dd7237ab01e90a3409899c1bac0401ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Treatment Modalities Ayda G. Nambayan, RN, DSN International Outreach Program St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital Memphis, TN
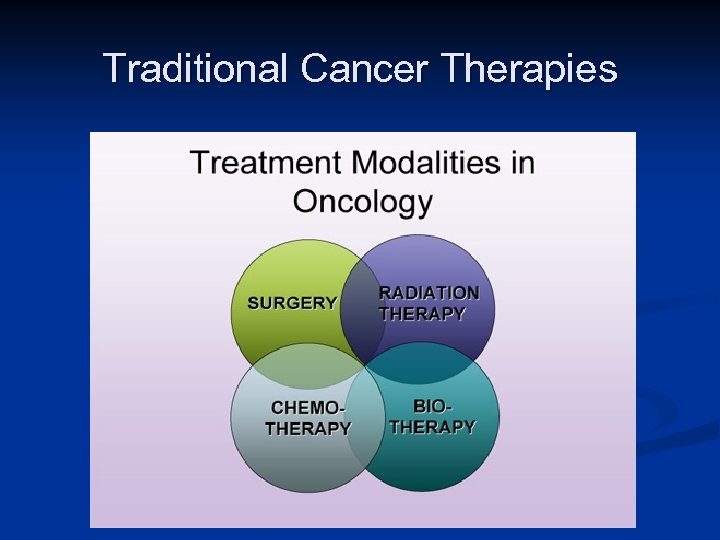
Traditional Cancer Therapies

Novel Cancer Therapy Evolves n n n n n Surgery -- less invasive Radiation – more focused and intense Chemotherapy – still the mainstay Hormone therapy – as adjuvant/maintenance Bone marrow/stem cell transplantation Biologic/Immunologic therapy - promising Molecularly targeted therapy Gene therapy – experimental stage Supportive Therapy Complementary and Alternative Therapies

Chemotherapy Science is Rapidly Unfolding n Chemotherapy still mainstay of treatment n n Metastatic Elderly Adjuvant Novel therapies hold promise n n n Novel combinations Different settings Hope for breast, colorectal, pancreatic cancer - EGFR survival outcomes for patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer 1 n Development of chemoprevention strategies Kim ES, Astra-Zeneca

Chemotherapy – What’s new n Combination modality n n Dosing schema n n Agents that are complementary Inclusion of protective agents Critical timing of administration Dose dense Dose intensification Dose escalation Individualized dosing n n Drug pharmacokinetics Pharmacogenomics


Surgery – What’s New n Cryosurgery – freezing the cells n n Reconstructive Surgery n n n Prostate Breast Head and Neck/ dental Less Invasive/ tissue sparing n n n Percutaneous procedures Stereotactic methods Use of biomedically engineered devices n n Repiphysis for limb sparing Reconstruction/prosthetic surgeries
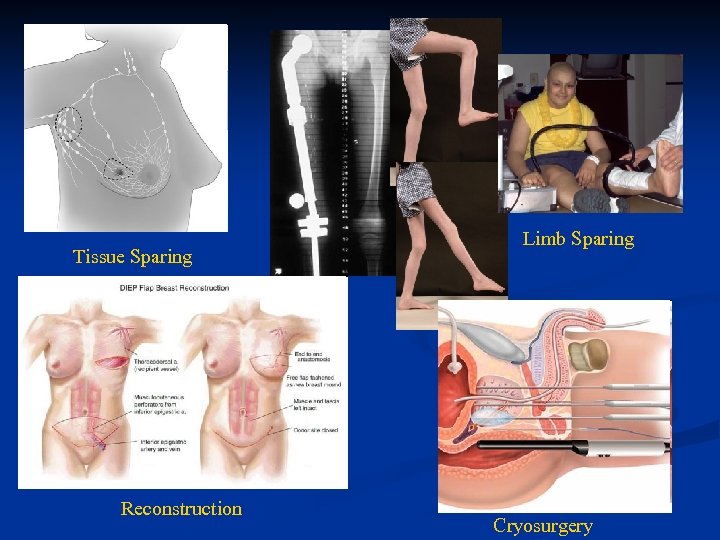
Tissue Sparing Reconstruction Limb Sparing Cryosurgery

Radiation Therapy – What’s New n More focused n n Prevention of immediate and late SE’s n n n Brachytherapy/ implanted Stereotactic Radioimmunotherapy – target RT Protection of RT-sensitive tissues Protective medications Normal tissue sparing n n IMRT Conformal

Radiation Therapy - types n External n n n n Total Body Irradiation Radioimmunotherapy n n n Conformal RT Intensity Modulated RT Image Guided RT Stereotactic RT Palliative Zevalin (Ibritumomab tiuxetan; anti-CD 20 + Yttrium-90) Bexxar (Tositumomab Iodine-131; anti-CD 20 + Iodine 131) Internal n n Brachytherapy Implanted Targeted Radioisotope Therapy (RIT)
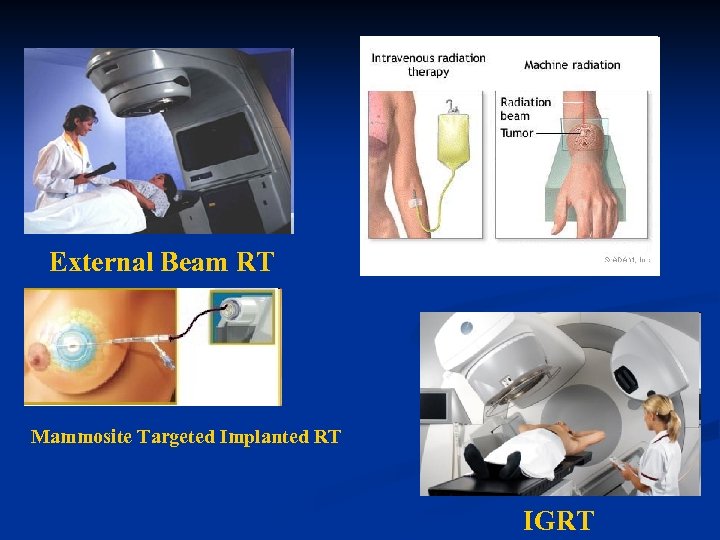
External Beam RT Mammosite Targeted Implanted RT IGRT
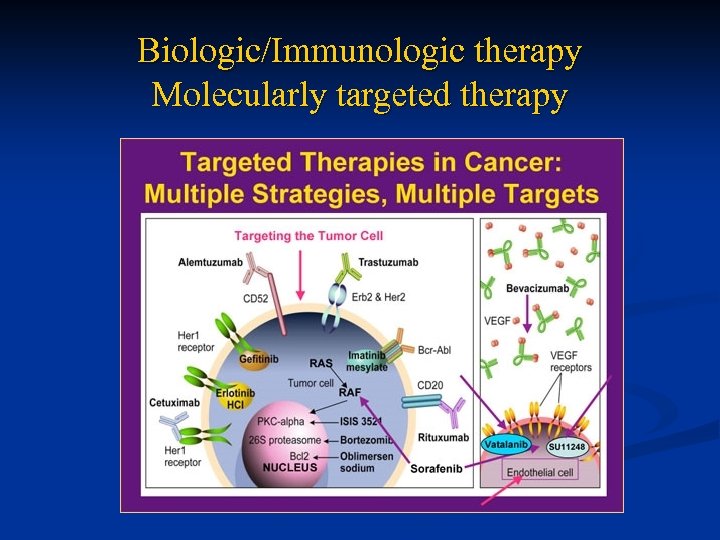
Biologic/Immunologic therapy Molecularly targeted therapy

Target Therapy n Targeting specific antigens (Biologic/Immunotx) n n Targeting mutation-activated kinases (Molecular) n n HER 2, CD 20, CTLA-4 KIT, PDGF-R, BCR-ABL, EGF-R Targeting specific pathways n n Angiogenesis inhibition via VEGF-receptors Cp. G immunosyimulation through TLR-9
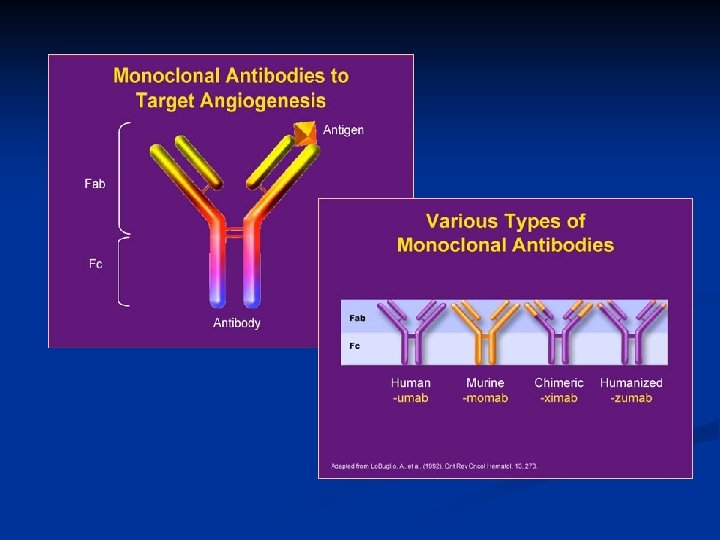
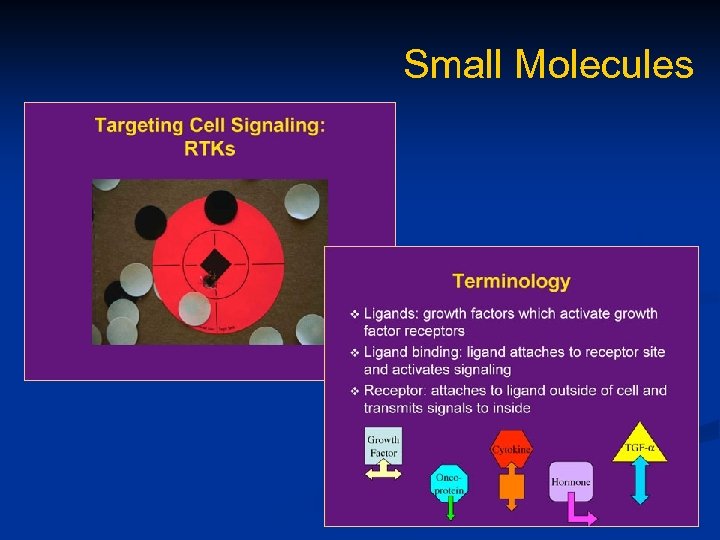
Small Molecules
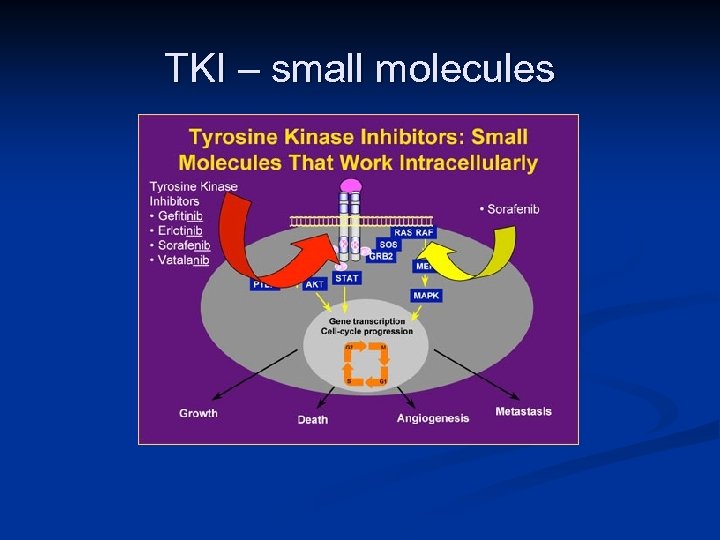
TKI – small molecules
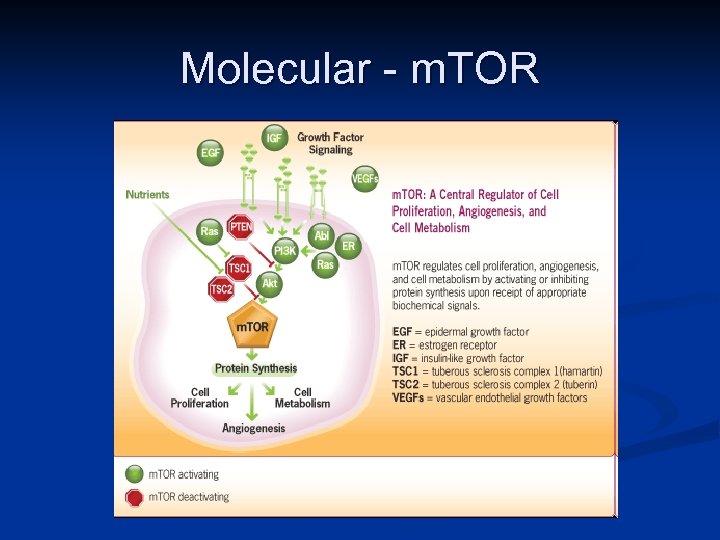
Molecular - m. TOR
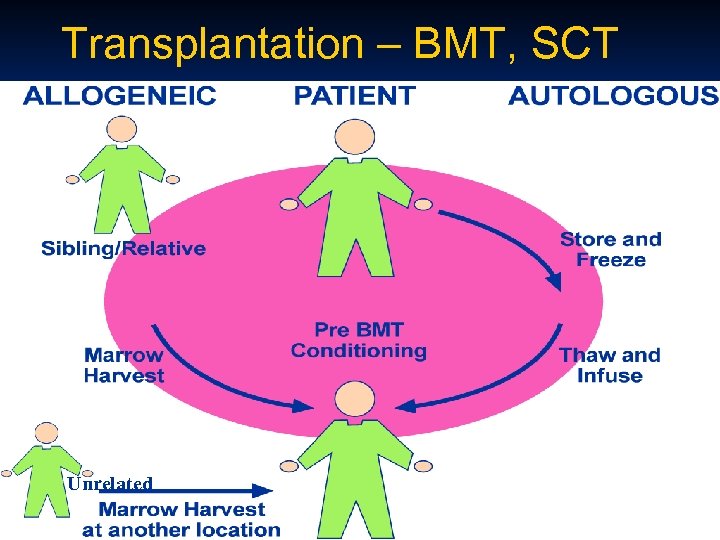
Transplantation – BMT, SCT Unrelated
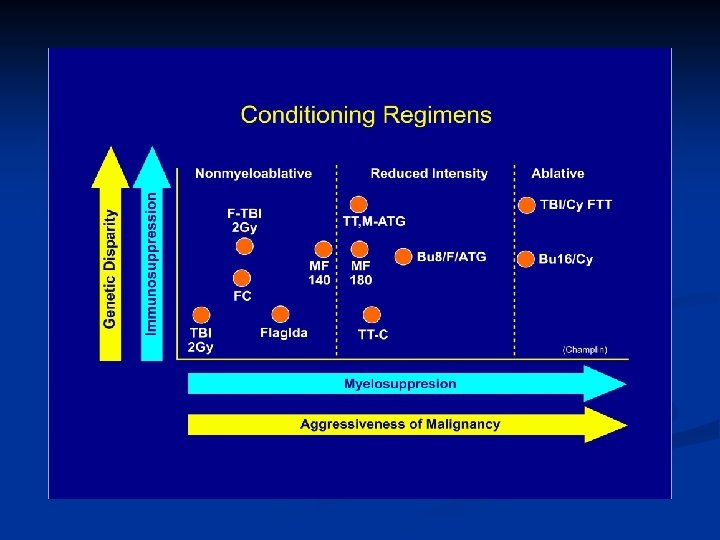
Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Transplantation n Conditioning Regimen n n Donor Sources n n n Cord Blood Mismatch family member (Haploidentical transplantation) Use of specialized machines to decrease side-effects n n Less toxicity Clinimac separator machine Newer drugs to combat Gv. HD
Clini. MACS Selection System
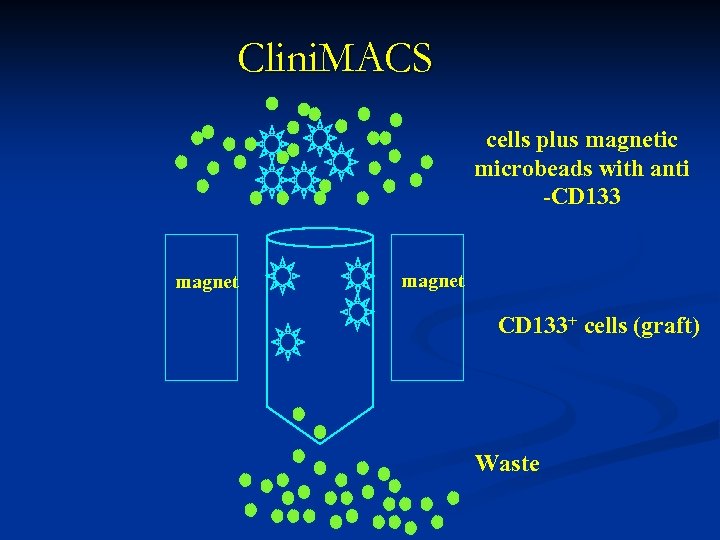
Clini. MACS cells plus magnetic microbeads with anti -CD 133 magnet CD 133+ cells (graft) Waste
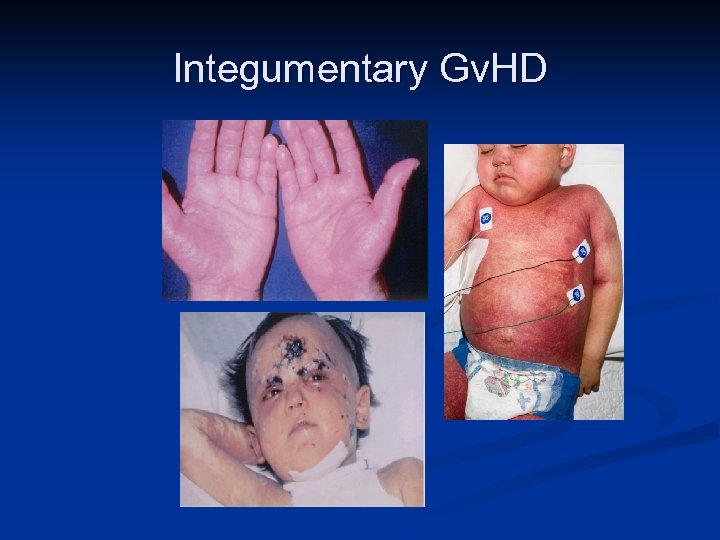
Integumentary Gv. HD

Hormonal Therapies n Steroids – Dexamethasone, Prednisone n Estrogen Receptor blockers – Breast cancers n n n Tamoxifen (Nolvadex) Aromatase Inhibitors (Aromasin, Femara, Arimidex) Anti-androgen drugs - Prostate cancer n n n Flutamide (Eulexin; Flutamin) Bicalutamide (Casodex, Cosudex, Calutide, Kalumid) Nilutamide (Nilandron; Anandron)

Gene Therapies Types n Replacement - healthy variant of an otherwise mutated gene is re-introduced into the cell, thereby repairing the function of the mutated gene and reverting the phenotype n Suicide - the delivery of a cytotoxic gene into the cancer cells, which upon activation, results in the production of a toxic component causing cell death
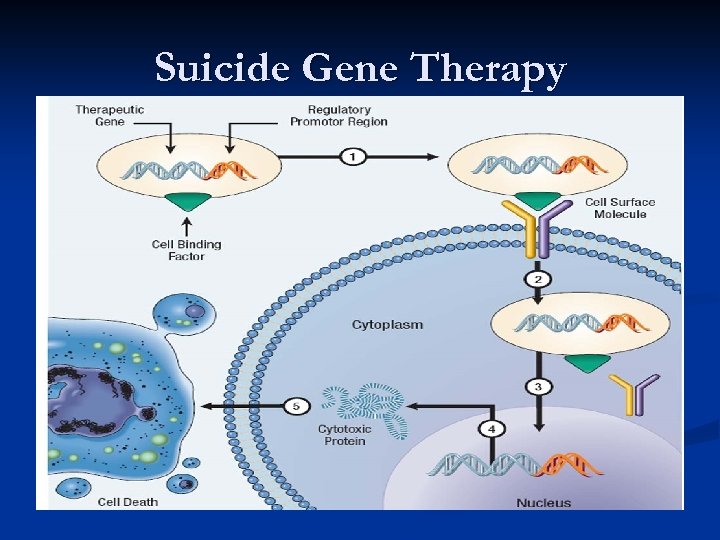
Suicide Gene Therapy

Supportive Therapies Important dimension of cancer therapy n Treatment modalities prevents, alleviate disease and treatment – related effects n Proven to an effective ally in decreasing morbidity and mortality from cancer therapies n Improves patient’s quality of life n

Goal Prevent or treat as early as possible the symptoms of the disease, side effects caused by treatment of the disease, n Manage psychological, social, and spiritual problems related to the disease or its treatment. n Improve patient’s quality of life n

Types of Supportive Therapies n Management of fever and neutropenia n n n Prevention of Infection n n Blood transfusions for anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia Monitoring and management of drug toxicity n n Prophylactic use of antibiotics Blood component therapy n n Use of growth factors – Neupogen, Procrit, Neumega Proactive use of antibiotic therapy Patient/family Education Nutritional support n Calorie boosters

Other aspect of supportive care Palliative Care given to improve the quality of life of patients who have a serious or lifethreatening disease. n Aggressive EOL symptom management n

Complementary and Alternative Therapy n group of diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not presently considered to be part of conventional medicine n Considered part of supportive care

CAM n Complementary therapy - used together with conventional medicine. n n Massage and Hydrotherapy Music, relaxation, imagery Vitamins and herbal supplements Alternative medicine is used in place of conventional medicine. n n Arbolaryo, hilot Faith healers

Nursing Requirements n Thorough knowledge of the treatment modalities available n n Competency in patient assessments Competency in drug administration n Actions Side-effects and its management Venous access skills Ability to observe and recognize adverse reactions and complications of therapy Competency in patient and family education

n It’s all to do with training. You can do a lot if you are properly trained. Queen Elizabeth

n Questions? ? ?

n Thank you / Salamat po!!!!!
dd7237ab01e90a3409899c1bac0401ad.ppt