58cfea533eb21f1c21ac5dd461fe5f5a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Transport Fundamentals When the Chinese write the word “crisis, ” they do so in two characters—one meaning danger, the other opportunity. Chapter 6 CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 1
Transport Fundamentals When the Chinese write the word “crisis, ” they do so in two characters—one meaning danger, the other opportunity. Chapter 6 CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 1
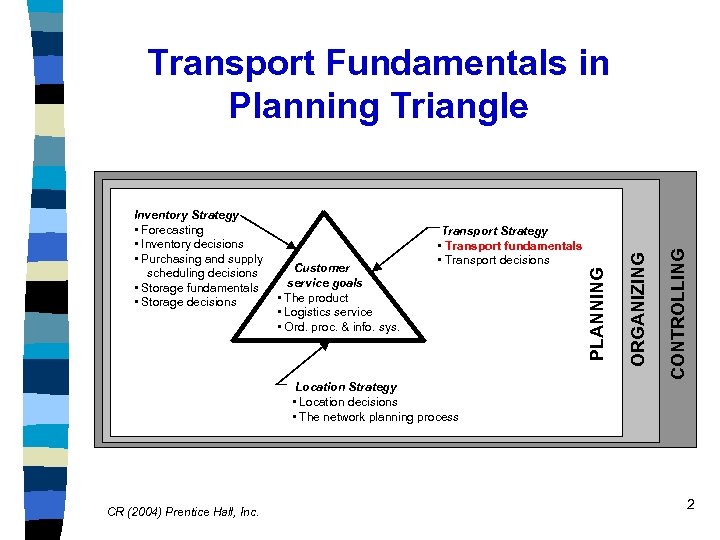 CONTROLLING Customer service goals The product Logistics service Ord. proc. & info. sys. Transport Strategy • Transport fundamentals • Transport decisions PLANNING Inventory Strategy • Forecasting • Inventory decisions • Purchasing and supply scheduling decisions • Storage fundamentals • • Storage decisions • • ORGANIZING Transport Fundamentals in Planning Triangle Location Strategy • Location decisions • The network planning process CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 2
CONTROLLING Customer service goals The product Logistics service Ord. proc. & info. sys. Transport Strategy • Transport fundamentals • Transport decisions PLANNING Inventory Strategy • Forecasting • Inventory decisions • Purchasing and supply scheduling decisions • Storage fundamentals • • Storage decisions • • ORGANIZING Transport Fundamentals in Planning Triangle Location Strategy • Location decisions • The network planning process CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 2
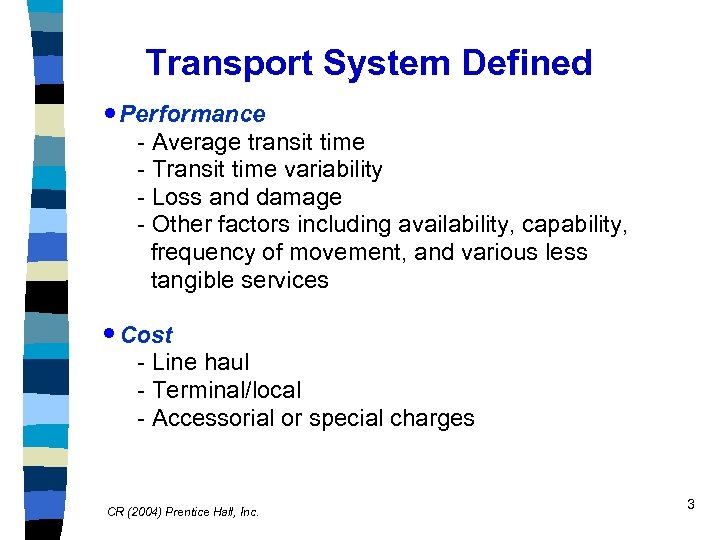 Transport System Defined · Performance - Average transit time - Transit time variability - Loss and damage - Other factors including availability, capability, frequency of movement, and various less tangible services · Cost - Line haul - Terminal/local - Accessorial or special charges CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 3
Transport System Defined · Performance - Average transit time - Transit time variability - Loss and damage - Other factors including availability, capability, frequency of movement, and various less tangible services · Cost - Line haul - Terminal/local - Accessorial or special charges CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 3
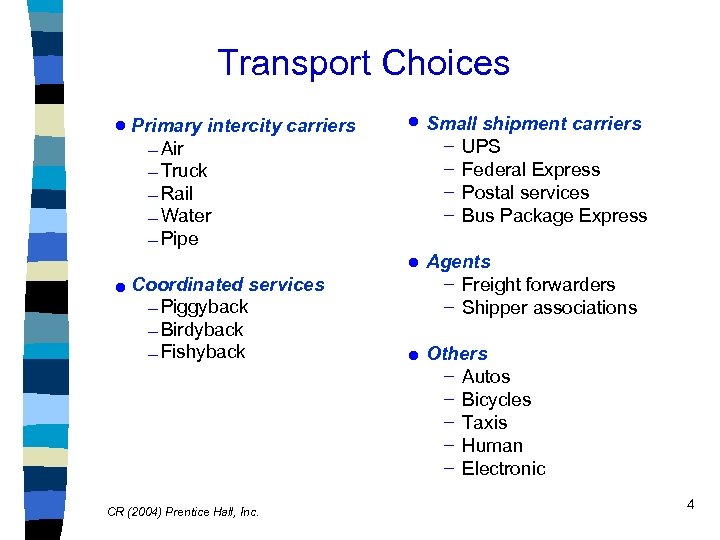 Transport Choices · Primary intercity carriers - Air - Truck - Rail - Water - Pipe · Coordinated services - Piggyback - Birdyback - Fishyback CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. · Small shipment carriers - · UPS Federal Express Postal services Bus Package Express Agents - Freight forwarders - Shipper associations · Others - Autos Bicycles Taxis Human Electronic 4
Transport Choices · Primary intercity carriers - Air - Truck - Rail - Water - Pipe · Coordinated services - Piggyback - Birdyback - Fishyback CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. · Small shipment carriers - · UPS Federal Express Postal services Bus Package Express Agents - Freight forwarders - Shipper associations · Others - Autos Bicycles Taxis Human Electronic 4
 Importance of Modes By Products Hauled · Air--very high-valued, time sensitive products · Truck--moderately high -valued, time sensitive products. Many finished and semifinished goods · Rail--low-valued products including many raw materials · Water--very low-valued products moved domestically, high valued if moved internationally · Pipe--generally limited to petroleum products and natural gas CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 5
Importance of Modes By Products Hauled · Air--very high-valued, time sensitive products · Truck--moderately high -valued, time sensitive products. Many finished and semifinished goods · Rail--low-valued products including many raw materials · Water--very low-valued products moved domestically, high valued if moved internationally · Pipe--generally limited to petroleum products and natural gas CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 5
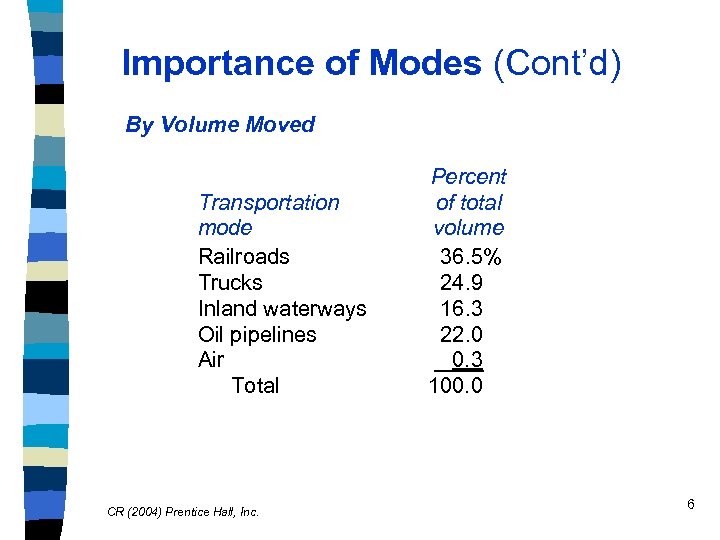 Importance of Modes (Cont’d) By Volume Moved Transportation mode Railroads Trucks Inland waterways Oil pipelines Air Total CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. Percent of total volume 36. 5% 24. 9 16. 3 22. 0 0. 3 100. 0 6
Importance of Modes (Cont’d) By Volume Moved Transportation mode Railroads Trucks Inland waterways Oil pipelines Air Total CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. Percent of total volume 36. 5% 24. 9 16. 3 22. 0 0. 3 100. 0 6
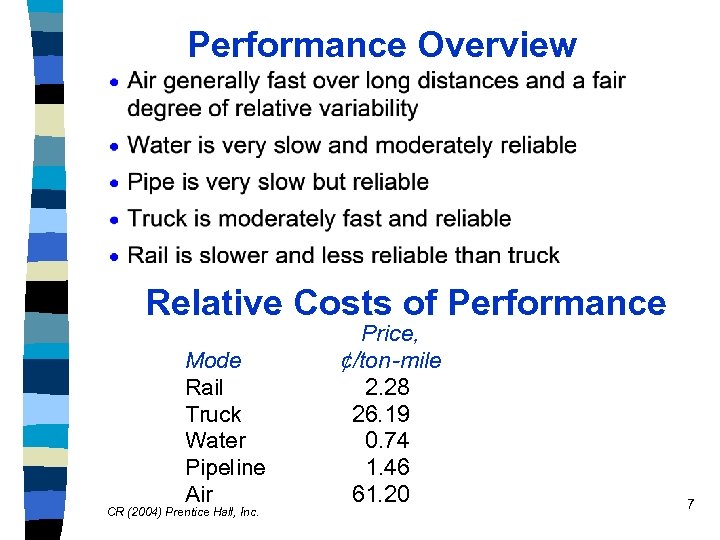 Performance Overview Relative Costs of Performance Mode Rail Truck Water Pipeline Air CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. Price, ¢/ton-mile 2. 28 26. 19 0. 74 1. 46 61. 20 7
Performance Overview Relative Costs of Performance Mode Rail Truck Water Pipeline Air CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. Price, ¢/ton-mile 2. 28 26. 19 0. 74 1. 46 61. 20 7
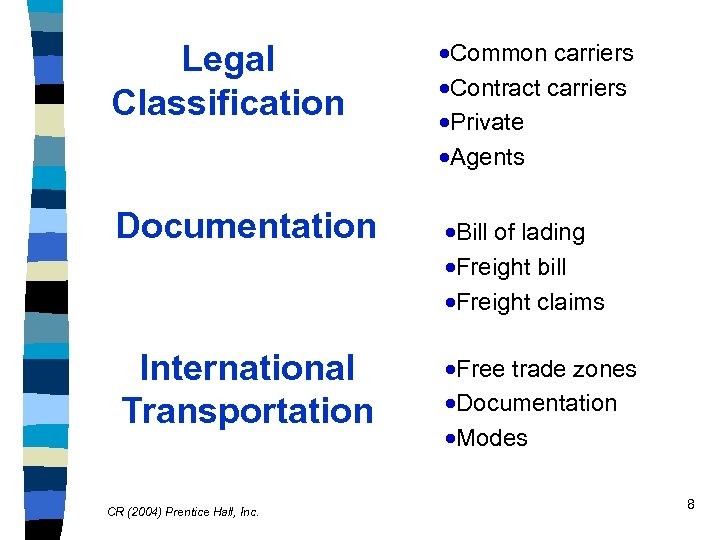 Legal Classification ·Common carriers ·Contract carriers ·Private ·Agents Documentation ·Bill of lading ·Freight bill ·Freight claims International Transportation ·Free trade zones ·Documentation ·Modes CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 8
Legal Classification ·Common carriers ·Contract carriers ·Private ·Agents Documentation ·Bill of lading ·Freight bill ·Freight claims International Transportation ·Free trade zones ·Documentation ·Modes CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 8
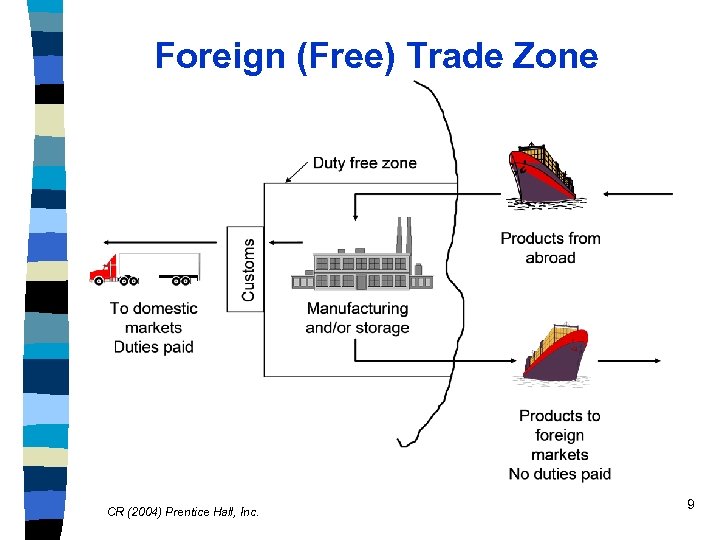 Foreign (Free) Trade Zone CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 9
Foreign (Free) Trade Zone CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 9
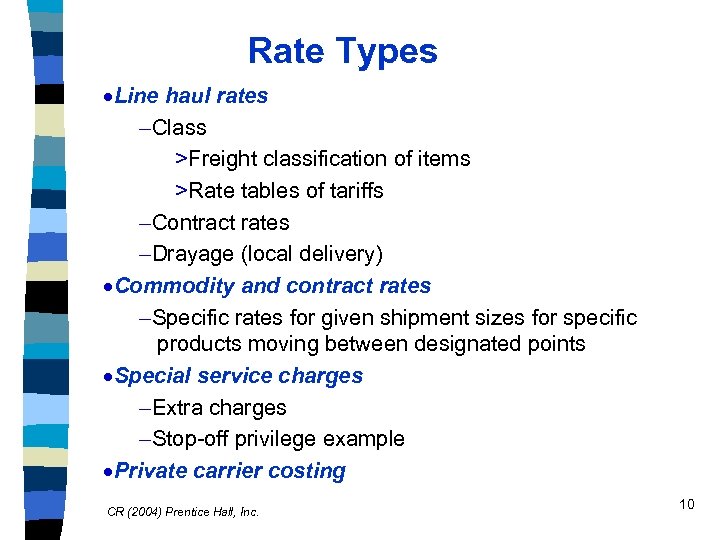 Rate Types ·Line haul rates -Class >Freight classification of items >Rate tables of tariffs -Contract rates -Drayage (local delivery) ·Commodity and contract rates -Specific rates for given shipment sizes for specific products moving between designated points ·Special service charges -Extra charges -Stop-off privilege example ·Private carrier costing CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 10
Rate Types ·Line haul rates -Class >Freight classification of items >Rate tables of tariffs -Contract rates -Drayage (local delivery) ·Commodity and contract rates -Specific rates for given shipment sizes for specific products moving between designated points ·Special service charges -Extra charges -Stop-off privilege example ·Private carrier costing CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 10
 Class Rate Example Suppose we wish to ship 15, 000 lb. (150 cwt. ) of wheat flour from New York to Los Angeles by truck. The trucker offers a 40% discount from the published tariff. What is the transportation charge? Table 6 -4 From the freight classification table, this is item number 1090 --00. It shows a minimum weight of 36, 000 lb. , which is less than this shipment size. Therefore, the class rating is 55, or less-than-truckload. From the class 100 tariff, the rate is 6065, or $60. 65 per cwt. With a 40% discount, the effective rate is (1 -. 40) x Table 6 -5 60. 65 = $36. 39. The shipment charges are 0. 55 x 36. 39 x 150 = $3, 002. 18. Should always check to see if shipment can be declared at the next higher weight break for a lower rate and lower total charges CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 11 6 -11
Class Rate Example Suppose we wish to ship 15, 000 lb. (150 cwt. ) of wheat flour from New York to Los Angeles by truck. The trucker offers a 40% discount from the published tariff. What is the transportation charge? Table 6 -4 From the freight classification table, this is item number 1090 --00. It shows a minimum weight of 36, 000 lb. , which is less than this shipment size. Therefore, the class rating is 55, or less-than-truckload. From the class 100 tariff, the rate is 6065, or $60. 65 per cwt. With a 40% discount, the effective rate is (1 -. 40) x Table 6 -5 60. 65 = $36. 39. The shipment charges are 0. 55 x 36. 39 x 150 = $3, 002. 18. Should always check to see if shipment can be declared at the next higher weight break for a lower rate and lower total charges CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 11 6 -11
 Break Weight Question Suppose 9, 000 lb. of Class 100 merchandise is to be shipped from New York to Dallas. From Table 6 -4, the rate would be $52. 21/cwt. However, should the shipment be priced at the next higher weight break rate of $40. 11/cwt. for a lower cost? where: Break Weight = Weight above which the next higher weight break rate should be used for lower transport costs Rate. Next = Rate for next higher weight break Weight. Next = Minimum weight of next higher weight break Rate. Current = Rate for true weight of shipment. CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 12 6 -12
Break Weight Question Suppose 9, 000 lb. of Class 100 merchandise is to be shipped from New York to Dallas. From Table 6 -4, the rate would be $52. 21/cwt. However, should the shipment be priced at the next higher weight break rate of $40. 11/cwt. for a lower cost? where: Break Weight = Weight above which the next higher weight break rate should be used for lower transport costs Rate. Next = Rate for next higher weight break Weight. Next = Minimum weight of next higher weight break Rate. Current = Rate for true weight of shipment. CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 12 6 -12
 Break Weight (Cont’d) Answer Calculate break weight Since the 9, 000 lb. shipment size exceeds the break weight of 7, 682 lb. , size as if a 10, 000 lb. , shipment for a total cost of $40. 11 x 100 = $4, 011. Otherwise, the shipment would have cost $52. 21 x 90 = $4, 699. CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 13 6 -13
Break Weight (Cont’d) Answer Calculate break weight Since the 9, 000 lb. shipment size exceeds the break weight of 7, 682 lb. , size as if a 10, 000 lb. , shipment for a total cost of $40. 11 x 100 = $4, 011. Otherwise, the shipment would have cost $52. 21 x 90 = $4, 699. CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 13 6 -13
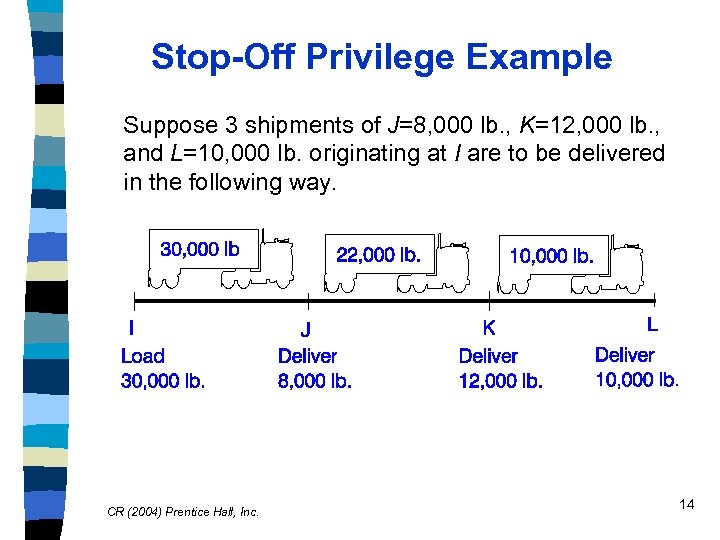 Stop-Off Privilege Example Suppose 3 shipments of J=8, 000 lb. , K=12, 000 lb. , and L=10, 000 lb. originating at I are to be delivered in the following way. CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 14
Stop-Off Privilege Example Suppose 3 shipments of J=8, 000 lb. , K=12, 000 lb. , and L=10, 000 lb. originating at I are to be delivered in the following way. CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 14
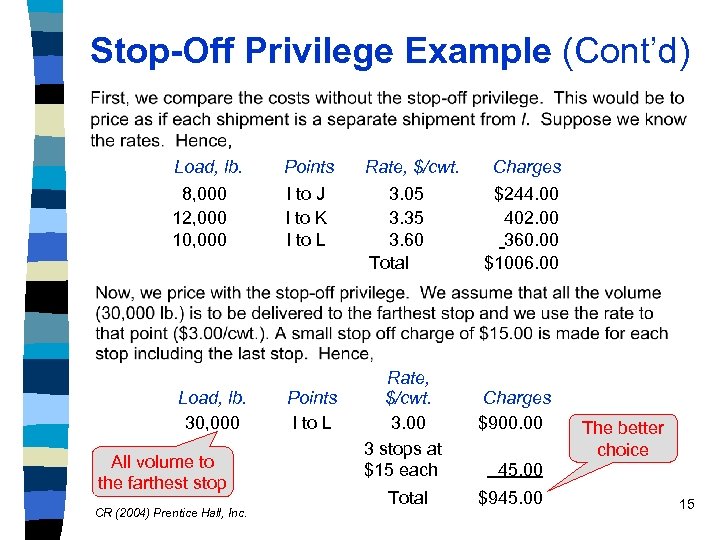 Stop-Off Privilege Example (Cont’d) Load, lb. 8, 000 12, 000 10, 000 Points I to J I to K I to L Rate, $/cwt. Charges 3. 05 $244. 00 3. 35 402. 00 3. 60 360. 00 Total $1006. 00 Rate, Load, lb. Points $/cwt. Charges 30, 000 I to L 3. 00 $900. 00 3 stops at All volume to $15 each 45. 00 the farthest stop Total $945. 00 CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. The better choice 15
Stop-Off Privilege Example (Cont’d) Load, lb. 8, 000 12, 000 10, 000 Points I to J I to K I to L Rate, $/cwt. Charges 3. 05 $244. 00 3. 35 402. 00 3. 60 360. 00 Total $1006. 00 Rate, Load, lb. Points $/cwt. Charges 30, 000 I to L 3. 00 $900. 00 3 stops at All volume to $15 each 45. 00 the farthest stop Total $945. 00 CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. The better choice 15
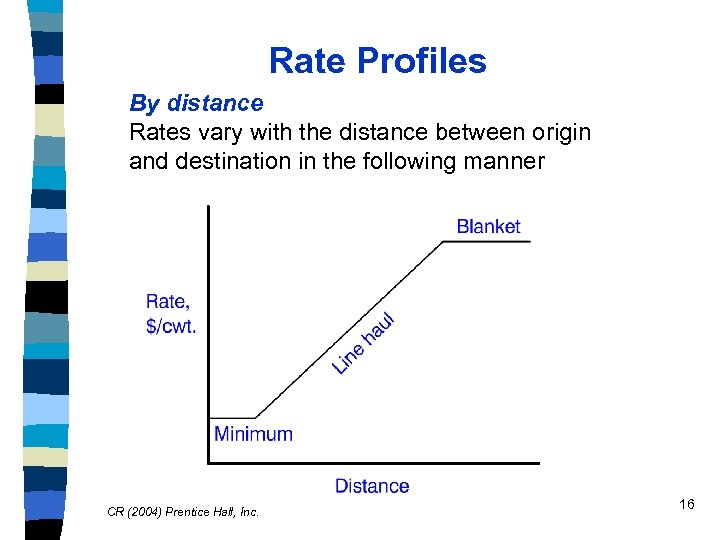 Rate Profiles By distance Rates vary with the distance between origin and destination in the following manner CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 16
Rate Profiles By distance Rates vary with the distance between origin and destination in the following manner CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 16
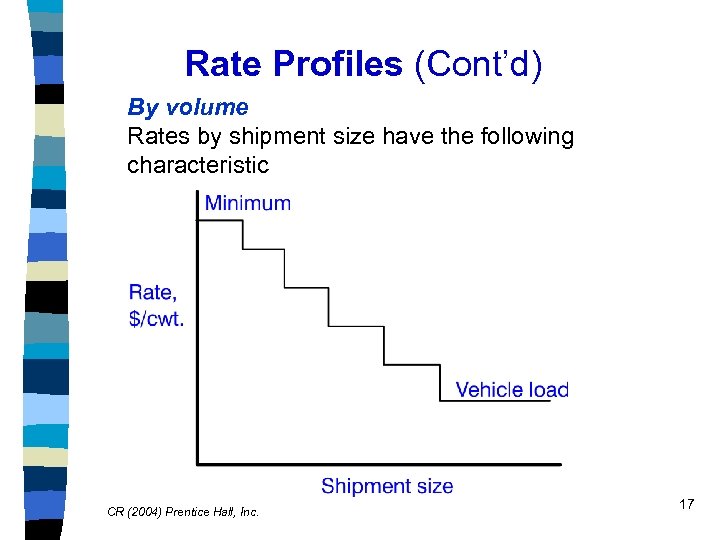 Rate Profiles (Cont’d) By volume Rates by shipment size have the following characteristic CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 17
Rate Profiles (Cont’d) By volume Rates by shipment size have the following characteristic CR (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc. 17


