6856f59c2ac6e5976ef50cf8c81af933.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Trends in Site Selection: A Location Strategist’s Perspective City of Madison Economic Development Commission July 27, 2004 Darin M. Buelow
Trends in Site Selection: A Location Strategist’s Perspective City of Madison Economic Development Commission July 27, 2004 Darin M. Buelow
 Today’s Theme • Madison – A Forbes 2004 Best Place • Why (or why not) Madison for a business location? Outline • A quick profile of Deloitte’s Site Selection practice • The location selection process • Trends driving location decisions • “Best practices” in business attraction City of Madison EDC
Today’s Theme • Madison – A Forbes 2004 Best Place • Why (or why not) Madison for a business location? Outline • A quick profile of Deloitte’s Site Selection practice • The location selection process • Trends driving location decisions • “Best practices” in business attraction City of Madison EDC
 Darin Buelow • Senior Manager with Deloitte Consulting’s Fantus group, based in Chicago • 13 years development experience, including site selection, due diligence, negotiation, location strategy, and construction services • Corporate clients include: Best Buy, HP, UBE Automotive, Sherwin-Williams, Thyssen. Krupp, Cintas, Suzuki, Schwan, Kohler, Pitt Plastics, Radio Flyer, Volkswagen • Negotiated over $100 M in incentives across dozens of projects • Economic development clients include: State of Iowa, State of Washington, Cape Breton (Nova Scotia), Lake County (IL), Altoona-Blair County (PA), La. Porte County (IN) City of Madison EDC
Darin Buelow • Senior Manager with Deloitte Consulting’s Fantus group, based in Chicago • 13 years development experience, including site selection, due diligence, negotiation, location strategy, and construction services • Corporate clients include: Best Buy, HP, UBE Automotive, Sherwin-Williams, Thyssen. Krupp, Cintas, Suzuki, Schwan, Kohler, Pitt Plastics, Radio Flyer, Volkswagen • Negotiated over $100 M in incentives across dozens of projects • Economic development clients include: State of Iowa, State of Washington, Cape Breton (Nova Scotia), Lake County (IL), Altoona-Blair County (PA), La. Porte County (IN) City of Madison EDC
 Deloitte’s Fantus Group • The first and largest specialized location strategy consulting practice • Began in 1919 • Many thousands of engagements • Dedicated practices in Chicago, LA, New York, San Francisco, Atlanta, and Brussels • Focus on facility and location strategy, site selection, economic development, real estate portfolio structuring/management, and real estate operations. City of Madison EDC
Deloitte’s Fantus Group • The first and largest specialized location strategy consulting practice • Began in 1919 • Many thousands of engagements • Dedicated practices in Chicago, LA, New York, San Francisco, Atlanta, and Brussels • Focus on facility and location strategy, site selection, economic development, real estate portfolio structuring/management, and real estate operations. City of Madison EDC
 Client base across industry and facility type City of Madison EDC
Client base across industry and facility type City of Madison EDC
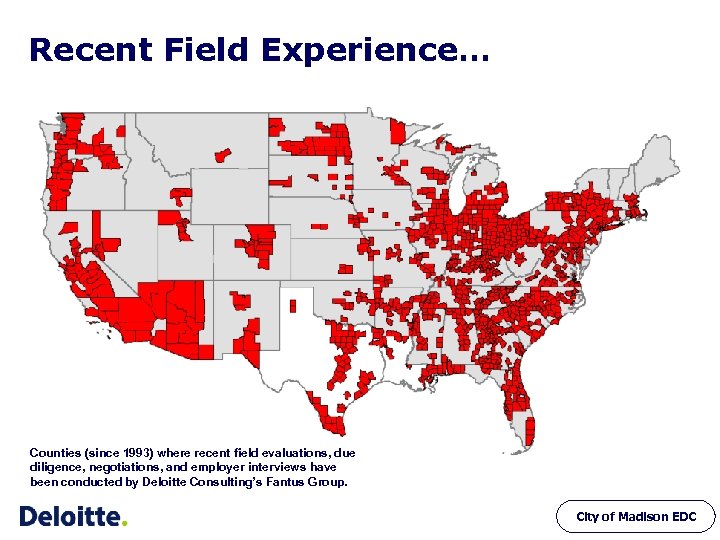 Recent Field Experience… Counties (since 1993) where recent field evaluations, due diligence, negotiations, and employer interviews have been conducted by Deloitte Consulting’s Fantus Group. City of Madison EDC
Recent Field Experience… Counties (since 1993) where recent field evaluations, due diligence, negotiations, and employer interviews have been conducted by Deloitte Consulting’s Fantus Group. City of Madison EDC
 Fantus typically conducts between 100 and 200 engagements annually • An ever-evolving mix including: • Manufacturing – our traditional “bread and butter, ” especially for Midwest practice and during industry growth cycles • HQ/Call Centers/Shared Service – strongest in the Midwest and West Coast practices; increasingly global • Distribution/Warehouse – strongest in Midwest; focused on large, big-box retailers and consumer products companies • Technology – emphasis on bio-med; many projects international; strong base in West Coast practices • Public Sector/Economic Development – State, local, and international City of Madison EDC
Fantus typically conducts between 100 and 200 engagements annually • An ever-evolving mix including: • Manufacturing – our traditional “bread and butter, ” especially for Midwest practice and during industry growth cycles • HQ/Call Centers/Shared Service – strongest in the Midwest and West Coast practices; increasingly global • Distribution/Warehouse – strongest in Midwest; focused on large, big-box retailers and consumer products companies • Technology – emphasis on bio-med; many projects international; strong base in West Coast practices • Public Sector/Economic Development – State, local, and international City of Madison EDC
 The Location Selection Process
The Location Selection Process
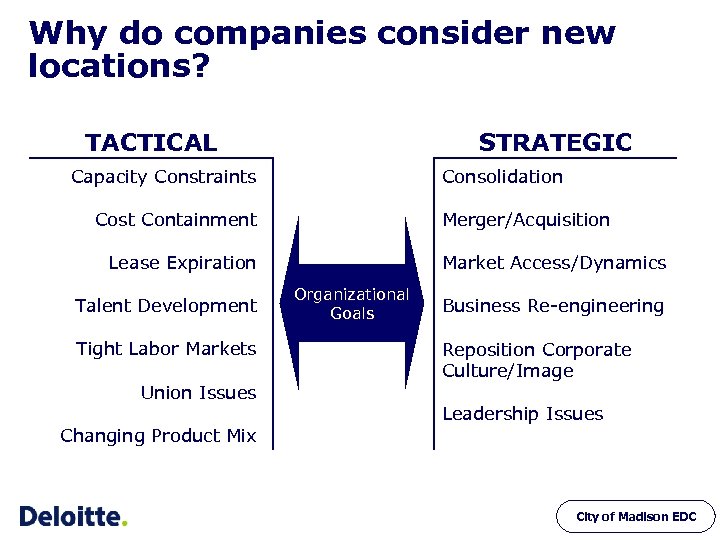 Why do companies consider new locations? TACTICAL STRATEGIC Capacity Constraints Consolidation Cost Containment Merger/Acquisition Lease Expiration Talent Development Tight Labor Markets Union Issues Changing Product Mix Market Access/Dynamics Organizational Goals Business Re-engineering Reposition Corporate Culture/Image Leadership Issues City of Madison EDC
Why do companies consider new locations? TACTICAL STRATEGIC Capacity Constraints Consolidation Cost Containment Merger/Acquisition Lease Expiration Talent Development Tight Labor Markets Union Issues Changing Product Mix Market Access/Dynamics Organizational Goals Business Re-engineering Reposition Corporate Culture/Image Leadership Issues City of Madison EDC
 Location decisions can be very troublesome for companies… • Long-term and significant allocation of major capital and human resources • Occur infrequently — internal skills are rare or rusty • Huge commitment of resources over a short period of time • High degree of uncertainty and risk • Emotionally charged and politically sensitive City of Madison EDC
Location decisions can be very troublesome for companies… • Long-term and significant allocation of major capital and human resources • Occur infrequently — internal skills are rare or rusty • Huge commitment of resources over a short period of time • High degree of uncertainty and risk • Emotionally charged and politically sensitive City of Madison EDC
 Who are the “Consultants”? • A wide range of companies have specialized site selection practices • The Big 4: Deloitte Consulting - Fantus, KPMG, E&Y, PWC • Engineering and construction firms: Fluor Daniel, Lockwood Greene • Large real estate brokerage firms: JLL, Grubb & Ellis, CB Richard Ellis, Staubach • The boutiques: • smaller, specialized companies of 1 -5 experienced consultants • spin-offs of the other firms and ex-ED professionals • Assorted others: general management consulting, HR consulting, logistics consulting, architecture firms, etc. City of Madison EDC
Who are the “Consultants”? • A wide range of companies have specialized site selection practices • The Big 4: Deloitte Consulting - Fantus, KPMG, E&Y, PWC • Engineering and construction firms: Fluor Daniel, Lockwood Greene • Large real estate brokerage firms: JLL, Grubb & Ellis, CB Richard Ellis, Staubach • The boutiques: • smaller, specialized companies of 1 -5 experienced consultants • spin-offs of the other firms and ex-ED professionals • Assorted others: general management consulting, HR consulting, logistics consulting, architecture firms, etc. City of Madison EDC
 And why should anyone pay attention to them? • They lead an increasing number of location studies • Location “influencers” are believed to be involved in nearly half of all major site selections • Tend to manage larger projects and companies that produce significant economic impact • Have many repeat clients • MOST know what they are doing and can manage a project to a successful conclusion City of Madison EDC
And why should anyone pay attention to them? • They lead an increasing number of location studies • Location “influencers” are believed to be involved in nearly half of all major site selections • Tend to manage larger projects and companies that produce significant economic impact • Have many repeat clients • MOST know what they are doing and can manage a project to a successful conclusion City of Madison EDC
 Typical Site Selection Process Strategy Screening w project drivers w countries/ regions/states w success factors w fatal flaw w project analysis specifications w search area w compare costs and conditions Due Diligence w field investigations Negotiations w risk analysis w real estate w verify screening w incentives and processdrill down w identify specific opportunities w identify 6 -10 top and risks areas Implementation w transition planning w facilities plan w vendor selection w construction ramp-up w best 3 -5 community/site options City of Madison EDC
Typical Site Selection Process Strategy Screening w project drivers w countries/ regions/states w success factors w fatal flaw w project analysis specifications w search area w compare costs and conditions Due Diligence w field investigations Negotiations w risk analysis w real estate w verify screening w incentives and processdrill down w identify specific opportunities w identify 6 -10 top and risks areas Implementation w transition planning w facilities plan w vendor selection w construction ramp-up w best 3 -5 community/site options City of Madison EDC
 Factors that are most critical to a corporate global location decision 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Access to customers Stable social/political environment Ease of doing business Reliability/quality of other utilities Ability to hire tech professionals Ability to hire management staff Level of corruption Cost of labor Ability to hire skilled laborers Crime & safety National taxes Cost of utilities Roads Avail/quality - university/tech training Local taxes 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Access to raw materials Available land – all services in place Air service Labor relations/unionization Access to suppliers Preferential trade agreements Available building/space – all services Cost of shipping (freight cost) Labor regulations Cost of real estate Access to finance Ports Healthcare Ability to hire general laborers Availability of grants/incentives City of Madison EDC
Factors that are most critical to a corporate global location decision 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Access to customers Stable social/political environment Ease of doing business Reliability/quality of other utilities Ability to hire tech professionals Ability to hire management staff Level of corruption Cost of labor Ability to hire skilled laborers Crime & safety National taxes Cost of utilities Roads Avail/quality - university/tech training Local taxes 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Access to raw materials Available land – all services in place Air service Labor relations/unionization Access to suppliers Preferential trade agreements Available building/space – all services Cost of shipping (freight cost) Labor regulations Cost of real estate Access to finance Ports Healthcare Ability to hire general laborers Availability of grants/incentives City of Madison EDC
 Location Process Drivers • Domestically, costs are the key factor for the majority of competitive projects • Some companies screen strictly on costs to narrow the field • Often very focused on costs early in the engagement, but may lower the bar once trade-offs are understood • A threshold screen • “…eliminate all areas with wages over 10% above the regional/national averages” • Performance-based solutions are key for some talent and market driven projects • Screen almost entirely on non-cost, operational factors such availability of technical talent, access to a specific customer, etc. City of Madison EDC
Location Process Drivers • Domestically, costs are the key factor for the majority of competitive projects • Some companies screen strictly on costs to narrow the field • Often very focused on costs early in the engagement, but may lower the bar once trade-offs are understood • A threshold screen • “…eliminate all areas with wages over 10% above the regional/national averages” • Performance-based solutions are key for some talent and market driven projects • Screen almost entirely on non-cost, operational factors such availability of technical talent, access to a specific customer, etc. City of Madison EDC
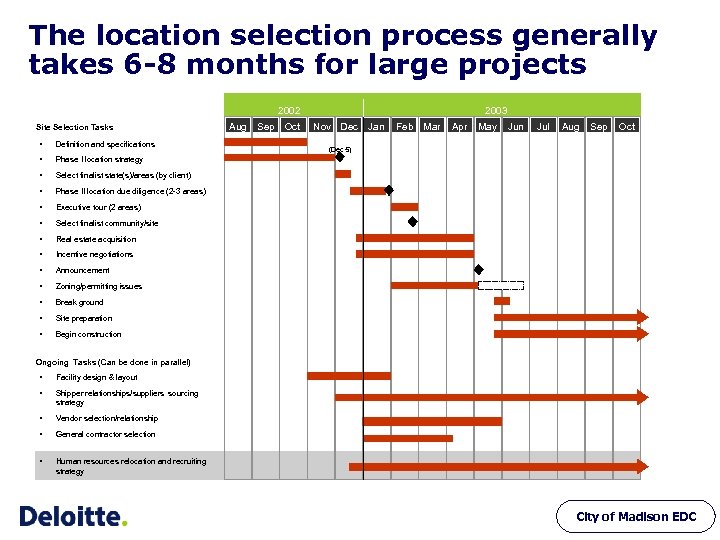 The location selection process generally takes 6 -8 months for large projects 2002 Site Selection Tasks • Definition and specifications • Oct Site preparation • Sep Break ground • Aug Zoning/permitting issues • Jul Announcement • Jun Incentive negotiations • May Real estate acquisition • Apr Select finalist community/site • Feb Mar Executive tour (2 areas) • Jan Phase II location due diligence (2 -3 areas) • Nov Dec Select finalist state(s)/areas (by client) • Sep Oct Phase I location strategy • Aug 2003 Begin construction (Dec 5) Ongoing Tasks (Can be done in parallel) • Facility design & layout • Shipper relationships/suppliers sourcing strategy • Vendor selection/relationship • General contractor selection • Human resources relocation and recruiting strategy City of Madison EDC
The location selection process generally takes 6 -8 months for large projects 2002 Site Selection Tasks • Definition and specifications • Oct Site preparation • Sep Break ground • Aug Zoning/permitting issues • Jul Announcement • Jun Incentive negotiations • May Real estate acquisition • Apr Select finalist community/site • Feb Mar Executive tour (2 areas) • Jan Phase II location due diligence (2 -3 areas) • Nov Dec Select finalist state(s)/areas (by client) • Sep Oct Phase I location strategy • Aug 2003 Begin construction (Dec 5) Ongoing Tasks (Can be done in parallel) • Facility design & layout • Shipper relationships/suppliers sourcing strategy • Vendor selection/relationship • General contractor selection • Human resources relocation and recruiting strategy City of Madison EDC
 Trends Driving Location Decisions
Trends Driving Location Decisions
 Trends in Site Selection • Cost reduction • Globalization • Functional Trends and Issues City of Madison EDC
Trends in Site Selection • Cost reduction • Globalization • Functional Trends and Issues City of Madison EDC
 Cost reduction continues to be a corporate imperative… issues / trends w intense pressure to reduce costs w w pre and post economic downturn consolidation, relocation, and rationalization of operations increasing global competition products and services factors of production actions / impacts w job reductions w real estate consolidation and disposition severing lower value functions from core relocations to lower cost environments w expanded search areas multi-country searches, not just multi-state focused off-shore, particularly for labor intensive operations Asia Mexico, Central America and Brazil E. Europe w JVs and outsourcing City of Madison EDC
Cost reduction continues to be a corporate imperative… issues / trends w intense pressure to reduce costs w w pre and post economic downturn consolidation, relocation, and rationalization of operations increasing global competition products and services factors of production actions / impacts w job reductions w real estate consolidation and disposition severing lower value functions from core relocations to lower cost environments w expanded search areas multi-country searches, not just multi-state focused off-shore, particularly for labor intensive operations Asia Mexico, Central America and Brazil E. Europe w JVs and outsourcing City of Madison EDC
 Globalization and Offshoring issues / trends w increasing need to compete globally w w create/improve market access reduce cost create/improve access to source materials labor availability barriers to entry fall technology enables globalization risk a growing concern global taxation actions / impacts w foreign direct investment (FDI) more likely, even for mid-sized companies contract manufacturing JV/outsource greenfield w mitigation of FDI risk through country/city selection (political, labor, human, natural disaster etc. ) w mobile income tax strategies City of Madison EDC
Globalization and Offshoring issues / trends w increasing need to compete globally w w create/improve market access reduce cost create/improve access to source materials labor availability barriers to entry fall technology enables globalization risk a growing concern global taxation actions / impacts w foreign direct investment (FDI) more likely, even for mid-sized companies contract manufacturing JV/outsource greenfield w mitigation of FDI risk through country/city selection (political, labor, human, natural disaster etc. ) w mobile income tax strategies City of Madison EDC
 Who is Madison Competing With? • The usual suspects: • Other Wisconsin communities/counties • Illinois, Minnesota, Michigan, Iowa • Tier 1 U. S. R&D Centers: Boston, San Diego, San Jose, Research Triangle, Atlanta, Front Range, etc. • Mexico (manufacturing) • The unusual suspects: • China • India • Central America (CAFTA) City of Madison EDC
Who is Madison Competing With? • The usual suspects: • Other Wisconsin communities/counties • Illinois, Minnesota, Michigan, Iowa • Tier 1 U. S. R&D Centers: Boston, San Diego, San Jose, Research Triangle, Atlanta, Front Range, etc. • Mexico (manufacturing) • The unusual suspects: • China • India • Central America (CAFTA) City of Madison EDC
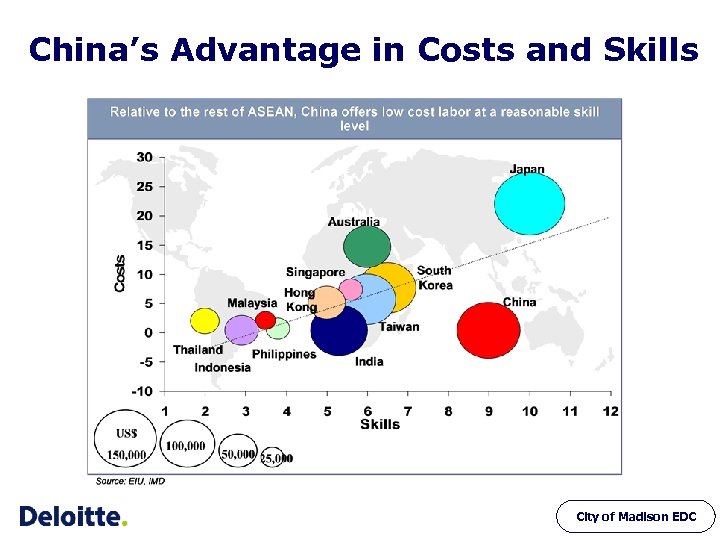 Commercial Environment Labor Force China’s Advantage in Costs and Skills City of Madison EDC
Commercial Environment Labor Force China’s Advantage in Costs and Skills City of Madison EDC
 “The Sky is Falling”…. !!! Is everything moving offshore? No. 1. Food manufacturing 2. High cube to weight ratio products (e. g. , tissue) 3. Distribution 4. Defense, Homeland Security 5. Critical time-to-market products (e. g. , Tier 1 automotive) 6. Small or specialized manufacturing 7. Entrepreneurial enterprise 8. High water content product manufacturing (e. g. , Windex) 9. Healthcare related industries 10. R&D requiring unique linkages to universities City of Madison EDC
“The Sky is Falling”…. !!! Is everything moving offshore? No. 1. Food manufacturing 2. High cube to weight ratio products (e. g. , tissue) 3. Distribution 4. Defense, Homeland Security 5. Critical time-to-market products (e. g. , Tier 1 automotive) 6. Small or specialized manufacturing 7. Entrepreneurial enterprise 8. High water content product manufacturing (e. g. , Windex) 9. Healthcare related industries 10. R&D requiring unique linkages to universities City of Madison EDC
 Manufacturers face intense global cost competition issues / trends w exodus of US labor intensive industry shedding lower skilled operations still struggling with higher and technical skilled labor availability w wage pressures US wages increasingly high w need for global positioning new markets/customers global JIT suppliers w outsourcing actions / impacts w US companies focused offshore, particularly for labor intensive operations w non-US companies also looking offshore, but… heightened focus on Mexico and Canada to serve North America w areas with abundant technical and skilled production labor will thrive w need for advanced training, training partnerships City of Madison EDC
Manufacturers face intense global cost competition issues / trends w exodus of US labor intensive industry shedding lower skilled operations still struggling with higher and technical skilled labor availability w wage pressures US wages increasingly high w need for global positioning new markets/customers global JIT suppliers w outsourcing actions / impacts w US companies focused offshore, particularly for labor intensive operations w non-US companies also looking offshore, but… heightened focus on Mexico and Canada to serve North America w areas with abundant technical and skilled production labor will thrive w need for advanced training, training partnerships City of Madison EDC
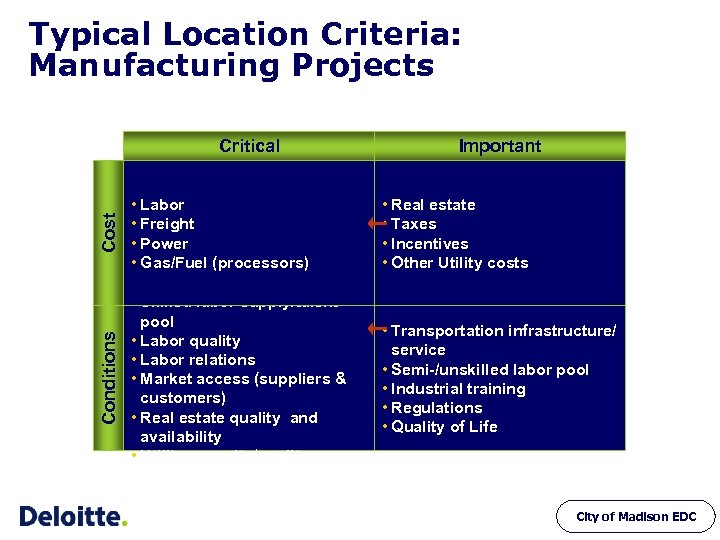 Typical Location Criteria: Manufacturing Projects Cost Important • Labor • Freight • Power • Gas/Fuel (processors) • Real estate • Taxes • Incentives • Other Utility costs Conditions Critical • Skilled labor supply/talent pool • Labor quality • Labor relations • Market access (suppliers & customers) • Real estate quality and availability • Utility capacity/quality • Transportation infrastructure/ service • Semi-/unskilled labor pool • Industrial training • Regulations • Quality of Life City of Madison EDC
Typical Location Criteria: Manufacturing Projects Cost Important • Labor • Freight • Power • Gas/Fuel (processors) • Real estate • Taxes • Incentives • Other Utility costs Conditions Critical • Skilled labor supply/talent pool • Labor quality • Labor relations • Market access (suppliers & customers) • Real estate quality and availability • Utility capacity/quality • Transportation infrastructure/ service • Semi-/unskilled labor pool • Industrial training • Regulations • Quality of Life City of Madison EDC
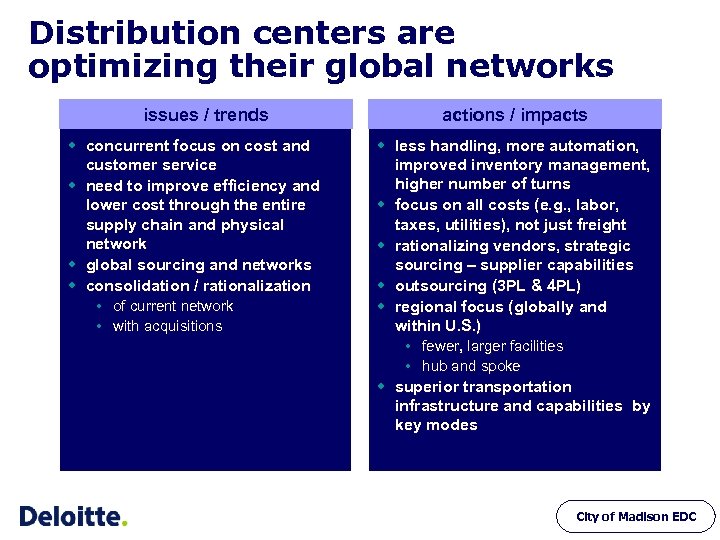 Distribution centers are optimizing their global networks issues / trends w concurrent focus on cost and customer service w need to improve efficiency and lower cost through the entire supply chain and physical network w global sourcing and networks w consolidation / rationalization of current network with acquisitions actions / impacts w less handling, more automation, improved inventory management, higher number of turns w focus on all costs (e. g. , labor, taxes, utilities), not just freight w rationalizing vendors, strategic sourcing – supplier capabilities w outsourcing (3 PL & 4 PL) w regional focus (globally and within U. S. ) fewer, larger facilities hub and spoke w superior transportation infrastructure and capabilities by key modes City of Madison EDC
Distribution centers are optimizing their global networks issues / trends w concurrent focus on cost and customer service w need to improve efficiency and lower cost through the entire supply chain and physical network w global sourcing and networks w consolidation / rationalization of current network with acquisitions actions / impacts w less handling, more automation, improved inventory management, higher number of turns w focus on all costs (e. g. , labor, taxes, utilities), not just freight w rationalizing vendors, strategic sourcing – supplier capabilities w outsourcing (3 PL & 4 PL) w regional focus (globally and within U. S. ) fewer, larger facilities hub and spoke w superior transportation infrastructure and capabilities by key modes City of Madison EDC
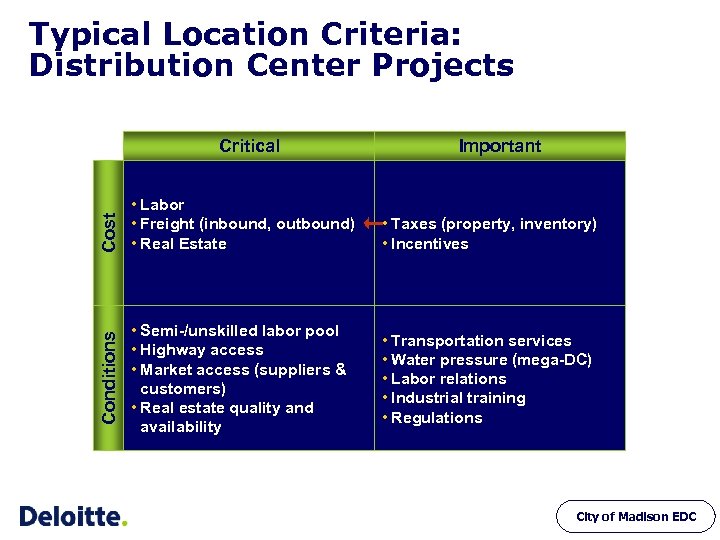 Typical Location Criteria: Distribution Center Projects Conditions Cost Critical • Labor • Freight (inbound, outbound) • Real Estate • Semi-/unskilled labor pool • Highway access • Market access (suppliers & customers) • Real estate quality and availability Important • Taxes (property, inventory) • Incentives • Transportation services • Water pressure (mega-DC) • Labor relations • Industrial training • Regulations City of Madison EDC
Typical Location Criteria: Distribution Center Projects Conditions Cost Critical • Labor • Freight (inbound, outbound) • Real Estate • Semi-/unskilled labor pool • Highway access • Market access (suppliers & customers) • Real estate quality and availability Important • Taxes (property, inventory) • Incentives • Transportation services • Water pressure (mega-DC) • Labor relations • Industrial training • Regulations City of Madison EDC
 Shared services/contact centers are cost and customer service focused… issues / trends w consolidation, rationalization and relocation w operating costs (labor, labor) w customer needs and geographic coverage drive deployment – globally w re-engineering process and technology enabled greater mobility w skill requirements both higher and lower w data and call volume management actions / impacts shared services centers w large regional centers Americas, Asia/Oceania, EMEA w locations with broad financial skills and multi-lingual w diversification of risk customer contact centers w outsourcing wave w 3 rd and 4 th tier US locations and lowcost offshore locations w multiple operations to cover time zone and maintain reasonable size w low-risk, technology-capable locations (phone, internet etc. ) City of Madison EDC
Shared services/contact centers are cost and customer service focused… issues / trends w consolidation, rationalization and relocation w operating costs (labor, labor) w customer needs and geographic coverage drive deployment – globally w re-engineering process and technology enabled greater mobility w skill requirements both higher and lower w data and call volume management actions / impacts shared services centers w large regional centers Americas, Asia/Oceania, EMEA w locations with broad financial skills and multi-lingual w diversification of risk customer contact centers w outsourcing wave w 3 rd and 4 th tier US locations and lowcost offshore locations w multiple operations to cover time zone and maintain reasonable size w low-risk, technology-capable locations (phone, internet etc. ) City of Madison EDC
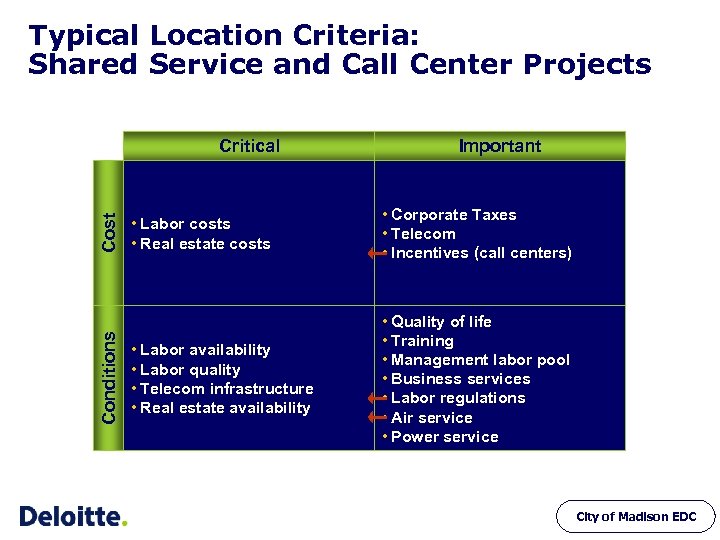 Typical Location Criteria: Shared Service and Call Center Projects Conditions Cost Critical Important • Labor costs • Real estate costs • Corporate Taxes • Telecom • Incentives (call centers) • Labor availability • Labor quality • Telecom infrastructure • Real estate availability • Quality of life • Training • Management labor pool • Business services • Labor regulations • Air service • Power service City of Madison EDC
Typical Location Criteria: Shared Service and Call Center Projects Conditions Cost Critical Important • Labor costs • Real estate costs • Corporate Taxes • Telecom • Incentives (call centers) • Labor availability • Labor quality • Telecom infrastructure • Real estate availability • Quality of life • Training • Management labor pool • Business services • Labor regulations • Air service • Power service City of Madison EDC
 Technology companies no longer focus on “growth at any cost” issues / trends w consolidation and downsizing w increased FDI w new production operations more focused on traditional locational measures w still driven by talent and the environment in which to attract them w cluster in regions with a substantial scientific, technical and/or academic presence and eminence actions / impacts w exodus of labor intense operations to low cost countries overseas outsourcing to reduce costs assembly operations focus on low-cost countries multi-country R&D efforts w paying more attention to labor, freight, taxes, and utility costs w focus on the ability to effectively recruit scientific, engineering, technical, and skilled production talent critical mass of existing local talent access to top universities and programs City of Madison EDC
Technology companies no longer focus on “growth at any cost” issues / trends w consolidation and downsizing w increased FDI w new production operations more focused on traditional locational measures w still driven by talent and the environment in which to attract them w cluster in regions with a substantial scientific, technical and/or academic presence and eminence actions / impacts w exodus of labor intense operations to low cost countries overseas outsourcing to reduce costs assembly operations focus on low-cost countries multi-country R&D efforts w paying more attention to labor, freight, taxes, and utility costs w focus on the ability to effectively recruit scientific, engineering, technical, and skilled production talent critical mass of existing local talent access to top universities and programs City of Madison EDC
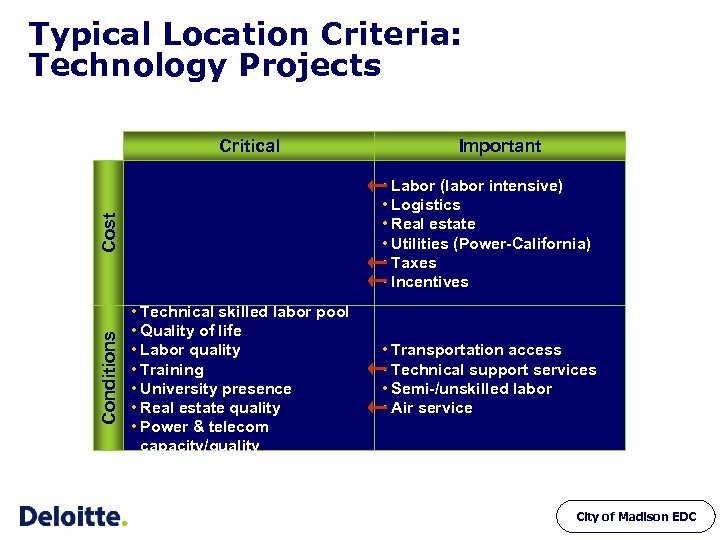 Typical Location Criteria: Technology Projects Critical • Labor (labor intensive) • Logistics • Real estate • Utilities (Power-California) • Taxes • Incentives Cost Conditions Important • Technical skilled labor pool • Quality of life • Labor quality • Training • University presence • Real estate quality • Power & telecom capacity/quality • Transportation access • Technical support services • Semi-/unskilled labor • Air service City of Madison EDC
Typical Location Criteria: Technology Projects Critical • Labor (labor intensive) • Logistics • Real estate • Utilities (Power-California) • Taxes • Incentives Cost Conditions Important • Technical skilled labor pool • Quality of life • Labor quality • Training • University presence • Real estate quality • Power & telecom capacity/quality • Transportation access • Technical support services • Semi-/unskilled labor • Air service City of Madison EDC
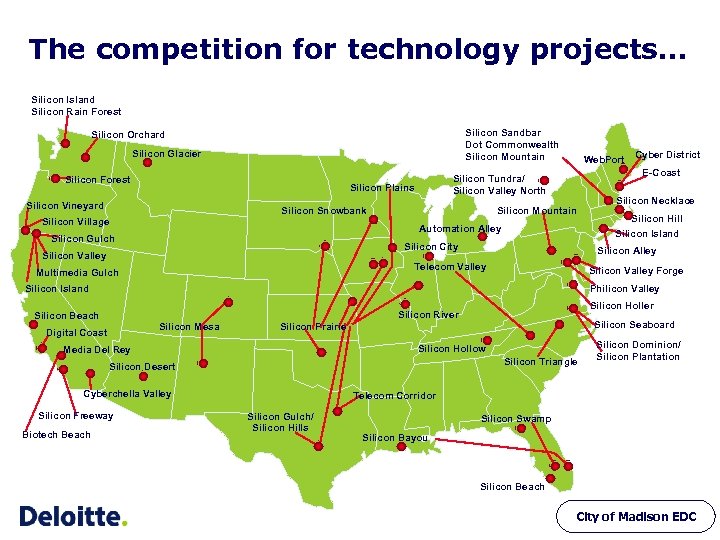 The competition for technology projects… Silicon Island Silicon Rain Forest Silicon Sandbar Dot Commonwealth Silicon Mountain Silicon Orchard Silicon Glacier Silicon Forest Silicon Snowbank Silicon Village Silicon Mountain Automation Alley Silicon Gulch Silicon Valley Forge Silicon Island Philicon Valley Silicon Holler Silicon River Silicon Beach Silicon Mesa Digital Coast Silicon Hollow Silicon Triangle Silicon Desert Cyberchella Valley Silicon Freeway Silicon Seaboard Silicon Prairie Media Del Rey Biotech Beach Silicon Hill Silicon Alley Telecom Valley Multimedia Gulch Silicon Necklace Silicon Island Silicon City Silicon Valley Cyber District E-Coast Silicon Tundra/ Silicon Valley North Silicon Plains Silicon Vineyard Web. Port Silicon Dominion/ Silicon Plantation Telecom Corridor Silicon Gulch/ Silicon Hills Silicon Swamp Silicon Bayou Silicon Beach City of Madison EDC
The competition for technology projects… Silicon Island Silicon Rain Forest Silicon Sandbar Dot Commonwealth Silicon Mountain Silicon Orchard Silicon Glacier Silicon Forest Silicon Snowbank Silicon Village Silicon Mountain Automation Alley Silicon Gulch Silicon Valley Forge Silicon Island Philicon Valley Silicon Holler Silicon River Silicon Beach Silicon Mesa Digital Coast Silicon Hollow Silicon Triangle Silicon Desert Cyberchella Valley Silicon Freeway Silicon Seaboard Silicon Prairie Media Del Rey Biotech Beach Silicon Hill Silicon Alley Telecom Valley Multimedia Gulch Silicon Necklace Silicon Island Silicon City Silicon Valley Cyber District E-Coast Silicon Tundra/ Silicon Valley North Silicon Plains Silicon Vineyard Web. Port Silicon Dominion/ Silicon Plantation Telecom Corridor Silicon Gulch/ Silicon Hills Silicon Swamp Silicon Bayou Silicon Beach City of Madison EDC
 Biotech / Biopharma is Growing… • Sales of biopharmaceuticals grew from $8 billion in 1993 to $22. 3 billion in 2000 – small compared to the pharmaceutical industry: $400 billion (2002) • The future looks bright, with an estimated 371 biotechbased drugs in development. At the end of 2002, approximately 122 biotech-based drugs were in Phase III trials or awaiting approval in the United States. • The top 10 biopharmaceutical companies accounted for 64. 7% of the segment’s global sales in 2002. Of those, six companies had sales of $1 billion or more 2002: Amgen, Genentech, Serono, Chiron, Biogen, and Genzyme Corp. City of Madison EDC
Biotech / Biopharma is Growing… • Sales of biopharmaceuticals grew from $8 billion in 1993 to $22. 3 billion in 2000 – small compared to the pharmaceutical industry: $400 billion (2002) • The future looks bright, with an estimated 371 biotechbased drugs in development. At the end of 2002, approximately 122 biotech-based drugs were in Phase III trials or awaiting approval in the United States. • The top 10 biopharmaceutical companies accounted for 64. 7% of the segment’s global sales in 2002. Of those, six companies had sales of $1 billion or more 2002: Amgen, Genentech, Serono, Chiron, Biogen, and Genzyme Corp. City of Madison EDC
 Competition for Biotech / Biopharma Investment • Clinical development (R&D) locations vs. manufacturing locations • Top cluster locations include: • Boston • San Francisco • San Diego • Long Island – Princeton – Philadelphia corridor • Los Angeles / Thousand Oaks • Washington – Baltimore corridor • Raleigh-Durham • Seattle • International manufacturing candidate locations include: • Singapore • Switzerland • Puerto Rico • Ireland City of Madison EDC
Competition for Biotech / Biopharma Investment • Clinical development (R&D) locations vs. manufacturing locations • Top cluster locations include: • Boston • San Francisco • San Diego • Long Island – Princeton – Philadelphia corridor • Los Angeles / Thousand Oaks • Washington – Baltimore corridor • Raleigh-Durham • Seattle • International manufacturing candidate locations include: • Singapore • Switzerland • Puerto Rico • Ireland City of Madison EDC
 Headquarters examining redeployment at a steady pace issues / trends w corporate and personal tax issues w rationalizing deployment of global vs. national HQ w More willing to consider relocation from “granddad’s” hometown w image w customer/operational access w ease of doing business (regulations) w politics actions / impacts w evaluating joint deployment with existing operations: w shared service w regional HQ w R&D w Taxes and incentives seem to be more compelling to the C-suite than operational issues City of Madison EDC
Headquarters examining redeployment at a steady pace issues / trends w corporate and personal tax issues w rationalizing deployment of global vs. national HQ w More willing to consider relocation from “granddad’s” hometown w image w customer/operational access w ease of doing business (regulations) w politics actions / impacts w evaluating joint deployment with existing operations: w shared service w regional HQ w R&D w Taxes and incentives seem to be more compelling to the C-suite than operational issues City of Madison EDC
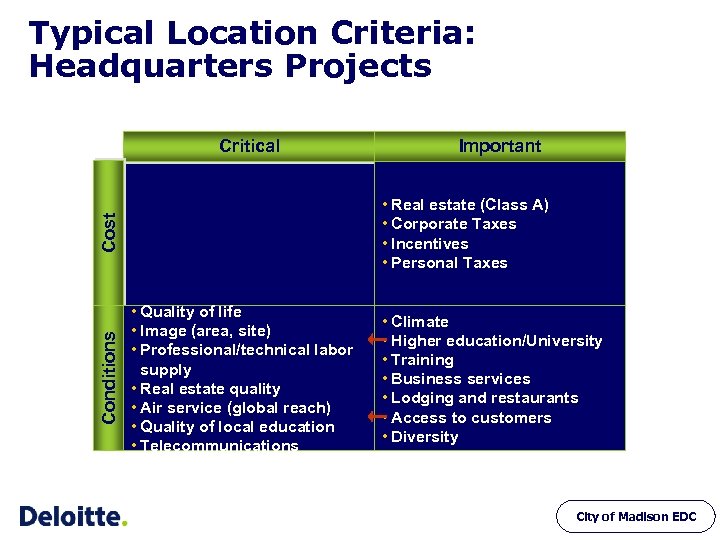 Typical Location Criteria: Headquarters Projects Critical • Real estate (Class A) • Corporate Taxes • Incentives • Personal Taxes Cost Conditions Important • Quality of life • Image (area, site) • Professional/technical labor supply • Real estate quality • Air service (global reach) • Quality of local education • Telecommunications • Climate • Higher education/University • Training • Business services • Lodging and restaurants • Access to customers • Diversity City of Madison EDC
Typical Location Criteria: Headquarters Projects Critical • Real estate (Class A) • Corporate Taxes • Incentives • Personal Taxes Cost Conditions Important • Quality of life • Image (area, site) • Professional/technical labor supply • Real estate quality • Air service (global reach) • Quality of local education • Telecommunications • Climate • Higher education/University • Training • Business services • Lodging and restaurants • Access to customers • Diversity City of Madison EDC
 “Best Practices” in Business Attraction
“Best Practices” in Business Attraction
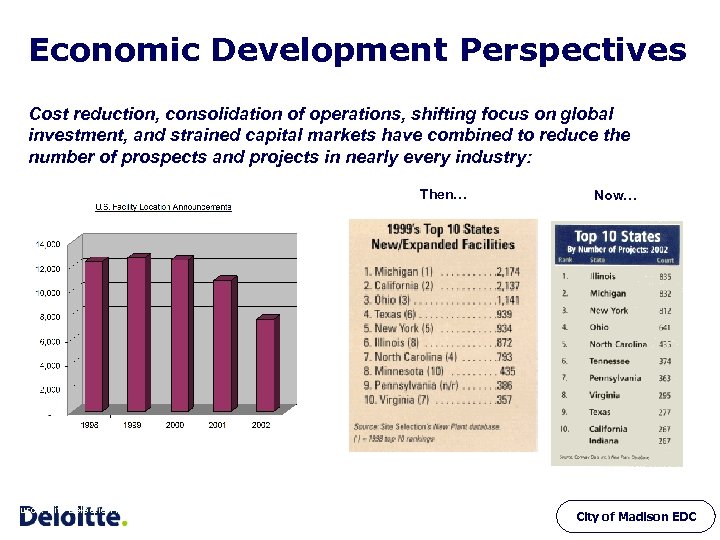 Economic Development Perspectives Cost reduction, consolidation of operations, shifting focus on global investment, and strained capital markets have combined to reduce the number of prospects and projects in nearly every industry: Then… Source: Site Selection Magazine Now… City of Madison EDC
Economic Development Perspectives Cost reduction, consolidation of operations, shifting focus on global investment, and strained capital markets have combined to reduce the number of prospects and projects in nearly every industry: Then… Source: Site Selection Magazine Now… City of Madison EDC
 What are Leading Economic Development Agencies Doing to Stay Competitive? • Understand the “Hooks” that attract business investment • Develop an Economic Development Strategy: Vision – Reality – Mission • Market wisely • Get prepared on all fronts • Data/information, sites, training, incentives, infrastructure • Focus on meaningful targets • Build coalitions to help in the effort • Be organized and industry-knowledgeable City of Madison EDC
What are Leading Economic Development Agencies Doing to Stay Competitive? • Understand the “Hooks” that attract business investment • Develop an Economic Development Strategy: Vision – Reality – Mission • Market wisely • Get prepared on all fronts • Data/information, sites, training, incentives, infrastructure • Focus on meaningful targets • Build coalitions to help in the effort • Be organized and industry-knowledgeable City of Madison EDC
 What are the “Hooks” That Draw Prospects to Communities? • Past successes • Favorable infrastructure / geography • Available real estate • Favorable statistics • Deep / unique labor skills • Low operating costs • Incentives • Strong E. D. strategies • Aggressive marketing • Market access / business synergies City of Madison EDC
What are the “Hooks” That Draw Prospects to Communities? • Past successes • Favorable infrastructure / geography • Available real estate • Favorable statistics • Deep / unique labor skills • Low operating costs • Incentives • Strong E. D. strategies • Aggressive marketing • Market access / business synergies City of Madison EDC
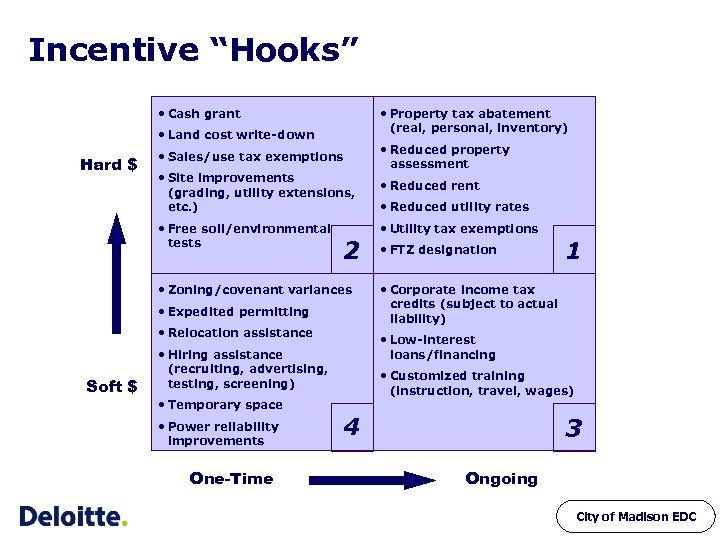 Incentive “Hooks” • Cash grant • Property tax abatement (real, personal, inventory) • Land cost write-down Hard $ • Sales/use tax exemptions • Site improvements (grading, utility extensions, etc. ) • Free soil/environmental tests 2 • Zoning/covenant variances • Expedited permitting • Relocation assistance Soft $ • Power reliability improvements One-Time • Reduced rent • Reduced utility rates • Utility tax exemptions • FTZ designation 1 • Corporate income tax credits (subject to actual liability) • Low-interest loans/financing • Hiring assistance (recruiting, advertising, testing, screening) • Temporary space • Reduced property assessment • Customized training (instruction, travel, wages) 4 3 Ongoing City of Madison EDC
Incentive “Hooks” • Cash grant • Property tax abatement (real, personal, inventory) • Land cost write-down Hard $ • Sales/use tax exemptions • Site improvements (grading, utility extensions, etc. ) • Free soil/environmental tests 2 • Zoning/covenant variances • Expedited permitting • Relocation assistance Soft $ • Power reliability improvements One-Time • Reduced rent • Reduced utility rates • Utility tax exemptions • FTZ designation 1 • Corporate income tax credits (subject to actual liability) • Low-interest loans/financing • Hiring assistance (recruiting, advertising, testing, screening) • Temporary space • Reduced property assessment • Customized training (instruction, travel, wages) 4 3 Ongoing City of Madison EDC
 E. D. Strategy “Hooks” • Targeted industries • Regional cooperation / co-opetition • Leadership • The E. D. strategic plan • Companies have strategic plans; these are tracked by analysts (Wall St. ) • Corporations expect communities to also maintain a strategic plan; these are tracked by people like Deloitte City of Madison EDC
E. D. Strategy “Hooks” • Targeted industries • Regional cooperation / co-opetition • Leadership • The E. D. strategic plan • Companies have strategic plans; these are tracked by analysts (Wall St. ) • Corporations expect communities to also maintain a strategic plan; these are tracked by people like Deloitte City of Madison EDC
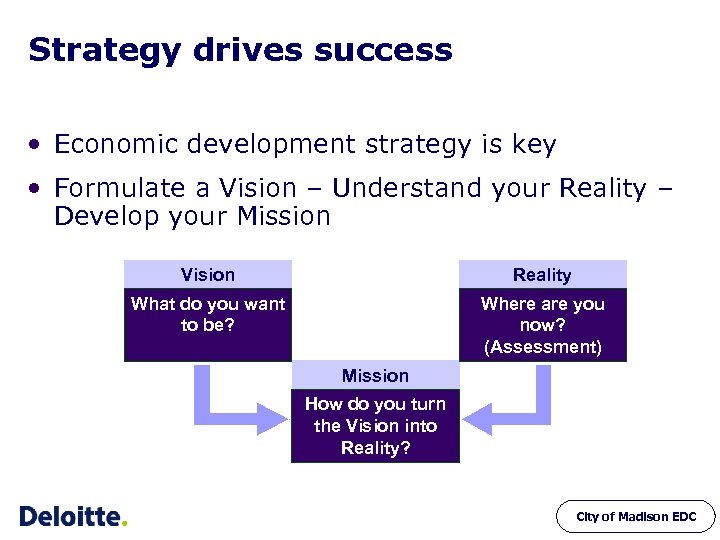 Strategy drives success • Economic development strategy is key • Formulate a Vision – Understand your Reality – Develop your Mission Vision Reality What do you want to be? Where are you now? (Assessment) Mission How do you turn the Vision into Reality? City of Madison EDC
Strategy drives success • Economic development strategy is key • Formulate a Vision – Understand your Reality – Develop your Mission Vision Reality What do you want to be? Where are you now? (Assessment) Mission How do you turn the Vision into Reality? City of Madison EDC
 Our Perspective on Madison’s Competitive Position • Substantial and continued successes in the areas of biotech and other high-technology R&D • Solid track record of incubation and support of entrepreneurial growth (WARF, some venture capital) • Healthy local economic indicators for residents: housing growth, low unemployment, etc. • Well-known as a great place to live and raise a family City of Madison EDC
Our Perspective on Madison’s Competitive Position • Substantial and continued successes in the areas of biotech and other high-technology R&D • Solid track record of incubation and support of entrepreneurial growth (WARF, some venture capital) • Healthy local economic indicators for residents: housing growth, low unemployment, etc. • Well-known as a great place to live and raise a family City of Madison EDC
 Our Perspective on Madison’s Competitive Position But, • Evolution towards service industries and R&D is continuing – functional diversification • Distinct disadvantage in several key indicators and cost metrics: labor availability, labor cost, tax, etc. • The competition regularly out-markets Madison • Not as well-known as a business location, certainly not perceived to be on par with Tier 1 R&D locations • Wisconsin ranked 27 in Milkin Institute’s 2004 State Technology and Science Index, down from 25 in 2002 • Massachusetts and California ranked #1 & 2 City of Madison EDC
Our Perspective on Madison’s Competitive Position But, • Evolution towards service industries and R&D is continuing – functional diversification • Distinct disadvantage in several key indicators and cost metrics: labor availability, labor cost, tax, etc. • The competition regularly out-markets Madison • Not as well-known as a business location, certainly not perceived to be on par with Tier 1 R&D locations • Wisconsin ranked 27 in Milkin Institute’s 2004 State Technology and Science Index, down from 25 in 2002 • Massachusetts and California ranked #1 & 2 City of Madison EDC
 Concluding Thoughts • The challenge is before you • The stakes are high – for all involved • The competition is tremendous • Proactive, not reactive strategies tend to win investment • Play to Madison’s strengths • Corporate retention is key • Address development needs City of Madison EDC
Concluding Thoughts • The challenge is before you • The stakes are high – for all involved • The competition is tremendous • Proactive, not reactive strategies tend to win investment • Play to Madison’s strengths • Corporate retention is key • Address development needs City of Madison EDC
 © 2004 Deloitte Consulting LLP. All rights reserved. A member firm of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu
© 2004 Deloitte Consulting LLP. All rights reserved. A member firm of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu


