7dbcf9cff80754ee83ece66bae5be291.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41


Troubled Waters

Discussion Outline § Enterprise Risk Management What is ERM and why is it important? Differences between ERM and Risk Management Benefits and Obstacles of implementing an ERM Program § ERM Process Overview Sarbanes-Oxley and COSO Financial Aspects of ERM Risk Management Property Risks-Exposures & Controls Linking Risks and Processes § Implementing an ERM Program Risk identification & Mapping Risk response paths Resources and Tools Sample Case Study § Questions & Discussion

What is ERM? “… a process, effected by an entity’s board of directors, management and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risks to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives. ” Source: COSO Enterprise Risk Management-Integrated Framework. 2004

Enterprise Risk Management § enables management to effectively deal with uncertainty and associated risks and opportunities § creates Stakeholder value through leveraging of risks and opportunities § identifies potential events that may affect an entity § aligns risk appetite and strategy through risk quantification and risk mapping § leverages collaborative “knowledge” to enhance risk response decisions § reduces operational surprises and losses § improves deployment of capital § allows proactively realizing opportunities § supports achievement of key objectives

Why is ERM important? § every entity, whether for profit or not, exists to realize value for its stakeholders § value is created, preserved or eroded by management decisions in all activities, from setting strategy to operating the enterprise day to day. § business risks are increasing § changing regulatory requirements § boards not performing optimally in risk oversight § corporate governance needs to be improved
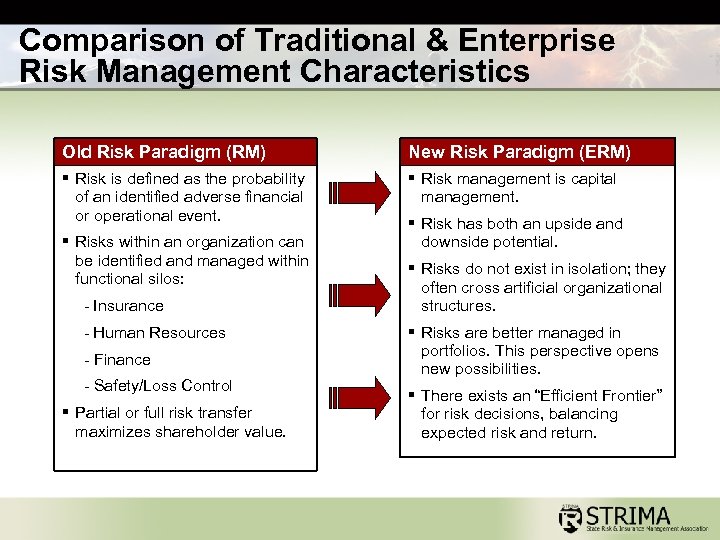
Comparison of Traditional & Enterprise Risk Management Characteristics Old Risk Paradigm (RM) New Risk Paradigm (ERM) § Risk is defined as the probability of an identified adverse financial or operational event. § Risk management is capital management. § Risks within an organization can be identified and managed within functional silos: - Insurance - Human Resources - Finance - Safety/Loss Control § Partial or full risk transfer maximizes shareholder value. § Risk has both an upside and downside potential. § Risks do not exist in isolation; they often cross artificial organizational structures. § Risks are better managed in portfolios. This perspective opens new possibilities. § There exists an “Efficient Frontier” for risk decisions, balancing expected risk and return.

ERM and Risk Management Differences between ERM and RM § RM deals primarily with operational risks • developing risk transfer/financing solutions • funding for losses • mitigating risk • loss control • claims management

ERM and Risk Management ERM deals with broader risks including: § strategic-mergers & acquisitions, business execution, research & development, customers § operational-business interruption, supply chain, fraud, efficiency, safety § human capital-employment practices, turnover, leadership, absence management § legal/regulatory-compliance § technology- intellectual property, information security § financial- foreign exchange, credit § reputation- market share

Charting the Course
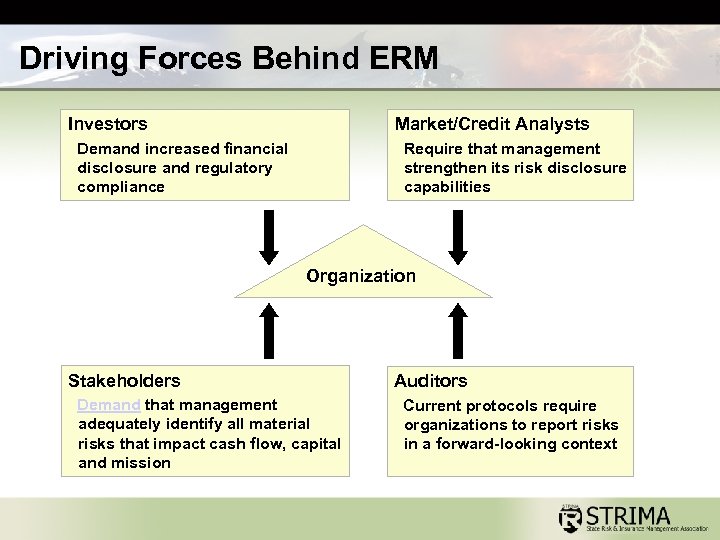
Driving Forces Behind ERM Investors Market/Credit Analysts Demand increased financial disclosure and regulatory compliance Require that management strengthen its risk disclosure capabilities Organization Stakeholders Demand that management adequately identify all material risks that impact cash flow, capital and mission Auditors Current protocols require organizations to report risks in a forward-looking context

ERM Benefits and Obstacles Obstacle Benefit § inadequate senior management support § aligns management consensus and buy in § inability to show immediate ROI § provides process to measure business threats & ROI § time & resources required § enhances capital allocation process § cultural incompatibilities § inadequate IT systems § risk silo thinking § links operations, strategic and financial decision making via portfolio management § improves achievement of business objectives

The COSO Framework ERM as defined in the framework: § Is a process § Is effected by people § Is applied in strategy setting § Is applied across the enterprise § Is designed to identify potential events § Manages risks within risk appetite § Provides “reasonable assurance” § Supports achievement of key objectives Source: COSO Enterprise Risk Management – Integrated Framework, 2004

ERM & Sarbanes-Oxley § Sarbanes-Oxley Section 404 • focuses immediate management attention on financial reporting risk and internal control systems • sets forth an ongoing requirement for annual attestation • financial reporting risks are closely linked to enterprise wide risk monitoring and reporting § COSO Framework • provides a comprehensive framework for addressing risk across the organization • helps to organize project based initiatives surrounding Sarbanes -Oxley towards a process oriented and sustainable approach

Linking Risks & Processes § Reduce Operational Surprises and Losses - Identify • Weather • Terrorism • Skyrocketing Costs - Workers’ Compensation - Health Care - Retirement Funding - Insurance Cycles • Major Transportation System Failures • Economic Downturns - Baby Boomers Retiring - Fuel Prices • Consent Decrees
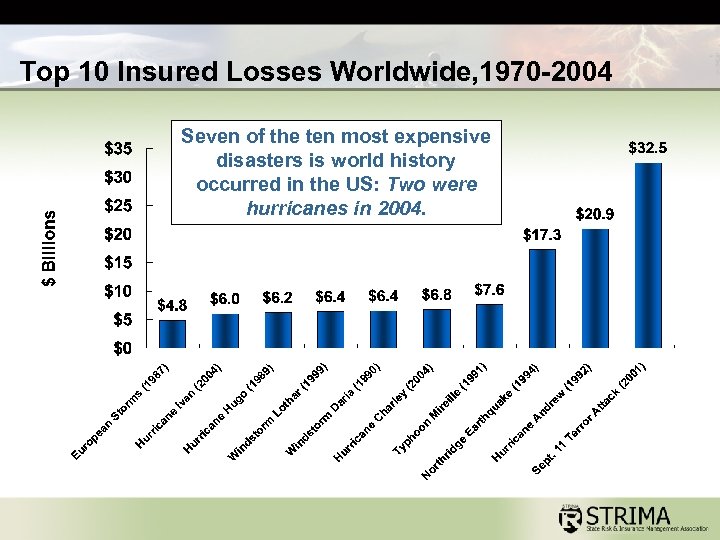
Top 10 Insured Losses Worldwide, 1970 -2004 Seven of the ten most expensive disasters is world history occurred in the US: Two were hurricanes in 2004.

Handling Exposures

Financial Aspects § Reduce Operational Surprises and Losses - Finance • Retention - Auto PD, Working layers for GL, EPL, LEL, W/C, Property, Auto Liability - Deductible/SIR > Can you afford your SIR Program? ù Stop Loss ù Gaps ù Multiple Lines Loss - Uninsurable Losses

Financial Aspects § Reduce Operational Surprises and Losses - Finance • Insure – A Financial Transfer - Excess - Auto, GL, EPL, LEL, W/C, PROPERTY ù Variable Attachment Points ù Aggregate Limits ù “Basket Aggregates” ù Blanket Property – Single Loss limits - Auto Liability

Financial Aspects § Reduce Operational Surprises and Losses - Controls • Contractual Transfer - Road Construction – “Big Dig” - Prisons - Medical Malpractice - Sub-Contractors - “State Bids”

Risk Management § Reduce Operational Surprises and Losses - Controls • Claim Management - Third Party Administrators - In-House ù Guardrail Reimbursement Program ù Workers’ Compensation Fraud Units

Risk Management § Reduce Operational Surprises and Losses - Controls • Prevention - Investments ù Diversify - Audits - Mandatory Vacations - Safety Programs
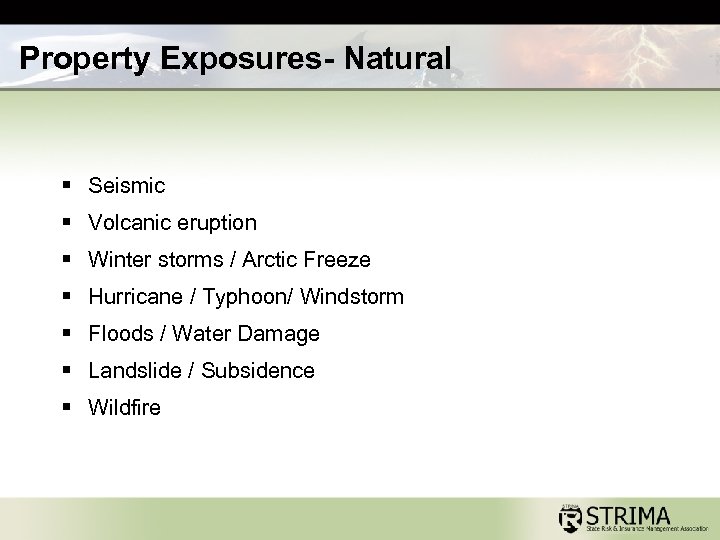
Property Exposures- Natural § Seismic § Volcanic eruption § Winter storms / Arctic Freeze § Hurricane / Typhoon/ Windstorm § Floods / Water Damage § Landslide / Subsidence § Wildfire

Property Exposures- Man Made § Bomb threats / Terrorist Attacks § Civil disturbance § Explosion § Structural fire § Sabotage § Hazardous materials release § Theft § Transportation accident § Computer crime § Utility failure § Unauthorized access § Machinery Breakdown

Property Risk Control § Risk Assessments § Systems § Management Programs • Security § Management of Change • Fire Protection § Contingency Planning § Training / Drills § Recovery Planning § Media Management § Facility Location & Site Features § Physical / Construction Features § Communication • Voice • Data

Positive Change

Implementing an ERM Program § § § Establish a vision and plan with objectives Develop a supporting business case Obtain senior level support Form a cross functional team to lead the process Communicate activities and progress

Implementing an ERM Program Step 1 § § Identify key risks via interviews and surveys Link key risks to corporate strategic objectives Benchmark risks Map risks Step 2 § § Quantify identified risks Assess the entity’s risk appetite and operating environment Step 3 § Identify insurance and non-insurance risk responses Step 4 § § Create specific, measurable and time-limited response plans that are acceptable and realistic to control risks Implement continuous monitoring and improvement processes
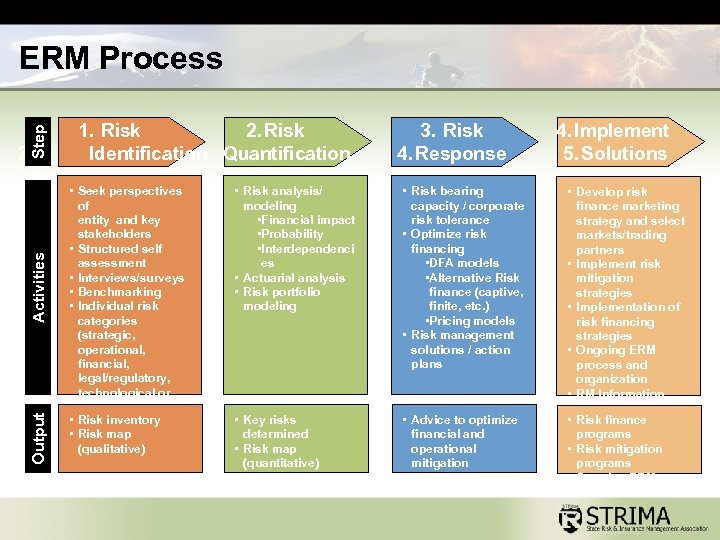
Step ERM Process Output Activities 2. 1. Risk 2. Risk Identification Quantification • Seek perspectives of entity and key stakeholders • Structured self assessment • Interviews/surveys • Benchmarking • Individual risk categories (strategic, operational, financial, legal/regulatory, technological or human capital) inventory • Risk mapping • Risk map (qualitative) 3. Risk 4. Response • Risk analysis/ modeling • Financial impact • Probability • Interdependenci es • Actuarial analysis • Risk portfolio modeling • Risk bearing capacity / corporate risk tolerance • Optimize risk financing • DFA models • Alternative Risk finance (captive, finite, etc. ) • Pricing models • Risk management solutions / action plans • Key risks determined • Risk map (quantitative) • Quantitative risk profile • Advice to optimize financial and operational mitigation strategies 4. Implement 5. Solutions • Develop risk finance marketing strategy and select markets/trading partners • Implement risk mitigation strategies • Implementation of risk financing strategies • Ongoing ERM process and organization • RM Information Systems and • monitoring Risk finance programs capabilities • Risk mitigation programs • Ongoing ERM process
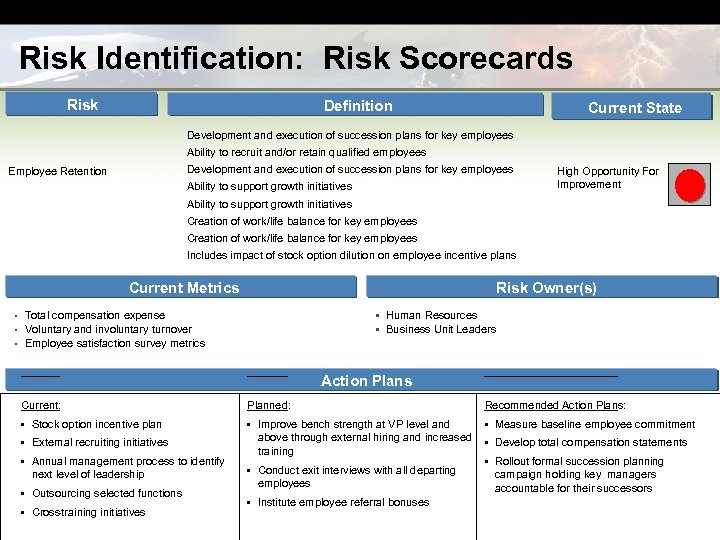
Risk Identification: Risk Scorecards Risk Definition Current State Development and execution of succession plans for key employees Ability to recruit and/or retain qualified employees Development and execution of succession plans for key employees Employee Retention Ability to support growth initiatives High Opportunity For Improvement Ability to support growth initiatives Creation of work/life balance for key employees Includes impact of stock option dilution on employee incentive plans Current Metrics Risk Owner(s) Total compensation expense • Voluntary and involuntary turnover • Employee satisfaction survey metrics • Human Resources • Business Unit Leaders • Action Plans Current: Planned: Recommended Action Plans: • Stock option incentive plan • Improve bench strength at VP level and above through external hiring and increased training • Measure baseline employee commitment • External recruiting initiatives • Annual management process to identify next level of leadership • Outsourcing selected functions • Cross -training initiatives • Conduct exit interviews with all departing employees • Institute employee referral bonuses • Develop total compensation statements • Rollout formal succession planning campaign holding key managers accountable for their successors
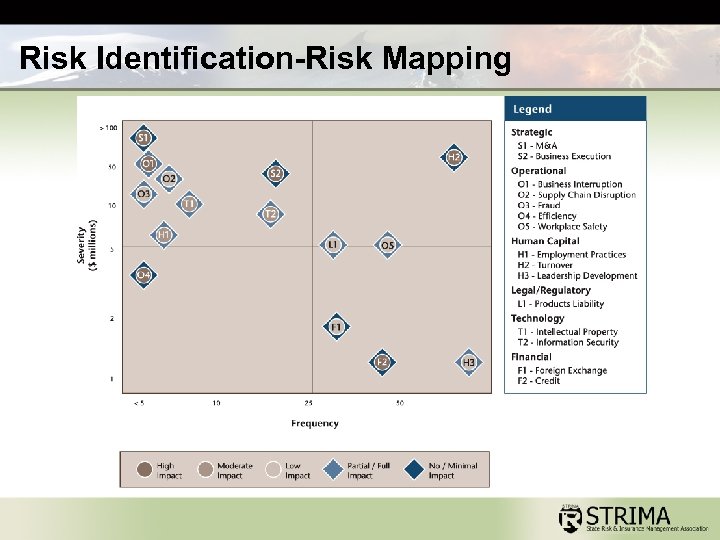
Risk Identification-Risk Mapping
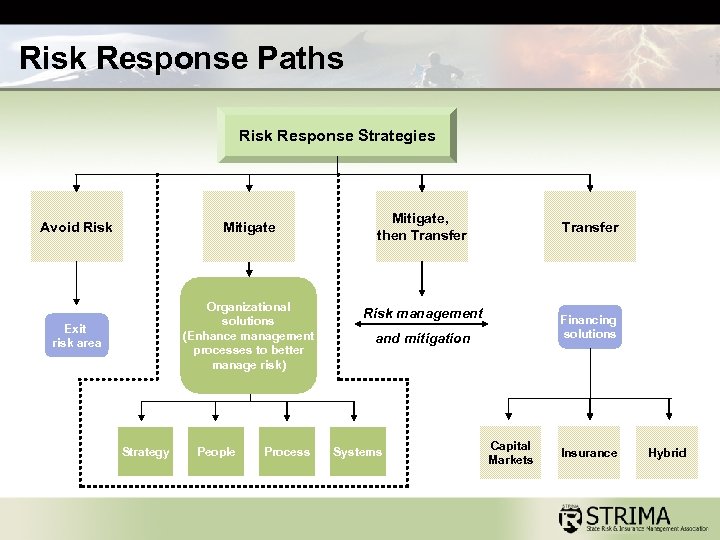
Risk Response Paths Risk Response Strategies Avoid Risk Mitigate Exit risk area Organizational solutions (Enhance management processes to better manage risk) Strategy People Process Mitigate, then Transfer Risk management Financing solutions and mitigation Systems Capital Markets Insurance Hybrid

Case Study XYZ Company § $4 Billion Financial Services & Publishing Company § Wanted an Insurance-related Risk Assessment § Driven by CFO, Treasurer and Risk Manager § Interview Process to Obtain Information § Scope Changed Immediately during Interview with Chairman

XYZ Company - Parameters Scope Original: § “Insurance-related risks to the organization. ” Revised: § “Any business risk having an impact on the organization exceeding a certain financial threshold. ”

XYZ Company - Process Team Interview Candidates – 60 Corporate and Divisional Managers Time Horizon Perspective Three to Five Years None / Financial Impact on Organization
Structured Interview Process § Cross Section of Senior Management § Duration 1 to 1. 5 Hours § Topics - General, Function, Division, Company § Follow-Up Required
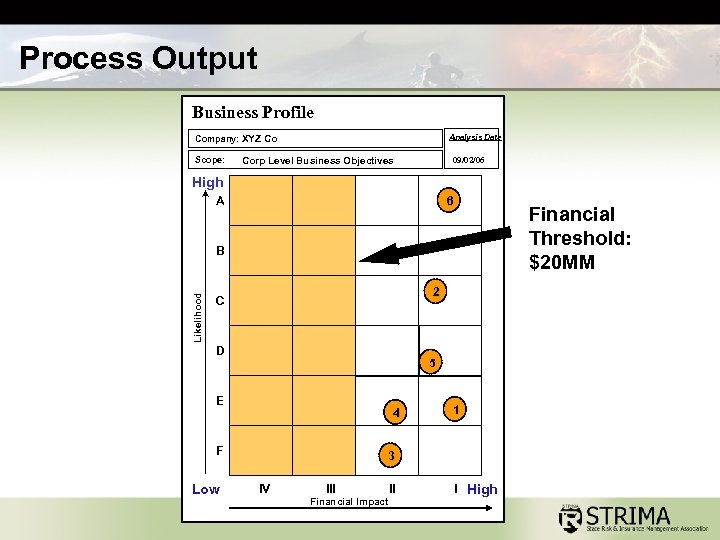
Process Output Business Profile Analysis Date Company: XYZ Co Scope: 09/02/06 Corp Level Business Objectives High A 6 Financial Threshold: $20 MM Likelihood B 2 C D 5 E 4 F Low 1 3 IV III Financial Impact II I High

XYZ Company - Results § Identified and Quantified Risks; Developed Specific Plans to Mitigate (Above Financial Threshold) § IT and Facility Business Continuation Exposures for Multiple Locations (One Representing >40% Net Income) § Chairman Set Up a Cross Functional Team to Reduce the IT / Facility Exposure § Insurance – Increase Limits for Two Major Coverages
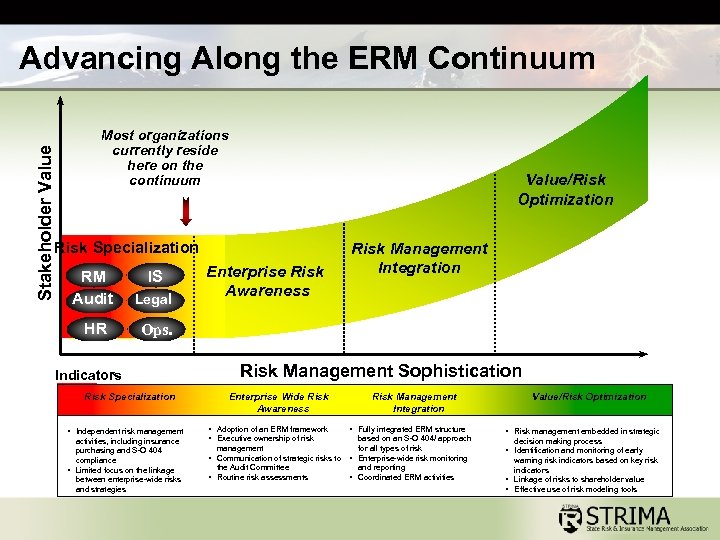
Stakeholder Value Advancing Along the ERM Continuum Most organizations currently reside here on the continuum Value/Risk Optimization Risk Specialization RM Audit Legal HR Enterprise Risk Awareness Risk Management Integration Ops. IS Indicators Risk Specialization • Independent risk management activities, including insurance purchasing and S-O 404 compliance • Limited focus on the linkage between enterprise-wide risks and strategies Risk Management Sophistication Enterprise Wide Risk Awareness • Adoption of an ERM framework • Executive ownership of risk Risk Management Integration • Fully integrated ERM structure based on an S-O 404/ approach management for all types of risk • Communication of strategic risks to • Enterprise-wide risk monitoring the Audit Committee and reporting • Routine risk assessments • Coordinated ERM activities Value/Risk Optimization • Risk management embedded in strategic decision making process • Identification and monitoring of early warning risk indicators based on key risk indicators • Linkage of risks to shareholder value • Effective use of risk modeling tools

Security Blanket
ERM § Questions and Discussion
7dbcf9cff80754ee83ece66bae5be291.ppt