fd2407ce137bcf752acb7e09d4505778.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Trends in Banking
Product Innovation • Investment products • Gold / silver coins • Marketing of insurance product • Credit cards and debit cards • Innovative services • Automatic Teller Machines • Facilitate issue of capital market products

Internet Banking • Web site information of banks. • Bank products and services. • Web transactions. • Submission of applications, instructions, account balance queries etc. • Website enabling complete transactions. • Account operations such as transfer of funds, payment of bills, payment for other bank products.

Virtual Banks • Do not have a physical presence in a country however offer their services to customers. • Electronic delivery channels provide banking services. • Internet services of banking products. • Termed as ‘i-banking’.

Features of Internet Banking • Performance beyond physical borders. • Security of banking transactions. • Changing / updating technology frequently. • Additional risk to the banking system. • Changes in risk control measures to cope with technology risk. • Strategic business models to cope with the new entrants.

Regulation of Internet Banking • Legal issues • Jurisdiction of services offered • Security issues • Money transfer • Technology issues • Loopholes in technology and change in technology • Operational issues • Control and supervision of banking operations

Benefits from Internet Banking • Less cost of services when compared to traditional banking practices. • Helps banks to offer several products desired by customers. • Banks can offer their services efficiently. • Large base of customers have shifted to internet usage and hence banks benefit through access of such customer base.
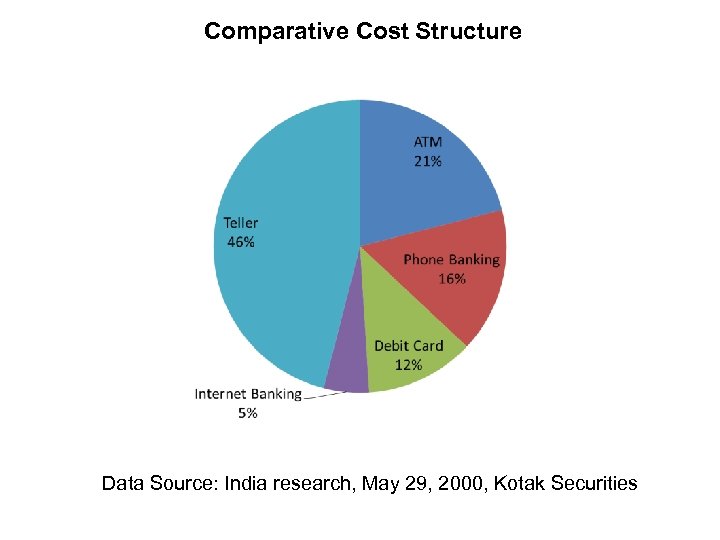
Comparative Cost Structure Data Source: India research, May 29, 2000, Kotak Securities

Illustrative Banks offering Internet based Services in India • ICICI bank • HDFC bank • Axis bank • City bank • Bank of Punjab • Bank of Madura • Federal bank • Allahabad bank • State bank of India
Electronic Fund Transfer • Facilitates one-to-one fund transfer • Customers through the accounts are provided services to transfer funds across banks and branches • Transfer of funds across individual, firm or corporate level account holdings

National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) • Bank branches are NEFT enabled • Reserve Bank of India associates itself with the NEFT enabling of banks • Customers with accounts in the bank branches are allowed to transfer funds through NEFT • Cash restriction on fund transfers is Rs. 50, 000 per transaction • NEFT also enables fund transfer without bank account after required details are furnished by the customers

Operating Details of NEFT • Settlement of funds between receiving and paying banks takes place centrally from Mumbai. • Bank branches participating with NEFT can be located anywhere in the country. • Customer through an application form provides details of the required transfer. • Customer operating through a net banking facility can also initiate the fund transfer through their bank. • Through the Indian Financial System Code (IFSC) the bank branch participant is identified and is used in the transfer of funds.
Benefits of using NEFT • No physical transfer of cheque or demand draft • Possibility of loss of funds in transfer is not there • Transaction cost is less when compared with other payment methods • Service is enabled through internet banking / email / mobile and thus minimizes the effort of the transfer • Real time transfer of funds

Risks Associated with Innovative Banking Services Operational risk • Transactional risk associated with processing transactions, data integration, data confidentiality. of Security risk • Financial transaction movement through unauthorized access. Technology risk • Inappropriate choice of technology, such as file transfer protocol, hyper text transfer protocol, telnet use.

Risks Associated with Innovative Banking Services Reputation risk • Customer confidence management. and bank customer relationship Legal risk • Compliance of legal rules and regulations imposed by the country in which the bank is operating. Fraud • Criminal and fraudulent activities that are encountered in a banking transaction. International Transaction risk • Banker’s inability to track foreign customers resulting in credit risk for the banks.
fd2407ce137bcf752acb7e09d4505778.ppt