on MSC § support of graphical test development § differ in deepness of test features ØMSC ØGFT ØUTP TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 23
Comparison I § all three concepts were based on MSC § support of graphical test development § differ in deepness of test features ØMSC ØGFT ØUTP TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 23
 Comparison II § Test Case Generation from MSCs Ø centred on test purposes Ø is focussed on manual, scenario testing Ø abstracts from details Ø no support of all TTCN-3 features Ø direct mapping to test case templates Ø requires less knowledge about TTCN-3 Ø timed. TTCN-3 support § GFT Ø MSC based representation format for TTCN-3 Ø has to present all TTCN-3 features Ø timed. TTCN-3 support Ø not desired as graphical specification language TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 24
Comparison II § Test Case Generation from MSCs Ø centred on test purposes Ø is focussed on manual, scenario testing Ø abstracts from details Ø no support of all TTCN-3 features Ø direct mapping to test case templates Ø requires less knowledge about TTCN-3 Ø timed. TTCN-3 support § GFT Ø MSC based representation format for TTCN-3 Ø has to present all TTCN-3 features Ø timed. TTCN-3 support Ø not desired as graphical specification language TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 24
 Comparison III § UTP Ø representation and specification of all aspects Ø independent of TTCN-3 Ø no complete mapping to TTCN-3 Ø enhanced testing concepts Ø better integration to UML Ø meta-model for testing Ø wide application area (mapping to JUnit and TTCN-3) TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 25
Comparison III § UTP Ø representation and specification of all aspects Ø independent of TTCN-3 Ø no complete mapping to TTCN-3 Ø enhanced testing concepts Ø better integration to UML Ø meta-model for testing Ø wide application area (mapping to JUnit and TTCN-3) TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 25
 Summary § MSC as powerful means for test purpose and test case specifications § MSC like presentation formats § Test case generation from MSC test purposes TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 26
Summary § MSC as powerful means for test purpose and test case specifications § MSC like presentation formats § Test case generation from MSC test purposes TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 26
 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from Message Sequence Charts Michael Ebner Institute for Informatics · University of Göttingen · Germany WITUL 2004 (IEEE Conference ISSRE)
TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from Message Sequence Charts Michael Ebner Institute for Informatics · University of Göttingen · Germany WITUL 2004 (IEEE Conference ISSRE)
 END TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 28
END TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 28
 Backup TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 29
Backup TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 29
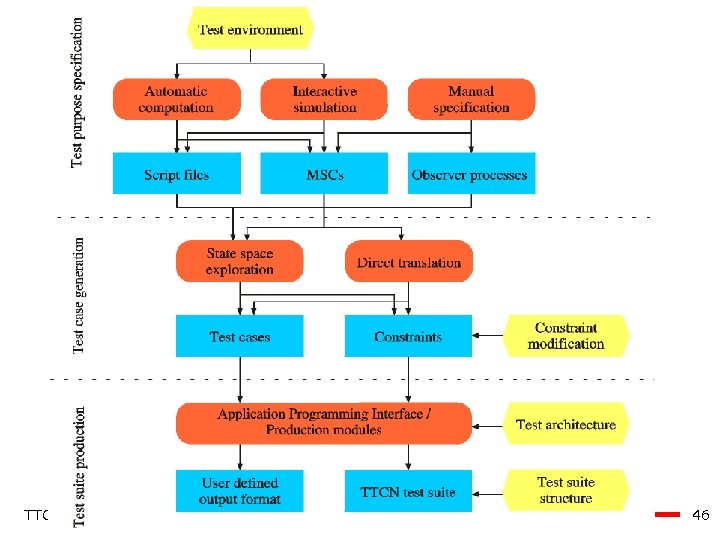
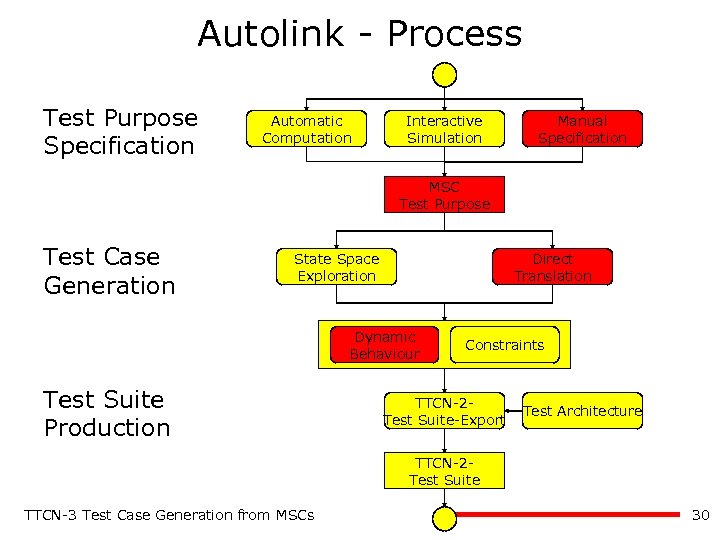 Autolink - Process Test Purpose Specification Automatic Computation Interactive Simulation Manual Specification MSC Test Purpose Test Case Generation State Space Exploration Direct Translation Dynamic Behaviour Test Suite Production Constraints TTCN-2 Test Suite-Export Test Architecture TTCN-2 Test Suite TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 30
Autolink - Process Test Purpose Specification Automatic Computation Interactive Simulation Manual Specification MSC Test Purpose Test Case Generation State Space Exploration Direct Translation Dynamic Behaviour Test Suite Production Constraints TTCN-2 Test Suite-Export Test Architecture TTCN-2 Test Suite TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 30
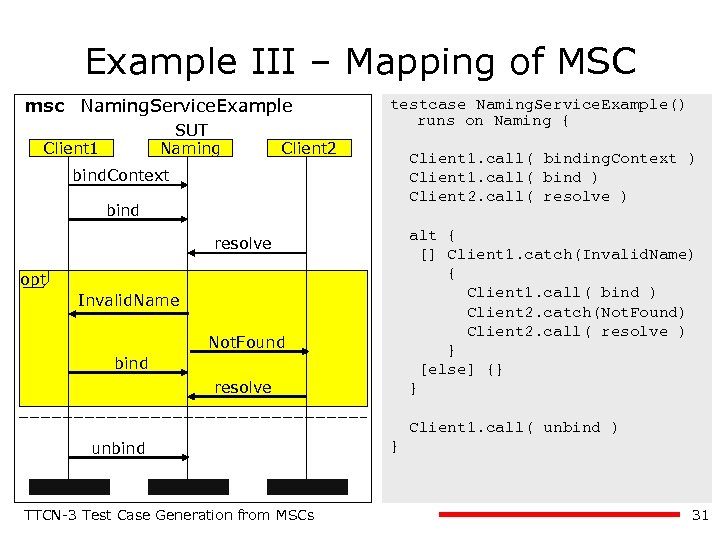 Example III – Mapping of MSC msc Naming. Service. Example SUT Naming Client 1 testcase Naming. Service. Example() runs on Naming { Client 2 Client 1. call( binding. Context ) Client 1. call( bind ) Client 2. call( resolve ) bind. Context bind alt { [] Client 1. catch(Invalid. Name) { Client 1. call( bind ) Client 2. catch(Not. Found) Client 2. call( resolve ) } [else] {} } resolve opt Invalid. Name Not. Found bind resolve Client 1. call( unbind ) unbind TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs } 31
Example III – Mapping of MSC msc Naming. Service. Example SUT Naming Client 1 testcase Naming. Service. Example() runs on Naming { Client 2 Client 1. call( binding. Context ) Client 1. call( bind ) Client 2. call( resolve ) bind. Context bind alt { [] Client 1. catch(Invalid. Name) { Client 1. call( bind ) Client 2. catch(Not. Found) Client 2. call( resolve ) } [else] {} } resolve opt Invalid. Name Not. Found bind resolve Client 1. call( unbind ) unbind TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs } 31
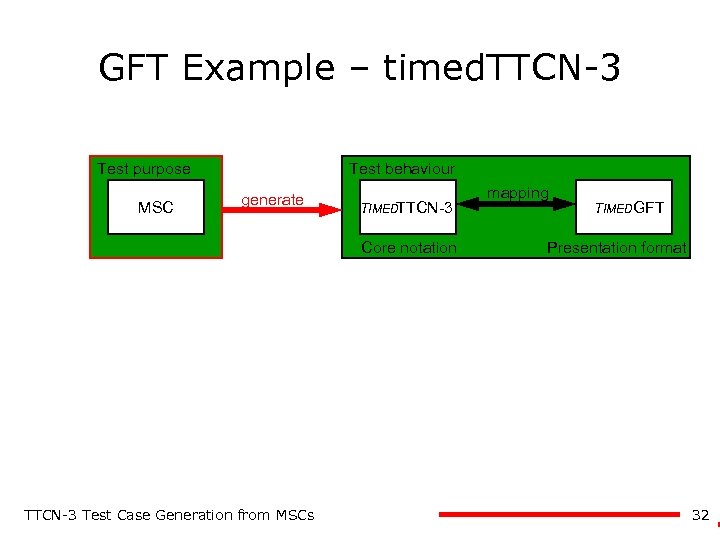 GFT Example – timed. TTCN-3 Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format 32
GFT Example – timed. TTCN-3 Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format 32
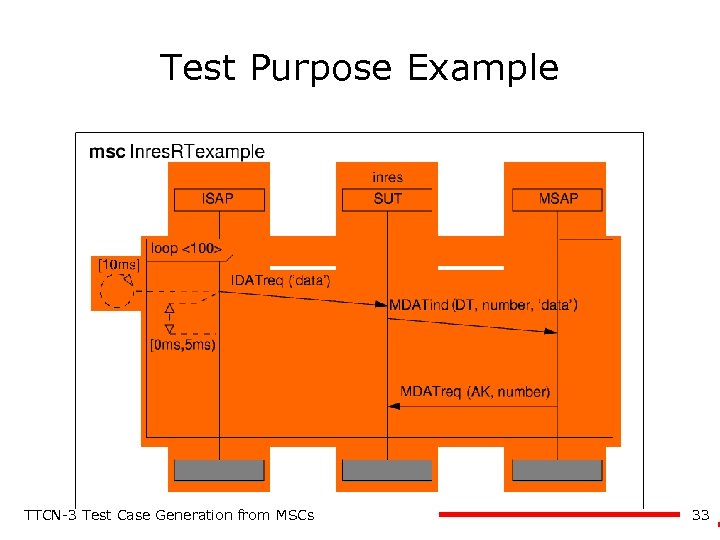 Test Purpose Example TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 33
Test Purpose Example TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 33
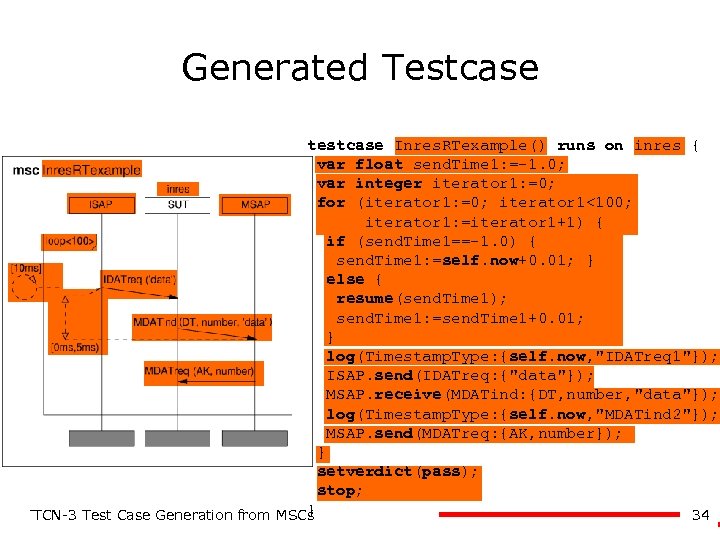 Generated Testcase testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres { var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } 34 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs
Generated Testcase testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres { var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } 34 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs
 sd Test. Roaming_no. Warning(): Verdict sd BT-Roaming <
sd Test. Roaming_no. Warning(): Verdict sd BT-Roaming <
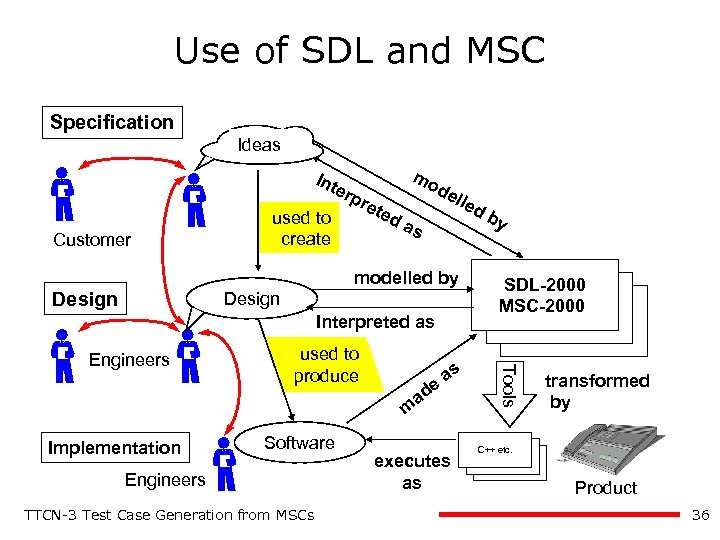 Use of SDL and MSC Specification Ideas Int erp Customer used to create ret mo ed de lle as modelled by Design Interpreted as used to produce de a as m Implementation Software Engineers TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs executes as y SDL-2000 MSC-2000 Tools Engineers db transformed by C++ etc. Product 36
Use of SDL and MSC Specification Ideas Int erp Customer used to create ret mo ed de lle as modelled by Design Interpreted as used to produce de a as m Implementation Software Engineers TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs executes as y SDL-2000 MSC-2000 Tools Engineers db transformed by C++ etc. Product 36
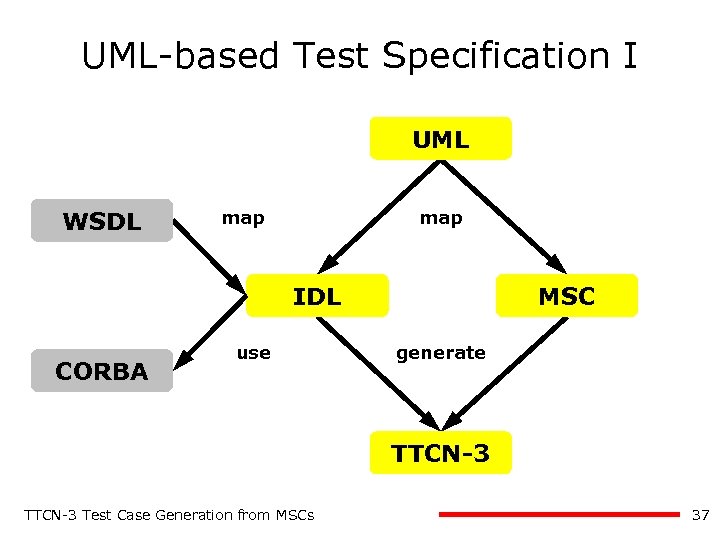 UML-based Test Specification I UML WSDL map IDL CORBA use MSC generate oo. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 37
UML-based Test Specification I UML WSDL map IDL CORBA use MSC generate oo. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 37
 Graphical Format for TTCN-3 (GFT) § Provides a test specific profile for MSC-2000 ØUses a subset of MSC-2000 ØDefines test specific extensions ØDefines general extensions § Formerly called Test Sequence Charts (TSC) § Supports different forms to represent test cases TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 38
Graphical Format for TTCN-3 (GFT) § Provides a test specific profile for MSC-2000 ØUses a subset of MSC-2000 ØDefines test specific extensions ØDefines general extensions § Formerly called Test Sequence Charts (TSC) § Supports different forms to represent test cases TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 38
 UTP Methodology Wrap-Up § Test preparations Ø Define a test package with a test suite. Ø Determine SUT and import its implementation. Ø Determine test objectives. § Test configuration Ø Assign roles: SUT, test components, utility part. Ø Attach stereotypes. § Test cases Ø Group instances. Ø Attach stereotypes. Ø Define re-usable test fragments to functions. Ø Assign verdicts. Ø Specify timers. Ø Specify default behaviours TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 39
UTP Methodology Wrap-Up § Test preparations Ø Define a test package with a test suite. Ø Determine SUT and import its implementation. Ø Determine test objectives. § Test configuration Ø Assign roles: SUT, test components, utility part. Ø Attach stereotypes. § Test cases Ø Group instances. Ø Attach stereotypes. Ø Define re-usable test fragments to functions. Ø Assign verdicts. Ø Specify timers. Ø Specify default behaviours TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 39
 Use of Inline Expressions and HMSCs § Problem Ø Several alternative test sequences referred to in one diagram. § Two possibilities Ø All alternatives are put in one test case. Ø For each alternative a separate test case is generated. § Strategy Ø Alternatives described in form of HMSCs are translated into separate test cases. Ø Alternatives described by inline expressions are put into the same test case. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 40
Use of Inline Expressions and HMSCs § Problem Ø Several alternative test sequences referred to in one diagram. § Two possibilities Ø All alternatives are put in one test case. Ø For each alternative a separate test case is generated. § Strategy Ø Alternatives described in form of HMSCs are translated into separate test cases. Ø Alternatives described by inline expressions are put into the same test case. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 40
 To. C der Dissertation 1. Introduction 2. A General Metamodel For Testing 3. Graphical Test Development (with case study) v With TTCN-3 v With U 2 TP (UML Based Metamodel) v Relationship and Mapping Between TTCN 3 and U 2 TP 4. Graphical Realtime Testing with TTCN -3 and U 2 TP (with case study) 5. Conclusion TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 41
To. C der Dissertation 1. Introduction 2. A General Metamodel For Testing 3. Graphical Test Development (with case study) v With TTCN-3 v With U 2 TP (UML Based Metamodel) v Relationship and Mapping Between TTCN 3 and U 2 TP 4. Graphical Realtime Testing with TTCN -3 and U 2 TP (with case study) 5. Conclusion TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 41
 UTP Outlook § FTF submission: April 2004 § Upcoming tool support: Ø Ø IBM/Rational: Eclipse Project Hyades Telelogic: Tau G 2 Microsoft: Visual Studio Daimler/FOKUS/Nokia/Testing. Tech: ITEA-Project TT-Medal § Automated test generation TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 42
UTP Outlook § FTF submission: April 2004 § Upcoming tool support: Ø Ø IBM/Rational: Eclipse Project Hyades Telelogic: Tau G 2 Microsoft: Visual Studio Daimler/FOKUS/Nokia/Testing. Tech: ITEA-Project TT-Medal § Automated test generation TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 42
 To. C der Dissertation 1. Introduction 2. A General Metamodel For Testing 3. Graphical Test Development (with case study) v With TTCN-3 v With U 2 TP (UML Based Metamodel) v Relationship and Mapping Between TTCN 3 and U 2 TP 4. Graphical Realtime Testing with TTCN -3 and U 2 TP (with case study) 5. Conclusion TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 43
To. C der Dissertation 1. Introduction 2. A General Metamodel For Testing 3. Graphical Test Development (with case study) v With TTCN-3 v With U 2 TP (UML Based Metamodel) v Relationship and Mapping Between TTCN 3 and U 2 TP 4. Graphical Realtime Testing with TTCN -3 and U 2 TP (with case study) 5. Conclusion TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 43
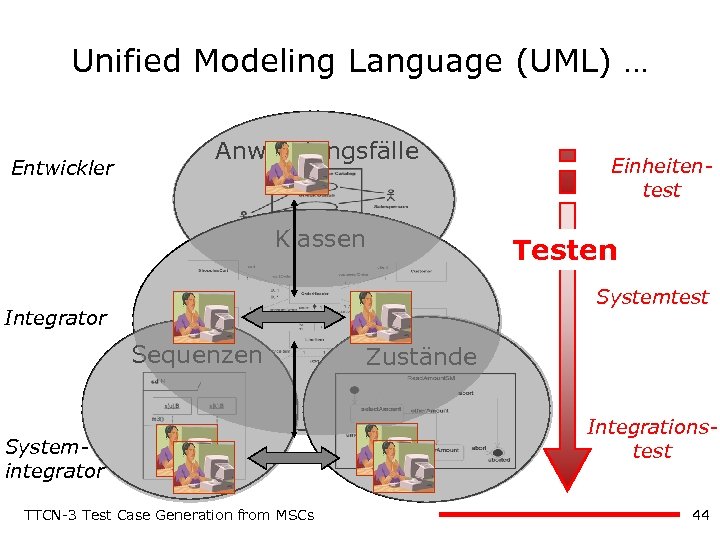 Unified Modeling Language (UML) … Entwickler Anwendungsfälle Klassen Einheitentest Testen Systemtest Integrator Sequenzen Systemintegrator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs Zustände Integrationstest 44
Unified Modeling Language (UML) … Entwickler Anwendungsfälle Klassen Einheitentest Testen Systemtest Integrator Sequenzen Systemintegrator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs Zustände Integrationstest 44
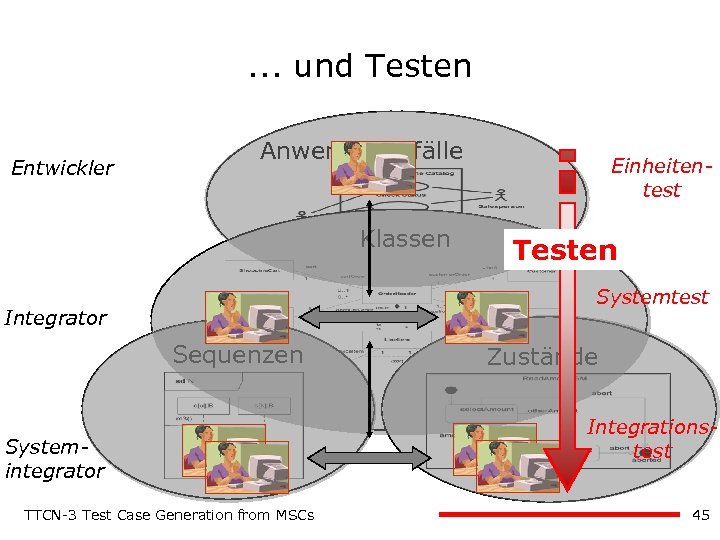 . . . und Testen Entwickler Anwendungsfälle Klassen Einheitentest Testen Systemtest Integrator Sequenzen Systemintegrator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs Zustände Integrationstest 45
. . . und Testen Entwickler Anwendungsfälle Klassen Einheitentest Testen Systemtest Integrator Sequenzen Systemintegrator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs Zustände Integrationstest 45
 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 46
TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 46
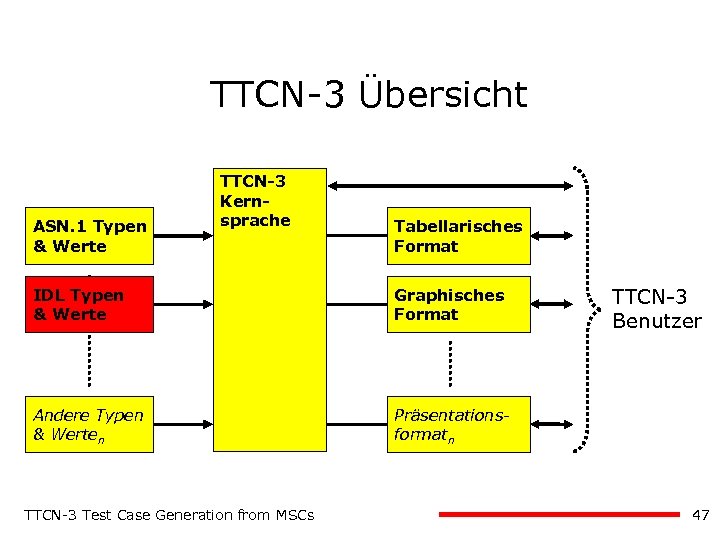 TTCN-3 Übersicht ASN. 1 Typen & Werte TTCN-3 Kernsprache Tabellarisches Format IDL Typen & Werte Graphisches Format Andere Typen & Werten TTCN-3 Benutzer Präsentationsformatn TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 47
TTCN-3 Übersicht ASN. 1 Typen & Werte TTCN-3 Kernsprache Tabellarisches Format IDL Typen & Werte Graphisches Format Andere Typen & Werten TTCN-3 Benutzer Präsentationsformatn TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 47
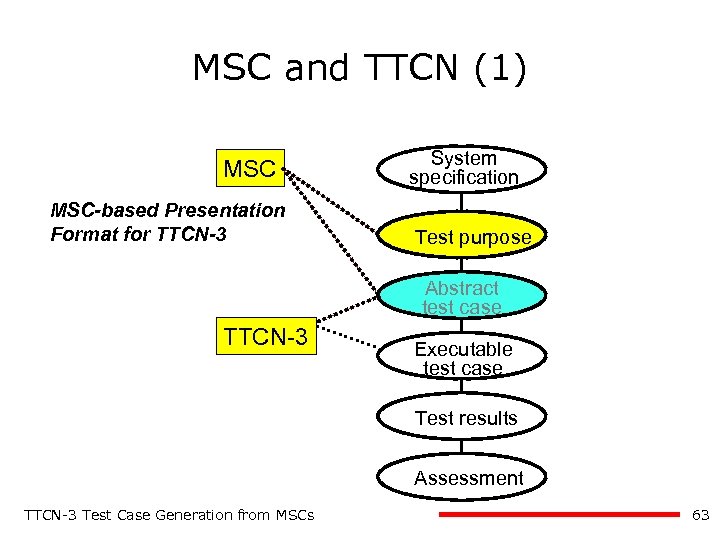
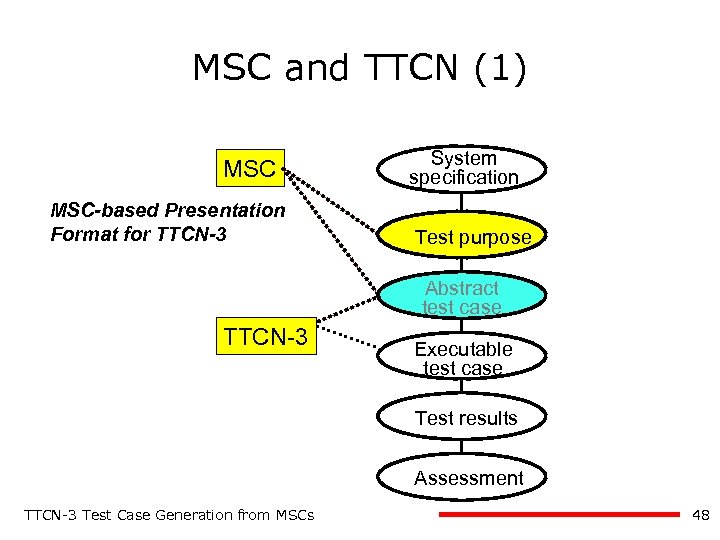 MSC and TTCN (1) MSC-based Presentation Format for TTCN-3 System specification Test purpose Abstract test case TTCN-3 Executable test case Test results Assessment TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 48
MSC and TTCN (1) MSC-based Presentation Format for TTCN-3 System specification Test purpose Abstract test case TTCN-3 Executable test case Test results Assessment TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 48
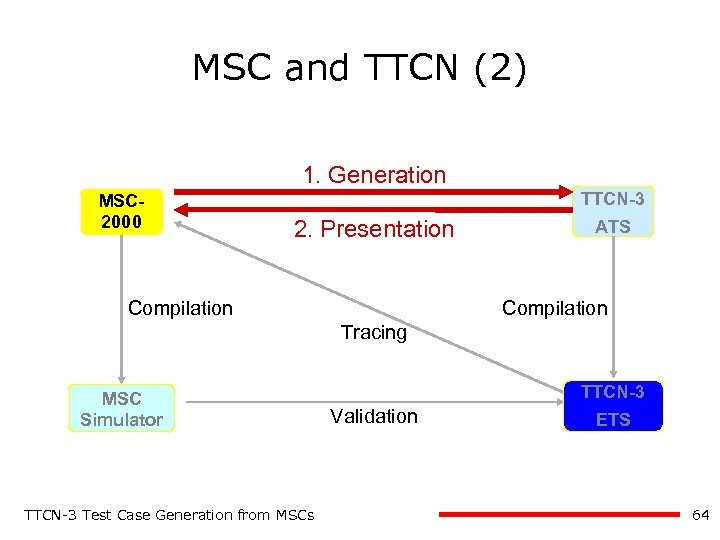
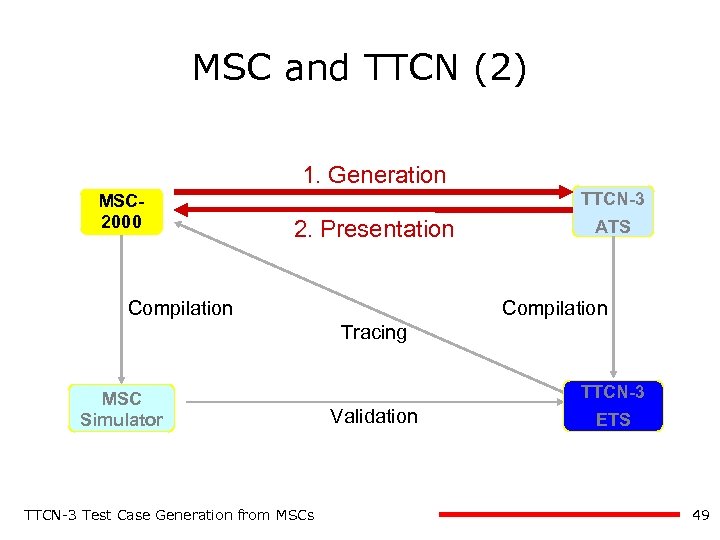 MSC and TTCN (2) 1. Generation MSC 2000 TTCN-3 2. Presentation Compilation ATS Compilation Tracing MSC Simulator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TTCN-3 Validation ETS 49
MSC and TTCN (2) 1. Generation MSC 2000 TTCN-3 2. Presentation Compilation ATS Compilation Tracing MSC Simulator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TTCN-3 Validation ETS 49
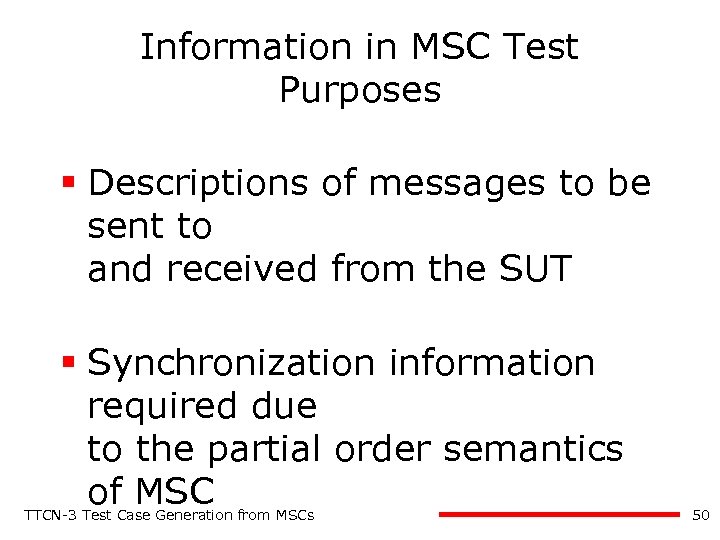 Information in MSC Test Purposes § Descriptions of messages to be sent to and received from the SUT § Synchronization information required due to the partial order semantics of MSC TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 50
Information in MSC Test Purposes § Descriptions of messages to be sent to and received from the SUT § Synchronization information required due to the partial order semantics of MSC TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 50
 MSC Objectives § is a scenario language § supports complete and incomplete specifications § is a graphical language § is widely applicable § can be used throughout the engineering process § supports structured design § is often used in conjunction with other methods and languages TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 51
MSC Objectives § is a scenario language § supports complete and incomplete specifications § is a graphical language § is widely applicable § can be used throughout the engineering process § supports structured design § is often used in conjunction with other methods and languages TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 51
 The Tutorial Example § INRES - Initiator-Responder protocol § an abridged version of the Abracadabra protocol used for academic studies and illustrative purposes. § a connection-oriented, asymmetric communication protocol § a medium with uncorrupted data, loss of data, misordering TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 52
The Tutorial Example § INRES - Initiator-Responder protocol § an abridged version of the Abracadabra protocol used for academic studies and illustrative purposes. § a connection-oriented, asymmetric communication protocol § a medium with uncorrupted data, loss of data, misordering TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 52
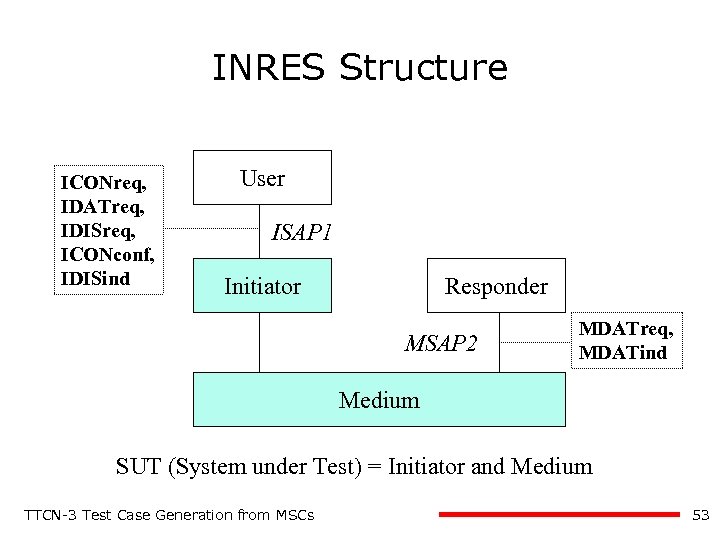 INRES Structure ICONreq, IDATreq, IDISreq, ICONconf, IDISind User ISAP 1 Initiator Responder MSAP 2 MDATreq, MDATind Medium SUT (System under Test) = Initiator and Medium TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 53
INRES Structure ICONreq, IDATreq, IDISreq, ICONconf, IDISind User ISAP 1 Initiator Responder MSAP 2 MDATreq, MDATind Medium SUT (System under Test) = Initiator and Medium TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 53
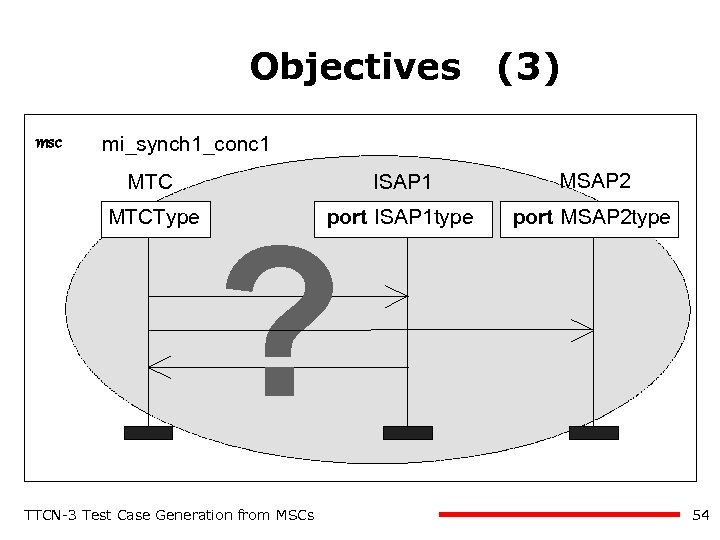 Objectives (3) msc mi_synch 1_conc 1 MTC ISAP 1 MSAP 2 MTCType port ISAP 1 type port MSAP 2 type ? TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 54
Objectives (3) msc mi_synch 1_conc 1 MTC ISAP 1 MSAP 2 MTCType port ISAP 1 type port MSAP 2 type ? TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 54
 MSC Test Purpose Development View TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 55
MSC Test Purpose Development View TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 55
 Objektorientierung für TTCN-3 § Kein Objekttyp und Portinstanzen können nicht übertragen werden ØObjektreferenzen in IUT nicht handhabbar § Einführung von Klassen § Erweiterung vorhandener Konzepte ØVererbung von Templates § Hierarchie von Komponenten TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 56
Objektorientierung für TTCN-3 § Kein Objekttyp und Portinstanzen können nicht übertragen werden ØObjektreferenzen in IUT nicht handhabbar § Einführung von Klassen § Erweiterung vorhandener Konzepte ØVererbung von Templates § Hierarchie von Komponenten TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 56
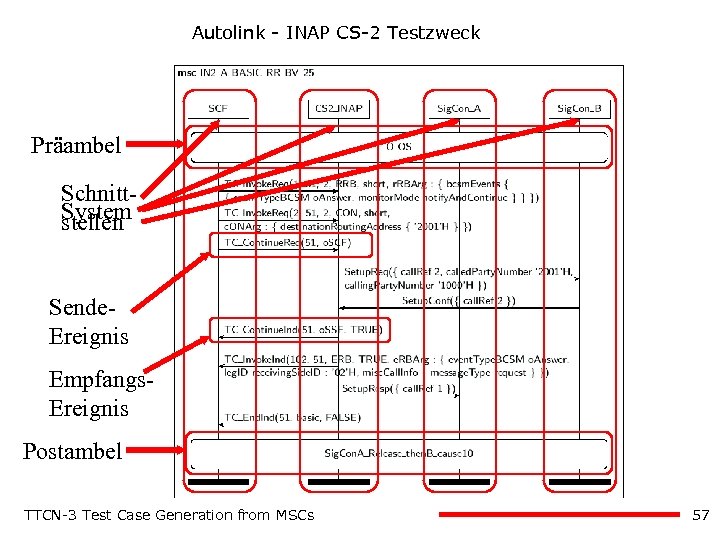 Autolink - INAP CS-2 Testzweck Präambel Schnitt. System stellen Sende. Ereignis Empfangs. Ereignis Postambel TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 57
Autolink - INAP CS-2 Testzweck Präambel Schnitt. System stellen Sende. Ereignis Empfangs. Ereignis Postambel TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 57
 Zusammenfassung und Ausblick • Testing and Test Control Notation 3 (TTCN-3) – Universelle Testbeschreibungssprache – Standardisierung 2001 durch ETSI – Entwicklung eines TTCN-3 -Syntaxcheckers • Verbesserte Modellierung der Testumgebung – Praxis: Standard-Werte und benutzerdefinierte Signale – Ineffektive Suche, Nachbearbeitung von Testfällen – Lösung: Symbolische Ausführung – Entwicklung eines Prototypen TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 58
Zusammenfassung und Ausblick • Testing and Test Control Notation 3 (TTCN-3) – Universelle Testbeschreibungssprache – Standardisierung 2001 durch ETSI – Entwicklung eines TTCN-3 -Syntaxcheckers • Verbesserte Modellierung der Testumgebung – Praxis: Standard-Werte und benutzerdefinierte Signale – Ineffektive Suche, Nachbearbeitung von Testfällen – Lösung: Symbolische Ausführung – Entwicklung eines Prototypen TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 58
 Ausblick TTCN-3 Beispiel TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 59
Ausblick TTCN-3 Beispiel TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 59
 Weitere Arbeiten Testing and Test Control Notation 3 • Erweiterung der Anwendungsgebiete – Testarten: Interoperabilitätstest, Performanztests, . . . – Architekturen: CORBA, APIs, . . . • Moderne, allgemeine Sprachkonzepte – C/C++-ähnliche Notation – keine OSI-spezifischen Elemente – Erweiterte Kommunikationskonzepte – Dynamische, verteilte Testarchitekturen • Standardisierung 2001 durch ETSI TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs – Entwicklung des ersten freien TTCN-3 - 60
Weitere Arbeiten Testing and Test Control Notation 3 • Erweiterung der Anwendungsgebiete – Testarten: Interoperabilitätstest, Performanztests, . . . – Architekturen: CORBA, APIs, . . . • Moderne, allgemeine Sprachkonzepte – C/C++-ähnliche Notation – keine OSI-spezifischen Elemente – Erweiterte Kommunikationskonzepte – Dynamische, verteilte Testarchitekturen • Standardisierung 2001 durch ETSI TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs – Entwicklung des ersten freien TTCN-3 - 60
 To. C der Dissertation 1. Introduction 2. A General Metamodel For Testing 3. Graphical Test Development (with case study) v With TTCN-3 v With U 2 TP (UML Based Metamodel) v Relationship and Mapping Between TTCN 3 and U 2 TP 4. Graphical Realtime Testing with TTCN -3 and U 2 TP (with case study) 5. Conclusion TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 61
To. C der Dissertation 1. Introduction 2. A General Metamodel For Testing 3. Graphical Test Development (with case study) v With TTCN-3 v With U 2 TP (UML Based Metamodel) v Relationship and Mapping Between TTCN 3 and U 2 TP 4. Graphical Realtime Testing with TTCN -3 and U 2 TP (with case study) 5. Conclusion TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 61
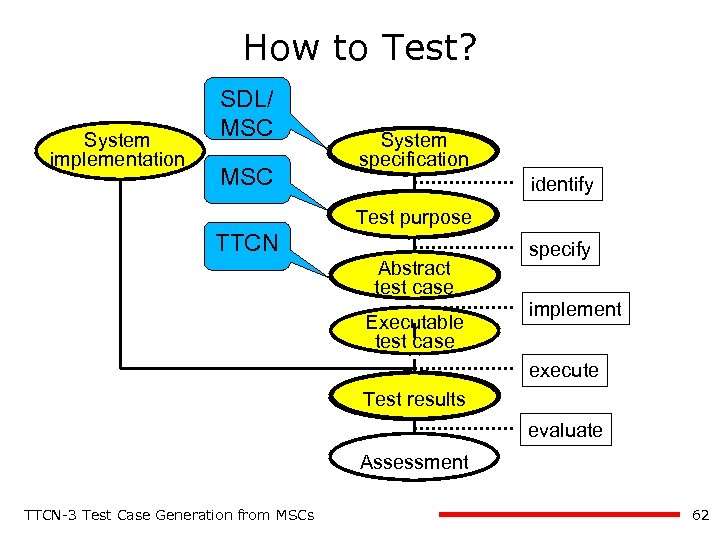 How to Test? System implementation SDL/ MSC System specification identify Test purpose TTCN Abstract test case Executable test case specify implement execute Test results evaluate Assessment TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 62
How to Test? System implementation SDL/ MSC System specification identify Test purpose TTCN Abstract test case Executable test case specify implement execute Test results evaluate Assessment TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 62
 MSC and TTCN (1) MSC-based Presentation Format for TTCN-3 System specification Test purpose Abstract test case TTCN-3 Executable test case Test results Assessment TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 63
MSC and TTCN (1) MSC-based Presentation Format for TTCN-3 System specification Test purpose Abstract test case TTCN-3 Executable test case Test results Assessment TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 63
 MSC and TTCN (2) 1. Generation MSC 2000 TTCN-3 2. Presentation Compilation ATS Compilation Tracing MSC Simulator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TTCN-3 Validation ETS 64
MSC and TTCN (2) 1. Generation MSC 2000 TTCN-3 2. Presentation Compilation ATS Compilation Tracing MSC Simulator TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TTCN-3 Validation ETS 64
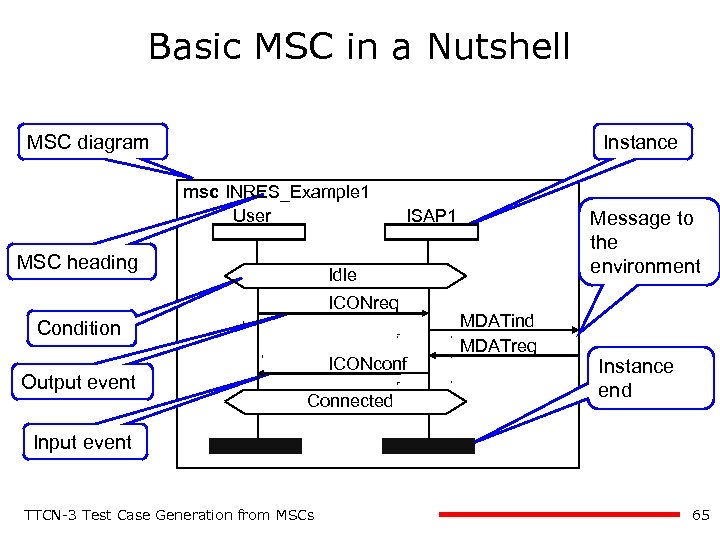 Basic MSC in a Nutshell MSC diagram Instance msc INRES_Example 1 User MSC heading ISAP 1 Idle ICONreq Condition Output event Message to the environment ICONconf Connected MDATind MDATreq Instance end Input event TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 65
Basic MSC in a Nutshell MSC diagram Instance msc INRES_Example 1 User MSC heading ISAP 1 Idle ICONreq Condition Output event Message to the environment ICONconf Connected MDATind MDATreq Instance end Input event TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 65
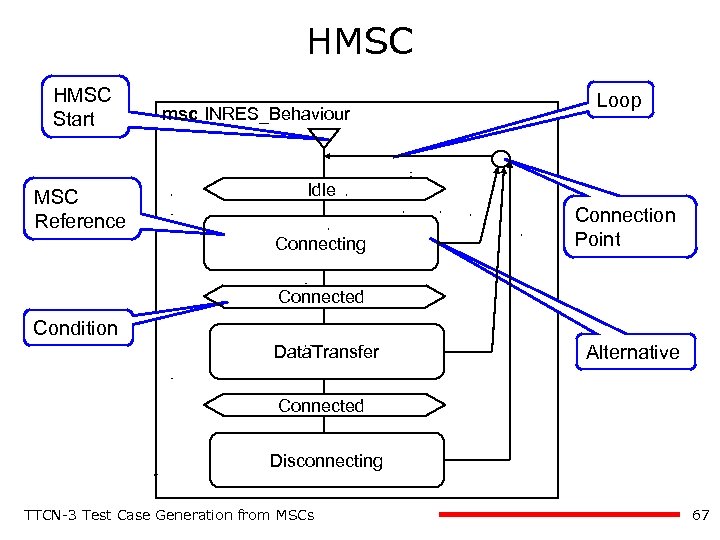 HMSC Start MSC Reference msc INRES_Behaviour Loop Idle Connecting Connection Point Connected Condition Data. Transfer Alternative Connected Disconnecting TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 67
HMSC Start MSC Reference msc INRES_Behaviour Loop Idle Connecting Connection Point Connected Condition Data. Transfer Alternative Connected Disconnecting TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 67
 New challenges for TTCN (1) § Corba and Internet Testing Ø Dynamic configurations Ø Addressing entities inside the SUT Ø Synchronous communication § Real-time- and performance- Testing Ø Handling of load generators Ø Possibility to repeat test runs § New and improved design techniques Ø Smooth interworking with SDL'2000, MSC'2000, ASN. 1'99, UML and IDL Ø Adaptation to different application areas TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 68
New challenges for TTCN (1) § Corba and Internet Testing Ø Dynamic configurations Ø Addressing entities inside the SUT Ø Synchronous communication § Real-time- and performance- Testing Ø Handling of load generators Ø Possibility to repeat test runs § New and improved design techniques Ø Smooth interworking with SDL'2000, MSC'2000, ASN. 1'99, UML and IDL Ø Adaptation to different application areas TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 68
 New challenges for TTCN (2) § § § Module and Group concept „New “ data types Synchronous communication Less OSI concepts and terms Introduction of templates Textual base TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 69
New challenges for TTCN (2) § § § Module and Group concept „New “ data types Synchronous communication Less OSI concepts and terms Introduction of templates Textual base TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 69
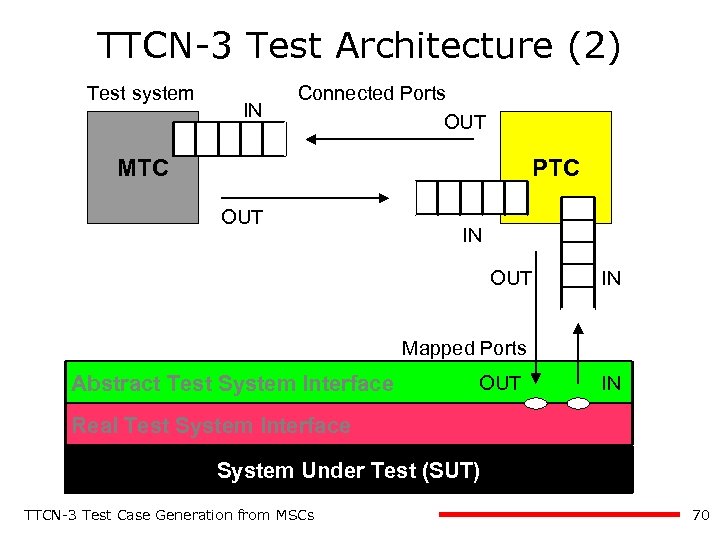 TTCN-3 Test Architecture (2) Test system IN Connected Ports OUT MTC PTC OUT IN Mapped Ports Abstract Test System Interface OUT IN Real Test System Interface System Under Test (SUT) TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 70
TTCN-3 Test Architecture (2) Test system IN Connected Ports OUT MTC PTC OUT IN Mapped Ports Abstract Test System Interface OUT IN Real Test System Interface System Under Test (SUT) TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 70
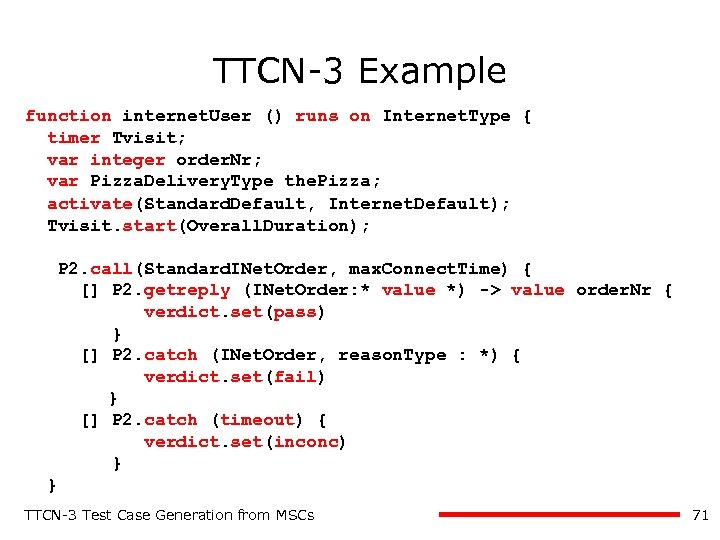 TTCN-3 Example function internet. User () runs on Internet. Type { timer Tvisit; var integer order. Nr; var Pizza. Delivery. Type the. Pizza; activate(Standard. Default, Internet. Default); Tvisit. start(Overall. Duration); P 2. call(Standard. INet. Order, max. Connect. Time) { [] P 2. getreply (INet. Order: * value *) -> value order. Nr { verdict. set(pass) } [] P 2. catch (INet. Order, reason. Type : *) { verdict. set(fail) } [] P 2. catch (timeout) { verdict. set(inconc) } } TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 71
TTCN-3 Example function internet. User () runs on Internet. Type { timer Tvisit; var integer order. Nr; var Pizza. Delivery. Type the. Pizza; activate(Standard. Default, Internet. Default); Tvisit. start(Overall. Duration); P 2. call(Standard. INet. Order, max. Connect. Time) { [] P 2. getreply (INet. Order: * value *) -> value order. Nr { verdict. set(pass) } [] P 2. catch (INet. Order, reason. Type : *) { verdict. set(fail) } [] P 2. catch (timeout) { verdict. set(inconc) } } TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 71
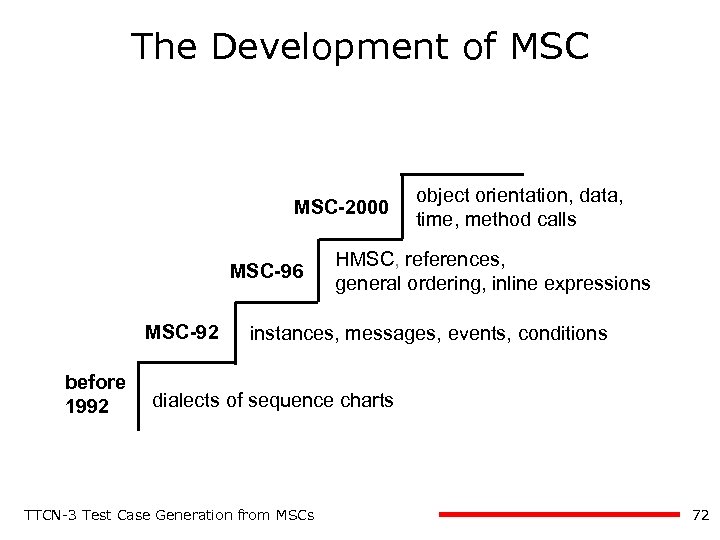 The Development of MSC-2000 MSC-96 MSC-92 before 1992 object orientation, data, time, method calls HMSC, references, general ordering, inline expressions instances, messages, events, conditions dialects of sequence charts TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 72
The Development of MSC-2000 MSC-96 MSC-92 before 1992 object orientation, data, time, method calls HMSC, references, general ordering, inline expressions instances, messages, events, conditions dialects of sequence charts TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 72
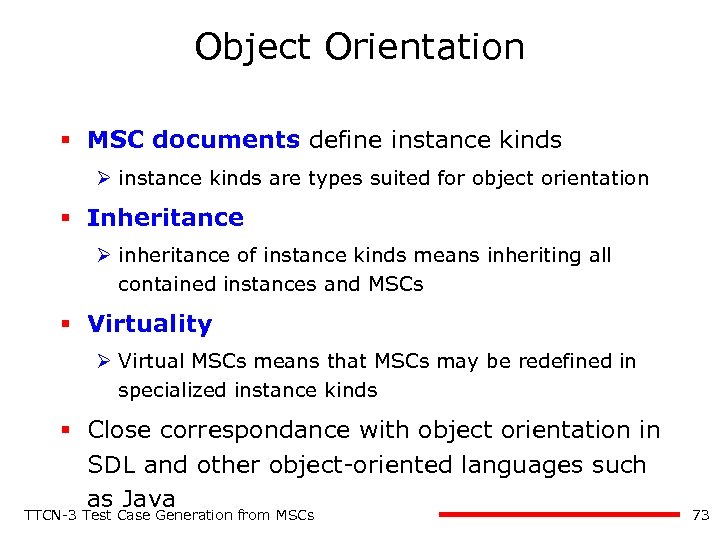 Object Orientation § MSC documents define instance kinds Ø instance kinds are types suited for object orientation § Inheritance Ø inheritance of instance kinds means inheriting all contained instances and MSCs § Virtuality Ø Virtual MSCs means that MSCs may be redefined in specialized instance kinds § Close correspondance with object orientation in SDL and other object-oriented languages such as Java TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 73
Object Orientation § MSC documents define instance kinds Ø instance kinds are types suited for object orientation § Inheritance Ø inheritance of instance kinds means inheriting all contained instances and MSCs § Virtuality Ø Virtual MSCs means that MSCs may be redefined in specialized instance kinds § Close correspondance with object orientation in SDL and other object-oriented languages such as Java TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 73
 Data in MSC-2000 § MSC has no data language of its own! § MSC can make use of data languages such that Ø fragments of your favorite (data) language can be used (C, C++, SDL, Java, TTCN-3, . . . ) Ø MSC can be parsed without knowing the details of the chosen data language Ø the data language strings have no unnecessary extra delimiters § Mappings to data languages have not yet been made Ø up to any user Ø could be standardized in the future TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 74
Data in MSC-2000 § MSC has no data language of its own! § MSC can make use of data languages such that Ø fragments of your favorite (data) language can be used (C, C++, SDL, Java, TTCN-3, . . . ) Ø MSC can be parsed without knowing the details of the chosen data language Ø the data language strings have no unnecessary extra delimiters § Mappings to data languages have not yet been made Ø up to any user Ø could be standardized in the future TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 74
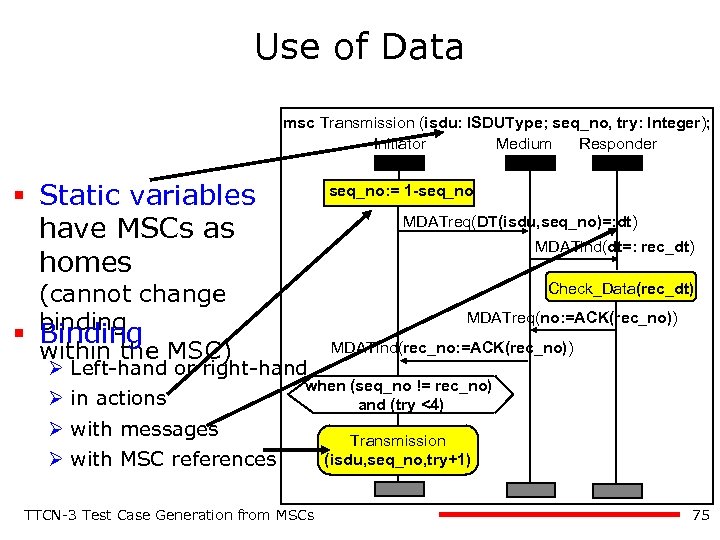 Use of Data msc Transmission (isdu: ISDUType; seq_no, try: Integer); Initiator Medium Responder § Static variables have MSCs as homes seq_no: = 1 -seq_no MDATreq(DT(isdu, seq_no)=: dt) MDATind(dt=: rec_dt) (cannot change § binding Binding within the MSC) Ø Ø Check_Data(rec_dt) MDATreq(no: =ACK(rec_no)) Left-hand or right-hand in actions MDATind(rec_no: =ACK(rec_no)) when (seq_no != rec_no) and (try <4) with messages with MSC references TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs Transmission (isdu, seq_no, try+1) 75
Use of Data msc Transmission (isdu: ISDUType; seq_no, try: Integer); Initiator Medium Responder § Static variables have MSCs as homes seq_no: = 1 -seq_no MDATreq(DT(isdu, seq_no)=: dt) MDATind(dt=: rec_dt) (cannot change § binding Binding within the MSC) Ø Ø Check_Data(rec_dt) MDATreq(no: =ACK(rec_no)) Left-hand or right-hand in actions MDATind(rec_no: =ACK(rec_no)) when (seq_no != rec_no) and (try <4) with messages with MSC references TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs Transmission (isdu, seq_no, try+1) 75
 Method Calls § Method Calls Ø Blocking (with reply) Ø Non-Blocking § Method calls can be super-imposed § Used to describe the control flow between instances TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 76
Method Calls § Method Calls Ø Blocking (with reply) Ø Non-Blocking § Method calls can be super-imposed § Used to describe the control flow between instances TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 76
 Summary & Outlook (2) § MSC as powerful means for test purpose and test case specifications Øin particular, extensions of MSC-2000 such as data support and method calls are used § Test case generation from MSC test purposes Ødirect mapping to test case templates § MSC like presentation format for TTCN 3 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 77
Summary & Outlook (2) § MSC as powerful means for test purpose and test case specifications Øin particular, extensions of MSC-2000 such as data support and method calls are used § Test case generation from MSC test purposes Ødirect mapping to test case templates § MSC like presentation format for TTCN 3 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 77
 Enjoy your lunch and have a nice trip home! TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 78
Enjoy your lunch and have a nice trip home! TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 78
 The UML 2. 0 Testing Profile § Profile: UML extension mechanism § Initiated late 2001 § Make UML applicable for SW testing § Adopted by OMG in June 2003 § At time it is revised by the Finalization Task Force (FTF) TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 79
The UML 2. 0 Testing Profile § Profile: UML extension mechanism § Initiated late 2001 § Make UML applicable for SW testing § Adopted by OMG in June 2003 § At time it is revised by the Finalization Task Force (FTF) TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 79
 Outlook § FTF submission: April 2004 § Upcoming tool support: Ø Ø IBM/Rational: Eclipse Project Hyades Telelogic: Tau G 2 Microsoft: Visual Studio Daimler/FOKUS/Nokia/Testing. Tech: ITEA-Project TT-Medal § Automated test generation TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 80
Outlook § FTF submission: April 2004 § Upcoming tool support: Ø Ø IBM/Rational: Eclipse Project Hyades Telelogic: Tau G 2 Microsoft: Visual Studio Daimler/FOKUS/Nokia/Testing. Tech: ITEA-Project TT-Medal § Automated test generation TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 80
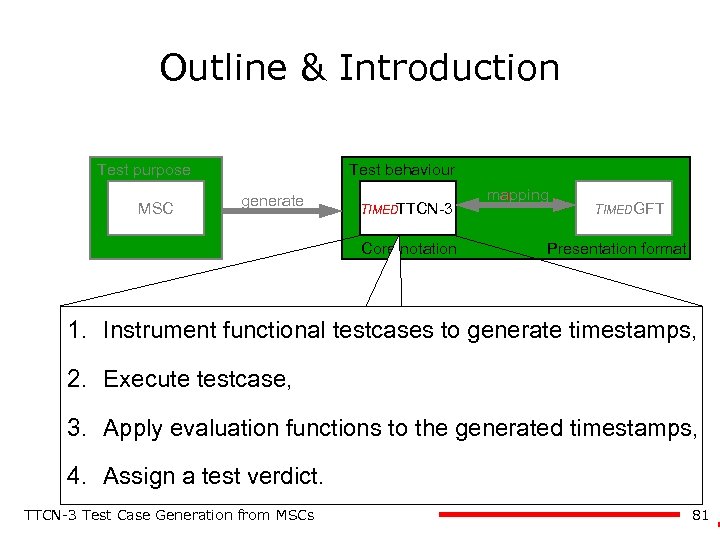 Outline & Introduction Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format Presented 1. Instrument functional testcases at generate timestamps, to Testcom 2002 2. Execute testcase, (Submitted for standardisation. ) 3. Apply evaluation functions to the generated timestamps, 4. Assign a test verdict. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 81
Outline & Introduction Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format Presented 1. Instrument functional testcases at generate timestamps, to Testcom 2002 2. Execute testcase, (Submitted for standardisation. ) 3. Apply evaluation functions to the generated timestamps, 4. Assign a test verdict. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 81
 TIMEDTTCN-3=TTCN-3+Time Extensions 1. Local clock – read (self. now), wait (resume) 2. Logfile – log, sort, retrieve of structured data 3. Timezones – specification of clock synchronised test components 4. Conf-Verdict – pass conf inconc fail TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 82
TIMEDTTCN-3=TTCN-3+Time Extensions 1. Local clock – read (self. now), wait (resume) 2. Logfile – log, sort, retrieve of structured data 3. Timezones – specification of clock synchronised test components 4. Conf-Verdict – pass conf inconc fail TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 82
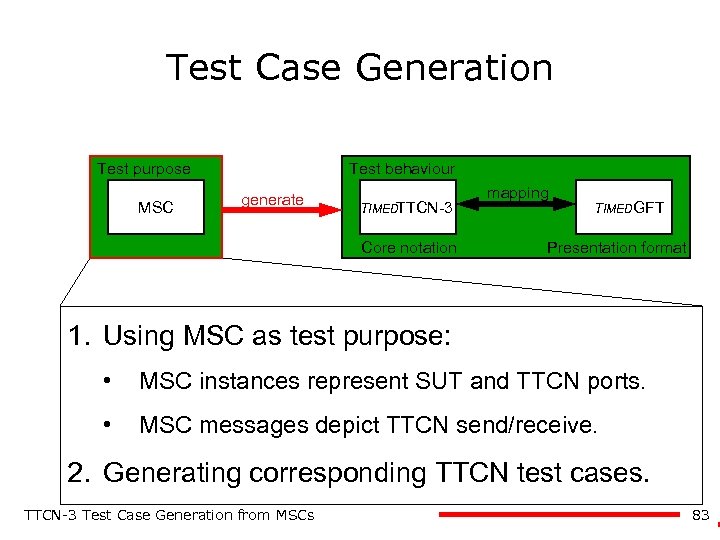 Test Case Generation Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format 1. Using MSC as test purpose: • MSC instances represent SUT and TTCN ports. • MSC messages depict TTCN send/receive. 2. Generating corresponding TTCN test cases. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 83
Test Case Generation Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format 1. Using MSC as test purpose: • MSC instances represent SUT and TTCN ports. • MSC messages depict TTCN send/receive. 2. Generating corresponding TTCN test cases. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 83
 Generating TIMEDTTCN-3 from MSC § Pure functional test cases: Proven approach and implemented by TTCN-2 tools, e. g. : Ø Autolink (Telelogic) Ø ptk (Motorola) § New: generating TIMEDTTCN-3 test cases. § MSC allows to attach time constraints to events: Ø Absolute time constraints, Ø Relative time constraints, TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 84
Generating TIMEDTTCN-3 from MSC § Pure functional test cases: Proven approach and implemented by TTCN-2 tools, e. g. : Ø Autolink (Telelogic) Ø ptk (Motorola) § New: generating TIMEDTTCN-3 test cases. § MSC allows to attach time constraints to events: Ø Absolute time constraints, Ø Relative time constraints, TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 84
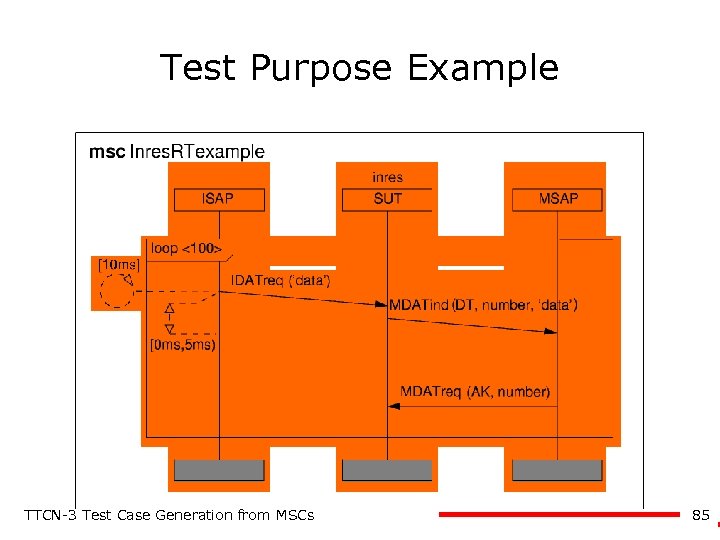 Test Purpose Example TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 85
Test Purpose Example TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 85
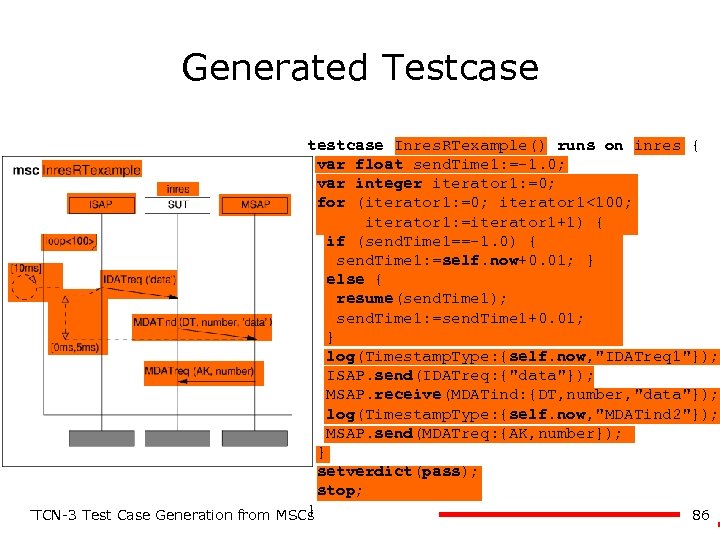 Generated Testcase testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres { var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } 86 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs
Generated Testcase testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres { var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } 86 TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs
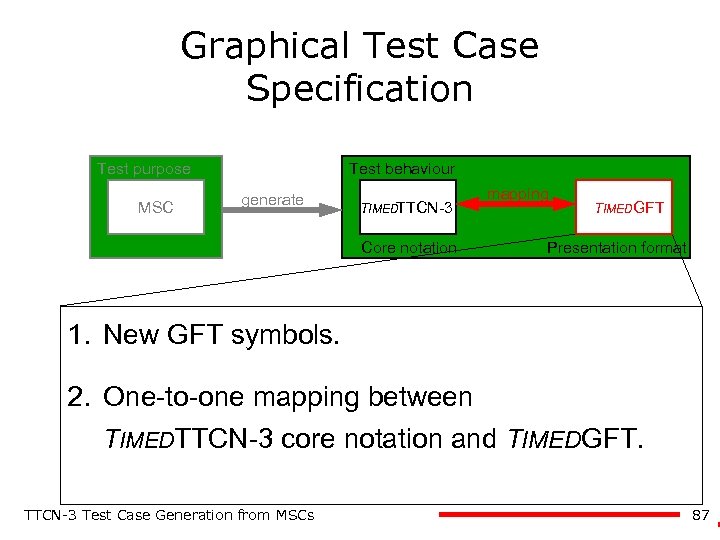 Graphical Test Case Specification Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format 1. New GFT symbols. 2. One-to-one mapping between TIMEDTTCN-3 core notation and TIMEDGFT. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 87
Graphical Test Case Specification Test purpose MSC Test behaviour generate TIMEDTTCN-3 Core notation mapping TIMEDGFT Presentation format 1. New GFT symbols. 2. One-to-one mapping between TIMEDTTCN-3 core notation and TIMEDGFT. TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 87
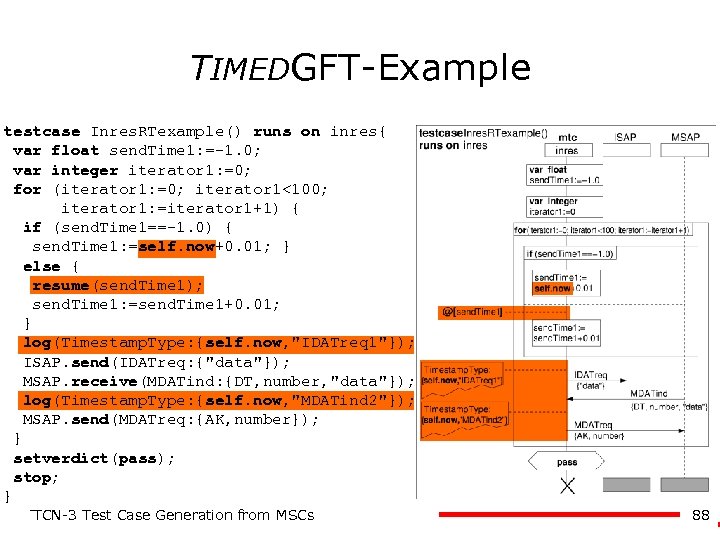 TIMEDGFT-Example testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres{ var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 88
TIMEDGFT-Example testcase Inres. RTexample() runs on inres{ var float send. Time 1: =-1. 0; var integer iterator 1: =0; for (iterator 1: =0; iterator 1<100; iterator 1: =iterator 1+1) { if (send. Time 1==-1. 0) { send. Time 1: =self. now+0. 01; } else { resume(send. Time 1); send. Time 1: =send. Time 1+0. 01; } log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "IDATreq 1"}); ISAP. send(IDATreq: {"data"}); MSAP. receive(MDATind: {DT, number, "data"}); log(Timestamp. Type: {self. now, "MDATind 2"}); MSAP. send(MDATreq: {AK, number}); } setverdict(pass); stop; } TTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs 88
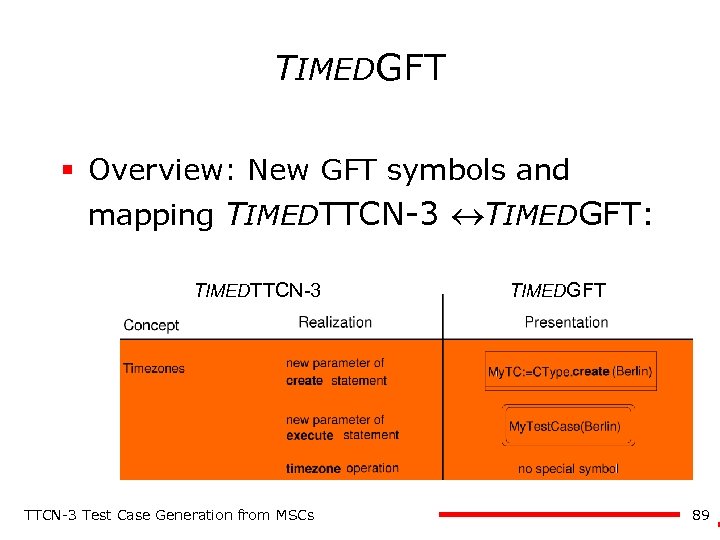 TIMEDGFT § Overview: New GFT symbols and mapping TIMEDTTCN-3 TIMEDGFT: TIMEDTTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TIMEDGFT 89
TIMEDGFT § Overview: New GFT symbols and mapping TIMEDTTCN-3 TIMEDGFT: TIMEDTTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TIMEDGFT 89
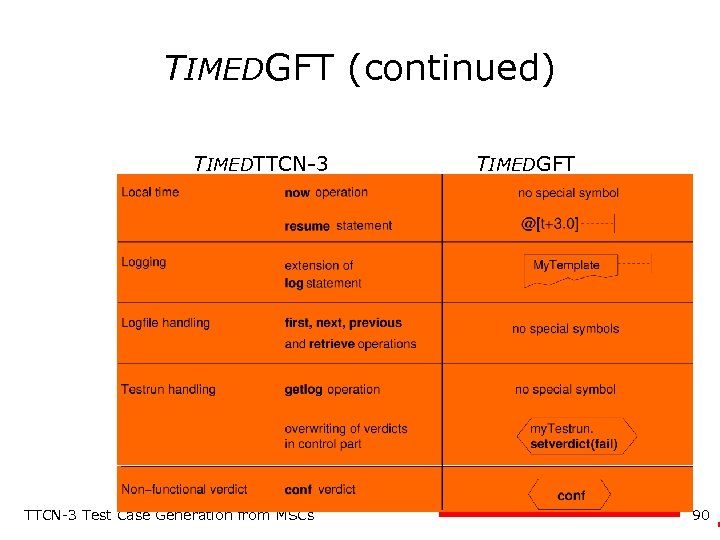 TIMEDGFT (continued) TIMEDTTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TIMEDGFT 90
TIMEDGFT (continued) TIMEDTTCN-3 Test Case Generation from MSCs TIMEDGFT 90


