12127217905aa9c3898fb043126731fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 TRANSP and PTRANSP: Status and Plans Presented at JET/MAST TRANSP Users’ Meeting, Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 1
TRANSP and PTRANSP: Status and Plans Presented at JET/MAST TRANSP Users’ Meeting, Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 1
 TRANSP: Vision Statement Provide a comprehensive end -to-end modeling capability for magnetic confinement fusion energy experiments of today and tomorrow. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 2
TRANSP: Vision Statement Provide a comprehensive end -to-end modeling capability for magnetic confinement fusion energy experiments of today and tomorrow. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 2
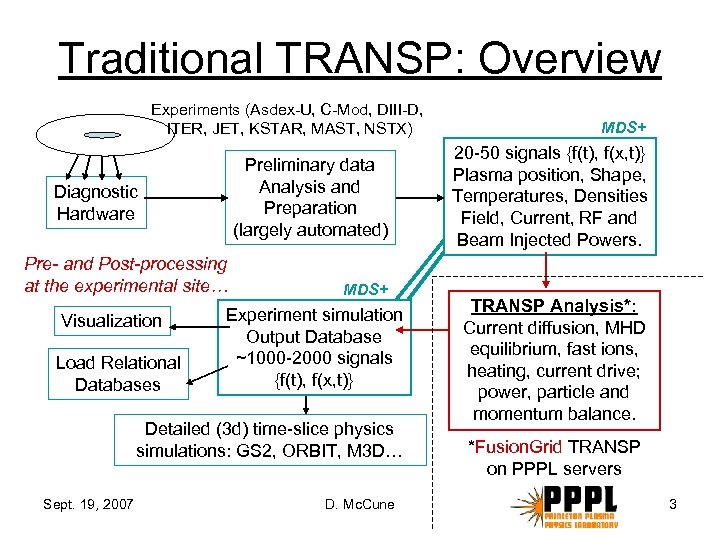 Traditional TRANSP: Overview Experiments (Asdex-U, C-Mod, DIII-D, ITER, JET, KSTAR, MAST, NSTX) Preliminary data Analysis and Preparation (largely automated) Diagnostic Hardware Pre- and Post-processing at the experimental site… Visualization Load Relational Databases MDS+ Experiment simulation Output Database ~1000 -2000 signals {f(t), f(x, t)} Detailed (3 d) time-slice physics simulations: GS 2, ORBIT, M 3 D… Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune MDS+ 20 -50 signals {f(t), f(x, t)} Plasma position, Shape, Temperatures, Densities Field, Current, RF and Beam Injected Powers. TRANSP Analysis*: Current diffusion, MHD equilibrium, fast ions, heating, current drive; power, particle and momentum balance. *Fusion. Grid TRANSP on PPPL servers 3
Traditional TRANSP: Overview Experiments (Asdex-U, C-Mod, DIII-D, ITER, JET, KSTAR, MAST, NSTX) Preliminary data Analysis and Preparation (largely automated) Diagnostic Hardware Pre- and Post-processing at the experimental site… Visualization Load Relational Databases MDS+ Experiment simulation Output Database ~1000 -2000 signals {f(t), f(x, t)} Detailed (3 d) time-slice physics simulations: GS 2, ORBIT, M 3 D… Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune MDS+ 20 -50 signals {f(t), f(x, t)} Plasma position, Shape, Temperatures, Densities Field, Current, RF and Beam Injected Powers. TRANSP Analysis*: Current diffusion, MHD equilibrium, fast ions, heating, current drive; power, particle and momentum balance. *Fusion. Grid TRANSP on PPPL servers 3
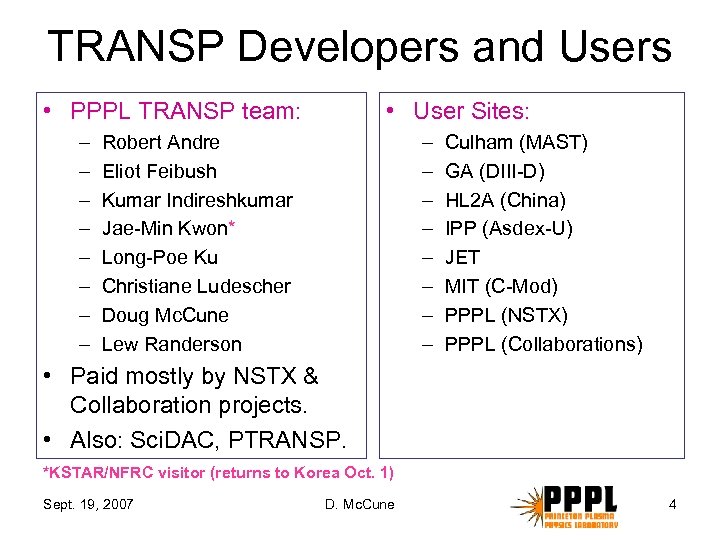 TRANSP Developers and Users • PPPL TRANSP team: – – – – • User Sites: – – – – Robert Andre Eliot Feibush Kumar Indireshkumar Jae-Min Kwon* Long-Poe Ku Christiane Ludescher Doug Mc. Cune Lew Randerson Culham (MAST) GA (DIII-D) HL 2 A (China) IPP (Asdex-U) JET MIT (C-Mod) PPPL (NSTX) PPPL (Collaborations) • Paid mostly by NSTX & Collaboration projects. • Also: Sci. DAC, PTRANSP. *KSTAR/NFRC visitor (returns to Korea Oct. 1) Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 4
TRANSP Developers and Users • PPPL TRANSP team: – – – – • User Sites: – – – – Robert Andre Eliot Feibush Kumar Indireshkumar Jae-Min Kwon* Long-Poe Ku Christiane Ludescher Doug Mc. Cune Lew Randerson Culham (MAST) GA (DIII-D) HL 2 A (China) IPP (Asdex-U) JET MIT (C-Mod) PPPL (NSTX) PPPL (Collaborations) • Paid mostly by NSTX & Collaboration projects. • Also: Sci. DAC, PTRANSP. *KSTAR/NFRC visitor (returns to Korea Oct. 1) Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 4
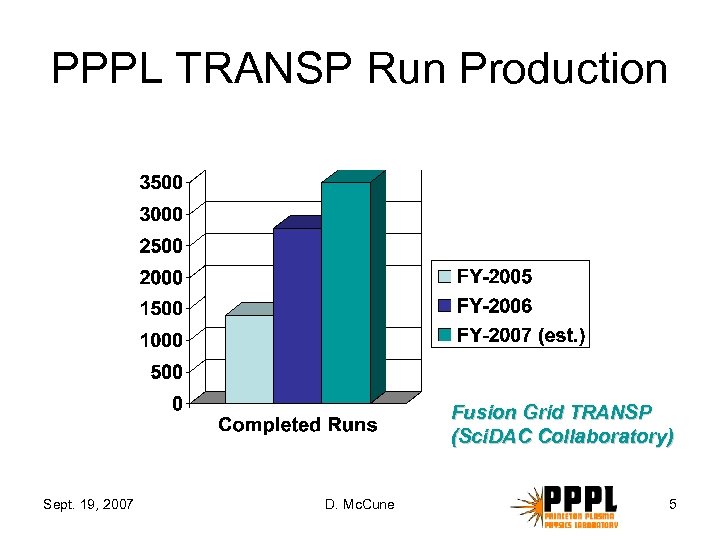 PPPL TRANSP Run Production Fusion Grid TRANSP (Sci. DAC Collaboratory) Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 5
PPPL TRANSP Run Production Fusion Grid TRANSP (Sci. DAC Collaboratory) Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 5
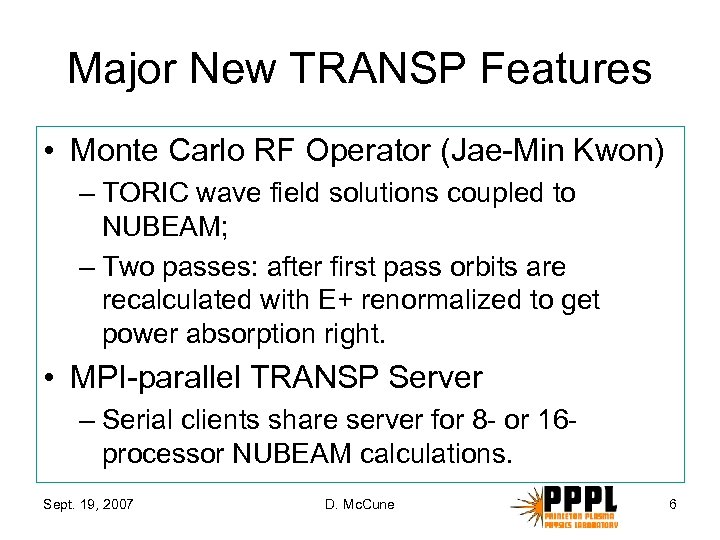 Major New TRANSP Features • Monte Carlo RF Operator (Jae-Min Kwon) – TORIC wave field solutions coupled to NUBEAM; – Two passes: after first pass orbits are recalculated with E+ renormalized to get power absorption right. • MPI-parallel TRANSP Server – Serial clients share server for 8 - or 16 processor NUBEAM calculations. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 6
Major New TRANSP Features • Monte Carlo RF Operator (Jae-Min Kwon) – TORIC wave field solutions coupled to NUBEAM; – Two passes: after first pass orbits are recalculated with E+ renormalized to get power absorption right. • MPI-parallel TRANSP Server – Serial clients share server for 8 - or 16 processor NUBEAM calculations. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 6
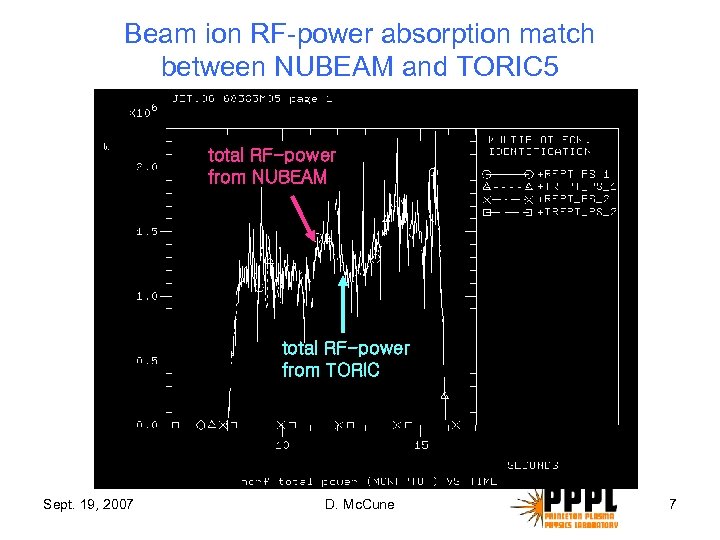 Beam ion RF-power absorption match between NUBEAM and TORIC 5 total RF-power from NUBEAM total RF-power from TORIC Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 7
Beam ion RF-power absorption match between NUBEAM and TORIC 5 total RF-power from NUBEAM total RF-power from TORIC Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 7
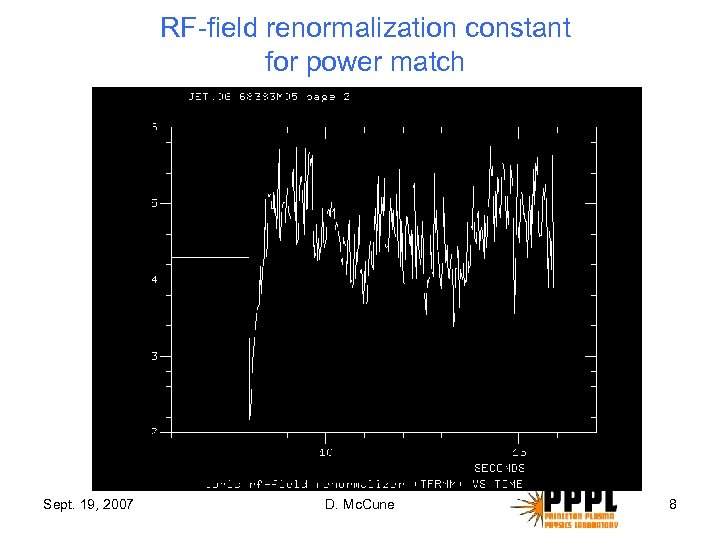 RF-field renormalization constant for power match Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 8
RF-field renormalization constant for power match Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 8
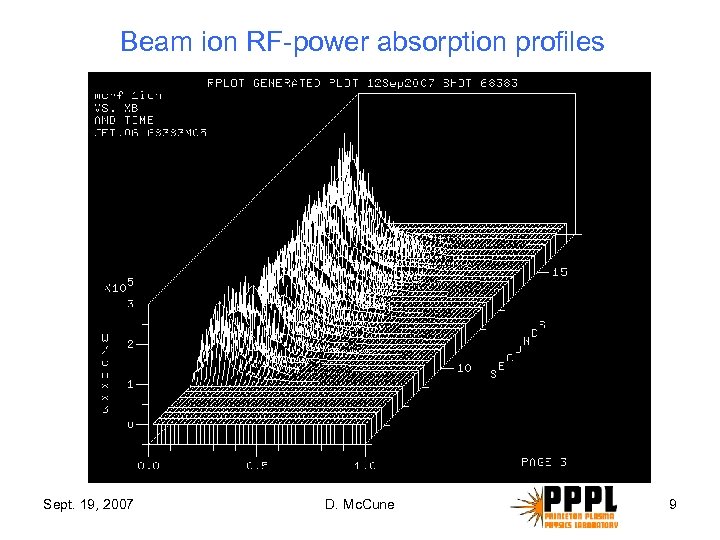 Beam ion RF-power absorption profiles Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 9
Beam ion RF-power absorption profiles Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 9
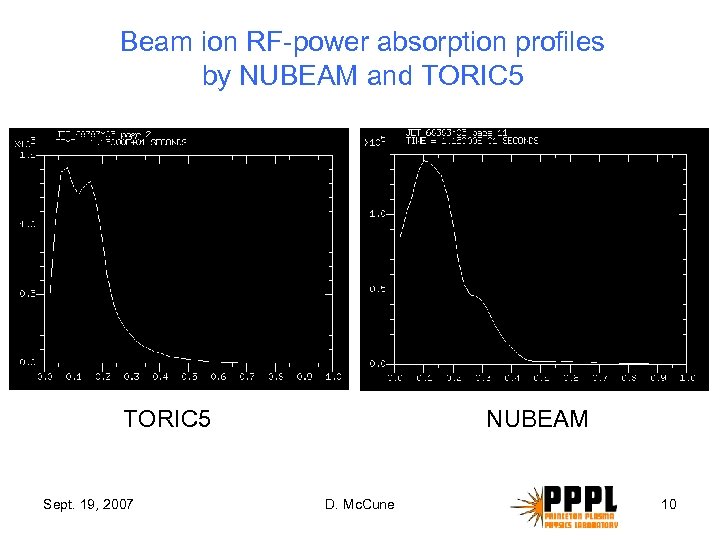 Beam ion RF-power absorption profiles by NUBEAM and TORIC 5 Sept. 19, 2007 NUBEAM D. Mc. Cune 10
Beam ion RF-power absorption profiles by NUBEAM and TORIC 5 Sept. 19, 2007 NUBEAM D. Mc. Cune 10
 NUBEAM RF Operator Issues • MPI runs needed for better statistics. • Wave code needs non-Maxwellian target distribution function. – Non. Max version of TORIC exists. – Need to install and test in TRANSP. – Need to learn how to fit “noisy” MC-binned distribution function data in TORIC. • Extensive validation will be needed. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 11
NUBEAM RF Operator Issues • MPI runs needed for better statistics. • Wave code needs non-Maxwellian target distribution function. – Non. Max version of TORIC exists. – Need to install and test in TRANSP. – Need to learn how to fit “noisy” MC-binned distribution function data in TORIC. • Extensive validation will be needed. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 11
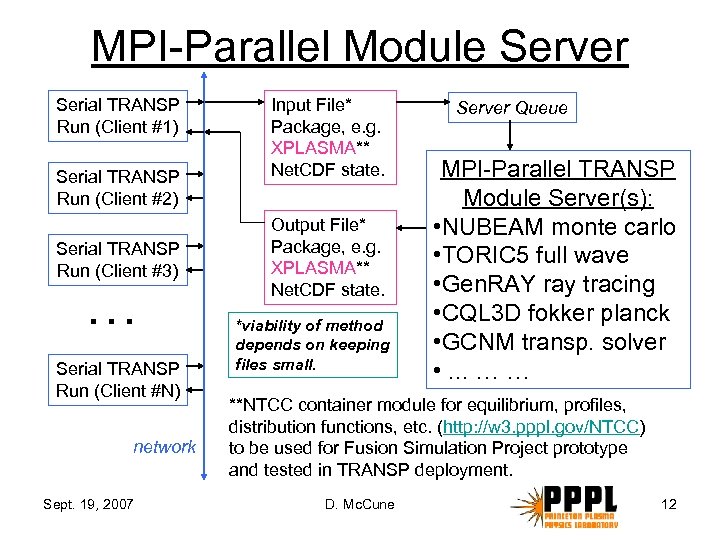 MPI-Parallel Module Server Serial TRANSP Run (Client #1) Serial TRANSP Run (Client #2) Serial TRANSP Run (Client #3) … Serial TRANSP Run (Client #N) network Sept. 19, 2007 Input File* Package, e. g. XPLASMA** Net. CDF state. Output File* Package, e. g. XPLASMA** Net. CDF state. *viability of method depends on keeping files small. Server Queue MPI-Parallel TRANSP Module Server(s): • NUBEAM monte carlo • TORIC 5 full wave • Gen. RAY ray tracing • CQL 3 D fokker planck • GCNM transp. solver • . . . … … **NTCC container module for equilibrium, profiles, distribution functions, etc. (http: //w 3. pppl. gov/NTCC) to be used for Fusion Simulation Project prototype and tested in TRANSP deployment. D. Mc. Cune 12
MPI-Parallel Module Server Serial TRANSP Run (Client #1) Serial TRANSP Run (Client #2) Serial TRANSP Run (Client #3) … Serial TRANSP Run (Client #N) network Sept. 19, 2007 Input File* Package, e. g. XPLASMA** Net. CDF state. Output File* Package, e. g. XPLASMA** Net. CDF state. *viability of method depends on keeping files small. Server Queue MPI-Parallel TRANSP Module Server(s): • NUBEAM monte carlo • TORIC 5 full wave • Gen. RAY ray tracing • CQL 3 D fokker planck • GCNM transp. solver • . . . … … **NTCC container module for equilibrium, profiles, distribution functions, etc. (http: //w 3. pppl. gov/NTCC) to be used for Fusion Simulation Project prototype and tested in TRANSP deployment. D. Mc. Cune 12
 NUBEAM Parallel Server • In operation for “early volunteer” users. • Reliability and performance evaluation in progress. • Client server file communications overhead is significant: – Only large NPTCLS runs will benefit – We plan to evaluate a more traditional (no client-server) deployment for midrange runs. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 13
NUBEAM Parallel Server • In operation for “early volunteer” users. • Reliability and performance evaluation in progress. • Client server file communications overhead is significant: – Only large NPTCLS runs will benefit – We plan to evaluate a more traditional (no client-server) deployment for midrange runs. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 13
 More TRANSP Improvements • Incremental improvements to equilibrium: – TEQ somewhat more reliable for STs. – Some cases still fail. – “Equal Arc” poloidal angle option for LEVGEO=8 (scrunch 2) runs. • NUBEAM deposition distribution function data: set OUTTIM(…) in namelist; use get_fbm on
More TRANSP Improvements • Incremental improvements to equilibrium: – TEQ somewhat more reliable for STs. – Some cases still fail. – “Equal Arc” poloidal angle option for LEVGEO=8 (scrunch 2) runs. • NUBEAM deposition distribution function data: set OUTTIM(…) in namelist; use get_fbm on
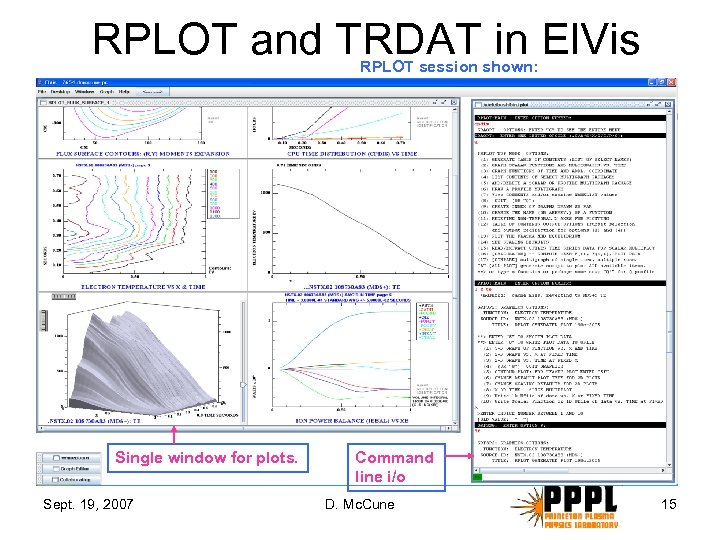 RPLOT and TRDAT in El. Vis RPLOT session shown: Single window for plots. Sept. 19, 2007 Command line i/o D. Mc. Cune 15
RPLOT and TRDAT in El. Vis RPLOT session shown: Single window for plots. Sept. 19, 2007 Command line i/o D. Mc. Cune 15
 Future Directions • More MPI services: TORIC, GENRAY, … • Better MHD equilibrium reconstruction • Continued improvement to Monte Carlo RF operator and wave code coupling. • More code development collaboration for more rapid progress. • PTRANSP… Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 16
Future Directions • More MPI services: TORIC, GENRAY, … • Better MHD equilibrium reconstruction • Continued improvement to Monte Carlo RF operator and wave code coupling. • More code development collaboration for more rapid progress. • PTRANSP… Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 16
 TRANSP is Big Software • Source builds 219 executable programs • Sources for 199 subroutine libraries • 418 (219+199) directories containing F 90, C, and C++ source code. • 26 directories of scripts and documents (not compiled). • 178 directories with changes in CY-2007. • 1. 66 Mlines of source (w/comments); 1. 13 Mlines of source (comments not counted). Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 17
TRANSP is Big Software • Source builds 219 executable programs • Sources for 199 subroutine libraries • 418 (219+199) directories containing F 90, C, and C++ source code. • 26 directories of scripts and documents (not compiled). • 178 directories with changes in CY-2007. • 1. 66 Mlines of source (w/comments); 1. 13 Mlines of source (comments not counted). Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 17
 Code Development is Feasible • Unified source code control (cvs server at PPPL). • Unified build system with makefile generator. • Precise control of contents of “debug” executables for code development. • Lehigh University physicist Glenn Bateman and student Federico Halpern acquired TRANSP code developer skills after one week visit to PPPL. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 18
Code Development is Feasible • Unified source code control (cvs server at PPPL). • Unified build system with makefile generator. • Precise control of contents of “debug” executables for code development. • Lehigh University physicist Glenn Bateman and student Federico Halpern acquired TRANSP code developer skills after one week visit to PPPL. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 18
 PTRANSP Phase 1 (2006 APS) • Stiff solver upgrades completed: – Free Boundary (TSC): L. P. Ku, JP 1. 00123 – Prescribed Boundary: G. Bateman, JP 1. 00126 • PTRANSP Client-Server Configuration: – TSC free boundary predictive code client: • Compute evolution of equilibrium and profiles; – TRANSP server: • Compute heating and current drive sources; • Standard analysis of predictive code results. – See JP 1. 00123. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 19
PTRANSP Phase 1 (2006 APS) • Stiff solver upgrades completed: – Free Boundary (TSC): L. P. Ku, JP 1. 00123 – Prescribed Boundary: G. Bateman, JP 1. 00126 • PTRANSP Client-Server Configuration: – TSC free boundary predictive code client: • Compute evolution of equilibrium and profiles; – TRANSP server: • Compute heating and current drive sources; • Standard analysis of predictive code results. – See JP 1. 00123. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 19
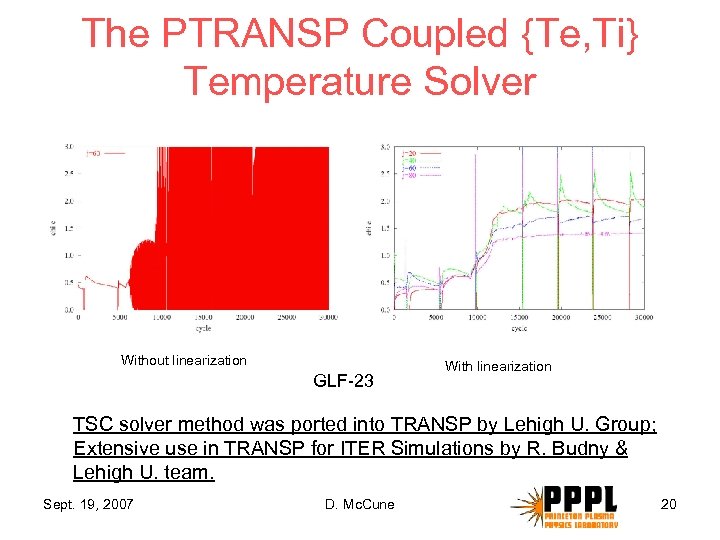 The PTRANSP Coupled {Te, Ti} Temperature Solver Without linearization GLF-23 With linearization TSC solver method was ported into TRANSP by Lehigh U. Group; Extensive use in TRANSP for ITER Simulations by R. Budny & Lehigh U. team. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 20
The PTRANSP Coupled {Te, Ti} Temperature Solver Without linearization GLF-23 With linearization TSC solver method was ported into TRANSP by Lehigh U. Group; Extensive use in TRANSP for ITER Simulations by R. Budny & Lehigh U. team. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 20
 Phase 2: PTRANSP is TRANSP • A project to upgrade TRANSP predictive capability. • Retained from TRANSP: – Code base – Production system – Connection to experimental data – Connection to post-processors – Connection to user community. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 21
Phase 2: PTRANSP is TRANSP • A project to upgrade TRANSP predictive capability. • Retained from TRANSP: – Code base – Production system – Connection to experimental data – Connection to post-processors – Connection to user community. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 21
 PTRANSP Phase 2 • “non-renewable” 3 Year Grant, ~$650 k/year – Funding approved late in FY-2007 – General Atomics (25%) – Lehigh University (25%) – LLNL (25%) – PPPL (25%). • Work scope of grant clearly focused on predictive upgrades to TRANSP itself. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 22
PTRANSP Phase 2 • “non-renewable” 3 Year Grant, ~$650 k/year – Funding approved late in FY-2007 – General Atomics (25%) – Lehigh University (25%) – LLNL (25%) – PPPL (25%). • Work scope of grant clearly focused on predictive upgrades to TRANSP itself. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 22
 PTRANSP Phase 2 – GA Role • Add GCNM-P Solver to TRANSP – Allow flexible applications: • • Prescribe electron density (T/F) Prescribe ion densities and impurity levels (T/F) Include depletion by fast species. Separately computed: MHD equilibrium and q(r, t). • Import TGLF predictive Transport Model into TRANSP via GCNM-P. • Likely to use SWIM Plasma State software. • Support other uses of TGLF as needed. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 23
PTRANSP Phase 2 – GA Role • Add GCNM-P Solver to TRANSP – Allow flexible applications: • • Prescribe electron density (T/F) Prescribe ion densities and impurity levels (T/F) Include depletion by fast species. Separately computed: MHD equilibrium and q(r, t). • Import TGLF predictive Transport Model into TRANSP via GCNM-P. • Likely to use SWIM Plasma State software. • Support other uses of TGLF as needed. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 23
 PTRANSP Phase 2 – Lehigh U. • Program of direct improvements to TRANSP internal solvers (with PPPL). • Predictive Sawtooth and Pedestal models. • Intensive use of PTRANSP for research applications. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 24
PTRANSP Phase 2 – Lehigh U. • Program of direct improvements to TRANSP internal solvers (with PPPL). • Predictive Sawtooth and Pedestal models. • Intensive use of PTRANSP for research applications. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 24
 PTRANSP Phase 2 -- LLNL • Provide Free Boundary TEQ model to PPPL. • Enhance TEQ to enable concurrent prediction of poloidal field diffusion and MHD equilibrium. • Additional TEQ enhancements (e. g. hyperresistivity). Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 25
PTRANSP Phase 2 -- LLNL • Provide Free Boundary TEQ model to PPPL. • Enhance TEQ to enable concurrent prediction of poloidal field diffusion and MHD equilibrium. • Additional TEQ enhancements (e. g. hyperresistivity). Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 25
 PTRANSP Phase 2 -- PPPL • Provide TRANSP system and development support to all participants. • Install the TEQ model upgrades provided by LLNL. • Place PTRANSP capabilities in production and trouble-shoot applications. • Provide additional TRANSP/PTRANSP upgrades as may be needed. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 26
PTRANSP Phase 2 -- PPPL • Provide TRANSP system and development support to all participants. • Install the TEQ model upgrades provided by LLNL. • Place PTRANSP capabilities in production and trouble-shoot applications. • Provide additional TRANSP/PTRANSP upgrades as may be needed. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 26
 PTRANSP Focus on Plasma Core • True whole device predictive modeling requires validation with close coupling to: – Scrape-off Layer (Edge) Plasma Model. – Wall Model. – Many other things– SOL Atomic Physics, etc. • Current PTRANSP plans are short term. – Not high performance super-computing. – No true whole device predictive model. – Such capabilities require a much larger effort. • Fusion Simulation Project $24 M/year…? ? Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 27
PTRANSP Focus on Plasma Core • True whole device predictive modeling requires validation with close coupling to: – Scrape-off Layer (Edge) Plasma Model. – Wall Model. – Many other things– SOL Atomic Physics, etc. • Current PTRANSP plans are short term. – Not high performance super-computing. – No true whole device predictive model. – Such capabilities require a much larger effort. • Fusion Simulation Project $24 M/year…? ? Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 27
 Collaboration Opportunities • Improve TRANSP RF capabilities. • Improve PTRANSP capabilities: – Performance options (e. g. fast source models). – TGLF installation in TRANSP-native solver (when TGLF is available). • Significant commitment required for success: ~ 0. 5 person-year / collaboration. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 28
Collaboration Opportunities • Improve TRANSP RF capabilities. • Improve PTRANSP capabilities: – Performance options (e. g. fast source models). – TGLF installation in TRANSP-native solver (when TGLF is available). • Significant commitment required for success: ~ 0. 5 person-year / collaboration. Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 28
 TRANSP Users’ Group at APS • • Annual TRANSP Users’ Group Meeting. Review/discuss (P)TRANSP status & plans. Monday evening satellite meeting at APS. This year: – Orlando, Florida APS-DPP conference. – Monday, Nov. 12, 8 pm. • Apologies in advance for the inevitable schedule conflicts… Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 29
TRANSP Users’ Group at APS • • Annual TRANSP Users’ Group Meeting. Review/discuss (P)TRANSP status & plans. Monday evening satellite meeting at APS. This year: – Orlando, Florida APS-DPP conference. – Monday, Nov. 12, 8 pm. • Apologies in advance for the inevitable schedule conflicts… Sept. 19, 2007 D. Mc. Cune 29


