1c9daa6b0e22caa5bcac96f3d54780eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Translation memory systems to enhance the quality and productivity of localization of teaching materials Sam Joachim 6 th Workshop Software Engineering Education and Reverse Engineering, Ravda (Nessebar), Bulgaria, 18 – 23 September 2006
Translation memory systems to enhance the quality and productivity of localization of teaching materials Sam Joachim 6 th Workshop Software Engineering Education and Reverse Engineering, Ravda (Nessebar), Bulgaria, 18 – 23 September 2006
 Last years suggestion for future development of S-Bahn Tool Transformation of our Power. Point material in an independent XML format (perhaps based on
Last years suggestion for future development of S-Bahn Tool Transformation of our Power. Point material in an independent XML format (perhaps based on
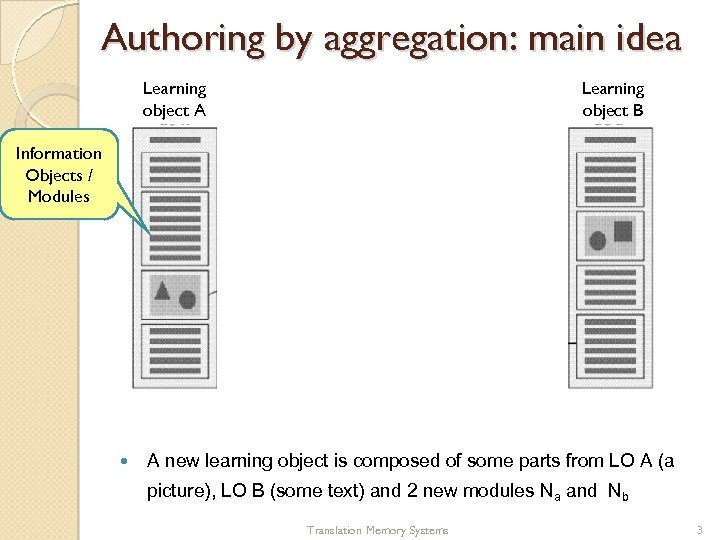 Authoring by aggregation: main idea Learning object A New learning object Learning object B Modul Na Information Objects / Modules Modul Nb A new learning object is composed of some parts from LO A (a picture), LO B (some text) and 2 new modules Na and Nb Translation Memory Systems 3
Authoring by aggregation: main idea Learning object A New learning object Learning object B Modul Na Information Objects / Modules Modul Nb A new learning object is composed of some parts from LO A (a picture), LO B (some text) and 2 new modules Na and Nb Translation Memory Systems 3
 Some problems to solve Learning object models adapted to ‚Authoring by aggregation‘ XML representation of our slides / material S-Bahn tool problems with respect to localization (quality, efficiency of translation) Translation Memory Systems 4
Some problems to solve Learning object models adapted to ‚Authoring by aggregation‘ XML representation of our slides / material S-Bahn tool problems with respect to localization (quality, efficiency of translation) Translation Memory Systems 4
 Learning object models adapted to ‚Authoring by aggregation’ & XML representation of our slides / material Translation Memory Systems 6
Learning object models adapted to ‚Authoring by aggregation’ & XML representation of our slides / material Translation Memory Systems 6
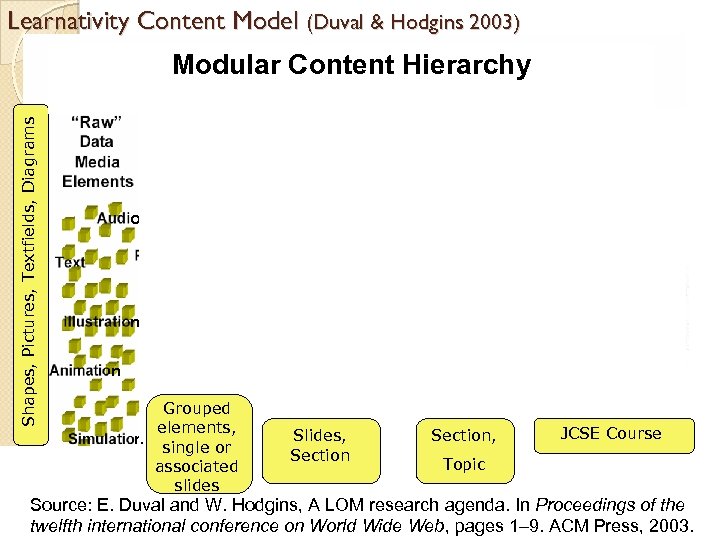 Learnativity Content Model (Duval & Hodgins 2003) Shapes, Pictures, Textfields, Diagrams Modular Content Hierarchy o e t n n s s e e e s t y w y Grouped elements, n single or associated slides w g Slides, Section s Section, JCSE Course Topic Source: E. Duval and W. Hodgins, A LOM research agenda. In Proceedings of the twelfth international conference on Translation. Wide Web, pages 1– 9. ACM Press, 2003. 7 7 World Memory Systems
Learnativity Content Model (Duval & Hodgins 2003) Shapes, Pictures, Textfields, Diagrams Modular Content Hierarchy o e t n n s s e e e s t y w y Grouped elements, n single or associated slides w g Slides, Section s Section, JCSE Course Topic Source: E. Duval and W. Hodgins, A LOM research agenda. In Proceedings of the twelfth international conference on Translation. Wide Web, pages 1– 9. ACM Press, 2003. 7 7 World Memory Systems
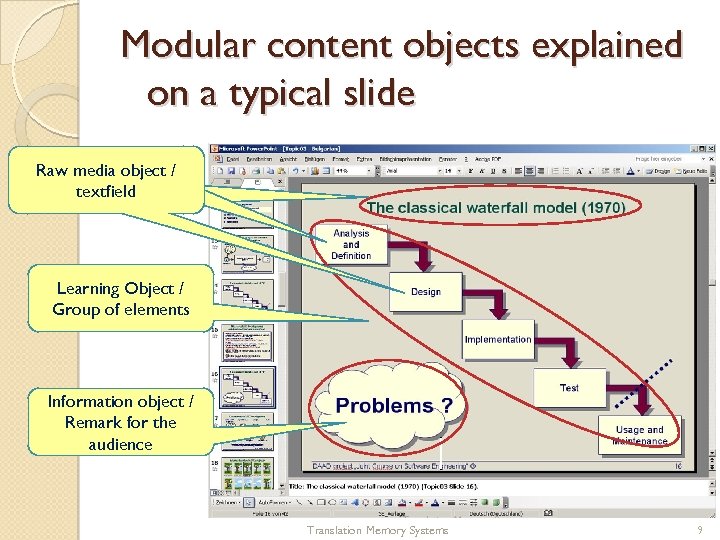 Modular content objects explained on a typical slide Raw media object /// Raw media object textfield Learning Object / Group of elements Information object / Remark for the audience Translation Memory Systems 9
Modular content objects explained on a typical slide Raw media object /// Raw media object textfield Learning Object / Group of elements Information object / Remark for the audience Translation Memory Systems 9
 Generation of fine-granular objects Use / adaptation of an existing XML teaching material language Automatic generation of ◦ Raw media objects (shapes, textfields) ◦ Information objects (groups of objects, graphics) Semi-automatic by selecting from the automatically generated elements ◦ Learning objects (associated slides, . . ) ◦ Higher level objects like Aggregate assemblies (topics) Collections (whole JCSE) Translation Memory Systems 10
Generation of fine-granular objects Use / adaptation of an existing XML teaching material language Automatic generation of ◦ Raw media objects (shapes, textfields) ◦ Information objects (groups of objects, graphics) Semi-automatic by selecting from the automatically generated elements ◦ Learning objects (associated slides, . . ) ◦ Higher level objects like Aggregate assemblies (topics) Collections (whole JCSE) Translation Memory Systems 10
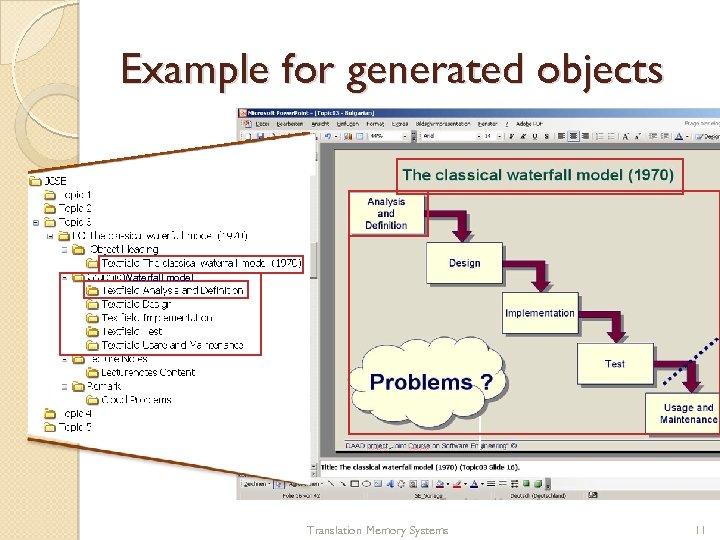 Example for generated objects Waterfall model Translation Memory Systems 11
Example for generated objects Waterfall model Translation Memory Systems 11
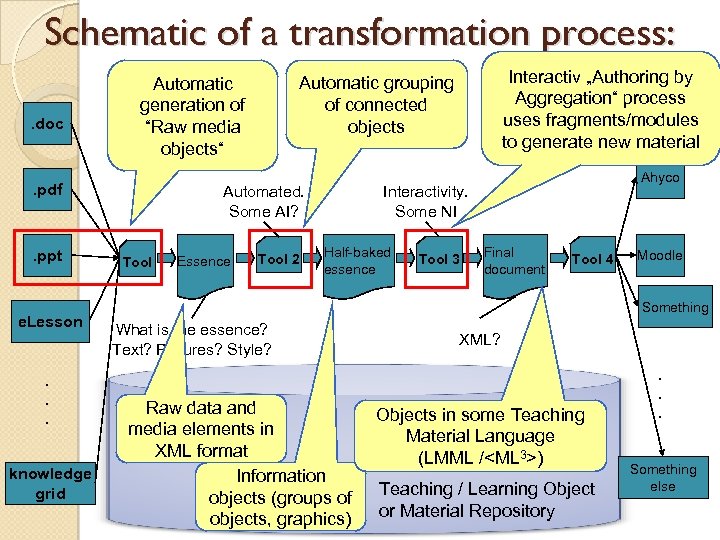 Schematic of a transformation process: . doc . pdf . ppt e. Lesson . . . knowledge grid Automated. Some AI? Tool Essence Interactiv „Authoring by Aggregation“ process uses fragments/modules to generate new material Automatic grouping of connected objects Automatic generation of “Raw media objects“ Tool 2 Ahyco Interactivity. Some NI Half-baked essence Tool 3 Final document Tool 4 Moodle Something What is the essence? Text? Pictures? Style? Raw data and media elements in XML format Information objects (groups of objects, graphics) XML? Objects in some Teaching Material Language (LMML /
Schematic of a transformation process: . doc . pdf . ppt e. Lesson . . . knowledge grid Automated. Some AI? Tool Essence Interactiv „Authoring by Aggregation“ process uses fragments/modules to generate new material Automatic grouping of connected objects Automatic generation of “Raw media objects“ Tool 2 Ahyco Interactivity. Some NI Half-baked essence Tool 3 Final document Tool 4 Moodle Something What is the essence? Text? Pictures? Style? Raw data and media elements in XML format Information objects (groups of objects, graphics) XML? Objects in some Teaching Material Language (LMML /
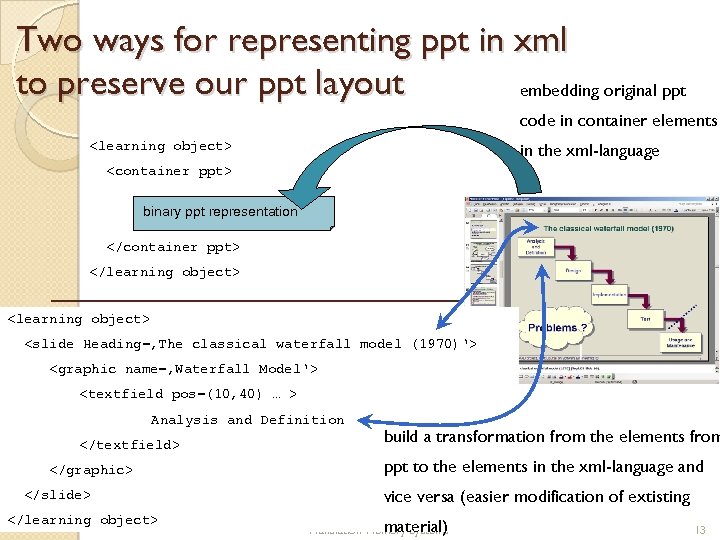 Two ways for representing ppt in xml to preserve our ppt layout embedding original ppt code in container elements
Two ways for representing ppt in xml to preserve our ppt layout embedding original ppt code in container elements
 Translation Memory Systems 14
Translation Memory Systems 14
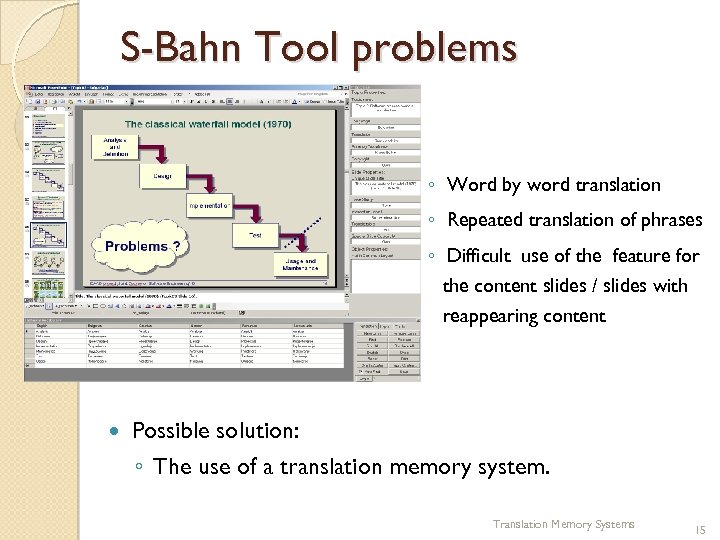 S-Bahn Tool problems ◦ Word by word translation ◦ Repeated translation of phrases ◦ Difficult use of the feature for the content slides / slides with reappearing content Possible solution: ◦ The use of a translation memory system. Translation Memory Systems 15
S-Bahn Tool problems ◦ Word by word translation ◦ Repeated translation of phrases ◦ Difficult use of the feature for the content slides / slides with reappearing content Possible solution: ◦ The use of a translation memory system. Translation Memory Systems 15
 TM-Systeme: Introduction two main types of translation support ◦ Machine Translation (fully automatic) Try to translate autonomous, in most cases nonsatisfying ◦ Machine Assisted Human Translation (computer-aided) Mainly with Translation Memory Systems 16
TM-Systeme: Introduction two main types of translation support ◦ Machine Translation (fully automatic) Try to translate autonomous, in most cases nonsatisfying ◦ Machine Assisted Human Translation (computer-aided) Mainly with Translation Memory Systems 16
 Background - History Who: Target group - professional translators Where: professional translation agencies / specialized companies What: Big translation projects with lots of different media and/or documents and dicument versions ◦ Documents to translate: Technical / project / product documentation Texts with technical /natural science background Software in different language variants and during different program versions Including GUI elements, user / product documentation Translation Memory Systems 17
Background - History Who: Target group - professional translators Where: professional translation agencies / specialized companies What: Big translation projects with lots of different media and/or documents and dicument versions ◦ Documents to translate: Technical / project / product documentation Texts with technical /natural science background Software in different language variants and during different program versions Including GUI elements, user / product documentation Translation Memory Systems 17
 TM System Is a data base Records sentences or word groups (segments) with the corresponding translation During translation, the TM-System searches the already translated segments for similarities with the actual segment The translator can easily use already translated segments Translation Memory Systems 18
TM System Is a data base Records sentences or word groups (segments) with the corresponding translation During translation, the TM-System searches the already translated segments for similarities with the actual segment The translator can easily use already translated segments Translation Memory Systems 18
 TM System (cont. ) Every sentence / segment will be checked during translating of other texts If it is already in the data base, it is possible to adopt the translation as it stands ◦ No segment /sentence should be translatet two times. (Similar to the S-Bahn Tool content slides feature, but much more generic in practice. ) Highly effective TM Systems ease routine jobs of the translator. He/she can concentrate more on the creative task of translating. Translation Memory Systems 19
TM System (cont. ) Every sentence / segment will be checked during translating of other texts If it is already in the data base, it is possible to adopt the translation as it stands ◦ No segment /sentence should be translatet two times. (Similar to the S-Bahn Tool content slides feature, but much more generic in practice. ) Highly effective TM Systems ease routine jobs of the translator. He/she can concentrate more on the creative task of translating. Translation Memory Systems 19
 Fuzzy searches In realworld texts, a sentence or seqment is very seldom exactly repeated. The most TM systems search not only for exact matches but also for matches with a certain similarity, the so called Fuzzy Matches: only marginal differences, e. g. numbers , names, additional words… Of course, the translator has to do a manual adaptation when taking over a fuzzy match Example from JCSE Topic 3 Slide 26: Already known: Part of the phase ‚Analysis and Design‘, in which the basic use cases of the systems will be detected: use case diagrams New: Part of the phase ‚Analysis and Design‘, in which the basic classes of the problem will be detected: class diagrams Translation Memory Systems 20
Fuzzy searches In realworld texts, a sentence or seqment is very seldom exactly repeated. The most TM systems search not only for exact matches but also for matches with a certain similarity, the so called Fuzzy Matches: only marginal differences, e. g. numbers , names, additional words… Of course, the translator has to do a manual adaptation when taking over a fuzzy match Example from JCSE Topic 3 Slide 26: Already known: Part of the phase ‚Analysis and Design‘, in which the basic use cases of the systems will be detected: use case diagrams New: Part of the phase ‚Analysis and Design‘, in which the basic classes of the problem will be detected: class diagrams Translation Memory Systems 20
 Existing TM Systems Trados ◦ http: //www. trados. com SDLX ◦ http: //www. sdlint. com Transit ◦ http: //www. star-ag. ch/products/transit DéjàVu ◦ http: //www. atril. com Omega. T ◦ http: //www. omegat. org/ Transolution ◦ http: //transolution. python-hosting. com/ Translation Memory Systems 21
Existing TM Systems Trados ◦ http: //www. trados. com SDLX ◦ http: //www. sdlint. com Transit ◦ http: //www. star-ag. ch/products/transit DéjàVu ◦ http: //www. atril. com Omega. T ◦ http: //www. omegat. org/ Transolution ◦ http: //transolution. python-hosting. com/ Translation Memory Systems 21
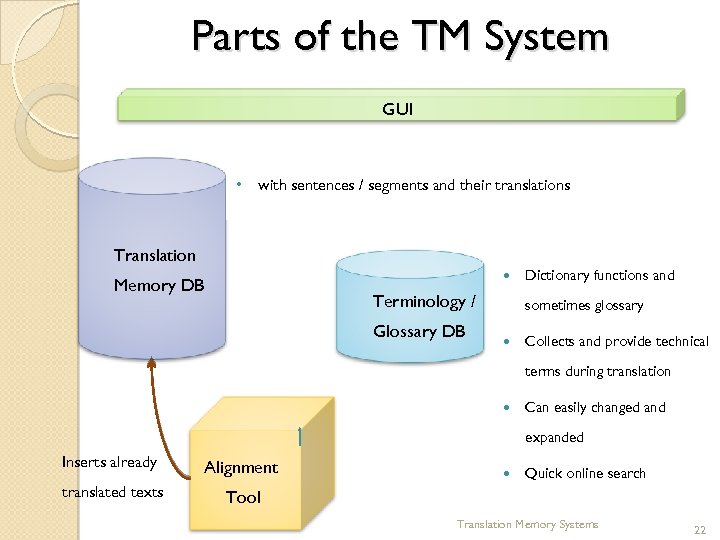 Parts of the TM System GUI • with sentences / segments and their translations Translation Memory DB Terminology / Glossary DB Dictionary functions and sometimes glossary Collects and provide technical terms during translation Can easily changed and expanded Inserts already Alignment translated texts Tool Quick online search Translation Memory Systems 22
Parts of the TM System GUI • with sentences / segments and their translations Translation Memory DB Terminology / Glossary DB Dictionary functions and sometimes glossary Collects and provide technical terms during translation Can easily changed and expanded Inserts already Alignment translated texts Tool Quick online search Translation Memory Systems 22
 Alignment Tool: Example GPL Translation Memory Systems 24
Alignment Tool: Example GPL Translation Memory Systems 24
 Typical user interface Two windows for source and target language Fuzzy index with matches Terminology dictionary Translation Memory Systems 25
Typical user interface Two windows for source and target language Fuzzy index with matches Terminology dictionary Translation Memory Systems 25
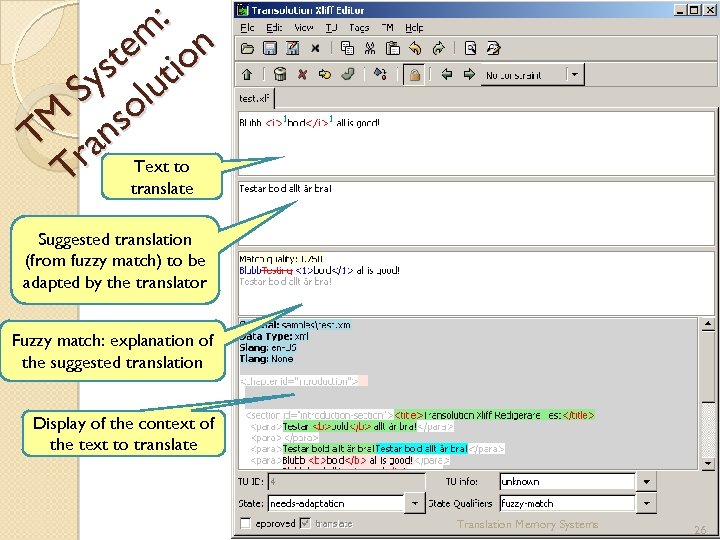 : m n te tio ys lu S o M ns T ra Text to T translate Suggested translation (from fuzzy match) to be adapted by the translator Fuzzy match: explanation of the suggested translation Display of the context of the text to translate Translation Memory Systems 26
: m n te tio ys lu S o M ns T ra Text to T translate Suggested translation (from fuzzy match) to be adapted by the translator Fuzzy match: explanation of the suggested translation Display of the context of the text to translate Translation Memory Systems 26
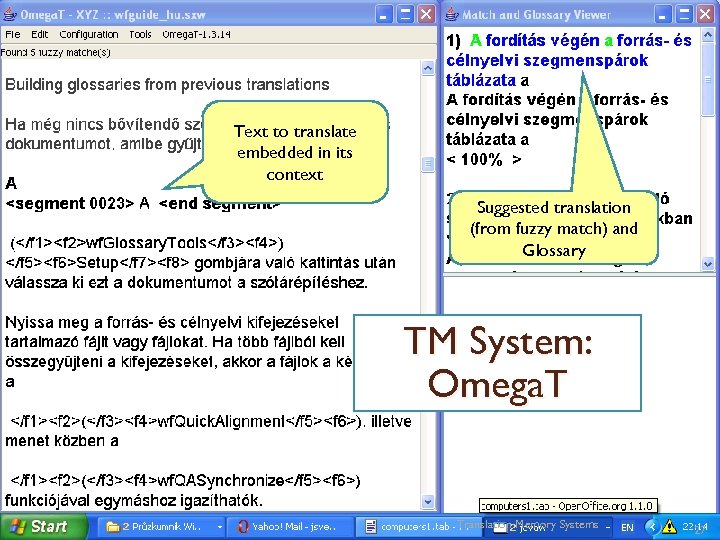 Text to translate embedded in its context Suggested translation (from fuzzy match) and Glossary TM System: Omega. T Translation Memory Systems 27
Text to translate embedded in its context Suggested translation (from fuzzy match) and Glossary TM System: Omega. T Translation Memory Systems 27
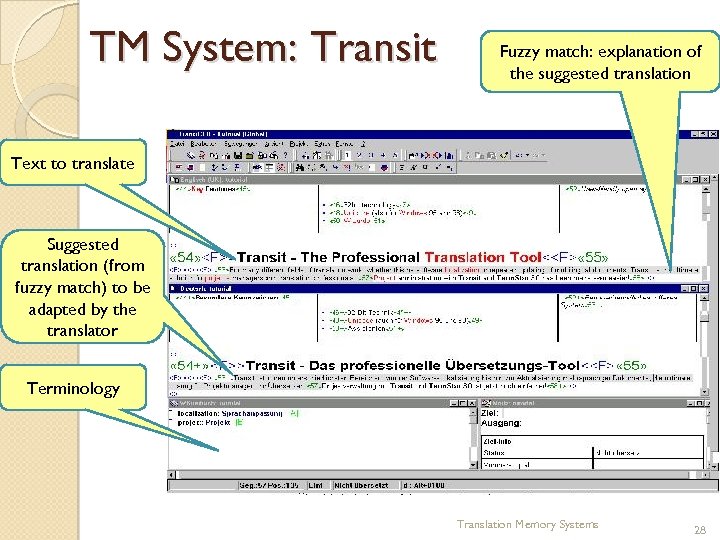 TM System: Transit Fuzzy match: explanation of the suggested translation Text to translate Suggested translation (from fuzzy match) to be adapted by the translator Terminology Translation Memory Systems 28
TM System: Transit Fuzzy match: explanation of the suggested translation Text to translate Suggested translation (from fuzzy match) to be adapted by the translator Terminology Translation Memory Systems 28
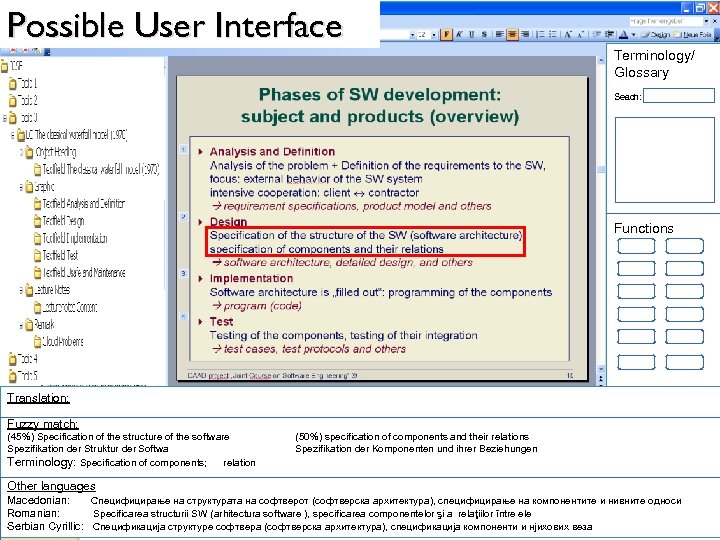 Possible User Interface Terminology/ Glossary Seach: Functions Translation: Fuzzy match: (45%) Specification of the structure of the software Spezifikation der Struktur der Softwa Terminology: Specification of components; relation (50%) specification of components and their relations Spezifikation der Komponenten und ihrer Beziehungen Other languages Macedonian: Специфицирање на структурата на софтверот (софтверска архитектура), специфицирање на компонентите и нивните односи Romanian: Specificarea structurii SW (arhitectura software ), specificarea componentelor şi a relaţiilor între ele Serbian Cyrillic: Спецификација структуре софтвера (софтверска архитектура), спецификација компоненти и нјихових веза
Possible User Interface Terminology/ Glossary Seach: Functions Translation: Fuzzy match: (45%) Specification of the structure of the software Spezifikation der Struktur der Softwa Terminology: Specification of components; relation (50%) specification of components and their relations Spezifikation der Komponenten und ihrer Beziehungen Other languages Macedonian: Специфицирање на структурата на софтверот (софтверска архитектура), специфицирање на компонентите и нивните односи Romanian: Specificarea structurii SW (arhitectura software ), specificarea componentelor şi a relaţiilor între ele Serbian Cyrillic: Спецификација структуре софтвера (софтверска архитектура), спецификација компоненти и нјихових веза
 Use of a TM system for localization of teaching materials Applicabe especially for PPT materials because ◦ High number of reappearing text segments ◦ Not too much complete sentences, more phrases, segments Higher support for translators higher productivity Not restricted to PPT, open for any other document format Possibility for a TM system web service for Software Engineering materials Nessesary adaption: not only two languages but many Translation Memory Systems 30
Use of a TM system for localization of teaching materials Applicabe especially for PPT materials because ◦ High number of reappearing text segments ◦ Not too much complete sentences, more phrases, segments Higher support for translators higher productivity Not restricted to PPT, open for any other document format Possibility for a TM system web service for Software Engineering materials Nessesary adaption: not only two languages but many Translation Memory Systems 30
 Thank You. Space for Questions
Thank You. Space for Questions


