0597c65982ea46d402a69057fa83d8da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Treatment of heroin/opiate addiction: current evidence, failure to apply, and areas warranting special attention Professor John Strang National Addiction Centre, London, UK
Treatment of heroin/opiate addiction: current evidence, failure to apply, and areas warranting special attention Professor John Strang National Addiction Centre, London, UK
 declaration • DH, NTA, Home Office, NACD, WHO, UNODC • Diamo, Reckitt-Benkiser, Schering-Plough, Genus-Britannia, GW, Napp, Titan, Martindale, Catalent, Viro. Pharma-Auralis, Lundbeck, Astra. Zeneca • Phoenix House, Clouds House, Lifeline, Kent Council on Addictions, Action on Addiction, Society for the Study of Addiction
declaration • DH, NTA, Home Office, NACD, WHO, UNODC • Diamo, Reckitt-Benkiser, Schering-Plough, Genus-Britannia, GW, Napp, Titan, Martindale, Catalent, Viro. Pharma-Auralis, Lundbeck, Astra. Zeneca • Phoenix House, Clouds House, Lifeline, Kent Council on Addictions, Action on Addiction, Society for the Study of Addiction
 • major scientific reviews of evidence about methadone maintenance and buprenorphine maintenance (NICE; Cochrane); • NICE review of naltrexone maintenance; • NICE review of psychosocial aspects of opiate addiction treatment; • three recent/current research areas, being – * take-home emergency naloxone; – * major reduction of methadone deaths – * substantial benefits seen in the RIOTT trial
• major scientific reviews of evidence about methadone maintenance and buprenorphine maintenance (NICE; Cochrane); • NICE review of naltrexone maintenance; • NICE review of psychosocial aspects of opiate addiction treatment; • three recent/current research areas, being – * take-home emergency naloxone; – * major reduction of methadone deaths – * substantial benefits seen in the RIOTT trial
 Key references • Babor et al, (2010). Drug Policy and the Public Good. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010. • Connock M et al, (2007). Methadone and buprenorphine: systematic review. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (9). • Adi Y et al, (2007). Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (6). • FEAD website– critique of UK drug treatment provision – on website www. fead. org. uk – interview number 10 at http: //www. fead. org. uk/video 289/John-Strang-critiques-thequality-of-drug-service-provision-and-oral-methadone-prescribing. html • NICE (2007) Psychosocial aspects of treatment of drug misuse (CG 51). • Strang et al (2006). Take-home naloxone to prevent heroin overdose deaths. BMJ, 333; 614 -615. • Strang et al (2010). Methadone, supervision and deaths: OD 4 analyses. BMJ, 341; c 4851. • Strang et al (2010) RIOTT main outcome results. Lancet, 375; 1885 -1895.
Key references • Babor et al, (2010). Drug Policy and the Public Good. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010. • Connock M et al, (2007). Methadone and buprenorphine: systematic review. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (9). • Adi Y et al, (2007). Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (6). • FEAD website– critique of UK drug treatment provision – on website www. fead. org. uk – interview number 10 at http: //www. fead. org. uk/video 289/John-Strang-critiques-thequality-of-drug-service-provision-and-oral-methadone-prescribing. html • NICE (2007) Psychosocial aspects of treatment of drug misuse (CG 51). • Strang et al (2006). Take-home naloxone to prevent heroin overdose deaths. BMJ, 333; 614 -615. • Strang et al (2010). Methadone, supervision and deaths: OD 4 analyses. BMJ, 341; c 4851. • Strang et al (2010) RIOTT main outcome results. Lancet, 375; 1885 -1895.
 MMT + BMT
MMT + BMT
 Structured oral methadone maintenance programmes • • It’s in the title Maintenance Dose – medication Dose – psychosocial component Context – staff attitudes Coercion (soft); reinforcers/rewards Methadone; buprenorphine; LAAM; SROM; … Recovery-Orientated Methadone Maintenance
Structured oral methadone maintenance programmes • • It’s in the title Maintenance Dose – medication Dose – psychosocial component Context – staff attitudes Coercion (soft); reinforcers/rewards Methadone; buprenorphine; LAAM; SROM; … Recovery-Orientated Methadone Maintenance

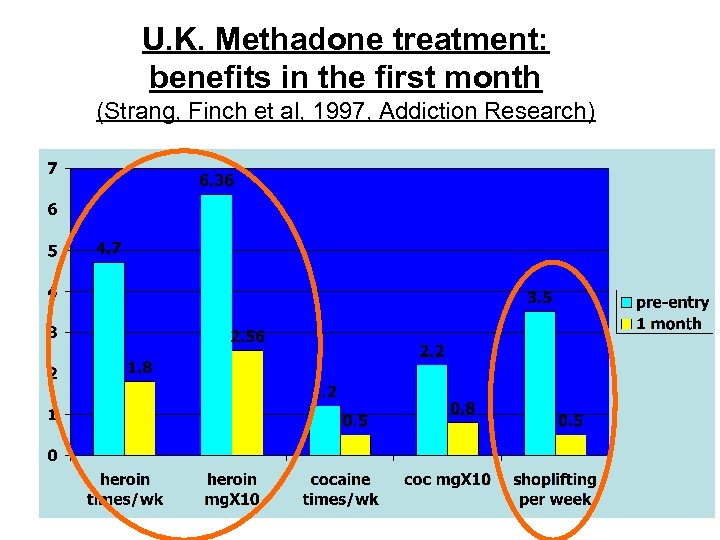 U. K. Methadone treatment: benefits in the first month (Strang, Finch et al, 1997, Addiction Research)
U. K. Methadone treatment: benefits in the first month (Strang, Finch et al, 1997, Addiction Research)
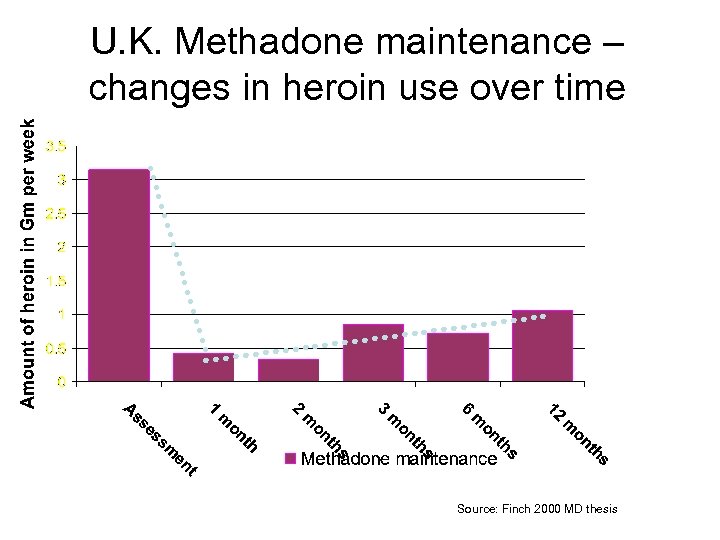 U. K. Methadone maintenance – changes in heroin use over time Source: Finch 2000 MD thesis
U. K. Methadone maintenance – changes in heroin use over time Source: Finch 2000 MD thesis
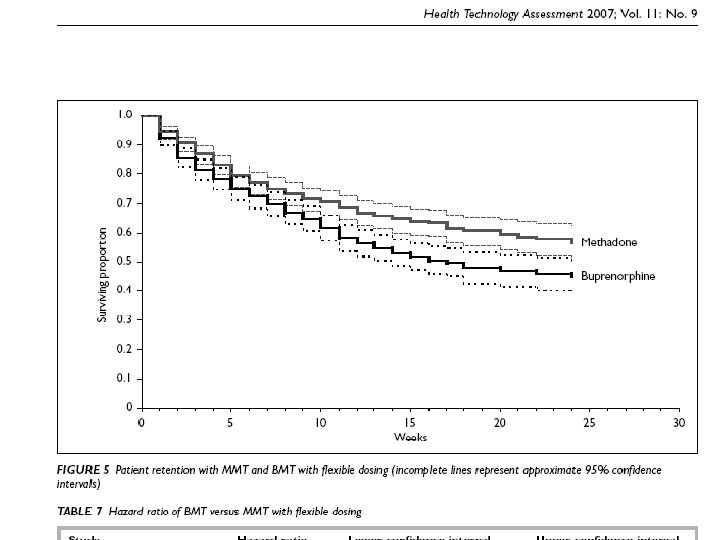
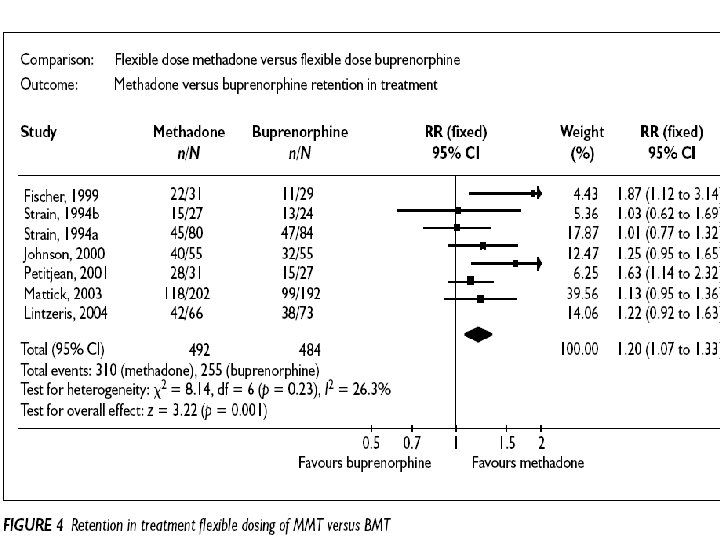
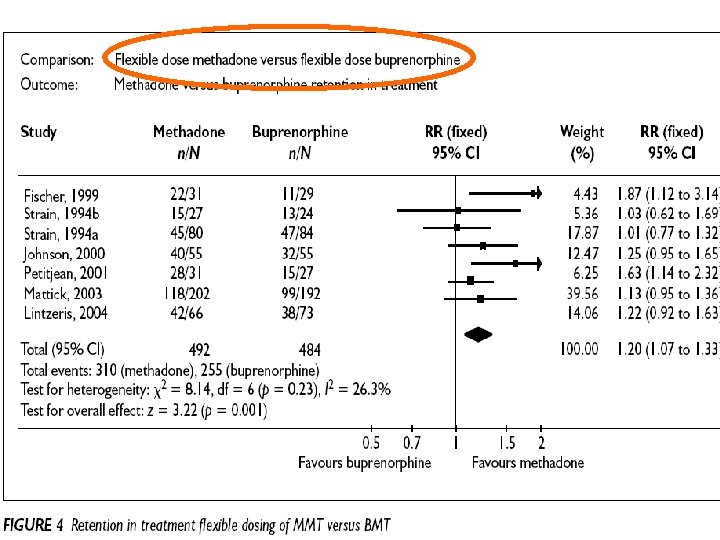
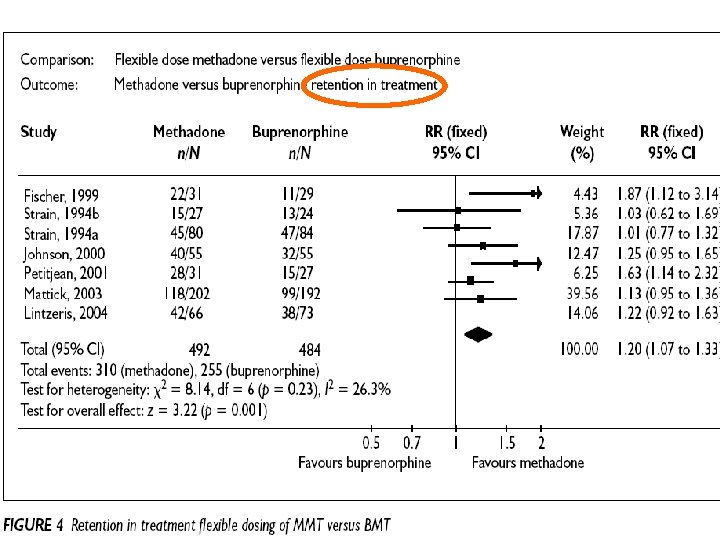
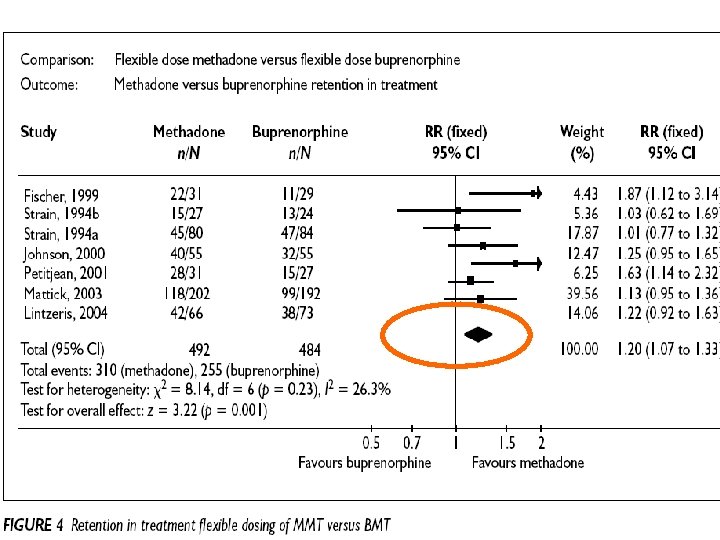
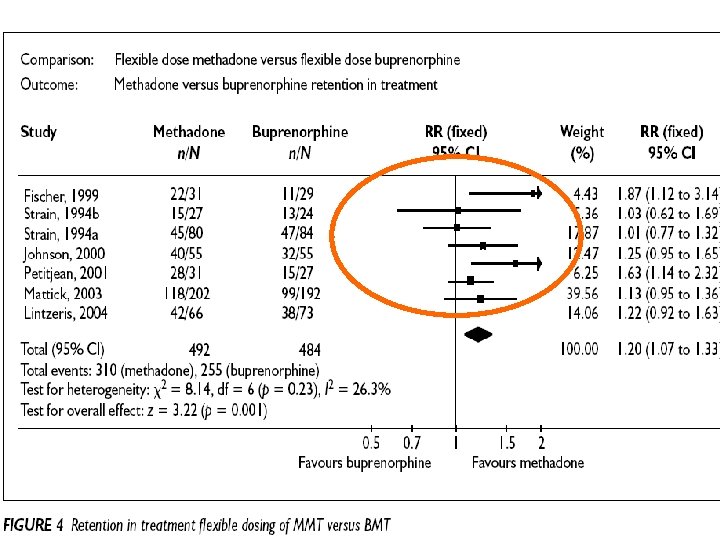
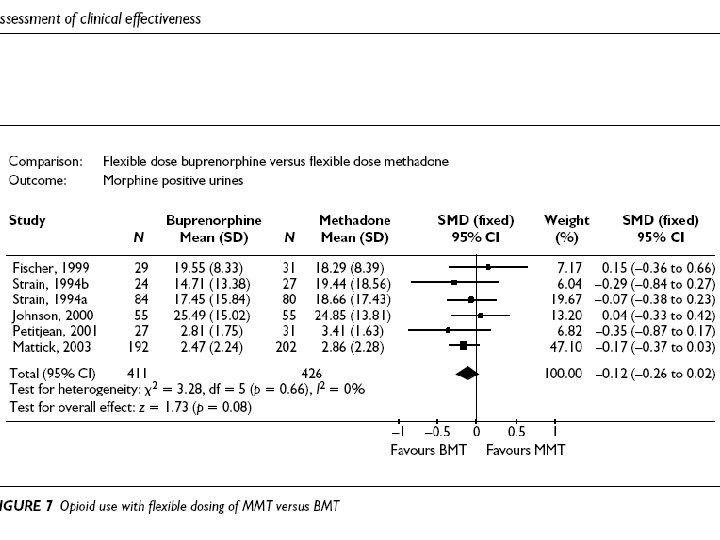
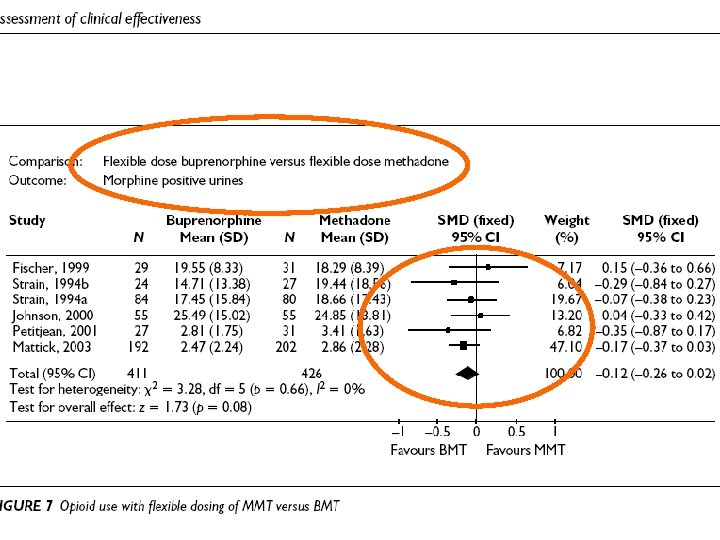
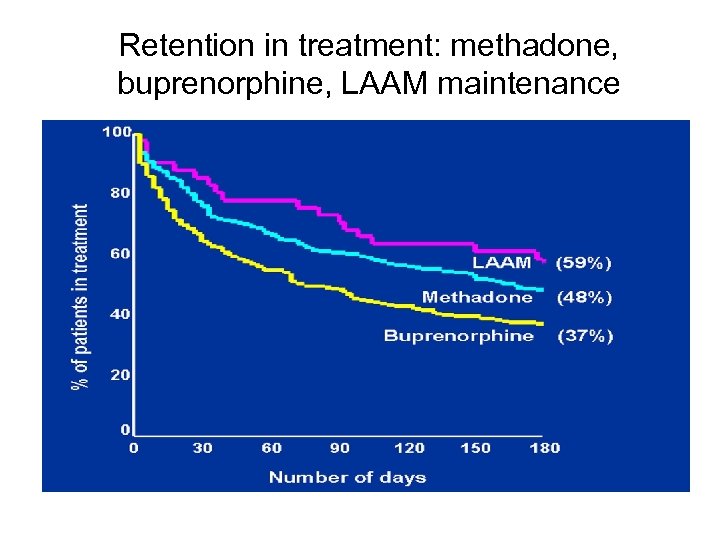 Retention in treatment: methadone, buprenorphine, LAAM maintenance
Retention in treatment: methadone, buprenorphine, LAAM maintenance
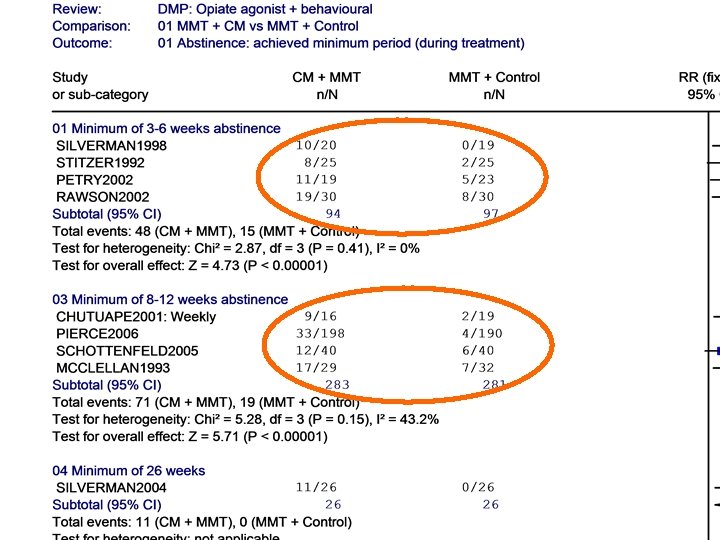
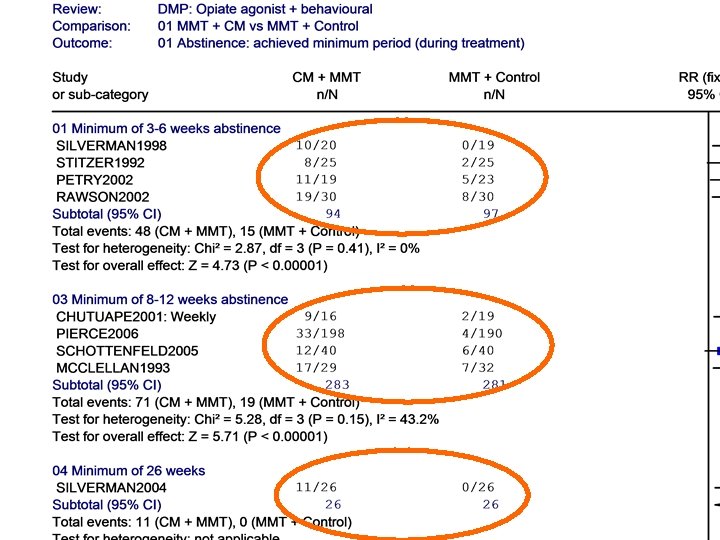
 MMT + CM
MMT + CM
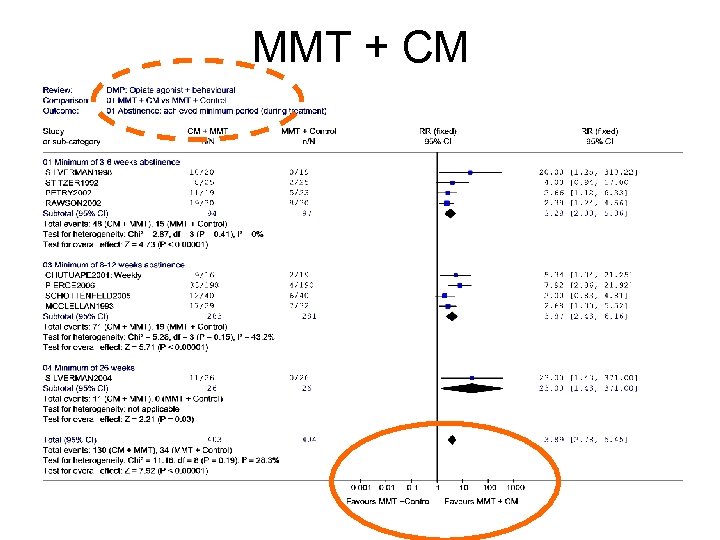 MMT + CM
MMT + CM
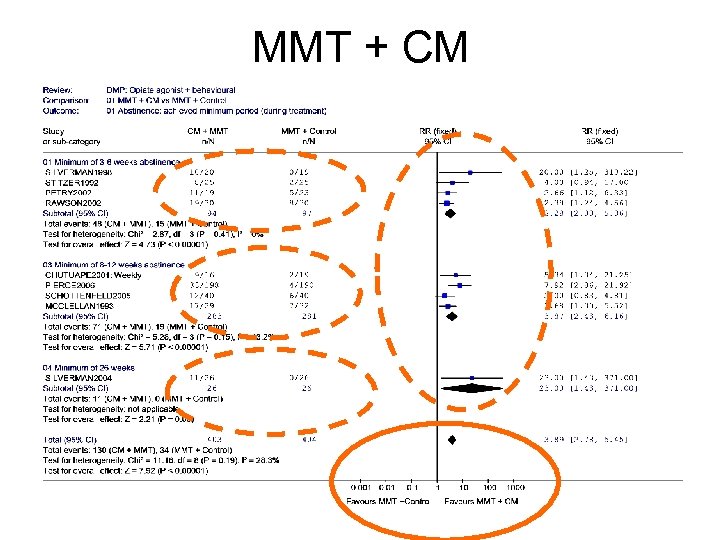 MMT + CM
MMT + CM
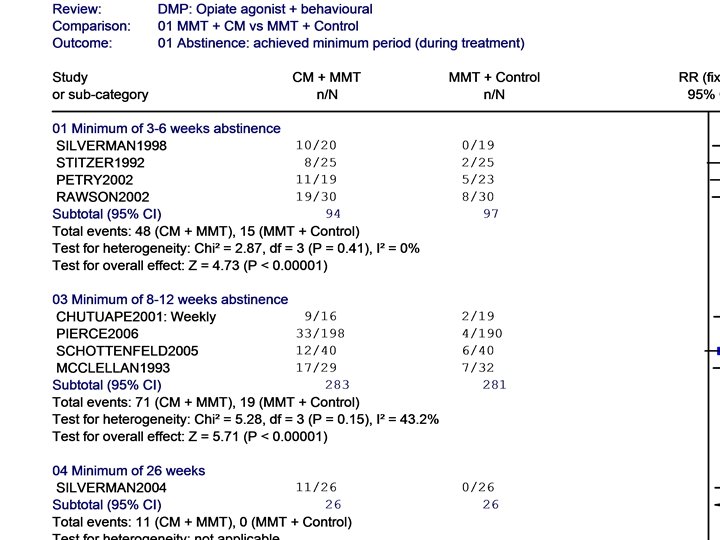
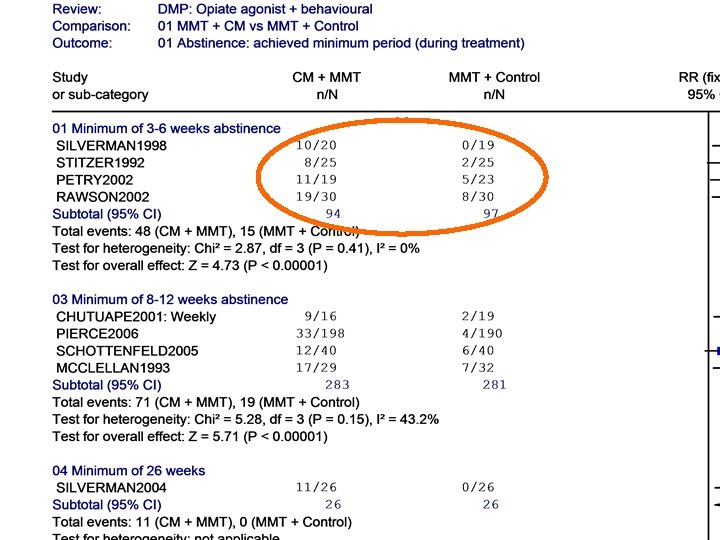
 Naltrexone
Naltrexone
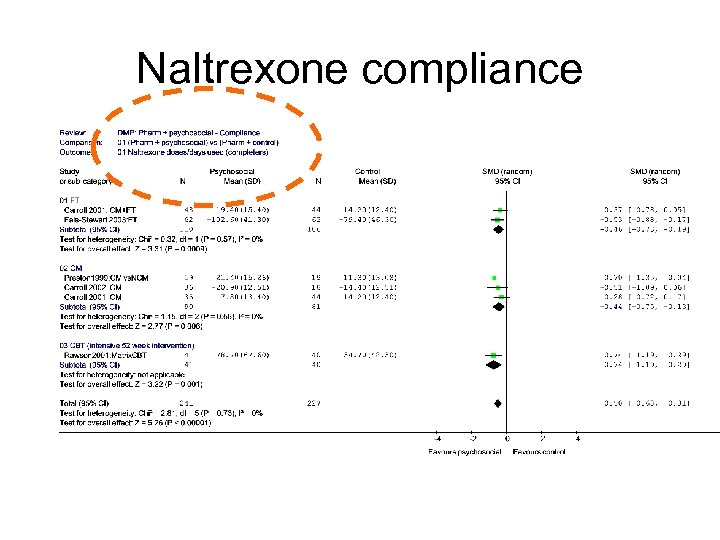 Naltrexone compliance
Naltrexone compliance
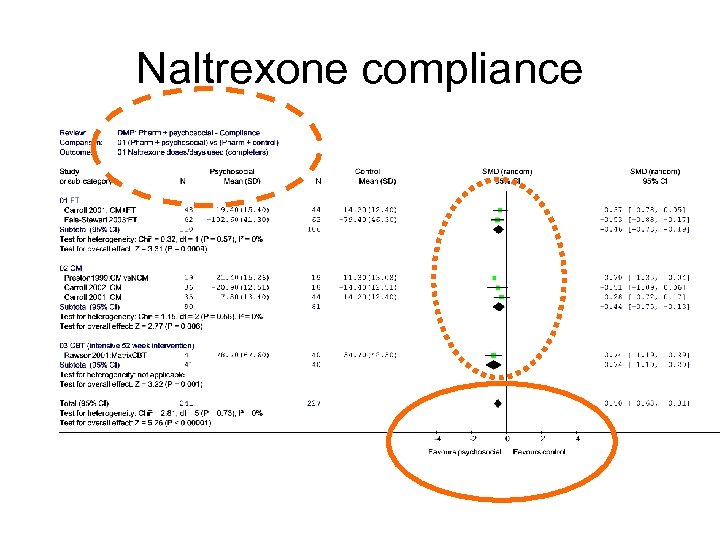 Naltrexone compliance
Naltrexone compliance
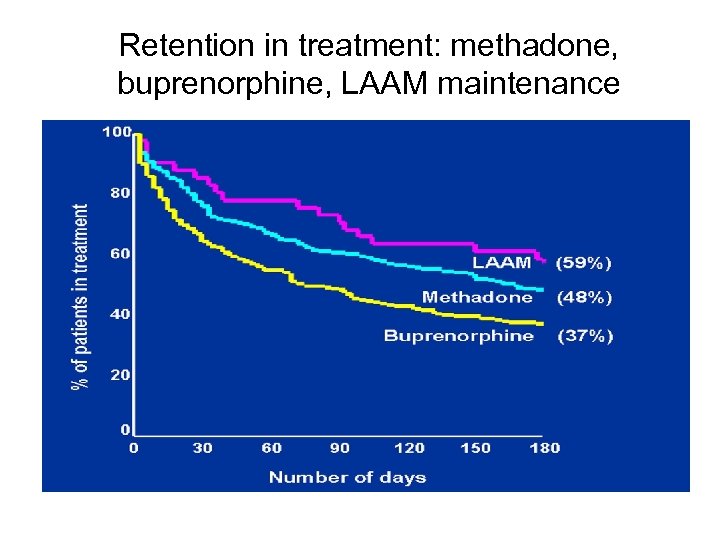 Retention in treatment: methadone, buprenorphine, LAAM maintenance
Retention in treatment: methadone, buprenorphine, LAAM maintenance
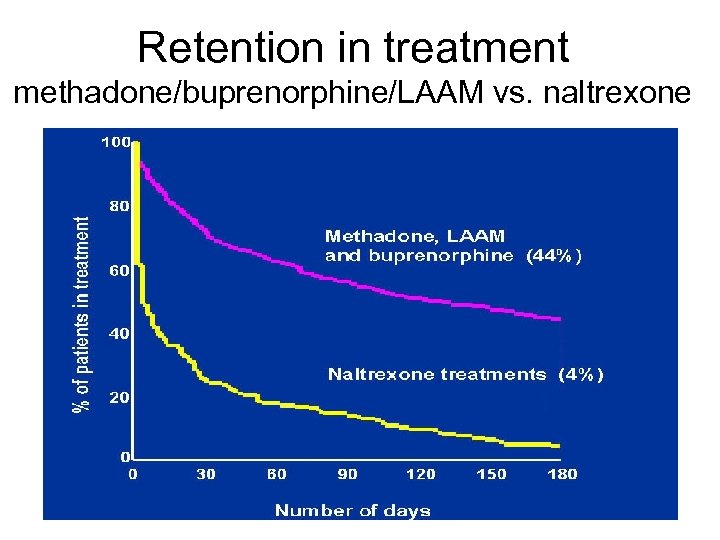 Retention in treatment methadone/buprenorphine/LAAM vs. naltrexone
Retention in treatment methadone/buprenorphine/LAAM vs. naltrexone
 Supervised methadone: a story of successful change
Supervised methadone: a story of successful change
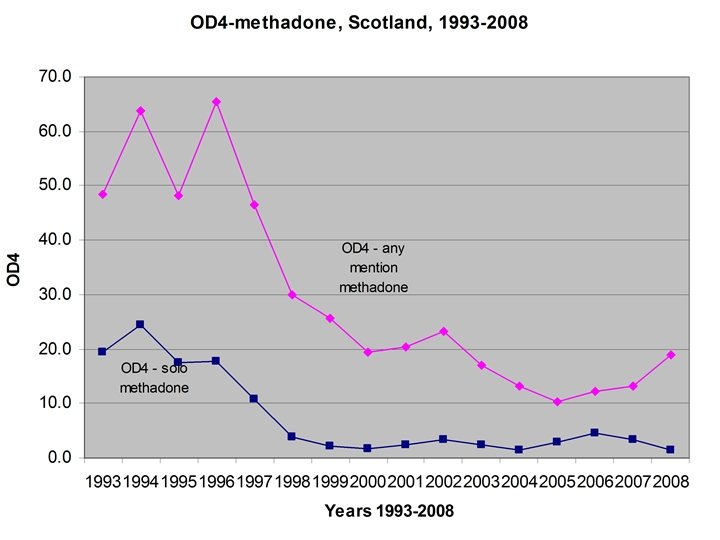
 OD 4 • Defined Daily Doses • Overdose Deaths per (million) Defined Daily Doses (OD 4)
OD 4 • Defined Daily Doses • Overdose Deaths per (million) Defined Daily Doses (OD 4)
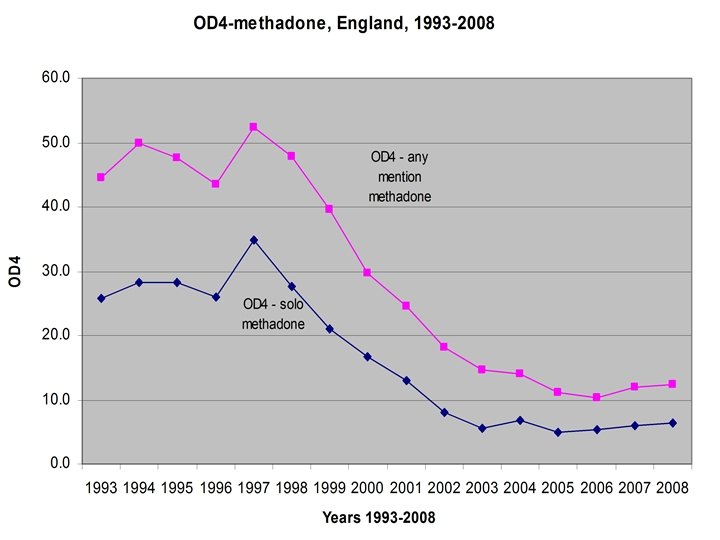
 RIOTT trial of supervised heroin maintenance
RIOTT trial of supervised heroin maintenance

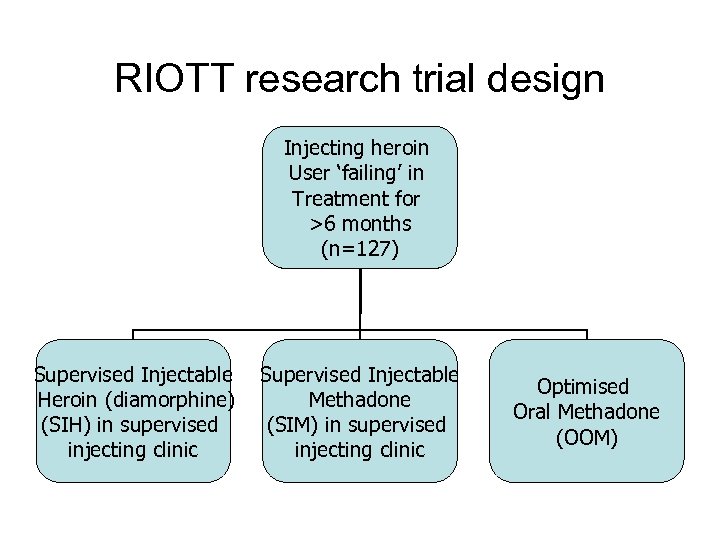 RIOTT research trial design Injecting heroin User ‘failing’ in Treatment for >6 months (n=127) Supervised Injectable Heroin (diamorphine) (SIH) in supervised injecting clinic Supervised Injectable Methadone (SIM) in supervised injecting clinic Optimised Oral Methadone (OOM)
RIOTT research trial design Injecting heroin User ‘failing’ in Treatment for >6 months (n=127) Supervised Injectable Heroin (diamorphine) (SIH) in supervised injecting clinic Supervised Injectable Methadone (SIM) in supervised injecting clinic Optimised Oral Methadone (OOM)
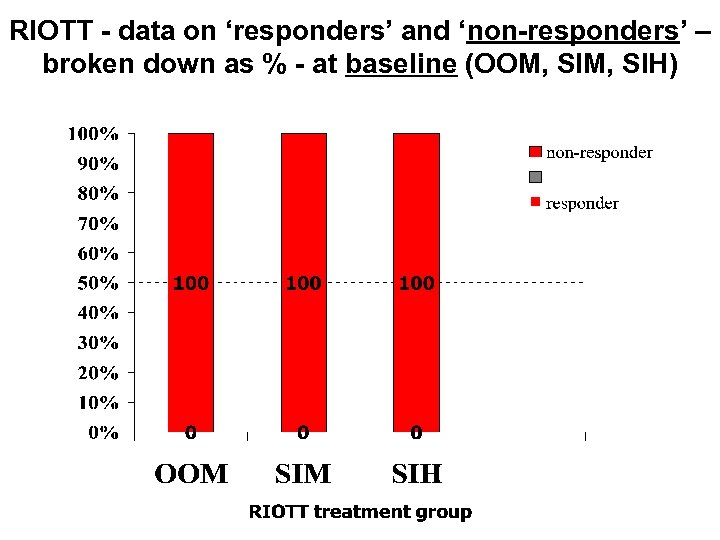 RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at baseline (OOM, SIH)
RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at baseline (OOM, SIH)
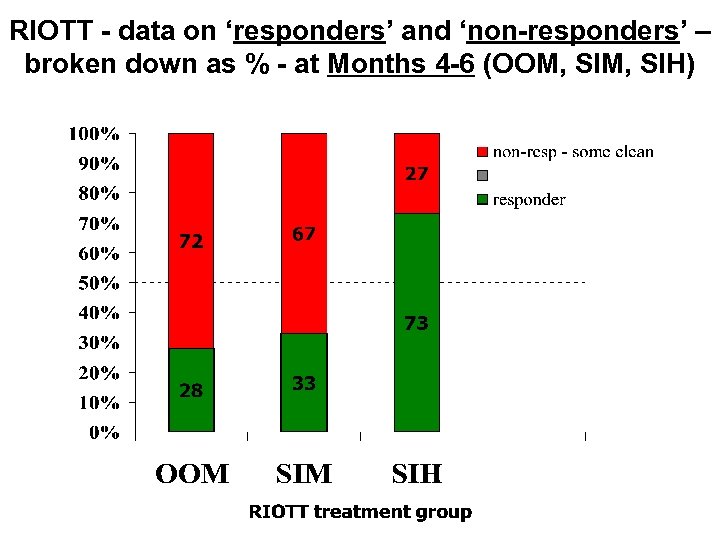 RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
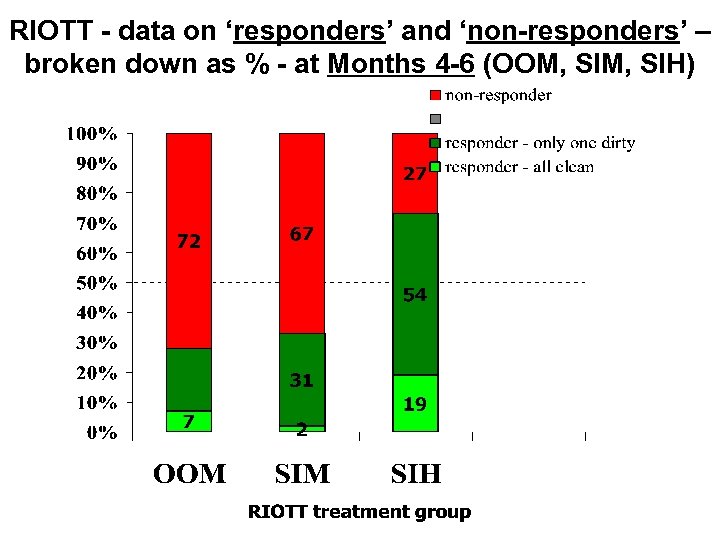 RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
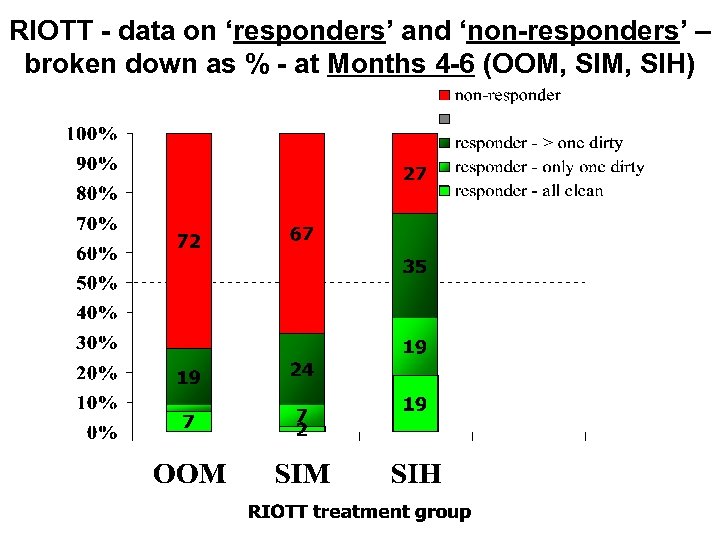 RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
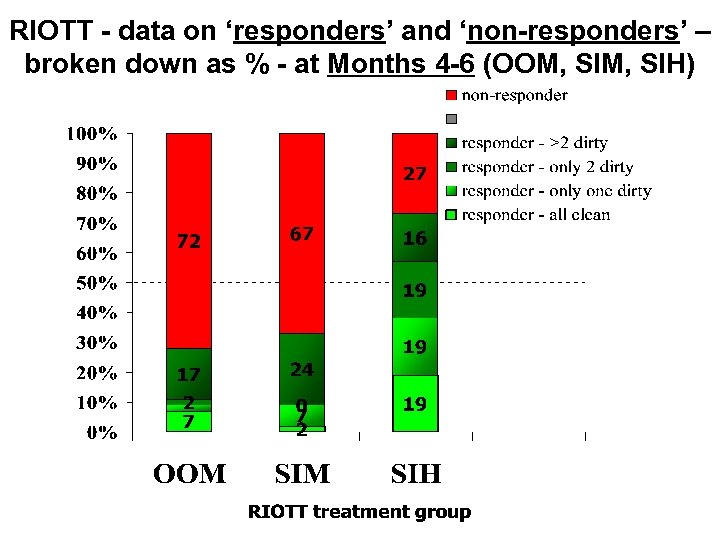 RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
RIOTT - data on ‘responders’ and ‘non-responders’ – broken down as % - at Months 4 -6 (OOM, SIH)
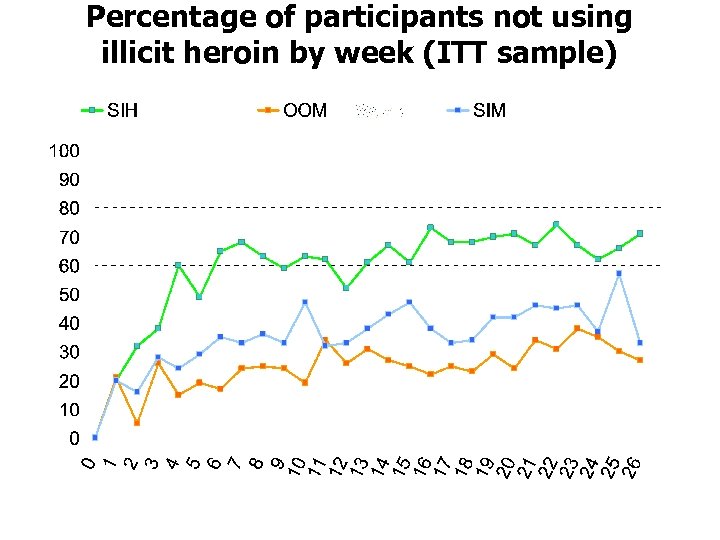 Percentage of participants not using illicit heroin by week (ITT sample)
Percentage of participants not using illicit heroin by week (ITT sample)
 Take-home naloxone
Take-home naloxone
 Drug-related deaths in England Wales 1997 – 2002 (ONS) Drug Prevalence in No. of deaths in general population the last 5 years (use in last year, age 16 -59) Cannabis 10. 8% 78 Cocaine 2. 4% 508 Amphetamine 1. 5% 436 Ecstasy 2% 200 Opiates (inc heroin & methadone) 0. 2% 6, 194
Drug-related deaths in England Wales 1997 – 2002 (ONS) Drug Prevalence in No. of deaths in general population the last 5 years (use in last year, age 16 -59) Cannabis 10. 8% 78 Cocaine 2. 4% 508 Amphetamine 1. 5% 436 Ecstasy 2% 200 Opiates (inc heroin & methadone) 0. 2% 6, 194
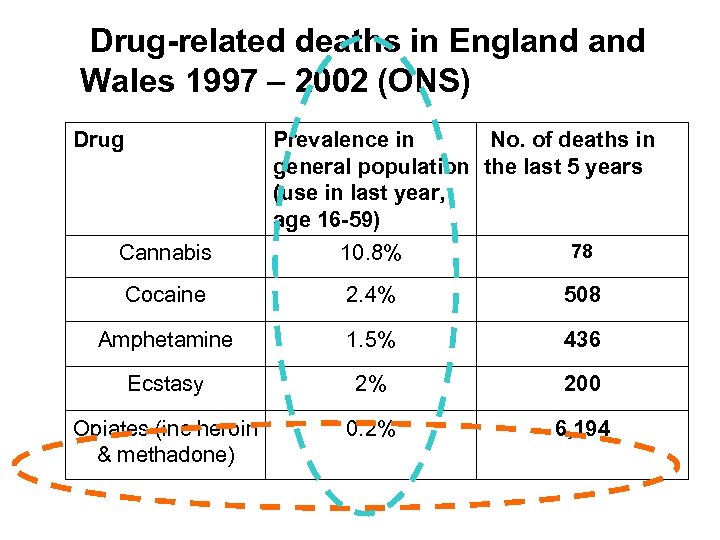 Drug-related deaths in England Wales 1997 – 2002 (ONS) Drug Prevalence in No. of deaths in general population the last 5 years (use in last year, age 16 -59) Cannabis 10. 8% 78 Cocaine 2. 4% 508 Amphetamine 1. 5% 436 Ecstasy 2% 200 Opiates (inc heroin & methadone) 0. 2% 6, 194
Drug-related deaths in England Wales 1997 – 2002 (ONS) Drug Prevalence in No. of deaths in general population the last 5 years (use in last year, age 16 -59) Cannabis 10. 8% 78 Cocaine 2. 4% 508 Amphetamine 1. 5% 436 Ecstasy 2% 200 Opiates (inc heroin & methadone) 0. 2% 6, 194

 Key references • Babor et al, (2010). Drug Policy and the Public Good. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010. • Connock M et al, (2007). Methadone and buprenorphine: systematic review. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (9). • Adi Y et al, (2007). Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (6). • FEAD website– critique of UK drug treatment provision – on website www. fead. org. uk – interview number 10 at http: //www. fead. org. uk/video 289/John-Strang-critiques-thequality-of-drug-service-provision-and-oral-methadone-prescribing. html • NICE (2007) Psychosocial aspects of treatment of drug misuse (CG 51). • Strang et al (2006). Take-home naloxone to prevent heroin overdose deaths. BMJ, 333; 614 -615. • Strang et al (2010). Methadone, supervision and deaths: OD 4 analyses. BMJ 341; c 4851. • Strang et al (2010) RIOTT main outcome results. Lancet, 375; 1885 -1895.
Key references • Babor et al, (2010). Drug Policy and the Public Good. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010. • Connock M et al, (2007). Methadone and buprenorphine: systematic review. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (9). • Adi Y et al, (2007). Oral naltrexone as a treatment for relapse prevention in formerly opioid-dependent drug users: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technology Assessment, 11 (6). • FEAD website– critique of UK drug treatment provision – on website www. fead. org. uk – interview number 10 at http: //www. fead. org. uk/video 289/John-Strang-critiques-thequality-of-drug-service-provision-and-oral-methadone-prescribing. html • NICE (2007) Psychosocial aspects of treatment of drug misuse (CG 51). • Strang et al (2006). Take-home naloxone to prevent heroin overdose deaths. BMJ, 333; 614 -615. • Strang et al (2010). Methadone, supervision and deaths: OD 4 analyses. BMJ 341; c 4851. • Strang et al (2010) RIOTT main outcome results. Lancet, 375; 1885 -1895.


