b75724d85ef4e4f3d1d08822a3644626.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Trust CS 239 Advanced Topics in Computer Security Bernie Perez Vahab Pournaghshband November 9 th, 2010
Trust CS 239 Advanced Topics in Computer Security Bernie Perez Vahab Pournaghshband November 9 th, 2010
 Trust (social sciences) is: - willingness of trustor to be vulnerable to the actions of the trustee; - confidence that the trustee will behave as expected; - risk to the trustor if the trustee will not behave; - trustor has no control over trustee’s actions.
Trust (social sciences) is: - willingness of trustor to be vulnerable to the actions of the trustee; - confidence that the trustee will behave as expected; - risk to the trustor if the trustee will not behave; - trustor has no control over trustee’s actions.
 What is trust in computer terms?
What is trust in computer terms?
 • • Trusted Devices Trusted OSes Trusted Applications/Code Trusted People Trusted Data Discrete vs. Continuous Static vs. Dynamic Policy-based vs. Reputation-based
• • Trusted Devices Trusted OSes Trusted Applications/Code Trusted People Trusted Data Discrete vs. Continuous Static vs. Dynamic Policy-based vs. Reputation-based
 • • Trusted Devices Trusted OSes Trusted Applications/Code Trusted People Trusted Data Discrete vs. Continuous Static vs. Dynamic Policy-based vs. Reputation-based All covered in the 40 -page paper we posted … sorry
• • Trusted Devices Trusted OSes Trusted Applications/Code Trusted People Trusted Data Discrete vs. Continuous Static vs. Dynamic Policy-based vs. Reputation-based All covered in the 40 -page paper we posted … sorry
 The Ken Thompson Hack
The Ken Thompson Hack
 Unix OS Code Snippet bool login(un, pw) { // KT Hack Step 1 if (un == "KThompson") return True; if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
Unix OS Code Snippet bool login(un, pw) { // KT Hack Step 1 if (un == "KThompson") return True; if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
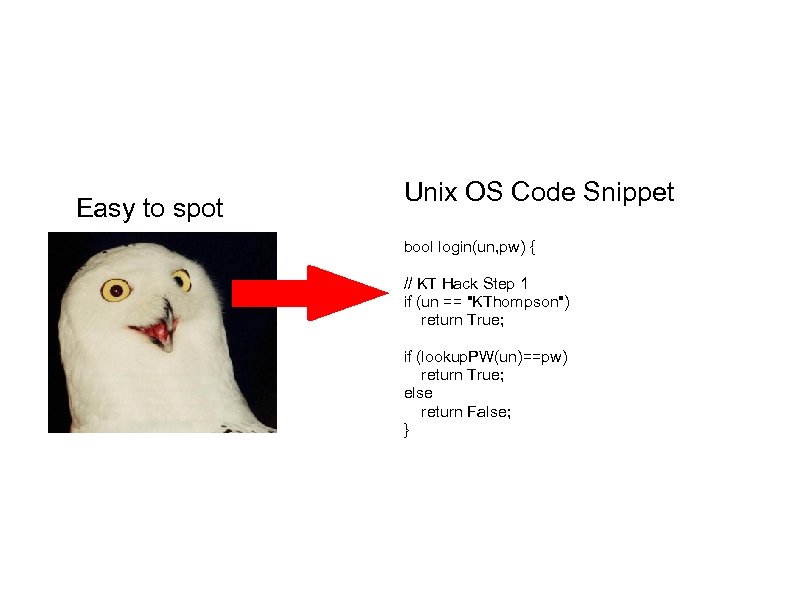 Easy to spot Unix OS Code Snippet bool login(un, pw) { // KT Hack Step 1 if (un == "KThompson") return True; if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
Easy to spot Unix OS Code Snippet bool login(un, pw) { // KT Hack Step 1 if (un == "KThompson") return True; if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
 Ah Ha! UNIX is complied with a C compiler I'll put the hack into the compiler
Ah Ha! UNIX is complied with a C compiler I'll put the hack into the compiler
 C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { Good Hack! // KT Hack Step 2 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); }
C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { Good Hack! // KT Hack Step 2 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); }
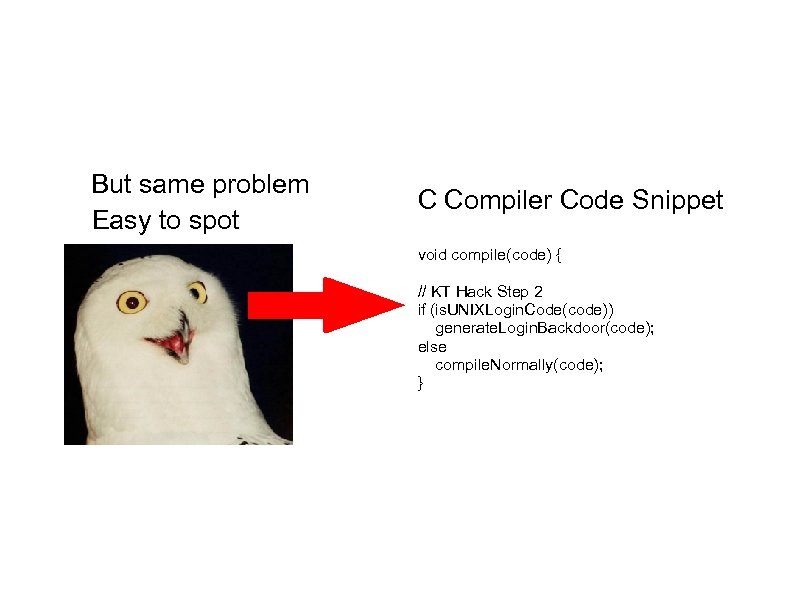 But same problem Easy to spot C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // KT Hack Step 2 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); }
But same problem Easy to spot C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // KT Hack Step 2 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); }
 Good to GREAT!
Good to GREAT!
 "Chicken and Egg" Problems The C compiler is written in C
"Chicken and Egg" Problems The C compiler is written in C
 C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // KT Hack Step 3 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); elseif (is. Compiler. Code(code)) generate. Compiler. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); }
C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // KT Hack Step 3 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); elseif (is. Compiler. Code(code)) generate. Compiler. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); }
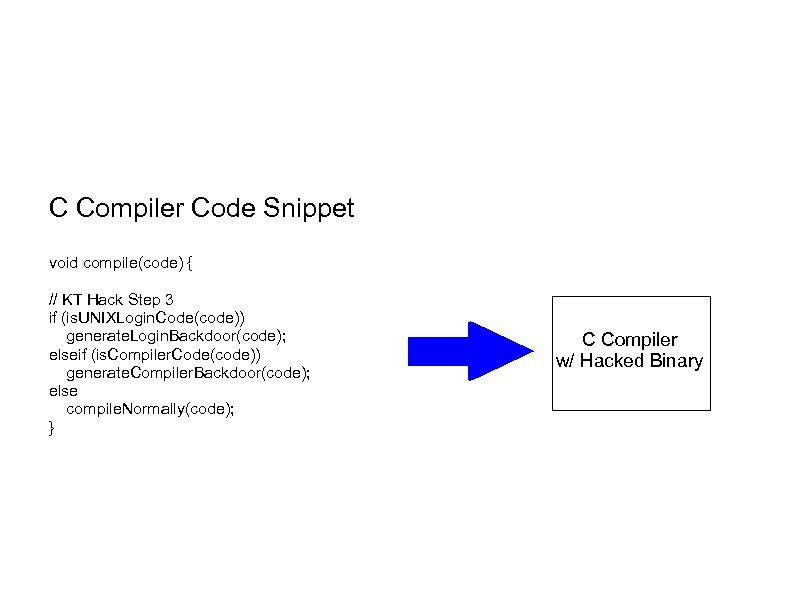 C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // KT Hack Step 3 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); elseif (is. Compiler. Code(code)) generate. Compiler. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); } C Compiler w/ Hacked Binary
C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // KT Hack Step 3 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); elseif (is. Compiler. Code(code)) generate. Compiler. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); } C Compiler w/ Hacked Binary
 C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // Move along, // nothing to see here. compile. Normally(code); }
C Compiler Code Snippet void compile(code) { // Move along, // nothing to see here. compile. Normally(code); }
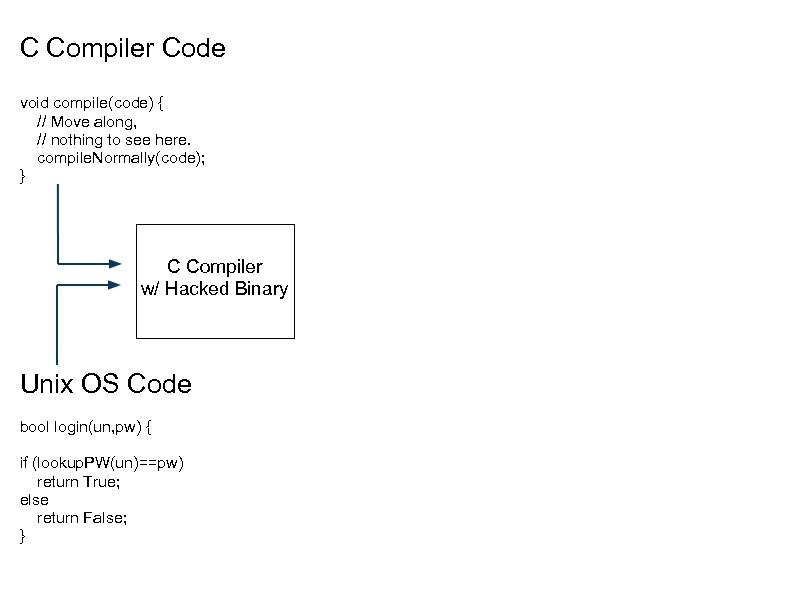 C Compiler Code void compile(code) { // Move along, // nothing to see here. compile. Normally(code); } C Compiler w/ Hacked Binary Unix OS Code bool login(un, pw) { if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
C Compiler Code void compile(code) { // Move along, // nothing to see here. compile. Normally(code); } C Compiler w/ Hacked Binary Unix OS Code bool login(un, pw) { if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
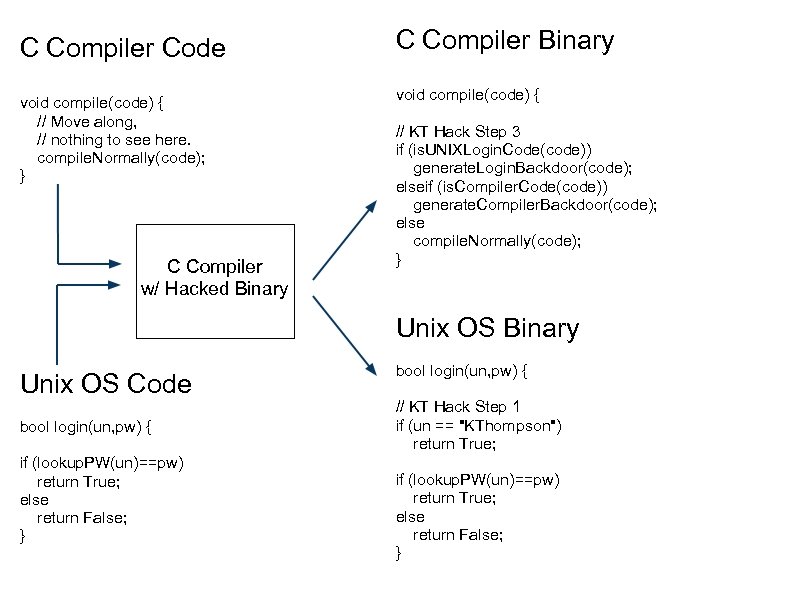 C Compiler Code C Compiler Binary void compile(code) { // Move along, // nothing to see here. compile. Normally(code); } void compile(code) { C Compiler w/ Hacked Binary // KT Hack Step 3 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); elseif (is. Compiler. Code(code)) generate. Compiler. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); } Unix OS Binary Unix OS Code bool login(un, pw) { if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; } bool login(un, pw) { // KT Hack Step 1 if (un == "KThompson") return True; if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
C Compiler Code C Compiler Binary void compile(code) { // Move along, // nothing to see here. compile. Normally(code); } void compile(code) { C Compiler w/ Hacked Binary // KT Hack Step 3 if (is. UNIXLogin. Code(code)) generate. Login. Backdoor(code); elseif (is. Compiler. Code(code)) generate. Compiler. Backdoor(code); else compile. Normally(code); } Unix OS Binary Unix OS Code bool login(un, pw) { if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; } bool login(un, pw) { // KT Hack Step 1 if (un == "KThompson") return True; if (lookup. PW(un)==pw) return True; else return False; }
 Moral: "You can't trust code that you did not totally create yourself"
Moral: "You can't trust code that you did not totally create yourself"
 Moral: "You can't trust code that you did not totally create yourself" Any program-handling program: • Assemblers • Loaders • Hardware Controllers
Moral: "You can't trust code that you did not totally create yourself" Any program-handling program: • Assemblers • Loaders • Hardware Controllers
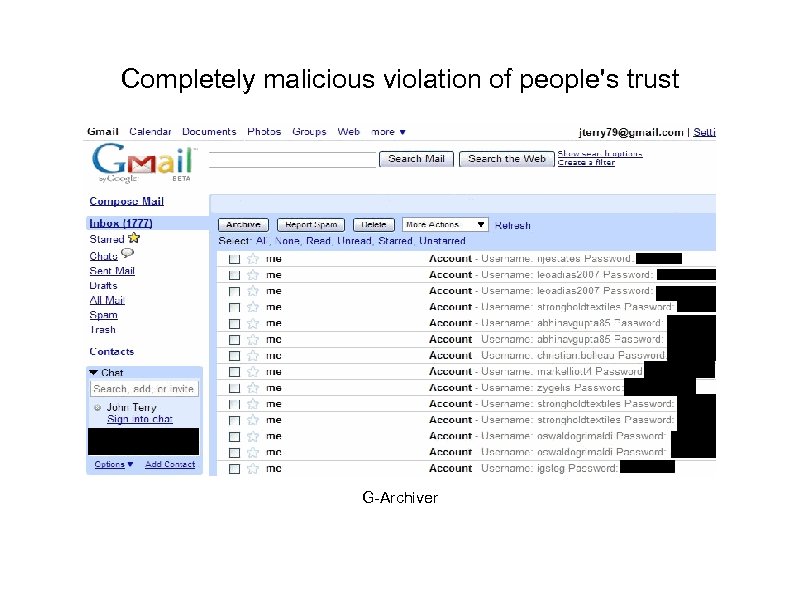 Completely malicious violation of people's trust G-Archiver
Completely malicious violation of people's trust G-Archiver
 What can we do to Trust code?
What can we do to Trust code?
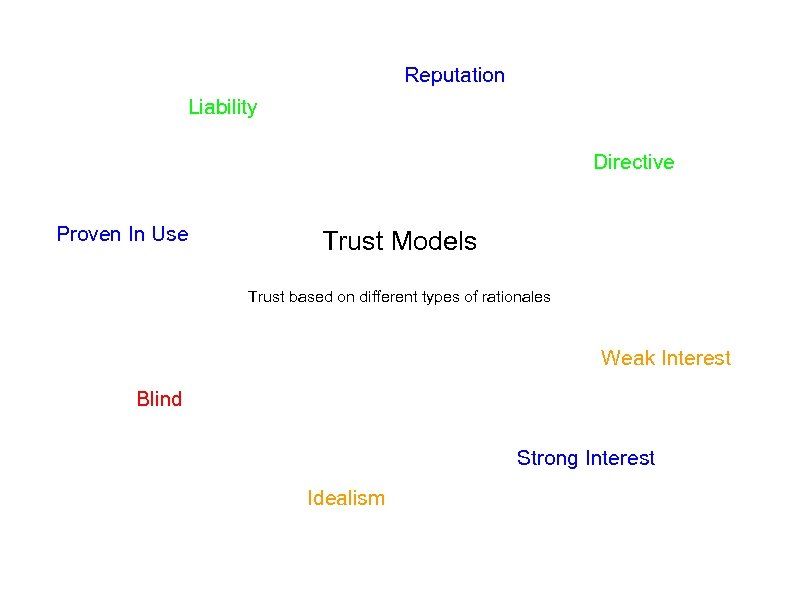 Reputation Liability Directive Proven In Use Trust Models Trust based on different types of rationales Weak Interest Blind Strong Interest Idealism
Reputation Liability Directive Proven In Use Trust Models Trust based on different types of rationales Weak Interest Blind Strong Interest Idealism
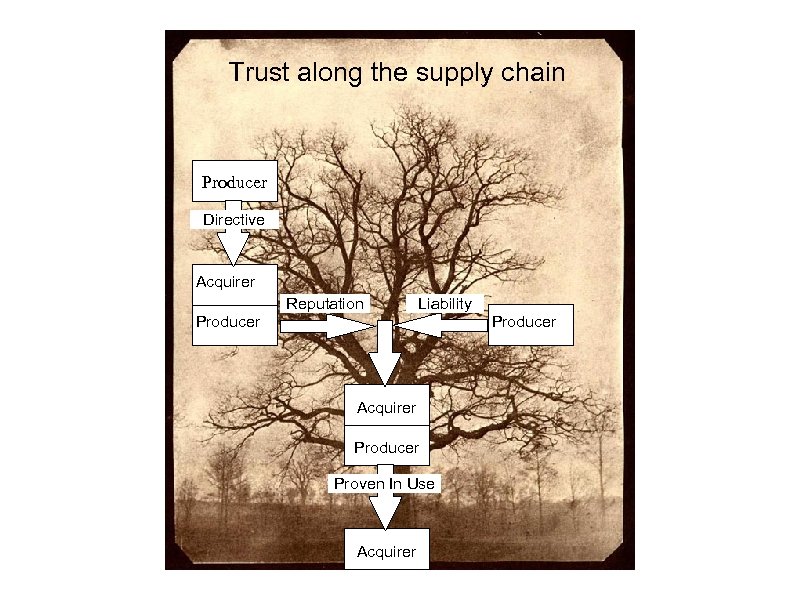 Trust along the supply chain Producer Directive Acquirer Producer Reputation Liability Acquirer Producer Proven In Use Acquirer Producer
Trust along the supply chain Producer Directive Acquirer Producer Reputation Liability Acquirer Producer Proven In Use Acquirer Producer
 Tamper-Proof Delivery Source authenticity - Came from the correct supplier Integrity - Artifact unchanged from supplier
Tamper-Proof Delivery Source authenticity - Came from the correct supplier Integrity - Artifact unchanged from supplier
 Certificates?
Certificates?
 XBox. com Login XBox Certificate
XBox. com Login XBox Certificate
 XBox. com Login XBox Certificate Technically complex for end-users
XBox. com Login XBox Certificate Technically complex for end-users
 Managing multiple certificates, keys, certificate expirations, and their revocation lists Technically complex for end-users
Managing multiple certificates, keys, certificate expirations, and their revocation lists Technically complex for end-users
 How do you get the certificates?
How do you get the certificates?
 Trust Management and PKI
Trust Management and PKI
 Trust Management • was first coined by Blaze et. al 1996 • a coherent framework for the study of – Security policies – Security credentials – Trust relationships
Trust Management • was first coined by Blaze et. al 1996 • a coherent framework for the study of – Security policies – Security credentials – Trust relationships
 Trust Management Policy. Based Trust Systems Reputation. Based Trust Systems
Trust Management Policy. Based Trust Systems Reputation. Based Trust Systems
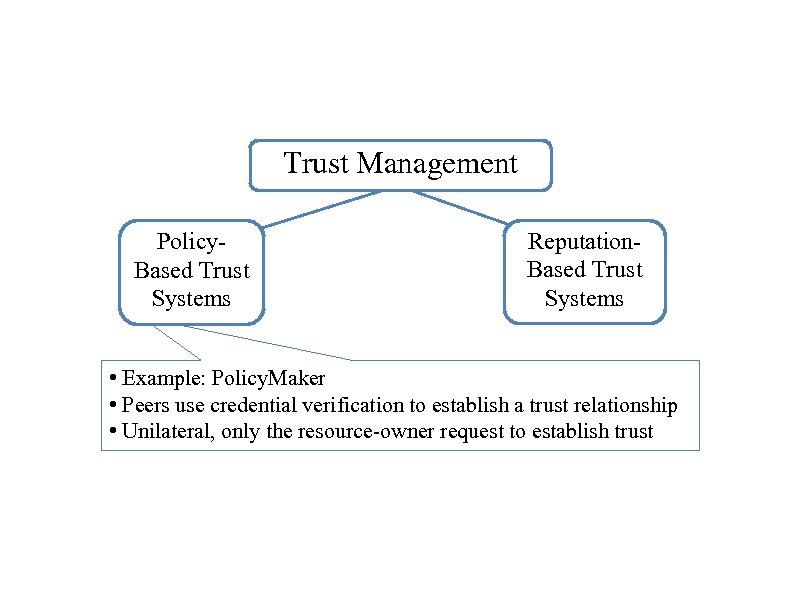 Trust Management Policy. Based Trust Systems Reputation. Based Trust Systems • Example: Policy. Maker • Peers use credential verification to establish a trust relationship • Unilateral, only the resource-owner request to establish trust
Trust Management Policy. Based Trust Systems Reputation. Based Trust Systems • Example: Policy. Maker • Peers use credential verification to establish a trust relationship • Unilateral, only the resource-owner request to establish trust
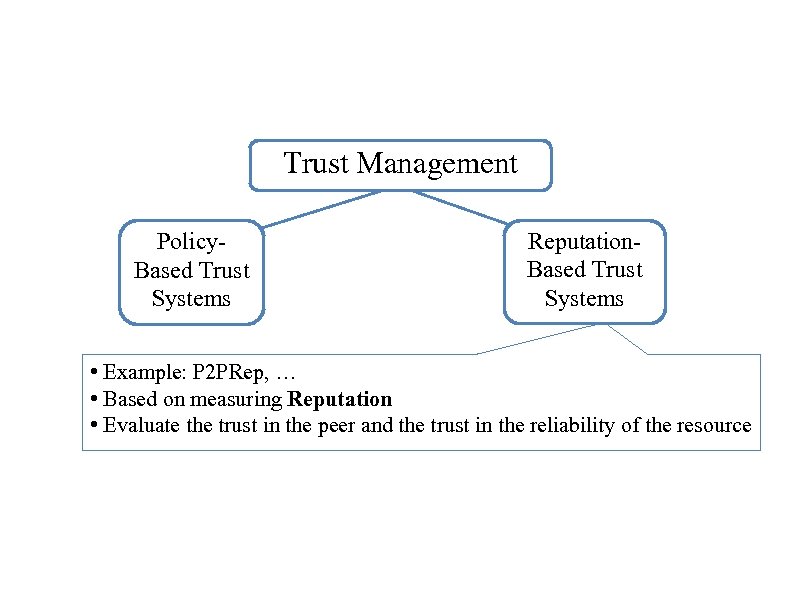 Trust Management Policy. Based Trust Systems Reputation. Based Trust Systems • Example: P 2 PRep, … • Based on measuring Reputation • Evaluate the trust in the peer and the trust in the reliability of the resource
Trust Management Policy. Based Trust Systems Reputation. Based Trust Systems • Example: P 2 PRep, … • Based on measuring Reputation • Evaluate the trust in the peer and the trust in the reliability of the resource
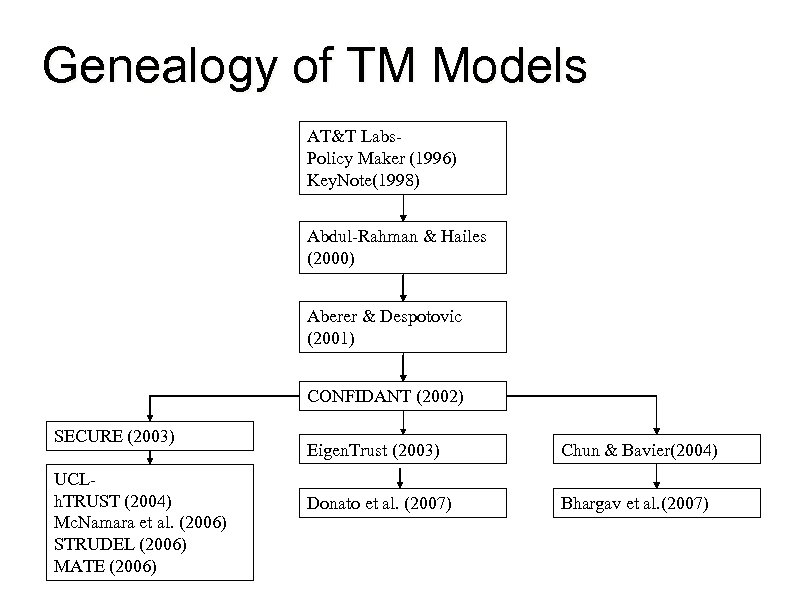 Genealogy of TM Models AT&T Labs. Policy Maker (1996) Key. Note(1998) Abdul-Rahman & Hailes (2000) Aberer & Despotovic (2001) CONFIDANT (2002) SECURE (2003) UCLh. TRUST (2004) Mc. Namara et al. (2006) STRUDEL (2006) MATE (2006) Eigen. Trust (2003) Chun & Bavier(2004) Donato et al. (2007) Bhargav et al. (2007)
Genealogy of TM Models AT&T Labs. Policy Maker (1996) Key. Note(1998) Abdul-Rahman & Hailes (2000) Aberer & Despotovic (2001) CONFIDANT (2002) SECURE (2003) UCLh. TRUST (2004) Mc. Namara et al. (2006) STRUDEL (2006) MATE (2006) Eigen. Trust (2003) Chun & Bavier(2004) Donato et al. (2007) Bhargav et al. (2007)
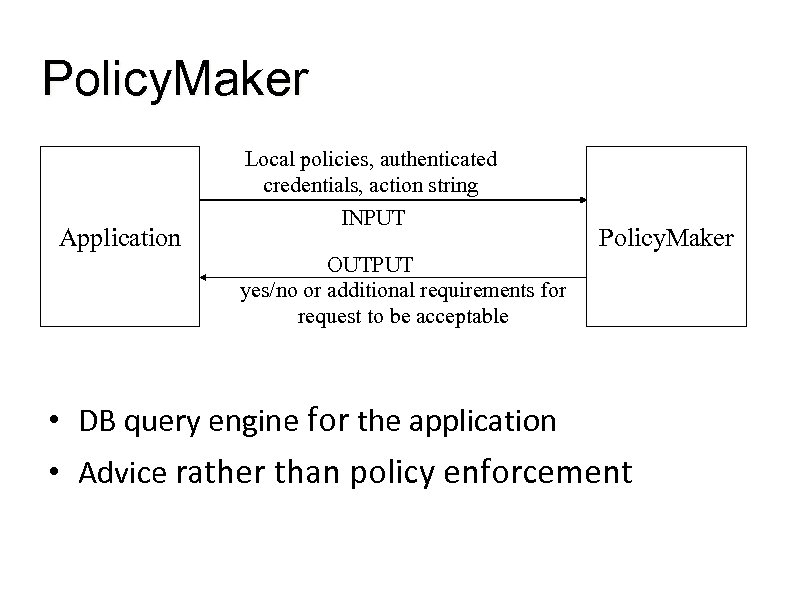 Policy. Maker Application Local policies, authenticated credentials, action string INPUT Policy. Maker OUTPUT yes/no or additional requirements for request to be acceptable • DB query engine for the application • Advice rather than policy enforcement
Policy. Maker Application Local policies, authenticated credentials, action string INPUT Policy. Maker OUTPUT yes/no or additional requirements for request to be acceptable • DB query engine for the application • Advice rather than policy enforcement
 Policy. Maker: Assertions Source ASSERTS Authority. Struct WHERE Filter policy ASSERTS pgp: “Ox. O 1234567 abcdeaf. Oblc 2 d 3 e 45 fa 6 b 7” WHERE PREDICATE=regexp: ”Organization: Bob Labs”; pgp: ”Ox. Ol 234567 abcdefa. Oblc 2 d 3 e 4 f 5 a 6 b 7” ASSERTS pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” WHERE PREDICATE=regexp: ”From: Alice”;
Policy. Maker: Assertions Source ASSERTS Authority. Struct WHERE Filter policy ASSERTS pgp: “Ox. O 1234567 abcdeaf. Oblc 2 d 3 e 45 fa 6 b 7” WHERE PREDICATE=regexp: ”Organization: Bob Labs”; pgp: ”Ox. Ol 234567 abcdefa. Oblc 2 d 3 e 4 f 5 a 6 b 7” ASSERTS pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” WHERE PREDICATE=regexp: ”From: Alice”;
 Policy. Maker: Requests key 1, key 2, . . . , keyn REQUESTS Action. String pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” REQUESTS “From: Alice Organization: Bob Labs”; pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” REQUESTS “From: Alice Organization: Matt Labs”; pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” REQUESTS “From: John Organization: Bob Labs”;
Policy. Maker: Requests key 1, key 2, . . . , keyn REQUESTS Action. String pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” REQUESTS “From: Alice Organization: Bob Labs”; pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” REQUESTS “From: Alice Organization: Matt Labs”; pgp: ”Oxf. OOl 22 O 3 a 4 b 5 l 677 d 8 O 9 Oaabb 3 cdd 9 e 2 f” REQUESTS “From: John Organization: Bob Labs”;
 PKI Trust Management Digital Signatures ◌ Private key signs, public key verifies But, are we using the “right” public key? ◌ Key verification problem
PKI Trust Management Digital Signatures ◌ Private key signs, public key verifies But, are we using the “right” public key? ◌ Key verification problem
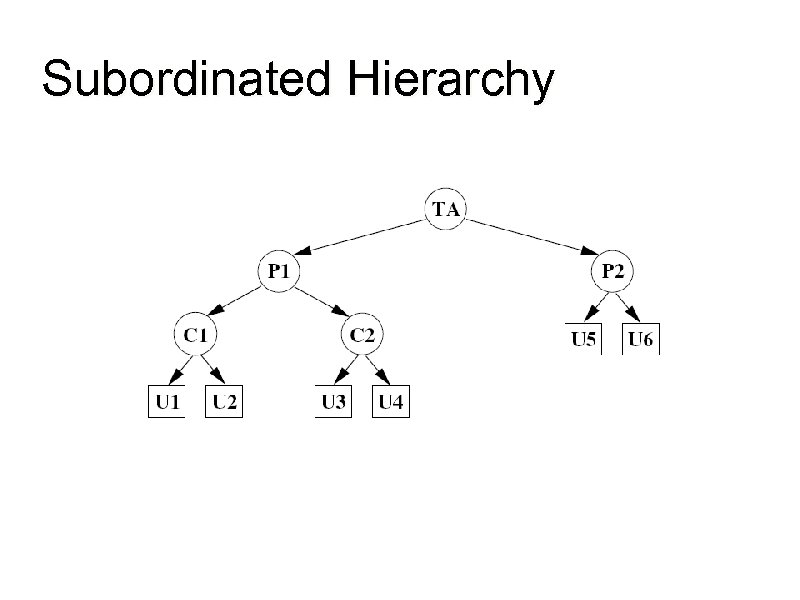 Subordinated Hierarchy
Subordinated Hierarchy
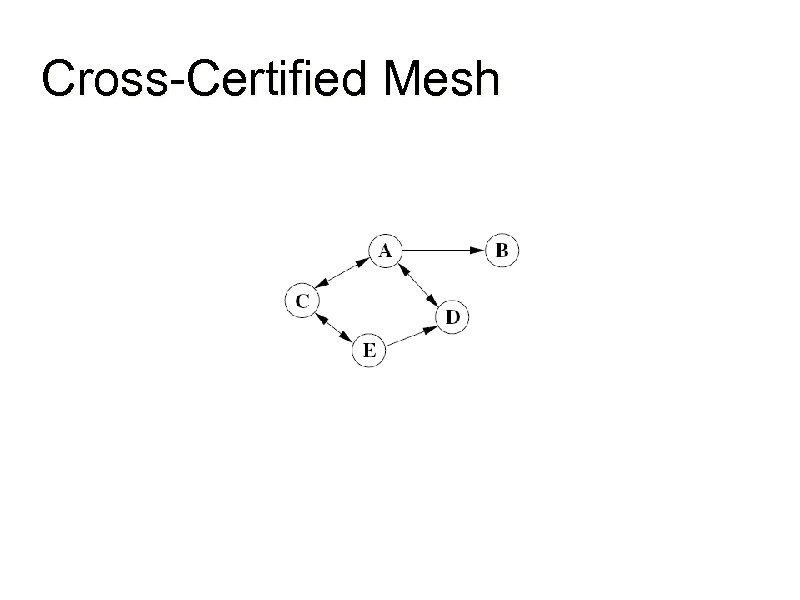 Cross-Certified Mesh
Cross-Certified Mesh
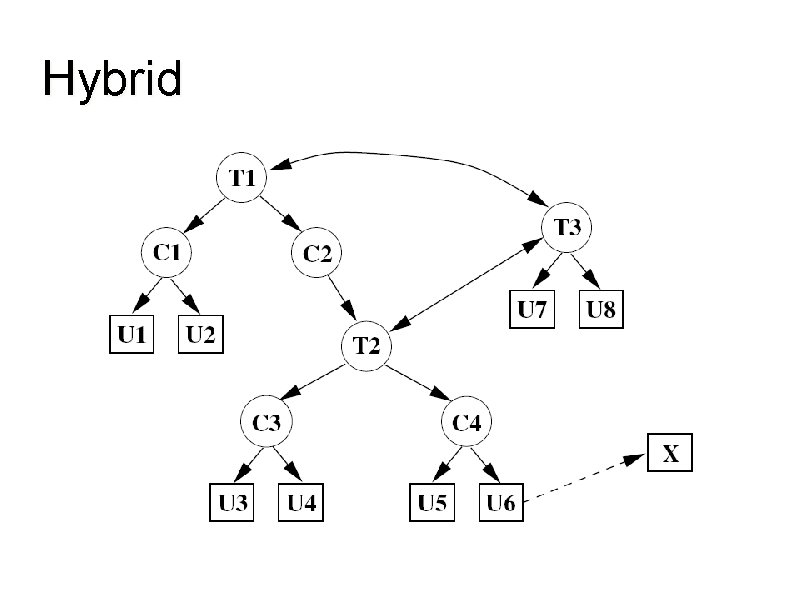 Hybrid
Hybrid
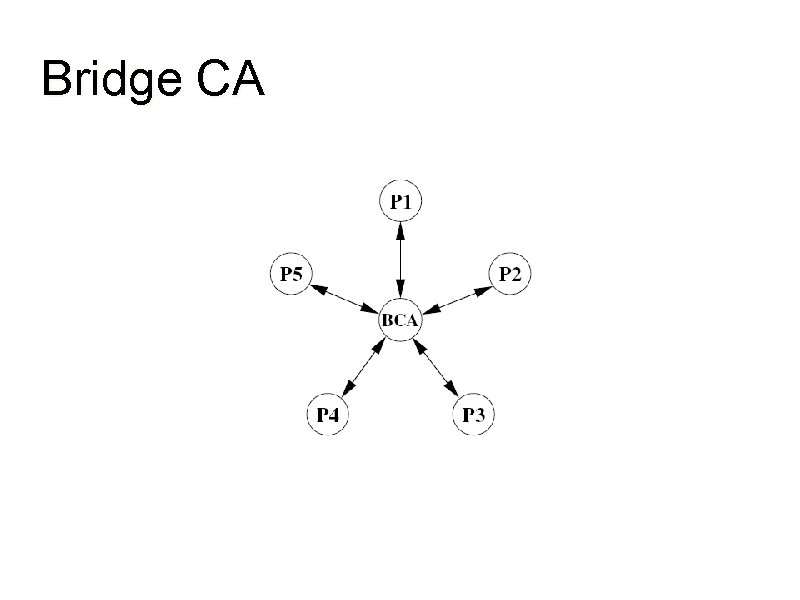 Bridge CA
Bridge CA
 Review • • • Defined Trust Example mis-trust in applications Software Trust Models Trust Management PKI Trust Models
Review • • • Defined Trust Example mis-trust in applications Software Trust Models Trust Management PKI Trust Models
 Questions? Discussion…
Questions? Discussion…


