03760267b1f681a06cb6c1c24c8cb2e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Trouble Shooting Common Blast Design Pitfalls 19 th Annual Surface Mined Land Reclamation Technology Transfer Seminar The Jasper, Indiana December 5 th & 6 th, 2005 Wm. J. Reisz

Common Blast Design Pitfalls Ø Improper Hole Placement ü holes to close to the face ü optimal burdens & spacings Ø Transient Pressures/Dynamic Shock ü deadpress ü basic blast design ü insufficient decking Ø Electronic Initiation Systems ü why electronics? ü pyrotechnic demonstration
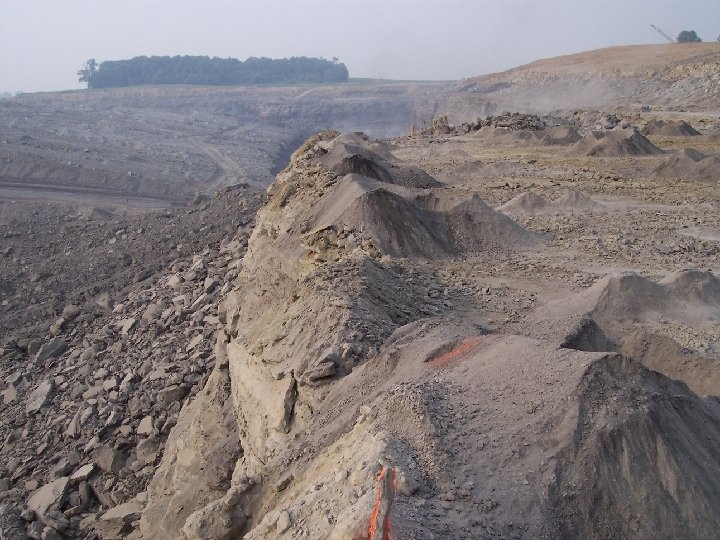

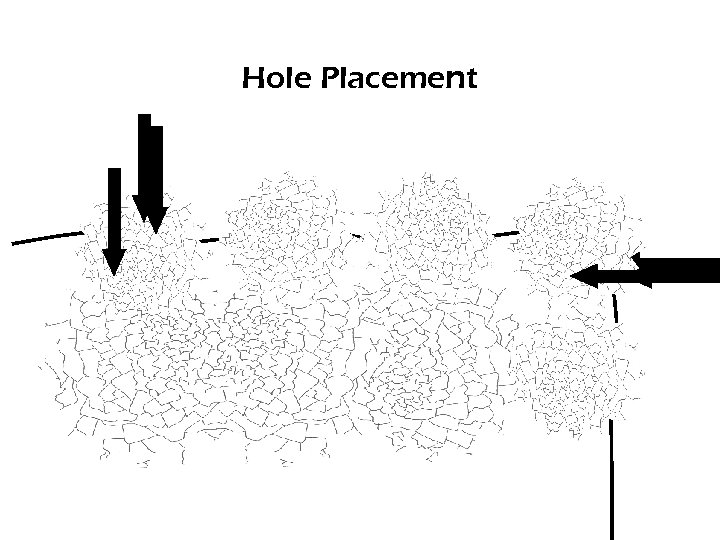
Hole Placement
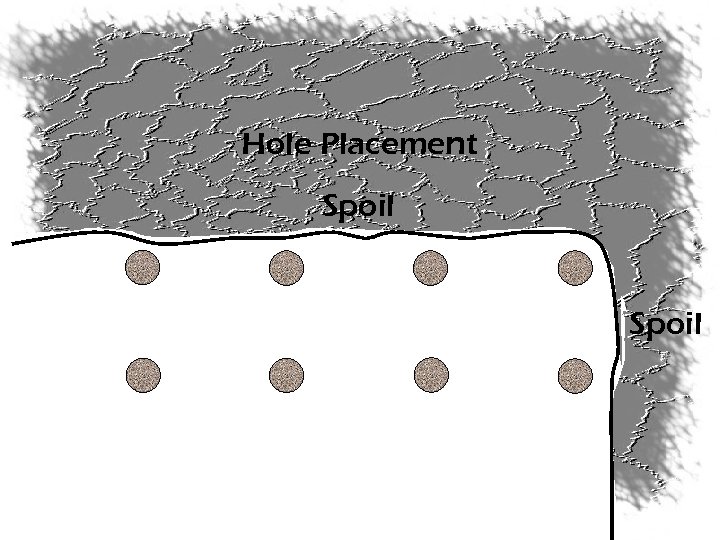
Hole Placement Spoil

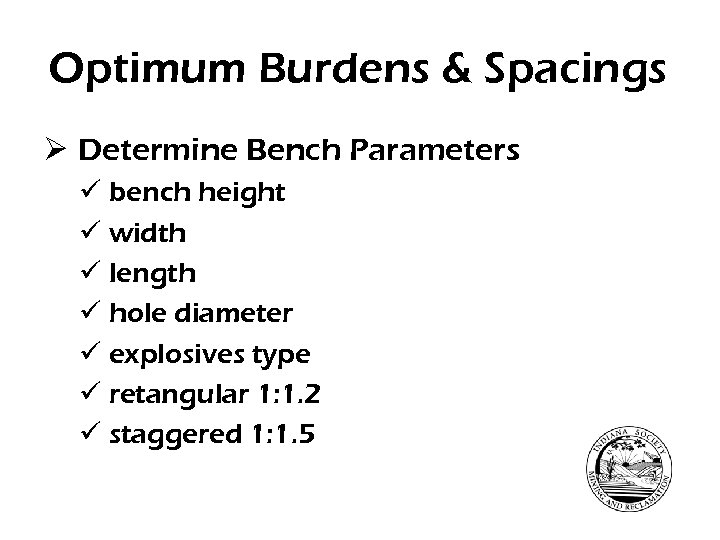
Optimum Burdens & Spacings Ø Determine Bench Parameters ü bench height ü width ü length ü hole diameter ü explosives type ü retangular 1: 1. 2 ü staggered 1: 1. 5
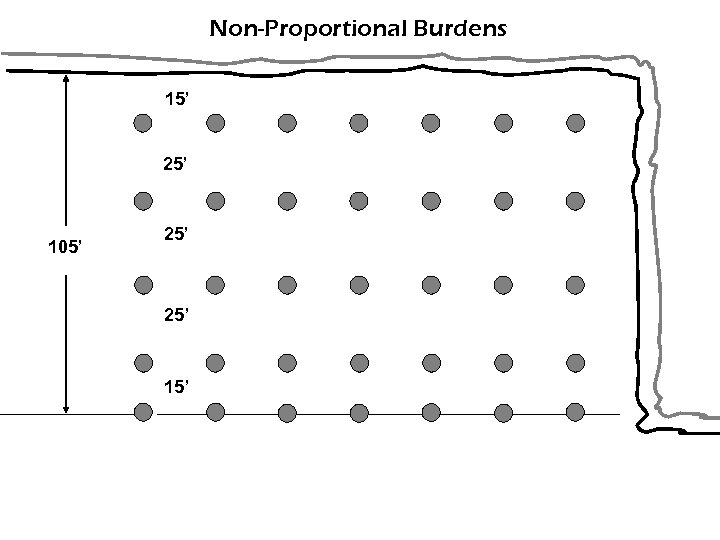
Non-Proportional Burdens 15’ 25’ 105’ 25’ 15’
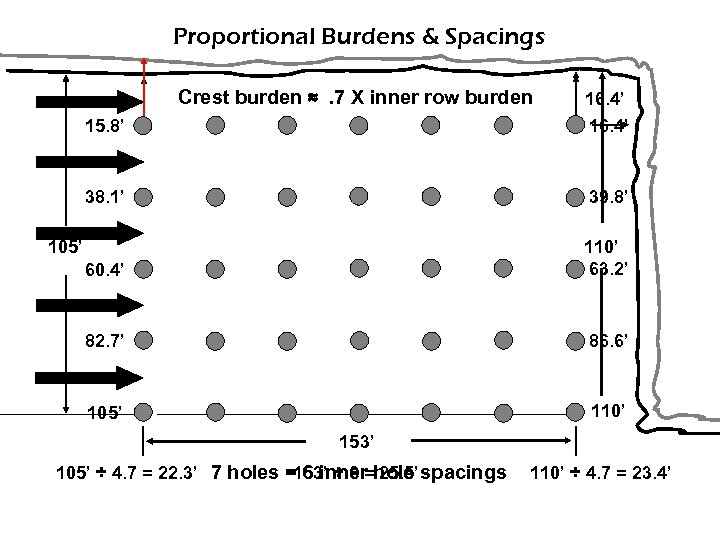
Proportional Burdens & Spacings Crest burden ≈. 7 X inner row burden 15. 8’ 16. 4’ 38. 1’ 39. 8’ 60. 4’ 110’ 63. 2’ 82. 7’ 86. 6’ 105’ 110’ 105’ 153’ 105’ ÷ 4. 7 = 22. 3’ 7 holes = 6 inner hole spacings 153’ ÷ 6 = 25. 5’ 110’ ÷ 4. 7 = 23. 4’

Blast Design ISEE Certificate Program, Level One-Practical Blasting Fundamentals

Transient Pressures Ø Deadpress Fire at a low order ü Total failure of the explosive charge ü Ø Dynamic Shock Damage the initiator ü Destroy the booster ü Fire at the wrong time ü Sympathetic Detonation ü
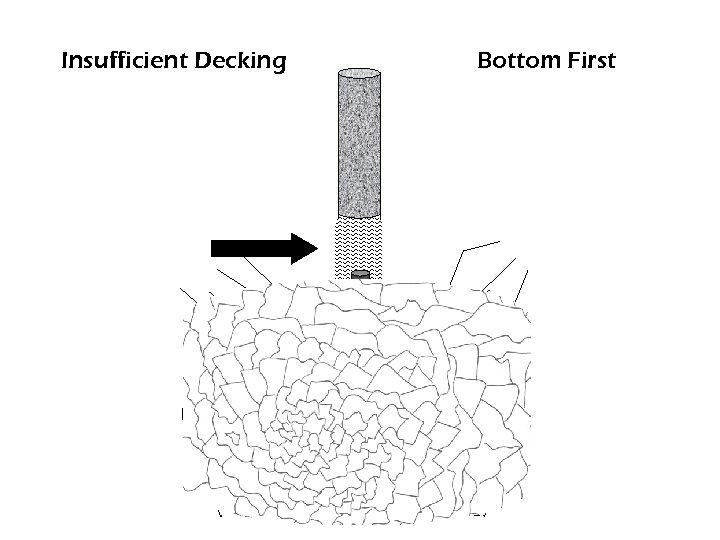
Insufficient Decking Bottom First
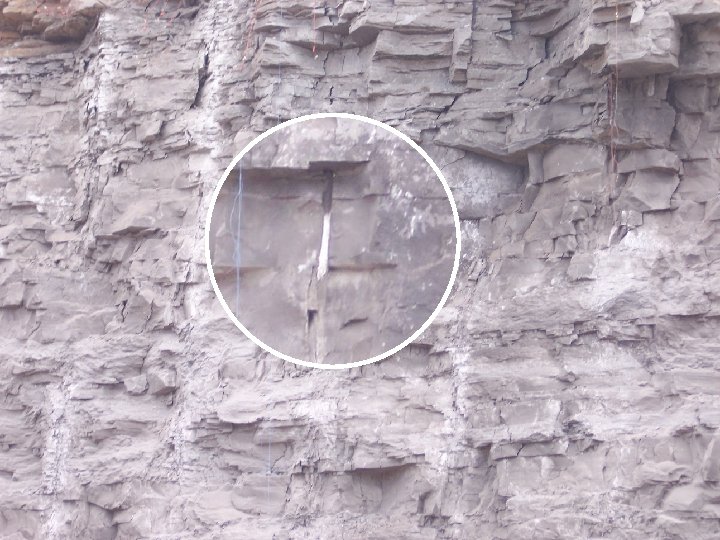



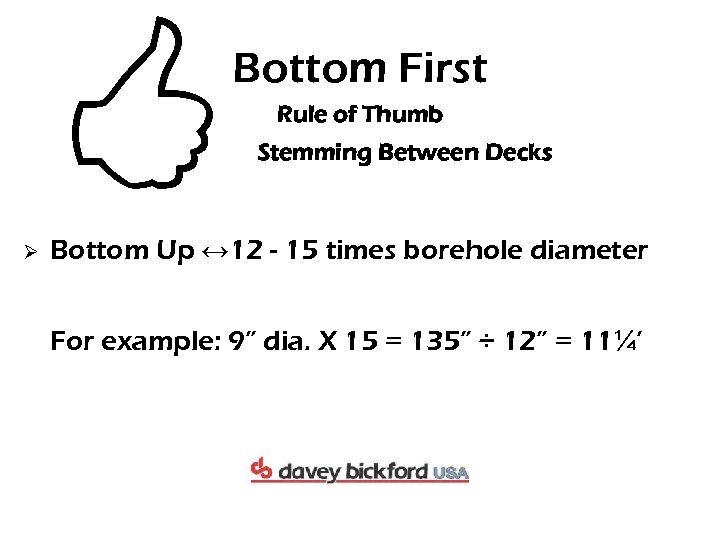
< Bottom First Ø Rule of Thumb Stemming Between Decks Bottom Up ↔ 12 - 15 times borehole diameter For example: 9” dia. X 15 = 135” ÷ 12” = 11¼’
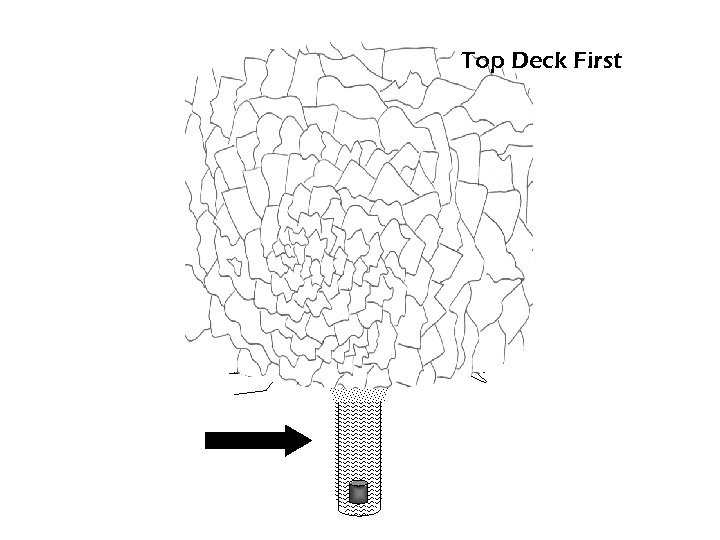
Top Deck First

Top First Rule of Thumb < Stemming Between Decks Ø Top Down ↔ 1 foot for every inch of borehole diameter For example: 9” dia. X 1’ = 9’ stem

Why Electronics?

Why Electronic Detonator Systems? Ø Eliminate ü ü pyrotechnic scatter poor rock fragmentation high ground vibration levels high air blast levels greater flyrock potential






Why Electronic Detonator Systems? Ø Eliminate pyrotechnic scatter Ø Delay selection, site specific Ø Safety üimmunity to RF, EMI and Stray Current ücompletely testable üautomated self-test and disarm features ürequires specific blast machine to fire

Why Electronic Detonator Systems? Eliminate pyrotechnic scatter Ø Delay selection, site specific Ø Safety Ø Optimized Blast Performance Ø ü ü ü Vibration Control Flyrock Control Floor Control Wall Control Improved Cast Percentage

Why Electronic Detonator Systems? Ø Eliminate pyrotechnic scatter Ø Delay selection, site specific Ø Safety Ø Autonomous Operation Ø Optimized Blast Performance Ø Inventory Control

What Electronic Detonator Systems Will Not Do ü overcome poor blast design ü make your job easier

Comparison to pyrotechnic dets

Detonators Attached to Grade Stake Shock Tube 400 ms Daveytronic 400 ms
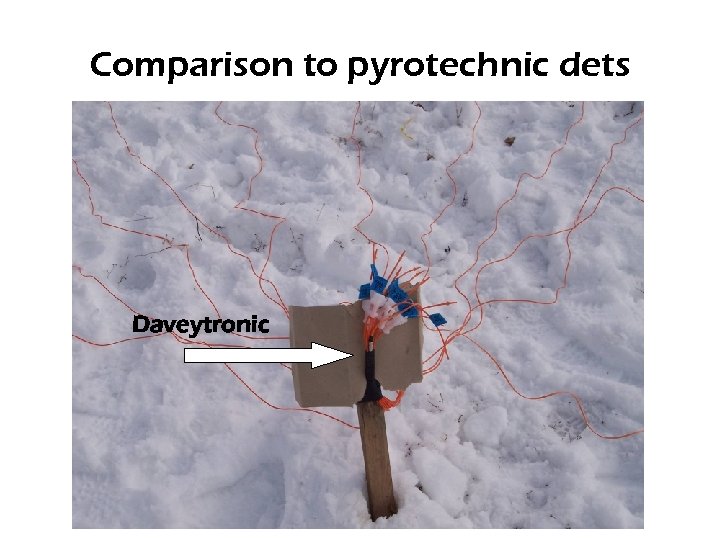
Comparison to pyrotechnic dets Daveytronic

Comparison to pyrotechnic dets
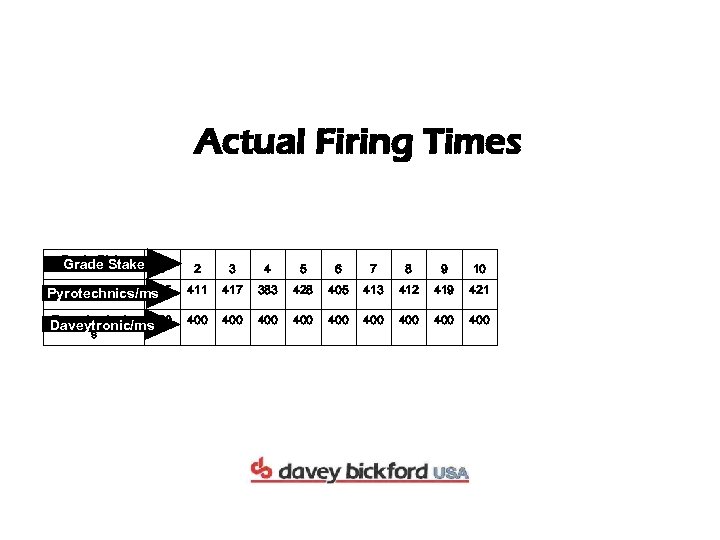
Actual Firing Times Grade Stake 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Pyrotechnics/ms 405 Pyrotechnics/ms 411 417 383 428 405 413 412 419 421 Daveytronics/m Daveytronic/ms 400 400 400 s 1
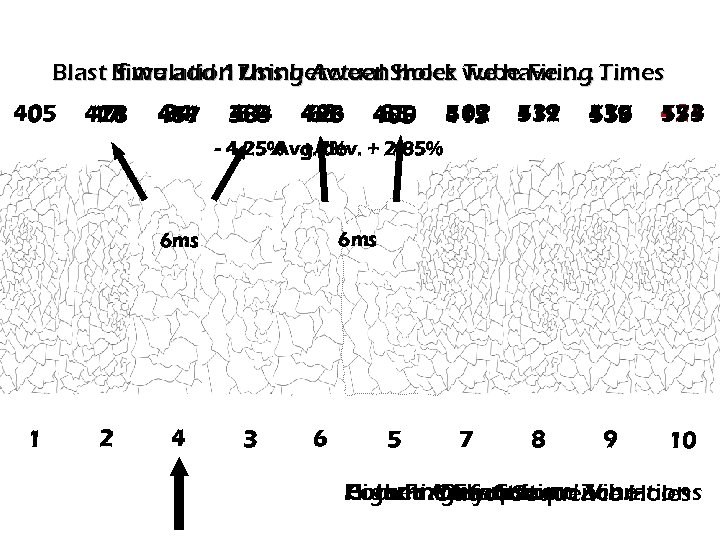
Blast If we add 17 ms between. Shock we have. . . Times Simulation Using Actual holes Tube Firing. 405 0 411 428 17 34 451 417 51 383 434 68 496 428 85 490 405 515 102 413 119 412 531 136 419 555 421 153 574 7 8 9 10 - 4. 25% + 7% + 2. 85% Avg. dev. 6 ms 1 2 4 3 6 5 Higher Air &of Sequence Holes Poor Fragmentation Zone Potential Flyrock Column. Out Ground Vibrations Disruption

Blast Design ISEE Certificate Program, Level One-Practical Blasting Fundamentals

Questions or Comments?

Thanks www. daveytronic. com Wm. J. Reisz
03760267b1f681a06cb6c1c24c8cb2e8.ppt